Gypenoside-14 Reduces Depression via Downregulation of the Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-kB) Signaling Pathway on the Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Depression Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
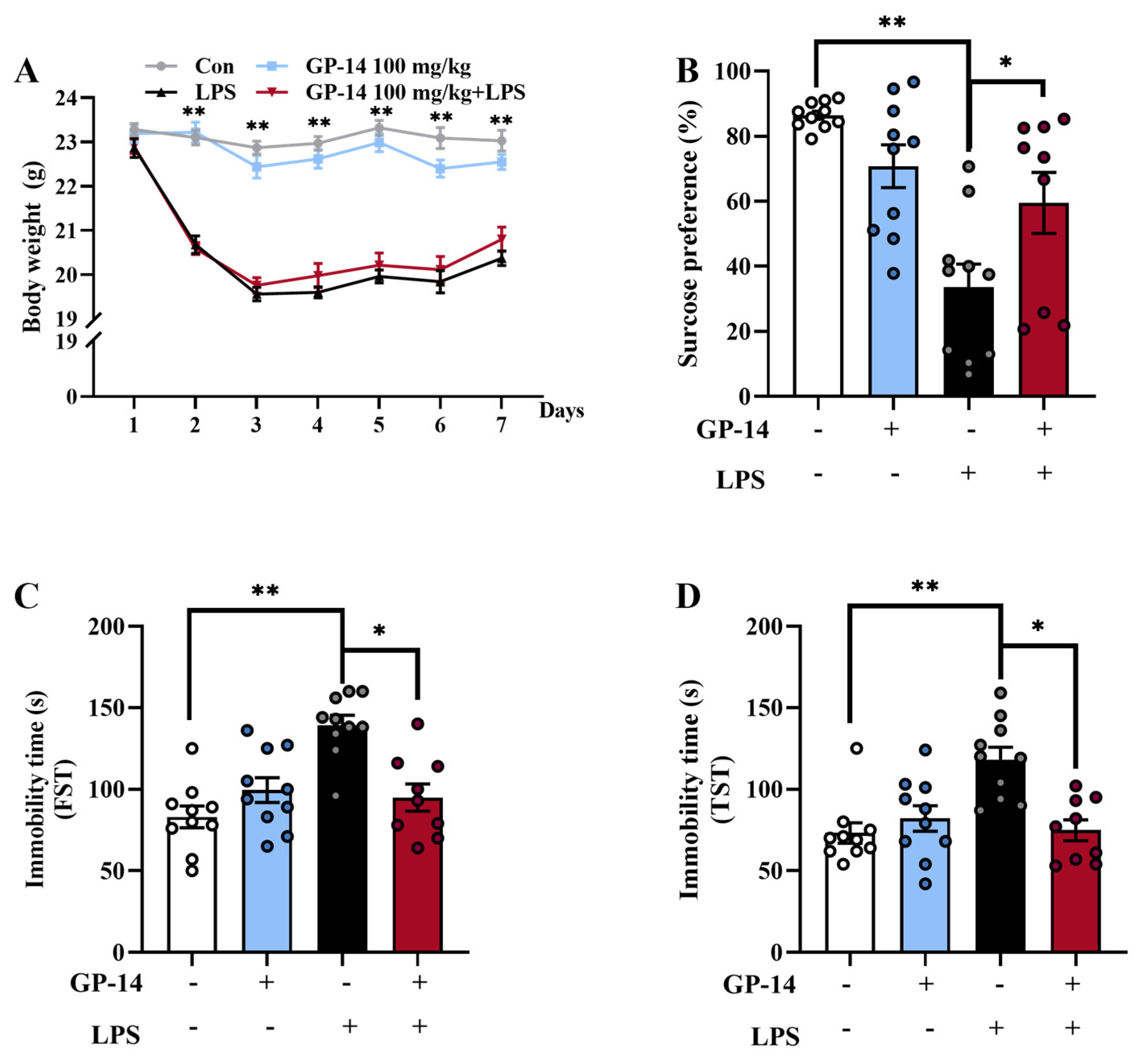
2.1. GP-14 Reversed Depressive-like Behaviors Induced with LPS
2.2. GP-14 Attenuated LPS-Induced Anxiety-like Behavior
2.3. GP-14 Improved Impairments of Learning and Memory Induced with LPS
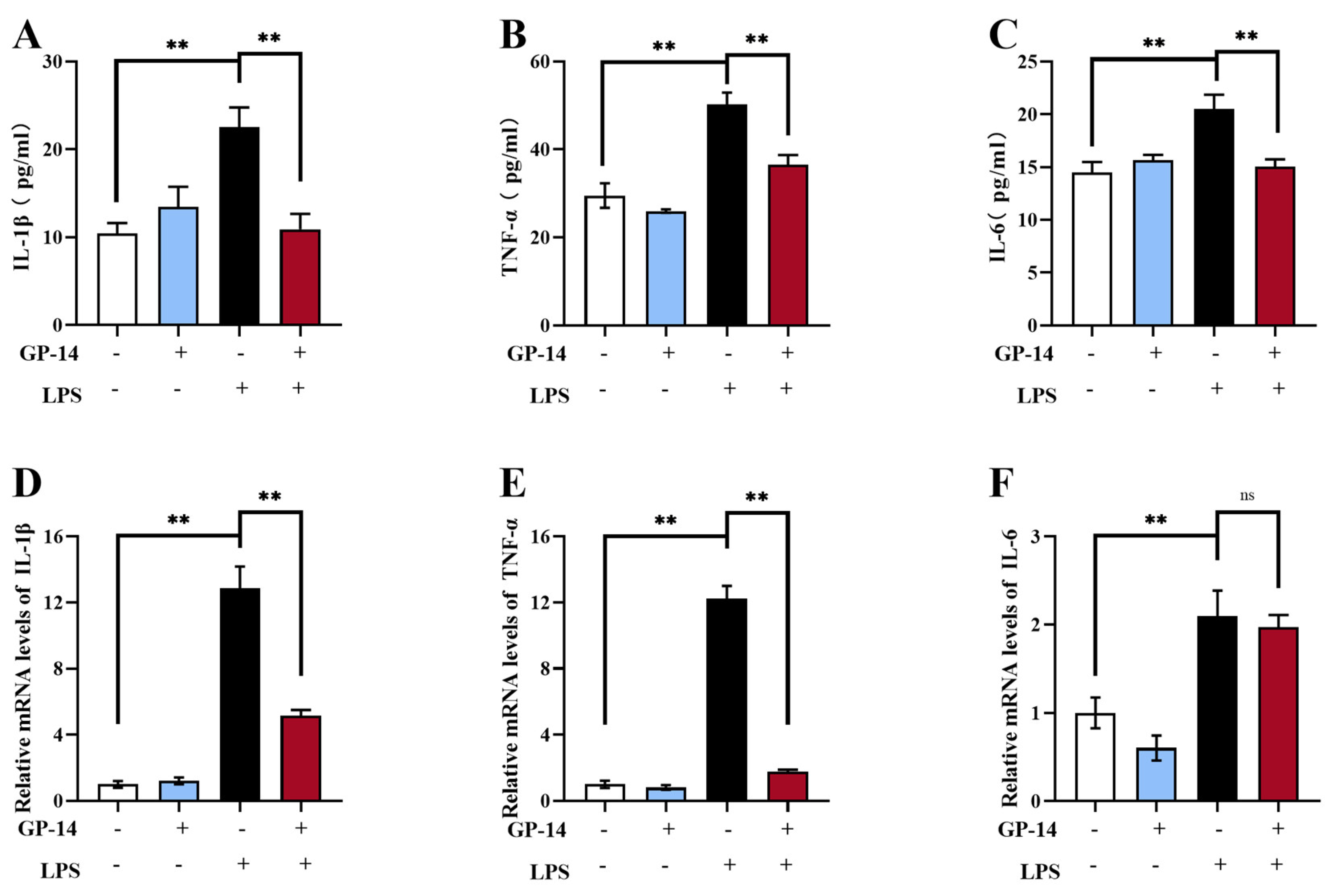
2.4. GP-14 Alleviated LPS-Induced Neuroinflammation
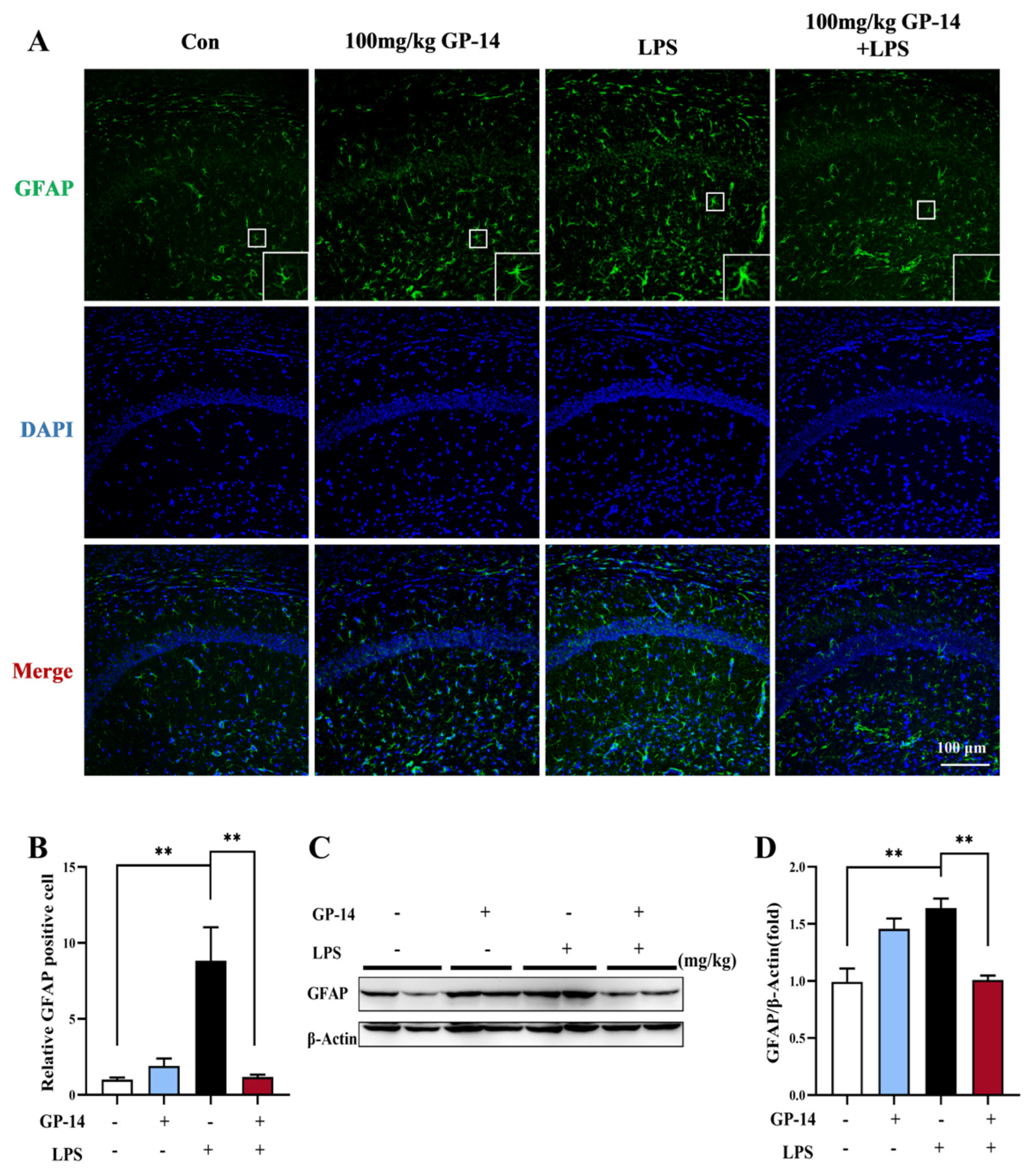
2.5. GP-14 Inhibited LPS-Induced Activation of Astrocytes
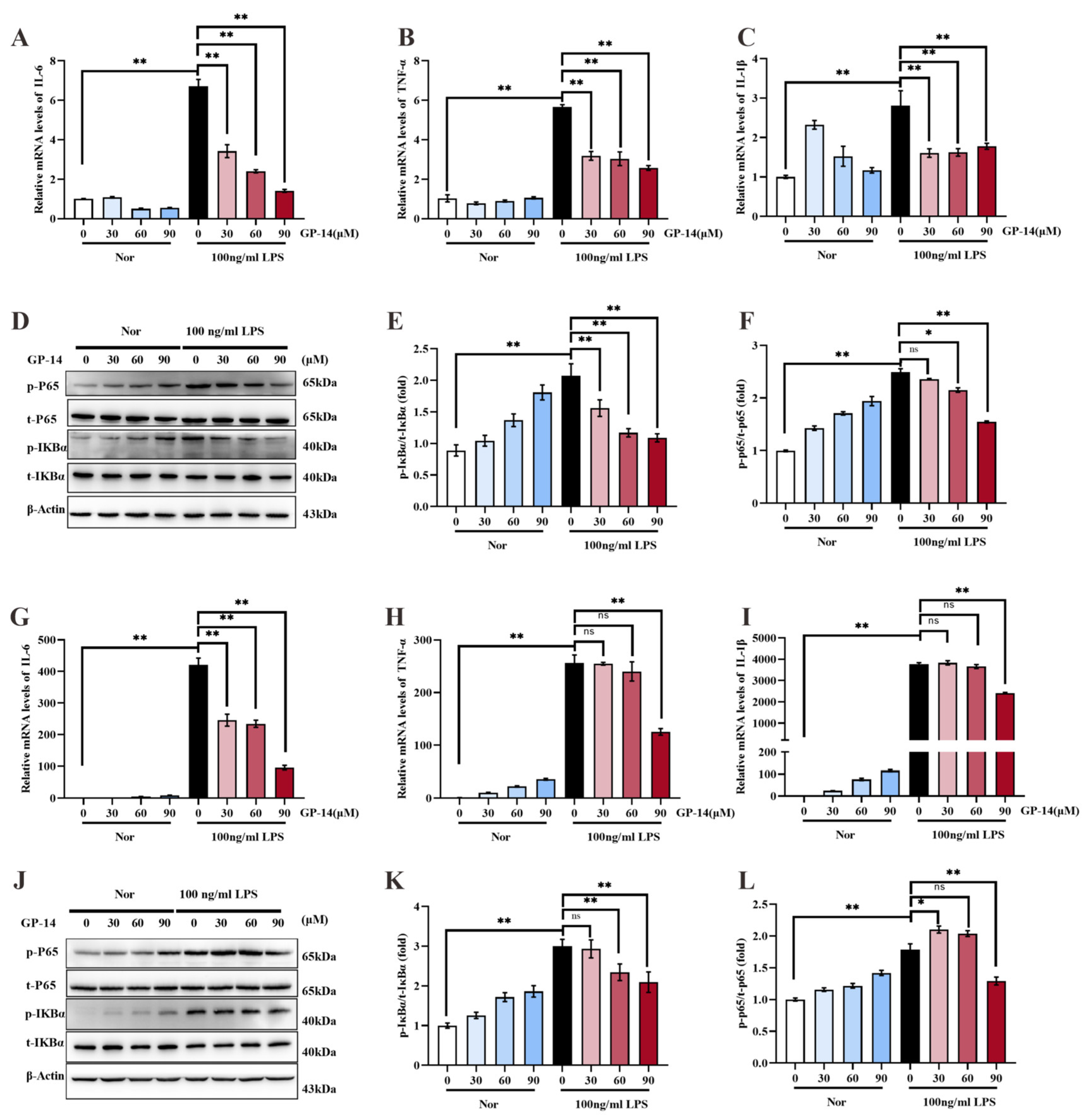
2.6. Suppression of Inflammatory Response and NF-κB Pathway Activation with GP-14 in C8 Cells and Primary Astrocytes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Treatment
4.2. Behavioral Tests
4.2.1. Sucrose Preference Test (SPT)
4.2.2. Open Field Test (OFT)
4.2.3. Tail Suspension Test (TST)
4.2.4. Force Swimming Test (FST)
4.2.5. New Object Recognition Experiment (NOR)
4.2.6. Morris Water Maze Test (MWM)
4.3. Biochemical Assessment
4.3.1. C8 Cell Culture and Treatments
4.3.2. Primary Astrocytes Culture and Treatments
4.3.3. Immunofluorescence
4.3.4. Western Blotting
4.3.5. Quantitative PCR
4.3.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
4.4. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saveanu, R.V.; Nemeroff, C.B. Etiology of depression: Genetic and environmental factors. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 35, 51–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, C.; Newport, D.J.; Mletzko, T.; Miller, A.H.; Nemeroff, C.B. The link between childhood trauma and depression: Insights from HPA axis studies in humans. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2008, 33, 693–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, P.L. Depression: The case for a monoamine deficiency. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2000, 61 (Suppl. 6), 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, M.J.F.; Boulle, F.; Steinbusch, H.W.; van den Hove, D.L.A.; Kenis, G.; Lanfumey, L. Neurotrophic factors and neuroplasticity pathways in the pathophysiology and treatment of depression. Psychopharmacology 2018, 235, 2195–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beurel, E.; Toups, M.; Nemeroff, C.B. The Bidirectional Relationship of Depression and Inflammation: Double Trouble. Neuron 2020, 107, 234–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, A.; Scheurlen, M.; Seufert, J.; Keicher, C.; Weissbrich, B.; Rieger, P.; Kraus, M.R. Platelet serotonin (5-HT) levels in interferon-treated patients with hepatitis C and its possible association with interferon-induced depression. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.M.; Lin, W.J.; Pan, Y.Q.; Guan, X.T.; Li, Y.C. Hippocampal neurogenesis dysfunction linked to depressive-like behaviors in a neuroinflammation induced model of depression. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 161, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannestad, J.; DellaGioia, N.; Bloch, M. The effect of antidepressant medication treatment on serum levels of inflammatory cytokines: A meta-analysis. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 2452–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesripour, A.; Shahnooshi, S.; Hajhashemi, V. Celecoxib, ibuprofen, and indomethacin alleviate depression-like behavior induced by interferon-alfa in mice. J. Complement. Integr. Med. 2019, 17, 20190016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Ma, C.; Li, H.; Dev, S.; He, J.; Qu, X. Medicinal Value and Potential Therapeutic Mechanisms of Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb.) Makino and Its Derivatives: An Overview. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 2855–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.J.; Sun, T.; Kong, L.; Shang, Z.H.; Yang, K.Q.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Jing, F.M.; Dong, L.; Xu, X.F.; Liu, J.X.; et al. Gypenosides pre-treatment protects the brain against cerebral ischemia and increases neural stem cells/progenitors in the subventricular zone. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. Off. J. Int. Soc. Dev. Neurosci. 2014, 33, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Shim, I.; Lee, H.; Hahm, D.H. Gypenosides attenuate lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation and anxiety-like behaviors in rats. Anim. Cells Syst. 2018, 22, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.Q.; Zhang, Q.P.; Zhu, J.X.; Chen, M.; Li, C.F.; Liu, Q.; Geng, D.; Yi, L.T. Gypenosides reverses depressive behavior via inhibiting hippocampal neuroinflammation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shi, G.; Liu, M.; Chen, R.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Y. Four new dammarane-type triterpenes derivatives from hydrolyzate of total Gynostemma pentaphyllum saponins and their bioactivities. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 1605–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Yang, L.; Xing, F.; Yang, H.; Qin, L.; Lan, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, B.; Shi, H.; et al. Gypenoside IX Suppresses p38 MAPK/Akt/NFκB Signaling Pathway Activation and Inflammatory Responses in Astrocytes Stimulated by Proinflammatory Mediators. Inflammation 2017, 40, 2137–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, M.; Cheng, X.; Han, Y.; Zhao, T.; Fan, M.; Zhu, L.; Yang, J.L. Dammarane-Type Saponins from Gynostemma pentaphyllum Prevent Hypoxia-Induced Neural Injury through Activation of ERK, Akt, and CREB Pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Y.; Yang, J.; Cheng, X.; Han, Y.; Yan, F.; Wang, C.; Jiang, X.; Meng, X.; Fan, M.; Zhao, M.; et al. A bioactive gypenoside (GP-14) alleviates neuroinflammation and blood brain barrier (BBB) disruption by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway in a mouse high-altitude cerebral edema (HACE) model. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 107, 108675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.N.; Zhao, M.; Yang, J.L.; Cheng, X.; Han, Y.; Wang, C.B.; Jiang, X.F.; Fan, M.; Zhu, L.L. GP-14 protects against severe hypoxia-induced neuronal injury through the AKT and ERK pathways and its induced transcriptome profiling alteration. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2022, 448, 116092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałecki, P.; Talarowska, M. Inflammatory theory of depression. Psychiatr. Pol. 2018, 52, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raison, C.L.; Capuron, L.; Miller, A.H. Cytokines sing the blues: Inflammation and the pathogenesis of depression. Trends Immunol. 2006, 27, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, C.A.; Freitas, T.H.; Maes, M.; de Andrade, N.Q.; Liu, C.S.; Fernandes, B.S.; Stubbs, B.; Solmi, M.; Veronese, N.; Herrmann, N.; et al. Peripheral cytokine and chemokine alterations in depression: A meta-analysis of 82 studies. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2017, 135, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, L.; Caraveo-Anduaga, J.J.; Berglund, P.; Bijl, R.V.; De Graaf, R.; Vollebergh, W.; Dragomirecka, E.; Kohn, R.; Keller, M.; Kessler, R.C.; et al. The epidemiology of major depressive episodes: Results from the International Consortium of Psychiatric Epidemiology (ICPE) Surveys. Int. J. Methods Psychiatr. Res. 2003, 12, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Luo, Z.; He, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y. Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption by Lipopolysaccharide and Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 768108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, P.P.; Hu, K.L.; Li, L.N.; Yu, X.; Lu, Y.; Chang, H.S. Antidepressant-Like Effect and Mechanism of Action of Honokiol on the Mouse Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Depression Model. Molecules 2019, 24, 2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Fu, M.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ding, M. Oridonin Alleviates LPS-Induced Depression by Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome via Activation of Autophagy. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 813047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, R.B.; Duman, R. Neuroplasticity in cognitive and psychological mechanisms of depression: An integrative model. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqurashi, G.K.; Hindi, E.A.; Zayed, M.A.; Abd El-Aziz, G.S.; Alturkistani, H.A.; Ibrahim, R.F.; Al-Thepyani, M.A.; Bakhlgi, R.; Alzahrani, N.A.; Ashraf, G.M.; et al. The Impact of Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress-Induced Depression on Spatial, Recognition and Reference Memory Tasks in Mice: Behavioral and Histological Study. Behav. Sci. 2022, 12, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, R.; Bracchi-Ricard, V.; Hu, W.H.; Frydel, B.; Bramwell, A.; Karmally, S.; Green, E.J.; Bethea, J.R. Inhibition of astroglial nuclear factor kappaB reduces inflammation and improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, R.; Dvoriantchikova, G.; Barakat, D.; Ivanov, D.; Bethea, J.R.; Shestopalov, V.I. Transgenic inhibition of astroglial NF-κB protects from optic nerve damage and retinal ganglion cell loss in experimental optic neuritis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeuerle, P.A.; Baltimore, D. NF-kappa B: Ten years after. Cell 1996, 87, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Román, R.; Salazar-González, D.; Rosas, S.; Arellanes-Robledo, J.; Beltrán-Ramírez, O.; Fattel-Fazenda, S.; Villa-Treviño, S. The differential NF-kB modulation by S-adenosyl-L-methionine, N-acetylcysteine and quercetin on the promotion stage of chemical hepatocarcinogenesis. Free Radic. Res. 2008, 42, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnerbauer, M.; Wheeler, M.A.; Quintana, F.J. Astrocyte Crosstalk in CNS Inflammation. Neuron 2020, 108, 608–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adzic, M.; Djordjevic, J.; Mitic, M.; Brkic, Z.; Lukic, I.; Radojcic, M. The contribution of hypothalamic neuroendocrine, neuroplastic and neuroinflammatory processes to lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behaviour in female and male rats: Involvement of glucocorticoid receptor and C/EBP-β. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 291, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Zhao, M.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, T.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, M.; Zhu, L. FG-4592 Improves Depressive-Like Behaviors through HIF-1-Mediated Neurogenesis and Synapse Plasticity in Rats. Neurother. J. Am. Soc. Exp. Neurother. 2020, 17, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Genes | Sequences |
|---|---|
| IL-6 | forward:5′-ACTGTCGAGTCGCGTCCA-3′ reverse:5′-GTCATCCATGGCGAACTGGT-3′ |
| IL-1β | forward:5′-TTCAGGCAGGCAGTATCACTC-3′ reverse: 5′-GAAGGTCCACGGGAAAGACAC-3′ |
| TNF-α | forward: 5′-CCCTCACACTCAGATCATCTTCT-3′ reverse: 5′-GCTACGACGTGGGCTACAG-3′ |
| β-actin | forward: 5′-ACTGTCGAGTCGCGTCCA-3′ reverse: 5′-GTCATCCATGGCGAACTGGT-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Z.; Yue, X.; Geng, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, C.; et al. Gypenoside-14 Reduces Depression via Downregulation of the Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-kB) Signaling Pathway on the Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Depression Model. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081152
Jiang Y, Cheng X, Zhao M, Zhao T, Zhang M, Shi Z, Yue X, Geng Y, Gao J, Wang C, et al. Gypenoside-14 Reduces Depression via Downregulation of the Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-kB) Signaling Pathway on the Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Depression Model. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(8):1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081152
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Yaqun, Xiang Cheng, Ming Zhao, Tong Zhao, Mengya Zhang, Zibi Shi, Xiangpei Yue, Yanan Geng, Jiayue Gao, Chengbo Wang, and et al. 2023. "Gypenoside-14 Reduces Depression via Downregulation of the Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-kB) Signaling Pathway on the Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Depression Model" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 8: 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081152
APA StyleJiang, Y., Cheng, X., Zhao, M., Zhao, T., Zhang, M., Shi, Z., Yue, X., Geng, Y., Gao, J., Wang, C., Yang, J., & Zhu, L. (2023). Gypenoside-14 Reduces Depression via Downregulation of the Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-kB) Signaling Pathway on the Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Depression Model. Pharmaceuticals, 16(8), 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081152







