Synthesis and Evaluation of 5-(Heteroarylmethylene)hydantoins as Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β Inhibitors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
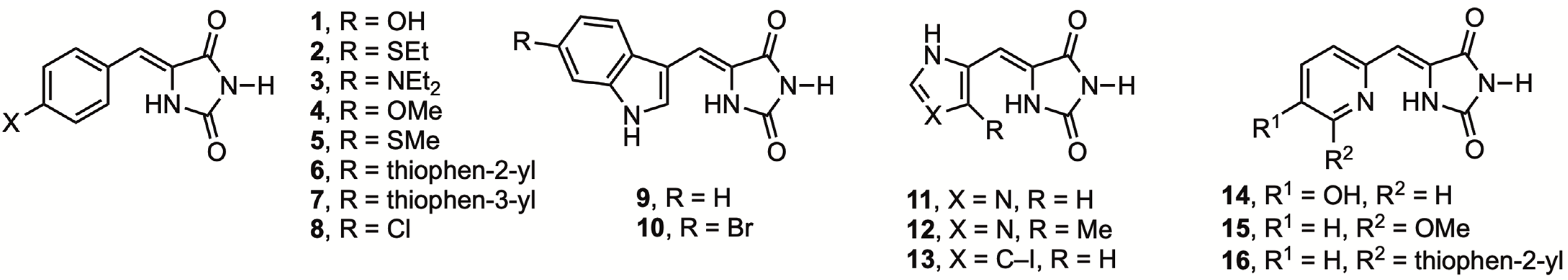
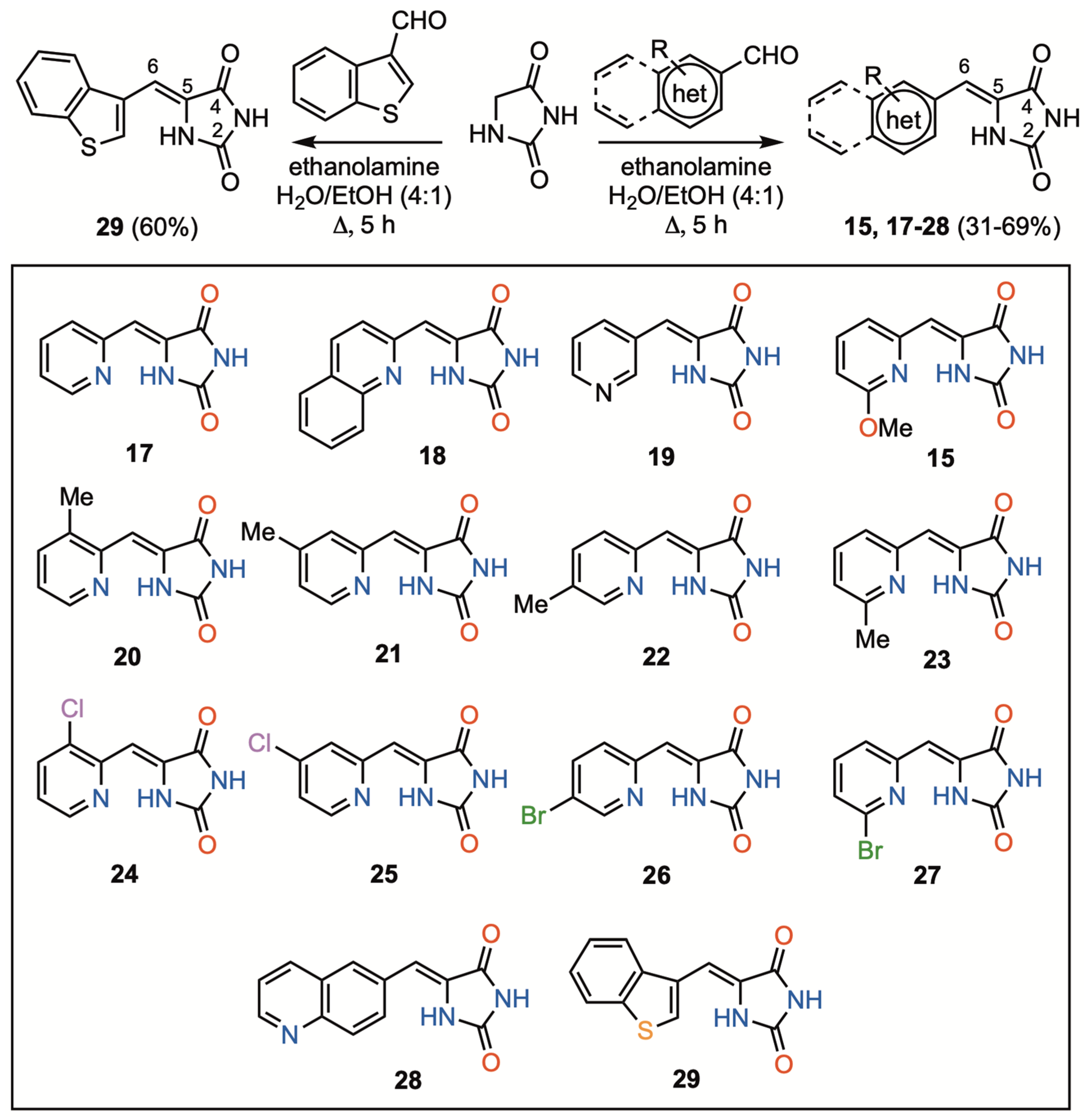
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Evaluation
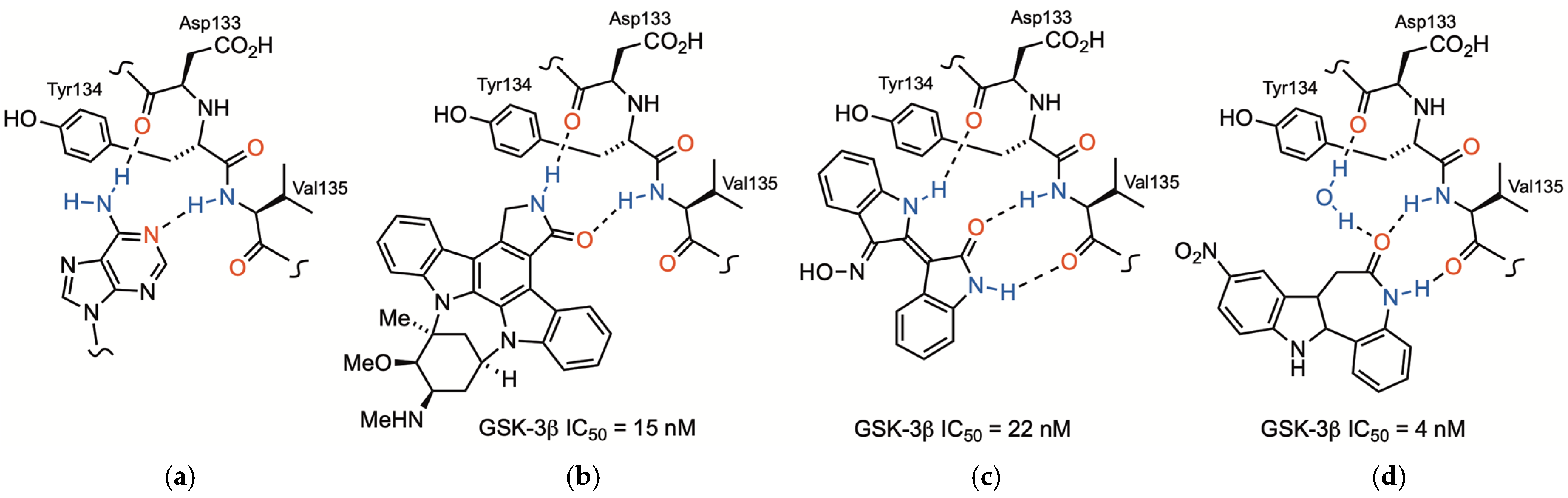
2.2.1. Inhibition of GSK-3β
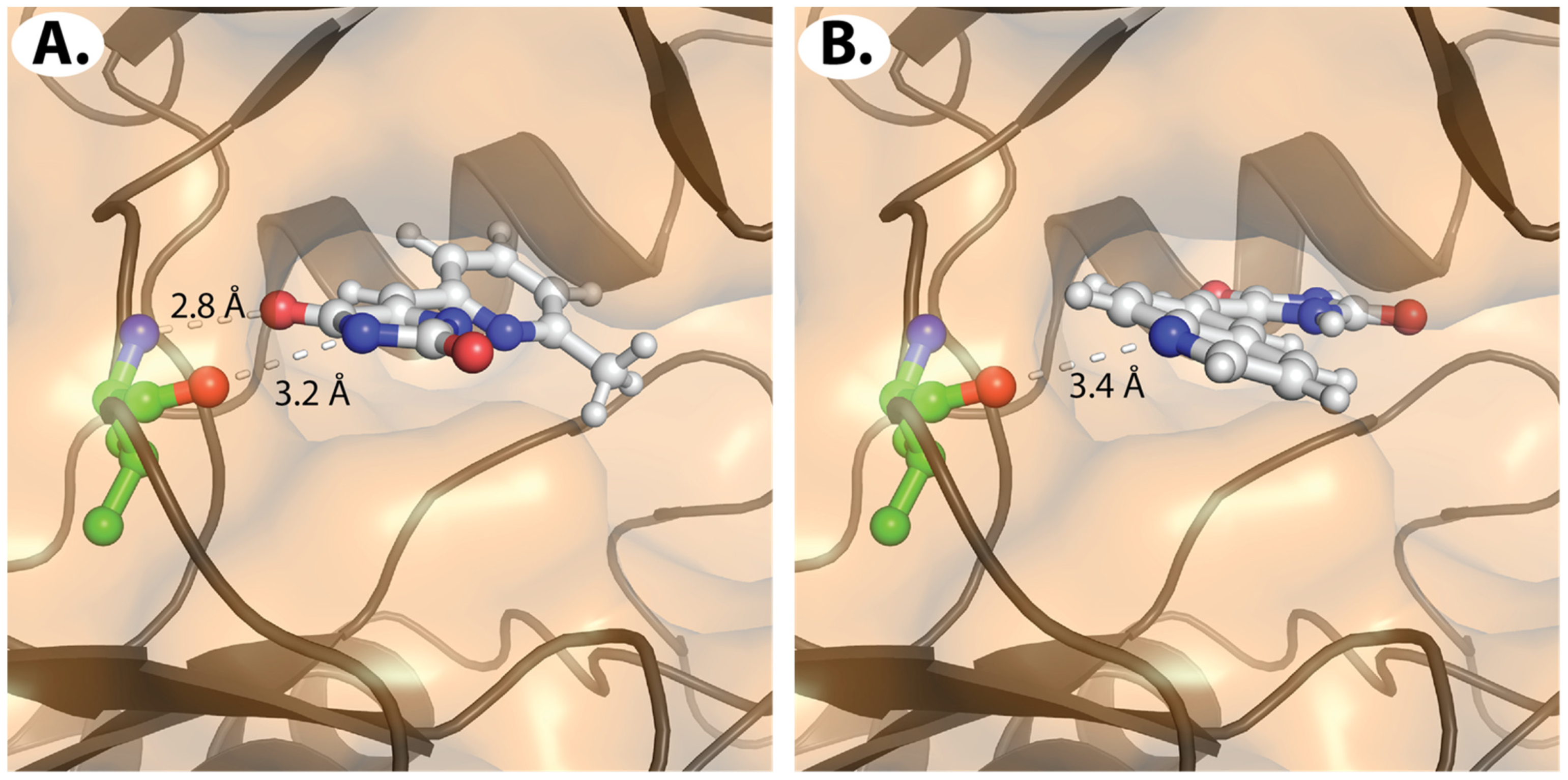
2.2.2. Molecular Docking
2.2.3. Evaluation of Selected Compounds against MMP-12, hCAII, and SaPC
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. General Experimental Information
3.1.2. General Procedure for the Preparation of 5-(Heteroarylmethylene)hydantoins
3.2. Biological Evaluation
3.2.1. Inhibition of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β
3.2.2. Inhibition of Matrix Metalloproteinase-12
3.2.3. Inhibition of Human Carbonic Anhydrase II
3.2.4. Inhibition of S. aureus Pyruvate Carboxylase (SaPC)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Embi, N.; Rylatt, D.B. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Separation from cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase and phosphorylase kinase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1980, 107, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, K.; Nikolakaki, E.; Plyte, S.E.; Totty, N.F.; Woodgett, J.R. Modulation of the glycogen synthase kinase-3 family by tyrosine phosphorylation. EMBO 1993, 12, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beurel, E.; Greico, S.F.; Jope, R.S. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3): Regulation, actions and diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 148, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Hoeflich, K.P.; Woodgett, J.R. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3: Properties, Function, and Regulation. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 2527–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodgett, J.R. Molecular cloning and expression of glycogen synthase kinase-2/Factor A. EMBO 1990, 9, 2431–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoulina, S.E.; Ciaraldi, T.P.; Mualiar, S.; Carter, L.; Johnson, K.; Henry, R.R. Inhibition of Synthase Kinase 3 Improves Insulin Action and Glucose Metabolism in Human Skeletal Muscle. Diabetes 2002, 51, 2190–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jope, R.S.; Roh, M.-S. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK3) in Psychiatric Diseases and Therapeutic Interventions. Curr. Drug Targets 2006, 7, 1421–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozikowski, A.P.; Gaisina, I.N.; Yuan, H.; Petukhov, P.A.; Blond, S.Y.; Fedolak, A.; Caldarone, B.; McGonigle, P. Structure-Based Design Leads to the Identification of Lithium Mimetics that Block Mania-like Effects in Rodents. Possible New GSK-3b Therapies for Bipolar Disorders. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 8328–8332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlotti, G.; Alisi, M.A.; Cazzolla, N.; Dragone, P.; Durando, L.; Magaro, G.; Mancini, F.; Mangano, G.; Ombrato, R.; Vitiello, M.; et al. Hit Optimization of 5-Substituted-N-(piperidin-4-ylmethyl)-1Hindazole-3-carboxamides: Potent Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK-3) Inhibitors with in Vivo Activity in Model of Mood Disorders. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 8920–8937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, S.M.A.; Eldar-Finkelman, H. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Inhibitors: Preclinical and Clinical focus on CNS-A Decade Onward. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 14, 792364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walz, A.; Ugolkov, A.; Chandra, S.; Kozikowski, A.; Carneiro, B.A.; O’Halloran, T.V.; Giles, F.J.; Billadeau, D.D.; Mazar, A.P. Molecular Pathways: Revisiting Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3b as a Target for the Treatment of Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 1891–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borden, B.A.; Baca, Y.; Xiu, J.; Tavora, F.; Winer, I.; Weinberg, B.A.; Vanderwalde, A.M.; Darabi, S.; Korn, W.M.; Mazar, A.P.; et al. The Landscape of Glycogen Synthease Kinase-3 Beta Genomic Alterations in Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Tian, Y.-N.; Zhou, L.-N.; Li, M.-Z.; Chen, H.-D.; Song, S.-S.; Huan, X.-J.; Bao, X.-B.; Zhang, A.; Miao, Z.-H.; et al. Glycogen synthase kinase 3b inhibition synergizes with PARP inhibitors through the induction of homologous recombination deficiency in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, J.; Hernandez, F. GLK-3 inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2007, 7, 1527–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Begum, A.N.; Jones, M.R.; Oh, M.S.; Beech, W.K.; Beech, B.H.; Yang, F.; Chen, P.; Ubeda, O.J.; Kim, P.C.; et al. GSK3 inhibitors show benefits in an Alzheimer’s disease AD model of neurodegeneration but adverse effects in control animals. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 33, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griebel, G.; Stemmelin, J.; Lopez-Grancha, M.; Boulay, D.; Boquet, G.; Slowinski, F.; Pichat, P.; Beeske, S.; Tanaka, S.; Mori, A.; et al. The selective GSK3 inhibitor, SAR502250, displays neuroprotective activity and attenuates behavioral impairments in models of neuropsychiatric symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease in rodents. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapira, T.; Vimalanathan, S.; Rens, C.; Pichler, V.; Pena-Diaz, S.; Jordana, G.; Rees, W.; Winkler, D.F.H.; Sarai, I.; Steiner, T.; et al. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3-beta (GSK3b) blocks nucleocapsid phosphorylation and SARS-CoV-2 replication. Mol. Biomed. 2022, 3, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ter Haar, E.; Coll, J.T.; Austen, D.A.; Hsiao, H.-M.; Swenson, L.; Jain, J. Structure of GSK3b reveals a primed phosphorylation mechanism. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2001, 8, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, J.A.; Thieffine, S.; Vulpetti, A.; Cristiani, C.; Valsasina, B.; Knapp, S.; Kalisz, H.M.; Flocco, M. Structural Characterization of the GSK-3b Active Site Using Selective and Non-selective ATP-mimetic Inhibitors. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 333, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, T.; Schmidt, B.; Lo Monte, F. Small-Molecule Inhibitors of GSK-3: Structural Insights and Their Application to Alzheimer’s Disease Models. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2012, 2012, 381029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudit, M.; Khanfar, M.; Muralidharan, A.; Thomas, S.; Shah, G.V.; van Soest, R.W.M.; El Sayed, K.A. Discovery, design, and synthesis of anti-metastatic lead phenylmethylene hydantoins inspired by marine natural products. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 1731–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guella, G.; Mancini, I.; Zibrowius, H.; Pietra, F. Novel Aplysinopsin-Type Alkaloids from Scleractinian Corals of the Family Dendrophylliidae of the Mediterranean and the Philippines. Configurational-Assignment Criteria, Stereospecific Synthesis, and Photoisomerization. Helv. Chim. Acta 1988, 71, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanfar, M.A.; Abu Asal, B.; Mudit, M.; Kaddoumi, A.; El Sayed, K.A. The marine natural-derived inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3b phenylmethylene hydantoins: In vitro and in vivo activities and pharmacophore modeling. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 6032–6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanfar, M.A.; El Sayed, K.A. Phenylmethylene hydantoins as prostate cancer invasion as migration inhibitors. CoMFA approach and QSAR analysis. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 5397–5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.-F.; Ang, K.-P.; How, G.-F. NMR Spectroscopic Study of Configurations and Conformations of 5-Pyridylmethylenehydantoins. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 1990, 3, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Castaneda, M.; Rodriguez, A.M.; Aboo, A.H.; Manzano, B.R.; Espino, G.; Xiao, J.; Jalon, F.A. Iridium complexes with a new type of N^N′-donor anionic ligand catalyze the N-benzylation of amines via borrowing hydrogen. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e6003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkett, D.J.; Wyatt, B.N.; Mews, M.; Bautista, A.; Engel, R.; Dockendorff, C.; Donaldson, W.A.; St. Maurice, M. Evaluation of α-hydroxycinnamic acids as pyruvate carboxylase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 4041–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elks, J.; Hems, B.A.; Ryman, B.E. The synthesis of some α-Amino-acids. J. Chem. Soc. 1948, 1386–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benassi, R.; Bregulla, A.; Freidrich, A.; Henning, D.; Heydenreich, M.; Mickler, W.; Kleinpeter, G.; Schilde, U.; Taddei, F. NMR spectroscopic and theoretical study of 5-exo-methylene-substituted hydantoins. J. Mol. Struct. 1998, 441, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with a New Scoring Function, Efficient Optimization, and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastassiadis, T.; Deacon, S.W.; Devarajan, K.; Ma, H.; Peterson, J.R. Comprehensive assay of kinase catalytic activity reveals features of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat. Biotech. 2011, 29, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, J.A.; Cohen, S.M. Investigating the Selectivity of Metalloenzyme Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 7997–8007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Compd | GSK-3β % Activity @ 25 μM | GSK-3β IC50 | GSK-3β Docking Score 1 | MMP-12 % Activity @ 200 μM/25 μM | hCAII % Activity @ 200 μM | SaPC IC50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | 55.4 | ND | –7.1 | ND | ND | ND |
| 18 | 32.9 | ND | –8.7 | 57.6/94.1 | ND | >1000 μM |
| 19 | 71.8 | ND | –7.1 | 50.6/84.2 | 88.9 ± 12.3 | >1000 μM |
| 15 | 17.3 | 4.06 ± 0.30 μM | –7.4 | 74.0/87.5 | 82.1 ± 11.0 | >1000 μM |
| 20 | 31.6 | ND | –7.6 | 39.6/108 | ND | ND |
| 21 | 42.0 | ND | –7.6 | 28.5/71.6 | 94.8 ± 12.8 | >1000 μM |
| 22 | 47.0 | ND | –7.3 | 40.7/101 | 87.4 ± 11.8 | >1000 μM |
| 23 | 28.4 | 8.34 ± 0.27 μM | –7.4 | 46.5/86.4 | 88.9 ± 12.3 | >1000 μM |
| 24 | 44.6 | ND | –7.2 | 39.2/69.1 | 91.8 ± 14.7 | >1000 μM |
| 25 | 15.4 | 2.14 ± 0.18 μM | –7.5 | 50.0/73.9 | 57.0 ± 16.4 | >1000 μM |
| 26 | 35.3 | ND | –6.7 | 72.9/98.6 | ND | ND |
| 27 | 17.0 | 3.39 ± 0.16 μM | –7.5 | 88.7/85.8 | 86.7 ± 12.1 | >1000 μM |
| 28 | 22.5 | 7.82 ± 0.12 μM | –8.8 | 61.6/81.8 | ND | ND |
| 29 | 27.9 | ND | –7.8 | 88.0/98.1 | 62.7 ± 9.8 | >1000 μM |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schneider, N.O.; Gilreath, K.; Burkett, D.J.; St. Maurice, M.; Donaldson, W.A. Synthesis and Evaluation of 5-(Heteroarylmethylene)hydantoins as Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17050570
Schneider NO, Gilreath K, Burkett DJ, St. Maurice M, Donaldson WA. Synthesis and Evaluation of 5-(Heteroarylmethylene)hydantoins as Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(5):570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17050570
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchneider, Nicholas O., Kendra Gilreath, Daniel J. Burkett, Martin St. Maurice, and William A. Donaldson. 2024. "Synthesis and Evaluation of 5-(Heteroarylmethylene)hydantoins as Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β Inhibitors" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 5: 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17050570
APA StyleSchneider, N. O., Gilreath, K., Burkett, D. J., St. Maurice, M., & Donaldson, W. A. (2024). Synthesis and Evaluation of 5-(Heteroarylmethylene)hydantoins as Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals, 17(5), 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17050570








