Five-Membered Nitrogen Heterocycles Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors Induced Angioedema: An Underdiagnosed Condition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Clinical Presentation
3. Time of Onset of AE
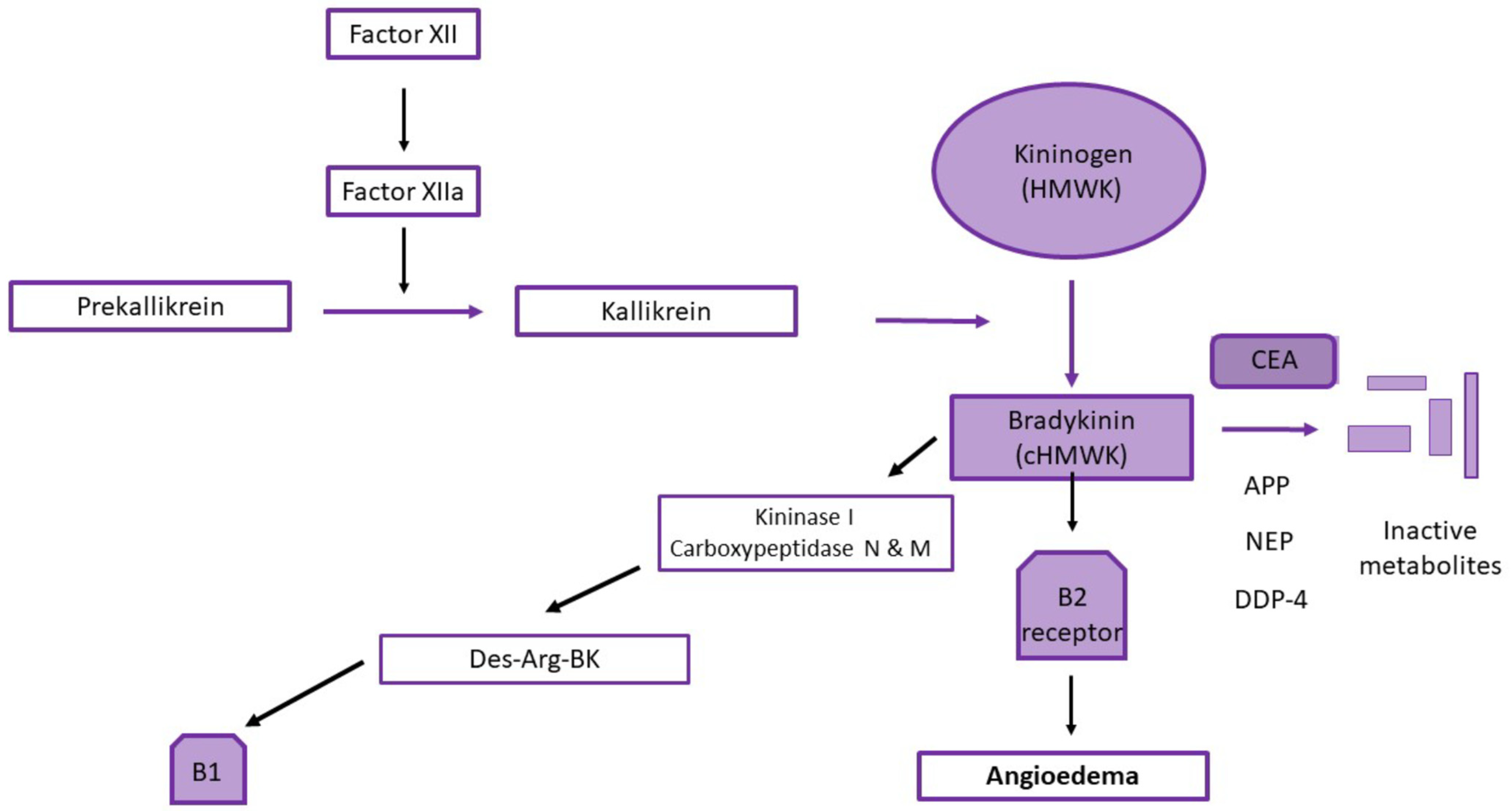
4. Suggested Mechanisms
4.1. The Role of ACE in Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Pathway and Degradation of Bradykinin
4.2. The Role of ACE inhibitors in AE
5. Risk Factors
6. Diagnosis
Mast-Cell-Mediated Versus Bradykinin-Mediated AE
7. Management
- ▯
- Fresh frozen plasma (FFP)
- ▯
- Icatibant
- ▯
- Ecallantide
- ▯
- C1 inhibitor concentrate
8. Prognosis
9. Future Perspectives: Related Drugs and AE
10. Addressing ACE Inhibitor-Induced Angioedema through Tailored Interventions
11. Cutting-Edge Horizons
12. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arora, P.; Arora, V.; Lamba, H.; Wadhwa, D. Importance of heterocyclic chemistry: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2012, 3, 2947. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3021–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heravi, M.M.; Zadsirjan, V. Prescribed drugs containing nitrogen heterocycles: An overview. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 44247–44311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faisant, C.; Armengol, G.; Bouillet, L.; Boccon-Gibod, I.; Villier, C.; Lévesque, H.; Cottin, J.; Massy, N.; Benhamou, Y. Angioedema Triggered by Medication Blocking the Renin/Angiotensin System: Retrospective Study Using the French National Pharmacovigilance Database. J. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 36, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudpour, S.H.; Baranova, E.V.; Souverein, P.C.; Asselbergs, F.W.; de Boer, A.; Maitland-van der Zee, A.H. Determinants of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI) intolerance and angioedema in the UK Clinical Practice Research Datalink. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 82, 1647–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerji, A.; Clark, S.; Blanda, M.; LoVecchio, F.; Snyder, B.; Camargo, C.A., Jr. Multicenter study of patients with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced angioedema who present to the emergency department. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008, 100, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerji, A.; Blumenthal, K.G.; Lai, K.H.; Zhou, L. Epidemiology of ACE Inhibitor Angioedema Utilizing a Large Electronic Health Record. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Saucedo, J.C.; Trejo-Gutierrez, J.F.; Volcheck, G.W.; Park, M.A.; Gonzalez-Estrada, A. Incidence and risk factors of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced angioedema: A large case-control study. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021, 127, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messerli, F.H.; Nussberger, J. Vasopeptidase inhibition and angio-oedema. Lancet 2000, 356, 608–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostis, W.J.; Shetty, M.; Chowdhury, Y.S.; Kostis, J.B. ACE Inhibitor-Induced Angioedema: A Review. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, C.R.; Lip, G.Y.; Beevers, D.G. Angioedema due to ACE inhibitors: Increased risk in patients of African origin. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 48, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamil, R.J.; Jerschow, E.; Loftus, P.A.; Tan, M.; Fried, M.P.; Smith, R.V.; Foster, D.; Ow, T.J. Case-control study evaluating competing risk factors for angioedema in a high-risk population. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 1823–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichman, M.E.; Wernecke, M.; Graham, D.J.; Liao, J.; Yap, J.; Chillarige, Y.; Southworth, M.R.; Keeton, S.; Goulding, M.R.; Mott, K.; et al. Antihypertensive drug associated angioedema: Effect modification by race/ethnicity. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2017, 26, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, P.J.; Christiansen, S.C. Hereditary Angioedema. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1136–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, A.P.; Ghebrehiwet, B. The plasma bradykinin-forming pathways and its interrelationships with complement. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 47, 2161–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, M.; Magerl, M.; Betschel, S.; Aberer, W.; Ansotegui, I.J.; Aygören-Pürsün, E.; Banerji, A.; Bara, N.A.; Boccon-Gibod, I.; Bork, K.; et al. The international WAO/EAACI guideline for the management of hereditary angioedema-The 2021 revision and update. Allergy 2022, 77, 1961–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanani, A.; Schellenberg, R.; Warrington, R. Urticaria and angioedema. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2011, 7 (Suppl. 1), S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, N.N.; Deeb, Z.E.; Chia, S.H. Clinical experience with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced angioedema. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2007, 137, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloom, A.S.; Schranz, C. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor-Induced Angioedema of the Small Bowel-A Surgical Abdomen Mimic. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 48, e127–e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, B.J.; Koyfman, A.; Gottlieb, M. Evaluation and Management of Angioedema in the Emergency Department. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2019, 20, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, A.G.; Newkirk, K.A.; Davidson, B.J.; Burningham, A.R.; Krowiak, E.J.; Deeb, Z.E. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced angioedema: A multicenter review and an algorithm for airway management. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2001, 110, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, E.E.; Merrill, D.D.; Guess, H.A.; Roylance, P.J.; Cooper, W.D.; Inman, W.H.; Ewan, P.W. Clinical profile of angioedema associated with angiotensin converting-enzyme inhibition. JAMA 1988, 260, 967–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, S.; Reichman, M.E.; Houstoun, M.; Ross Southworth, M.; Ding, X.; Hernandez, A.F.; Levenson, M.; Li, L.; McCloskey, C.; Shoaibi, A.; et al. Comparative risk for angioedema associated with the use of drugs that target the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Arch. Intern. Med. 2012, 172, 1582–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr, K.K.; Myers, J.R. Intermittent visceral edema induced by long-term enalapril administration. Ann. Pharmacother. 2004, 38, 825–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, D. ACE inhibitor angioedema—A very late presentation. Aust. Fam. Physician 2013, 42, 860–862. [Google Scholar]
- Norman, J.L.; Holmes, W.L.; Bell, W.A.; Finks, S.W. Life-threatening ACE inhibitor-induced angioedema after eleven years on lisinopril. J. Pharm. Pract. 2013, 26, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nia, A.M.; Er, F. Angioedema associated with the use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2013, 185, E80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Goyal, A.; Cusick, A.S.; Thielemier, B. ACE Inhibitors. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Messerli, F.H.; Bangalore, S.; Bavishi, C.; Rimoldi, S.F. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors in Hypertension: To Use or Not to Use? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 1474–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, M.; Bader, M.; Bas, M.; Bossi, F.; Cicardi, M.; Cugno, M.; Howarth, P.; Kaplan, A.; Kojda, G.; Leeb-Lundberg, F.; et al. New topics in bradykinin research. Allergy 2011, 66, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magerl, M.; Bader, M.; Gompel, A.; Joseph, K.; Kaplan, A.P.; Kojda, G.; Renné, T.; Wirth, M.; Maurer, M.; Church, M.K. Bradykinin in health and disease: Proceedings of the Bradykinin Symposium 2012, Berlin 23–24 August 2012. Inflamm. Res. 2014, 63, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.B.; Adam, A.; Brown, N.J. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-associated angioedema. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2006, 26, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, A.; Cugno, M.; Molinaro, G.; Perez, M.; Lepage, Y.; Agostoni, A. Aminopeptidase P in individuals with a history of angio-oedema on ACE inhibitors. Lancet 2002, 359, 2088–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinaro, G.; Cugno, M.; Perez, M.; Lepage, Y.; Gervais, N.; Agostoni, A.; Adam, A. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-associated angioedema is characterized by a slower degradation of des-arginine(9)-bradykinin. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 303, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nussberger, J.; Cugno, M.; Amstutz, C.; Cicardi, M.; Pellacani, A.; Agostoni, A. Plasma bradykinin in angio-oedema. Lancet 1998, 351, 1693–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, S.; Tomaszewski, M. Prediction and prevention of ACE-inhibitor-induced angioedema—An unmet clinical need in management of hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 2024, 47, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.J.; Ray, W.A.; Snowden, M.; Griffin, M.R. Black Americans have an increased rate of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor-associated angioedema. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1996, 60, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostis, J.B.; Kim, H.J.; Rusnak, J.; Casale, T.; Kaplan, A.; Corren, J.; Levy, E. Incidence and characteristics of angioedema associated with enalapril. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodard-Grice, A.V.; Lucisano, A.C.; Byrd, J.B.; Stone, E.R.; Simmons, W.H.; Brown, N.J. Sex-dependent and race-dependent association of XPNPEP2 C-2399A polymorphism with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-associated angioedema. Pharmacogenet Genom. 2010, 20, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaten, H.K.; Monte, A.A. The Pharmacogenomic and Metabolomic Predictors of ACE Inhibitor and Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker Effectiveness and Safety. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2017, 31, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilia La Corte, A.L.; Carter, A.M.; Rice, G.I.; Duan, Q.L.; Rouleau, G.A.; Adam, A.; Grant, P.J.; Hooper, N.M. A functional XPNPEP2 promoter haplotype leads to reduced plasma aminopeptidase P and increased risk of ACE inhibitor-induced angioedema. Hum. Mutat. 2011, 32, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.L.; Nikpoor, B.; Dube, M.P.; Molinaro, G.; Meijer, I.A.; Dion, P.; Rochefort, D.; Saint-Onge, J.; Flury, L.; Brown, N.J.; et al. A variant in XPNPEP2 is associated with angioedema induced by angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitors. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 77, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.B.; Touzin, K.; Sile, S.; Gainer, J.V.; Yu, C.; Nadeau, J.; Adam, A.; Brown, N.J. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV in angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor associated angioedema. Hypertension 2008, 51, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroteau, C.; Siddiqui, M.K.; Veluchamy, A.; Carr, F.; White, M.; Cassidy, A.J.; Baranova, E.V.; Rasmussen, E.R.; Eriksson, N.; Bloch, K.M.; et al. Exome Sequencing Reveals Common and Rare Variants in F5 Associated With ACE Inhibitor and Angiotensin Receptor Blocker-Induced Angioedema. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 108, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathey, C.M.; Maj, C.; Eriksson, N.; Krebs, K.; Westmeier, J.; David, F.S.; Koromina, M.; Scheer, A.B.; Szabo, N.; Wedi, B.; et al. Meta-analysis of ACE inhibitor-induced angioedema identifies novel risk locus. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, S0091-6749(23)02457-0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duerr, M.; Glander, P.; Diekmann, F.; Dragun, D.; Neumayer, H.H.; Budde, K. Increased incidence of angioedema with ACE inhibitors in combination with mTOR inhibitors in kidney transplant recipients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.J.; Byiers, S.; Carr, D.; Maldonado, M.; Warner, B.A. Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitor use associated with increased risk of ACE inhibitor-associated angioedema. Hypertension 2009, 54, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, T.; Gandhi, T.K.; Fiskio, J.M.; Seger, A.C.; So, J.W.; Cook, E.F.; Fukui, T.; Bates, D.W. An evaluation of risk factors for adverse drug events associated with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2004, 10, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.R.; Oliveria, S.A.; Berlowitz, D.R.; Fincke, B.G.; Stang, P.; Lillienfeld, D.E. Angioedema incidence in US veterans initiating angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Hypertension 2008, 51, 1624–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douillard, M.; Deheb, Z.; Bozon, A.; Raison-Peyron, N.; Dereure, O.; Moulis, L.; Soria, A.; Du-Thanh, A. Over diagnosis of bradykinin angioedema in patients treated with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers. World Allergy Organ. J. 2023, 16, 100809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, M.; Magerl, M. Differences and Similarities in the Mechanisms and Clinical Expression of Bradykinin-Mediated vs. Mast Cell-Mediated Angioedema. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 61, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, M.K.; Kolkhir, P.; Metz, M.; Maurer, M. The role and relevance of mast cells in urticaria. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 282, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, M.; Weller, K.; Bindslev-Jensen, C.; Giménez-Arnau, A.; Bousquet, P.J.; Bousquet, J.; Canonica, G.W.; Church, M.K.; Godse, K.V.; Grattan, C.E.; et al. Unmet clinical needs in chronic spontaneous urticaria. A GA²LEN task force report. Allergy 2011, 66, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, M.; Costa, C.; Gimenez Arnau, A.; Guillet, G.; Labrador-Horrillo, M.; Lapeere, H.; Meshkova, R.; Savic, S.; Chapman-Rothe, N. Antihistamine-resistant chronic spontaneous urticaria remains undertreated: 2-year data from the AWARE study. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2020, 50, 1166–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fricke, J.; Ávila, G.; Keller, T.; Weller, K.; Lau, S.; Maurer, M.; Zuberbier, T.; Keil, T. Prevalence of chronic urticaria in children and adults across the globe: Systematic review with meta-analysis. Allergy 2020, 75, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Borges, M.; Caballero-Fonseca, F.; Capriles-Hulett, A.; González-Aveledo, L.; Maurer, M. Factors linked to disease severity and time to remission in patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 964–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, P.J.; Smith, T. Histaminergic Angioedema. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2017, 37, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuberbier, T.; Abdul Latiff, A.H.; Abuzakouk, M.; Aquilina, S.; Asero, R.; Baker, D.; Ballmer-Weber, B.; Bangert, C.; Ben-Shoshan, M.; Bernstein, J.A.; et al. The international EAACI/GA²LEN/EuroGuiDerm/APAAACI guideline for the definition, classification, diagnosis, and management of urticaria. Allergy 2022, 77, 734–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicardi, M.; Aberer, W.; Banerji, A.; Bas, M.; Bernstein, J.A.; Bork, K.; Caballero, T.; Farkas, H.; Grumach, A.; Kaplan, A.P.; et al. Classification, diagnosis, and approach to treatment for angioedema: Consensus report from the Hereditary Angioedema International Working Group. Allergy 2014, 69, 602–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Marquez, M.L.; Christiansen, S.C.; Riedl, M.A.; Herschbach, J.; Zuraw, B.L. Threshold-stimulated kallikrein activity distinguishes bradykinin- from histamine-mediated angioedema. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindke, G.; Gehring, M.; Wieczorek, D.; Kapp, A.; Buhl, T.; Wedi, B. Identification of novel biomarkers to distinguish bradykinin-mediated angioedema from mast cell-/histamine-mediated angioedema. Allergy 2022, 77, 946–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.Y.; Masood, A. Fresh-frozen plasma as a treatment for life-threatening ACE-inhibitor angioedema. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 109, 370–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warrier, M.R.; Copilevitz, C.A.; Dykewicz, M.S.; Slavin, R.G. Fresh frozen plasma in the treatment of resistant angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor angioedema. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2004, 92, 573–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adebayo, O.; Wilkerson, R.G. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced angioedema worsened with fresh frozen plasma. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2017, 35, 192.e191–192.e192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javaud, N.; Karami, A.; Stirnemann, J.; Pilot, F.; Branellec, A.; Boubaya, M.; Chassaignon, C.; Adnet, F.; Fain, O. Bradykinin-mediated angioedema: Factors prompting ED visits. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2013, 31, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, P.W.; Hirschl, M.M.; Trautinger, F. Treatment of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-related angioedema with the bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist icatibant. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2010, 63, 913–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baş, M.; Greve, J.; Stelter, K.; Havel, M.; Strassen, U.; Rotter, N.; Veit, J.; Schossow, B.; Hapfelmeier, A.; Kehl, V.; et al. A randomized trial of icatibant in ACE-inhibitor-induced angioedema. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straka, B.T.; Ramirez, C.E.; Byrd, J.B.; Stone, E.; Woodard-Grice, A.; Nian, H.; Yu, C.; Banerji, A.; Brown, N.J. Effect of bradykinin receptor antagonism on ACE inhibitor-associated angioedema. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 242–248.e242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinert, R.; Levy, P.; Bernstein, J.A.; Body, R.; Sivilotti, M.L.A.; Moellman, J.; Schranz, J.; Baptista, J.; Kimura, A.; Nothaft, W. Randomized Trial of Icatibant for Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor-Induced Upper Airway Angioedema. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 1402–1409.e1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, J.A.; Moellman, J.J.; Collins, S.P.; Hart, K.W.; Lindsell, C.J. Effectiveness of ecallantide in treating angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced angioedema in the emergency department. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015, 114, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, L.M.; Graffeo, C.; Crosley, P.; Klausner, H.A.; Clark, C.L.; Frank, A.; Miner, J.; Iarrobino, R.; Chyung, Y. Ecallantide for the acute treatment of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced angioedema: A multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2015, 65, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, T.J.; Rojavin, M.A.; Machnig, T.; Keinecke, H.O.; Bernstein, J.A. Effect of time to treatment on response to C1 esterase inhibitor concentrate for hereditary angioedema attacks. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013, 111, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, E.R.; Bygum, A. ACE-inhibitor induced angio-oedema treated with complement C1-inhibitor concentrate. BMJ Case Rep. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipski, S.M.; Casimir, G.; Vanlommel, M.; Jeanmaire, M.; Dolhen, P. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors-induced angioedema treated by C1 esterase inhibitor concentrate (Berinert®): About one case and review of the therapeutic arsenal. Clin. Case Rep. 2015, 3, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greve, J.; Bas, M.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Schuler, P.J.; Weller, P.; Kojda, G.; Strassen, U. Effect of C1-Esterase-inhibitor in angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced angioedema. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, E198–E202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strassen, U.; Bas, M.; Wirth, M.; Wirth, M.; Gröger, M.; Stelter, K.; Volkenstein, S.; Kehl, V.; Kojda, G.; Hoffmann, T.K.; et al. Efficacy of human C1 esterase inhibitor concentrate for treatment of ACE-inhibitor induced angioedema. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2023, 64, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltrami, L.; Zanichelli, A.; Zingale, L.; Vacchini, R.; Carugo, S.; Cicardi, M. Long-term follow-up of 111 patients with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-related angioedema. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, 2273–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, J.A.; Cremonesi, P.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Hollingsworth, J. Angioedema in the emergency department: A practical guide to differential diagnosis and management. Int. J. Emerg. Med. 2017, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beavers, C.J.; Dunn, S.P.; Macaulay, T.E. The role of angiotensin receptor blockers in patients with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced angioedema. Ann. Pharmacother. 2011, 45, 520–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haymore, B.R.; Yoon, J.; Mikita, C.P.; Klote, M.M.; DeZee, K.J. Risk of angioedema with angiotensin receptor blockers in patients with prior angioedema associated with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors: A meta-analysis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008, 101, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, E.R.; Pottegård, A.; Bygum, A.; von Buchwald, C.; Homøe, P.; Hallas, J. Angiotensin II receptor blockers are safe in patients with prior angioedema related to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors—A nationwide registry-based cohort study. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 285, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makani, H.; Messerli, F.H.; Romero, J.; Wever-Pinzon, O.; Korniyenko, A.; Berrios, R.S.; Bangalore, S. Meta-analysis of randomized trials of angioedema as an adverse event of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors. Am. J. Cardiol. 2012, 110, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, S.I.; Andersen, M.F.; Aagaard, L.; Buchwald, C.V.; Rasmussen, E.R. Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Induced Angioedema—An Overlooked Adverse Drug Reaction? Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2018, 14, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Jiao, Y.; Luo, M.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Liu, C. Detection of Various Traditional Chinese Medicinal Metabolites as Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors: Molecular Docking, Activity Testing, and Surface Plasmon Resonance Approaches. Molecules 2023, 28, 7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, S.; Shao, S.; Mu, G.; Shah, S.J.; Yu, X.; Sun, W.; Shi, Z.; Xing, L.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, L.; et al. Highly selective and pH responsive adsorption of ZIF-8 for angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory active peptides and its mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 324, 124620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, G.A.; Dhanya, T.M.; Shanty, A.A.; Raghu, K.G.; Mohanan, P.V. Transition metal complexes of imidazole derived Schiff bases: Antioxidant/anti-inflammatory/antimicrobial/enzyme inhibition and cytotoxicity properties. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1274, 134384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Xiu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ke, M.; Lin, L.; Yan, H.; Hu, P.; Xiao, M.; He, X.; Zhang, T. Learning and Investigation of the Role of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme in Radiotherapy for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Angioedema Disorder | C4 | C1 INH Levels | C1 Inhibitor Function | C1q | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAE with C1inhibitor deficiency Type I | Low | Low | Low (usually < 50%) | Normal | |
| HAE with C1 inhibitor deficiency type II | Low | Normal or elevated | Low (usually < 50%) | Normal | |
| HAE with normal C1 inhibitor | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | |
| Acquired AE with C1 inhibitor Deficiency | Low | Normal or Low | Low (usually < 50%) | Normal or low | Anti C1 Inhibitor antibodies |
| ACEI- AE | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | |
| Mast cell mediated AE | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal |
| Mast Cell Mediated AE | Bradykinin Mediated AE (ACEIs-Induced AE) | |
|---|---|---|
| Wheals/history of recurrent wheals | + | - |
| Recurrent Laryngeal AE | - | + |
| Tongue AE | + | ++ |
| Angioedema triggered by NSAIDs | + | - |
| Rate of onset | minutes | hours |
| Duration | <48 h | >48 h |
| Response to antihistamines/ corticosteroids/ adrenaline | + | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papapostolou, N.; Gregoriou, S.; Katoulis, A.; Makris, M. Five-Membered Nitrogen Heterocycles Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors Induced Angioedema: An Underdiagnosed Condition. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17030360
Papapostolou N, Gregoriou S, Katoulis A, Makris M. Five-Membered Nitrogen Heterocycles Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors Induced Angioedema: An Underdiagnosed Condition. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(3):360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17030360
Chicago/Turabian StylePapapostolou, Niki, Stamatios Gregoriou, Alexander Katoulis, and Michael Makris. 2024. "Five-Membered Nitrogen Heterocycles Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors Induced Angioedema: An Underdiagnosed Condition" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 3: 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17030360
APA StylePapapostolou, N., Gregoriou, S., Katoulis, A., & Makris, M. (2024). Five-Membered Nitrogen Heterocycles Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors Induced Angioedema: An Underdiagnosed Condition. Pharmaceuticals, 17(3), 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17030360










