Anti-Vasculogenic, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Sulfated Polysaccharide Derived from Codium tomentosum: Pharmacokinetic Assay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Extraction Yield and Chemical Analysis
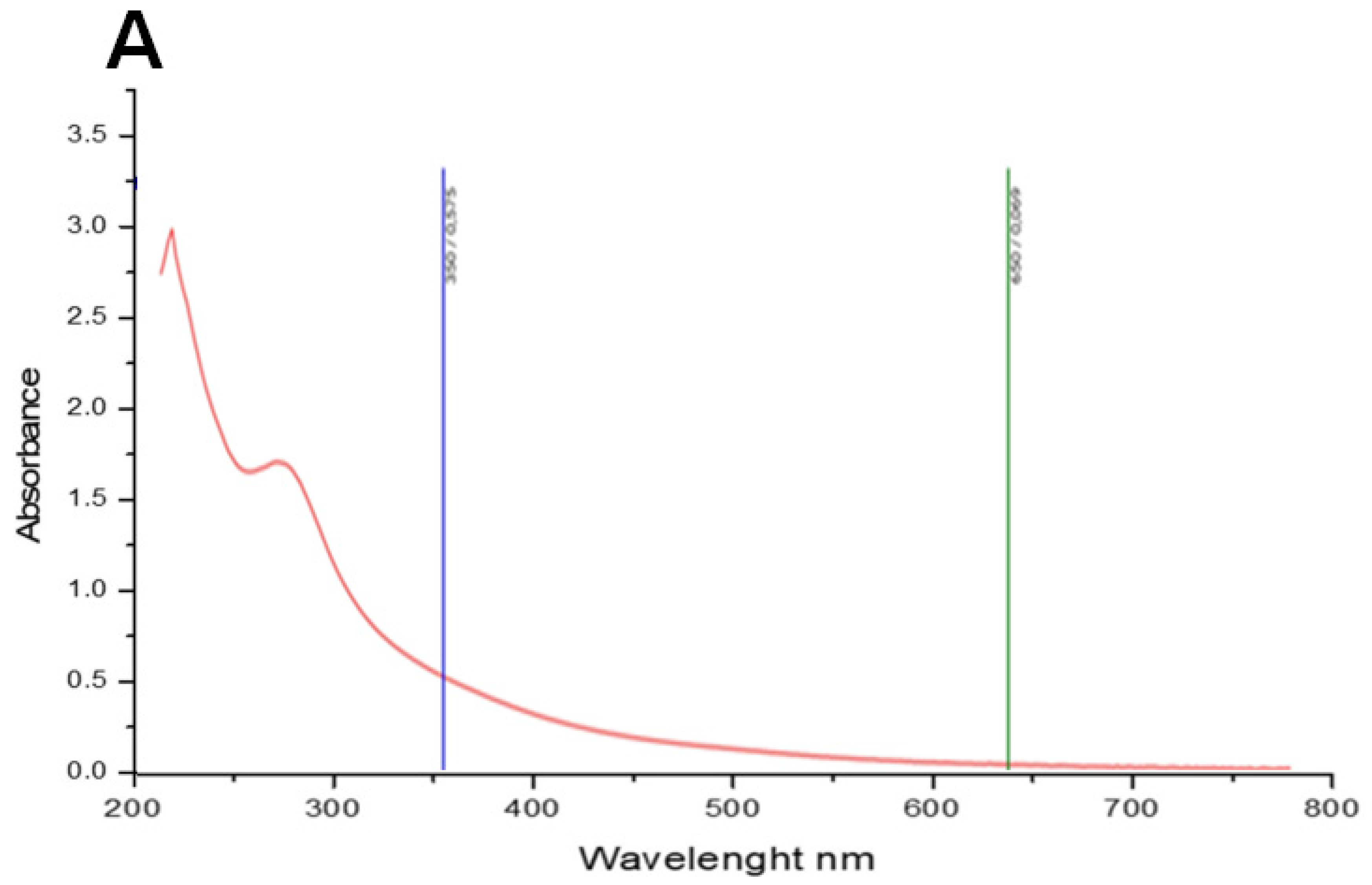
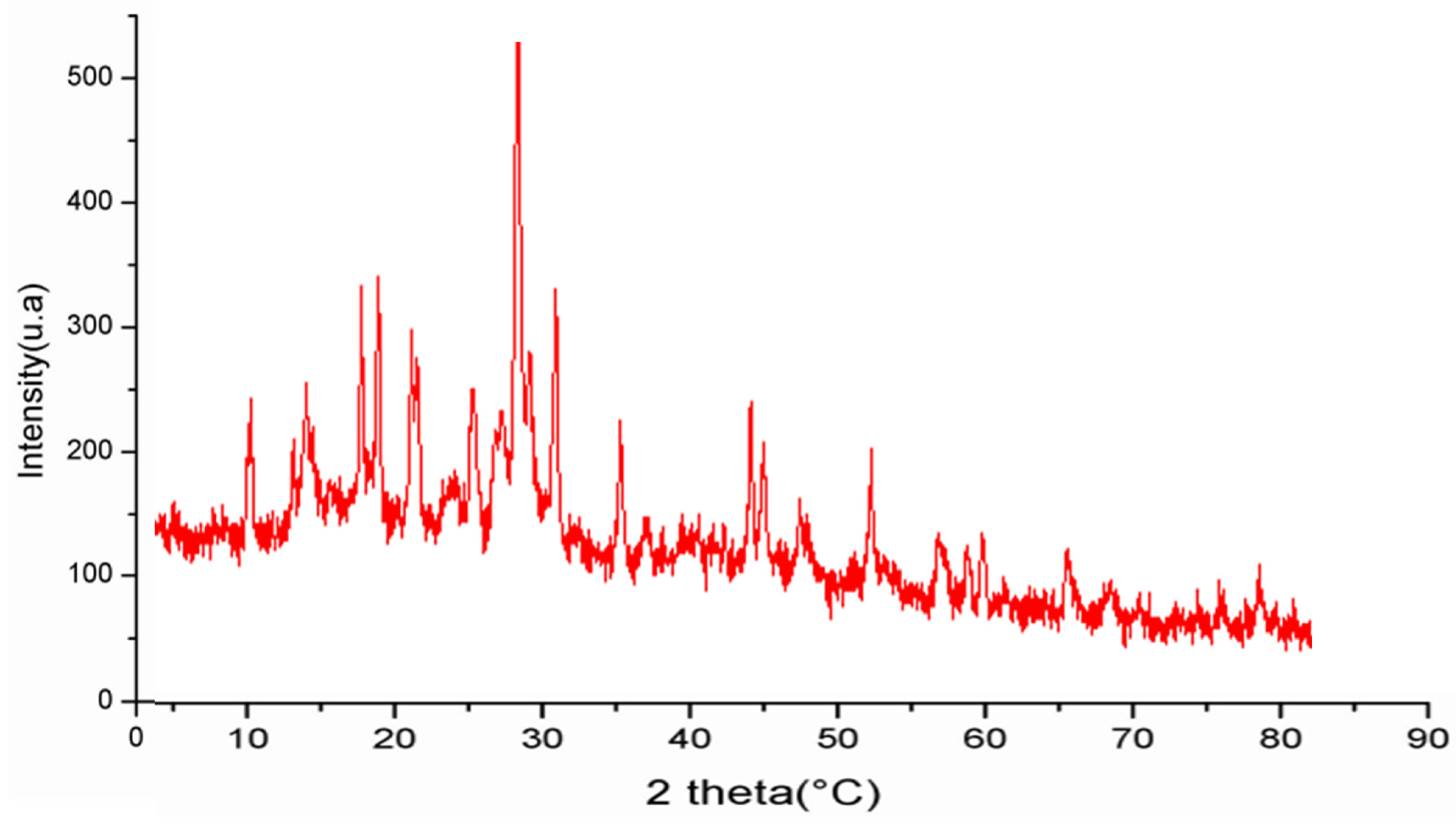
2.2. Spectroscopic Analysis of PCT
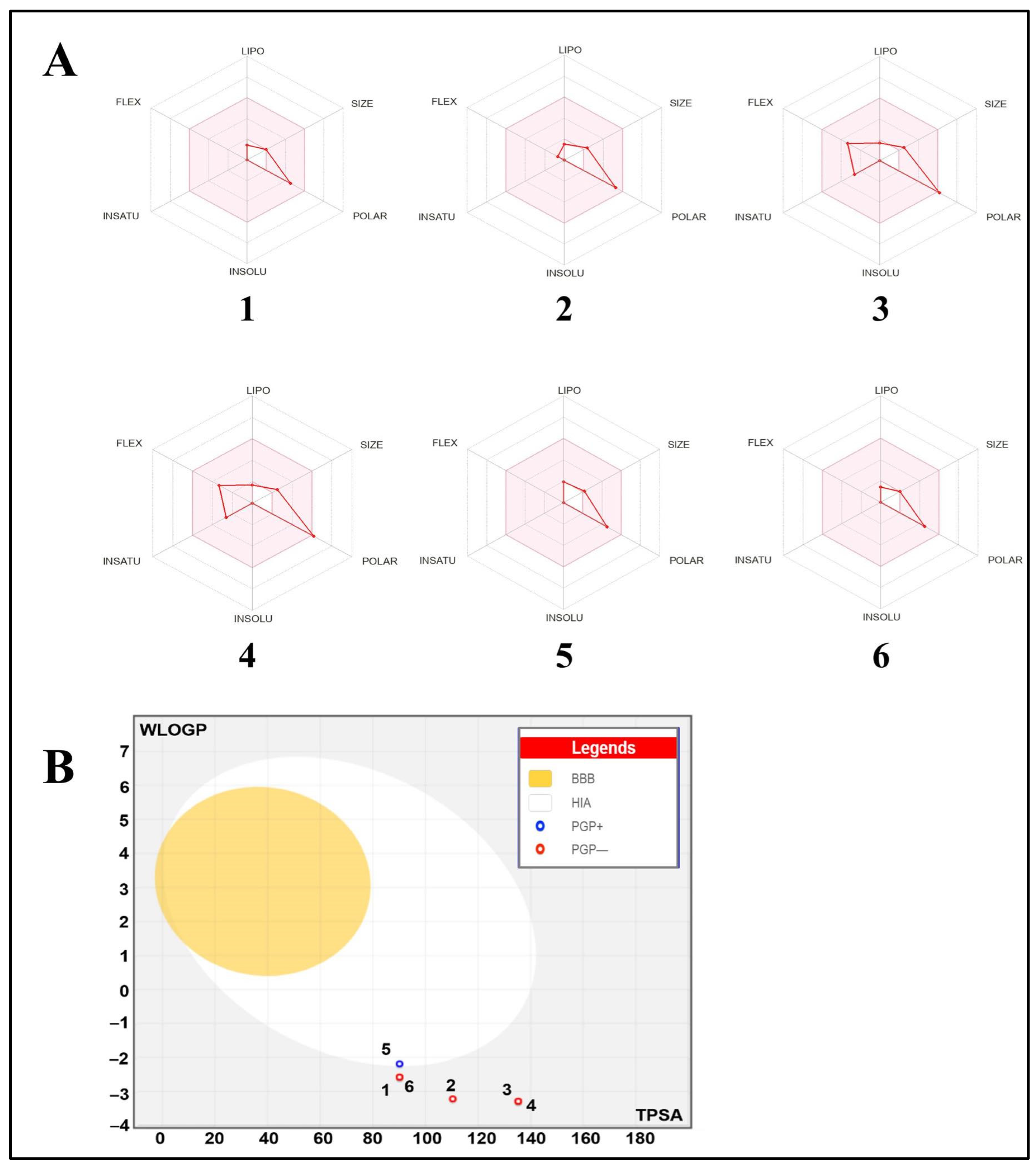
2.3. Druggability, Bioavailability, and Pharmacokinetics
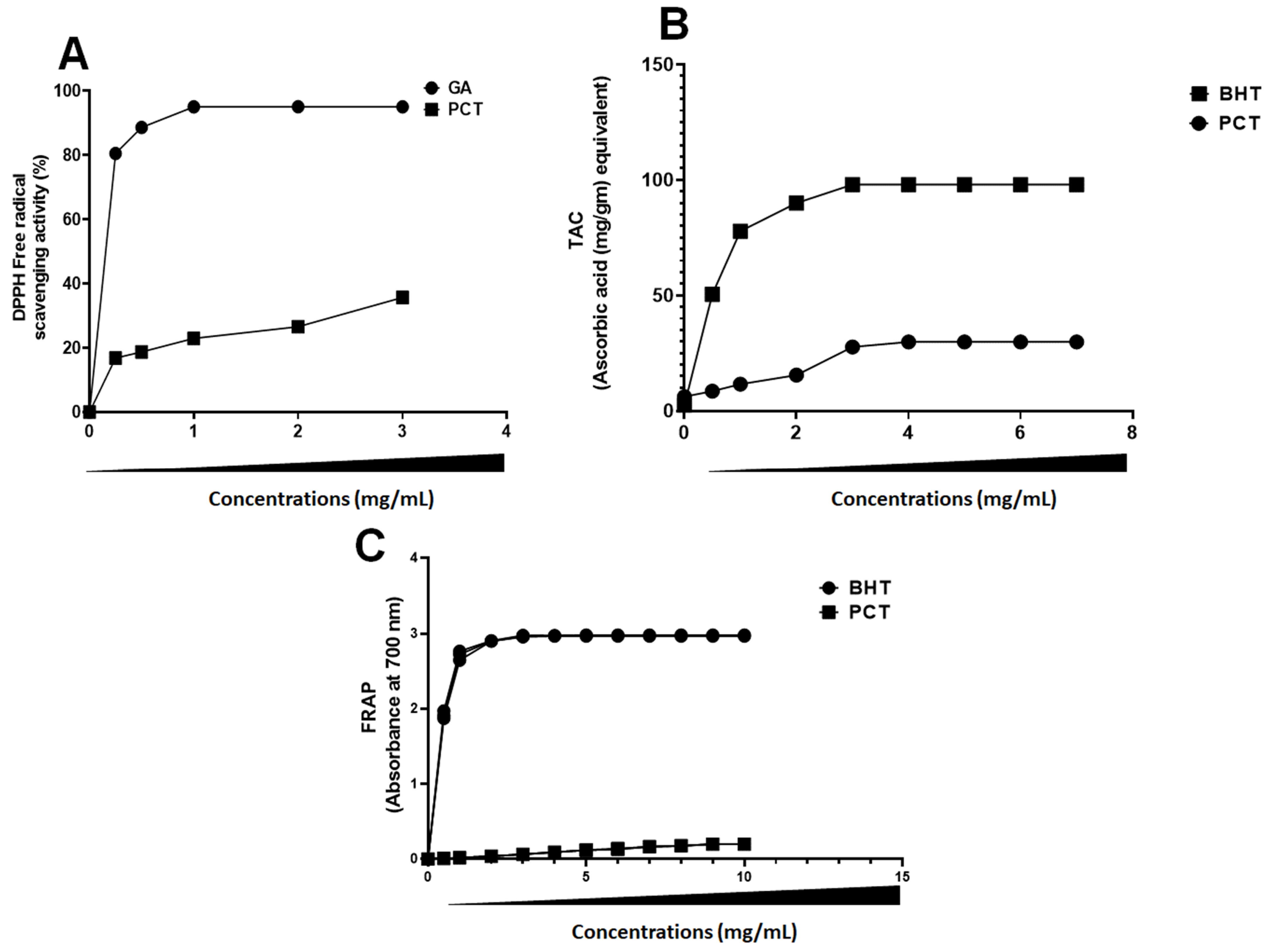
2.4. Antioxidant Activity of PCT
| Algae Species | Monosaccharide Unities | Sulfates Degree | Activities | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chondrus canaliculatus | arabinose mannose glucoronic acid | 0.0025 | antioxidant | [30] |
| Chaetomorpha linum | arabinose, mannose glucoronic acid | 0.02 | antioxidant | [29] |
| Falkenbergia rufolanosa | mannose glucuronic acid | 5.97 | antioxidant anti-inflammatory anti-coagulant | [54] |
| Codium cylindricum | mannose galactose arabinose glucose ribose | 2.44 | anti-coagulant anti-angiogenic | [27] |
| Codium tomentosum | arabinose fructose, xylose rhamnose glucoronic acid | 5.30 | anti-inflammatory antioxidant anti-angiogenic | our results |
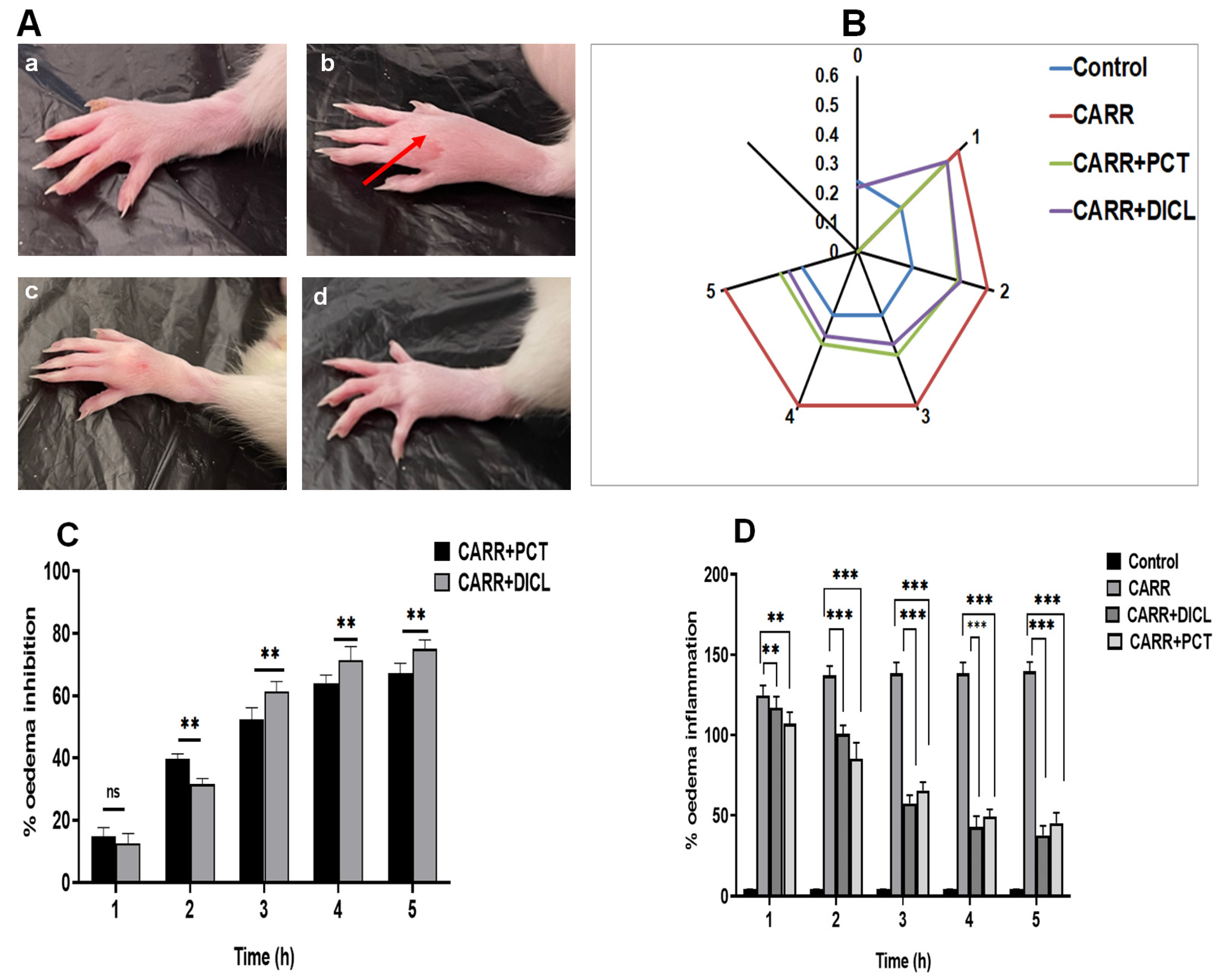
2.5. Effect of PCT on Inflammatory Edematous Symptoms
2.5.1. Influence of PCT on Hematological Parameters
2.5.2. Effect of Inflammation on Serum Protein Levels
2.5.3. Evaluation of Oxidative Stress Parameters in Erythrocytes and Edema Tissue
2.5.4. PCT Attenuates Histopathological Alterations
2.6. Ex Vivo Anti-Angiogenic Effect of PCT
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Algae Collection and Species Identification
3.2. Polysaccharide Extraction
3.3. Analysis of Biochemical Composition
3.4. Polysaccharide Spectroscopic Analysis
3.4.1. UV Absorption Peak Detection and X-ray Diffraction
3.4.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
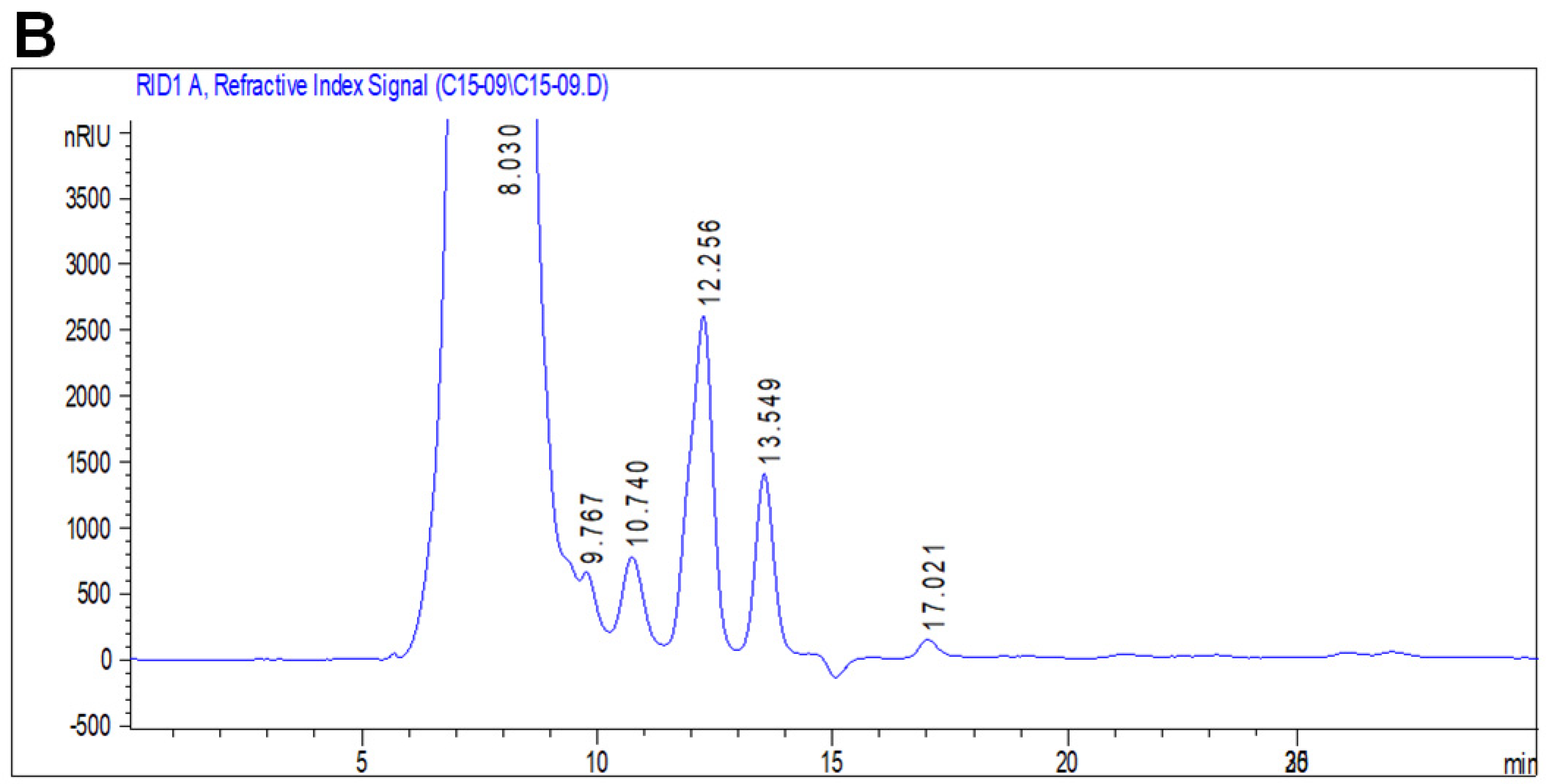
3.4.3. Monosaccharide Analysis by HPLC-FID
3.5. Druggability, Bioavailability, and Pharmacokinetic Properties
3.6. In Vitro Biological Activity
3.6.1. DPPH Free Radical Scavenging Assay
3.6.2. Determination of Total Antioxidant Capacity
3.6.3. Determination of Reducing Power
3.6.4. Energy Value
3.7. Anti-Inflammatory In Vivo Assay
3.7.1. Animals
3.7.2. Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema
3.7.3. Blood and Tissue Sample Collection
3.7.4. Determination of Hematological Parameters
3.7.5. Exploration of Oxidative Stress
3.7.6. Histopathological Study
3.7.7. MN Assay in the Peripheral Blood
3.8. Evaluation of Angiogenic Activity Using Chorioallantoic Membrane Assay
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, W. Angiogenesis Inhibitors as Therapeutic Agents in Cancer: Challenges and Future Directions. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 793, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folkman, J. Tumor Angiogenesis: Therapeutic Implications. N. Engl. J. Med. 1971, 285, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, M.R.M.; Boller, C.; Zibetti, R.G.M.; de Souza, D.; Pedroso, L.L.; Soccol, C.R. Anti-Inflammatory and Angiogenic Activity of Polysaccharide Extract Obtained from Tibetan kefir. Microvasc. Res. 2016, 108, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, N.; Kerbel, R.S. Angiogenesis as a Therapeutic Target. Nature 2005, 438, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, R.H.; Alitalo, K. Molecular Regulation of Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayson, G.C.; Kerbel, R.; Ellis, L.M.; Harris, A.L. Antiangiogenic Therapy in Oncology: Current Status and Future Directions. Lancet 2016, 388, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Balkwill, F. Cancer-Related Inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, K.; Muruganandan, S.; Lal, J.; Chandra, S.; Tandan, S.K.; Ravi Prakash, V. Evaluation of Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Pongamia pinnata Leaves in Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2001, 78, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.C.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Aggarwal, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Inflammation, a Double-Edge Sword for Cancer and Other Age-Related Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Tan, L.-H.; Feng, Y.-J.; Yao, L.; Yan, X.-W.; Cao, W.-G. Evaluation of Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory Activity and Identification of Active Compounds of Humulus scandens. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 141, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osifo, M.; Ihim, S.A.; Ani, N.; Nworu, C.S.; Akah, P. Wound Healing and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Ceiba pentendra (l.) Gaertn. Pharmacol. Res.-Mod. Chin. Med. 2022, 3, 100077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Huang, C.; Shi, C.; Xiang, X. Biomedical Potency and Mechanisms of Marine Polysaccharides and Oligosaccharides: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 265, 131007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ale, M.T.; Maruyama, H.; Tamauchi, H.; Mikkelsen, J.D.; Meyer, A.S. Fucoidan from Sargassum sp. and Fucus vesiculosus Reduces Cell Viability of Lung Carcinoma and Melanoma Cells in Vitro and Activates Natural Killer Cells in Mice in vivo. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumashi, A.; Ushakova, N.A.; Preobrazhenskaya, M.E.; D’Incecco, A.; Piccoli, A.; Totani, L.; Tinari, N.; Morozevich, G.E.; Berman, A.E.; Bilan, M.I.; et al. A Comparative Study of the Anti-Inflammatory, Anticoagulant, Antiangiogenic, and Antiadhesive Activities of Nine Different Fucoidans from Brown Seaweeds. Glycobiology 2007, 17, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.E.C.; Brito, T.V.; Damasceno, R.O.S.; Sousa, W.M.; Barros, F.C.N.; Sombra, V.G.; Júnior, J.S.C.; Magalhães, D.A.; Souza, M.H.L.P.; Medeiros, J.-V.R.; et al. Chemical Structure, Anti-Inflammatory and Antinociceptive Activities of a Sulfated Polysaccharide from Gracilaria Intermedia Algae. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, L.A.R.; Dore, C.M.P.G.; Castro, A.J.G.; de Azevedo, T.C.G.; deOliveira, M.T.B.; de Fátima, M.F.V.; Benevides, N.M.B.; Leite, E.L. Galactans from the Red Seaweed Amansia multifida and Their Effects on Inflammation, Angiogenesis, Coagulation and Cell Viability. Biomed. Prev. Nutr. 2012, 2, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, S.G.; Oliveira, L.A.; de Aguiar Magalhães, D.; de Brito, T.V.; Batista, J.A.; Pereira, C.M.C.; de Souza Costa, M.; Mazulo, J.C.R.; de Carvalho Filgueiras, M.; Vasconselos, D.F.P.; et al. Chemical Structure and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Polysaccharide Extracted from Morinda citrifolia Linn (Noni). Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 197, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesekara, I.; Pangestuti, R.; Kim, S.-K. Biological Activities and Potential Health Benefits of Sulfated Polysaccharides Derived from Marine Algae. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Shi, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Huang, Z.; Cai, F.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Xiong, Q.; Wang, Y.; et al. Isolation, Identification, and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Polysaccharides of Typha angustifolia. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 2451–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, I.R.L.; Cordeiro, S.L.; Gomes, D.L.; Dreyfuss, J.L.; Filgueira, L.G.A.; Leite, E.L.; Nader, H.B.; Rocha, H.A.O. Evaluation of Anti-Nociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of a Heterofucan from Dictyota menstrualis. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2722–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthi, S.; Raghavendran, H.R.B.; Sunil, A.G.; Gayathri, V.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Vasanthi, H.R. In Vitro Antioxidant and in Vivo Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Crude Polysaccharide from Turbinaria ornata (Marine Brown Alga). Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Public Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2010, 48, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, J.G.; Rodrigues, J.A.G.; de Sousa Oliveira Vanderlei, E.; Souza, R.B.; Quinderé, A.L.G.; Coura, C.O.; de Araújo, I.W.F.; Chaves, H.V.; Bezerra, M.M.; Benevides, N.M.B. Peripheral Antinociception and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Sulphated Polysaccharides from the Alga Caulerpa mexicana. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 115, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, P.V.; Arata, P.X.; Ciancia, M. Polysaccharides from Codium Species. In Advances in Botanical Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 71, pp. 253–278. ISBN 978-0-12-408062-1. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Liu, R. Overview on Biological Activities and Molecular Characteristics of Sulfated Polysaccharides from Marine Green Algae in Recent Years. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4984–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celikler, S.; Vatan, O.; Yildiz, G.; Bilaloglu, R. Evaluation of Anti-Oxidative, Genotoxic and Antigenotoxic Potency of Codium tomentosum Stackhouse Ethanolic Extract in Human Lymphocytes in Vitro. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabarsa, M.; Karnjanapratum, S.; Cho, M.; Kim, J.-K.; You, S. Molecular Characteristics and Biological Activities of Anionic Macromolecules from Codium fragile. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 59, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, P.V.; Raffo, M.P.; Alberghina, J.; Ciancia, M. Polysaccharides from the Green Seaweed Codium decorticatum. Structure and Cell Wall Distribution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 117, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Mao, W.; Yan, M.; Liu, X.; Xia, Z.; Wang, S.; Xiao, B.; Chen, C.; Zhang, L.; Cao, S. Structural Characterization and Anticoagulant Activity of a Sulfated Polysaccharide from the Green Alga Codium divaricatum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 121, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzaoui, A.; Ghariani, M.; Sellem, I.; Hamdi, M.; Feki, A.; Jaballi, I.; Nasri, M.; Amara, I.B. Extraction, Characterization and Biological Properties of Polysaccharide Derived from Green Seaweed “Chaetomorpha linum” and Its Potential Application in Tunisian Beef Sausages. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 1156–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaballi, I.; Sallem, I.; Feki, A.; Cherif, B.; Kallel, C.; Boudawara, O.; Jamoussi, K.; Mellouli, L.; Nasri, M.; Amara, I.B. Polysaccharide from a Tunisian Red Seaweed Chondrus canaliculatus: Structural Characteristics, Antioxidant Activity and In Vivo Hemato-Nephroprotective Properties on Maneb Induced Toxicity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z. Antioxidant Activity of Sulfated Polysaccharide Fractions Extracted from Laminaria japonica. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 42, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubaki, S.; Oono, K.; Hiraoka, M.; Onda, A.; Mitani, T. Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal Extraction of Sulfated Polysaccharides from Ulva spp. and Monostroma latissimum. Food Chem. 2016, 210, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravchenko, A.O.; Byankina Barabanova, A.O.; Glazunov, V.P.; Yakovleva, I.M.; Yermak, I.M. Seasonal Variations in a Polysaccharide Composition of Far Eastern Red Seaweed Ahnfeltiopsis flabelliformis (Phyllophoraceae). J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, R.; Parimalanandhini, D.; Mahalakshmi, K.; Beulaja, M.; Arumugam, M.; Janarthanan, S.; Palanisamy, S.; You, S.; Prabhu, N.M. Studies on Isolation, Characterization of Fucoidan from Brown Algae Turbinaria decurrens and Evaluation of It’s In Vivo and In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 160, 1263–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolsi, R.B.A.; Jardak, N.; Hajkacem, F.; Chaaben, R.; El Feki, A.; Rebai, T.; Jamoussi, K.; Fki, L.; Belghith, H.; Belghith, K. Anti-Obesity Effect and Protection of Liver-Kidney Functions by Codium fragile Sulphated Polysaccharide on High Fat Diet Induced Obese Rats. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, F.A.; Abdala-Díaz, R.T.; Pérez, C.; Casas-Arrojo, V.; Nesic, A.; Tapia, C.; Durán, C.; Valdes, O.; Parra, C.; Bravo-Arrepol, G.; et al. Sulfated Polysaccharide Extracted from the Green Algae Codium bernabei: Physicochemical Characterization and Antioxidant, Anticoagulant and Antitumor Activity. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioux, L.-E.; Turgeon, S.L.; Beaulieu, M. Effect of Season on the Composition of Bioactive Polysaccharides from the Brown Seaweed Saccharina longicruris. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Qu, H.; Shan, S.; Song, C.; Baranenko, D.; Li, Y.; Lu, W. A Novel Polysaccharide Isolated from Ulva pertusa: Structure and Physicochemical Property. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 233, 115849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zammel, N.; Saeed, M.; Bouali, N.; Elkahoui, S.; Alam, J.M.; Rebai, T.; Kausar, M.A.; Adnan, M.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Badraoui, R. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Zingiber officinale roscoe and Allium subhirsutum: In Silico, Biochemical and Histological Study. Foods 2021, 10, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badraoui, R.; Saeed, M.; Bouali, N.; Hamadou, W.S.; Elkahoui, S.; Alam, M.J.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Adnan, M.; Saoudi, M.; Rebai, T. Expression Profiling of Selected Immune Genes and Trabecular Microarchitecture in Breast Cancer Skeletal Metastases Model: Effect of α-Tocopherol Acetate Supplementation. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2022, 110, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bédoui, I.; Nasr, H.; Ksouda, K.; Ayadi, W.; Louati, N.; Chamkha, M.; Choura, S.; Gargouri, J.; Hammami, S.; Affes, H.; et al. Phytochemical Composition, Bioavailability and Pharmacokinetics of Scorzonera undulata Methanolic Extracts: Antioxidant, Anticancer, and Apoptotic Effects on MCF7 Cells. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2023, 20, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmouni, F.; Badraoui, R.; Nasr, H.; Bardakci, F.; Elkahoui, S.; Siddiqui, A.; Saeed, M.; Mejdi, S.; Saoudi, M.; Rebai, T. Pharmacokinetics and Therapeutic Potential of Teucrium polium against Liver Damage Associated Hepatotoxicity and Oxidative Injury in Rats: Computational, Biochemical and Histological Studies. Life 2022, 12, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zammel, N.; Jedli, O.; Rebai, T.; Hamadou, W.; Elkahoui, S.; Jamal, A.; Alam, M.; Adnan, M.; Siddiqui, A.; Alreshidi, M.; et al. Kidney Injury and Oxidative Damage Alleviation by Zingiber officinale: Pharmacokinetics and Protective Approach in a Combined Murine Model of Osteoporosis. 3 Biotech 2022, 12, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Physico-Chemical Properties, Pharmacokinetics, Molecular Docking and In-Vitro Pharmacological Study of a Cobalt (II) Complex Based on 2-Aminopyridine—Mhadhbi—2022—ChemistrySelect—Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/slct.202103592 (accessed on 27 October 2023).
- Jedli, O.; Ben-Nasr, H.; Zammel, N.; Rebai, T.; Saoudi, M.; Elkahoui, S.; Jamal, A.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Sulieman, A.E.; Alreshidi, M.M.; et al. Attenuation of Ovalbumin-Induced Inflammation and Lung Oxidative Injury in Asthmatic Rats by Zingiber officinale Extract: Combined in Silico and in Vivo Study on Antioxidant Potential, STAT6 and TNF-α Pathways. 3 Biotech 2022, 12, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebahi, S.; Ben Salah, G.; Jarray, S.; Naffati, M.; Ahmad, M.A.; Brahmi, F.; Saeed, M.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Abdelmajid, K.; Badraoui, R. Chitosan-Based Gastric Dressing Materials Loaded with Pomegranate Peel as Bioactive Agents: Pharmacokinetics and Effects on Experimentally Induced Gastric Ulcers in Rabbits. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badraoui, R.; Adnan, M.; Bardakci, F.; Alreshidi, M. Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine Interact Differently with ACE2 Domains Reported to Bind with the Coronavirus Spike Protein: Mediation by ACE2 Polymorphism. Molecules 2021, 26, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Liu, H.; Song, W.; Zhu, L.; Yin, X. Polysaccharide from Caulerpa lentillifera: Extraction Optimization with Response Surface Methodology, Structure and Antioxidant Activities. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 3417–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Xu, X.; Jing, C.; Zou, P.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y. Microwave Assisted Hydrothermal Extraction of Polysaccharides from Ulva prolifera: Functional Properties and Bioactivities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarley, O.P.N.; Kojo, A.B.; Zhou, C.; Yu, X.; Gideon, A.; Kwadwo, H.H.; Richard, O. Reviews on Mechanisms of in Vitro Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Anticancer Activities of Water-Soluble Plant Polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 2262–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, M.; De Morais, R.; Bernardo de Morais, A. Bioactivity and Applications of Sulphated Polysaccharides from Marine Microalgae. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouahid, E.A.; Mohamed, R.; Soufiane, F. Green Seaweed Polysaccharides Inventory of Nador Lagoon in North East Morocco. In Polysaccharides; Inamuddin, Ahamed, M.I., Boddula, R., Altalhi, T., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 163–175. ISBN 978-1-119-71141-4. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Q.; Li, H.; Wei, Z.; Lv, K.; Gao, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L. Isolation, Structures and Biological Activities of Polysaccharides from Chlorella: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 2199–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feki, A.; Cherif, B.; Sellem, I.; Naifar, M.; Ben Amar, I.; Ben Azaza, Y.; Kallel, R.; Hariz, L.; Zeghal, S.; Makni Ayadi, F.; et al. Biomedical Applications of Polysaccharide Derived from Tetrasporophyte tufts of Asparagopsis armata (Falkenbergia rufolanosa): Focus on Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Coagulant and Hepato-Protective Activities. Algal Res. 2023, 69, 102958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraiem, M.; Ben Hamouda, S.; Eleroui, M.; Ajala, M.; Feki, A.; Dghim, A.; Boujhoud, Z.; Bouhamed, M.; Badraoui, R.; Pujo, J.M.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Properties of a Crude Polysaccharide Derived from Green Seaweed Halimeda tuna: Computational and Experimental Evidences. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Han, Y.; Yang, L.; Hu, L.; Duan, X.; Yang, X.; Huang, R. Structural Characterization and Immunostimulatory Activity of a Novel Polysaccharide from Green Alga Caulerpa racemosa var peltata. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, M.L.; Mogildea, M.; Moreno, I.; Lopes, A. Acute Inflammation and Metabolism. Inflammation 2018, 41, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, C.A.; Risley, E.A.; Nuss, G.W. Carrageenin-Induced Edema in Hind Paw of the Rat as an Assay for Antiinflammatory Drugs. Exp. Biol. Med. 1962, 111, 544–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posadas, I.; Bucci, M.; Roviezzo, F.; Rossi, A.; Parente, L.; Sautebin, L.; Cirino, G. Carrageenan-Induced Mouse Paw Oedema Is Biphasic, Age-Weight Dependent and Displays Differential Nitric Oxide Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 142, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.-Y.; Huang, X.; Cheong, K.-L. Recent Advances in Marine Algae Polysaccharides: Isolation, Structure, and Activities. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jesus Raposo, M.F.; de Morais, A.M.B.; de Morais, R.M.S.C. Marine Polysaccharides from Algae with Potential Biomedical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2967–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, M.; Mani, S.; Malarvizhi, R.; Sali, V.K.; Vasanthi, H.R. Immunomodulatory Activity of Brown Algae Turbinaria ornata Derived Sulfated Polysaccharide on LPS Induced Systemic Inflammation. Phytomedicine 2021, 89, 153615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouali, N.; Hamadou, W.S.; Badraoui, R.; Lajimi, R.H.; Hamdi, A.; Alreshidi, M.; Adnan, M.; Soua, Z.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Noumi, E.; et al. Phytochemical Composition, Antioxidant, and Anticancer Activities of Sidr Honey: In Vitro and In Silico Computational Investigation. Life 2022, 13, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germolec, D.R.; Shipkowski, K.A.; Frawley, R.P.; Evans, E. Markers of Inflammation. In Immunotoxicity Testing; DeWitt, J.C., Rockwell, C.E., Bowman, C.C., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1803, pp. 57–79. ISBN 978-1-4939-8548-7. [Google Scholar]
- Mzid, M.; Ben Khedir, S.; Bardaa, S.; Sahnoun, Z.; Rebai, T. Chemical Composition, Phytochemical Constituents, Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Urtica urens L. Leaves. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 123, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, C.G.; Lockhart, J.C.; Ferrell, W.R.; Day, S.M.; McLean, J.S. Pathophysiological Basis of Acute Inflammatory Hyperaemia in the Rat Knee: Roles of Cyclo-Oxygenase-1 and -2. J. Physiol. 2002, 539, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geboes, K. From Inflammation to Lesion. Acta Gastro-Enterol. Belg. 1994, 57, 273–284. [Google Scholar]
- Feki, A.; Jaballi, I.; Cherif, B.; Ktari, N.; Naifar, M.; Makni Ayadi, F.; Kallel, R.; Boudawara, O.; Kallel, C.; Nasri, M.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of Polysaccharide Extracted from Fenugreek Seeds against Thiamethoxam-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Genotoxicity in Wistar Adult Rats. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2019, 29, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Filippo, P.; Sousa, W.; Fujimoto, T.; Mota, F.; Alves, A. Acute Phase Proteins Response and Their Clinical Application in Veterinary Medicine. Veterinária Notícias 2020, 26, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tothova, C.; Nagy, O.; Kovac, G. Acute Phase Proteins and Their Use in the Diagnosis of Diseases in Ruminants: A Review. Veterinární Medicína 2014, 59, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holanda, B.F.; Freitas de Araujo, D.; da Silva, J.N.R.; Pereira, M.G.; de Freitas Pires, A.; Assreuy, A.M. Polysaccaride-Rich Extract of Caesalpina Ferrea Stem Barks Attenuates Mice Acute Inflammation Induced by Zymosan: Oxidative Stress Modulation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 267, 113501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaballi, I.; Saad, H.B.; Bkhairia, I.; Cherif, B.; Kallel, C.; Boudawara, O.; Droguet, M.; Magné, C.; Hakim, A.; Amara, I.B. Cytoprotective Effects of the Red Marine Alga Chondrus canaliculatus against Maneb-Induced Hematotoxicity and Bone Oxidative Damages in Adult Rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 184, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Amara, I.; Ben Saad, H.; Cherif, B.; Elwej, A.; Lassoued, S.; Kallel, C.; Zeghal, N. Methyl-Thiophanate Increases Reactive Oxygen Species Production and Induces Genotoxicity in Rat Peripheral Blood. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2014, 24, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, R.B.; Frota, A.F.; Silva, J.; Alves, C.; Neugebauer, A.Z.; Pinteus, S.; Rodrigues, J.A.G.; Cordeiro, E.M.S.; de Almeida, R.R.; Pedrosa, R.; et al. In Vitro Activities of Kappa-Carrageenan Isolated from Red Marine Alga Hypnea musciformis: Antimicrobial, Anticancer and Neuroprotective Potential. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgermeister, J.; Paper, D.H.; Vogl, H.; Linhardt, R.J.; Franz, G. LaPSvS1, a (1→3)-β-Galactan Sulfate and Its Effect on Angiogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Carbohydr. Res. 2002, 337, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Dong, Q.; Du, Z.; Wang, P.; Ding, K. Structural Elucidation of a Polysaccharide from Chrysanthemum morifolium Flowers with Anti-Angiogenic Activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Jia, W.; Cui, Y.; Jin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Liu, Y. Anti-Angiogenic Effect of a Chemically Sulfated Polysaccharide from Phellinus ribis by Inhibiting VEGF/VEGFR Pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, J.; Chang, A.K.; Liu, B.; Yang, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; Zou, X. Fucoidan Extract Derived from Undaria pinnatifida Inhibits Angiogenesis by Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Hao, H.; He, L.; Jing, Y.; Xu, T.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Hu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, X.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Angiogenic Activities of a Purified Polysaccharide from Flesh of Cipangopaludina chinensis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 176, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Willför, S.; Xu, C. A Review of Bioactive Plant Polysaccharides: Biological Activities, Functionalization, and Biomedical Applications. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2015, 5, 31–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.T.; Smith, F. Colorimetric Method for Determination of Sugars and Related Substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, A.G.; Dodgson, K.S.; Price, R.G. Comparative studies on cartilage aminopolysaccharide sulphates I. Polysaccharides from shark, skate, dogfish and fin whale. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) 1963, 69, 496. [Google Scholar]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, R.; Sun, P. Antioxidant and Antitumor Activities in vitro of Polysaccharides from E. sipunculoides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 78, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayar, N.; Kriaa, M.; Kammoun, R. Extraction and Characterization of Three Polysaccharides Extracted from Opuntia ficus Indica Cladodes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes-Lutz, D.; Alviano, D.S.; Alviano, C.S.; Kolodziejczyk, P.P. Screening of Chemical Composition, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of Artemisia Essential Oils. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 1732–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, P.; Pineda, M.; Aguilar, M. Spectrophotometric Quantitation of Antioxidant Capacity through the Formation of a Phosphomolybdenum Complex: Specific Application to the Determination of Vitamin E. Anal. Biochem. 1999, 269, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yıldırım, A.; Mavi, A.; Kara, A.A. Determination of Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of Rumex crispus L. Extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4083–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ijarotimi, O.S.; Adeoti, O.A.; Ariyo, O. Comparative Study on Nutrient Composition, Phytochemical, and Functional Characteristics of Raw, Germinated, and Fermented Moringa oleifera Seed Flour. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 1, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for Lipid Peroxides in Animal Tissues by Thiobarbituric Acid Reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witko, V.; Nguyen, A.T.; Descamps-Latscha, B. Microtiter Plate Assay for Phagocyte-Derived Taurine-Chloramines. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 1992, 6, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, C.; Fridovich, I. Superoxide Dismutase: Improved Assays and an Assay Applicable to Acrylamide Gels. Anal. Biochem. 1971, 44, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flohé, L.; Günzler, W.A. Assays of Glutathione Peroxidase. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 105, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moron, M.; Depierre, J.; Mannervik, B. Levels of Glutathione, Glutathione Reductase and Glutathione S-Transferase Activities in Rat Lung and Liver. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Gen. Subj. 1979, 582, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.S.; Kim, S.-H.; Sa, J.-H.; Jin, C.; Lim, C.-J.; Park, E.-H. Anti-Angiogenic and Inhibitory Activity on Inducible Nitric Oxide Production of the Mushroom Ganoderma lucidum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 90, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

 lymphocytes and
lymphocytes and  platelet aggregates. (B,C) Semi-quantitative scores of necrosis and platelet aggregates in the blood smears of adult rats, respectively. (D,E) Effect of PCT on lymphocytes and neutrophil cell infiltration in carrageenan-induced paw edema, respectively. Values are expressed as means ± SD; ns, no difference; * p < 0.05 and *** p < 0.001.
platelet aggregates. (B,C) Semi-quantitative scores of necrosis and platelet aggregates in the blood smears of adult rats, respectively. (D,E) Effect of PCT on lymphocytes and neutrophil cell infiltration in carrageenan-induced paw edema, respectively. Values are expressed as means ± SD; ns, no difference; * p < 0.05 and *** p < 0.001.
 lymphocytes and
lymphocytes and  platelet aggregates. (B,C) Semi-quantitative scores of necrosis and platelet aggregates in the blood smears of adult rats, respectively. (D,E) Effect of PCT on lymphocytes and neutrophil cell infiltration in carrageenan-induced paw edema, respectively. Values are expressed as means ± SD; ns, no difference; * p < 0.05 and *** p < 0.001.
platelet aggregates. (B,C) Semi-quantitative scores of necrosis and platelet aggregates in the blood smears of adult rats, respectively. (D,E) Effect of PCT on lymphocytes and neutrophil cell infiltration in carrageenan-induced paw edema, respectively. Values are expressed as means ± SD; ns, no difference; * p < 0.05 and *** p < 0.001.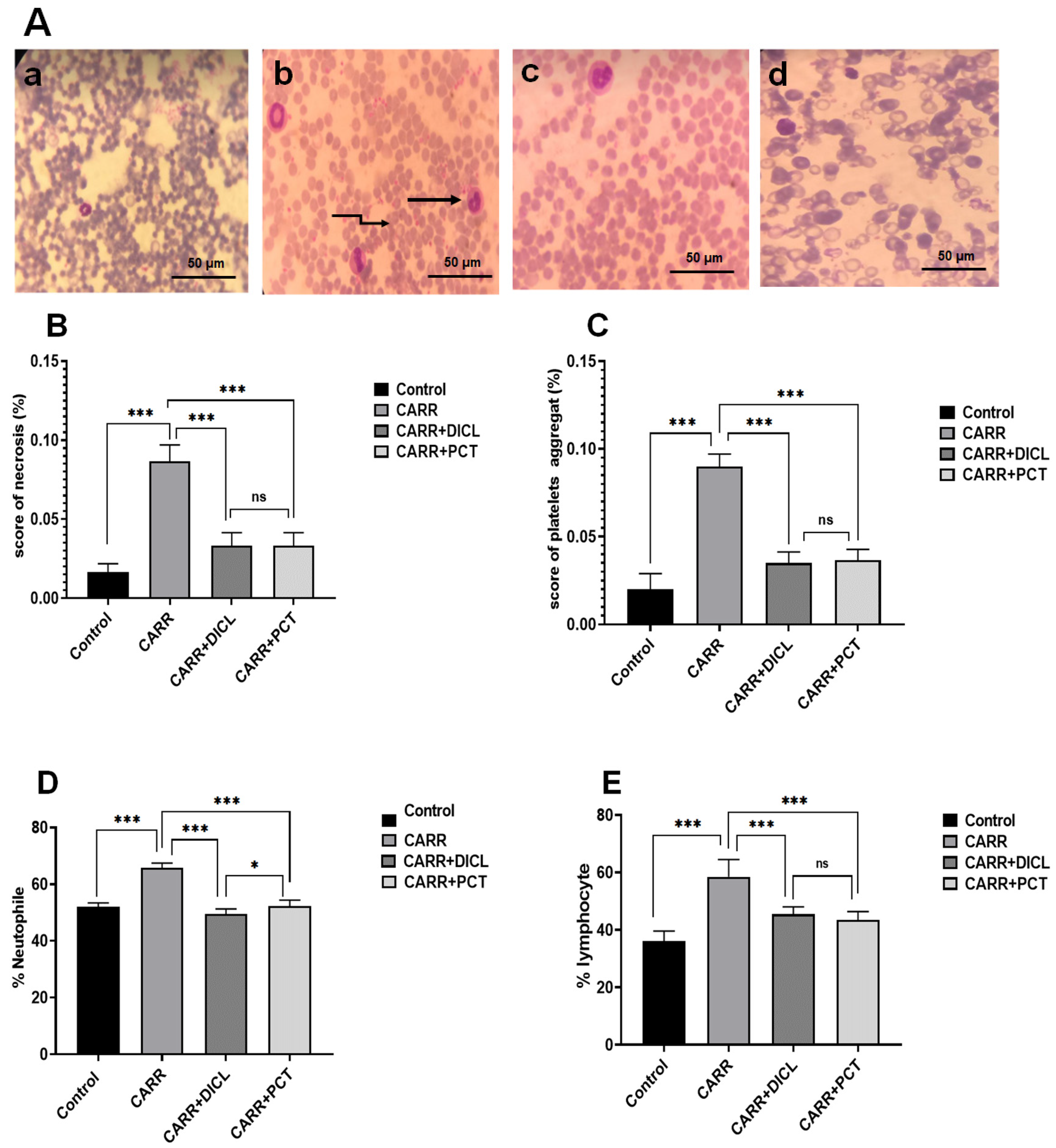
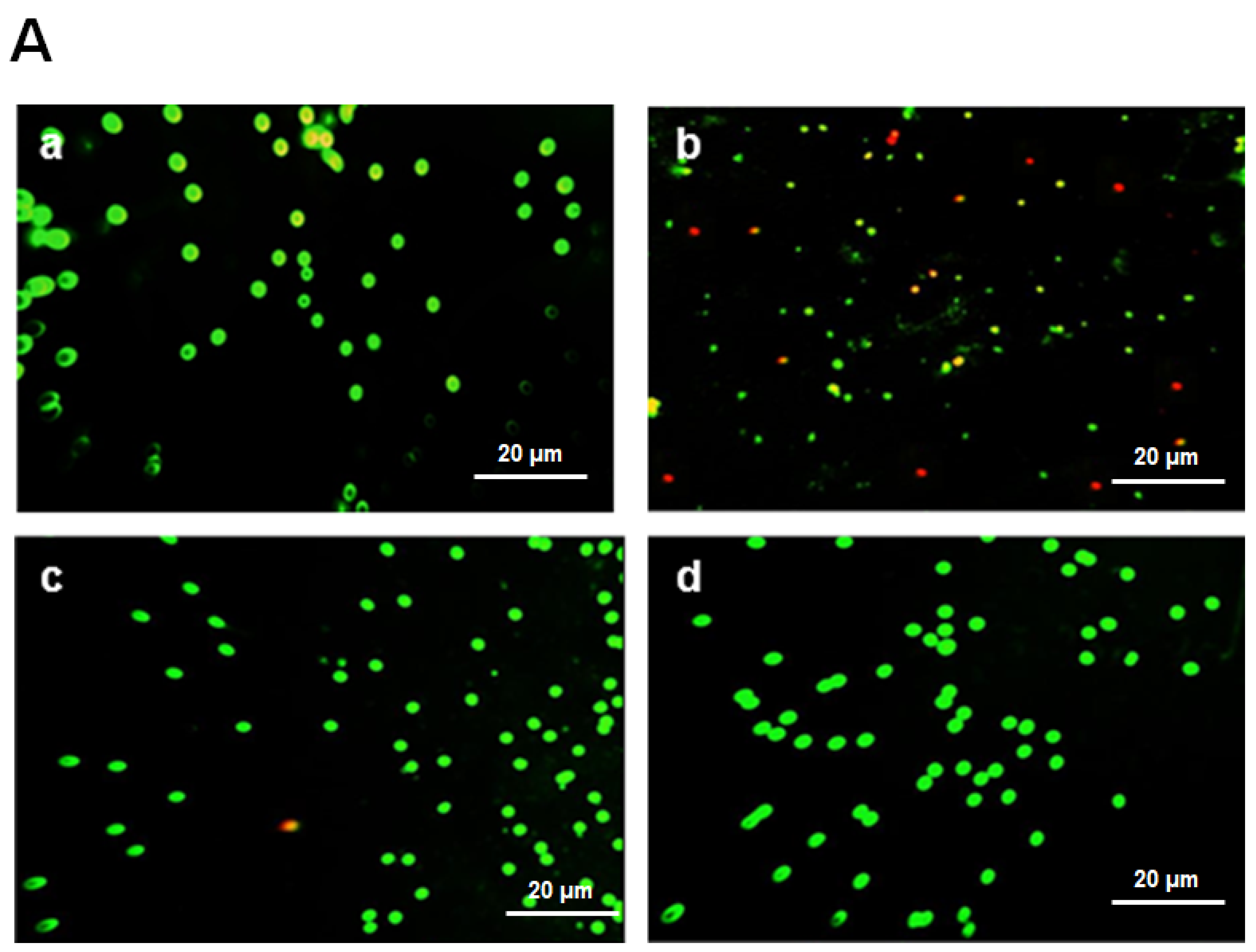
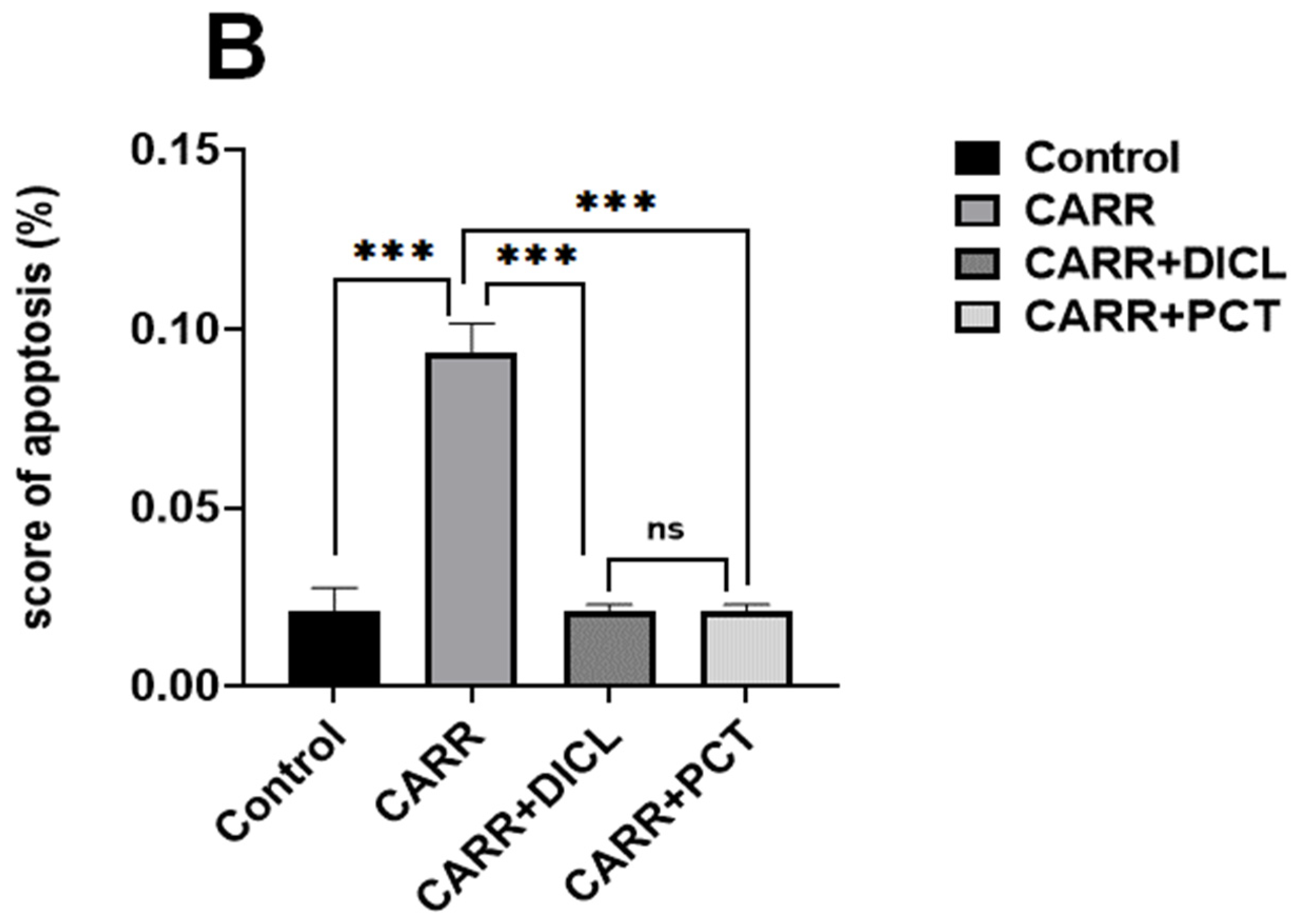
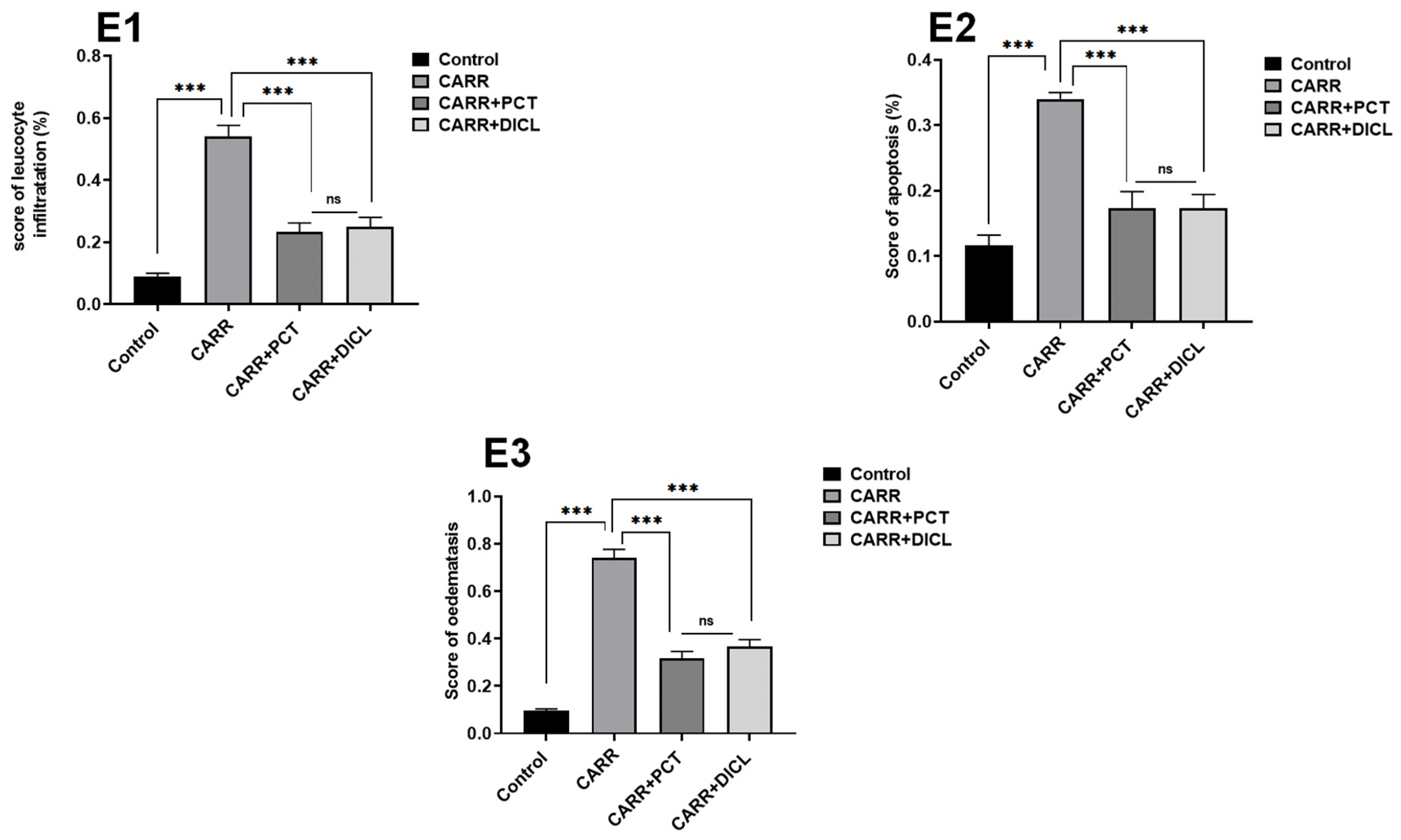
 lymphocyte infiltration,
lymphocyte infiltration,  edema. (E1–E3) Score of inflammatory infiltrate, apoptosis, and edema. Significance: ns: no difference; *** p < 0.001.
edema. (E1–E3) Score of inflammatory infiltrate, apoptosis, and edema. Significance: ns: no difference; *** p < 0.001.
 lymphocyte infiltration,
lymphocyte infiltration,  edema. (E1–E3) Score of inflammatory infiltrate, apoptosis, and edema. Significance: ns: no difference; *** p < 0.001.
edema. (E1–E3) Score of inflammatory infiltrate, apoptosis, and edema. Significance: ns: no difference; *** p < 0.001.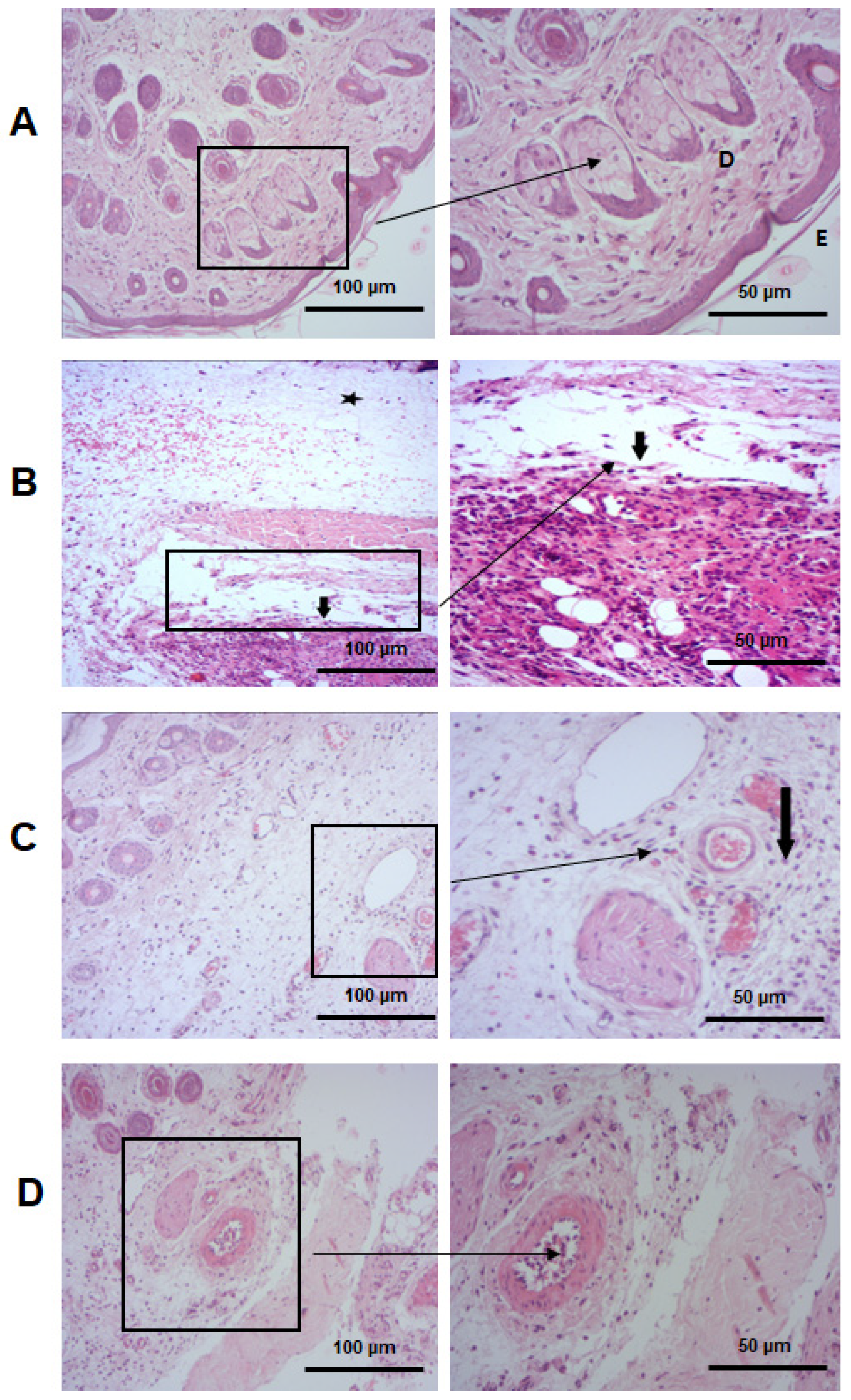
| PCT | |
|---|---|
| Yield (%) | 15.22% ± 0.05 |
| Total sugar (%) | 53.84% ± 0.19 |
| Protein content (%) | 2.05% ± 0.13 |
| Sulfated groups (%) | 5.71%± 0.07 |
| Energy value | 196.00 Kcal |
| Entry | Arabinose (1) | Fructose (2) | Galacturonic Acid (3) | Glucuronic Acid (4) | Rhamnose (5) | Xylose (6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lipophilicity and physicochemical properties | ||||||
| TPSA (Å2) | 90.15 | 110.38 | 135.29 | 135.29 | 90.15 | 90.15 |
| Log Po/w (iLOGP) | 0.39 | 0.52 | −0.68 | −0.04 | 0.85 | −0.39 |
| Consensus Log Po/w | −1.85 | −2.04 | −2.30 | −2.17 | −1.42 | −2.00 |
| Log S (ESOL) solubility | 1.13 | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.46 | 1.13 |
| Pharmacokinetics | ||||||
| GI absorption | Low | Low | Low | Low | High | Low |
| BBB permeant | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| P-gp substrate | No | No | No | No | Yes | No |
| CYP1A2 | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| CYP2C19 | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| CYP2C9 | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| CYP2D6 | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| CYP3A4 | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Parameters | Control | CARR | CARR + PCT | CARR + DICL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC (103/μL) | 3.65 ± 0.55 | 14.26 ± 0.43 a *** | 9.55 ± 0.97 b *** | 9.80 ± 0.71 b *** |
| RBC (106/μL) | 9.71 ± 0.39 | 7.78 ± 0.57 a *** | 8.53 ± 0.59 b *** | 8.78 ± 0.43 b *** |
| PLT (103/mm3) | 960.66 ± 26.27 | 1105 ± 59.24 a *** | 935.33 ± 21.08 b *** | 986.33 ± 12.07 b *** |
| Hb (g/dL) | 12.25 ± 0.66 | 10.80 ± 0.59 a *** | 13.36 ± 0.73 b *** | 12.31 ± 0.59 b *** |
| Ht (%) | 39.75 ±1.44 | 41.11 ±1.11 a * | 39.98 ± 1.48 | 43.00 ± 0.78 b * |
| MCV (mm3/RBC) | 52.67 ± 1.35 | 51.23 ± 0.69 a * | 51.79 ± 1.56 | 52.02 ± 1.79 |
| MCH (pg/RBC) | 18.76 ± 0.15 | 18.53 ± 0.85 | 18.54 ± 0.91 | 17.03 ± 0.05 b * |
| Control | CARR | CARR + PCT | CARR + DICL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total protein (g/dL) | 56.46 ± 0.64 | 64.00 ± 0.10 a *** | 57.05 ± 0.05 b *** | 58.50 ± 0.50 b *** |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 18.35 ± 0.35 | 17.30 ± 0.30 a *** | 18.20 ± 0.40 b *** | 18.51 ± 0.48 b *** |
| Alpha 1 globulins (g/dL) | 7.36 ± 0.16 | 10.30 ± 0.30 a *** | 7.50 ± 0.1 a * b *** | 7.90 ± 0.01 b *** |
| Alpha 2 globulins (g/dL) | 11.70 ± 0.10 | 12.55 ± 0.25 a *** | 11.35 ± 0.34 b *** | 11.32 ± 0.11 b *** |
| Beta 1 globulins (g/dL) | 6.55 ± 0.35 | 7.30 ± 0.20 a *** | 6.31 ± 0.29 b *** | 6.20 ± 0.17 b *** |
| Beta 2 globulins (g/dL) | 3.25 ± 0.25 | 4.45 ± 0.45 a *** | 3.56 ± 0.08 b *** | 3.90 ± 0.14 b ** |
| Gamma globulins (g/dL) | 7.06 ± 0.04 | 7.41 ± 0.08 a *** | 7.08 ± 0.04 b *** | 7.04 ± 0.04 |
| Parameters | Control | CARR | CARR + PCT | CARR + DICL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paw skin | ||||
| MDA | 18.75 ± 0.22 | 23.22 ± 0.13 a *** | 18.53 ± 0.99 b *** | 17.17 ± 0.13 b *** |
| AOPP | 0.58 ± 0.04 | 0.75 ± 0.03 a *** | 0.56 ± 0.07 b *** | 0.56 ± 0.08 b *** |
| SOD | 19.63 ± 1.12 | 13.97 ± 1.15 a *** | 18.40 ± 1.28 b ** | 18.26 ± 0.79 b *** |
| GPx | 10.49 ± 0.95 | 6.64 ± 0.99 a ** | 9.92 ± 0.56 b *** | 10.83 ± 0.67 b *** |
| GSH | 137.76 ± 0.98 | 147.11 ± 0.40 a *** | 135.13 ± 0.53 b *** | 138.78 ± 0.36 b *** |
| Erythrocytes | ||||
| MDA | 80.83 ± 0.71 | 107.02 ±3.11 a ** | 74.16 ± 2.94 b ** | 85.71 ± 2.96 b ** |
| AOPP | 1.67 ± 0.07 | 3.32 ± 0.17 a *** | 1.74 ± 0.08 b *** | 1.91 ± 0.07 b *** |
| SOD | 26.96 ± 1.33 | 14.15 ± 1.23 a *** | 25.19± 1.35 b *** | 26.98± 2.38 b *** |
| GPx | 3.23 ± 0.10 | 2.26 ± 0.15 a *** | 3.02 ± 0.39 b *** | 3.38 ± 0.12 b *** |
| GSH | 125.23 ± 2.34 | 137.98 ± 2.88 a *** | 114.08 ± 2.41 b *** | 117.02± 4.74 b *** |
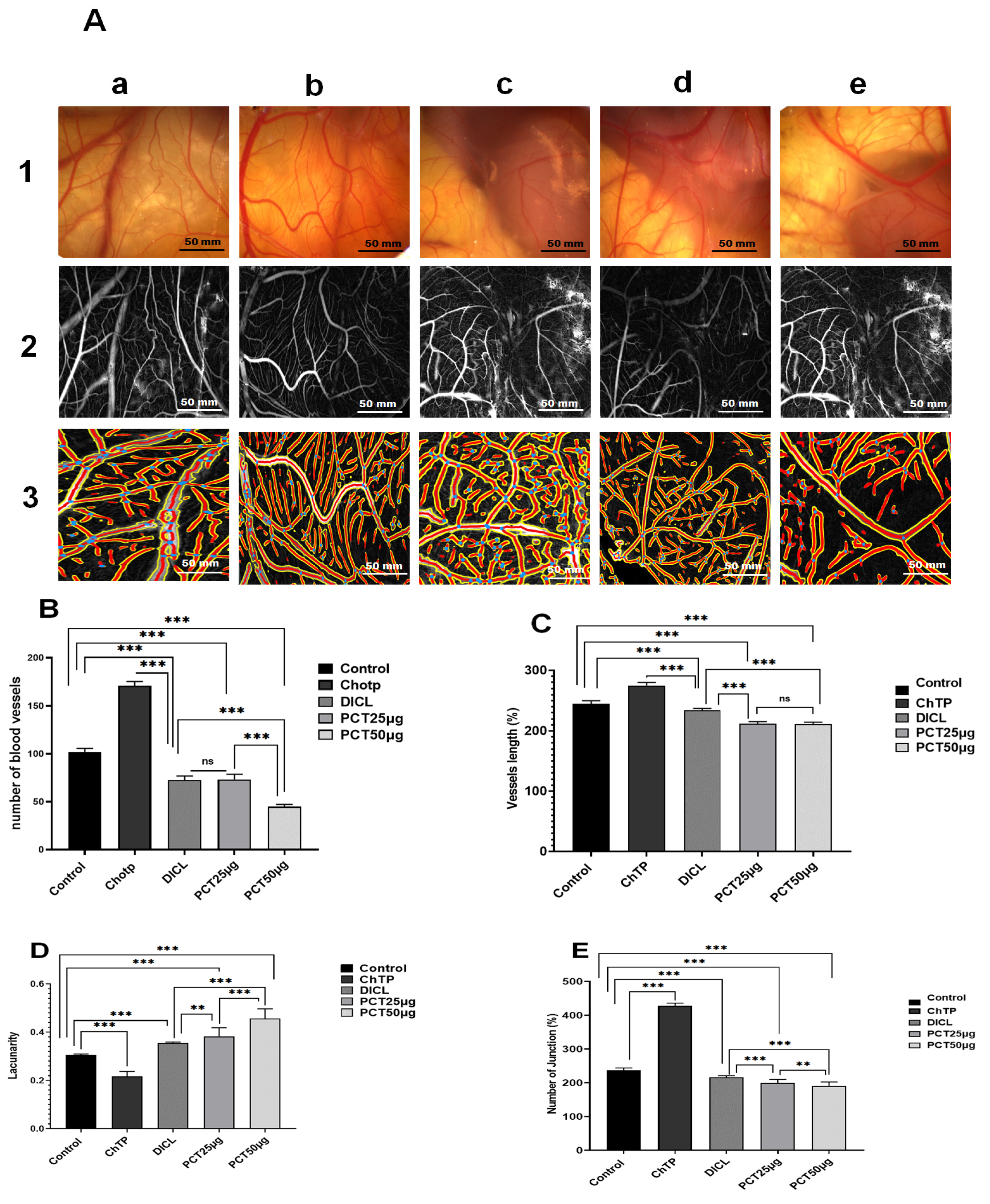
| Score Value | Potential Effect | Observed Effect |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | No effect | |
| 0.5 | Very weak effect | No capillary-free area Area with reduced capillary density around the pellet (not larger than the area of the pellet) |
| 1 | Weak–medium effect | Small capillary-free area or area with significantly reduced capillary density (effect not larger than double the size of the pellet) |
| 2 | Strong effect | Capillary-free area around the pellet (at least double the size of the pellet) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lakhrem, M.; Eleroui, M.; Boujhoud, Z.; Feki, A.; Dghim, A.; Essayagh, S.; Hilali, S.; Bouhamed, M.; Kallel, C.; Deschamps, N.; et al. Anti-Vasculogenic, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Sulfated Polysaccharide Derived from Codium tomentosum: Pharmacokinetic Assay. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060672
Lakhrem M, Eleroui M, Boujhoud Z, Feki A, Dghim A, Essayagh S, Hilali S, Bouhamed M, Kallel C, Deschamps N, et al. Anti-Vasculogenic, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Sulfated Polysaccharide Derived from Codium tomentosum: Pharmacokinetic Assay. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(6):672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060672
Chicago/Turabian StyleLakhrem, Marwa, Malek Eleroui, Zakaria Boujhoud, Amal Feki, Amel Dghim, Sanah Essayagh, Said Hilali, Marwa Bouhamed, Choumous Kallel, Nathalie Deschamps, and et al. 2024. "Anti-Vasculogenic, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Sulfated Polysaccharide Derived from Codium tomentosum: Pharmacokinetic Assay" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 6: 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060672
APA StyleLakhrem, M., Eleroui, M., Boujhoud, Z., Feki, A., Dghim, A., Essayagh, S., Hilali, S., Bouhamed, M., Kallel, C., Deschamps, N., Toffol, B. d., Pujo, J. M., Badraoui, R., Kallel, H., & Ben Amara, I. (2024). Anti-Vasculogenic, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Sulfated Polysaccharide Derived from Codium tomentosum: Pharmacokinetic Assay. Pharmaceuticals, 17(6), 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060672






