Isoorientin Improves Excisional Skin Wound Healing in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
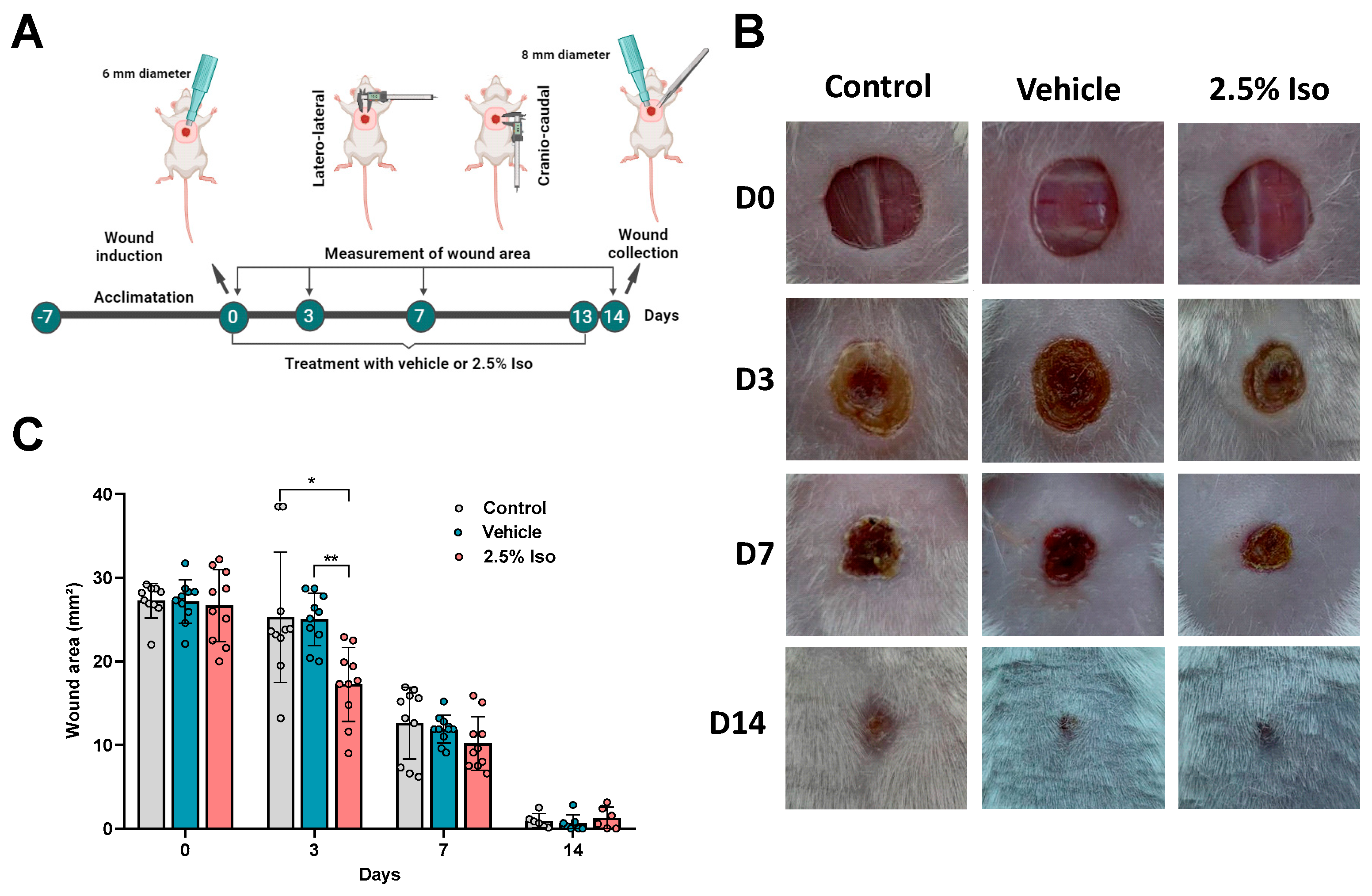
2.1. Isoorientin Reduces the Wound Area during the Inflammatory Phase
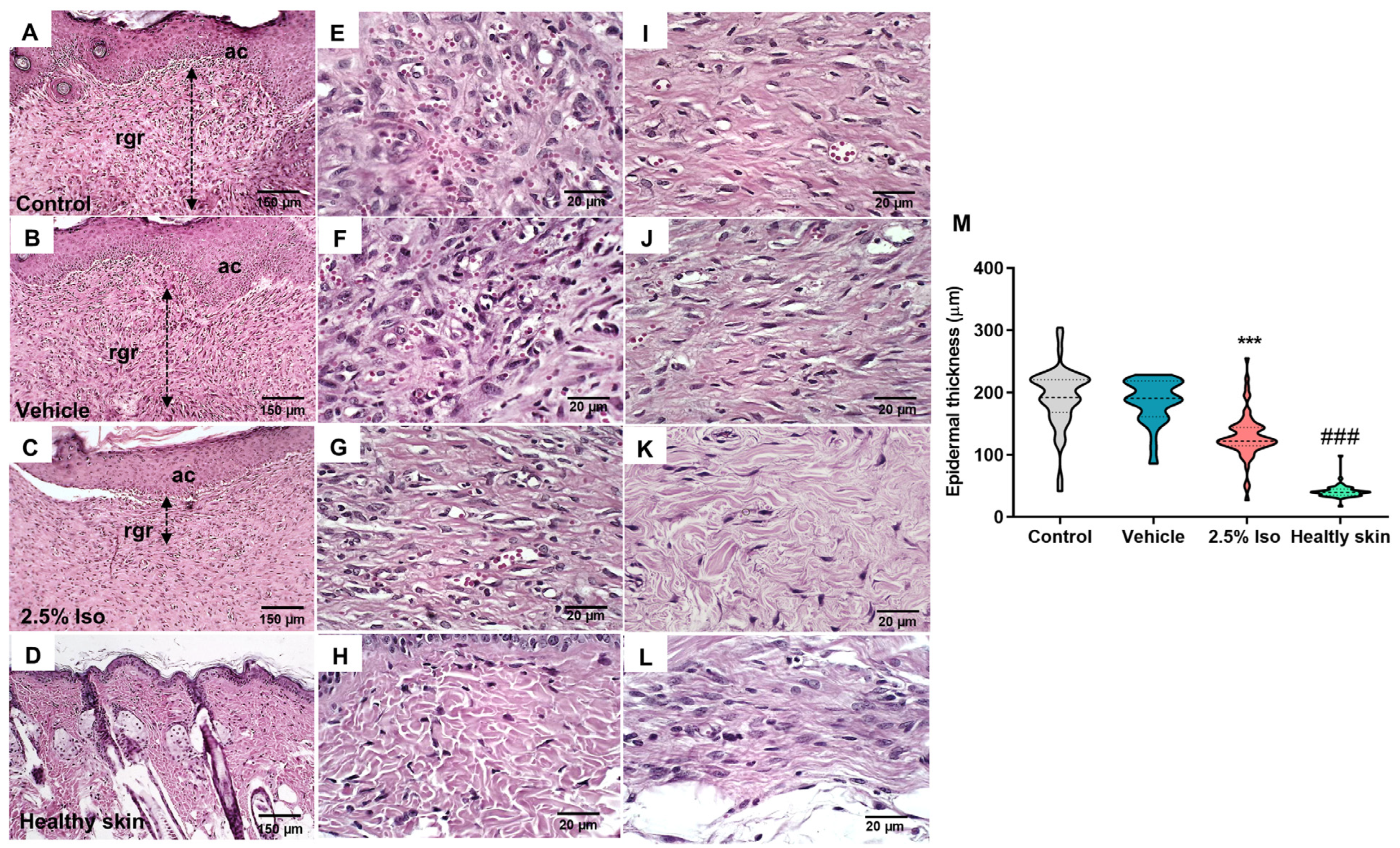
2.2. The Administration of Isoorientin Enhances the Quality of Wound Healing
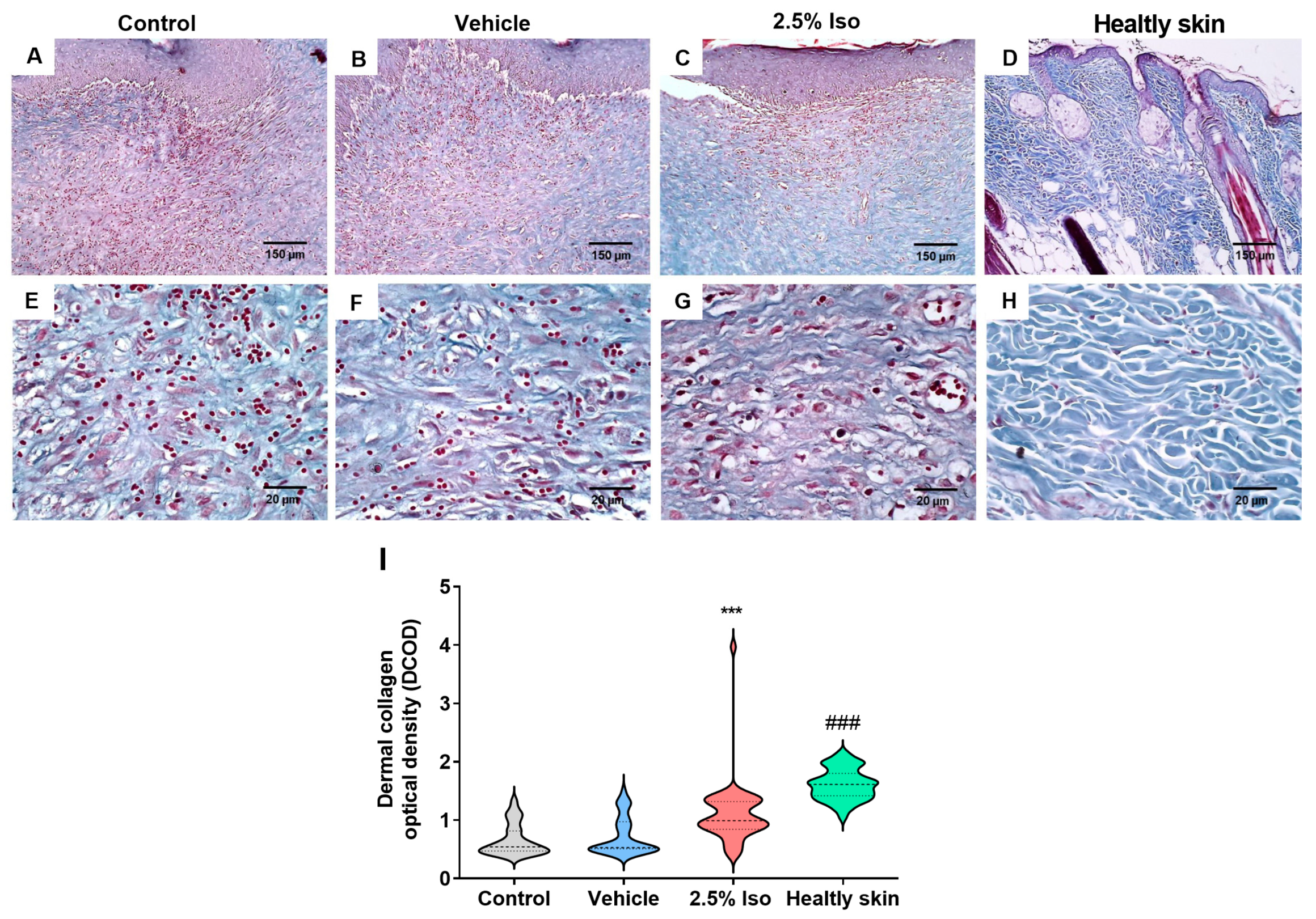
2.3. Isoorientin Promotes Greater Collagen Deposition in Injured Tissue
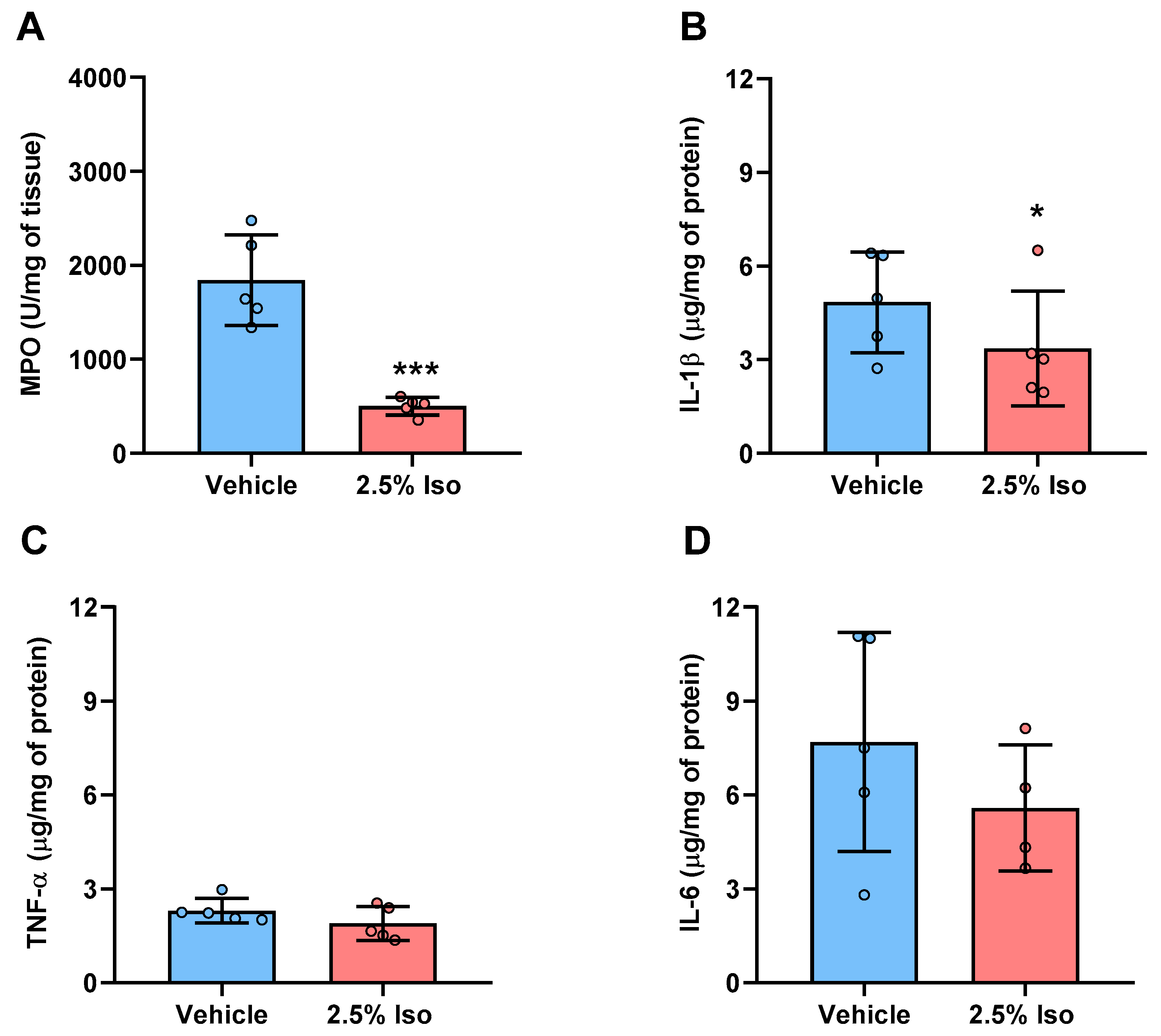
2.4. Inflammatory Markers Are Reduced in the Wounds of Animals Treated with Isoorientin
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Groups and Treatments
4.2. Wound Healing Model
4.3. Histopathology
4.4. MPO Activity
4.5. Determination of Cytokine Concentrations
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sen, C.K. Human Wound and Its Burden: Updated 2020 Compendium of Estimates. Adv. Wound Care 2021, 10, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, H.T.T.; Edwards, H.; Finlayson, K. Identifying Relationships between Symptom Clusters and Quality of Life in Adults with Chronic Mixed Venous and Arterial Leg Ulcers. Int. Wound J. 2016, 13, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, H.N.; Hardman, M.J. Wound Healing: Cellular Mechanisms and Pathological Outcomes. Open Biol. 2020, 10, 200223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorg, H.; Sorg, C.G.G. Skin Wound Healing: Of Players, Patterns, and Processes. Eur. Surg. Res. 2023, 64, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaydakov, M.E.; Ting, W.; Sadek, M.; Aziz, F.; Diaz, J.A.; Raffetto, J.D.; Marston, W.A.; Lal, B.K.; Welch, H.J.; Shaydakov, M.; et al. Review of the Current Evidence for Topical Treatment for Venous Leg Ulcers. J. Vasc. Surg. Venous Lymphat. Disord. 2022, 10, 241–247.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duque, A.P.d.N.; Pinto, N.d.C.C.; Mendes, R.d.F.; da Silva, J.M.; Aragão, D.M.d.O.; Castañon, M.C.M.N.; Scio, E. In Vivo Wound Healing Activity of Gels Containing Cecropia Pachystachya Leaves. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2016, 68, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okonkwo, U.A.; DiPietro, L.A. Diabetes and Wound Angiogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, J.; Landriscina, A.; Kutner, A.; Adler, B.L.; Krausz, A.E.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Friedman, A.J. Silver Sulfadiazine Retards Wound Healing in Mice via Alterations in Cytokine Expression. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 1459–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Izzo, A.A.; Papapetropoulos, A.; Alexander, S.P.H.; Cortese-Krott, M.; Kendall, D.A.; Martemyanov, K.A.; Mauro, C.; Panettieri, R.A.; Patel, H.H.; et al. Natural Product Pharmacology: The British Journal of Pharmacology Perspective. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 181, 3547–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.L.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Quinn, R.J. The Re-Emergence of Natural Products for Drug Discovery in the Genomics Era. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khayri, J.M.; Sahana, G.R.; Nagella, P.; Joseph, B.V.; Alessa, F.M.; Al-Mssallem, M.Q. Flavonoids as Potential Anti-Inflammatory Molecules: A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, K.W.; Murugan, D.; Leong, X.-F.; Abas, R.; Alias, A.; Mustafa, M.R. Flavonoids as Natural Anti-Inflammatory Agents Targeting Nuclear Factor-Kappa B (NFκB) Signaling in Cardiovascular Diseases: A Mini Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sychrová, A.; Škovranová, G.; Čulenová, M.; Fialová, S.B. Prenylated Flavonoids in Topical Infections and Wound Healing. Molecules 2022, 27, 4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, R.; Ballester, I.; López-Posadas, R.; Suárez, M.D.; Zarzuelo, A.; Martínez-Augustin, O.; Medina, F.S.D. Effects of Flavonoids and Other Polyphenols on Inflammation. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 331–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Wei, W.; Huang, J.; Liu, X.; Ci, X. Isoorientin Attenuates Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity Through the Inhibition of Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis via Activating the SIRT1/SIRT6/Nrf-2 Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Wu, Y.; Ren, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, X. Isoorientin Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced pro-Inflammatory Responses through down-Regulation of ROS-Related MAPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in BV-2 Microglia. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2014, 386, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Han, X.; Li, W.; Ren, D.; Yang, X. Isoorientin Prevents Hyperlipidemia and Liver Injury by Regulating Lipid Metabolism, Antioxidant Capability, and Inflammatory Cytokine Release in High-Fructose-Fed Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2682–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedler, J.; Daubitz, T.; Schlotterbeck, G.; Butterweck, V. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory and Wound-Healing Potential of a Phyllostachys Edulis Leaf Extract–Identification of Isoorientin as an Active Compound. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 1678–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sami, D.G.; Heiba, H.H.; Abdellatif, A. Wound Healing Models: A Systematic Review of Animal and Non-Animal Models. Wound Med. 2019, 24, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criollo-Mendoza, M.S.; Contreras-Angulo, L.A.; Leyva-López, N.; Gutiérrez-Grijalva, E.P.; Jiménez-Ortega, L.A.; Heredia, J.B. Wound Healing Properties of Natural Products: Mechanisms of Action. Molecules 2023, 28, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziqubu, K.; Dludla, P.V.; Joubert, E.; Muller, C.J.F.; Louw, J.; Tiano, L.; Nkambule, B.B.; Kappo, A.P.; Mazibuko-Mbeje, S.E. Isoorientin: A Dietary Flavone with the Potential to Ameliorate Diverse Metabolic Complications. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 158, 104867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña, O.A.; Martin, P. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Skin Wound Healing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2024, 25, 599–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altoé, L.S.; Alves, R.S.; Sarandy, M.M.; Morais-Santos, M.; Novaes, R.D.; Gonçalves, R.V. Does Antibiotic Use Accelerate or Retard Cutaneous Repair? A Systematic Review in Animal Models. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebaid, H. Neutrophil Depletion in the Early Inflammatory Phase Delayed Cutaneous Wound Healing in Older Rats: Improvements Due to the Use of Un-Denatured Camel Whey Protein. Diagn. Pathol. 2014, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanshahi, A.; Moradzad, M.; Ghalamkari, S.; Fadaei, M.; Cowin, A.J.; Hassanshahi, M. Macrophage-Mediated Inflammation in Skin Wound Healing. Cells 2022, 11, 2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boniakowski, A.E.; Kimball, A.S.; Jacobs, B.N.; Kunkel, S.L.; Gallagher, K.A. Macrophage-Mediated Inflammation in Normal and Diabetic Wound Healing. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes-Ricardo, M.; Gutiérrez-Uribe, J.; Serna-Saldívar, S.O. Anti-Inflammatory Glycosylated Flavonoids as Therapeutic Agents for Treatment of Diabetes-Impaired Wounds. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 2456–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, V.; Jangir, B.L.; Sharma, M.; Kumar, V.; Joshi, V.G. Topical Application of Quercetin Improves Wound Repair and Regeneration in Diabetic Rats. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2021, 43, 536–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodhi, S.; Singhai, A.K. Wound Healing Effect of Flavonoid Rich Fraction and Luteolin Isolated from Martynia annua Linn. on Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rats. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2013, 6, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landén, N.X.; Li, D.; Ståhle, M. Transition from Inflammation to Proliferation: A Critical Step during Wound Healing. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3861–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Ding, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Yang, P.; Tan, Q. Relevance of NLRP3 Inflammasome-Related Pathways in the Pathology of Diabetic Wound Healing and Possible Therapeutic Targets. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 9687925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, X.-Z.; Badamjav, R.; Zhang, J.-Z.; Kou, J.-P.; Yu, B.-Y.; Li, F. Isoorientin Protects Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice via Modulating Keap1/Nrf2-HO-1 and NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 917, 174748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.; Yu, X.; Zhang, R.; Chen, L. Isoorientin Alleviates Inflammatory Bowel Disease by Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation through Nrf2/NQO1 Pathway. Curr. Top. Nutraceutical Res. 2020, 18, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anilkumar, K.; Reddy, G.V.; Azad, R.; Yarla, N.S.; Dharmapuri, G.; Srivastava, A.; Kamal, M.A.; Pallu, R. Evaluation of Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Isoorientin Isolated from Tubers of Pueraria tuberosa. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 5498054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; He, C.; Hu, S.; Ni, H.; Tan, X.; Zhi, Y.; Yi, L.; Na, R.; Li, Y.; Du, Q.; et al. Anti-Oxidative Stress and Cognitive Improvement of a Semi-Synthetic Isoorientin-Based GSK-3β Inhibitor in Rat Pheochromocytoma Cell PC12 and Scopolamine-Induced AD Model Mice via AKT/GSK-3β/Nrf2 Pathway. Exp. Neurol. 2024, 380, 114881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, G.; Wang, C. Isoorientin Ameliorates OVA-Induced Asthma in a Murine Model of Asthma. Exp. Biol. Med. 2022, 247, 1479–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Qu, Z.; Hui, H.; He, B.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yan, L. Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Isoorientin in the Treatment of Osteoporosis: A Study Using Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation. Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunnill, C.; Patton, T.; Brennan, J.; Barrett, J.; Dryden, M.; Cooke, J.; Leaper, D.; Georgopoulos, N.T. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Wound Healing: The Functional Role of ROS and Emerging ROS-Modulating Technologies for Augmentation of the Healing Process. Int. Wound J. 2017, 14, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson-Meyers, D.S.; Andrade, T.A.M.; Caetano, G.F.; Guimaraes, F.R.; Leite, M.N.; Leite, S.N.; Frade, M.A.C. Experimental Models and Methods for Cutaneous Wound Healing Assessment. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2020, 101, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canesso, M.C.C.; Vieira, A.T.; Castro, T.B.R.; Schirmer, B.G.A.; Cisalpino, D.; Martins, F.S.; Rachid, M.A.; Nicoli, J.R.; Teixeira, M.M.; Barcelos, L.S. Skin Wound Healing Is Accelerated and Scarless in the Absence of Commensal Microbiota. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 5171–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, D.T.; Pope, E.R.; Wagner-Mann, C.; Berg, J.N.; Swaim, S.F. Effects of Three Occlusive Dressing Materials on Healing of Full-Thickness Skin Wounds in Dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1995, 56, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, P.P.; Priebat, D.A.; Christensen, R.D.; Rothstein, G. Measurement of Cutaneous Inflammation: Estimation of Neutrophil Content with an Enzyme Marker. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1982, 78, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hora, A.B.; Biano, L.S.; Nascimento, A.C.S.; Camargo, Z.T.; Heiden, G.I.; Albulquerque-Júnior, R.L.C.; Grespan, R.; Aragão, J.M.D.A.; Camargo, E.A. Isoorientin Improves Excisional Skin Wound Healing in Mice. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101368
Hora AB, Biano LS, Nascimento ACS, Camargo ZT, Heiden GI, Albulquerque-Júnior RLC, Grespan R, Aragão JMDA, Camargo EA. Isoorientin Improves Excisional Skin Wound Healing in Mice. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(10):1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101368
Chicago/Turabian StyleHora, Aline B., Laiza S. Biano, Ana Carla S. Nascimento, Zaine T. Camargo, Greice I. Heiden, Ricardo L. C. Albulquerque-Júnior, Renata Grespan, Jessica M. D. A. Aragão, and Enilton A. Camargo. 2024. "Isoorientin Improves Excisional Skin Wound Healing in Mice" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 10: 1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101368
APA StyleHora, A. B., Biano, L. S., Nascimento, A. C. S., Camargo, Z. T., Heiden, G. I., Albulquerque-Júnior, R. L. C., Grespan, R., Aragão, J. M. D. A., & Camargo, E. A. (2024). Isoorientin Improves Excisional Skin Wound Healing in Mice. Pharmaceuticals, 17(10), 1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101368







