Development and Validation of a Simple UV–HPLC Method to Quantify the Memantine Drug Used in Alzheimer’s Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
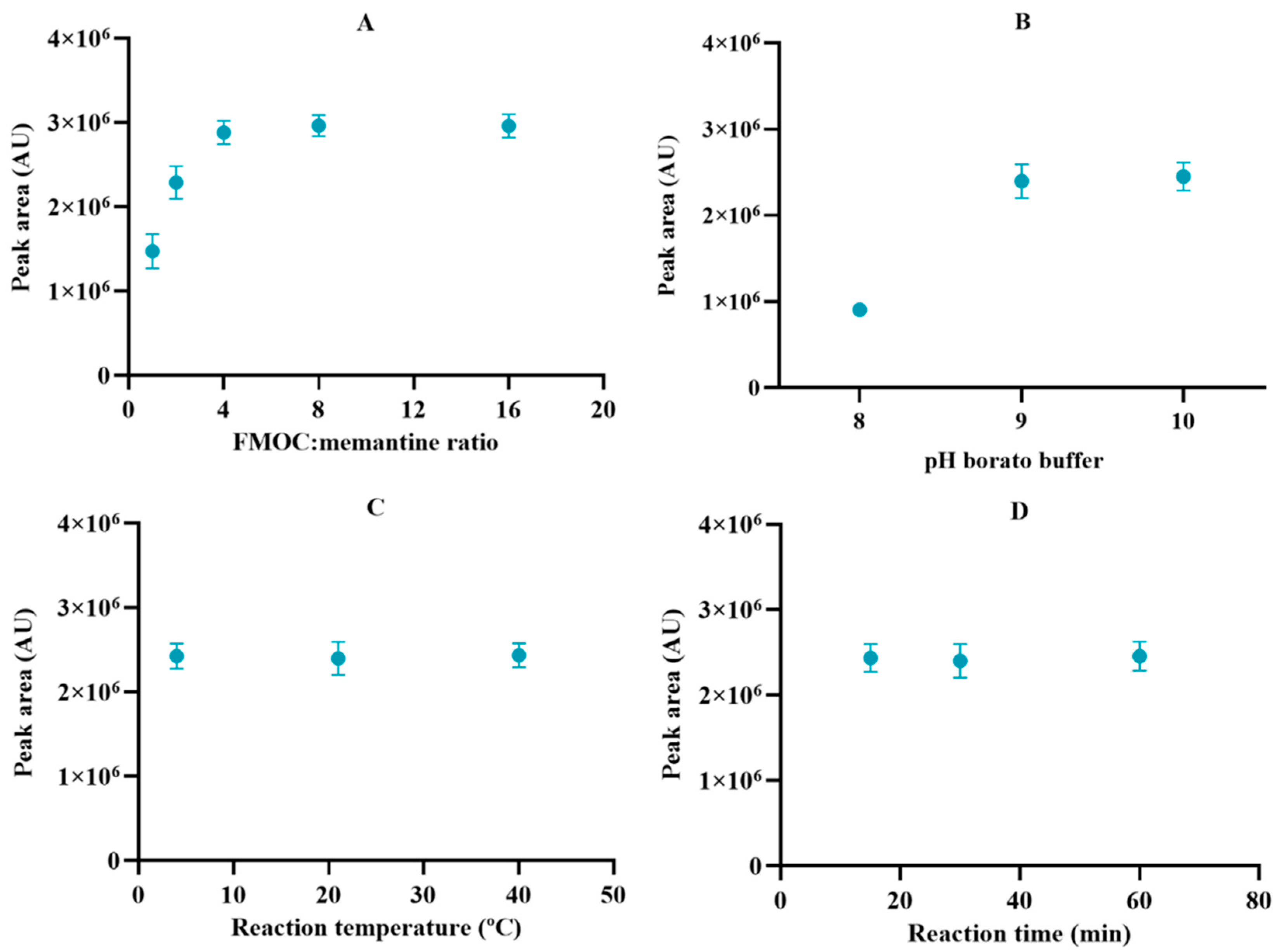
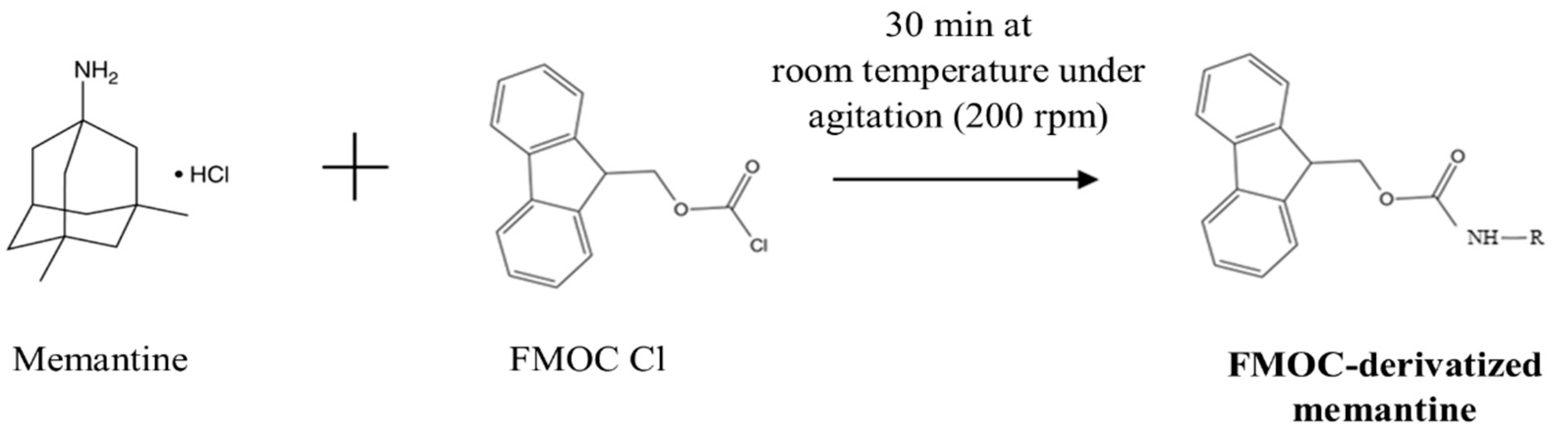
2.1. Optimization of Derivatization Method
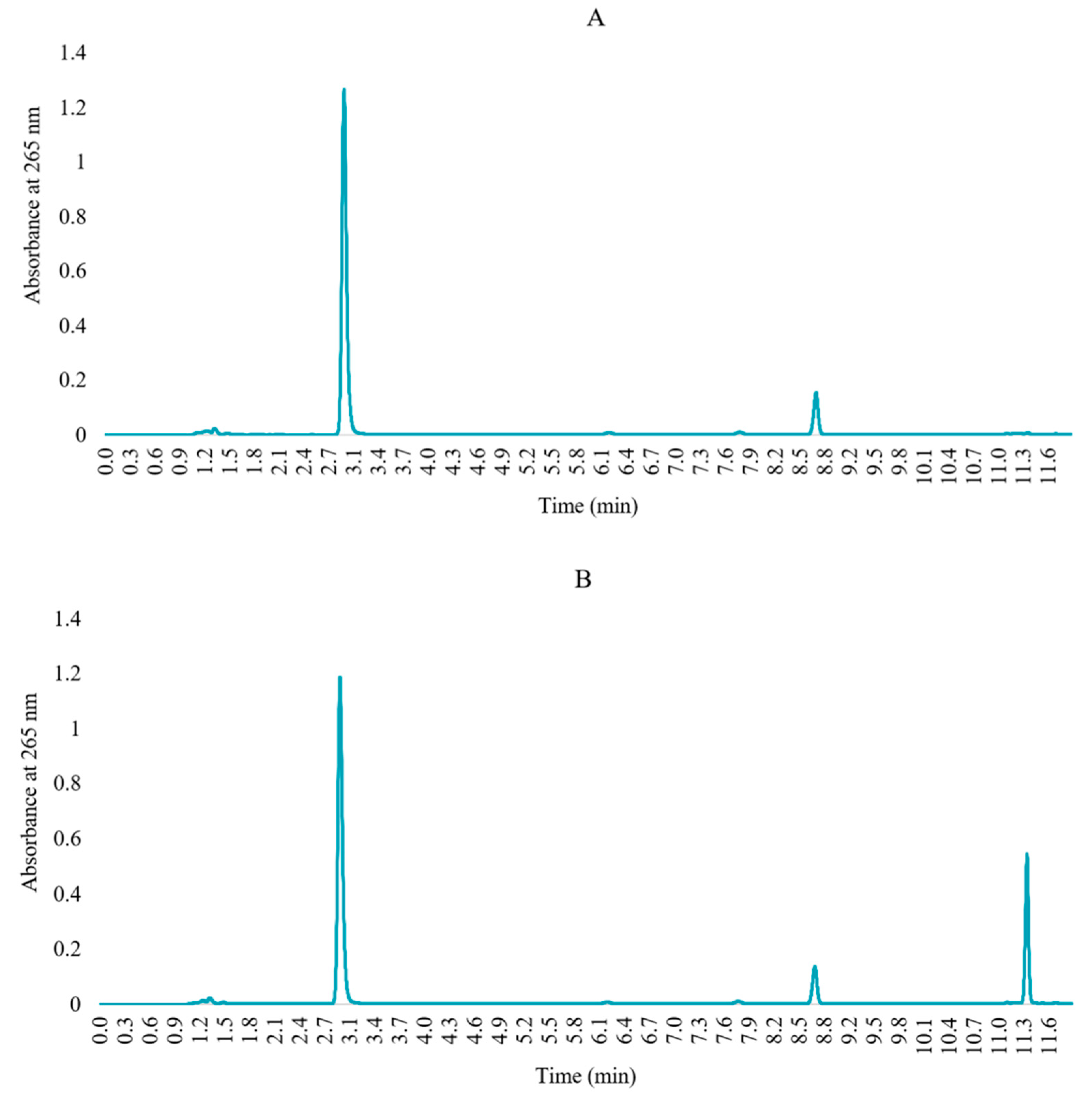
2.2. Method Validation
2.3. Applicability of the Method on a Nanoformulation: Evaluation of Encapsulation Efficiency
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Chromatographic System and Conditions
3.3. Derivatization Procedure
3.4. Optimization of Derivatization Procedure
3.5. Method Validation
3.5.1. Suitability
3.5.2. Specificity
3.5.3. Linearity
3.5.4. Sensitivity
3.5.5. Precision and Accuracy (Intraday and Interday)
3.5.6. Robustness
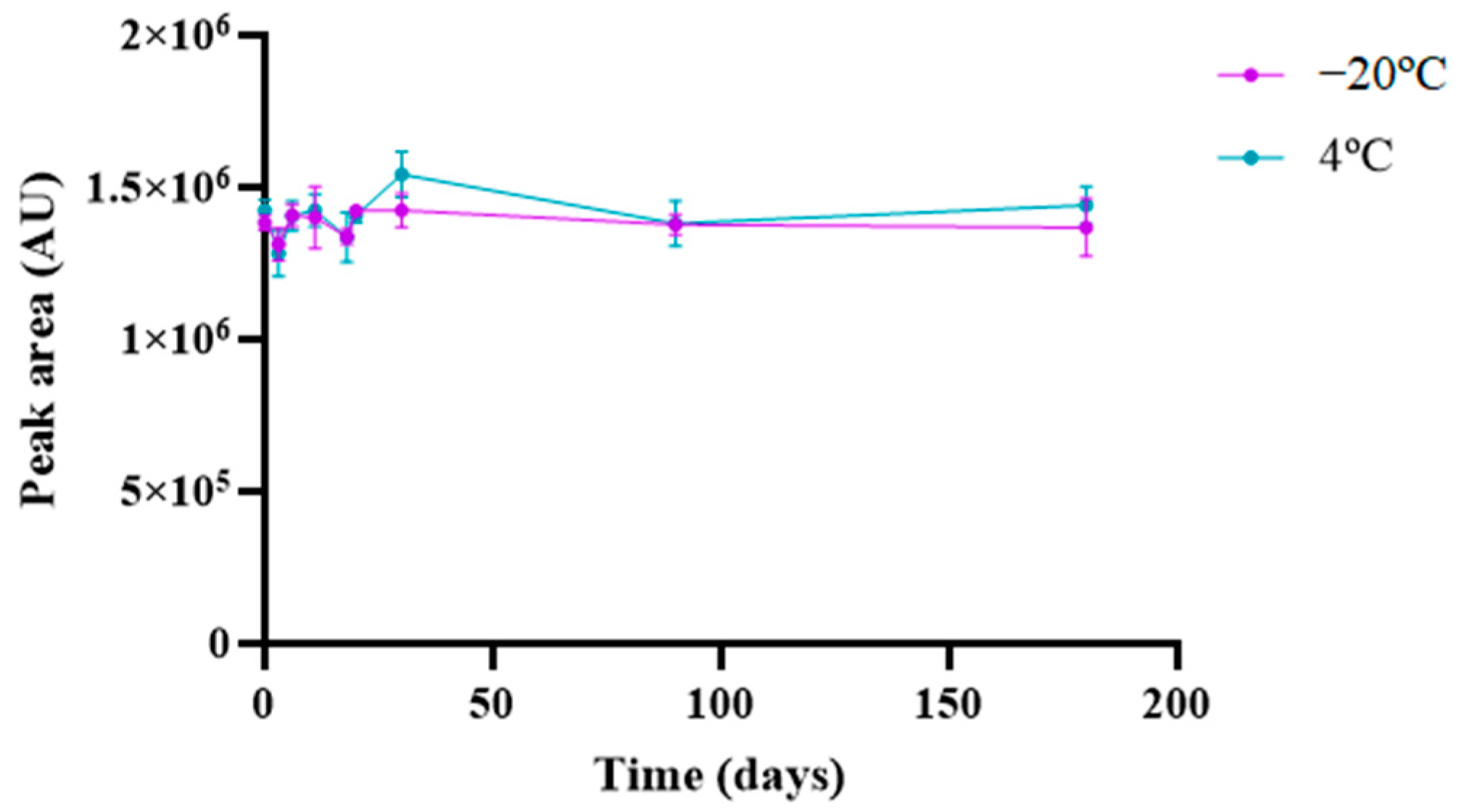
3.5.7. Stability Studies
3.6. Preparation and Characterization of Memantine-Loaded NPs
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Chang, L.; Song, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, Y. The Role of NMDA Receptors in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, C.G.; Stöffler, A.; Danysz, W. Memantine: A NMDA receptor antagonist that improves memory by restoration of homeostasis in the glutamatergic system—Too little activation is bad, too much is even worse. Neuropharmacology 2007, 53, 699–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, S.; Loureiro, J.A.; Pereira, M.C. The Role of Amyloid β-Biomembrane Interactions in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease: Insights from Liposomes as Membrane Models. ChemPhysChem 2021, 22, 1547–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, D.B. Progress update: Pharmacological treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2007, 3, 569–578. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, K.; Tatebe, T.; Suzuki, K.; Hirayama, T.; Hayakawa, M.; Kubo, H.; Tomita, T.; Makino, M. Memantine reduces the production of amyloid-β peptides through modulation of amyloid precursor protein trafficking. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 798, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, S.; Kishi, T.; Iwata, N. Memantine monotherapy for Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stazi, M.; Wirths, O. Chronic Memantine Treatment Ameliorates Behavioral Deficits, Neuron Loss, and Impaired Neurogenesis in a Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Krishnan, N.; Heo, J.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Nanoparticle-hydrogel superstructures for biomedical applications. J. Control. Release 2020, 324, 505–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begines, B.; Ortiz, T.; Pérez-Aranda, M.; Martínez, G.; Merinero, M.; Argüelles-Arias, F.; Alcudia, A. Polymeric Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery: Recent Developments and Future Prospects. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noetzli, M.; Choong, E.; Ansermot, N.; Eap, C.B. Simultaneous determination of antidementia drugs in human plasma for therapeutic drug monitoring. Ther. Drug Monit. 2011, 33, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, N.; Maffuid, K.; Kashuba, A.D.M. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Drugs in the Central Nervous System. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2018, 57, 1059–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, R.-N.; Chian, T.-Y.; Kuo, B.P.-C.; Pao, L.-H. Determination of Memantine in Human Plasma by LC–MS–MS: Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study. Chromatographia 2009, 70, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noetzli, M.; Ansermot, N.; Dobrinas, M.; Eap, C.B. Simultaneous determination of antidementia drugs in human plasma: Procedure transfer from HPLC–MS to UPLC–MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 64–65, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeng, H.-J.; Choi, S.-U.; Jang, D.-J.; Lee, D.; Ahn, B.-N.; Choi, M.-K.; Song, I.-S.; Cho, K. Validation and application of a simple reverse phase HPLC method for in vitro dissolution studies of memantine hydrochloride tablet. J. Pharm. Investig. 2015, 45, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, P.J.; Kuijt, N.; Kaya, M.; Rol, S.; van der Maaden, K. Nanoporous microneedle arrays seamlessly connected to a drug reservoir for tunable transdermal delivery of memantine. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 150, 105331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piponski, M.; Stoimenova, T.B.; Stefov, S.; Balkanov, T.; Serafimovska, G.T.; Logoyda, L. Development of a novel, fast, simple, nonderivative HPLC method with direct UV measurement for quantification of memantine hydrochloride in tablets. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 3482–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prapatpong, P.; Techa-In, T.; Padungpuak, W.; Buranaphalin, S.; Suntornsuk, L. HPLC-Fluorescent Analysis of Memantine: An Investigation on Fluorescent Derivative Formation. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 672183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, S.J.; Li, Q.L.; Jiang, Y. A new simultaneous derivatization and microextration method for the determination of memantine hydrochloride in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2016, 1008, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnayyan Sulochana, S.; Sharma, K.; Mullangi, R.; Sukumaran, S.K. Review of the validated HPLC and LC-MS/MS methods for determination of drugs used in clinical practice for Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2014, 28, 1431–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narola, B.; Singh, A.S.; Santhakumar, P.R.; Chandrashekhar, T.G. A Validated Stability-indicating Reverse Phase HPLC Assay Method for the Determination of Memantine Hydrochloride Drug Substance with UV-Detection Using Precolumn Derivatization Technique. Anal. Chem. Insights 2010, 5, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haen, E.; Koeber, R.; Klünemann, H.H.; Waimer, R.; Köstlbacher, A.; Wittmann, M.; Brandl, R.; Dörfelt, A.; Jahner, T.; Melchner, D. Implementation of a cost-effective HPLC/UV approach for routine medical quantification of memantine in human serum. Ther. Drug Monit. 2012, 34, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Rio-Sancho, S.; Serna-Jiménez, C.E.; Calatayud-Pascual, M.A.; Balaguer-Fernández, C.; Femenía-Font, A.; Merino, V.; López-Castellano, A. High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Ultraviolet Determination of Memantine Hydrochloride after In Vitro Transdermal Diffusion Studies. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 502652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarghi, A.; Shafaati, A.; Foroutan, S.M.; Khoddam, A.; Madadian, B. Sensitive and rapid HPLC method for determination of memantine in human plasma using OPA derivatization and fluorescence detection: Application to pharmacokinetic studies. Sci. Pharm. 2010, 78, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michail, K.; Daabees, H.; Beltagy, Y.; Elkhalek, M.A.; Khamis, M. High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Determination of Memantine in Human Urine Following Solid-Phase Extraction and Precolumn Derivatization. J. AOAC Int. 2013, 96, 1302–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.G.; Emara, K.M.; Mohamed, H.A.; Abdel-Wadood, H.M.; Ikeda, R.; Wada, M.; Kuroda, N.; Nakashima, K. Determination of memantine in rat plasma by HPLC-fluorescence method and its application to study of the pharmacokinetic interaction between memantine and methazolamide. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2012, 26, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente, B.; Hernandez, E.; Perez, S.; Pablo, L.; Prieto, E.; Garcia, M.A.; Bregante, M.A. Determination of memantine in plasma and vitreous humour by HPLC with precolumn derivatization and fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2011, 49, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.F.; Zhou, W.; Tong, X.Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Cai, Y.; Li, Y.; Duan, G.L. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of memantine hydrochloride in rat plasma using sensitive fluorometric derivatization. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). ICH Q2(R1): Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and methodology. In International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) of Technical Requirements for the Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use, Geneva, Switzerland; European Medicines Agency (EMA): Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kahsay, B.N.; Moeller, L.; Imming, P.; Neubert, R.H.H.; Gebre-Mariam, T. Development and Validation of a Simple, Selective, and Accurate Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatographic Method with Diode Array Detection (RP-HPLC/DAD) for the Simultaneous Analysis of 18 Free Amino Acids in Topical Formulations. Chromatographia 2022, 85, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, A.; Suarez-Merino, B.; Cerio, F. Nanoparticles and Blood-Brain Barrier: The Key to Central Nervous System Diseases. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 766–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Pereira, F.; Wojnowski, W.; Tobiszewski, M. AGREE—Analytical GREEnness Metric Approach and Software. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 10076–10082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC–MS | High sensitivity (LOQ = 0.1 ng/mL) Matrix free from endogenous substance interference Low run time (retention time: 2.9 min) | Complexity of the sample preparation Need for an internal standard | [12] |
| No peaks from endogenous compounds No interferences were apparent at the retention times of the analytes and internal standard High precision and accuracy (RSD < 5.3%) High sensitivity (LOQ = 1 ng/mL) | A twofold concentration step is needed The use of pure isotope-labeled internal standard High run time (retention time: 7.418 min) | [13] | |
| HPLC—UV detection | High specificity (LOQ = 1.0 µg/mL) High precision (RSD < 0.08%) and accuracy (between 97.8 to 99.0%) Cost-effective | Pre-column derivatization required Speed of analysis (retention time: 6.54 min) | [14] |
| High sensitivity (LOD = 0.36 µg/mL and LOQ = 1.09 µg/mL) High repeatability (RSDs < 6%) | Pre-column derivatization required | [15] | |
| No pre-column derivatization required Speed of analysis (retention time between 2.6 and 4 min) | High quantification calibration range (0.5–1.4 mg/mL) Low sensitivity (LOD = 0.035 mg/mL and LOQ 0.015 mg/mL) No method validation was performed | [16] | |
| HPLC—fluorescence detection | More sensitive than UV detection Speed of analysis (retention time: 4.5 min) High sensitivity (LOD = 0.79 µg/mL and LOQ = 2.42 µg/mL High accuracy (between 94.8 and 119.4%) | Derivatization with a fluorescent probe is required Extensive and complex sample preparation | [17] |
| More sensitive than UV detection High precision (RSD < 4.5%) High accuracy (between 94.3 and 100.7%) High sensitivity (LOD = 0.1 ng/mL) Simple sample preparation Excellent clean-up ability Requires negligible toxic organic reagent | Derivatization required | [18] |
| Injection | Retention Time (min) | Peak Area (AU) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11.395 | 2,528,500 | 97.0 |
| 2 | 11.397 | 2,271,436 | 87.1 |
| 3 | 11.394 | 2,409,041 | 92.4 |
| 4 | 11.390 | 2,439,740 | 93.6 |
| 5 | 11.389 | 2,463,800 | 94.5 |
| Mean | 11.393 | 2,422,503 | 92.9 |
| SD | 0.003 | 95,185 | 3.7 |
| RSD (%) | 0.03 | 3.9 | 3.9 |
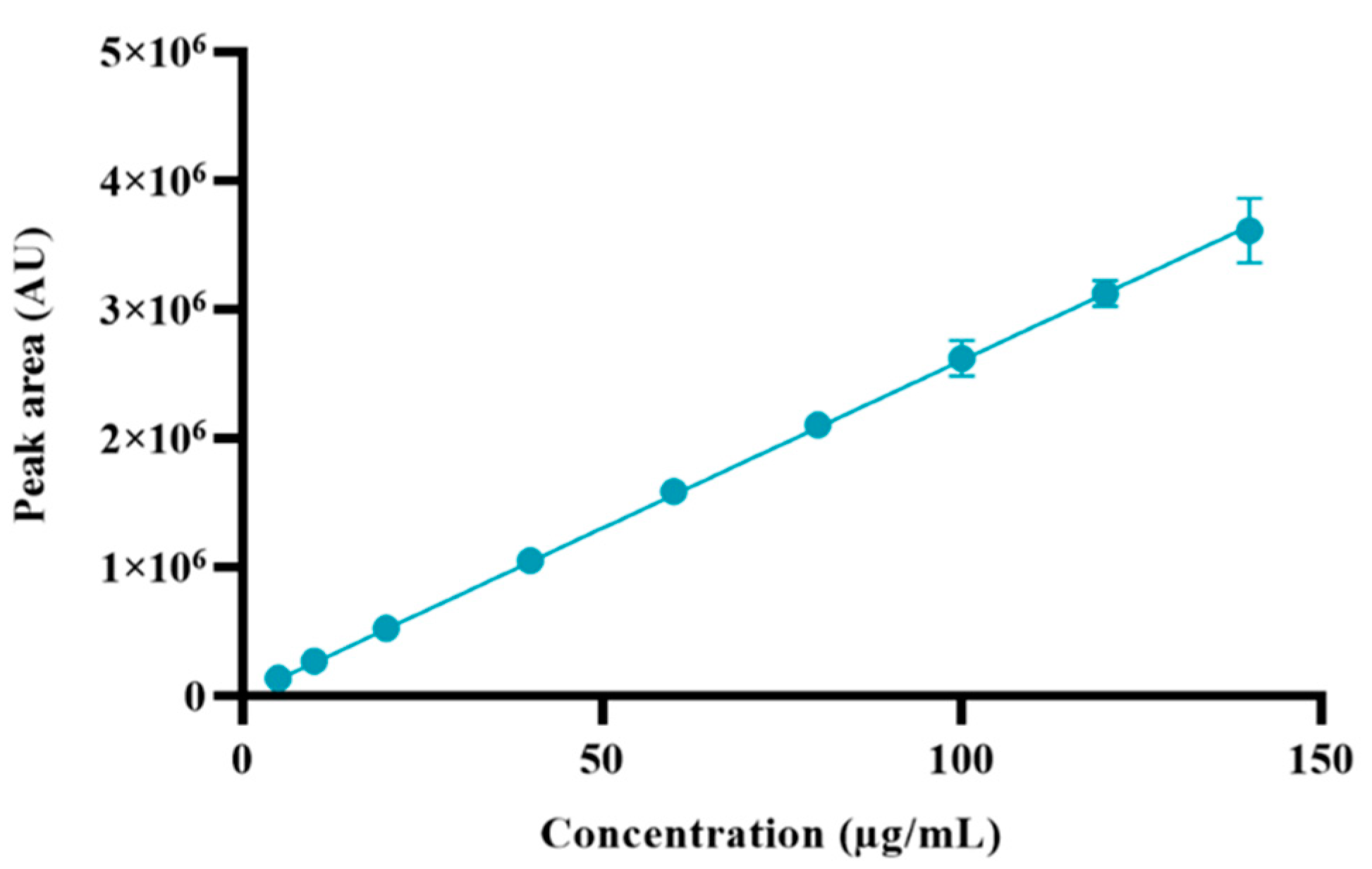
| Sample | Concentration (µg/mL) | Recovered Concentration (µg/mL) | Peak Area (AU) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 5.38 | 140,164 | 107.5 |
| 2 | 10 | 10.47 | 273,057 | 104.7 |
| 3 | 20 | 20.23 | 527,249 | 101.1 |
| 4 | 40 | 40.33 | 1,051,297 | 100.8 |
| 5 | 60 | 60.91 | 1,587,880 | 101.5 |
| 6 | 80 | 80.83 | 2,107,151 | 101.0 |
| 7 | 100 | 100.58 | 2,622,031 | 100.6 |
| 8 | 120 | 119.91 | 3,125,719 | 99.9 |
| 9 | 140 | 138.63 | 3,613,751 | 99.0 |
| Slope | 26,068 | |||
| Coefficient of determination (R2) | 0.9999 | |||
| Sample Con-Centration (µg/mL) | Measured Concentration (µg/mL) | Accuracy (Recovery, %) | Precision (%RSD) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intraday | Interday | Intraday | Interday | Intraday | Interday | |
| 80 | 76.3 ± 3.5 | 72.0 ± 3.1 | 95.4 ± 4.4 | 90.0 ± 3.9 | 4.6 | 4.3 |
| 100 | 92.9 ± 3.7 | 93.6 ± 3.9 | 92.9 ± 3.7 | 93.6 ± 3.9 | 3.9 | 4.2 |
| 120 | 115.9 ± 4.2 | 106.1 ± 9.8 | 96.6 ± 3.5 | 88.4 ± 8.2 | 3.6 | 9.3 |
| Parameter | Variation | Retention Time (min) | RSD (%) Retention Time | Mean Recovery (%) | RSD (%) Mean Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detection Wavelength (nm) | 262 | 11.393 ± 0.003 | 0.03 | 92.8 ± 3.7 | 3.9 |
| 265 | 11.393 ± 0.003 | 0.03 | 92.9 ± 3.7 | 3.9 | |
| 268 | 11.393 ± 0.003 | 0.03 | 83.2 ± 3.3 | 3.9 | |
| Flow Rate (mL/min) | 0.9 | 11.798 ± 0.004 | 0.03 | 103.0 ± 4.1 | 4.0 |
| 1 | 11.393 ± 0.003 | 0.03 | 92.9 ± 3.7 | 3.9 | |
| 1.1 | 11.030 ± 0.005 | 0.04 | 83.9 ± 3.5 | 4.1 | |
| Column Temperature (°C) | 30 | 11.506 ± 0.004 | 0.04 | 92.7 ± 3.9 | 4.2 |
| 35 | 11.393 ± 9.993 | 0.03 | 92.9 ± 3.7 | 3.9 | |
| 40 | 11.270 ± 0.004 | 0.03 | 90.7 ± 5.2 | 5.7 | |
| Injection Volume (µL) | 10 | 11.393 ± 0.002 | 0.02 | 92.7 ± 3.8 | 4.1 |
| 20 | 11.393 ± 0.003 | 0.03 | 92.9 ± 3.7 | 3.9 | |
| 30 | 11.391 ± 0.006 | 0.05 | 92.6 ± 3.7 | 4.0 |
| Formulation | Mean Size (nm) | PdI | ZP (mV) | EE (%) | LC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLNs | 101 ± 1 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | −17 ± 4 | - | - |
| SLNs–memantine | 130 ± 6 * | 0.26 ± 0.00 ** | −12 ± 7 | 49 ± 1 | 2.0 ± 0.1 |
| NLCs | 133 ± 15 | 0.20 ± 0.02 | −24 ± 3 | - | - |
| NLCs–memantine | 197 ± 16 ** | 0.19 ± 0.02 | −10 ± 3 * | 46 ± 6 | 1.9 ± 9.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nunes, D.; Tavares, T.G.; Malcata, F.X.; Loureiro, J.A.; Pereira, M.C. Development and Validation of a Simple UV–HPLC Method to Quantify the Memantine Drug Used in Alzheimer’s Treatment. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091162
Nunes D, Tavares TG, Malcata FX, Loureiro JA, Pereira MC. Development and Validation of a Simple UV–HPLC Method to Quantify the Memantine Drug Used in Alzheimer’s Treatment. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(9):1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091162
Chicago/Turabian StyleNunes, Débora, Tânia G. Tavares, Frenacisco Xavier Malcata, Joana A. Loureiro, and Maria Carmo Pereira. 2024. "Development and Validation of a Simple UV–HPLC Method to Quantify the Memantine Drug Used in Alzheimer’s Treatment" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 9: 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091162
APA StyleNunes, D., Tavares, T. G., Malcata, F. X., Loureiro, J. A., & Pereira, M. C. (2024). Development and Validation of a Simple UV–HPLC Method to Quantify the Memantine Drug Used in Alzheimer’s Treatment. Pharmaceuticals, 17(9), 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091162








