Early Stage Preclinical Formulation Strategies to Alter the Pharmacokinetic Profile of Two Small Molecule Therapeutics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Physiochemical Property and Compound Characterization
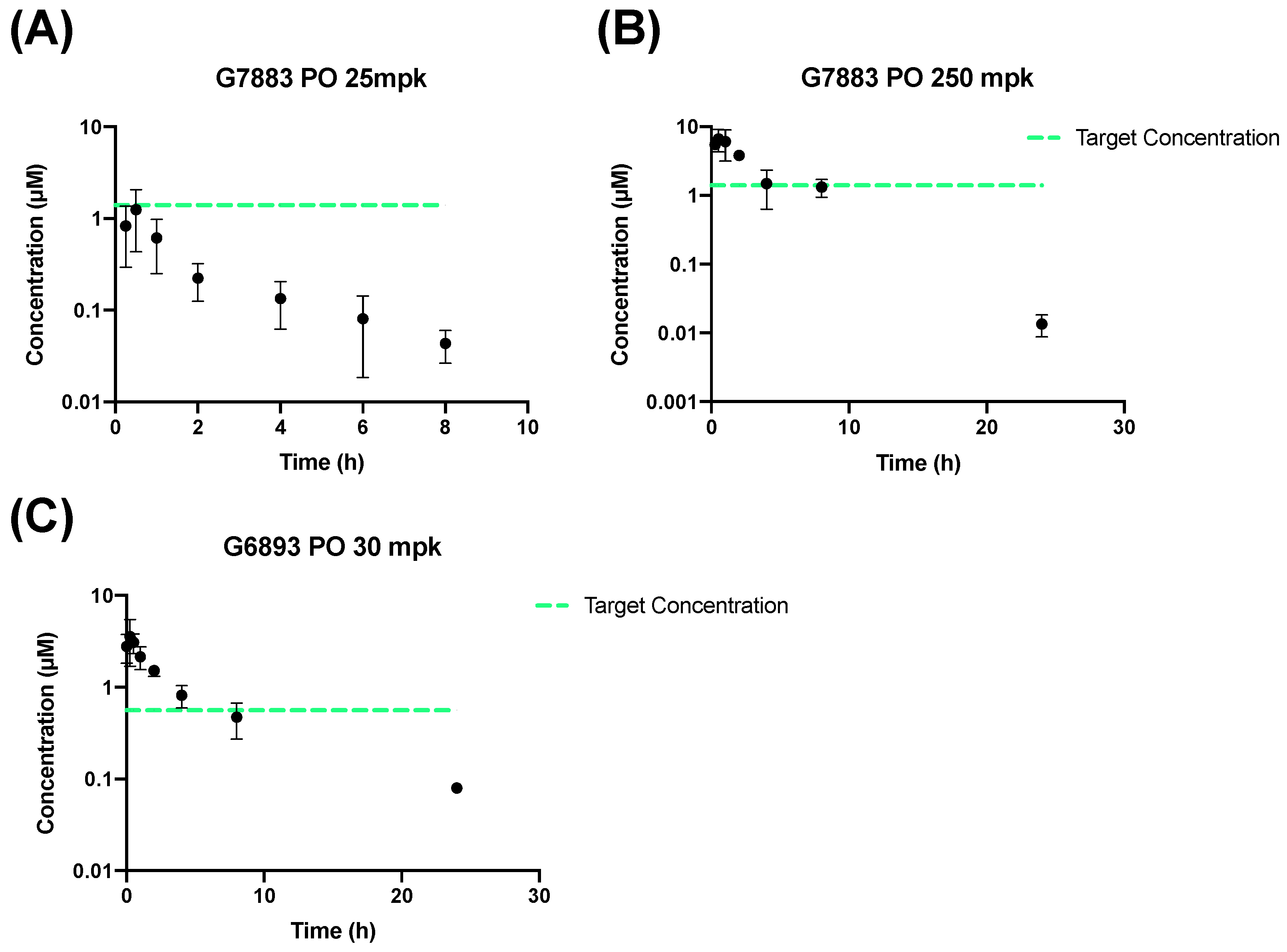
2.2. PO and IP Administration
2.3. IV Infusion Administration and Pharmacokinetics
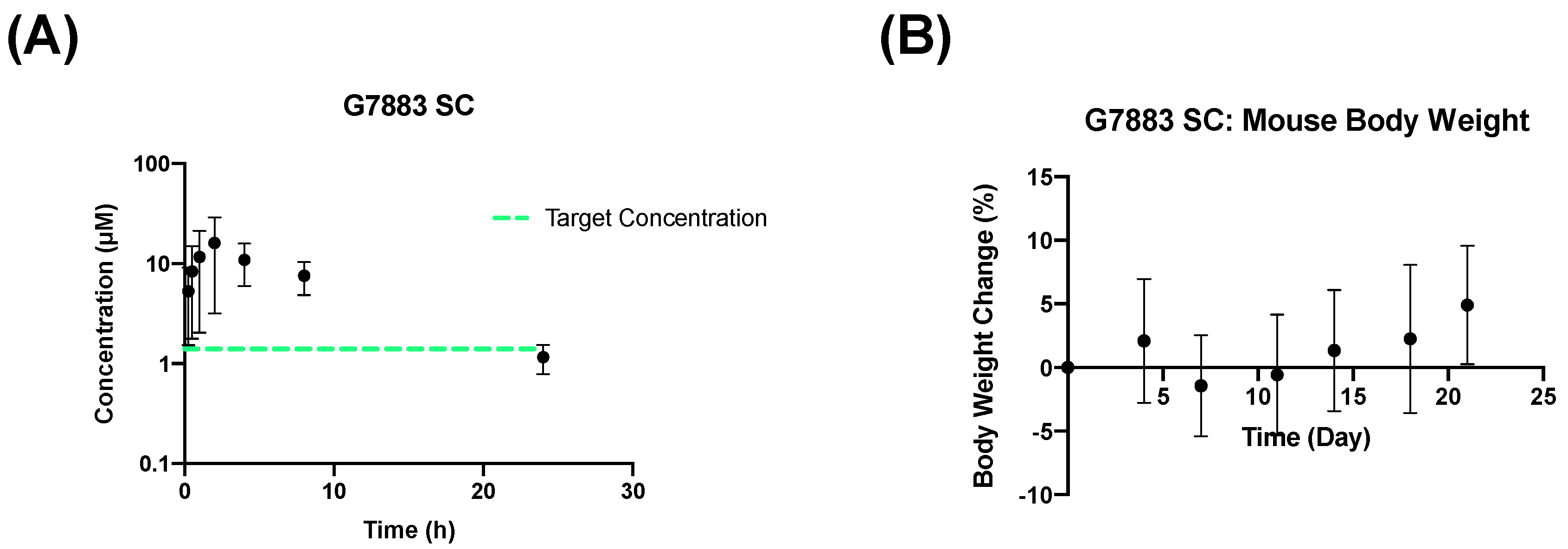
2.4. Subcutaneous Depot Development and Pharmacokinetics
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. PO and IP Vehicle and Formulation Preparation
3.3. PO Study
3.4. IP Study
3.5. IV Infusion Study
- Vehicle and Formulation Preparation
3.6. Subcutaneous (SC) Study
- Vehicle and Formulation Preparation
3.7. Bioanalytical Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Low, B.C.; Pan, C.Q.; Shivashankar, G.V.; Bershadsky, A.; Sudol, M.; Sheetz, M. YAP/TAZ as mechanosensors and mechanotransducers in regulating organ size and tumor growth. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 2663–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, J.K.; Cunningham, C.N. Targeting the hippo pathway and cancer through the TEAD family of transcription factors. Cancers 2018, 10, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, T.; Cheng, A.S.L.; Yu, J.; Kang, W.; To, K.F. The TEAD family and its oncogenic role in promoting tumorigenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pobbati, A.V.; Hong, W. A combat with the YAP/TAZ-TEAD oncoproteins for cancer therapy. Theranostics 2020, 10, 3622–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawasdikosol, S.; Burakoff, S. A perspective on hpk1 as a novel immuno-oncology drug target. eLife 2020, 9, 55122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boomer, J.S.; Tan, T.H. Functional interactions of HPK1 with adaptor proteins. J. Cell. Biochem. 2005, 95, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Sneeringer, C.J.; Pitts, K.E.; Day, E.S.; Chan, B.K.; Wei, B.; Lehoux, I.; Mortara, K.; Li, H.; Wu, J.; et al. Hematopoietic Progenitor Kinase-1 Structure in a Domain-Swapped Dimer. Structure 2019, 27, 125–133.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Ding, S.; Zhang, H. Interactions between hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 and its adaptor proteins (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 6472–6482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, B.K.; Seward, E.; Lainchbury, M.; Brewer, T.F.; An, L.; Blench, T.; Cartwright, M.W.; Chan, G.K.Y.; Choo, E.F.; Drummond, J.; et al. Discovery of Spiro-azaindoline Inhibitors of Hematopoietic Progenitor Kinase 1 (HPK1). ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Shoyaib, A.; Archie, S.R.; Karamyan, V.T. Intraperitoneal Route of Drug Administration: Should it Be Used in Experimental Animal Studies? Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagenbeek, T.J.; Zbieg, J.R.; Hafner, M.; Mroue, R.; Lacap, J.A.; Sodir, N.M.; Noland, C.L.; Afghani, S.; Kishore, A.; Bhat, K.P.; et al. An allosteric pan-TEAD inhibitor blocks oncogenic YAP/TAZ signaling and overcomes KRAS G12C inhibitor resistance. Nat. Cancer 2023, 4, 812–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, M.S.; Kazi, M.; Alsenaidy, M.A.; Ahmad, M.Z. Advances in Oral Drug Delivery. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 618411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homayun, B.; Lin, X.; Choi, H.J. Challenges and recent progress in oral drug delivery systems for biopharmaceuticals. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinarov, Z.; Abrahamsson, B.; Artursson, P.; Batchelor, H.; Berben, P.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Butler, J.; Ceulemans, J.; Davies, N.; Dupont, D.; et al. Current challenges and future perspectives in oral absorption research: An opinion of the UNGAP network. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 171, 289–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galetin, A.; Gertz, M.; Houston, J.B. Potential role of intestinal first-pass metabolism in the prediction of drug-drug interactions. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2008, 4, 909–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin-Arama, M.; Abraham, L.; Waner, T.; Harmelin, A.; Steinberg, D.M.; Lahav, T.; Harlev, M. Subcutaneous Compared with Intraperitoneal Ketamine–Xylazine for Anesthesia of Mice. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2016, 55, 794–800. [Google Scholar]
- Van Herck, S.; De Geest, B.G. Nanomedicine-mediated alteration of the pharmacokinetic profile of small molecule cancer immunotherapeutics. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 881–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongfen, Y.; He, H.; Wu, Y.; Fan, J.; Cao, Y. Physiologically-based pharmacokinetic modeling of nanoparticles Dongfen. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 59–72. [Google Scholar]
- Irby, D.; Du, C.; Li, F. Lipid–Drug Conjugate for Enhancing Drug Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 1325–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.; Watts, S.W.; Davis, R.P. Drug delivery: Enabling technology for drug discovery and development. iPRECIO® Micro Infusion Pump: Programmable, refillable, and implantable. Front. Pharmacol. 2011, 2, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnfeld, L.; Luciani, P. Injectable lipid-based depot formulations: Where do we stand? Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Ho, M.J.; Joung, M.Y.; Choi, Y.S.; Kang, M.J. Effect of Dispersion Medium on Pharmacokinetic Profile of Rotigotine Crystalline Suspension following Subcutaneous Injection. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| G7883 | G6893 | |
|---|---|---|
| MW (g/mol) | 500.57 | 450 |
| Water Solubility (µg/mL) | 85 | <1 |
| Log P | 1.83 | 2.69 |
| pKa | 5.51, 4.83 | 2.53, 3.87 |
| Permeability | 5.79 × 10−6 cm/s | 15 × 10−6 cm/s |
| Pharmacokinetic Parameter | PO 25 mpk (G7883) (Mean ± SD) | PO 250 mpk (G7883) (Mean ± SD) | PO 30 mpk (G6893) (Mean ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AUC0 to 8 (h·µM) | 1.99 ± 0.40 | 25.1 ± 5.43 | 19.5 |
| Cmax (µM) | 1.25 ± 0.82 | 6.85 ± 2.24 | 3.80 ± 1.68 |
| Tmax (h) | 0.5 | 0.583 ± 0.382 | 0.667 ± 0.289 |
| t1/2 (h) | 2.17 ± 0.73 | 2.74 ± 0.201 | 3.07 ± 1.92 |
| F (%) | 6.18 ± 1.24 | 7.80 ± 1.69 | 45.5 ± 14.0 |
| Pharmacokinetic Parameter | IP 50 mpk (Mean) | IP 150 mpk (Mean) |
|---|---|---|
| AUC0 to t (h·µM) | 31.2 | 217 |
| Cmax (µM) | 23.9 | 69.2 |
| Tmax (h) | 1 | 1 |
| t1/2 (h) | 0.895 | 1.53 |
| Pharmacokinetic Parameter | SC 250 mpk (G7883) (Mean ± SD) |
|---|---|
| AUC0 to t (h·µM) | 137 ± 51.1 |
| Cmax (µM) | 16.7 ± 12 |
| Tmax (h) | 2.67 ± 1.15 |
| t1/2 (h) | 6.94 ± 2.93 |
| F (%) | 46.4 ± 13.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, L.; De Bruyn, T.; Pang, J.; Ubhayakar, S.; Salphati, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Li, R.; Chan, B.; Dey, A.; et al. Early Stage Preclinical Formulation Strategies to Alter the Pharmacokinetic Profile of Two Small Molecule Therapeutics. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17020179
An L, De Bruyn T, Pang J, Ubhayakar S, Salphati L, Zhang X, Liu L, Li R, Chan B, Dey A, et al. Early Stage Preclinical Formulation Strategies to Alter the Pharmacokinetic Profile of Two Small Molecule Therapeutics. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(2):179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17020179
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Le, Tom De Bruyn, Jodie Pang, Savita Ubhayakar, Laurent Salphati, Xing Zhang, Liling Liu, Ruina Li, Bryan Chan, Anwesha Dey, and et al. 2024. "Early Stage Preclinical Formulation Strategies to Alter the Pharmacokinetic Profile of Two Small Molecule Therapeutics" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 2: 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17020179
APA StyleAn, L., De Bruyn, T., Pang, J., Ubhayakar, S., Salphati, L., Zhang, X., Liu, L., Li, R., Chan, B., Dey, A., & Levy, E. S. (2024). Early Stage Preclinical Formulation Strategies to Alter the Pharmacokinetic Profile of Two Small Molecule Therapeutics. Pharmaceuticals, 17(2), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17020179







