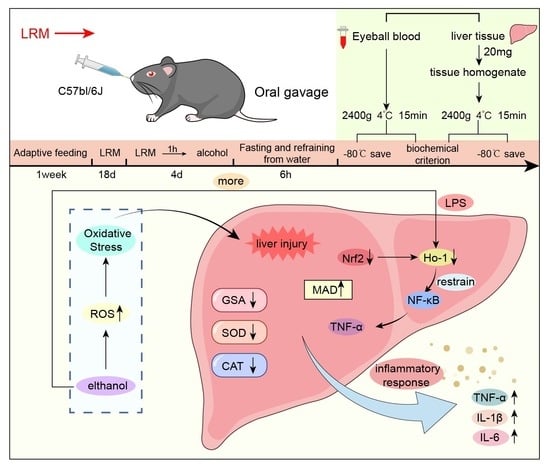
Protective Effects of Lycium ruthenicum Murray against Acute Alcoholic Liver Disease in Mice via the Nrf2/HO-1/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. LRM Chemical Components
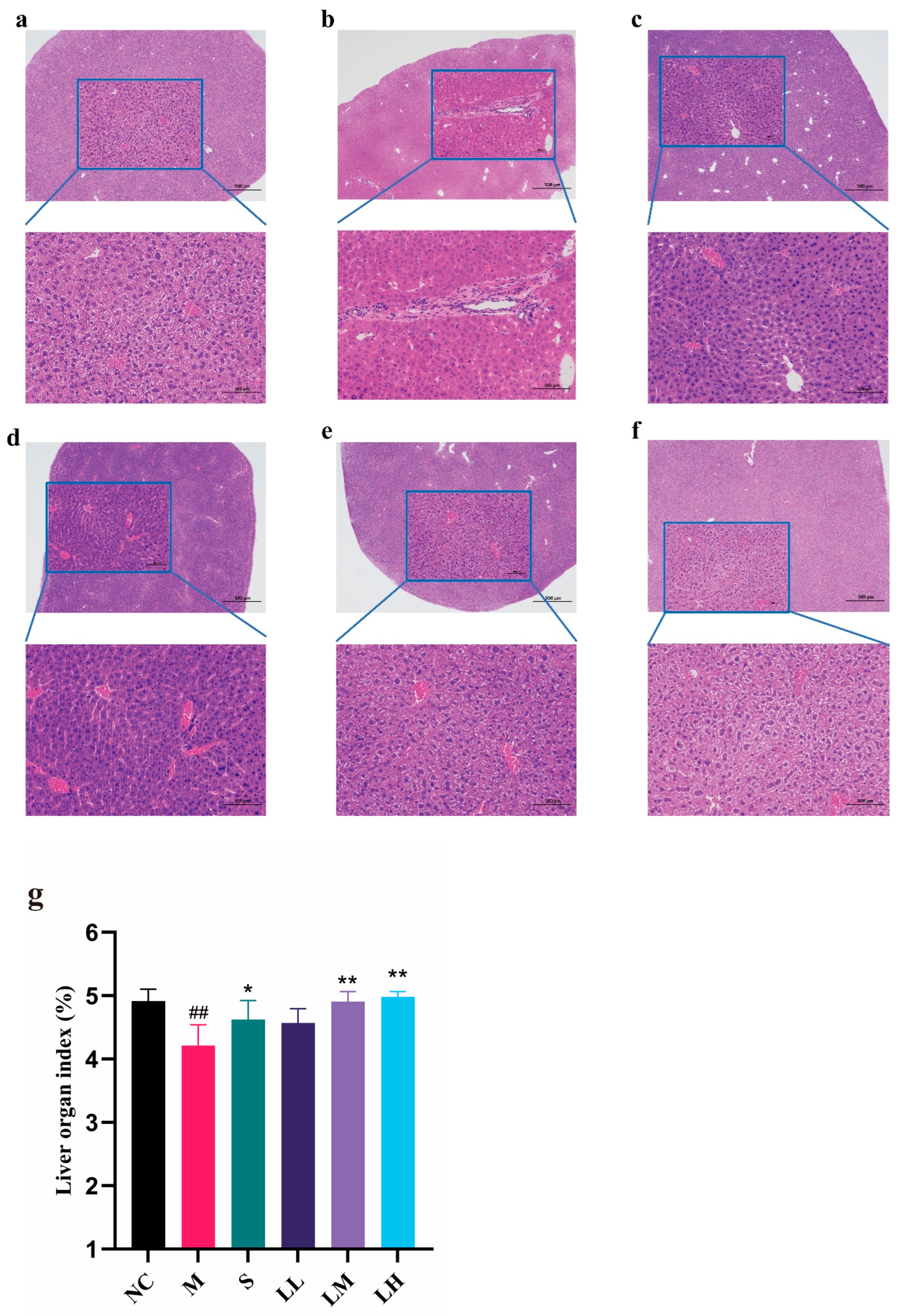
2.2. Effect of LRM on the Mouse Liver
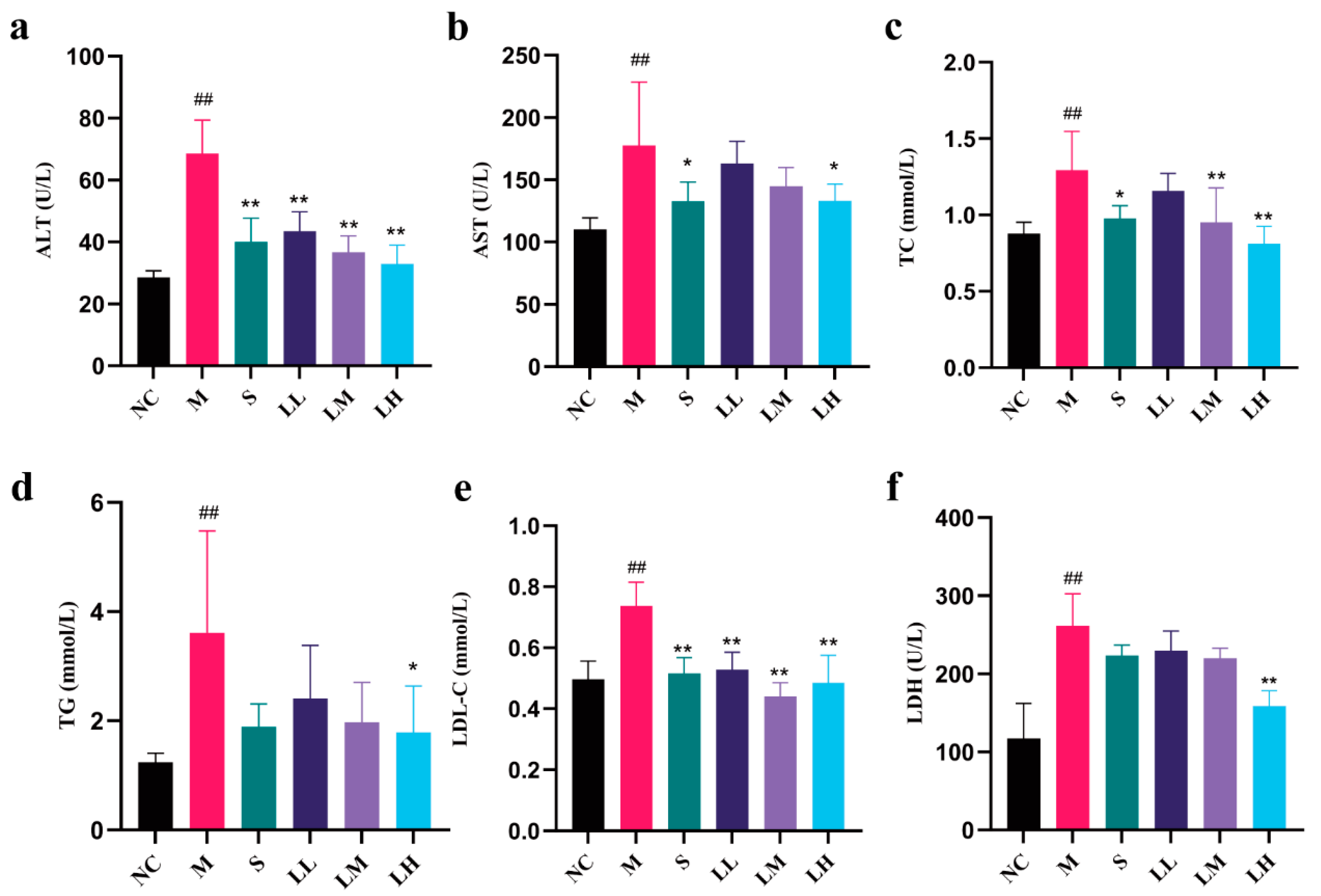
2.3. Role of LRM in Serum Biochemical Indicators of Alcohol-Mediated Liver Injury in Mice
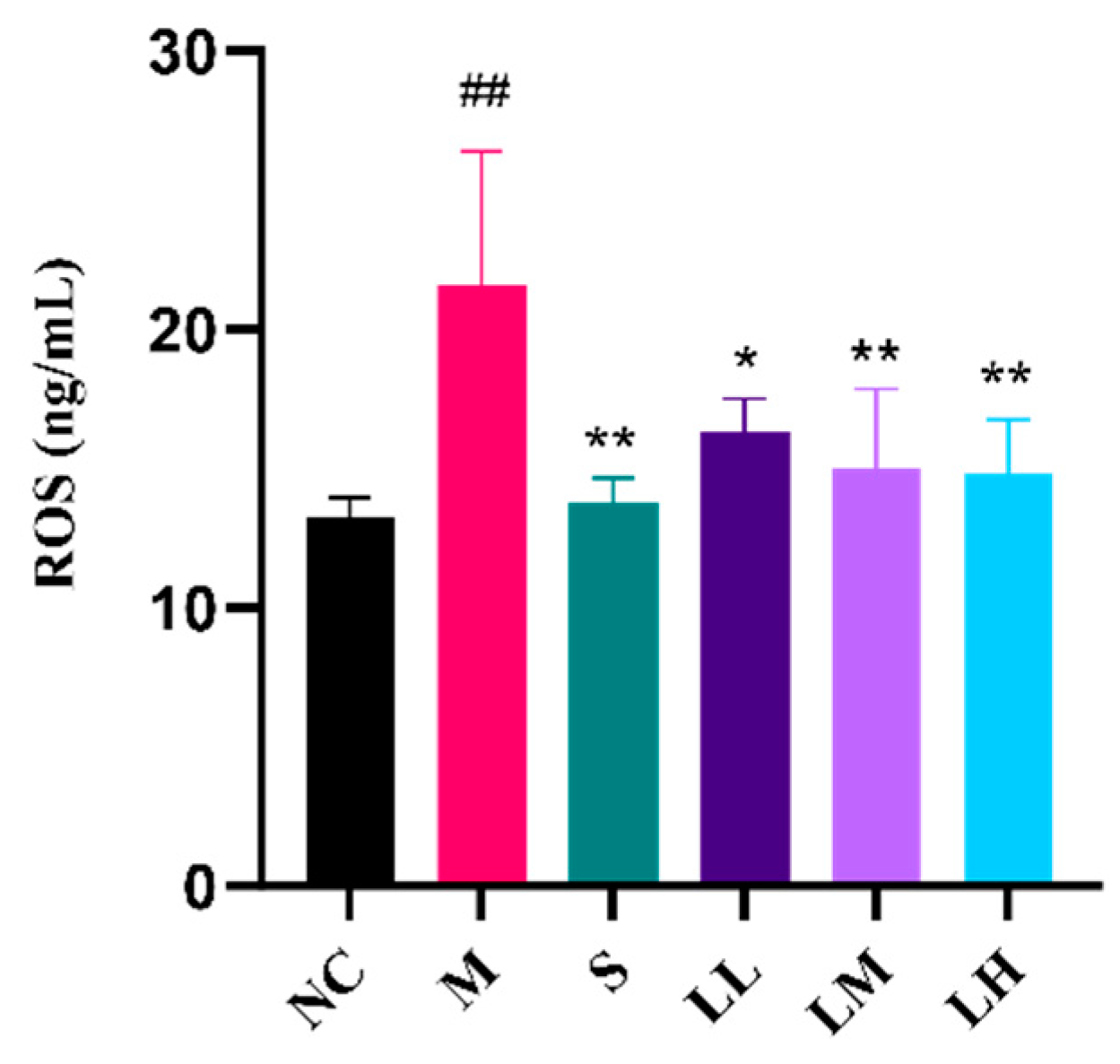
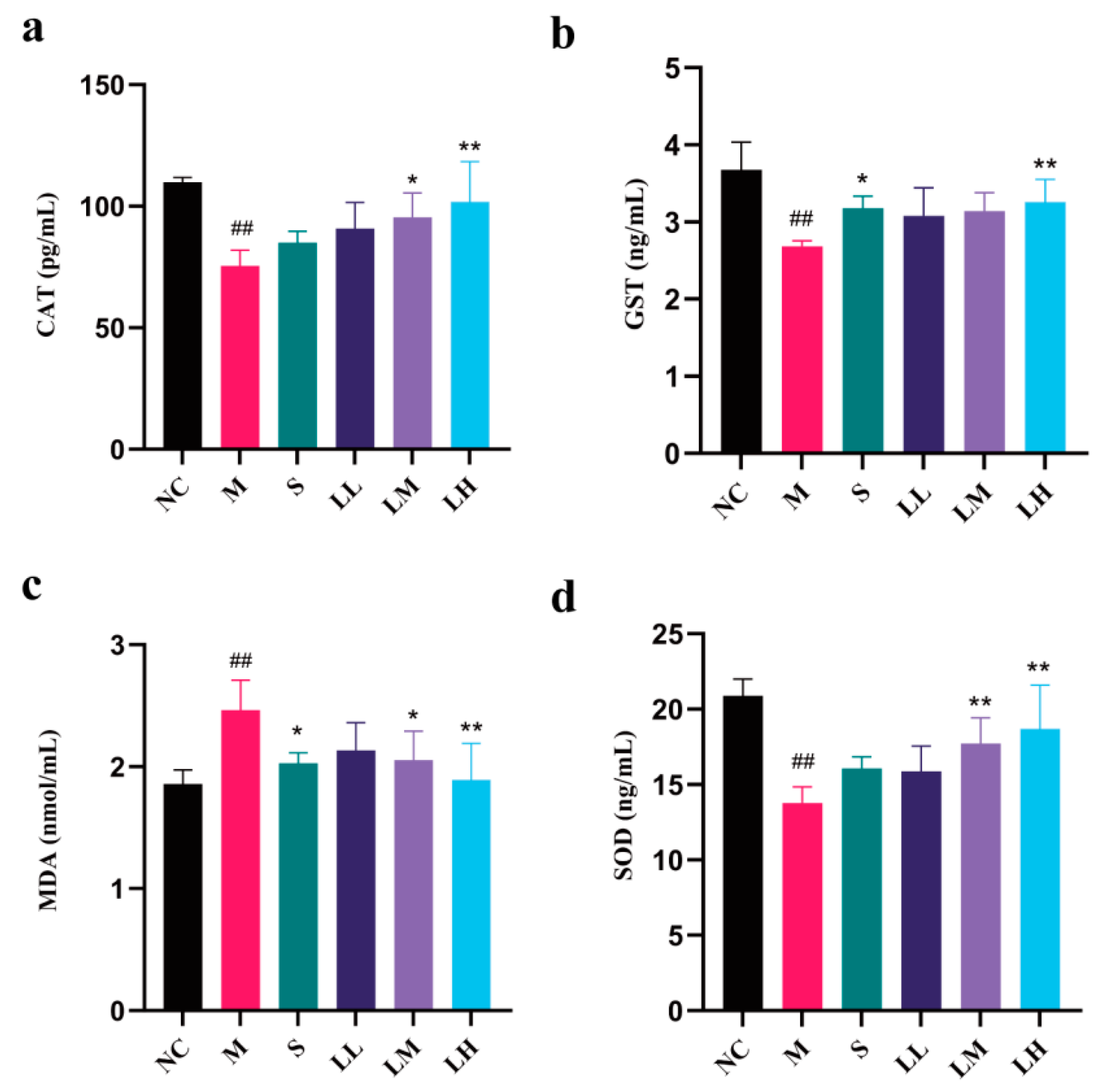
2.4. Role of LRM in Oxidative Damage in the Liver
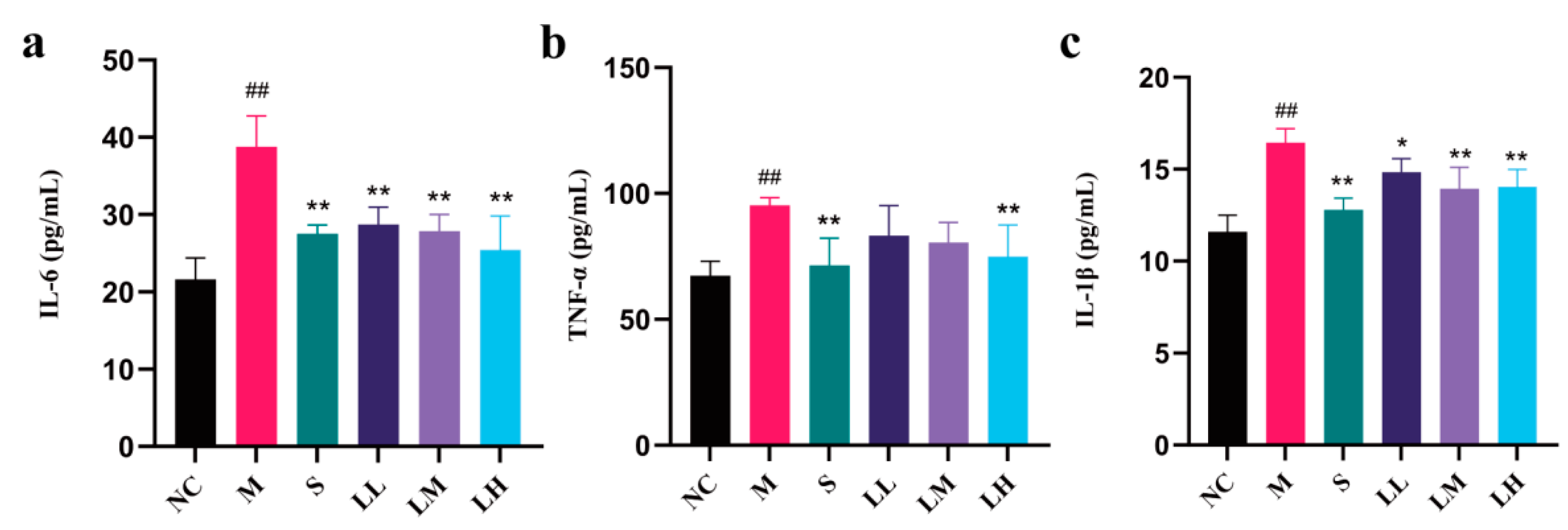
2.5. Role of LRM in Inflammatory Cytokines and Mediators of Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury in Mice
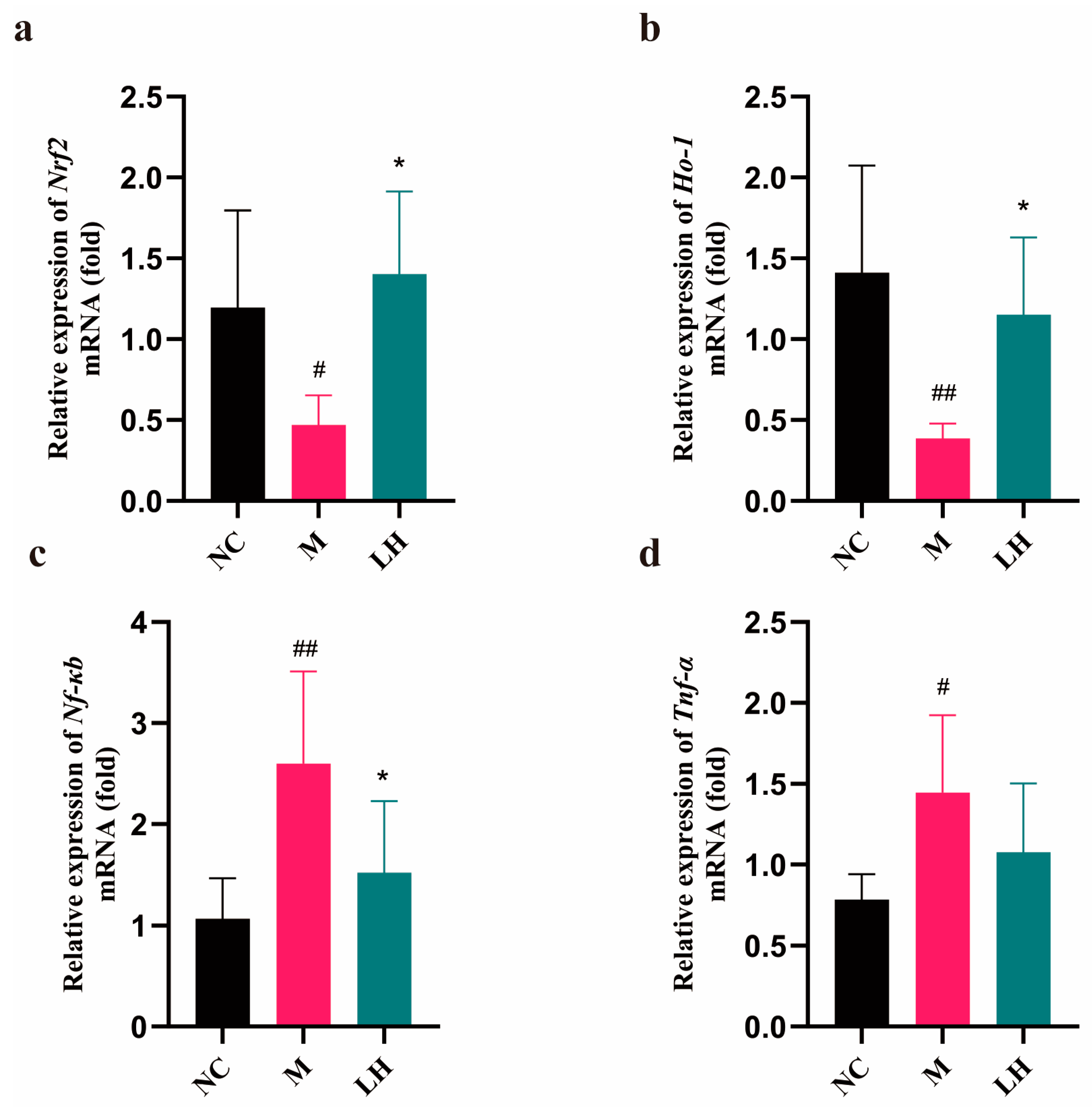
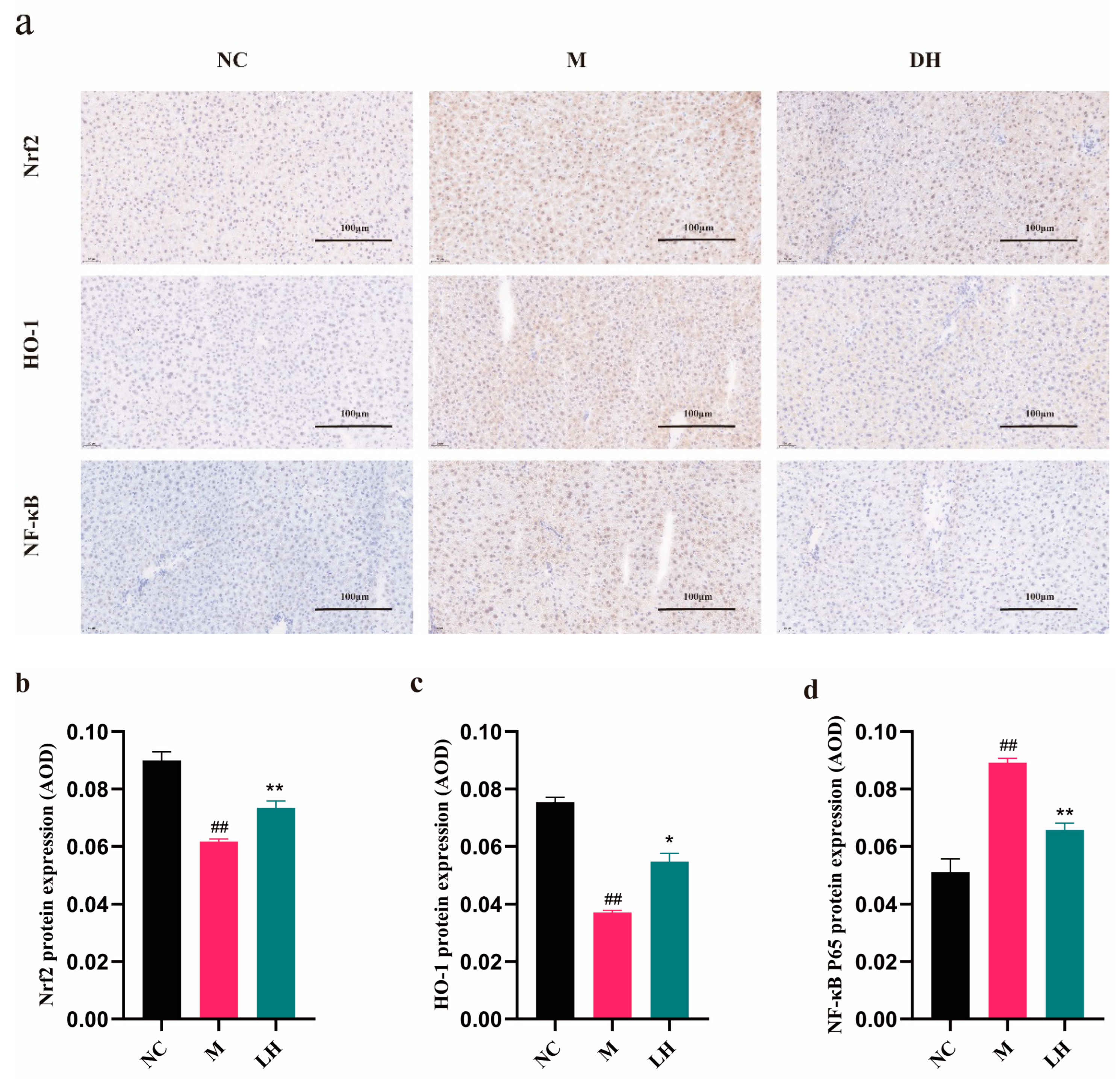
2.6. Role of LRM in Nrf2, HO-1, NF-κB, and TNF-α
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Chemicals
4.2. Animals
4.3. Grouping and Drug Use
4.4. Total Anthocyanin Content Determination
4.5. Histopathological Analyses of Liver Tissue
4.6. Liver Index Analysis
4.7. Serum Biochemical Analysis
4.8. ROS Analysis
4.9. Liver Oxidative Stress Analysis
4.10. Inflammation Analysis
4.11. Gene Levels
4.12. Immunohistochemistry
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Shea, R.S.; Dasarathy, S.; McCullough, A.J. Alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 2010, 51, 307–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, K.R.; Murray, M.M. Alcoholic liver disease and pancreatitis: Global health problems being addressed by the US National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28 (Suppl. 1), 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Hu, W.; Tu, J.; Li, J.; Liang, Q.; Han, S. Pathogenic mechanisms and regulatory factors involved in alcoholic liver disease. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Xie, W.; Li, R.; Wang, C. Novel potential biomarkers for severe alcoholic liver disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1051353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.K.; Bataller, R.; Ahn, J.; Kamath, P.S.; Shah, V.H. ACG Clinical Guideline: Alcoholic Liver Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 175–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuman, M.G.; Seitz, H.K.; Teschke, R.; Malnick, S.; Johnson-Davis, K.L.; Cohen, L.B.; German, A.; Hohmann, N.; Moreira, B.; Moussa, G.; et al. Molecular, Viral and Clinical Features of Alcohol- and Non-Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 1294–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Chao, X.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; Sun, Z.; Rülicke, T.; Zatloukal, K.; Ni, H.M.; Ding, W.X. Loss of SQSTM1/p62 Induces Obesity and Exacerbates Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury in Aged Mice. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 15, 1027–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.A.; Ding, W.X. Role of autophagy in alcohol and drug-induced liver injury. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 136, 111075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.M.; Cho, Y.E.; Hwang, S. Crosstalk between Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Liver Injury in the Pathogenesis of Alcoholic Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orman, E.S.; Odena, G.; Bataller, R. Alcoholic liver disease: Pathogenesis, management, and novel targets for therapy. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Tan, Q.; Wen, B.; Bai, Y.; Che, Q.; Cao, H.; Guo, J.; Su, Z. Galacto-Oligosaccharide Alleviates Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Metabolites 2022, 12, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plumb, G.W.; De Pascual-Teresa, S.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Cheynier, V.; Williamson, G. Antioxidant properties of catechins and proanthocyanidins: Effect of polymerisation, galloylation and glycosylation. Free Radic. Res. 1998, 29, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Hu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Mou, R.; Zhu, Z.; Beta, T. Phenolic acids, anthocyanins, proanthocyanidins, antioxidant activity, minerals and their correlations in non-pigmented, red, and black rice. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.X.; Liang, G.; Chai, W.M.; Feng, H.L.; Zhou, H.T.; Shi, Y.; Chen, Q.X. Antioxidant and antityrosinase proanthocyanidins from Polyalthia longifolia leaves. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2014, 118, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhou, A.; Li, X. Inhibition of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides and Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides against oxidative injury induced by γ-irradiation in rat liver mitochondria. Carbohyd. Polym. 2007, 69, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potterat, O. Goji (Lycium barbarum and L. chinense): Phytochemistry, pharmacology and safety in the perspective of traditional uses and recent popularity. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Tipoe, G.L.; Yang, C.; Nanji, A.A.; Hao, X.; So, K.F.; Xiao, J. Lycium barbarum Polysaccharide Supplementation Improves Alcoholic Liver Injury in Female Mice by Inhibiting Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase 1. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, e1800144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Lu, J.; Xue, H.; Lou, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, T.; Ding, Z.; Chen, X. Anthocyanins from Lycium ruthenicum Murray Mitigate Cadmium-Induced Oxidative Stress and Testicular Toxicity by Activating the Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Liong, E.C.; Ching, Y.P.; Chang, R.C.; Fung, M.L.; Xu, A.M.; So, K.F.; Tipoe, G.L. Lycium barbarum polysaccharides protect rat liver from non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-induced injury. Nutr. Diabetes 2013, 3, e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, L.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, D.; Li, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Olatunji, O.J.; Wan, P.; Gong, K. Kukoamine B Ameliorate Insulin Resistance, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Other Metabolic Abnormalities in High-Fat/High-Fructose-Fed Rats. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 1843–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.S.; Wu, S.J.; Tsai, Y.H.; Lin, Y.H.; Chao, J.C. Hot water extracted Lycium barbarum and Rehmannia glutinosa inhibit liver inflammation and fibrosis in rats. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2011, 39, 1173–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Dong, W.; Chen, G.; Mi, J.; Lu, L.; Xie, Z.; Xu, W.; Zhou, W.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, X.; et al. Anthocyanins from Lycium ruthenicum Murray Ameliorated High-Fructose Diet-Induced Neuroinflammation through the Promotion of the Integrity of the Intestinal Barrier and the Proliferation of Lactobacillus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 2864–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Cao, J.M.; Zhou, H.T.; Zhang, J.; Tian, Y.M.; Song, Y.Y.; Jiang, R.Y. Protective effects of Lycium ruthenicum Murr. juice on alcoholic liver injury in rats. Chin. J. Appl. Physiol. 2022, 38, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Zhao, J.; Xie, X.; Chen, T.; Yin, Y.; Zhai, R.; Wang, X.; An, W.; Li, J. Anthocyanins from the fruits of Lycium ruthenicum Murray improve high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance by ameliorating inflammation and oxidative stress in mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 3855–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.; Dong, M.; Mi, X.; Hu, M.; Lu, J.; Chen, X. The Protective Effect of Trichilia catigua A. Juss. on DEHP-Induced Reproductive System Damage in Male Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 832789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.; Li, S.; Wang, N.; Tan, H.-Y.; Cheung, F.; Feng, Y. A biomedical investigation of the hepatoprotective effect of radix salviae miltiorrhizae and network pharmacology-based prediction of the active compounds and molecular targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.S.; Yuan, M.H.; Zhang, C.Y.; Liu, H.M.; Liu, J.R.; Wei, A.L.; Ye, Q.; Zeng, B.; Li, M.F.; Guo, Y.P.; et al. Puerariae Lobatae radix flavonoids and puerarin alleviate alcoholic liver injury in zebrafish by regulating alcohol and lipid metabolism. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 134, 111121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Wang, H.F.; Chen, Y.M.; Bai, R.X.; Du, S.Y. Baicalin confers hepatoprotective effect against alcohol-associated liver disease by upregulating microRNA-205. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 107, 108553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Wo, L.; Du, Z.; Tang, L.; Song, Z.; Dou, X. Danshen protects against early-stage alcoholic liver disease in mice via inducing PPARα activation and subsequent 4-HNE degradation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Bataller, R. Alcoholic liver disease: Pathogenesis and new therapeutic targets. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1572–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertola, A.; Mathews, S.; Ki, S.H.; Wang, H.; Gao, B. Mouse model of chronic and binge ethanol feeding (the NIAAA model). Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, H.L.; Zhong, G.Y.; Zhu, J.X. Molecular mechanism and research progress on pharmacology of traditional Chinese medicine in liver injury. Pharm. Biol. 2018, 56, 594–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Hu, Y.Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, L.M.; Liu, C.H.; Sun, K.W.; Hu, D.C.; Yin, Y.K.; Zhou, X.Q.; Wan, M.B.; et al. Multicenter clinical study on Fuzhenghuayu capsule against liver fibrosis due to chronic hepatitis B. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 2892–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Nasser, M.I.; Masood, M.; Adlat, S.; Huang, Y.; Yang, B.; Luo, C.; Jiang, N. Efficiency of Traditional Chinese medicine targeting the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 126, 110074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Ci, X.; Cheng, H.; Yu, Q.; Li, D. Chicoric acid alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice through anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant activities. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 66, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morikawa, T.; Pan, Y.; Ninomiya, K.; Imura, K.; Matsuda, H.; Yoshikawa, M.; Yuan, D.; Muraoka, O. Acylated phenylethanoid oligoglycosides with hepatoprotective activity from the desert plant Cistanche tubulosa. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 1882–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loguercio, C.; Federico, A. Oxidative stress in viral and alcoholic hepatitis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandrekar, P.; Szabo, G. Signalling pathways in alcohol-induced liver inflammation. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Yan, Y.; Wan, P.; Chen, D.; Ding, Y.; Ran, L.; Mi, J.; Lu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; et al. Gut microbiota modulation and anti-inflammatory properties of anthocyanins from the fruits of Lycium ruthenicum Murray in dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 136, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, S.; Zhou, W.; Meng, J.; Deng, K.; Zhou, H.; Hu, N.; Suo, Y. Rapid qualitative and quantitative analyses of eighteen phenolic compounds from Lycium ruthenicum Murray by UPLC-Q-Orbitrap MS and their antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2018, 269, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.B.; Tian, K.; Huang, L.L.; He, C.W.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.T.; Wan, J.B. Herbal medicines for the prevention of alcoholic liver disease: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 144, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, W.; Shah, V.H. Pathogenesis of Alcoholic Liver Disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2016, 20, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannini, E.G.; Testa, R.; Savarino, V. Liver enzyme alteration: A guide for clinicians. Cmaj 2005, 172, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Shin, S.P.; Yang, Y.J.; Bang, C.S.; Baik, G.H.; Kim, D.J.; Ham, Y.L.; Choi, E.Y.; Suk, K.T. Immunological measurement of aspartate/alanine aminotransferase in predicting liver fibrosis and inflammation. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2020, 35, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraona, E.; Lieber, C.S. Effects of ethanol on lipid metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 1979, 20, 289–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieber, C.S. Effects of ethanol upon lipid metabolism. Lipids 1974, 9, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.F.; Quarfordt, S.H. The effect of ethanol on lipoprotein metabolism. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1981, 5, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Gu, L.; Hui, H.; Li, X.; Jin, L. Extracts of Dracocephalum tanguticum Maxim Ameliorate Acute Alcoholic Liver Disease via Regulating Transcription Factors in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 830532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.; Chen, C.; Feng, H.; Li, G.; Peng, W.; Liu, X.; Yang, J.; Hu, X. Protection of Ficus pandurata Hance against acute alcohol-induced liver damage in mice via suppressing oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 275, 114140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, J.; Han, J.; Lee, C.; Yoon, M.; Jung, Y. Pathophysiological Aspects of Alcohol Metabolism in the Liver. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramness, J.G.; Skulberg, K.R.; Skulberg, A.; Moe, J.S.; Mørland, J. The Self-Rated Effects of Alcohol Are Related to Presystemic Metabolism of Alcohol. Alcohol. Alcohol. 2023, 58, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabri, M.A.; Sani, M.; Rtibi, K.; Marzouki, L.; El-Benna, J.; Sakly, M.; Sebai, H. Chamomile decoction extract inhibits human neutrophils ROS production and attenuates alcohol-induced haematological parameters changes and erythrocytes oxidative stress in rat. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, S.; Zhao, Y.; Bao, W.; Xiao, X.; Wang, D.; Nussler, A.K.; Yan, H.; Yao, P.; Liu, L. Curcumin prevents chronic alcohol-induced liver disease involving decreasing ROS generation and enhancing antioxidative capacity. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apel, K.; Hirt, H. Reactive oxygen species: Metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2004, 55, 373–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadel, G.S.; Horvath, T.L. Mitochondrial ROS signaling in organismal homeostasis. Cell 2015, 163, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, P.D.; Huang, B.W.; Tsuji, Y. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis and redox regulation in cellular signaling. Cell. Signal. 2012, 24, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M.T.; Mazur, M.; Telser, J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, Y.; Moore, L.E.; Bradford, B.U.; Gao, W.; Thurman, R.G. Antibiotics prevent liver injury in rats following long-term exposure to ethanol. Gastroenterology 1995, 108, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matute-Blanch, C.; Brito, V.; Midaglia, L.; Villar, L.M.; Barriga, G.G.D.; de la Fuente, A.G.; Borrás, E.; Fernández-García, S.; Calvo-Barreiro, L.; Miguez, A. Inflammation in multiple sclerosis induces a specific reactive astrocyte state driving non-cell-autonomous neuronal damage. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, P.P.; Firestein, G.S. NF-kappaB: A key role in inflammatory diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.D.; Zhang, R.; Kang, K.A.; You, H.J.; Hyun, J.W. Increased glutathione synthesis following Nrf2 activation by vanadyl sulfate in human chang liver cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 8878–8894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishore, R.; Hill, J.R.; McMullen, M.R.; Frenkel, J.; Nagy, L.E. ERK1/2 and Egr-1 contribute to increased TNF-alpha production in rat Kupffer cells after chronic ethanol feeding. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2002, 282, G6–G15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, T.; Wang, C.; Meng, Q.; Huo, X.; Sun, H.; Sun, P.; Zheng, S.; Ma, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, K. Hepatoprotective effect of rhein against methotrexate-induced liver toxicity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 834, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casili, G.; Lanza, M.; Filippone, A.; Campolo, M.; Paterniti, I.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Esposito, E. Dimethyl fumarate alleviates the nitroglycerin (NTG)-induced migraine in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, M.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Tran, K.; Reddy, S.P.; Malik, A.B. Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue injury. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 1126–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Ruan, B.; Hu, G. Anti-intoxication and protective effects of a recombinant serine protease inhibitor from Lentinula edodes against acute alcohol-induced liver injury in mice. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 4985–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, M.; Su, G.; Sun, B. Chicken breast muscle hydrolysates ameliorate acute alcohol-induced liver injury in mice through alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) activation and oxidative stress reduction. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, D.; Kim, S.H.; Son, S.W.; Seo, J.; Jeong, T.B.; Kim, K.M.; Jung, J.C.; Jung, M.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Jung, Y.S. Germinated Soybean Embryo Extract Ameliorates Fatty Liver Injury in High-Fat Diet-Fed Obese Mice. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Lv, J.; Fu, Y.; Shang, Y.; Liu, J.; Lyu, Y.; Wei, M.; Yu, X. Optimization of Microwave-Assisted Extraction Process of Total Flavonoids from Salicornia bigelovii Torr. and Its Hepatoprotective Effect on Alcoholic Liver Injury Mice. Foods 2024, 13, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.K.; Tungalag, T.; Kang, H.S. Bulbils of Aerial Yam Attenuate Ethanol-Induced Hepatotoxicity in HepG2 Cells through Inhibition of Oxidative Stress by Activation of the Nuclear Factor Erythroid-2-Related Factor 2 Signaling Pathway. Nutrients 2024, 16, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ding, L.; Yan, Y.; Xing, Y.; Xu, J.; Qin, L. Lactoferrin Alleviates Ethanol-Induced Injury via Promoting Nrf2 Nuclear Translocation in BRL-3A Rat Liver Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Hou, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Hu, Z.; Chen, L.; Huang, J. High Fischer Ratio Oligopeptides of Gluten Alleviate Alcohol-Induced Liver Damage by Regulating Lipid Metabolism and Oxidative Stress in Rats. Foods 2024, 13, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, X.; Wang, X.; Wen, S.; Sun, L.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Cao, J.; Lai, Z.; Li, Z.; et al. Six Types of Tea Reduce Acute Alcoholism in Mice by Enhancing Ethanol Metabolism, Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 848918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kafache, D.; Deli, M.; Galani, B.R.T.; Agume, A.N.; Bouba, A.A.; Njintang, N.Y. Physicochemical and in Vitro Antioxidant Properties of Juice and Cake Filters from Carissa edulis Vahl Fruits. J. Explor. Res. Pharmacol. 2022, 7, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Species | Forward (5′–3′) | Reverse (3′–5′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nf-κb p65 | Mouse | CTTCTGGGCCTTATGTGGAGATC | GGTCCTGTGTAGCCATTGATCTT |
| Ho-1 | Mouse | GCTCGAATGAACACTCTGGAGAT | ACTCTGGTCTTTGTGTTCCTCTG |
| Nrf2 | Mouse | CAGAGTGATGGTTGCCCACT | CACACACTTTCTGCGTGCTC |
| Tnf-α | Mouse | GACCCCTCACACTCAGATCATCTT | CCTTGAAGAGAACCTGGGAGTAG |
| Il-1β | Mouse | TCCACCTCAATGGACAGAATATC | CCGTCTTTCATTACACAGGACA |
| Gapdh | Mouse | ACTCTTCCACCTTCGATGCC | TGGGATAGGGCCTCTCTTGC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, N.; Ding, Z.; Dong, M.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Xue, H.; Wang, Z.; Lu, J.; Chen, X. Protective Effects of Lycium ruthenicum Murray against Acute Alcoholic Liver Disease in Mice via the Nrf2/HO-1/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040497
Xia N, Ding Z, Dong M, Li S, Liu J, Xue H, Wang Z, Lu J, Chen X. Protective Effects of Lycium ruthenicum Murray against Acute Alcoholic Liver Disease in Mice via the Nrf2/HO-1/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(4):497. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040497
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Niantong, Zimian Ding, Mingran Dong, Shuyang Li, Jia Liu, Hongwei Xue, Zhigang Wang, Juan Lu, and Xi Chen. 2024. "Protective Effects of Lycium ruthenicum Murray against Acute Alcoholic Liver Disease in Mice via the Nrf2/HO-1/NF-κB Signaling Pathway" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 4: 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040497
APA StyleXia, N., Ding, Z., Dong, M., Li, S., Liu, J., Xue, H., Wang, Z., Lu, J., & Chen, X. (2024). Protective Effects of Lycium ruthenicum Murray against Acute Alcoholic Liver Disease in Mice via the Nrf2/HO-1/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals, 17(4), 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040497