A Comparative Pharmacokinetic Study of Fexuprazan 10 mg: Demonstrating Bioequivalence with the Reference Formulation and Evaluating Steady State
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Demographic Characteristics
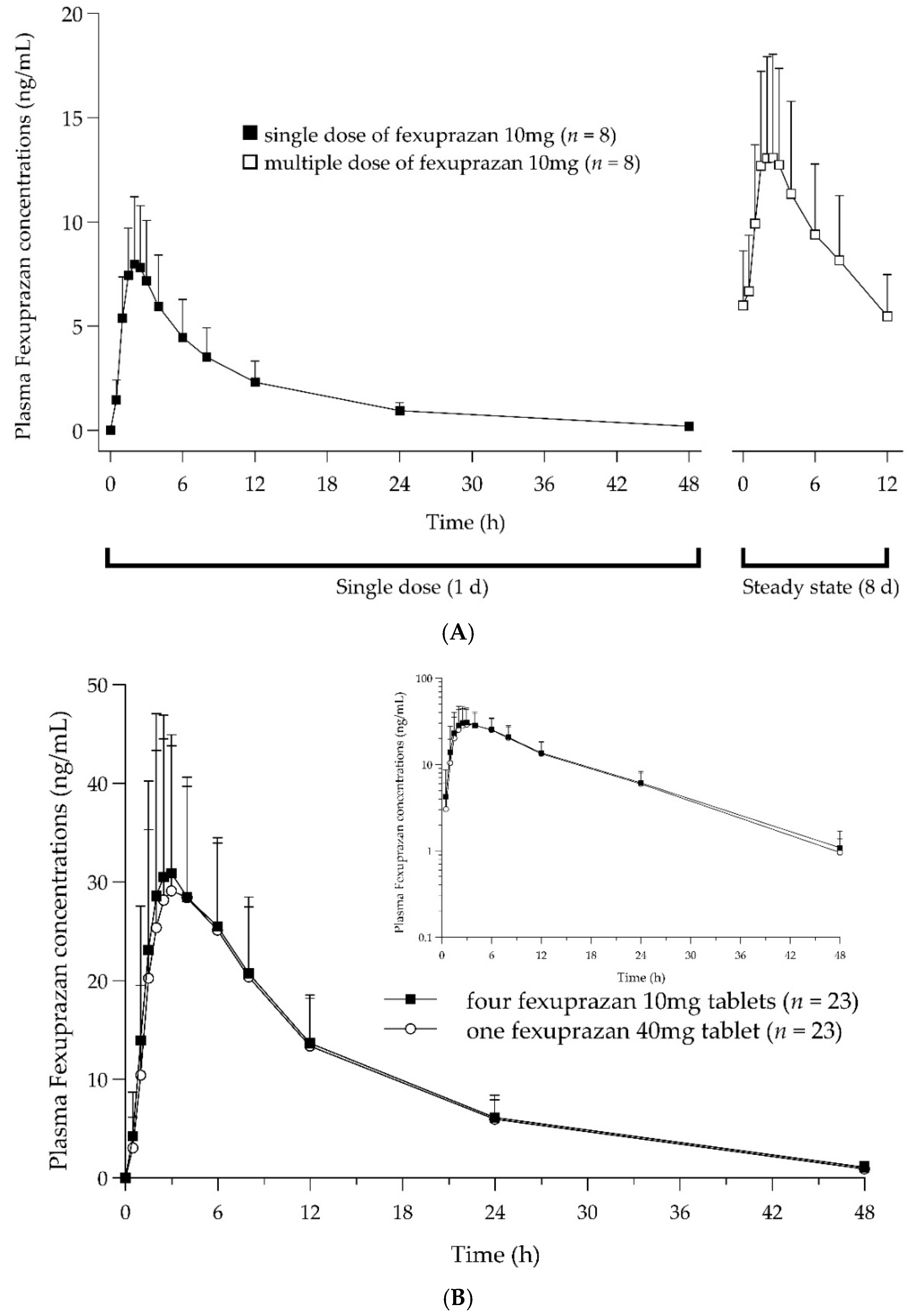
2.2. PKs of Fexuprazan 10 mg after Single and Multiple Administration (Part 1)
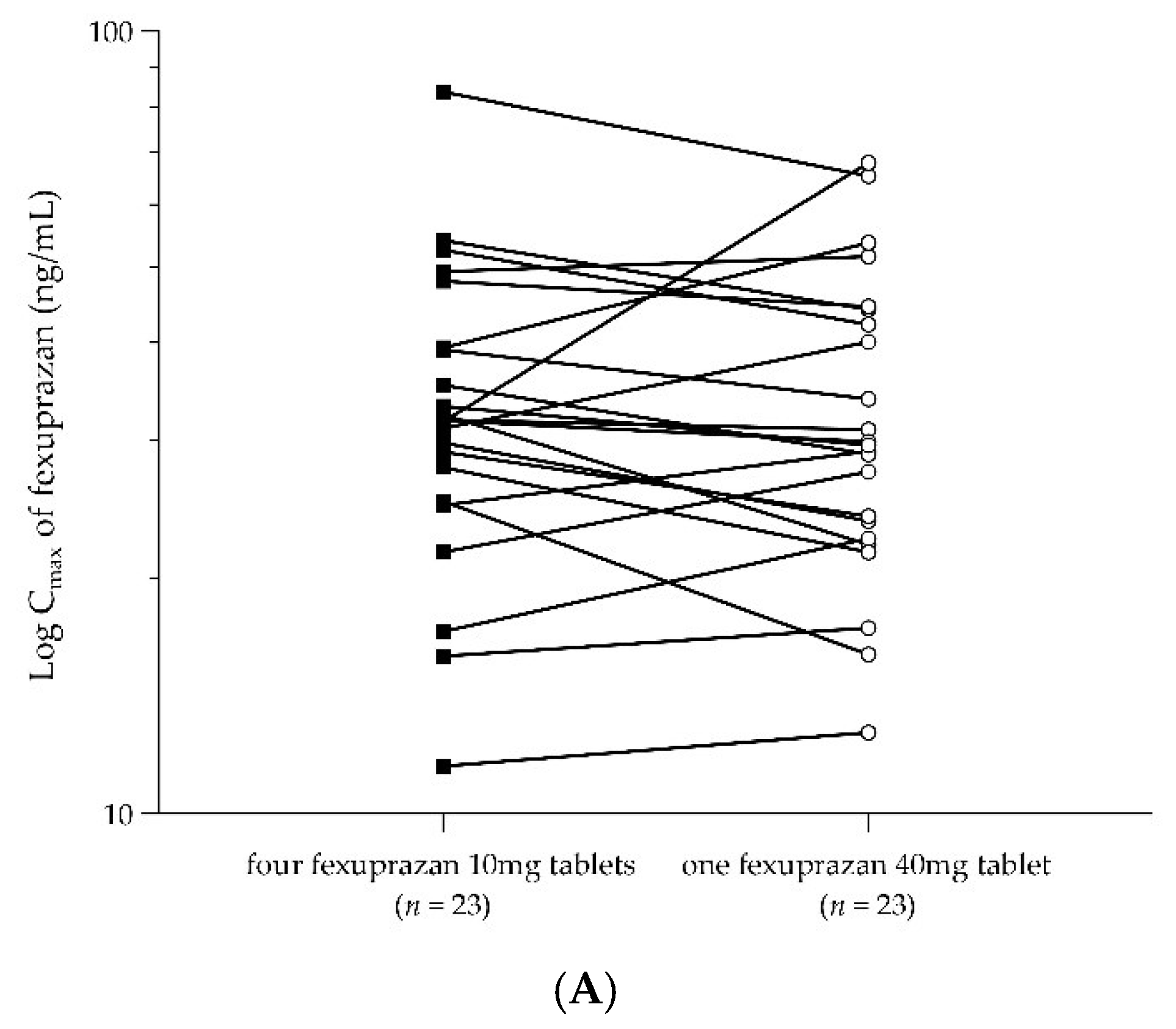
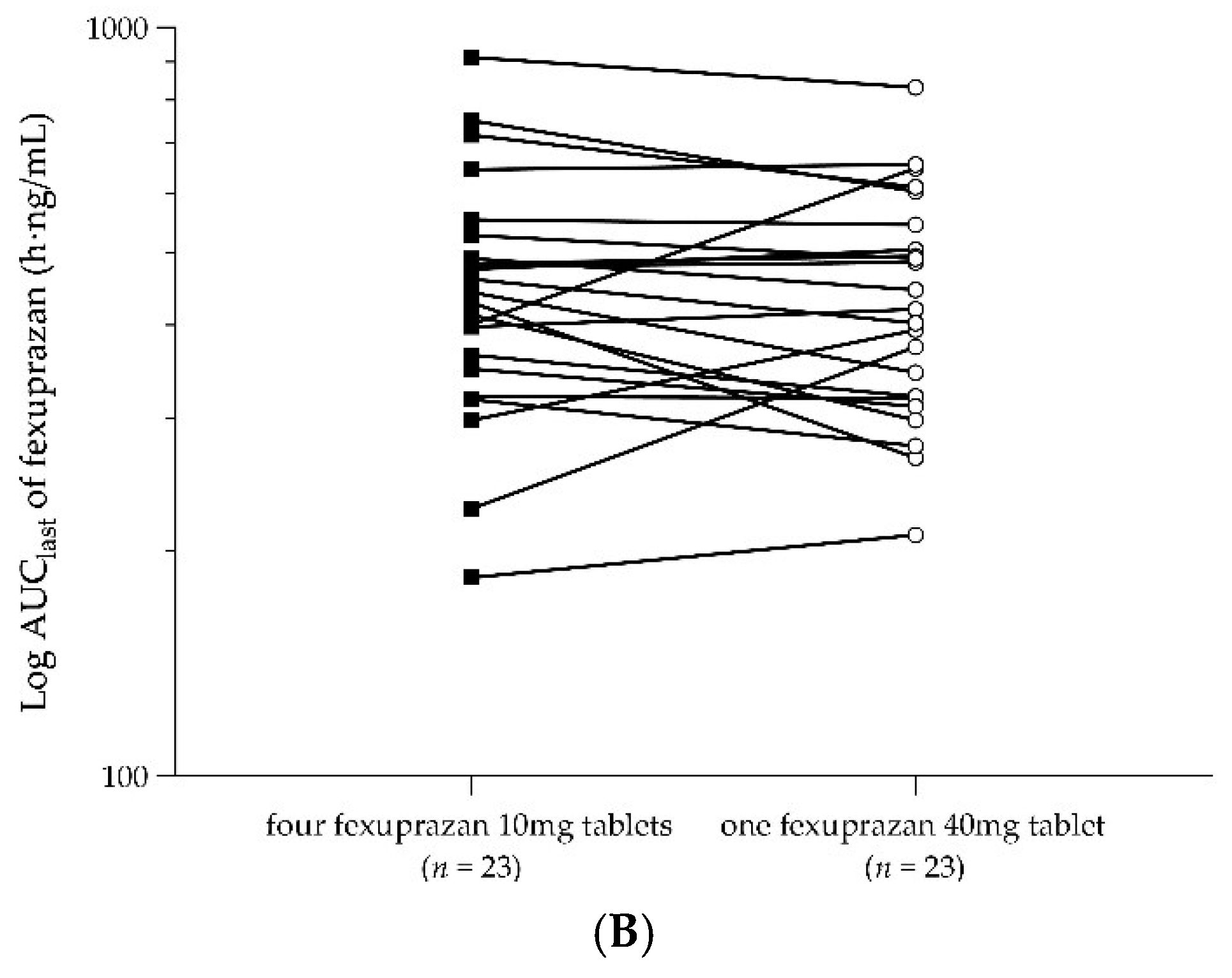
2.3. PKs of a Single Dose of Four Fexuprazan 10 mg Tablets and a Single Dose of One Fexuprazan 40 mg Tablet (Part 2)
2.4. Safety Assessment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
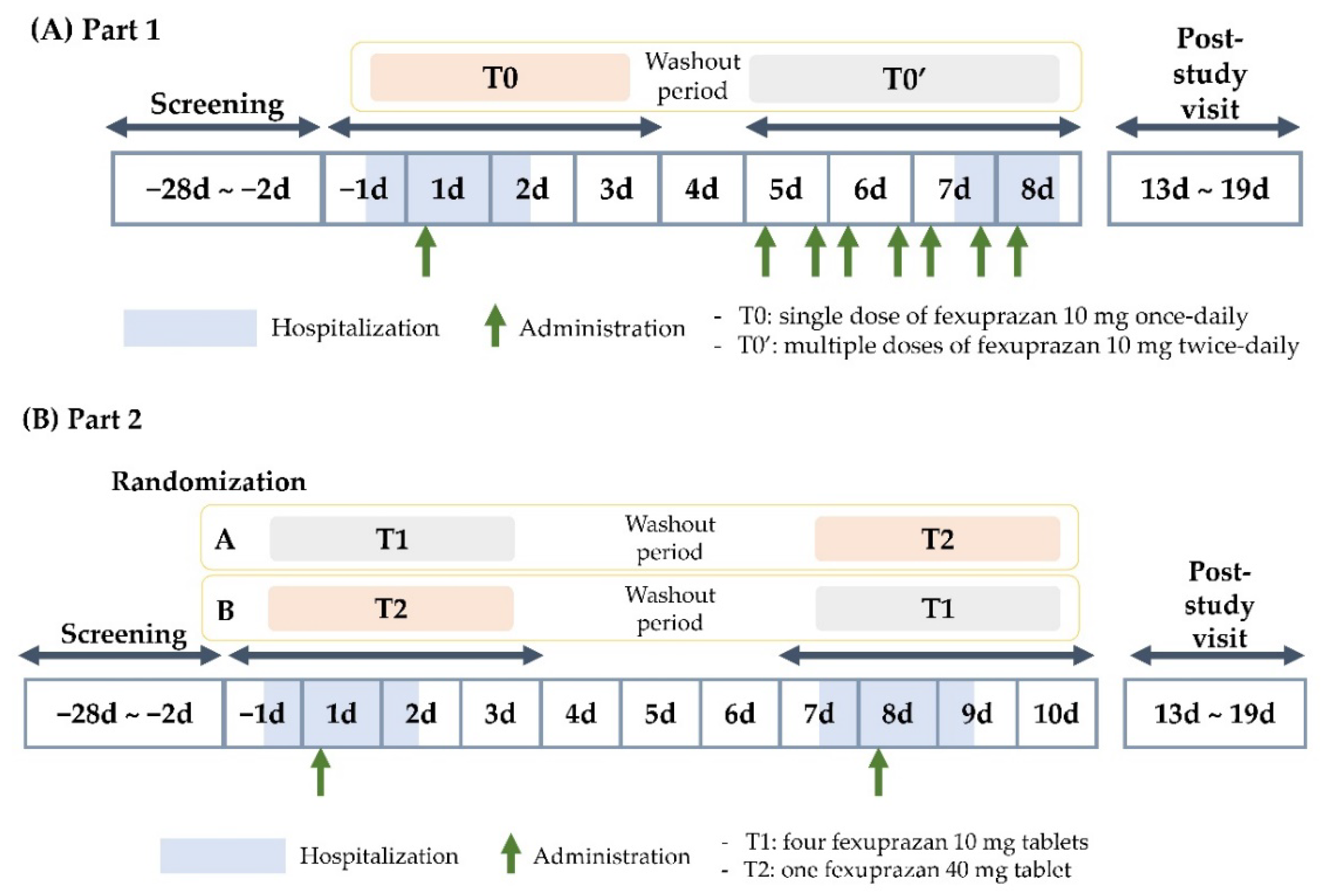
4.1. Participants and Study Design
4.2. Determination of Plasma Fexuprazan Concentration
4.3. PK Assessment
4.4. Safety and Tolerability Assessment
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Welage, L.S.; Berardi, R.R. Evaluation of omeprazole, lansoprazole, pantoprazole, and rabeprazole in the treatment of acid-related diseases. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 2000, 40, 52–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.K.; Ko, B.J.; Kim, E.Y.; Han, B.D.; Cho, K.H. Fast Eating Speed Increases the Risk of Endoscopic Erosive Gastritis in Korean Adults. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2015, 36, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Azer, S.A.; Akhondi, H. Gastritis; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, C.M.; Keam, S.J. Rabeprazole: A review of its use in the management of gastric acid-related diseases in adults. Drugs 2009, 69, 1373–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.M.; Vagin, O.; Munson, K.; Kidd, M.; Modlin, I.M.; Sachs, G. Molecular mechanisms in therapy of acid-related diseases. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 264–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- den Hollander, W.J.; Kuipers, E.J. Current pharmacotherapy options for gastritis. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2012, 13, 2625–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megha, R.; Farooq, U.; Lopez, P.P. Stress-Induced Gastritis; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hanafy, A.S.; Seleem, W.M. Refractory Helicobacter pylori gastritis: The hidden predictors of resistance. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 19, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiwagi, H. Ulcers and gastritis. Endoscopy 2005, 37, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshima, T.; Miwa, H. Potent Potassium-competitive Acid Blockers: A New Era for the Treatment of Acid-related Diseases. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 24, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachs, G.; Shin, J.M.; Hunt, R. Novel approaches to inhibition of gastric acid secretion. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2010, 12, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yoo, H.; Shin, W.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.; Kim, E.; Kim, A. Size-reduced fexuprazan 20 mg demonstrated the optimal bioavailability and bioequivalence with the reference formulation. Transl. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 31, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzka, D.A.; Kahrilas, P.J. Potassium-Competitive Acid Blocker Suppression of Gastric Acid in Erosive Esophagitis: Is Stronger and Longer Better? Gastroenterology 2023, 164, 14–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. 2022 Drug Approval Report. 2023. Available online: https://www.mfds.go.kr/eng/brd/m_19/view.do?seq=70438&srchFr=&srchTo=&srchWord=&srchTp=&itm_seq_1=0&itm_seq_2=0&multi_itm_seq=0&company_cd=&company_nm=&page=1 (accessed on 29 June 2023).
- Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. 2021 Drug Approval Report. 2022. Available online: https://www.mfds.go.kr/eng/brd/m_19/down.do?brd_id=eng0004&seq=70437&data_tp=A&file_seq=1 (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- Daewoong Pharmaceutical’s ‘Fexuclue’: First Domestic P-CAB Agent to Obtain Indication for Gastritis Korea Biomedical Review. 2022. Available online: http://www.docdocdoc.co.kr/news/articleView.html?idxno=2026314 (accessed on 20 August 2022).
- US Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research; Food Drug Adminsitration. Size, Shape, and Other Physical Attributes of Generic Tablets and Capsules Guidance for Industry. 2022. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/size-shape-and-other-physical-attributes-generic-tablets-and-capsules (accessed on 3 October 2022).
- Lee, K.N.; Lee, O.Y.; Chun, H.J.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, S.W.; Park, K.S.; Lee, K.L.; Choi, S.C.; Jang, J.Y.; et al. Randomized controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of fexuprazan compared with esomeprazole in erosive esophagitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 6294–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.H.; Choi, M.G.; Kim, J.I.; Lee, S.T.; Chun, H.J.; Lee, K.L.; Choi, S.C.; Jang, J.Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Kim, J.G.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Fexuprazan in Patients with Acute or Chronic Gastritis. Gut Liver 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunwoo, J.; Oh, J.; Moon, S.J.; Ji, S.C.; Lee, S.H.; Yu, K.S.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, A.; Jang, I.J. Safety, tolerability, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of DWP14012, a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker, in healthy male participants. Aliment Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 48, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibli, F.; Kitayama, Y.; Fass, R. Novel Therapies for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Beyond Proton Pump Inhibitors. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2020, 22, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakil, N.B.; Traxler, B.; Levine, D. Dysphagia in patients with erosive esophagitis: Prevalence, severity, and response to proton pump inhibitor treatment. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2004, 2, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiocca, J.C.; Olmos, J.A.; Salis, G.B.; Soifer, L.O.; Higa, R.; Marcolongo, M.; Argentinean Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Study Group. Prevalence, clinical spectrum and atypical symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux in Argentina: A nationwide population-based study. Aliment Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 22, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.G.; Jeon, I.; Park, S.A.; Lee, A.; Yu, K.S.; Jang, I.J.; Lee, S. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of DWP14012 (fexuprazan) in healthy subjects with different ethnicities. Aliment Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 52, 1648–1657. [Google Scholar]
- Maganti, L.; Panebianco, D.L.; Maes, A.L. Evaluation of methods for estimating time to steady state with examples from phase 1 studies. AAPS J. 2008, 10, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
| Part 1: Single Dose vs. Multiple Doses | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Single Dose Daily 1 (n = 8) | Two Doses Daily 1 (n = 8) |
| Cmax or Cmax,ss (ng/mL) | 8.26 ± 2.96 | 13.85 ± 4.96 |
| Cmin,ss (ng/mL) | 5.36 ± 2.07 | |
| Tmax or Tmax,ss (h) | 2.25 (1.50–3.00) | 2.00 (1.50–3.00) |
| AUC0–12h or AUC0–12h,ss (h∙ng/mL) | 53.47 ± 20.83 | 109.73 ± 40.52 |
| AUClast (h∙ng/mL) | 84.91 ± 36.82 | |
| Accumulation ratio | 2.11 | |
| Part 2: Four 10 mg Tablets vs. One 40 mg Tablet | ||
| Parameter | 4 × fexuprazan 10 mg 2 (n = 23) | 1 × fexuprazan 40 mg 2 (n = 23) |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 34.62 ± 15.44 | 33.87 ± 15.04 |
| Tmax (h) | 2.50 (1.50–6.00) | 3.00 (2.00–6.00) |
| AUClast (h∙ng/mL) | 463.19 ± 169.78 | 446.24 ± 152.94 |
| AUCinf (h∙ng/mL) | 479.88 ± 175.31 | 459.82 ± 154.55 |
| Vz/F (L) | 1372.91 ± 697.78 | 1341.60 ± 601.42 |
| t1/2 (h) | 9.91 ± 2.00 | 9.44 ± 1.65 |
| CL/F (L/h) | 94.60 ± 36.74 | 96.81 ± 32.69 |
| Pharmacokinetic Parameters | No. | Geometric LS Mean | Geometric LS Mean Ratio (T1/T2) | IntraCV(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 1 | T2 1 | Point Estimate | 90% CI | |||
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 23 | 31.46 | 30.57 | 1.0290 | 0.9352–1.1321 | 19.0 |
| AUClast (h∙ng/mL) | 23 | 431.30 | 419.15 | 1.0290 | 0.9476–1.1174 | 16.3 |
| Adverse Events | 4 × Fexuprazan 10 mg 1 (n = 24) | 1 × Fexuprazan 40 mg 1 (n = 24) | Total (n = 24) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Participants with TEAEs | 2 (8.3) (3) | 4 (16.7) (5) | 5 (20.8) (8) |
| Abdominal pain | 1 (4.2) (1) | 1 (4.2) (1) | 2 (8.3) (2) |
| Diarrhea | 1 (4.2) (1) | 1 (4.2) (1) | 1 (4.2) (2) |
| Haematochezia | 1 (4.2) (1) | 1 (4.2) (1) | |
| Nausea | 1 (4.2) (1) | 1 (4.2) (1) | |
| Oedema peripheral | 1 (4.2) (1) | 1 (4.2) (1) | |
| Headache | 1 (12.5) (1) | 1 (4.2) (1) | 1 (4.2) (2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, W.; Yang, A.-Y.; Park, H.; Lee, H.; Yoo, H.; Kim, A. A Comparative Pharmacokinetic Study of Fexuprazan 10 mg: Demonstrating Bioequivalence with the Reference Formulation and Evaluating Steady State. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081141
Shin W, Yang A-Y, Park H, Lee H, Yoo H, Kim A. A Comparative Pharmacokinetic Study of Fexuprazan 10 mg: Demonstrating Bioequivalence with the Reference Formulation and Evaluating Steady State. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(8):1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081141
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Wonsuk, A-Young Yang, Hyung Park, Hyejung Lee, Hyounggyoon Yoo, and Anhye Kim. 2023. "A Comparative Pharmacokinetic Study of Fexuprazan 10 mg: Demonstrating Bioequivalence with the Reference Formulation and Evaluating Steady State" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 8: 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081141
APA StyleShin, W., Yang, A.-Y., Park, H., Lee, H., Yoo, H., & Kim, A. (2023). A Comparative Pharmacokinetic Study of Fexuprazan 10 mg: Demonstrating Bioequivalence with the Reference Formulation and Evaluating Steady State. Pharmaceuticals, 16(8), 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081141






