Adenosine Increases the Immunosuppressive Capacity of Cervical Cancer Cells by Increasing PD-L1 Expression and TGF-β Production through Its Interaction with A2AR/A2BR
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
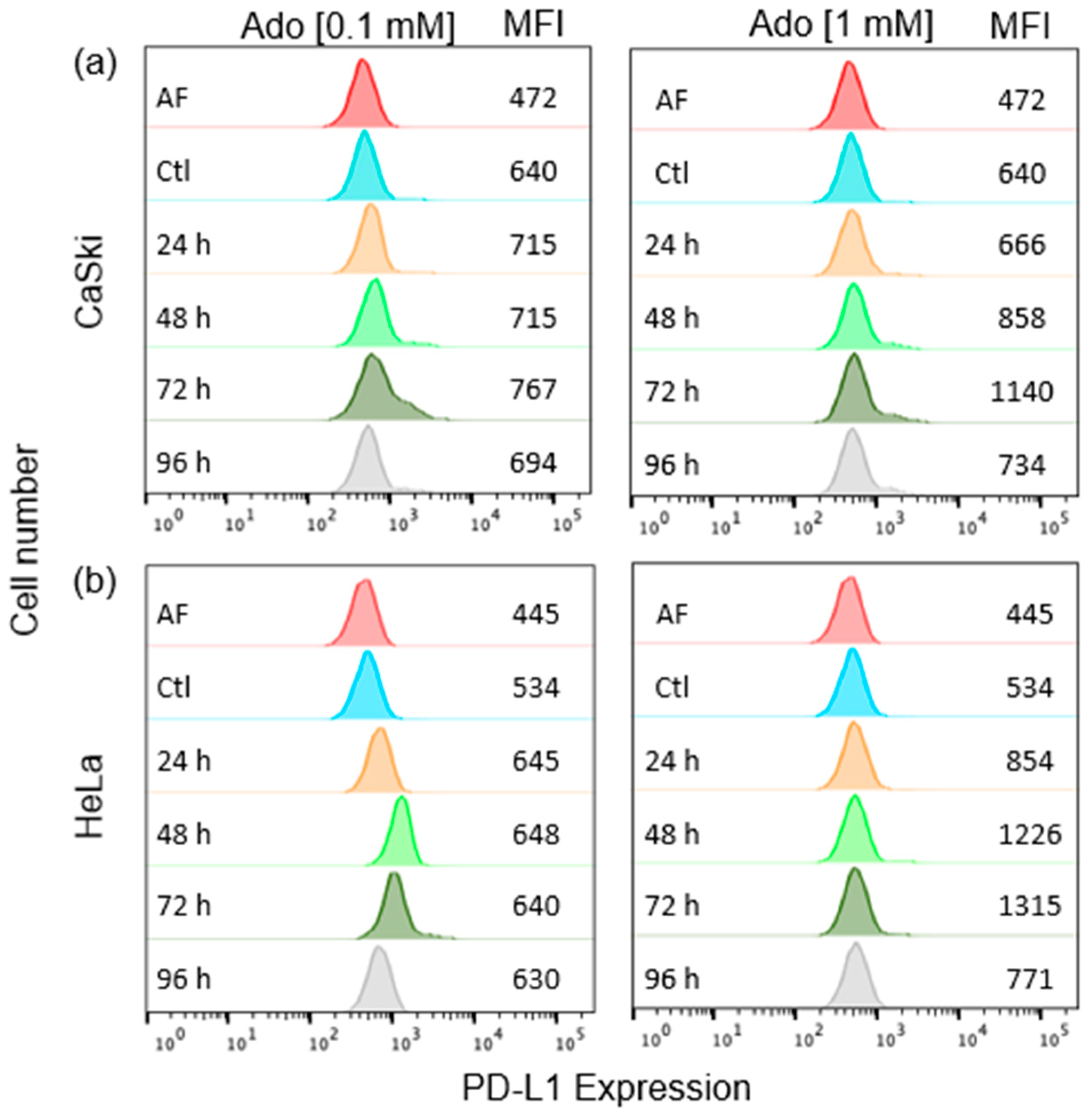
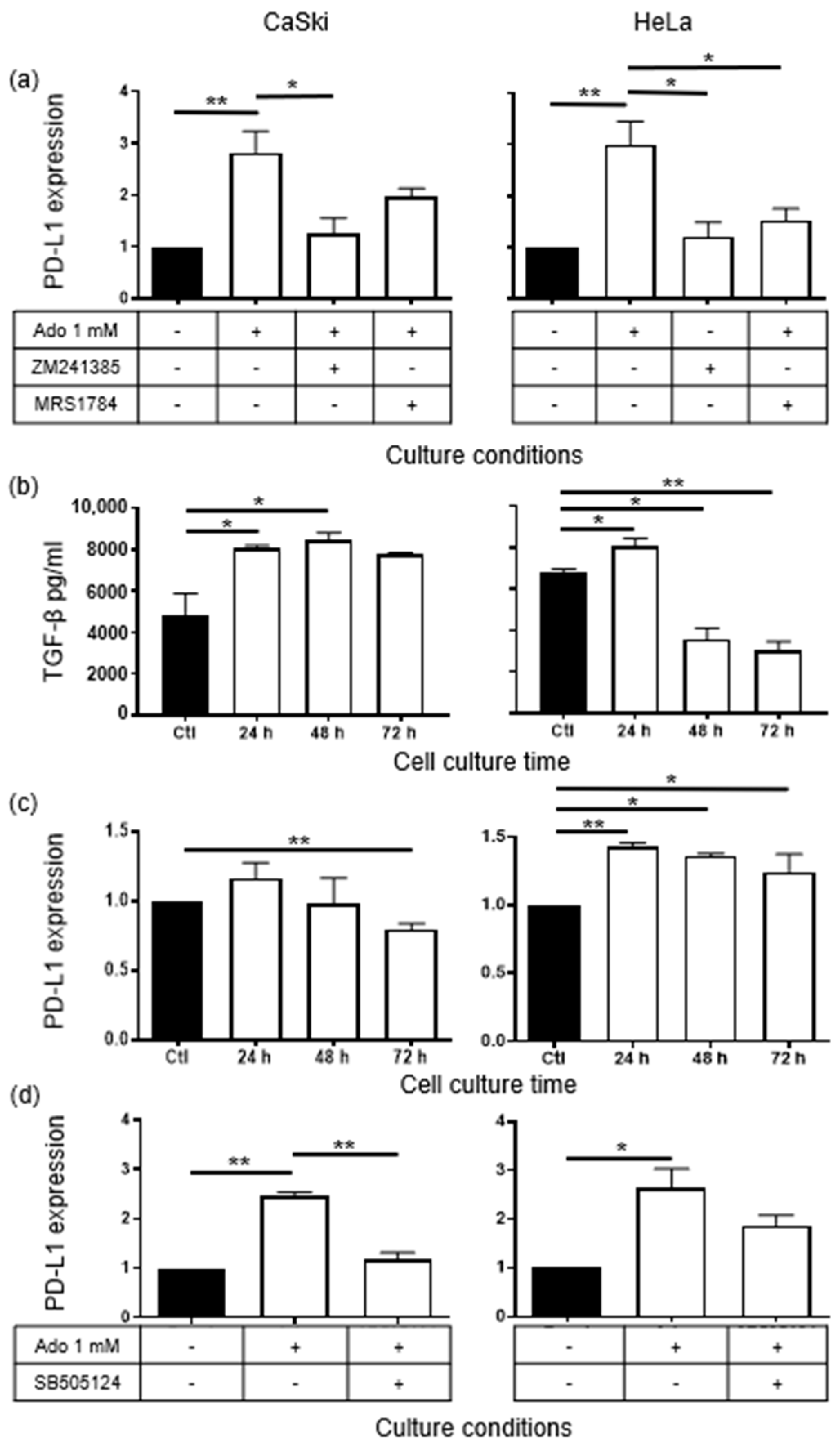
2.1. Ado Induces PD-L1 Expression in CeCa Cells through Its Interaction with A2AR/A2BR and the Autocrine Production of TGF-β1
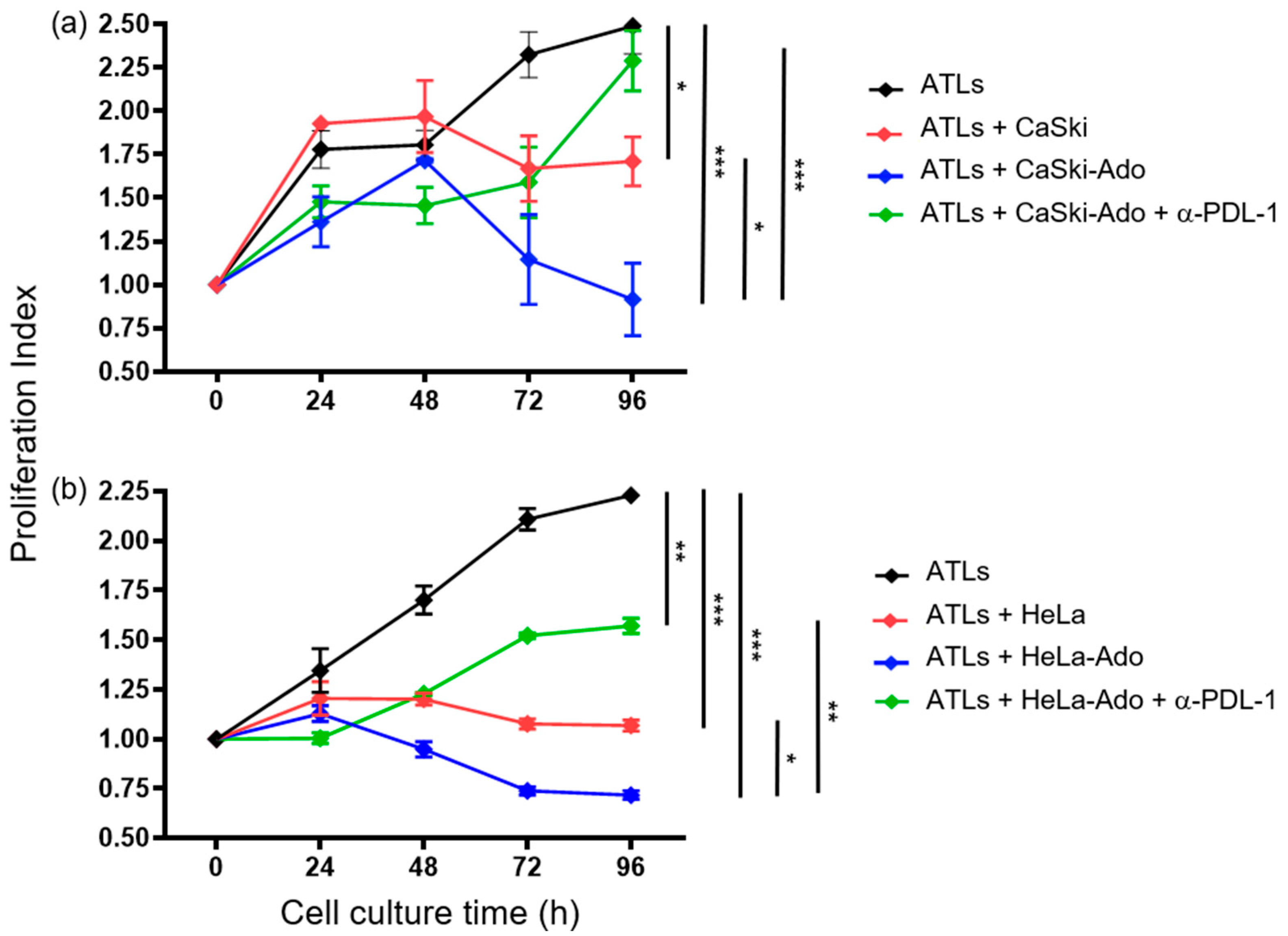
2.2. Ado-Treated CeCa Cells Inhibit the Proliferation of CD8+ T Lymphocytes through PD-L1 Expression
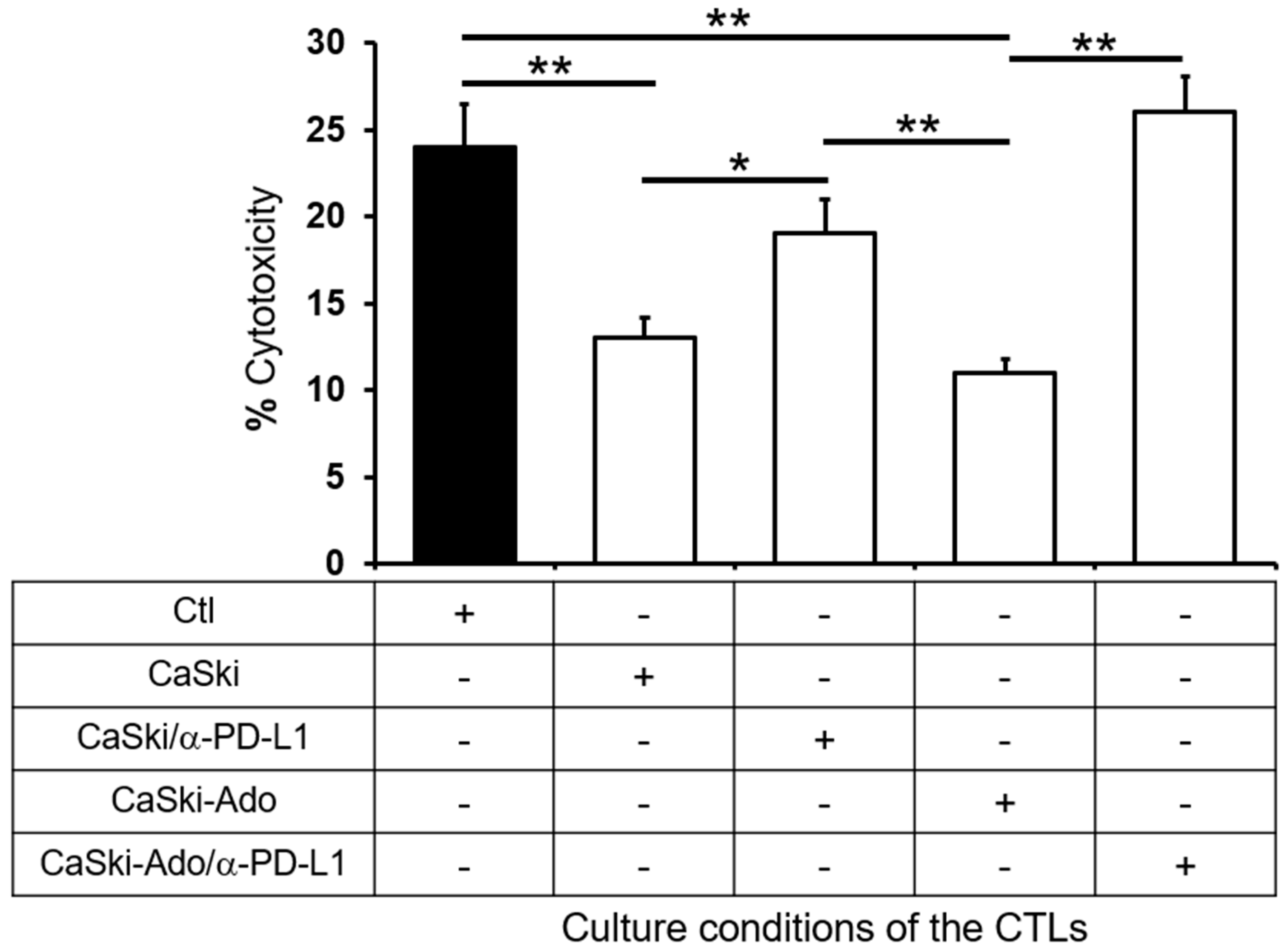
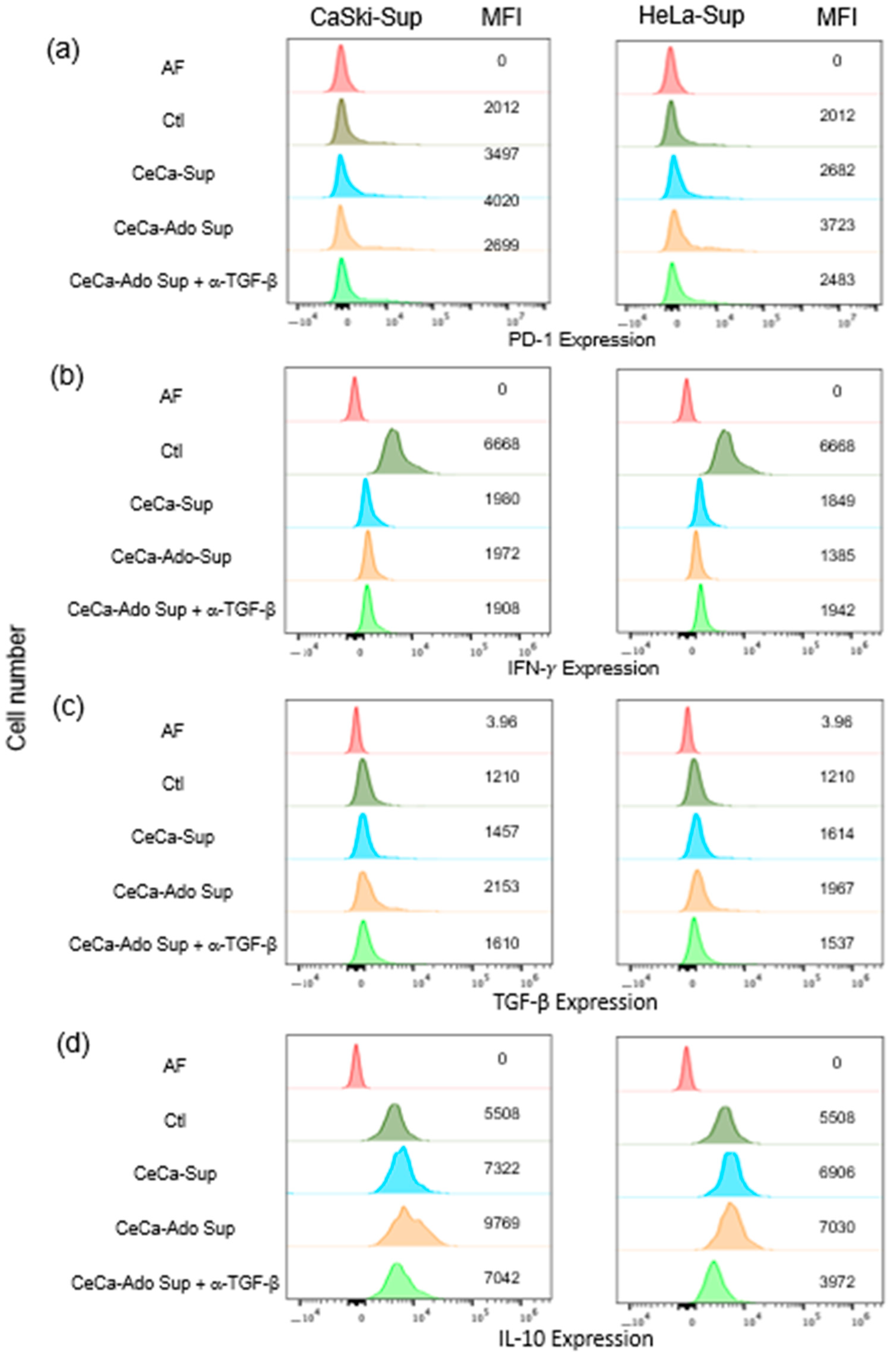
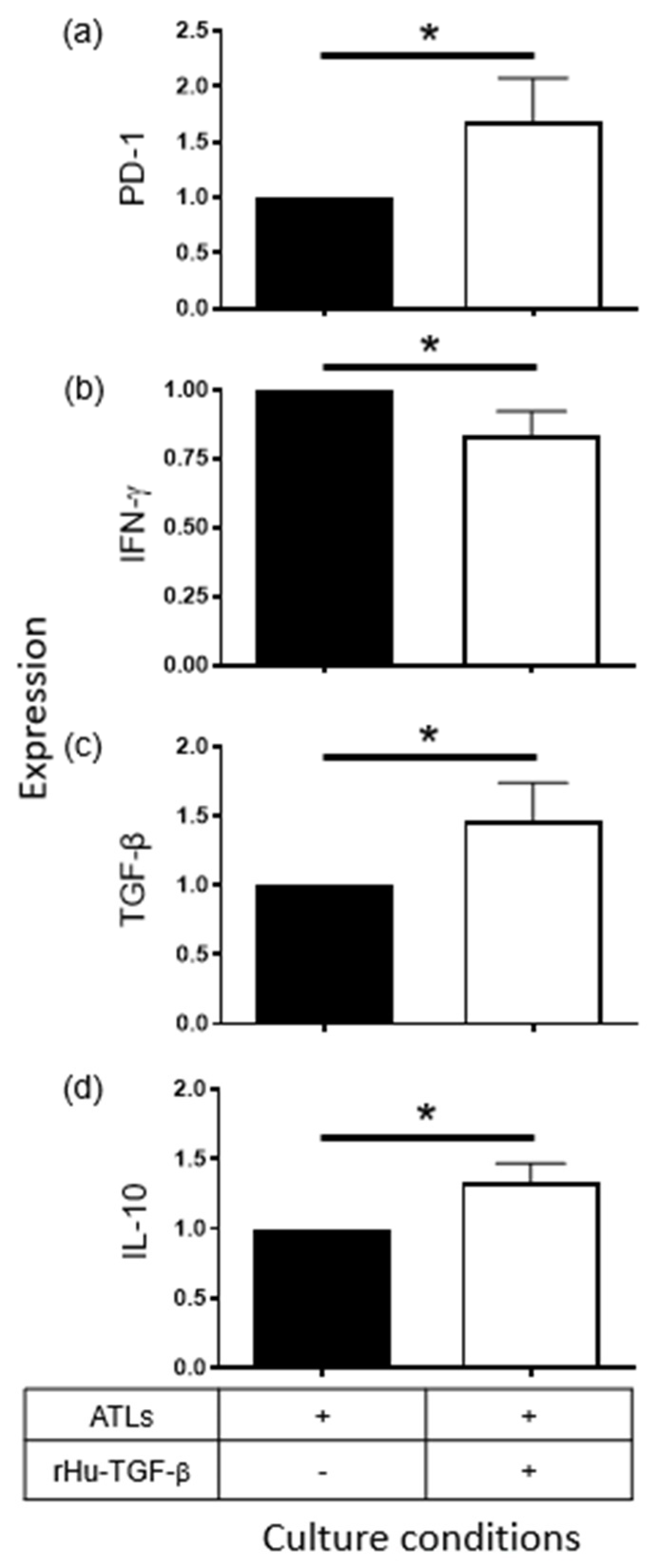
2.3. Supernatants Derived from CeCa/Ado Cells Strongly Suppress the Activation of CD8+ T Lymphocytes
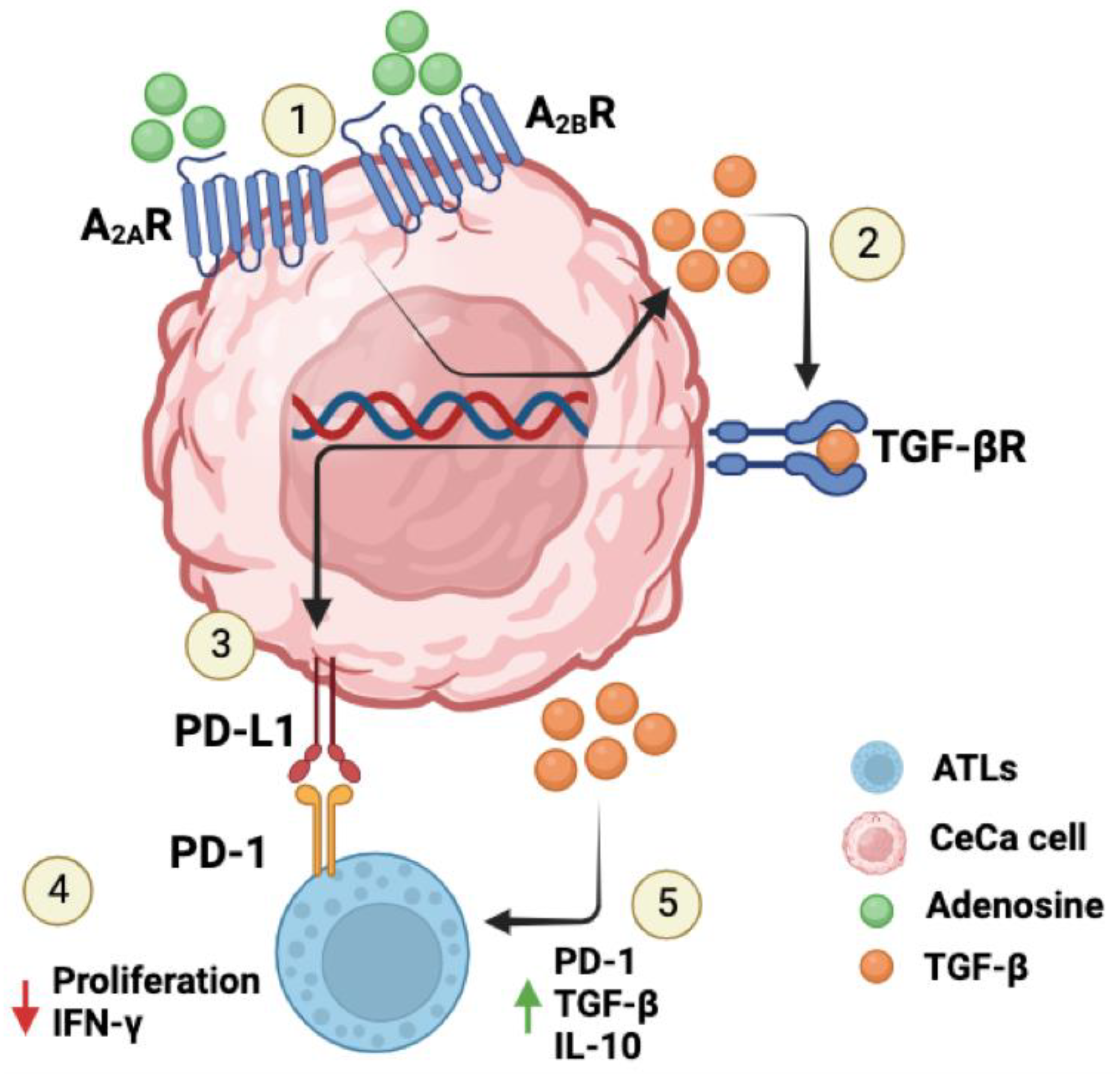
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. CeCa Cell Lines
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Isolation of Activated CD8+ T Lymphocytes (ATLs)
4.4. Inhibition of ATLs by CeCa Cells
4.5. Cytotoxicity Assays
4.6. Assessment of PD-1, TGF-β1 and IL-10 Expression in ATLs
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buskwofie, A.; David-West, G.; Clare, C.A. A review of cervical cancer: Incidence and disparities. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2020, 112, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosbie, E.J.; Einstein, M.H.; Franceschi, S.; Kitchener, H.C. Human papillomavirus and cervical cancer. Lancet 2013, 382, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, A.V.; Weinberg, T.; Darragh, K.; Smith-McCune, K. Evolving immunosuppressive microenvironment during human cervical carcinogenesis. Mucosal Immunol. 2008, 1, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.C.; Lu, X.Y.; Yu, M.; Lemos, H.; Huang, L.; Chandler, P.; Liu, K.; Walters, M.; Krasinski, A.; Mack, M.; et al. Immunosuppressive myeloid cells induced by chemotherapy attenuate antitumor CD4+ T Cell Responses through the PD-1/PD-L1 Axis. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3441–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, P.J.; Adams, V.R. PD-1 Pathway Inhibitors: Immuno-oncology agents for restoring antitumor immune responses. Pharmacotherapy 2016, 36, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, X.T. Immunosuppressive cells in tumor immune escape and metastasis. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellman, I.; Coukos, G.; Dranoff, G. Cancer immunotherapy comes of age. Nature 2011, 480, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Chehrazi-Raffle, A.; Reddi, S.; Salgia, R. Development of PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors as a form of cancer immunotherapy: A comprehensive review of registration trials and future considerations. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Wolchok, J.D.; Chen, L. PD-L1 (B7-H1) and PD-1 pathway blockade for cancer therapy: Mechanisms, response biomarkers, and combinations. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 328rv4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.H.; Chan, L.C.; Li, C.W.; Hsu, J.L.; Hung, M.C. Mechanisms Controlling PD-L1 Expression in Cancer. Mol. Cell 2019, 76, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbotti, G.; Barisione, G.; Airoldi, I.; Mezzanzanica, D.; Bagnoli, M.; Ferrero, S.; Petretto, A.; Fabbi, M.; Ferrini, S. IL-27 induces the expression of IDO and PD-L1 in human cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 43267–43280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Crabill, G.A.; Pritchard, T.S.; McMiller, T.L.; Wei, P.; Pardoll, D.M.; Pan, F.; Topalian, S.L. Mechanisms regulating PD-L1 expression on tumor and immune cells. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, H.; Gameiro, S.R.; Jochems, C.; Donahue, R.N.; Strauss, J.; Gulley, J.L.; Palena, C.; Schlom, J. Dual targeting of TGF-β and PD-L1 via a bifunctional anti-PD-L1/TGF-βRII agent: Status of preclinical and clinical advances. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariathasan, S.; Turley, S.; Nickles, D.; Castiglioni, A.; Yuen, K.; Wang, Y.; Kadel, E.E., III; Koeppen, H.; Astarita, J.L.; Cubas, R.; et al. TGFβ attenuates tumour response to PD-L1 blockade by contributing to exclusion of T cells. Nature 2018, 554, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, H.S.; Ren, J.; Camps, M.; Ossendorp, F.; Dijke, P.T. Combined Inhibition of TGF-β Signaling and the PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint Is Differentially Effective in Tumor Models. Cells 2019, 8, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Jung, M.Y.; Choudhury, M.; Leof, E.B. Transforming growth factor beta induces fibroblasts to express and release the immunomodulatory protein PD-L1 into extracellular vesicles. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 2213–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Poveda, K.; Bahena-Roman, M.; Madrid-Gonzalez, C.; Burguete-García, A.I.; Bermúdez-Morales, V.H.; Peralta-Zaragoza, O.; Madrid-Marina, V. Role of IL-10 and TGF-beta1 in local immunosuppression in HPV-associated cervical neoplasia. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 5, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezache, L.; Paniccia, B.; Nyinawabera, A.; Nuovo, G.J. Enhanced expression of PD L1 in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancers. Modern Pathol. 2015, 28, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Liang, H.; Hu, J.; Liu, S.; Hao, X.; Wong, M.S.K.; Li, X.; Hu, L. PD-L1 expression correlates with tumor infiltrating lymphocytes and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in cervical cancer. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 2938–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heeren, A.M.; Punt, S.; Bleeker, M.C.G.; Gaarenstroom, K.N.; van der Velden, J.; Kenter, G.G.; de Gruijl, T.D.; Jordanova, E.S. Prognostic effect of different PD-L1 expression patterns in squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the cervix. Mod. Pathol. 2016, 29, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.C.; Ji, W.L.; Yue, N.; Huang, Y.C.; Ma, X.M. The relationship between the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway and DNA mismatch repair in cervical cancer and its clinical significance. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Liu, J.; Xu, K.; Chen, H.; Bian, C. PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors for advanced or metastatic cervical cancer: From bench to bed. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 849352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saglam, O.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Conejo-Garcia, J.R. PD-L1 expression correlates with young age and CD8+ TIL density in poorly differentiated cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 2020, 39, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Song, Y.; Lu, Y.L.; Sun, J.Z.; Wang, H.W. Increased expression of programmed death (PD)-1 and its ligand PD-L1 correlates with impaired cell-mediated immunity in high-risk human papillomavirus-related cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Immunology 2013, 139, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahreyni, A.; Samani, S.S.; Ghorbani, E.; Rahmani, F.; Khayami, R.; Toroghian, Y.; Behnam-Rassouli, R.; Khazaei, M.; Ryzhikov, M.; Parizadeh, M.R.; et al. Adenosine: An endogenous mediator in the pathogenesis of gynecological cancer. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 2715–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffenzeller, M.S.; Franciosi, M.L.M.; Cardoso, A.M. Purinergic signaling and tumor microenvironment in cervical cancer. Purinergic Signal. 2020, 16, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaupel, P.; Mayer, A. Hypoxia-driven adenosine accumulation: A crucial microenvironmental factor promoting tumor progression. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 876, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Robson, S.C.; Sévigny, J.; Zimmermann, H. The ENTPDase family of ectonucleotidases: Structure function relationships and pathophysiological significance. Purinergic Signal. 2006, 2, 409–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, H.; Zebisch, M.; Sträer, N. Cellular function and molecular structure of ecto-nucleotidases. Purinergic Signal. 2012, 8, 437–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linden, J. Molecular approach to adenosine receptors: Receptor-mediated mechanisms of tissue protection. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2001, 41, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonioli, L.; Fornai, M.; Blandizzi, C.; Pacher, P.; Haskó, G. Adenosine signaling and the immune system: When a lot could be too much. Immunol. Lett. 2019, 205, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayan, D.; Young, A.; Teng, M.; Smyth, M. Targeting immunosuppressive adenosine in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 709–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, R.D.; Emens, L.A. Targeting adenosine for cancer immunotherapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Rocha, R.; Monroy-García, A.; Hernandez-Montes, J.; Benny Weiss-Steider, B.; Gutiérrez-Serrano, V.; Fuentes-Castañeda, M.C.; Ávila-Ibarra, L.-R.; Don-López, C.A.; Torres-Pineda, D.B.; Mora-García, M.L. Cervical cancer cells produce TGF-beta1 through the CD73-adenosine pathway and maintain CD73 expression through the autocrine activity of TGF-beta1. Cytokine 2019, 118, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Rocha, R.; Monroy-García, A.; Carrera-Martínez, M.; Hernández-Montes, J.; Don-López, C.A.; Weiss-Steider, B.; Monroy-Mora, K.A.; Ponce-Chavero, M.L.A.; Montesinos-Montesinos, J.J.; Escobar-Sánchez, M.L.; et al. Evidence that cervical cancer cells cultured as tumorspheres maintain high CD73 expression and increase their protumor characteristics through TGF-β production. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2022, 40, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora-García, M.L.; Ávila-Ibarra, L.R.; García-Rocha, R.; Weiss-Steider, B.; Hernández-Montes, J.; Don-López, C.A.; Gutiérrez-Serrano, V.; Titla-Vilchis, I.J.; Fuentes-Castañeda, M.C.; Monroy-Mora, A.; et al. Cervical cancer cells suppress effector functions of cytotoxic T cells through the adenosinergic pathway. Cell Immunol. 2017, 320, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-García, M.L.; García-Rocha, R.; Morales-Ramirez, O.; Montesinos, J.J.; Weiss-Steider, B.; Hernández-Montes, J.; Ávila-Ibarra, L.A.; Don-López, C.A.; Velasco-Velázquez, M.; Gutiérrez-Srrano, V.; et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells derived from cervical cancer produce high amounts of adenosine to suppress cytotoxic T lymphocyte functions. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.; Bauer, S.; Grubert, T.; Brucker, C.; Baur, S.; Heeg, K.; Wagner, H.; Lipford, G.B. HLA-A2-restricted peripheral blood cytolytic T lymphocyte response to HPV type 16 proteins E6 and E7 from patients with neoplastic cervical lesions. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 1996, 42, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Rocha, R.; Moreno-Lafont, M.C.; Mora-García, M.L.; Weiss-Steider, B.; Montesinos, J.J.; Piña-Sánchez, P.; Monroy-García, A. Mesenchymal stromal cells derived from cervical cancer tumors induce TGF-β1 expression and IL-10 expression and secretion in the cervical cancer cells, resulting in protection from cytotoxic T cell activity. Cytokine 2015, 76, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekik, R.; Hmida, N.B.; Hmid, A.B.; Zamali, I.; Kammoun, N.; Ahmed, M.B. PD-1 induction through TCR activation is partially regulated by endogenous TGF-β. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2015, 12, 648–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Tu, Q.; Xue, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, K.N. The Roles of Programmed Cell Death Ligand-1/Programmed Cell Death-1 (PD-L1/PD-1) in HPV-induced Cervical Cancer and Potential for their Use in Blockade Therapy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 893–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, O.L.; Shintaku, P.I.; Moatamed, N.A. Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is expressed in a significant number of the uterine cervical carcinomas. Diagn. Pathol. 2017, 12, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enwere, E.K.; Kornaga, E.N.; Dean, M.; Koulis, T.A.; Phan, T.; Kalantarian, M.; Köbel, M.; Ghatage, P.; Magliocco, A.M.; Lees-Miller, S.P.; et al. Expression of PD-L1 and presence of CD8-positive T cells in pre-treatment specimens of locally advanced cervical cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Si, F.; Bagley, D.; Ma, F.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, Y.; Shaw, E.; Peng, G. Blockades of effector T cell senescence and exhaustion synergistically enhance antitumor immunity and immunotherapy. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e005020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, A.; Perica, K.; Klebanoff, C.A.; Wolchok, J.D. Clinical implications of T cell exhaustion for cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottrell, T.R.; Taube, J.M. PD-L1 and emerging biomarkers in immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Cancer J. 2018, 24, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xie, K.; Liu, T. Cancer Immunotherapies: From Efficacy to Resistance Mechanisms –Not Only Checkpoint Matters. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 690112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzec, M.; Zhang, Q.; Goradia, A.; Raghunath, P.N.; Liu, X.; Paessler, M.; Wang, H.Y.; Wysocka, M.; Cheng, M.; Ruggeri, B.A.; et al. Oncogenic kinase NPM/ALK induces through STAT3 expression of immunosuppressive protein CD274 (PD-L1, B7-H1). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 20852–20857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.R.; Rodig, S.; Juszczynski, P.; Ouyang, J.; Sinha, P.; O’Donneli, E.; Neuberg, D.; Shipp, M.A. Constitutive AP-1 activity and EBV infection induce PD-L1 in Hodgkin lymphomas and posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders: Implications for targeted therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1611–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Gibbons, D.L.; Goswami, S.; Cortez, M.A.; Ahn, Y.H.; Byers, L.A.; Zhang, X.; Yi, X.; Dwyer, D.; Lin, W.; et al. Metastasis is regulated via microRNA-200/ZEB1 axis control of tumour cell PD-L1 expression and intratumoral immunosuppression. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhou, J.; Giobbie-Hurder, A.; Wargo, J.; Hodi, F.S. The activation of MAPK in melanoma cells resistant to BRAF inhibition promotes PD-L1 expression that is reversible by MEK and PI3K inhibition. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, C.; Panner, A.; Pieper, R.O.; Arbiser, J.; Parsa, A.T. Honokiol-mediated inhibition of PI3K/mTOR pathway: A potential strategy to overcome immunoresistance in glioma, breast, and prostate carcinoma without impacting T cell function. J. Immunother. 2009, 32, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellucci, R.; Martin, A.; Bommarito, D.; Wang, K.; Hansen, S.H.; Freeman, G.J.; Ritz, J. Interferon-gamma-induced activation of JAK1 and JAK2 suppresses tumor cell susceptibility to NK cells through upregulation of PD-L1 expression. Oncoimmunology 2015, 4, e1008824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirahara, K.; Ghoreschi, K.; Yang, X.P.; Takahashi, H.; Laurence, A.; Vahedi, G.; Sciumé, G.; Hall, A.O.; Dupont, C.D.; Francisco, L.M.; et al. Interleukin-27 priming of T cells controls IL-17 production in trans via induction of the ligand PD-L1. Immunity 2012, 36, 1017–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, A.; Tanaka, K.; Tsutsumi, H.; Nakanishi, T.; Yamashita, S.; Mizusaki, S.; Ishii, Y.; Ota, K.; Yoneshima, Y.; Iwama, E.; et al. Regulation of PD-L1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer by interleukin-1β. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1192861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Chatterjee, A.; Jana, S.; Dey, S.; Roy, H.; Das, M.K.; Alam, J.; Adhikary, A.; Chowdhury, A.; Biswas, A.; et al. Transforming growth factor beta orchestrates PD-L1 enrichment in tumor-derived exosomes and mediates CD8 T-cell dysfunction regulating early phosphorylation of TCR signalome in breast cancer. Carcinogenesis 2021, 42, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazemi, M.H.; Mohseni, S.R.; Hojjat-Farsangi, M.; Anvari, E.; Ghalamfarsa, G.; Mohammadi, H.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F. Adenosine and adenosine receptors in the immunopathogenesis and treatment of cancer. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 2032–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotman, J.; den Otter, L.A.S.; Bleeker, M.C.G.; Samuels, S.S.; Heeren, A.M.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Kenter, G.G.; Zijlmans, H.J.M.A.A.; van Trommel, N.E.; de Gruijl, T.D.; et al. PD-L1 and PD-L2 Expression in Cervical Cancer: Regulation and Biomarker Potential. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 596825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerdes, I.; Matikas, A.; Bergh, J.; Rassidakis, G.Z.; Foukakis, T. Genetic, transcriptional and post-translational regulation of the programmed death protein ligand 1 in cancer: Biology and clinical correlations. Oncogene 2018, 37, 4639–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Huang, C.C.; Ou, Y.C.; Huang, E.Y.; Changchien, C.C.; Tseng, C.W.; Fu, H.C.; Li, C.J.; Ma, Y.Y. High immunohistochemical expression of TGF-beta1 predicts a poor prognosis incervical cancer patients who harbor enriched endoglin microvessel density. Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 2012, 31, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhurst, R.J.; Derynck, R. TGF-beta signaling in cancer a double-edged sword. Trends Cell Biol. 2001, 11, S44–S51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yetişir, A.E.; Paydaş, S.; Gönlüşen, G.; Erdoğan, K.E.; Büyükşimşek, M.; Oğul, A.; Tohumcuoğlu, M.; Mirili, C.; Yetişir, A. Sarcoma-correlation between CD73 and PD-L1 and their relationship with prognosis. Pol. J. Pathol. 2022, 73, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahkola, K.; Ahtiainen, M.; Kellokumpu, I.; Mecklin, J.P.; Laukkarinen, J.; Laakkonen, J.; Kenessey, I.; Jalkanen, S.; Salmi, M.; Böhm, J. Prognostic impact of CD73 expression and its relationship to PD-L1 in patients with radically treated pancreatic cancer. Virchows Arch. 2021, 478, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, E.; McGlinchey, K.; Wang, J.; Martin, P.; Ching, S.L.; Floc’h, N.; Kurasawa, J.; Starrett, J.H.; Lazdun, Y.; Wetzel, L.; et al. Anti-PD-L1 and anti-CD73 combination therapy promotes T cell response to EGFR-mutated NSCLC. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e142843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Gavras, N.W.; Keeley, D.C.; Hughson, A.L.; Hannon, G.; Vrooman, T.G.; Lesch, M.L.; Johnston, C.J.; Lord, E.M.; Belt, B.A.; et al. CD73 and PD-L1 dual blockade amplifies antitumor efficacy of SBRT in murine PDAC models. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e006842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redman, J.M.; Friedman, J.; Robbins, Y.; Sievers, C.; Yang, X.; Lassoued, W.; Sinkoe, A.; Papanicolau-Sengos, A.; Lee, C.C.; Marte, J.L.; et al. Enhanced neoepitope-specific immunity following neoadjuvant PD-L1 and TGF-β blockade in HPV-unrelated head and neck cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e161400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Yeung, T.L.; Huang, H.; Wegener, A.A.; Saha, S.; Toister-Achituv, M.; Jenkins, M.H.; Chiu, L.Y.; Lazorrchack, A.; Tarcic, O.; et al. Colocalized targeting of TGF-β and PD-L1 by bintrafusp alfa elicits distinct antitumor responses. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e004122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birrer, M.J.; Fujiwara, K.; Oaknin, A.; Randall, l.; Ojalvo, L.S.; Valencia, C.; Ray-Coquard, I. The Changing Landscape of Systemic Treatment for Cervical Cancer: Rationale for Inhibition of the TGF-β and PD-L1 Pathways. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 814169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Rocha, R.; Monroy-García, A.; Vázquez-Cruz, A.L.; Marín-Aquino, L.A.; Weiss-Steider, B.; Hernández-Montes, J.; Don-López, C.A.; Molina-Castillo, G.; Mora-García, M.d.L. Adenosine Increases the Immunosuppressive Capacity of Cervical Cancer Cells by Increasing PD-L1 Expression and TGF-β Production through Its Interaction with A2AR/A2BR. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17030397
García-Rocha R, Monroy-García A, Vázquez-Cruz AL, Marín-Aquino LA, Weiss-Steider B, Hernández-Montes J, Don-López CA, Molina-Castillo G, Mora-García MdL. Adenosine Increases the Immunosuppressive Capacity of Cervical Cancer Cells by Increasing PD-L1 Expression and TGF-β Production through Its Interaction with A2AR/A2BR. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(3):397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17030397
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Rocha, Rosario, Alberto Monroy-García, Ana Luisa Vázquez-Cruz, Luis Antonio Marín-Aquino, Benny Weiss-Steider, Jorge Hernández-Montes, Christian Azucena Don-López, Gabriela Molina-Castillo, and María de Lourdes Mora-García. 2024. "Adenosine Increases the Immunosuppressive Capacity of Cervical Cancer Cells by Increasing PD-L1 Expression and TGF-β Production through Its Interaction with A2AR/A2BR" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 3: 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17030397
APA StyleGarcía-Rocha, R., Monroy-García, A., Vázquez-Cruz, A. L., Marín-Aquino, L. A., Weiss-Steider, B., Hernández-Montes, J., Don-López, C. A., Molina-Castillo, G., & Mora-García, M. d. L. (2024). Adenosine Increases the Immunosuppressive Capacity of Cervical Cancer Cells by Increasing PD-L1 Expression and TGF-β Production through Its Interaction with A2AR/A2BR. Pharmaceuticals, 17(3), 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17030397







