Cytotoxic and Infection-Controlled Investigations of Novel Dihydropyridine Hybrids: An Efficient Synthesis and Molecular-Docking Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
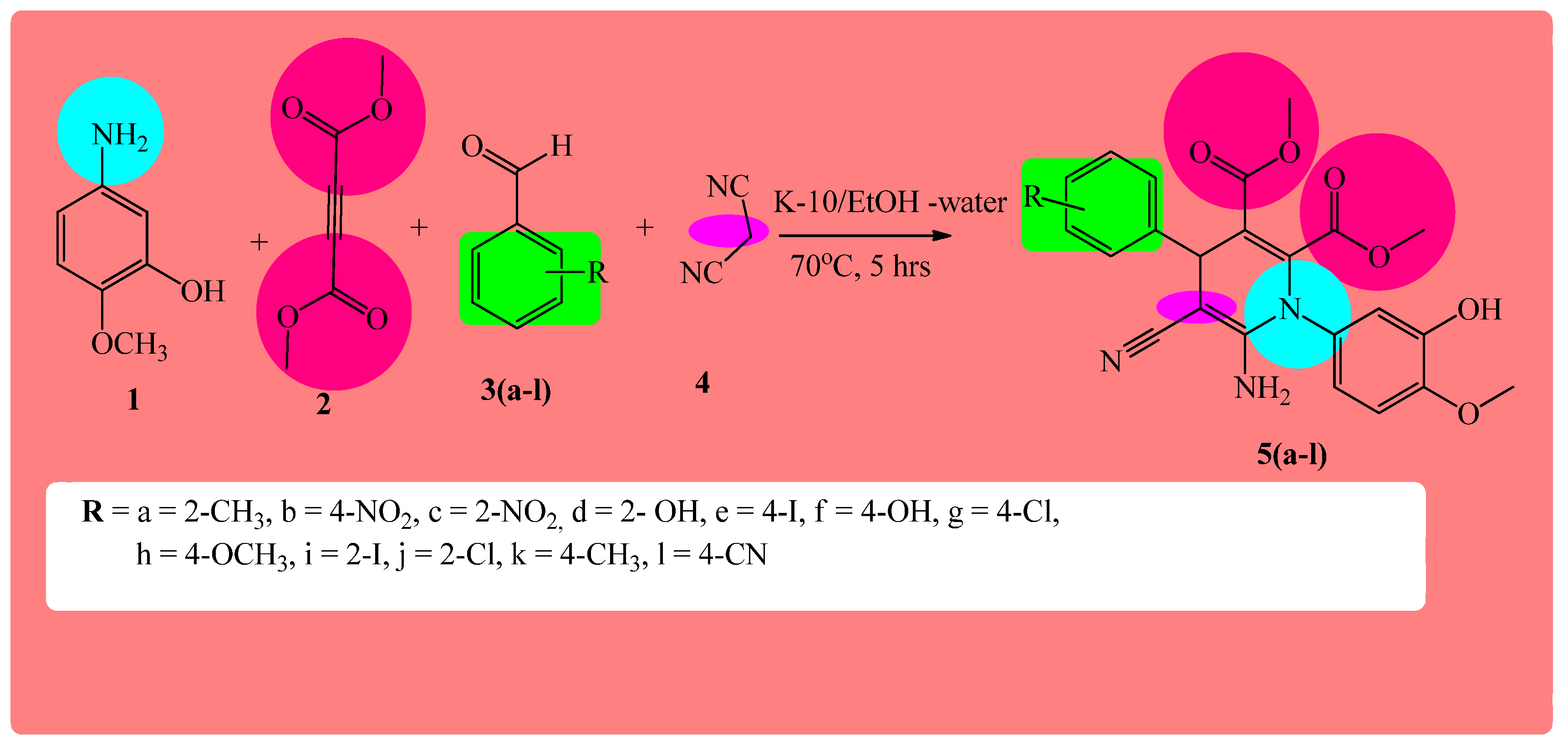
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Molecular Modelling
2.2.1. Molecular-Docking Studies, Binding Pose, and Interaction Profiling
Molecular-Docking Studies
Binding Poses and Interaction Profiling
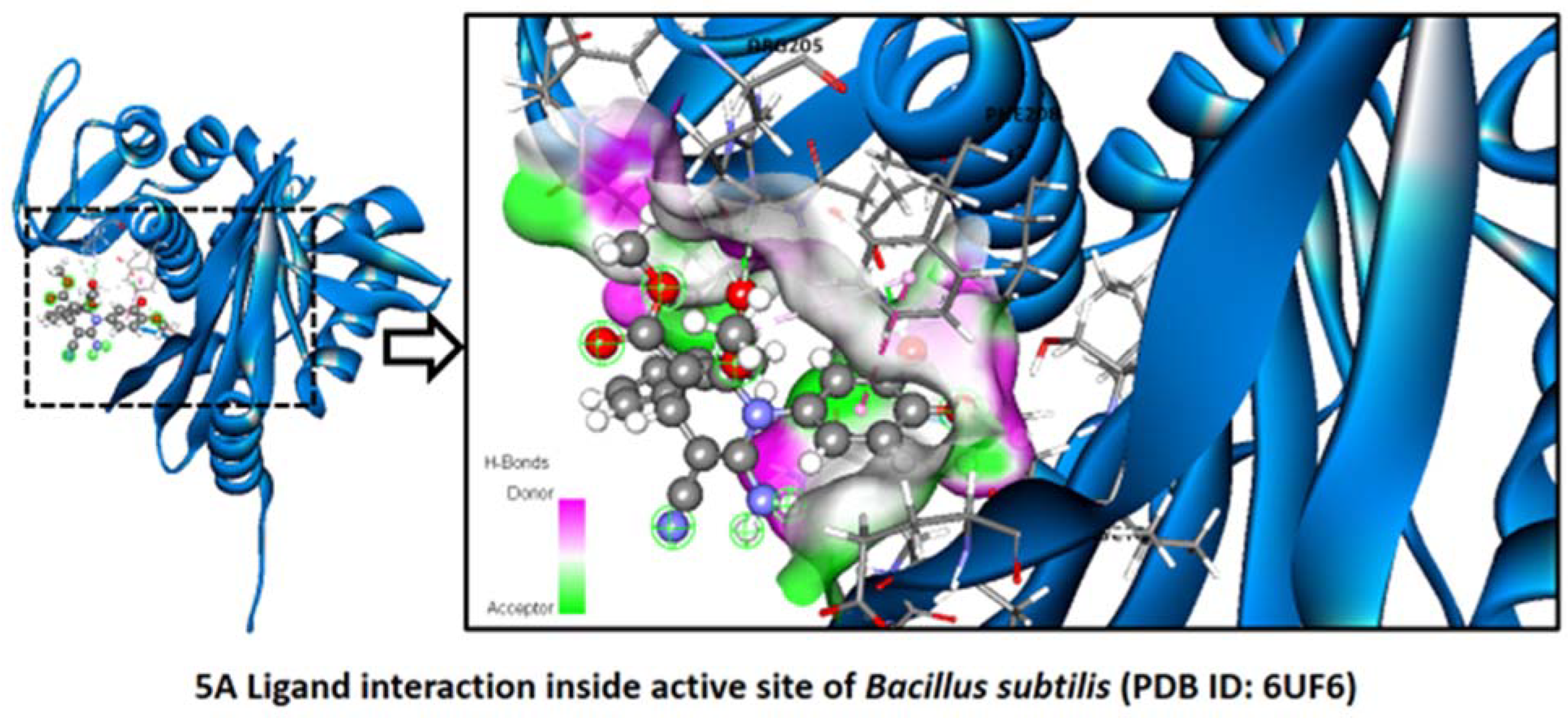
2.2.2. Bacillus subtilis
Binding Mode of Best Hit Ligands 5a and 5f with Bacillus subtilis
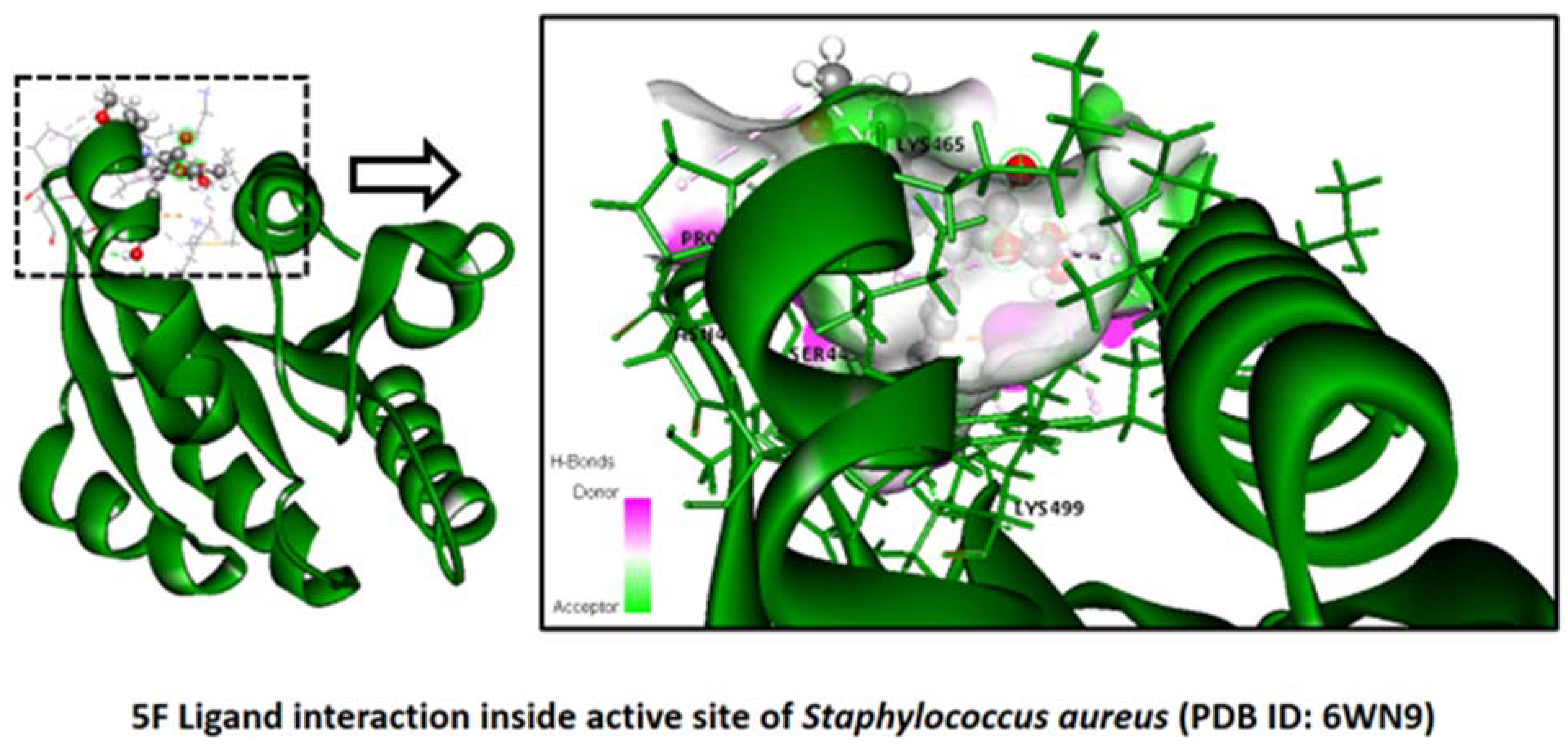
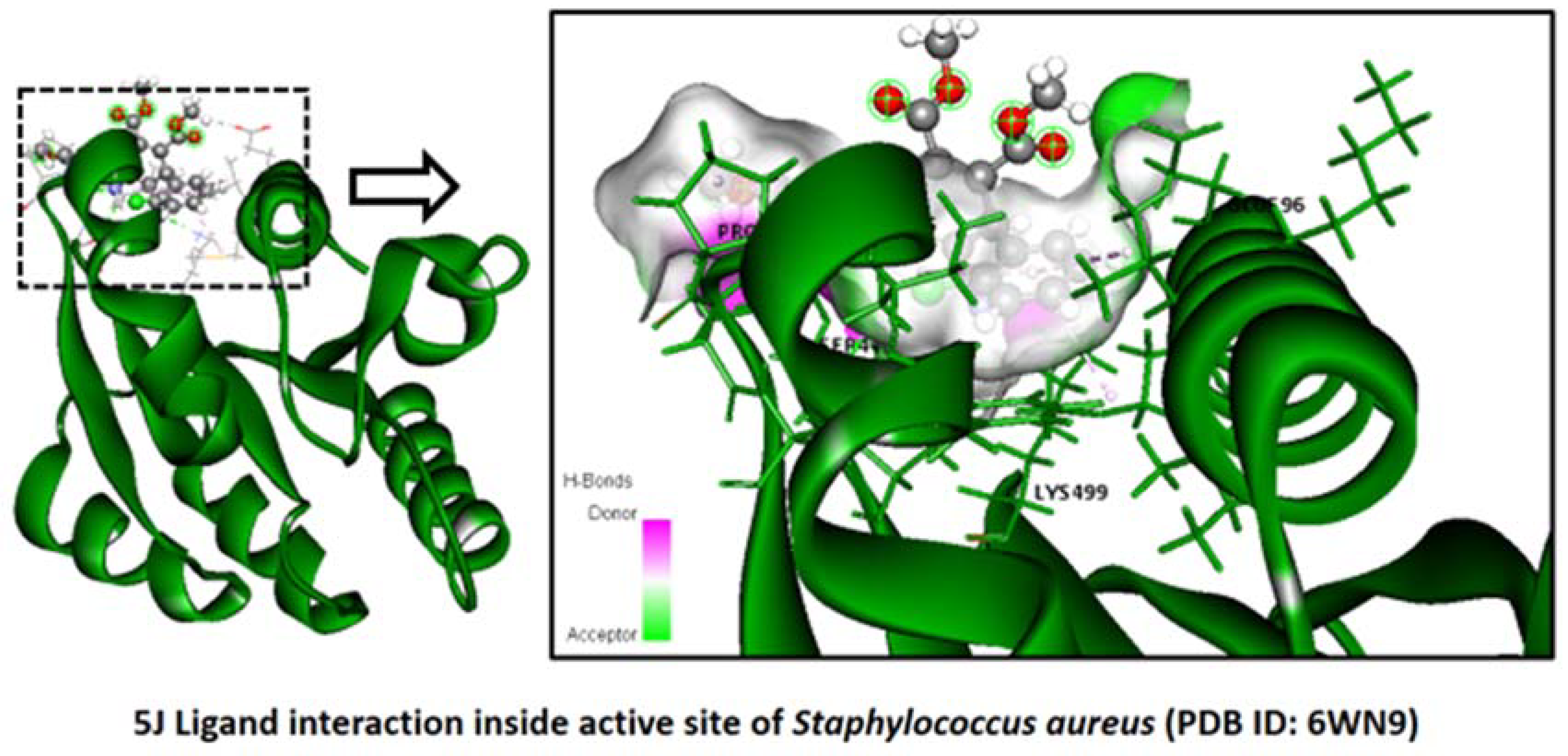
2.2.3. Staphylococcus aureus
Binding Mode of Best Ligands 5f and 5j with Staphylococcus aureus
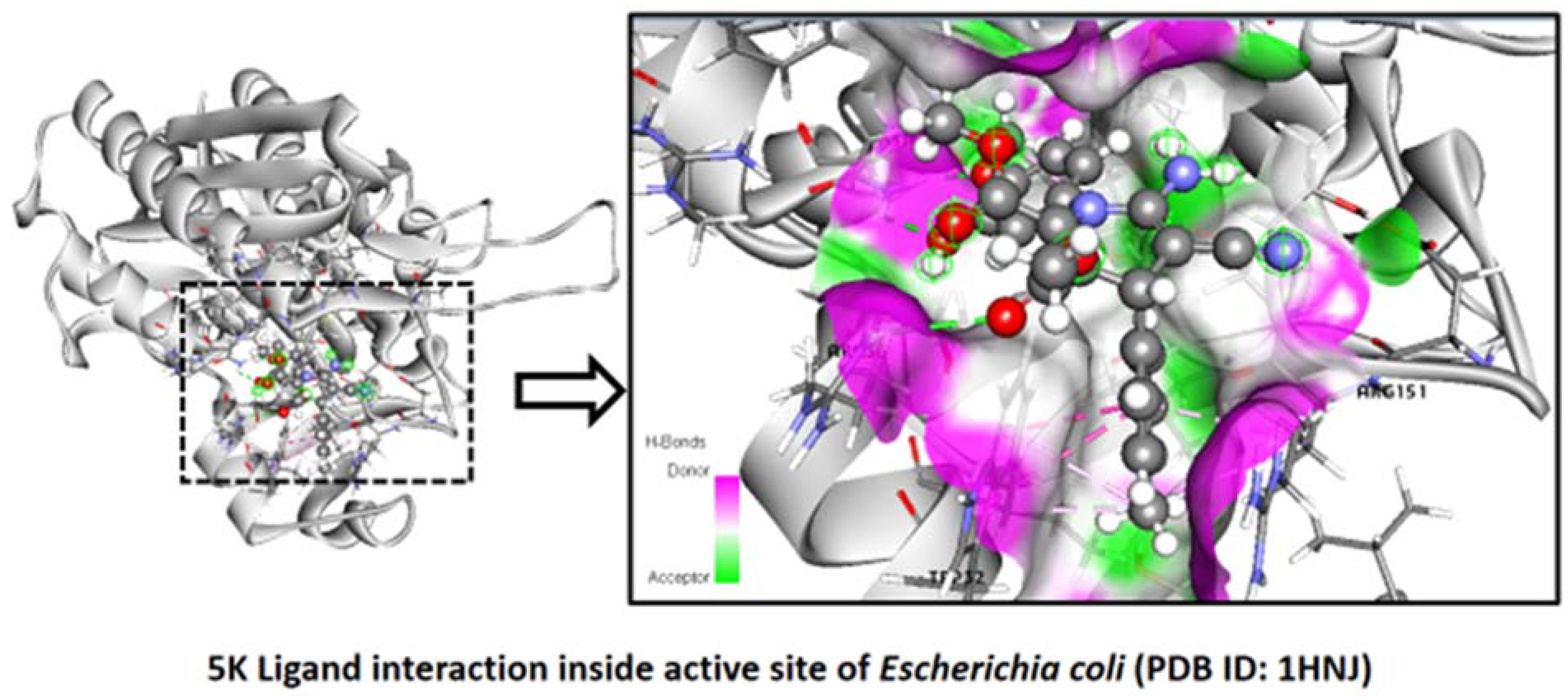
2.2.4. Escherichia coli
Binding Mode of Best Ligand 5k and 5l with Escherichia coli
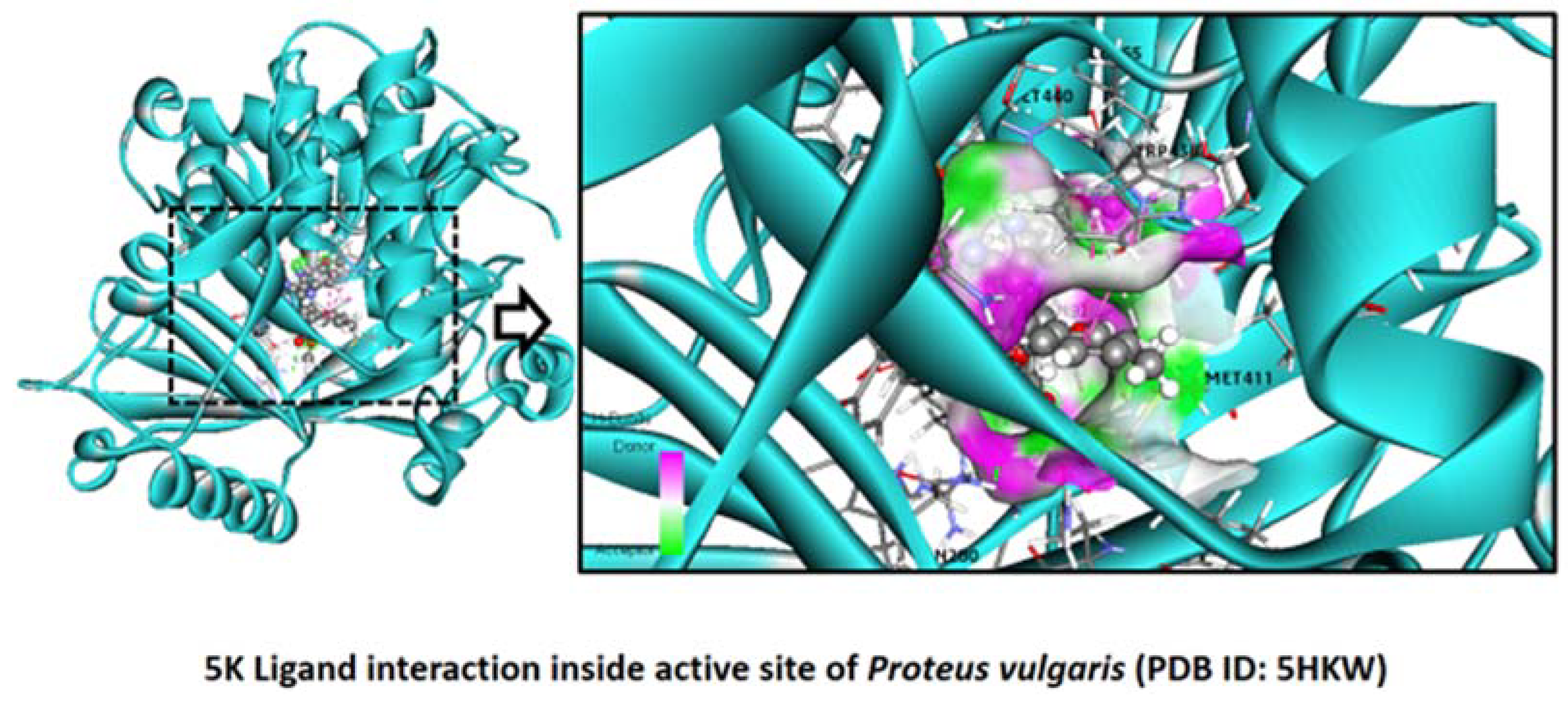
2.2.5. Proteus vulgaris
Binding Mode of Best Ligand 5f and 5k with Proteus vulgaris
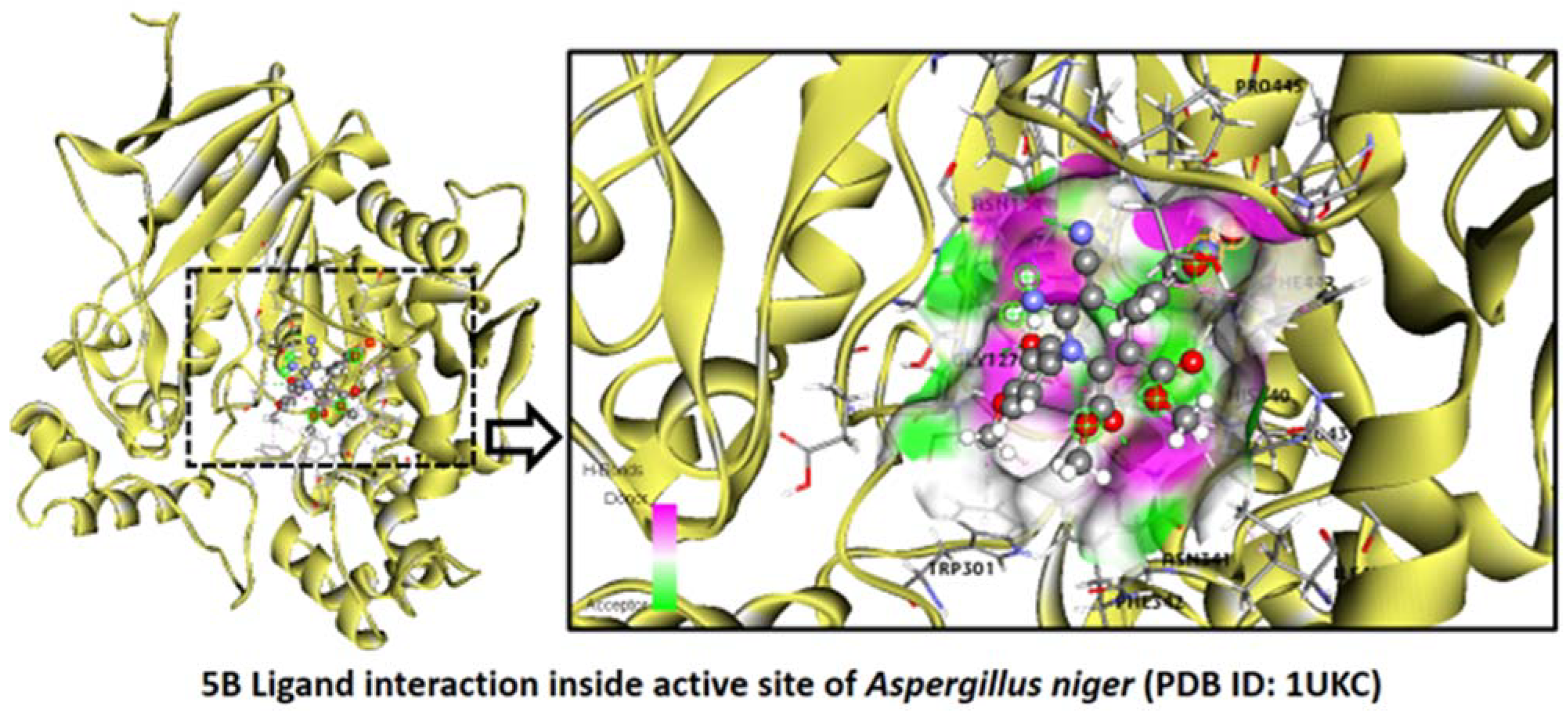
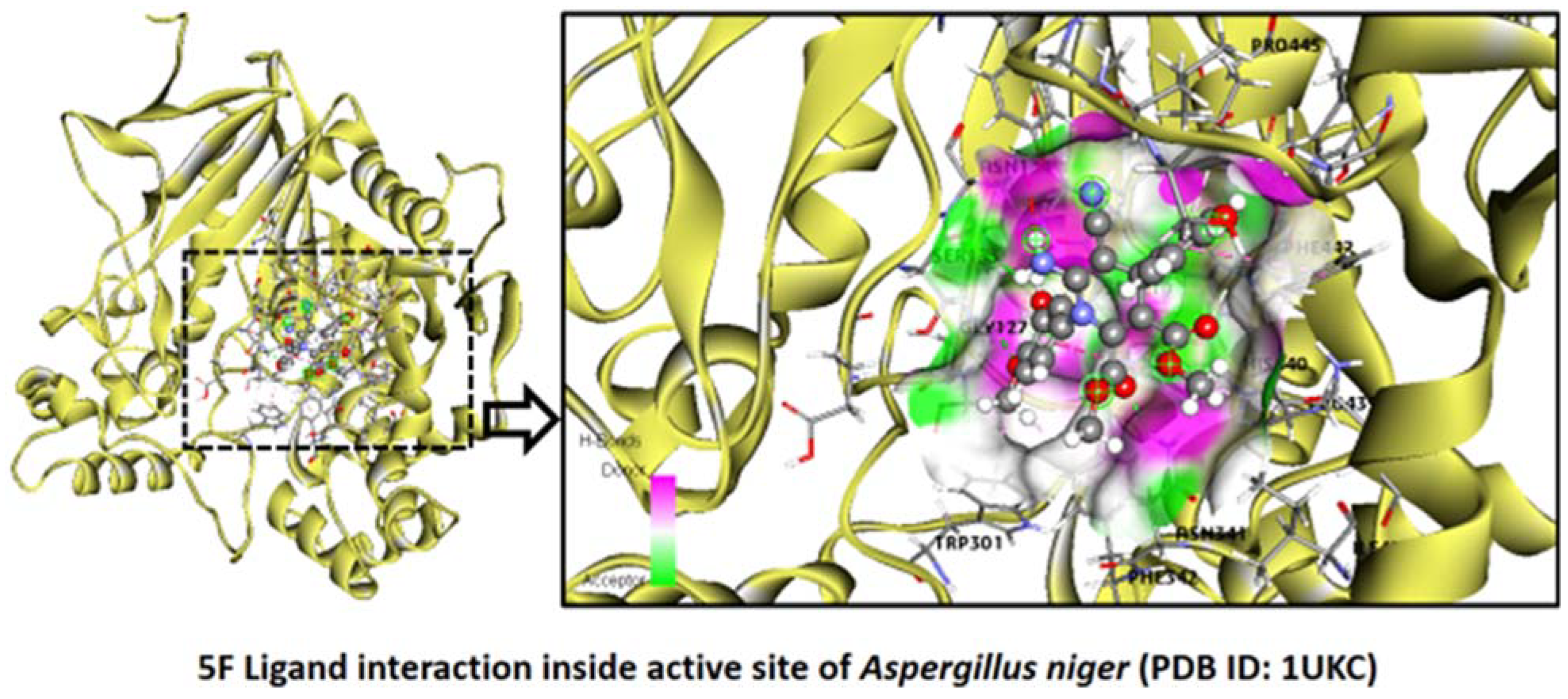
2.2.6. Aspergillus niger
Binding Mode of Best Ligand 5b and 5f with Aspergillus niger
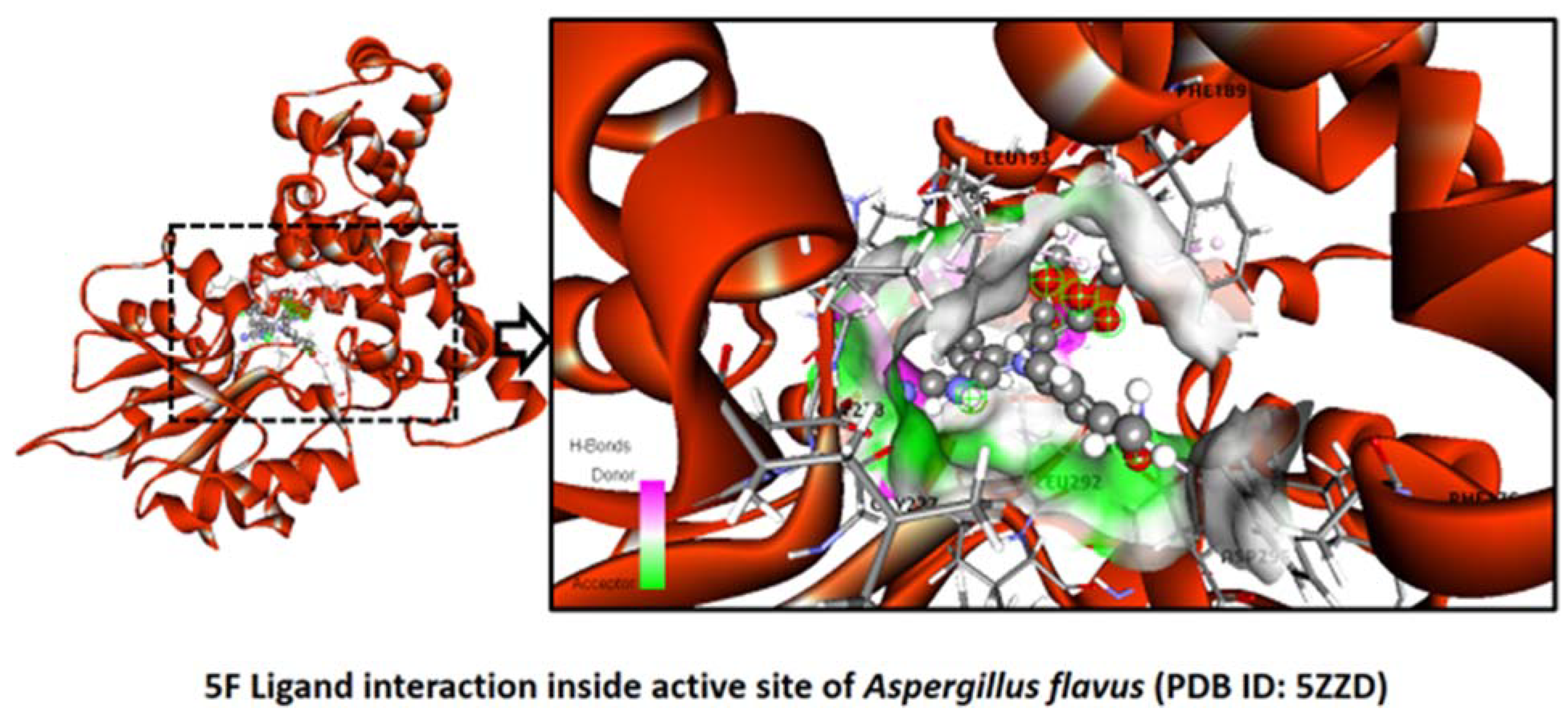
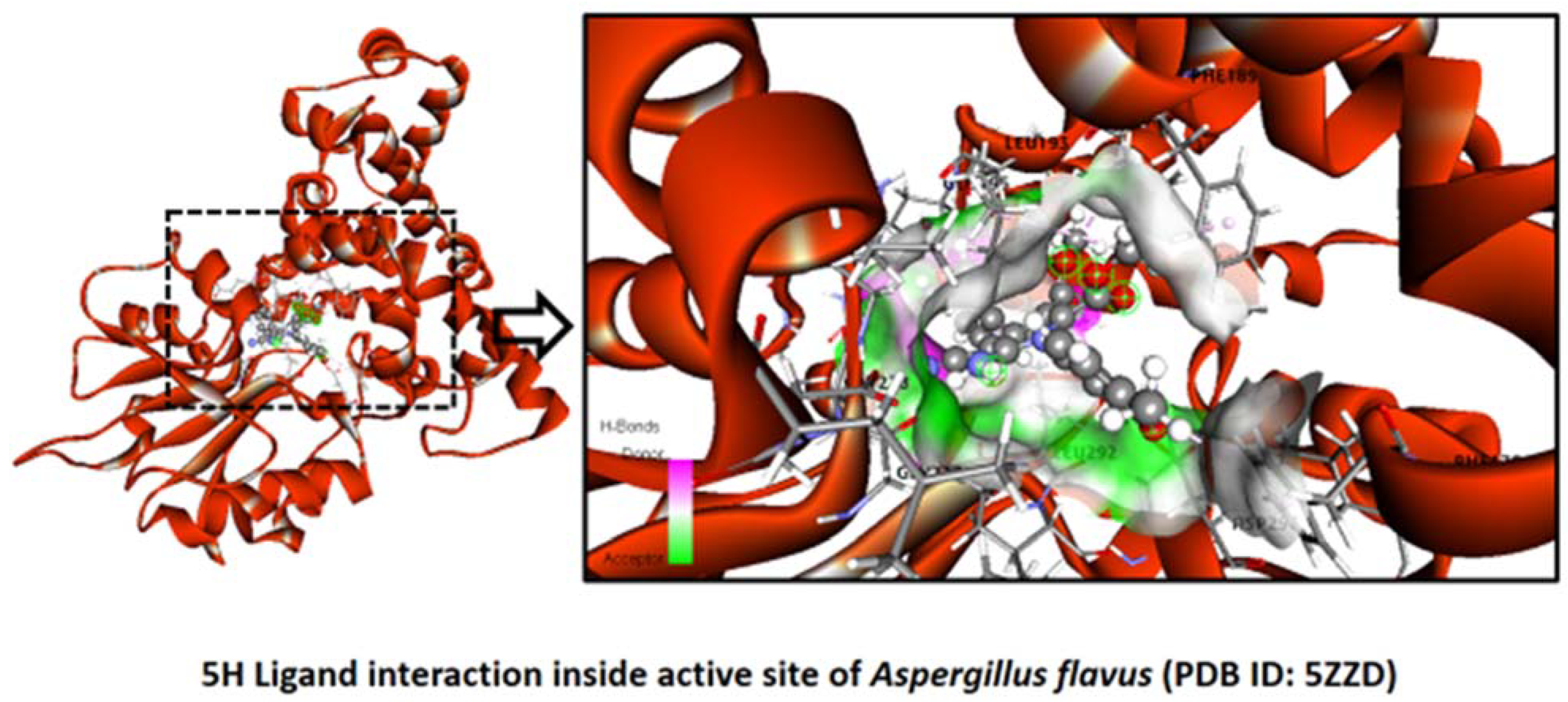
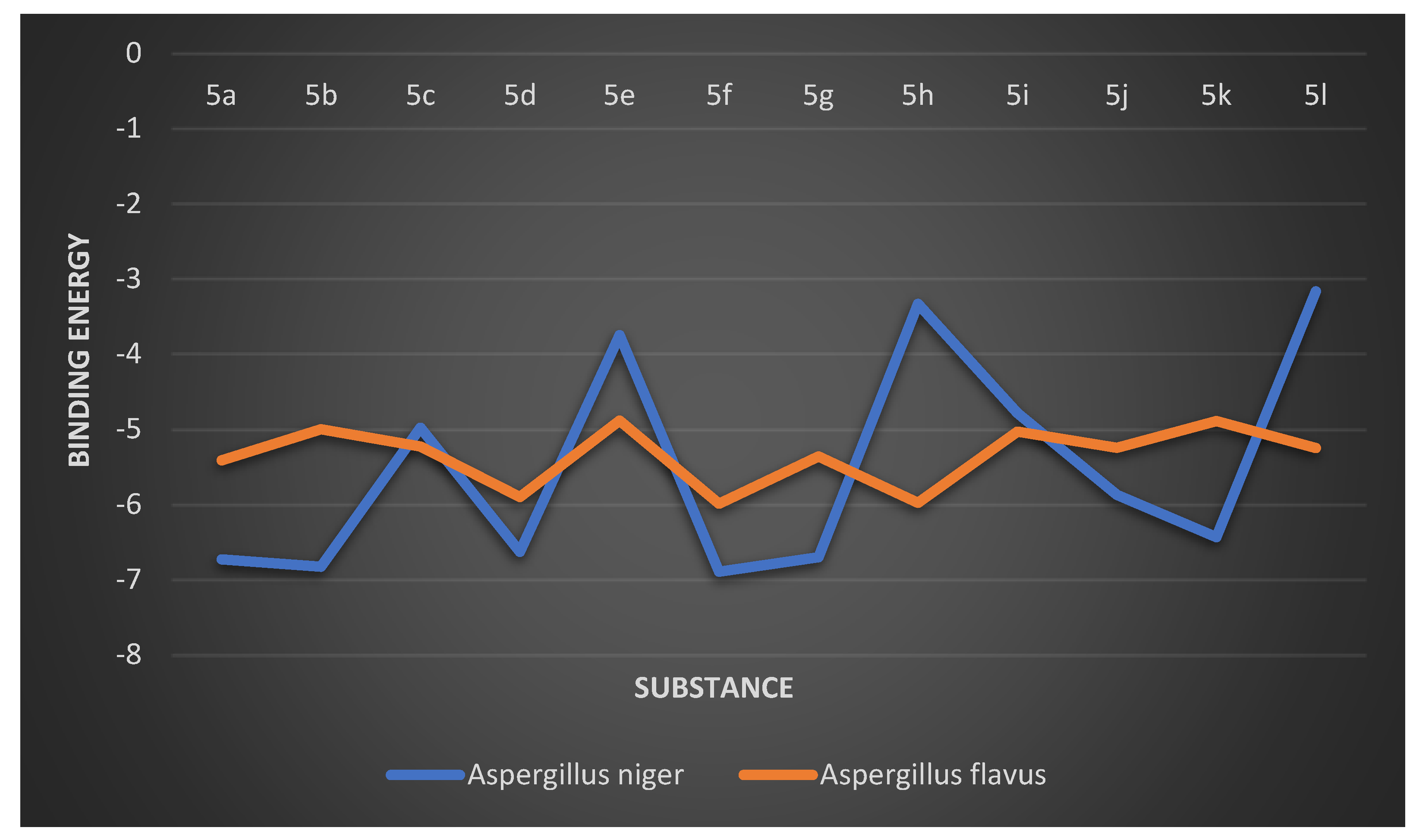
2.2.7. Aspergillus flavus
Binding Mode of Best Ligand 5f and 5h with Aspergillus flavus
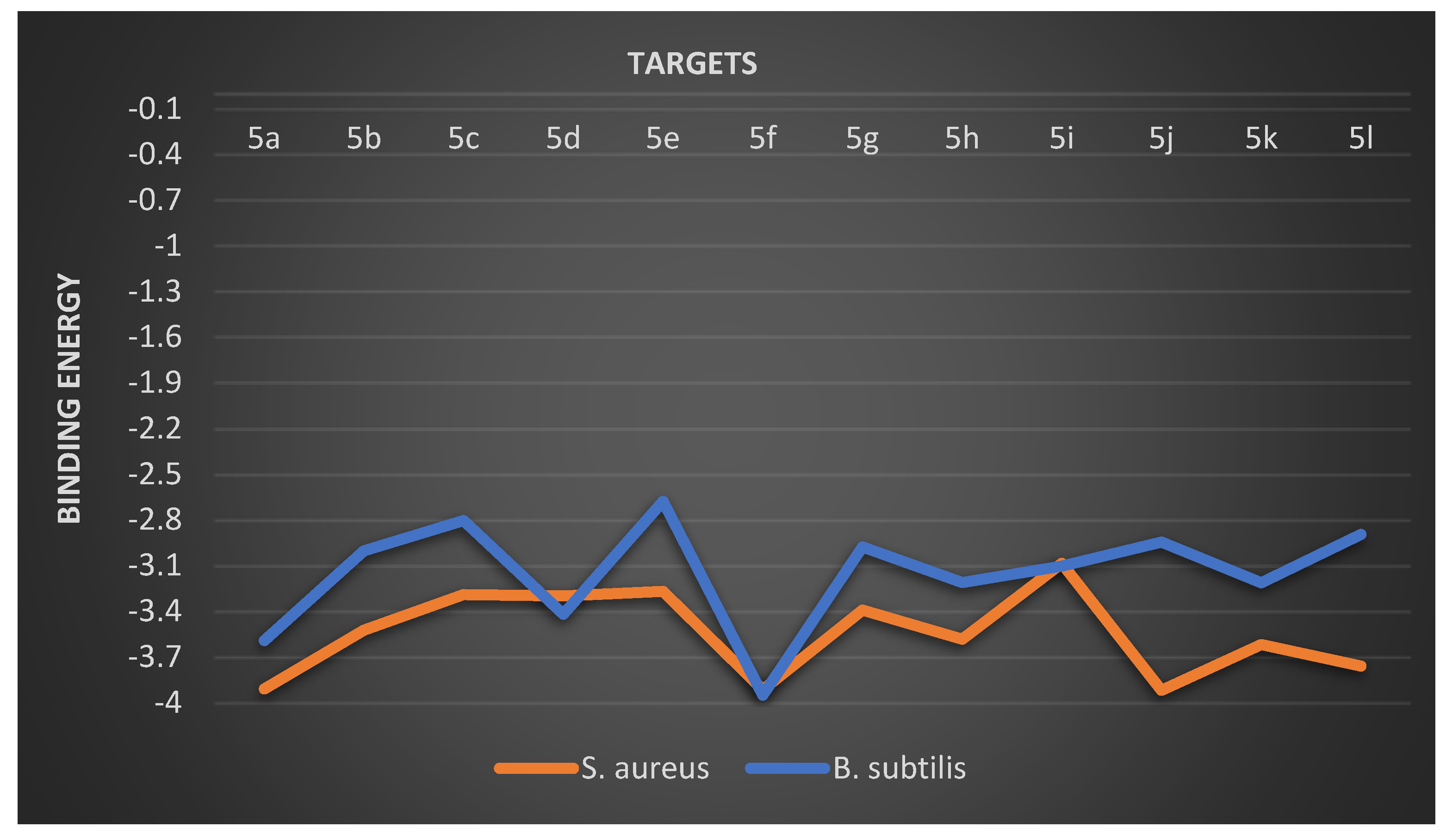
2.2.8. Overall Docking Results and Discussion
2.3. Biological Results
2.3.1. Antimicrobial Discussion
2.3.2. MIC and MBC/MFC Potency of Tested Compounds
2.4. The In Vitro Cytotoxic Assay
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Way of Preparation for the Target Compounds 5(a–l)
3.1.1. Dimethyl-6-amino-5-cyano-4-(o-Tolyl)-1-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-2,3-dicarboxylate (5a)
3.1.2. Dimethyl-6-amino-5-cyano-4-(p-nitrophenyl)-1-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-2,3-dicarboxylate (5b)
3.1.3. Dimethyl-6-amino-5-cyano-4-(o-nitrophenyl)-1-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-2,3-dicarboxylate (5c)
3.2. Protein-Structure Preparation
Ligand-Structure Preparation
3.3. Antimicrobial Experiment
3.3.1. Antibacterial Screening Test
3.3.2. Antifungal Screening
3.3.3. MIC and MBC/MFC Effectiveness
3.4. Cytotoxic Assessment
3.4.1. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
3.4.2. Concentrations Tested
3.4.3. Cytotoxicity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kappe, C.O.; Fabian, W.M.; Semones, M.A. Conformational analysis of 4-aryl-dihydropyrimidine calcium channel modulators. A comparison of ab initio, semiempirical and X-ray crystallographic studies. Tetrahedron 1997, 53, 2803–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovnyak, G.C.; Kimball, S.D.; Beyer, B.; Cucinotta, G.; DiMarco, J.D.; Gougoutas, J.; Hedberg, A.; Malley, M.; McCarthy, J.P. Calcium entry blockers and activators: Conformational and structural determinants of dihydropyrimidine calcium channel modulators. J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgeroth, A. Dimeric 4-Aryl-1, 4-dihydropyridines: Development of a third class of nonpeptidic HIV-1 protease inhibitors. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2022, 2, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.; Offerman, R.J.; Turner, G.A. Novel fluorescent 1,4-dihydropyridines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986, 108, 8283–8285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomha, S.M.; Edrees, M.M.; Muhammad, Z.A.; Kheder, N.A.; Abu-Melha, S.; Saad, A.M. Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial evaluation of some new 1, 4-dihydropyridines-1, 2, 4-triazole hybrid compounds. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2020, 42, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Luo, M.; Lu, Y.; Pan, X.; Chen, X.; Ding, L.; Che, J.; He, Q.; Dong, X. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of new dihydropyridine derivatives as PD-L1 degraders for enhancing antitumor immunity. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 125, 105820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, D.C.; Santa-Helena, E.; Leal, H.P.; de Moura, R.R.; Nery, L.E.M.; Gonçalves, C.A.N.; Russowsky, D.; D‘Oca, M.G.M. Synthesis and antioxidant activity of new lipophilic dihydropyridines. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 84, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, A.; Franssen, M.C.R.; Duburs, G.; de Groot, A.E. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of enantiopure 1, 4-dihydropyridine derivatives. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2004, 22, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchalín, S.; Chudík, M.; Mastihuba, V.; Decroix, B. Use of enzymes in preparation of enantiopure 1, 4-dihydropyridines. Heterocycles 1998, 48, 1943–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghzadeh, S.M. Bis(4-pyridylamino) triazine-stabilised magnetite KCC-1: A chemoselective, efficient, green and reusable nanocatalyst for the synthesis of Nsubstituted 1,4-dihydropyridines. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 99586–99594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoozadeh, A.; Rahmani, S.; Bitaraf, M.; Abadi, F.B.; Tabrizian, E. Nano-zirconia as an excellent nano support for immobilisation of sulfonic acid: A new, efficient and highly recyclable heterogeneous solid acid nanocatalyst for multicomponent reactions. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadebe, N.P.; Kerru, N.; Tukulula, M.; Jonnalagadda, S.B. A sustainable molybdenum oxide loaded on zirconia (MoO3/ZrO2) catalysed multicomponent reaction to synthesis novel dihydropyridines. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 25, 100578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastas, P.T. Benign by design chemistry. In Benign by Design; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; pp. 2–22. [Google Scholar]
- Majee, S.; Shilpa; Sarav, M.; Banik, B.K.; Ray, D. Recent Advances in the Green Synthesis of Active N-Heterocycles and Their Biological Activities. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tundo, P.; Anastas, P.T. Green Chemistry, Challenging Perspectives; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Anastas, P.T.; Warner, J.C. Green Chemistry: Theory and Practice; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Karadeniz, B.; Howarth, A.J.; Stolar, T.; Islamoglu, T.; Dejanovi’c, I.; Tireli, M.; Wasson, M.C.; Moon, S.Y.; Farha, O.K.; Friscic, T.; et al. Benign by design: Green and scalable synthesis of zirconium UiO-metal-organic frameworks by water-assisted mechanochemistry. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 15841–15849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zaydi, K.M.; Al-Boqami, M.; Elnagdi, N.M. Green Synthesis of Dihydropyrimidines and Pyridines Utilizing Biginelli Reaction. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2022, 42, 7298–7309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draye, M.; Chatel, G.; Duwald, R. Ultrasound for Drug Synthesis: A Green Approach. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dige, N.C.; Pore, D.M. Green Aspect for Multicomponent Synthesis of Spiro [4H-indeno [1,2-b] pyridine-4, 3′-[3H] indoles]. Synth. Commun. 2015, 45, 2498–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giridhar, R. Drug discovery: Past and present. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. JAPTR 2012, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Basha, N.M.; Venkatesh, B.C.; Reddy, G.M.; Zyryanov, G.V.; Subbaiah, M.V.; Wen, J.-C.; Gollakota, A.R.K. Synthesis, Antimicrobial Assay and SARs of Pyrazole Included Heterocyclic Derivatives. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2023, 43, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthick, R.; Velraj, G.; Karuppusamy, A.; Karthikeyan, S. Experimental, Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Investigation on Newly Synthesized Diethyl 4-(Anthracen-9-yl)-2, 6-Dimethyl-1, 4-Dihydropyridine-3, 5-Dicarboxylate. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2023, 43, 5769–5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, N.M.; Seenaiah, D.; Padmaja, A.; Padmavathi, V.; Bhargav, D.S.; Vijaya, T. Synthesis and antioxidant activity of Bis and Tris Heterocycles. Arch. Der Pharm. 2014, 347, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veligeti, R.; Madhu, R.B.; Anireddy, J.; Pasupuleti, V.R.; Avula, V.K.R.; Ethiraj, K.S.; Uppalanchi, S.; Kasturi, S.; Perumal, Y.; Anantaraju, H.S.; et al. Syn thesis of novel cytotoxic tetracyclic acridone derivatives and study of their molecular docking, AD MET, QSAR, bioactivity and protein binding properties. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gündüz, M.G.; Dengiz, C.; Aslan, E.K.; Bogojevic, S.S.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J. Attaching azoles to Hantzsch 1, 4-dihydropyridines: Synthesis, theoretical investigation of nonlinear optical properties, antimicrobial evaluation and molecular docking studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1247, 131316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glide; Version 6.4; Schrodinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2018.
- Dubey, A.; Marabotti, A.; Ramteke, P.W.; Facchiano, A. In silico approach to find chymase in hibitors among biogenic compounds. Future Med. Chem. 2016, 8, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, A.; Marabotti, A.; Ramteke, P.W.; Facchiano, A. Interaction of human chymase with gink golides, terpene trilactones of Ginkgo biloba investigated by molecular docking simulations. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 473, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, S.; Dubey, A.; Kamboj, N.K.; Sahoo, A.K.; Kang, S.G.; Yadava, U. Drug repurposing for ligand-induced rearrangement of Sirt2 active site-based inhibitors via molecular modeling and quantum mechanics calculations. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, A.; Dotolo, S.; Ramteke, P.W.; Facchiano, A.; Marabotti, A. Searching for Chymase Inhibitors among Chamomile Compounds Using a Computational-Based Approach. Biomolecules 2018, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, A.; Singh, V.; Doharey, P.K.; Sk, M.P.; Samanta, S.K.; Nema, V.; Sharma, B.; Varadwaj, P.K.; Sahoo, A.K. Modulating catalytic activity of human topoisomerase II α enzyme by fluorescent gold nanoclusters. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 170, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.K.K.; Rosell, F.I.; Gale, R.T.; Simorre, J.P.; Brown, E.D.; Strynadka, N.C.J. Crystallographic analysis of Staphylococcus aureus LcpA, the primary wall teichoic acid ligase. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 2629–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.S.; Sychantha, D.; Howell, P.L.; Clarke, A.J. Structural basis for the O-acetyltransferase function of the extracytoplasmic domain of OatA from Staphylococcus aureus. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 8204–8213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Janson, C.A.; Smith, W.W.; Head, M.; Lonsdale, J.; Konstantinidis, A.K. Refined structures of beta-ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthase III. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 307, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Tong, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Liu, Q.; Gu, Q.; Xu, J.; Niu, L.; Teng, M.; Zhou, H. Crystal structure of a membrane-bound l-amino acid deaminase from Proteus vulgaris. J. Struct. Biol. 2016, 195, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, Y.; Hasper, A.A.; Chahinian, H.; Juin, M.; De Graaff, L.H.; Marchot, P. Aspergillus niger protein EstA defines a new class of fungal esterases within the alpha/beta hydrolase fold superfamily of proteins. Structure 2004, 12, 677–687, Erratum in Structure 2004, 12, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Z.; Ansbacher, T.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Ko, T.P.; Zhang, G.; Liu, W.; Huang, J.W.; Dai, L.; Guo, R.T.; et al. Crystal structure of LepI, a multifunctional SAM-dependent enzyme which catalyzes pericyclic reactions in leporin biosynthesis. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 2070–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, P.W.; Prlic, A.; Bi, C.; Bluhm, W.F.; Christie, C.H.; Dutta, S.; Green, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Westbrook, J.D.; Woo, J.; et al. The RCSB Protein Data B ank: Views of structural biology for basic and applied research and education. Nucl. Acids Res. 2015, 43, D345–D356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastry, G.M.; Adzhigirey, M.; Day, T.; Annabhimoju, R.; Sherman, W. Protein and ligand preparation: Parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2013, 27, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrödinger. Release 2018-1: Schrödinger Suite 2018-1 Protein Preparation Wizard; Epik; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Avogadro: An Open-Source Molecular Builder and Visualization Tool. Version 1.XX. Available online: http://avogadro.cc/ (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Marcus, D.H.; Donald, E.C.; David, C.L.; Tim, V.; Eva, Z.; Geoffrey, R.H. Avogadro: An advanced semantic chemical editor, visualization, and analysis platform. J. Cheminf. 2012, 4, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Arima, H.; Ashida, H.; Danno, G.-I. Rutin-enhanced antibacterial activities of flavonoids against Bacillus cereus and Salmonella enteritidis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 66, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miah, M.A.T.; Ahmed, H.U.; Sharma, N.R.; Ali, A.; Miah, S.A. Antifungal activity of some plant extracts. Bangladesh J. Bot. 1990, 19, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Bishnu, J.; Sunil, L.; Anuja. Antibacterial property of different medicinal plants: Ocimum sanctum, Cinnamomum zeylanicum, Xanthoxylum armatum and Origanum majorana. S. J. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2009, 5, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- M7–A3; Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically Approved Standard, 3rd ed. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, NCCLS Publication: Wayne, PA, USA, 1993.
- M27-P; Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Yeasts. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards: Wayne, PA, USA, 1992.
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Entry No | Initiator | Solvent | Yield a |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PEG-400 b | - | 5a (45); 5b (39), 5c (41) |
| 2 | ZnCl2 | Cyanomethane | 5a (22); 5b (15), 5c (29) |
| 3 | InCl3 | Cyanomethane | 5a (11); 5b (19), 5c (15) |
| 4 | SnCl2.H2O | Cyanomethane | 5a (32); 5b (25), 5c (21) |
| 5 | Clay acid * | Ethanol–water | 5a (86); 5b (83), 5c (88) |
| Compound ID | Glide Score | Glide Emodel | Hydrogen Bond | Hydrophobic Interaction | Polar Interaction | Pi–Cation Interaction | Pi–Pi Stacking Interaction | Negative Interaction | Positive Interaction | Glycine Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillus subtilis (PDB: 6UF6) | ||||||||||
| 5a | −3.593 | −32.404 | Arg205, Asp212 | Ile88, Val102, Phe172, Phe208 | Ser103, Asn169, Thr171, Gln216, Gln270 | -- | Phe208 | Asp212, Glu272 | Mse101, Arg205, Arg215, Hip271 | -- |
| 5b | −3.004 | −31.562 | Asp212, Gln216, Hip271 | Phe208, Ile268 | Asn169, Thr171, Gln216, Gln270 | -- | -- | Asp212, Glu272 | Arg215, Hip271 | -- |
| 5c | −2.805 | −32.360 | Asp212, Gln216, Gln270 | Phe208, Ile268 | Asn169, Thr171, Gln216, Gln270 | -- | -- | Asp212, Glu272 | Arg205, Arg215, Hip271 | -- |
| 5d | −3.420 | −28.754 | Asn169, Gln216, Gln270 | Phe208, Ile268 | Asn169, Thr171, Gln216, Gln270 | -- | -- | Asp212, Glu272 | Arg205, Arg215, Lys269, Hip271 | -- |
| 5e | −2.677 | −24.648 | Arg205, Gln270 | Val102, Phe208, Ile268 | Ser103, Asn169, Thr171, Gln270 | -- | Phe208 | Asp212, Glu272 | Arg205, Arg215, Lys269, Hip271 | -- |
| 5f | −3.951 | −29.177 | Ser103, Arg205, Gln270, Hip271 | Val102, Phe208, Ile268 | Ser103, Asn169, Thr171, Gln270 | -- | Phe208 | Asp212, Glu272 | Arg205, Arg215, Lys269, Hip271 | -- |
| 5g | −2.978 | −26.916 | Arg205, Gln270 | Phe208, Ile268 | Ser103, Asn169, Thr171, Gln270 | -- | Phe208 | Asp212, Glu272 | Arg205, Arg215, Lhip271 | -- |
| 5h | −3.211 | −31.744 | Arg205, Asp212, Gln270 | Phe172, Pro204, Phe208, Ile268 | Asn169, Thr171, Gln216, Ser259, Gln270 | -- | -- | Asp212 | Arg205, Arg215 | -- |
| 5i | −3.103 | −36.652 | Arg205, Arg215, Gln216, Gln270 | Phe172, Phe208, Ile268 | Asn169, Thr171, Gln216, Ser259, Gln270 | -- | -- | Asp212 | Arg205, Arg215 | -- |
| 5j | −2.945 | −34.957 | Arg215, Gln216, Gln270 | Phe172, Phe208, Ile268 | Asn169, Thr171, Gln216, Ser259, Gln270 | -- | -- | Asp212 | Arg205, Arg215 | -- |
| 5k | −3.213 | −39.572 | Glu185 | Val168, Ile257, Ile268 | Thr99, Asn169, Gln216, Gln219 | -- | -- | Glu185 | Arg215 | -- |
| 5l | −2.896 | −34.358 | Arg205, Asp212, Gln270 | Phe172, Phe208, Ile268 | Asn169, Thr171, Gln216, Ser259, Gln270 | -- | -- | Asp212 | Arg205, Arg215 | -- |
| Compound ID | Glide Score | Glide E-Model | Hydrogen Bond | Hydrophobic Interaction | Polar Interaction | Pi–Cation Interaction | Pi–Pi Stacking Interaction | Negative Interaction | Positive Interaction | Glycine Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus (PDB: 6WN9) | ||||||||||
| 5a | −3.910 | −31.859 | Ser445, Lys499 | Pro447, Phe462, Ile466, Pro467 | Ser445, Asn468 | -- | -- | Glu596 | Lys499 | -- |
| 5b | −3.525 | −38.417 | Asn468 | Pro447, Ile466,Pro467, Val592, Met595 | Ser445, Asn468, Gln498 | -- | -- | Glu596 | Lys499 | -- |
| 5c | −3.291 | −39.247 | Gly497 | Pro447, Ile466, Val592, Met595 | Ser445, Gln498 | -- | -- | Glu596 | Lys499 | Gly497 |
| 5d | −3.299 | −38.468 | Ser445, Gly497 | Pro447, Ile466 Val592, Met595 | Ser445, Gln498, Hie598 | Lys499 | -- | Glu596 | Lys499 | Gly497 |
| 5e | −3.269 | −36.366 | Gly497 | Pro447, Phe462, Ile466, Val592, Met595 | Ser445, Ser446, Asn468, Gln498 | -- | -- | Glu596 | Lys499 | Gly497 |
| 5f | −3.916 | −44.854 | Ser445, Asn468, Lys499, | Pro447, Phe462, Ile466, Pro467, Val592, Met595 | Ser445, Asn468, Gln498, Hie598 | Lys499 | -- | Glu596 | Lys465, Lys499 | -- |
| 5g | −3.393 | −35.834 | Ser445, Gly497 | Pro447, Phe462, Ile466, Val592, Met595 | Ser445, Asn468, Gln498 | Lys499 | -- | Glu596 | Lys496, Lys499 | Gly497 |
| 5h | −3.584 | −33.437 | Ser445, Gly497 | Pro447, Phe462, Ile466, Val592, Met595 | Ser445, Asn468, Gln498 | Lys499 | -- | Glu596 | Lys496, Lys499 | Gly497 |
| 5I | −3.084 | −35.310 | Gly497 | Pro447, Ile466, Val592, Met595 | Ser445, Gln498, Hie598 | Lys499 | -- | Glu596 | Lys499 | Gly497 |
| 5j | −3.919 | −36.527 | Lys499 | Pro447, Phe462, Ile466, Pro467, Val592, Met595 | Ser445, Asn468, | -- | -- | Glu596 | Lys499 | -- |
| 5k | −3.619 | −38.594 | Asn468 | Pro447, Ile466, Pro467, Val592, Met595 | Ser445, Ser446, Asn468, Gln498 | -- | -- | Glu596 | Lys499 | Gly497 |
| 5l | −3.760 | −36.242 | Ser445, Gly497 | Pro447, Phe462, Ile466, Val592, Met595 | Ser445, Asn468, Gln498 | Lys499 | -- | Glu596 | Lys499 | Gly497 |
| Compound ID | Glide Score | Glide E-Model | Hydrogen Bond | Hydrophobic Interaction | Polar Interaction | Pi–Cation Interaction | Pi–Pi Stacking Interaction | Negative Interaction | Positive Interaction | Glycine Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Escherichia coli (PDB: 1HNJ) | ||||||||||
| 5a | −5.007 | −38.227 | Asn210 (2) | Trp32, Ile155, Ile156, Met207,Val212, Phe213, Ala246, Ile250 | Thr37, Thr153, Thr206, Asn210, Asn247 | Arg36 | -- | Asp150 | Arg36, Arg249 | Gly152, Gly209, |
| 5b | −4.810 | −48.379 | Asn247 (2) | Trp32, Ile155, Ile156, Met207, Phe213, Ala246 | Thr28, Thr37, Asn210, Asn247 | Arg36, | Trp32 | Asp27 | Arg36, Arg151, Arg249 | Gly152, Gly209, |
| 5c | −4.797 | −40.220 | Arg36, Gly209, Gly152 | Trp32, Ile156, Phe157, Met207, Val212, Phe213, Ala246, Ile250 | Thr37, Asn210, Asn247, Asn274 | -- | -- | -- | Arg36, Arg249 | Gly152, Gly209, |
| 5d | −4.570 | −40.380 | Arg36, Gly209 | Trp32, Ile155, Ile156,Met207, Phe213, Ala246 | Thr37, Asn210, Asn247 | Arg36, | Trp32 | -- | Arg36, Arg151, Arg249 | Gly152, Gly209, |
| 5e | −5.119 | −47.951 | Asn247 (2) | Trp32, Ile155, Ile156,Met207, Phe213, Ala246 | Thr28, Thr37, Asn210, Asn247 | -- | Trp32 | Asp27 | Arg36, Arg151 | Gly152, Gly209, |
| 5f | −4981 | −44.531 | Asn247 (2) | Trp32, Ile155, Ile156, Met207, Phe213, Ala246 | Thr28, Thr37, Asn210, Asn247 | -- | Trp32 | Asp27 | Arg36, Arg151 | Gly152, Gly209, |
| 5g | −5.099 | −46.773 | Asn247 (2) | Trp32, Ile155, Ile156, Met207, Phe213, Ala246, | Thr28, Thr37, Asn210, Asn247 | -- | Trp32 | Asp27 | Arg36, Arg151, | Gly152, Gly209, |
| 5h | −5.237 | −42.775 | Asn210 | Trp32, Ile155, Ile156, Met207, Val212, Phe213, Ala246, Ile250 | Thr37, Thr153, Asn210, Asn247 | Arg36, | -- | Asp150 | Arg36, Arg249 | Gly152, Gly209, |
| 5i | −5.012 | −38.890 | Met207, Asn210 (2) | Trp32, Ile155, Ile156, Met207, Ala208, Phe213, Ala246, Ile250 | Thr37, Thr153, Asn210, Asn247 | Arg36, | -- | -- | Arg36, Arg249 | Gly152, Gly209, |
| 5j | −4.753 | −35.678 | Asn210 (2) | Trp32, Ile155, Ile156, Met207, Phe213, Ala246, Ile250 | Thr37, Thr153, Asn210, Asn247 | Arg36, | -- | Asp150 | Arg36, Arg249 | Gly152, Gly209, |
| 5k | −5.414 | −46.281 | Asn247 (2) | Trp32, Ile155, Ile156, Met207, Phe213, Ala246 | Thr28, Ser29, Thr37, Asn210, Asn247 | -- | Trp32 | Asp27 | Arg36, Arg151 | Gly152, Gly209, |
| 5l | −5.900 | −49.830 | Asn210 (2) | Trp32, Ile155, Ile156, Met207, Val212, Phe213,Ala246, Ile250 | Thr37, Thr153, Thr206, Asn210, Asn247 | Arg36, | -- | Asp150 | Arg36, Arg249 | Gly152, Gly209, |
| Compound ID | Glide Score | Glide E-Model | Hydrogen Bond | Hydrophobic Interaction | Polar Interaction | Pi–Cation Interaction | Pi–Pi Stacking Interaction | Negative Interaction | Positive Interaction | Glycine Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proteus vulgaris (PDB: 5HXW) | ||||||||||
| 5a | −8.235 | −58.597 | Gln92, Gly98, Gln99 | Ile64, Leu65, Phe96, Tyr97, Phe201, Ile317, Trp407, Ala410, Met411, Ile413, Trp438, Met440 | Gln92, Ser93, Gln99, Gln278, Gln280, Thr436, Thr441 | -- | -- | Glu91 | Arg95 | Gly98, Gly257, Gly409, Gly437, Gly439 |
| 5b | −7.815 | −48.721 | Gln92, Gly98, Gln99, Gln278 | Ile64, Leu65, Phe96, Tyr97, Phe201, Ile317, Ala410, Met411, Trp438, Met440 | Gln92, Ser93, Gln99, Gln278, Gln280, Ser313, Thr436, Thr441 | Tyr97 | -- | -- | Arg95, Arg315 | Gly98, Gly257, Gly409, Gly437, Gly439 |
| 5c | −7.076 | −44.009 | Gln92, Tyr97, Gly98, Gln99, Thr436 | Ile64, Leu65, Phe96, Tyr97, Phe201 Ile317, Ala410, Met411, Trp438, Met440 | Gln92, Ser93, Gln99, Gln278, Gln280, Ser313, Thr436, Thr441 | -- | Trp438 | -- | Arg95 | Gly63, Gly98, Gly409, Gly437, Gly439 |
| 5d | −7.888 | −49.092 | Thr336, Met440, | Ile64, Leu65, Phe96, Tyr97, Ala100, Phe201, Ile317, Met411, Trp438, Met440 | Gln92, Ser93, Gln99, Gln278, Gln280, Ser313, Thr436, Thr441 | -- | -- | Glu442 | Arg95 | Gly98, Gly409, Gly437, Gly439 |
| 5e | −7.218 | −62.271 | Gly98, Gln99 | Ile64, Leu65, Phe96, Tyr97, Phe201, Trp407, Ala410, Met411, Trp438, Met440 | Gln92, Ser93, Gln99, Gln278, Gln280, Thr436, Thr441 | -- | -- | -- | Arg95 | Gly98, Gly257, Gly409, Gly437, Gly439 |
| 5f | −8.499 | −55.594 | Gln92, Gly98, Gln99 | Ile64, Leu65, Phe96, Tyr97, Phe201, Ile317, Trp407, Ala410, Met411, Trp438, Met440 | Gln92, Ser93, Gln99, Gln278, Gln280, Thr436, Thr441 | -- | Trp438 | Glu91 | Arg95 | Gly98, Gly409, Gly437, Gly439 |
| 5g | −7.163 | −60.285 | Gly98, Gln99 | Ile64, Leu65, Phe96, Tyr97, Phe201 Trp407, Ala410, Met411, Trp438, Met440 | Gln92, Ser93, Gln99, Gln278, Gln280, Thr436, Thr441 | -- | -- | -- | Arg95 | Gly98, Gly257, Gly409, Gly437, Gly439 |
| 5h | −7.733 | −38.497 | Gln92, Gly98, Gln99, Trp438 | Ile64, Leu65, Phe96, Tyr97, Phe201, Phe301, Ile317, Ala410, Met411, Trp438, Met440 | Gln92, Ser93, Gln99, Gln278, Gln280, Ser313 | -- | Trp438 | -- | Arg95 | Gly63, Gly98, Gly409, Gly437, Gly439 |
| 5i | −7.213 | −59.216 | Gly98, Gln99 | Ile64, Leu65, Phe96, Tyr97, Phe201, Trp407, Ala410, Met411, Ile413, Trp438, Met440 | Gln92, Ser93, Gln99, Gln278, Gln280, Thr436, Thr441 | -- | -- | -- | Arg95 | Gly98, Gly257, Gly409, Gly437, Gly439 |
| 5j | −8.053 | −60.362 | Gln92, Gly98, Gln99 | Ile64, Leu65, Phe96, Tyr97, Phe201, Trp407, Ala410, Met411, Ile413, Trp438, Met440 | Gln92, Ser93, Gln99, Gln278, Gln280, Thr436, Thr441 | -- | -- | Glu91 | Arg95 | Gly63, Gly98, Gly409, Gly437, Gly439 |
| 5k | −8.322 | −60.500 | Gln92, Tyr97, Gly98, Gln99 | Ile64, Leu65, Phe96, Tyr97, Phe201 Ile317, Trp407, Ala410, Met411, Trp438, Met440 | Gln92, Ser93, Gln99, Gln278, Gln280, Thr436, Thr441 | -- | -- | Glu91 | Arg95 | Gly98, Gly257, Gly409, Gly437, Gly439 |
| 5l | −7.866 | −63.768 | Gly98, Gln99, Thr436 | Ile64, Leu65, Phe96, Tyr97, Phe201, Trp407, Ala410, Met411, Trp438, Met440 | Gln92, Ser93, Gln99, Gln278, Gln280, Thr436, Thr441 | -- | -- | -- | Arg95 | Gly63, Gly98, Gly409, Gly437, Gly439 |
| Compound ID | Glide Score | Glide E-Model | Hydrogen Bond | Hydrophobic Interaction | Polar Interaction | Pi–Cation Interaction | Pi–Pi Stacking Interaction | Negative Interaction | Positive Interaction | Glycine Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aspergillus niger (PDB: 1UKC) | ||||||||||
| 5a | −6.731 | −64.828 | Asn134, Asn341 | Tyr137, Val209, Trp301, Phe342, Ile436, Pro439, Phe442, Leu444, Pro445, Leu456, Tyr462 | Ser133, Asn134, Ser210, Asn341, Asn431, His440, Thr441, Thr453, Ser460 | -- | -- | -- | -- | Gly126, Gly127, Gly128 |
| 5b | −6.828 | −70.326 | Asn134, Asn341 | Tyr137, Val209, Trp301, Phe342, Ile436, Pro439, Phe442, Leu444, Pro445, Leu456, Tyr462 | Ser133, Asn134, Ser210, Asn341,Asn431, His440, Thr441, Thr453, Ser460 | -- | -- | -- | -- | Gly126, Gly127, Gly128 |
| 5c | −4.982 | −45.227 | Asn134, Thr441, Thr453 | Tyr137, Val209, Phe342, Pro439, Phe442, Leu444, Pro445, Leu456, Tyr462 | Ser133, Asn134, Ser210, Asn341, Asn431, His440, Thr441, Thr453, Thr455, Ser457, Ser460 | -- | -- | -- | -- | Gly127, Gly454 |
| 5d | −6.632 | −66.774 | Asn134, Asn341 | Tyr137, Val209, Phe342, Ile436, Pro439, Phe442, Leu444,Pro445, Leu456, Tyr462 | Ser133, Asn134, Ser210, Asn341, Asn431, His440, Thr441, Thr453 | -- | His440 | -- | -- | Gly126, Gly127, Gly128 |
| 5e | −3.751 | −44.902 | -- | Ala211,Trp301, Phe342,Ile436, Pro439,Phe442, Leu444,Pro445 | Ser133, Asn134, Ser210, Asn341,His440, Thr441 | -- | -- | -- | -- | Gly126, Gly127, Gly128 |
| 5f | −6.895 | −67.799 | Asn134, Asn341 | Tyr137, Val209, Trp301, Phe342, Ile436, Pro439, Phe442, Leu444, Pro445, Leu456, Tyr462 | Ser133, Asn134, Ser210, Asn341, Asn431, His440, Thr441, Thr453, Ser460 | -- | -- | -- | -- | Gly126, Gly127, Gly128 |
| 5g | −6.703 | −68.366 | Ser522 | Tyr375, Leu381, Ala393, Val518, Pro519 | Thr336, Ser392, Thr401, Ser522 | Arg423 | -- | Ash334, Ash335, Asp337, Asp397, Asp525 | Arg423, Arg505 | Gly389 |
| 5h | −3.333 | −46.158 | Ser522, Arg423 | Tyr375, Leu381, Phe388, Ala393, Val518, Pro519 | Thr336, Ser340, Ser392, Thr401, Ser522 | Arg423 | -- | Ash334, Ash335, Asp337, Asp525 | Arg423, Arg505 | Gly389 |
| 5i | −4.785 | −45.484 | His440 | Tyr137, Trp301, Phe342, Ile436, Pro439, Phe442, Leu444, Pro445, Leu456, Tyr462 | Ser133, Asn134, Ser210, Asn341,Asn431, His440, Thr441, Thr453, Ser460 | -- | -- | -- | -- | Gly127, Gly454 |
| 5j | −5.873 | −58.046 | Ser210, Asn341 | Tyr137, Ala211, Trp301, Phe342, Ile436, Pro439, Phe442, Leu444, Pro445, Leu456, Tyr462 | Ser133, Asn134, Ser210, Asn341,Asn431, His440, Thr441, Thr453, Ser460 | -- | -- | Glh131 | -- | Gly126, Gly127, Gly128 |
| 5k | −6.435 | −64.546 | Asn134, Asn341 | Tyr137, Val209, Trp301, Phe342, Ile436, Pro439, Phe442, Leu444, Pro445, Leu456, Tyr462 | Ser133, Asn134, Ser210, Asn341,Asn431, His440, Thr441, Thr453, Ser460 | -- | -- | -- | -- | Gly126, Gly127, Gly128 |
| 5l | −3.167 | −46.817 | Ser522 | Tyr375,Leu381,Ala393, Val518, Pro519 | Thr336, Ser392, Ser522 | Arg423 | -- | Ash334, Ash335, Asp337, Asp397, Asp525 | Arg423, Arg505 | Gly389 |
| Compound ID | Glide Score | Glide E-Model | Hydrogen Bond | Hydrophobic Interaction | Polar Interaction | Pi–Cation Interaction | Pi–Pi Stacking Interaction | Negative Interaction | Positive Interaction | Glycine Interaction | Salt Bridge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aspergillus flavus (PDB: 5ZZD) | |||||||||||
| 5a | −5.415 | −66.838 | Gly227, Asp296 | Phe176, Leu192, Leu193, Met230, Leu292, Ile293 | Hie232 | -- | -- | Asp195, Glu196, Asp296 | Arg197, Arg291 | Gly227, Gly228, Gly229 | -- |
| 5b | −5.000 | −66.164 | Gly227 | Phe176, Phe189, Leu192, Leu193, Leu253, Val256, Phe276, Leu292, Ile293 | -- | -- | -- | Asp195, Glu196, Asp252, Asp296 | Arg197, Arg291, Arg295 | Gly227, Gly228, | Asp195 |
| 5c | −5.230 | −65.947 | Gly227, Gly228, Arg291 | Phe176, Phe189, Leu192, Leu193, Met230, Val256, Phe276, Leu292, Ile293 | Hie232 | -- | -- | Asp195, Glu196, Asp296 | Arg197, Arg291 | Gly227, Gly228, Gly229, Gly231 | -- |
| 5d | −5.902 | −68.806 | Gly227, Gly228, Arg291 | Phe176, Phe189, Leu192, Leu193, Met230, Phe276, leu292, Ile293 | Hie232 | -- | -- | Asp195, Glu196, Asp296 | Arg197, Arg291 | Gly227, Gly228, Gly229, Gly231 | -- |
| 5e | −4.885 | −63.587 | Gly227, Asp296 | Phe176, Phe189, Leu192, Leu193, Leu292, Ile293 | Hie232 | -- | -- | Asp195, Glu196, Asp296 | Arg197, Arg291 | Gly227, Gly228, Gly229 | -- |
| 5f | −5.991 | −72.025 | Arg197, Gly227, Asp296 | Phe176, Phe189, Leu192, Leu193, Leu292, Ile293 | Hie232 | -- | -- | Asp195, Glu196, Asp296 | Arg197, Arg291 | Gly227, Gly228, Gly229 | -- |
| 5g | −5.362 | −63.817 | Gly227, Asp296 | Phe176, Phe189, Leu192, Leu193, Leu292, Ile293 | Hie232 | -- | -- | Asp195, Glu196, Asp296 | Arg197, Arg291 | Gly227, Gly228, Gly229 | -- |
| 5h | −5.980 | −69.543 | Gly227, Asp296 | Phe176, Phe189, Leu192, Leu193, Leu253, Leu292, Ile293 | Asn200, Hie232 | -- | -- | Asp195, Glu196, Asp296 | Arg197, Arg291 | Gly227, Gly228, Gly229 | -- |
| 5i | −5.032 | −63.403 | Gly227, Asp296 | Phe176, Phe189, Leu192, Leu193, Leu292, Ile293 | Hie232 | -- | -- | Asp195, Glu196, Asp296 | Arg197, Arg291 | Gly227, Gly228, Gly229 | -- |
| 5j | −5.249 | −64.825 | Gly227, Asp296 | Phe176, Phe189, Leu192, Leu193, Leu292, Ile293 | Hie232 | -- | -- | Asp195, Glu196, Asp296 | Arg197, Arg291 | Gly227, Gly228, Gly229 | -- |
| 5k | −4.893 | −64.395 | Gly227 | Phe176, Phe189, Leu192, Leu193, Leu292, Ile293 | -- | -- | -- | Asp195, Glu196, Asp252, Asp296 | Arg197, Arg291, Arg295 | Gly227, Gly229, | -- |
| 5l | −5.250 | −62.550 | Arg197, Gly227, Asp296 | Phe176, Phe189, Leu192, Leu193, Leu253, Leu292, Ile293 | Hie232 | -- | -- | Asp195, Glu196, Asp252, Asp296 | Arg197, Arg291, Arg295 | Gly227, Gly228, Gly229 | -- |
| Compound No. | Zone of Inhibition for Antimicrobials (mm) after 1 Day at 200 g/mL Concentration | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial and Its Resistance | Fungal and Its Resistance | |||||
| Gram-Positive | Gram-Negative | |||||
| Bacillus subtilis | Staphylococcus aureus | Escherichia coli | Proteus vulgaris | Aspergillus niger | A. flavus | |
| 5a | 35.21 | 39.19 | 30.05 | 34.21 | 32.31 | 36.22 |
| 5b | 30.31 | 33.36 | 24.42 | 27.29 | 25.15 | 29.32 |
| 5c | 19.14 | 21.19 | 14.08 | 15.21 | 13.29 | 17.09 |
| 5d | 10.21 | 11.31 | 06.29 | 08.05 | 07.32 | 09.20 |
| 5e | 16.05 | 18.07 | 10.01 | 14.16 | 10.41 | 12.16 |
| 5f | 40.12 | 42.14 | 38.05 | 39.22 | 36.19 | 40.14 |
| 5g | 07.18 | 09.23 | 04.11 | 05.31 | 06.02 | 08.21 |
| 5h | 22.41 | 28.12 | 16.15 | 19.42 | 18.30 | 24.05 |
| 5i | 05.32 | 06.10 | 02.16 | 04.01 | 04.38 | 05.11 |
| 5j | 24.02 | 29.05 | 20.06 | 21.33. | 22.22 | 26.11 |
| 5k | 38.15 | 41.03 | 35.11 | 37.16 | 35.03 | 39.05 |
| 5l | 34.05 | 36.30 | 25.21 | 29.07 | 30.42 | 33.17 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 41.22 | 44.30 | 36.21 | 40.22 | - | - |
| Ketoconazole | - | - | - | - | 38.45 | 41.24 |
| Control(DMSO) | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Compound No. | MIC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC (MBC/MFC) μg/mL | ||||||
| B. subtilis | S. aureus | E. coli | P. vulgaris | A. niger | A. flavus | |
| 5a | 25 (50) | 12.5 (100) | 25 (100) | 50 (200) | 12.5 (50) | 50 (100) |
| 5b | 50 (200) | 25 (>200) | 50 (100) | 50 (200) | 12.5 (25) | 12.5 (100) |
| 5f | 25 (100) | 12.5 (25) | 50 (>200) | 50 (200) | 25 (50) | 50 (100) |
| 5k | 50 (200) | 100 (>200) | 12.5 (25) | 25 (100) | 50(>200) | 12.5 (25) |
| 5l | 12.5 (200) | 50 (100) | 25 (50) | 50 (>200) | 25 (100) | 12.5 (100) |
| Ciprofloxacin | 12.5 | 6.25 | 12.5 | 12.5 | - | - |
| Ketoconazole | - | - | - | - | 12.5 | 6.25 |
| Tested Target | IC50 (μg/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| HepG-2 | U937 | SKOV3 | |
| Etoposide | 2.02 ± 0.15 | 5.23 ± 3.01 | 6.81 ± 1.56 |
| 5a | 65.16 ± 1.45 | 101.49 ± 1.09 | 119.45 ± 1.35 |
| 5b | 86.32 ± 1.05 | 123.01 ± 1.65 | 160.23 ± 1.41 |
| 5c | 128.71 ± 1.30 | >200 | >200 |
| 5d | 57.45 ± 0.95 | 74.20 ± 2.01 | 88.14 ± 2.20 |
| 5e | 147.26 ± 1.01 | 168.71 ± 2.11 | >200 |
| 5f | 42.11 ± 2.11 | 60.12 ± 2.61 | 75.43 ± 0.99 |
| 5g | 71.94 ± 0.54 | >200 | >200 |
| 5h | 29.56 ± 1.20 | 36.05 ± 1.00 | 51.25 ± 0.22 |
| 5i | 112.55 ± 2.46 | 131.33 ± 1.05 | >200 |
| 5j | 84.46 ± 0.89 | 117.46 ± 1.19 | 129.50 ± 2.30 |
| 5k | 59.78 ± 1.12 | 83.12 ± 3.46 | 95.09 ± 2.14 |
| 5l | 80.28 ± 3.01 | 110.51 ± 0.51 | 124.13 ± 1.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guda, M.R.; Zyryanov, G.V.; Dubey, A.; Munagapati, V.S.; Wen, J.-C. Cytotoxic and Infection-Controlled Investigations of Novel Dihydropyridine Hybrids: An Efficient Synthesis and Molecular-Docking Studies. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081159
Guda MR, Zyryanov GV, Dubey A, Munagapati VS, Wen J-C. Cytotoxic and Infection-Controlled Investigations of Novel Dihydropyridine Hybrids: An Efficient Synthesis and Molecular-Docking Studies. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(8):1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081159
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuda, Mallikarjuna R., Grigory. V. Zyryanov, Amit Dubey, Venkata Subbaiah Munagapati, and Jet-Chau Wen. 2023. "Cytotoxic and Infection-Controlled Investigations of Novel Dihydropyridine Hybrids: An Efficient Synthesis and Molecular-Docking Studies" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 8: 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081159
APA StyleGuda, M. R., Zyryanov, G. V., Dubey, A., Munagapati, V. S., & Wen, J.-C. (2023). Cytotoxic and Infection-Controlled Investigations of Novel Dihydropyridine Hybrids: An Efficient Synthesis and Molecular-Docking Studies. Pharmaceuticals, 16(8), 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081159