Combined Bipolar Radiofrequency and Non-Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid Mesotherapy Protocol to Improve Skin Appearance and Epidermal Barrier Function: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
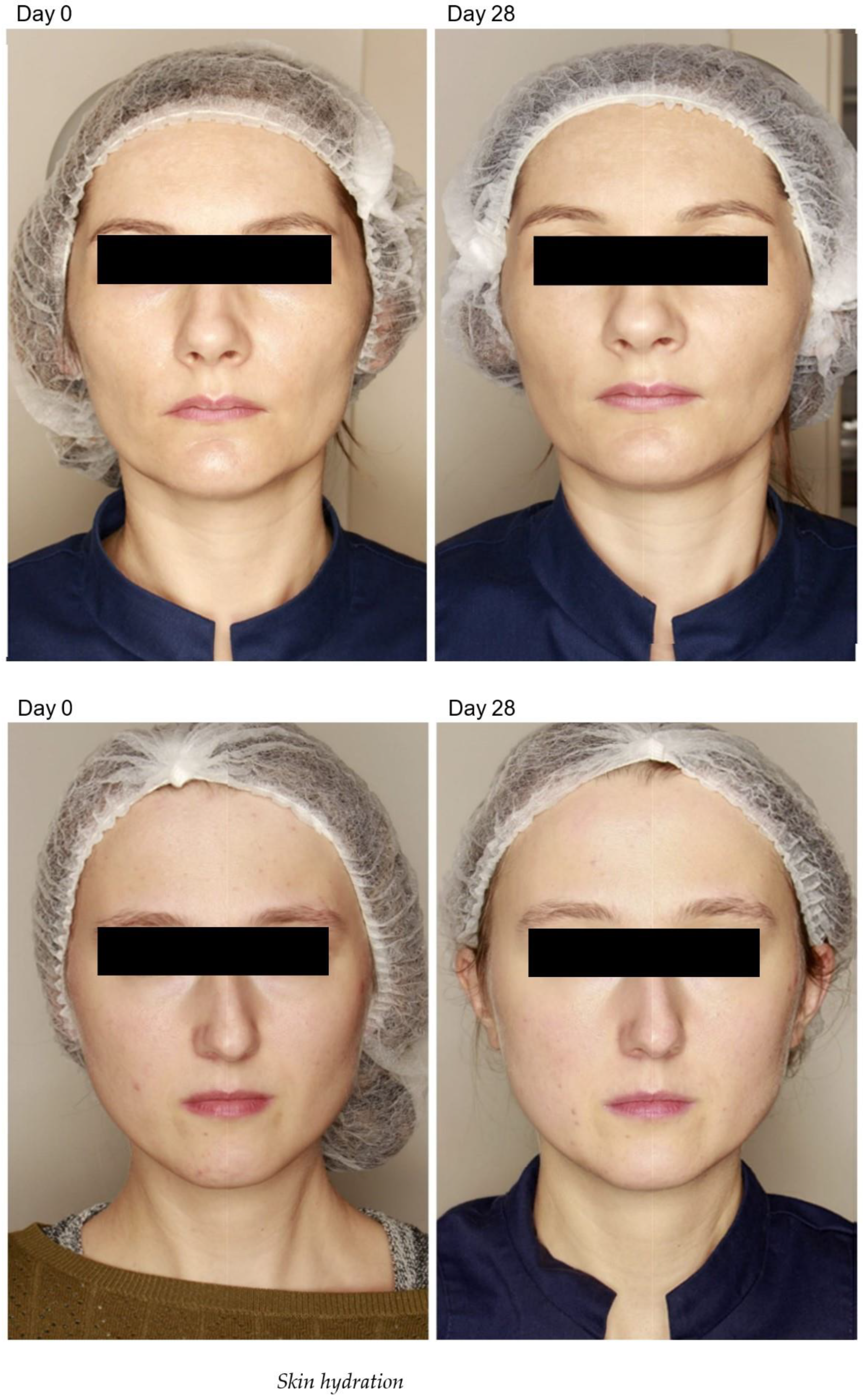
2.1. Skin Pigmentation
2.2. Epidermal Thickness and Density
2.3. Adverse Effects
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Participant Selection
3.2. Treatment Protocol
3.3. Radiofrequency Treatment
3.4. Hyaluronic Acid Treatment
3.5. Post Procedure Recommendations
3.6. Facial Skin Parameters
3.7. Ethical Considerations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baroni Edo, R.; Biondo-Simões, M.d.L.; Auersvald, A.; Auersvald, L.A.; Montemor Netto, M.R.; Ortolan, M.C.; Kohler, J.N. Influence of aging on the quality of the skin of white women: The role of collagen. Acta Cir. Bras. 2012, 27, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Duan, E. Fighting against Skin Aging: The Way from Bench to Bedside. Cell Transplant. 2018, 27, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biniek, K.; Kaczvinsky, J.; Matts, P.; Dauskardt, R.H. Understanding age-induced alterations to the biomechanical barrier function of human stratum corneum. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2015, 80, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naylor, E.C.; Watson, R.E.; Sherratt, M.J. Molecular aspects of skin ageing. Maturitas 2011, 69, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Domyati, M.; Attia, S.; Saleh, F.; Brown, D.; Birk, D.E.; Gasparro, F.; Ahmad, H.; Uitto, J. Intrinsic aging vs. photoaging: A comparative histopathological, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural study of skin. Exp. Dermatol. 2002, 11, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, J.P.; Pessa, J.E.; Hubbard, B.; Rohrich, R.J. The Science and Theory behind Facial Aging. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2013, 1, e8–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, Y.; Holmes, A.; Kwok, P.C.L.; Kumeria, T.; Namjoshi, S.; Imran, M.; Matteucci, L.; Ali, M.; Tai, W.; Benson, H.A.; et al. Advances and future perspectives in epithelial drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 186, 114293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Spicer, A.P. Hyaluronan: A multifunctional, megaDalton, stealth molecule. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2000, 12, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maytin, E.V.; Chung, H.H.; Seetharaman, V.M. Hyaluronan Participates in the Epidermal Response to Disruption of the Permeability Barrier In Vivo. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 165, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.J.; Stern, R. Age-Dependent Changes of Hyaluronan in Human Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1994, 102, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, E.F.; Underhill, C.B.; Hahn, P.J.; Brown, D.B.; Uitto, J. Chronic sun exposure alters both the content and distribution of dermal glycosaminoglycans. Br. J. Dermatol. 1996, 135, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzellos, T.G.; Klagas, I.; Vahtsevanos, K.; Triaridis, S.; Printza, A.; Kyrgidis, A.; Karakiulakis, G.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Papakonstantinou, E. Extrinsic ageing in the human skin is associated with alterations in the expression of hyaluronic acid and its metabolizing enzymes. Exp. Dermatol. 2009, 18, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, E.; Raghavan, S. Getting under the skin of epidermal morphogenesis. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khavkin, J.; Ellis, D.A. Aging skin: Histology, physiology, and pathology. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. 2011, 19, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, G. Keratin 17 in disease pathogenesis: From cancer to dermatoses. J. Pathol. 2019, 247, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadially, R.; Brown, B.E.; Sequeira-Martin, S.M.; Feingold, K.R.; Elias, P.M. The aged epidermal permeability barrier. Structural, functional, and lipid biochemical abnormalities in humans and a senescent murine model. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 2281–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.-H.; Kim, Y.K.; Jung, J.-Y.; Shin, J.-E.; Chung, J.H. Changes in glycosaminoglycans and related proteoglycans in intrinsically aged human skin in vivo. Exp. Dermatol. 2011, 20, 454–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourguignon, L.Y.; Wong, G.; Xia, W.; Man, M.-Q.; Holleran, W.M.; Elias, P.M. Selective matrix (hyaluronan) interaction with CD44 and RhoGTPase signaling promotes keratinocyte functions and overcomes age-related epidermal dysfunction. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2013, 72, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapfumaneyi, P.; Imran, M.; Mohammed, Y.; Roberts, M.S. Recent advances and future prospective of typical and transdermal delivery systems. Front. Drug Deliv. 2022, 2, 957732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Bule, M.L.; Toledano-Macías, E.; Naranjo, A.; de Andrés-Zamora, M.; Úbeda, A. In vitro stimulation with radiofrequency currents promotes proliferation and migration in human keratinocytes and fibroblasts. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2021, 40, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Domyati, M.; El-Ammawi, T.S.; Medhat, W.; Moawad, O.; Brennan, D.; Mahoney, M.G.; Uitto, J. Radiofrequency facial rejuvenation: Evidence-based effect. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2011, 64, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taub, A.F.; Tucker, R.; Palange, A. Facial tightening with an advanced 4-MHz monopolar radiofrequency device. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2012, 11, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar]
- Bloom, B.S.; Emer, J.; Goldberg, D.J. Assessment of safety and efficacy of a bipolar fractionated radiofrequency device in the treatment of photodamaged skin. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2012, 14, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.A.; Beynet, D.; Lask, G.P. A novel non-invasive radiofrequency dermal heating device for skin tightening of the face and neck. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2015, 17, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerbinati, N.; Sommatis, S.; Maccario, C.; Capillo, M.C.; Di Francesco, S.; Rauso, R.; Protasoni, M.; D’este, E.; Gasperina, D.D.; Mocchi, R. In Vitro Evaluation of the Effect of a Not Cross-Linked Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel on Human Keratinocytes for Mesotherapy. Gels 2021, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narurkar, V.A.; Fabi, S.G.; Bucay, V.W.; Tedaldi, R.; Downie, J.B.; Zeichner, J.A.; Butterwick, K.; Taub, A.; Kadoya, K.; Makino, E.T.; et al. Rejuvenating Hydrator: Restoring Epidermal Hyaluronic Acid Homeostasis with Instant Benefits. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2016, 15 (Suppl. S2), s24–s37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Makino, E.T.; Huang, P.C.; Emmerich, T.; Jiang, L.I.; Mehta, R.C. Efficacy and Tolerability of Cosmetic Serums Enriched with Five Forms of Hyaluronic Acid as Part of Biweekly Diamond Tip Microdermabrasion Treatments for Facial Skin Dryness and Age-Associated Features. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 16, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, D.M.-Y.; Bi, X.; Zhong, S.; Wu, Y. In Vivo Investigation of the Biostimulatory and Rejuvenating Effects of Small-Particle Cross-linked Hyaluronic Acid Injections in Photoaged Human Skin. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2023, 43, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Murawsky, M.; LaCount, T.; Kasting, G.B.; Li, S.K. Transepidermal water loss and skin conductance as barrier integrity tests. Toxicol. Vitr. 2018, 51, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rensburg, S.J.; Franken, A.; Du Plessis, J.L. Measurement of transepidermal water loss, stratum corneum hydration and skin surface pH in occupational settings: A review. Skin Res. Technol. 2019, 25, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, A.V.; Matts, P.J. Stratum Corneum Moisturization at the Molecular Level: An Update in Relation to the Dry Skin Cycle. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 124, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Seo, S.R.; Yoon, M.S.; Song, J.Y.; Lee, E.Y.; Lee, S.E. Microneedle fractional radiofrequency increases epidermal hyaluronan and reverses age-related epidermal dysfunction. Lasers Surg. Med. 2016, 48, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turlier, V.; Delalleau, A.; Casas, C.; Rouquier, A.; Bianchi, P.; Alvarez, S.; Josse, G.; Briant, A.; Dahan, S.; Saint-Martory, C.; et al. Association between collagen production and mechanical stretching in dermal extracellular matrix: In vivo effect of cross-linked hyaluronic acid filler. A randomised, placebo-controlled study. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2013, 69, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortonne, J.-P. Pigmentary changes of the ageing skin. Br. J. Dermatol. 1990, 122 (Suppl. S35), 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.-L.; Liu, W.; Gao, X.-M.; Yang, M.; Chang, J.-M. A Study of Normal Epidermal Melanocyte Distribution. Int. J. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 4, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, M.; Hearing, V.J. The Protective Role of Melanin Against UV Damage in Human Skin. Photochem. Photobiol. 2008, 84, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Makrantonaki, E. Clinical aspects and molecular diagnostics of skin aging. Clin. Dermatol. 2011, 29, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, T.L.; Christian, P.A.; Kesler, M.V.; Donohue, K.M.; Shelton, B.; Wakamatsu, K.; Ito, S.; D’Orazio, J. Pigment-independent cAMP-mediated epidermal thickening protects against cutaneous UV injury by keratinocyte proliferation. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, F.; Fujii, N.; Katsuyama, M.; Okumoto, S.; Matsusaki, M. Effects of radiofrequency and ultrasound on the turnover rate of skin aging components (skin extracellular matrix and epidermis) via HSP47-induced stimulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 525, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, H.; Koh, H.-J.; Park, S.-Y.; Park, W.-S.; Bae, I.-H.; Park, K.Y.; Kim, B.J. A combination trial of intradermal radiofrequency and hyaluronic acid filler for the treatment of nasolabial fold wrinkles: A pilot study. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2014, 16, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, E.J.; Choi, H.G.; Kim, H.; Park, W.-S.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, M.N. Novel Treatment Using Intradermal Radiofrequency and Hyaluronic Acid Filler to Correct Marionette Lines. Ann. Dermatol. 2015, 27, 351–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, M.Y.; Mun, S.K.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, H.; Park, W.-S. Efficacy and Safety of Hyaluronic Acid with and without Radiofrequency for Forehead Augmentation: A Pilot Study Using Three-Dimensional Imaging Analysis. Ann. Dermatol. 2016, 28, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.-K.; Jung, C.-J.; Lee, M.-Y.; Moon, I.-J.; Won, C.-H. The Evaluation of Efficacy and Safety of A Radiofrequency Hydro-Injector Device for the Skin around the Eye Area. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Almeida, A.T.; Figueredo, V.; da Cunha, A.L.G.; Casabona, G.; Costa de Faria, J.R.; Alves, E.V.; Sato, M.; Branco, A.; Guarnieri, C.; Palermo, E. Consensus Recommendations for the Use of Hyperdiluted Calcium Hydroxyapatite (Radiesse) as a Face and Body Biostimulatory Agent. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2019, 7, e2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.E.; Boo, Y.C. Combination of Glycinamide and Ascorbic Acid Synergistically Promotes Collagen Production and Wound Healing in Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina, V.; Gallo, A.; Tarantino, E.; Esposito, C.; Zerbinati, U.; Mocchi, R.; Monticelli, D.; Lotti, T.; Tirant, M.; Van Thuong, N.; et al. Viscoelastic properties and thermodynamic balance improvement of a hyaluronic acid hydrogel enriched with proline and glycyne. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2019, 33, 1955–1959. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kubik, P.; Jankau, J.; Rauso, R.; Galadari, H.; Protasoni, M.; Gruszczyński, W.; Grzanka, D.; Smolińska, M.; Antosik, P.; Piesiaków, M.L.; et al. HA PEGylated filler in association with an infrared energy device for the treatment of facial skin aging: 150 day follow-up data report. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurairattanaporn, N.; Amornpetkul, W.; Rutnin, S.; Vachiramon, V. The effect of combined hyaluronic acid filler injection and radiofrequency treatment: A clinic histological analysis. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 798–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrich, R.J.; Schultz, K.P.; Chamata, E.S.; Bellamy, J.L.; Alleyne, B. Minimally Invasive Approach to Skin Tightening of the Face and Body: A Systematic Review of Monopolar and Bipolar Radiofrequency Devices. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2022, 150, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Radiofrequency (% Change) | Radiofrequency + HA Mesotherapy (% Change) |
|---|---|---|
| Cutometer analysis | ||
| Stratum corneum hydration | +1.0 | +23.1 |
| TEWL | +3.9 | −5.8 |
| Melanin | −1.5 | −7.5 |
| Erythema | +3.0 | −7.2 |
| Smart Mirror-Skin analysis | ||
| RGB pore | - | −15.6 |
| RGB spots | - | −11.9 |
| UV pigmentation | - | −22.0 |
| UV damage | - | −10.8 |
| Pigmentation changes | - | −27.4 |
| Ultrasound analysis | ||
| Change in skin thickness | +1.4 | +2.7 |
| Change in epidermal thickness | +5.6 | +12.0 |
| Change in skin density | −18.1 | +12.4 |
| Change in epidermal density | +7.1 | +57.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Płatkowska, A.; Korzekwa, S.; Łukasik, B.; Zerbinati, N. Combined Bipolar Radiofrequency and Non-Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid Mesotherapy Protocol to Improve Skin Appearance and Epidermal Barrier Function: A Pilot Study. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081145
Płatkowska A, Korzekwa S, Łukasik B, Zerbinati N. Combined Bipolar Radiofrequency and Non-Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid Mesotherapy Protocol to Improve Skin Appearance and Epidermal Barrier Function: A Pilot Study. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(8):1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081145
Chicago/Turabian StylePłatkowska, Anna, Szymon Korzekwa, Bartłomiej Łukasik, and Nicola Zerbinati. 2023. "Combined Bipolar Radiofrequency and Non-Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid Mesotherapy Protocol to Improve Skin Appearance and Epidermal Barrier Function: A Pilot Study" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 8: 1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081145
APA StylePłatkowska, A., Korzekwa, S., Łukasik, B., & Zerbinati, N. (2023). Combined Bipolar Radiofrequency and Non-Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid Mesotherapy Protocol to Improve Skin Appearance and Epidermal Barrier Function: A Pilot Study. Pharmaceuticals, 16(8), 1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081145








