Identification of Metabolites from Catharanthus roseus Leaves and Stem Extract, and In Vitro and In Silico Antibacterial Activity against Food Pathogens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Assessment of the Antimicrobial Impact
2.2. Virtual Screening and Docking Results
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Plant Material
3.2. Preparation of Extract
3.3. Determination of Antibacterial Activity
3.4. Virtual Screening and Docking Studies
3.5. Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kahn, R.; Morozov, I.; Feldmann, H.; Richt, J.A. 6th International Conference on emerging zoonoses. Zoonoses Public Health 2012, 59, 2–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capita, R.; Alonso-Calleja, C. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria: A challenge for the food industry. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 11–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neethirajan, S. Recent advances in wearable sensors for animal health management. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2017, 12, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sounkaria, S.; Sachdeva, G.; Das, A.; Verma, S.R.; Saxena, S.C.; Singh, B.P.; Rahman, S.; Chandra, P. Potentialities of nanobiotechnology in nutrient management in the livestock products. In Nanobiotechnology for the Livestock Industry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 111–137. [Google Scholar]
- Nisar, P.; Ali, N.; Rahman, L.; Ali, M.; Shinwari, Z.K. Antimicrobial activities of biologically synthesized metal nanoparticles: An insight into the mechanism of action. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 24, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, K.; Slay, B.; Knackstedt, M.; Gaharwar, A.K. Antimicrobial activity of metal and metal-oxide based nanoparticles. Adv. Ther. 2018, 1, 1700033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parham, S.; Wicaksono, D.H.; Bagherbaigi, S.; Lee, S.L.; Nur, H. Antimicrobial treatment of different metal oxide nanoparticles: A critical review. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2016, 63, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonelimali, F.D.; Lin, J.; Miao, W.; Xuan, J.; Charles, F.; Chen, M.; Hatab, S.R. Antimicrobial properties and mechanism of action of some plant extracts against food pathogens and spoilage microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhaithloul, H.A.; Soliman, M.H.; Ameta, K.L.; El-Esawi, M.A.; Elkelish, A. Changes in ecophysiology, osmolytes, and secondary metabolites of the medicinal plants of Mentha piperita and Catharanthus roseus subjected to drought and heat stress. Biomolecules 2019, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dam, N.M.; van der Meijden, E. A role for metabolomics in plant ecology. In Biology of Plant Metabolomics; Annual Plant Reviews; Blackwell Publishing Ltd: Oxford, UK, 2011; Volume 43, pp. 87–107. [Google Scholar]
- Taher, Z.M.; Agouillal, F.; Marof, A.Q.; Dailin, D.J.; Nurjayadi, M.; Razif, E.N.; Gomaa, S.E.; El Enshasy, H.A. Anticancer molecules from Catharanthus roseus. Indones. J. Pharm. 2019, 30, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumaran, R.; Prendergast, G.C.; Gilman, P.B. Cytotoxic chemotherapy in clinical treatment of cancer. In Cancer Immunotherapy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 101–116. [Google Scholar]
- Pant, B. Application of plant cell and tissue culture for the production of phytochemicals in medicinal plants. In Infectious Diseases and Nanomedicine II, Proceedings of the First International Conference (ICIDN–2012), Kathmandu, Nepal, 15–18 December 2012; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2014; pp. 25–39. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Sarkar, S.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Gantait, S. Biotechnological advancements in Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 4811–4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnsworth, N.R.; Akerele, O.; Bingel, A.S.; Soejarto, D.D.; Guo, Z. Medicinal plants in therapy. Bull. World Health Organ. 1985, 63, 965–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajalakshmi, S.; Vijayalakshmi, S.; Devi, R.V. Pharmacological activities of Catharanthus roseus: A perspective review. Int. J. Pharma Bio Sci. 2013, 4, 431–439. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, D.; Chitara, M.K.; Chaturvedi, P. Study of phytochemicals, antioxidant activity and antimicrobial properties of Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don. Emergent Life Sci. Res. 2022, 8, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunanidhi, A.; Thomas, R.; van Belkum, A.; Neela, V. In vitro antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of chlorogenic acid against clinical isolates of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia including the trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole resistant strain. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 392058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Tian, Z.; Cui, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ma, X. Chlorogenic acid: A comprehensive review of the dietary sources, processing effects, bioavailability, beneficial properties, mechanisms of action, and future directions. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 3130–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, M.; Basit, A.; Wahab, A.; Li, W.-J.; Shah, S.T.; Mohamed, H.I. Response mechanism of plant stresses to secondary metabolites production. In Fungal Secondary Metabolites; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 469–492. [Google Scholar]
- Goboza, M.; Meyer, M.; Aboua, Y.G.; Oguntibeju, O.O. In vitro antidiabetic and antioxidant effects of different extracts of catharanthus roseus and its indole alkaloid, vindoline. Molecules 2020, 25, 5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Tian, W.; Cui, X.; Tu, P.; Li, J.; Shi, S.; Liu, X. Biosynthesis investigations of terpenoid, alkaloid, and flavonoid antimicrobial agents derived from medicinal plants. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthikeyan, G.; Swamy, M.K.; Viknesh, M.R.; Shurya, R.; Sudhakar, N. Bioactive Phytocompounds to fight against antimicrobial resistance. In Plant-Derived Bioactives: Production, Properties and Therapeutic Applications; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 335–381. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, M.A.; Perez de Souza, L.; Serag, A.; Fernie, A.R.; Farag, M.A.; Ezzat, S.M.; Alseekh, S. Metabolomics in the context of plant natural products research: From sample preparation to metabolite analysis. Metabolites 2020, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugé de Bernonville, T.; Foureau, E.; Parage, C.; Lanoue, A.; Clastre, M.; Londono, M.A.; Oudin, A.; Houillé, B.; Papon, N.; Besseau, S.; et al. Characterization of a second secologanin synthase isoform producing both secologanin and secoxyloganin allows enhanced de novo assembly of a Catharanthus roseus transcriptome. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, K.; Dong, L.; Navrot, N.; Schneider, T.; Burlat, V.; Pollier, J.; Woittiez, L.; Van Der Krol, S.; Lugan, R.; Ilc, T. The seco-iridoid pathway from Catharanthus roseus. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zou, L.; Ong, C.N. Multiorigination of chromatographic peaks in derivatized GC/MS metabolomics: A confounder that influences metabolic pathway interpretation. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 5657–5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guirimand, G.; Guihur, A.; Poutrain, P.; Héricourt, F.; Mahroug, S.; St-Pierre, B.; Burlat, V.; Courdavault, V. Spatial organization of the vindoline biosynthetic pathway in Catharanthus roseus. J. Plant Physiol. 2011, 168, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhu, S.; Ma, C.; Wang, Z. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of chlorogenic acid. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, M398–M403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yao, J.; Zhou, B.; Yang, J.; Chaudry, M.T.; Wang, M.; Xiao, F.; Li, Y.; Yin, W. Bacteriostatic Effect of Quercetin as an Antibiotic Alternative In Vivo and Its Antibacterial Mechanism In Vitro. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentz, A.B. A Review of Quercetin: Chemistry, antioxidant properties, and bioavailability. J. Young Investig. 2017, 10, 15. Available online: https://www.jyi.org/2009-april/2017/10/15/a-review-of-quercetin-chemistry-antioxidant-properties-and-bioavailability (accessed on 24 January 2024).
- Singh, P.; Arif, Y.; Bajguz, A.; Hayat, S. The role of quercetin in plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. PPB 2021, 166, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Cantor, A.B.; Orkin, S.H.; Wang, J. Use of in vivo biotinylation to study protein–protein and protein–DNA interactions in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizan, A.; Lee, A.X.; Abdul Hamid, N.A.; Maulidiani, M.; Mediani, A.; Abdul Ghafar, S.Z.; Zolkeflee, N.K.Z.; Abas, F. Potentially bioactive metabolites from pineapple waste extracts and their antioxidant and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities by 1H NMR. Foods 2020, 9, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schripsema, J. Application of NMR in plant metabolomics: Techniques, problems and prospects. Phytochem. Anal. Int. J. Plant Chem. Biochem. Tech. 2010, 21, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syeda, A.M.; Riazunnisa, K. Data on GC-MS analysis, in vitro anti-oxidant and anti-microbial activity of the Catharanthus roseus and Moringa oleifera leaf extracts. Data Brief 2020, 29, 105258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Thiessen, P.A.; Bolton, E.E.; Chen, J.; Fu, G.; Gindulyte, A.; Han, L.; He, J.; He, S.; Shoemaker, B.A.; et al. PubChem Substance and Compound databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D1202–D1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Linstead, E.; Swamidass, S.J.; Wang, D.; Baldi, P. ChemDB update—Full-text search and virtual chemical space. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2348–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishida, H.; Unzai, S.; Roper, D.I.; Lloyd, A.; Park, S.Y.; Tame, J.R. Crystal structure of penicillin binding protein 4 (dacB) from Escherichia coli, both in the native form and covalently linked to various antibiotics. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallakyan, S.; Olson, A.J. Small-molecule library screening by docking with PyRx. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1263, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamal, Q.M.S.; Khan, M.I.; Alharbi, A.H.; Ahmad, V.; Yadav, B.S. Identification of Natural Compounds of the Apple as Inhibitors against Cholinesterase for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: An In Silico Molecular Docking Simulation and ADMET Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BIOVIA Discovery Studio. Discovery Studio Visualizer. 2021, v. 21.1.0.20298. San Diego. Available online: https://discover.3ds.com/discovery-studio-visualizer-download (accessed on 8 January 2022).
- Wishart, D.S.; Tzur, D.; Knox, C.; Eisner, R.; Guo, A.C.; Young, N.; Cheng, D.; Jewell, K.; Arndt, D.; Sawhney, S.; et al. HMDB: The Human Metabolome Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D521–D526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.S.N.; Gupta, G.; Kumar, V.; Jagannathan, N.R.; Sinha, S.; Mewar, S.; Kumar, P. Differentiation between sepsis survivors and sepsis non-survivors through blood serum metabolomics: A proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) study. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 89, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Complex | Binding Energy | No. of Hydrogen Bonds | Residues Forming Hydrogen Bond | Residues Involved in Hydrophobic Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2exb- Flomoxef | −7.1 | 11 | SER62, ARG361, SER420,GLN422, SER357,SER306,LEU421,ASP155 | PRO152,SER398,THR418, GLY419,ASN308,ALA61, GLY358,LYS65,LEU359,ASP155,LYS417 |
| 2exb- Chlorogenic Acid | −7.7 | 6 | SER420,GLY358,SER357,SER306, | LEU421, SER62,LYS305,GLY419, THR418,LEU359,ALA61 |
| 2exb-quercetin | −7.5 | 3 | ASN308,ARG361,LEU359 | SER398,LYS417,THR418,SER420,LEU421,SER62, ALA61,GLY358,PHE160,LYS305,SER306 |
| 2exb-vindolinine | −6.9 | 2 | ASN308,SER420 | LYS65,ALA61,GLY358,LEU359,LEU421,LYS305,SER306, SER62,PHE160 |
| PubChem IDs | Compound Names | SMILES IDs | 2D Structures |
|---|---|---|---|
| CID:262 | 2,3-Butanediol | CC(C(C)O)O |  |
| CID:6508 | Quinic Acid | C1C(C(C(CC1(C(=O)O)O)O)O)O |  |
| CID: 260535 | Vindoline | CCC12C=CCN3C1C4(CC3)C(C(C2OC(=O)C)(C(=O)OC)O)N(C5=C4C=CC(=C5)OC)C |  |
| CID:525 | Malic Acid | C(C(C(=O)O)O)C(=O)O |  |
| CID:1794427 | Chlorogenic Acid | C1C(C(C(CC1(C(=O)O)O)OC(=O)C=CC2=CC(=C(C=C2)O)O)O)O |  |
| CID:444972 | Fumaric Acid | C(=CC(=O)O)C(=O)O |  |
| CID: 24148538 | Vindolinine | CC1C23CC(C14C5(C2N(CC5)CC=C3)C6=CC=CC=C6N4)C(=O)OC | 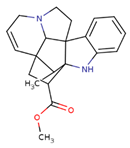 |
| CID: 161276 | Secologanin | COC(=O)C1=COC(C(C1CC=O)C=C)OC2C(C(C(C(O2)CO)O)O)O |  |
| CID: 5280343 | Quercetin | C1=CC(=C(C=C1C2=C(C(=O)C3=C(C=C(C=C3O2)O)O)O)O)O |  |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jamal, Q.M.S.; Ahmad, V. Identification of Metabolites from Catharanthus roseus Leaves and Stem Extract, and In Vitro and In Silico Antibacterial Activity against Food Pathogens. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040450
Jamal QMS, Ahmad V. Identification of Metabolites from Catharanthus roseus Leaves and Stem Extract, and In Vitro and In Silico Antibacterial Activity against Food Pathogens. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(4):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040450
Chicago/Turabian StyleJamal, Qazi Mohammad Sajid, and Varish Ahmad. 2024. "Identification of Metabolites from Catharanthus roseus Leaves and Stem Extract, and In Vitro and In Silico Antibacterial Activity against Food Pathogens" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 4: 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040450
APA StyleJamal, Q. M. S., & Ahmad, V. (2024). Identification of Metabolites from Catharanthus roseus Leaves and Stem Extract, and In Vitro and In Silico Antibacterial Activity against Food Pathogens. Pharmaceuticals, 17(4), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040450






