Pregabalin–Tolperisone Combination to Treat Neuropathic Pain: Improved Analgesia and Reduced Side Effects in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
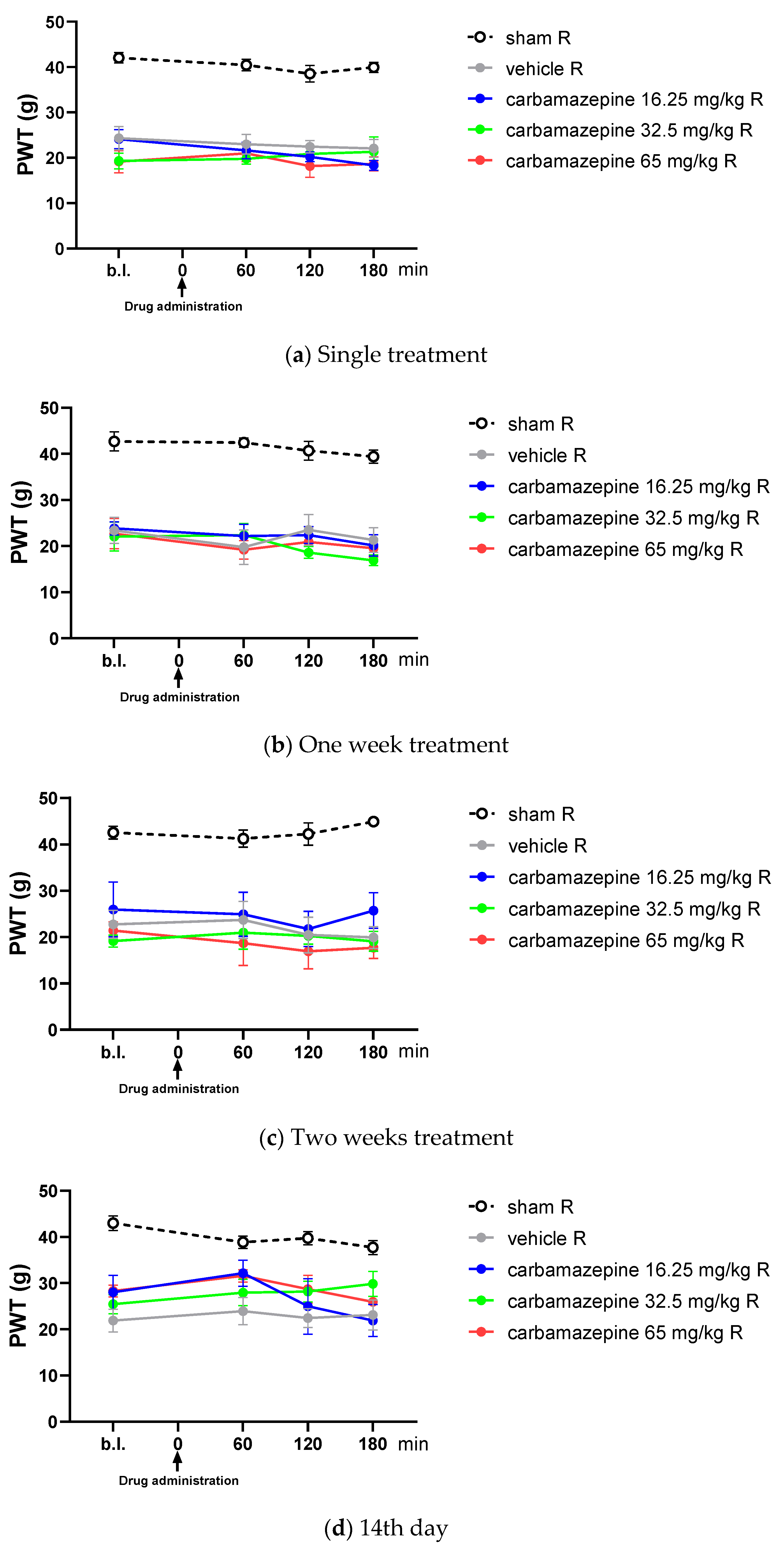
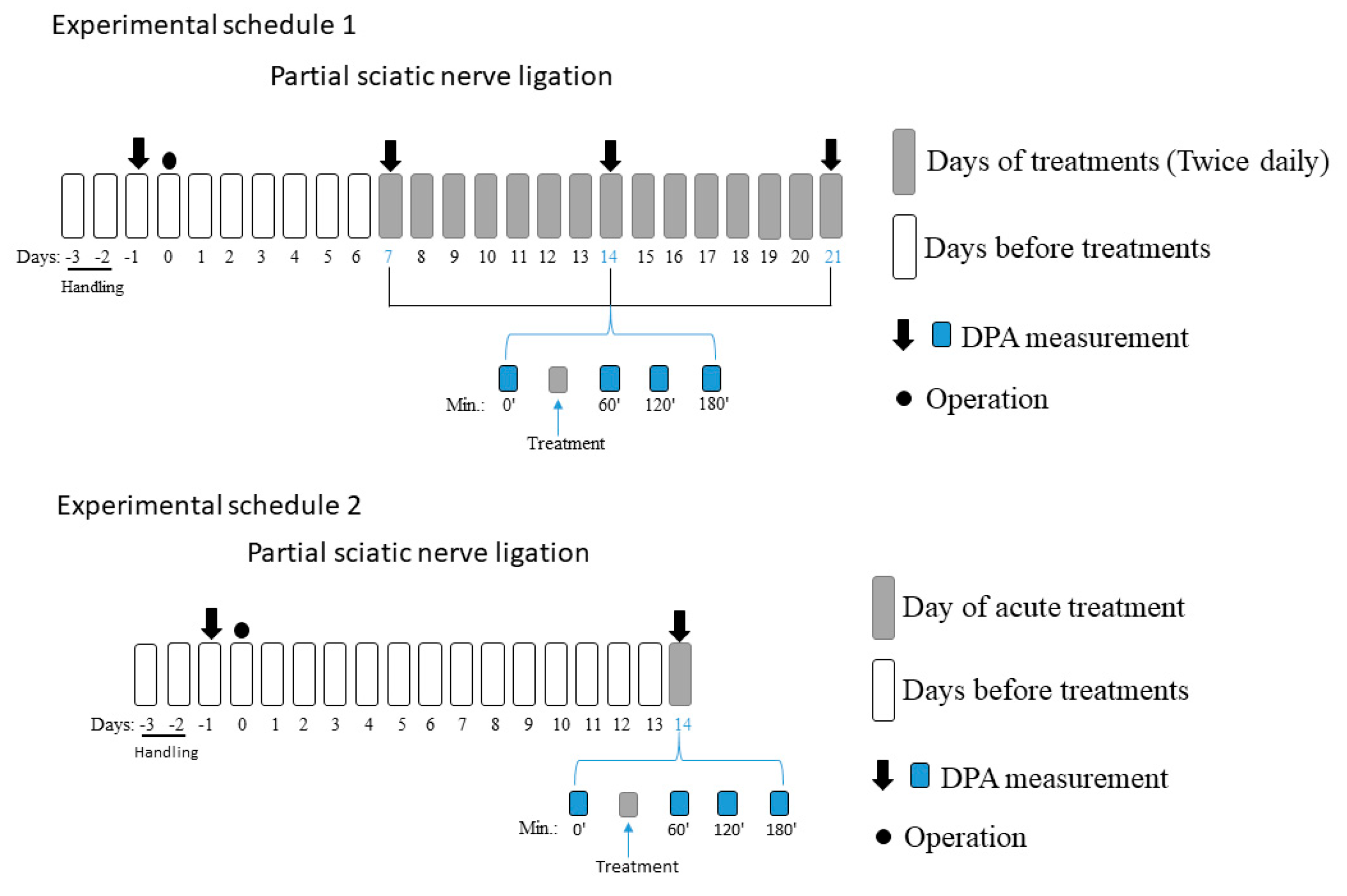
2.1. Chronic Treatment Is Essential for Both Tolperisone and Pregabalin to Alleviate Tactile Allodynia Evoked by Partial Sciatic Nerve Ligation (pSNL)
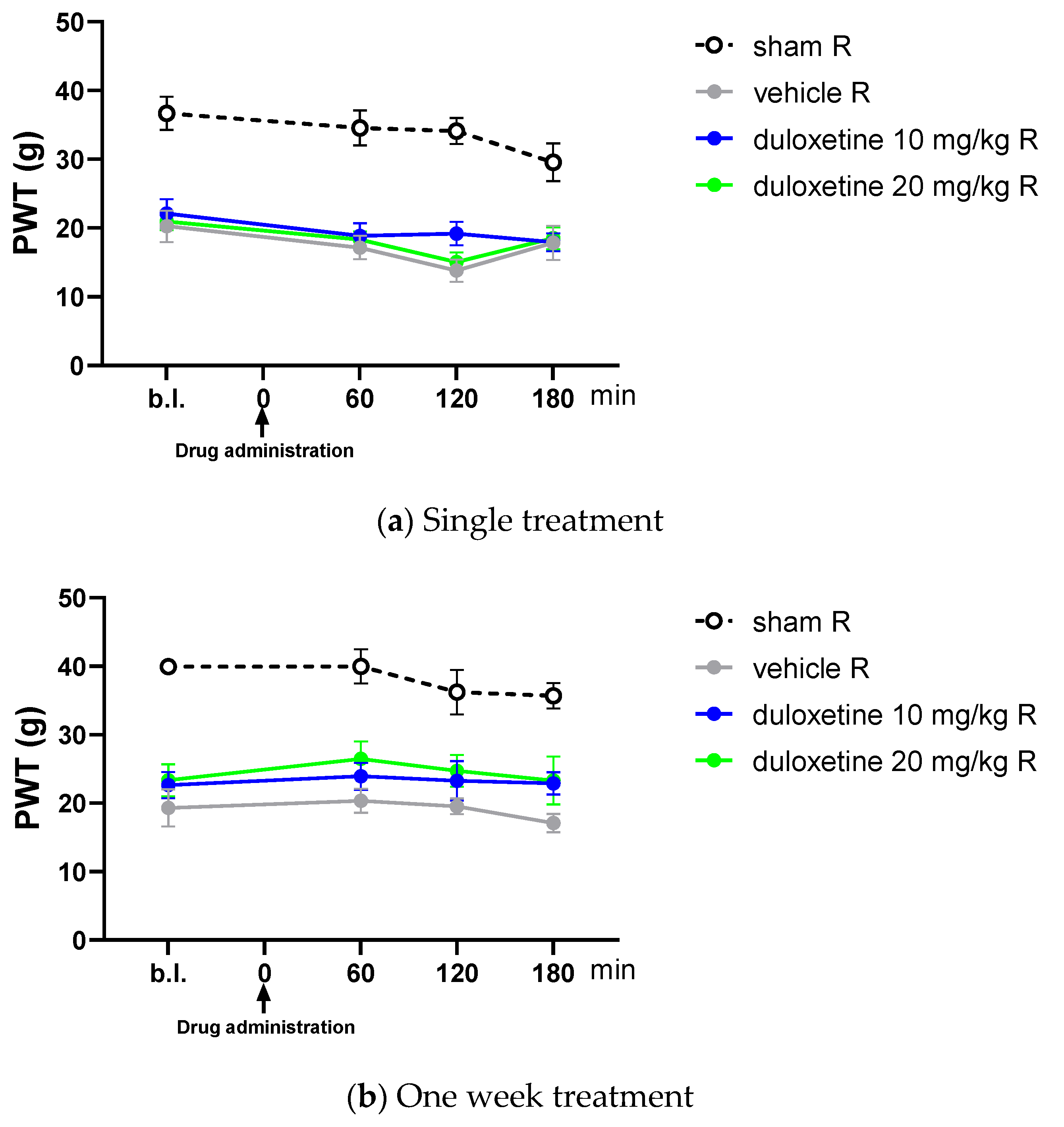
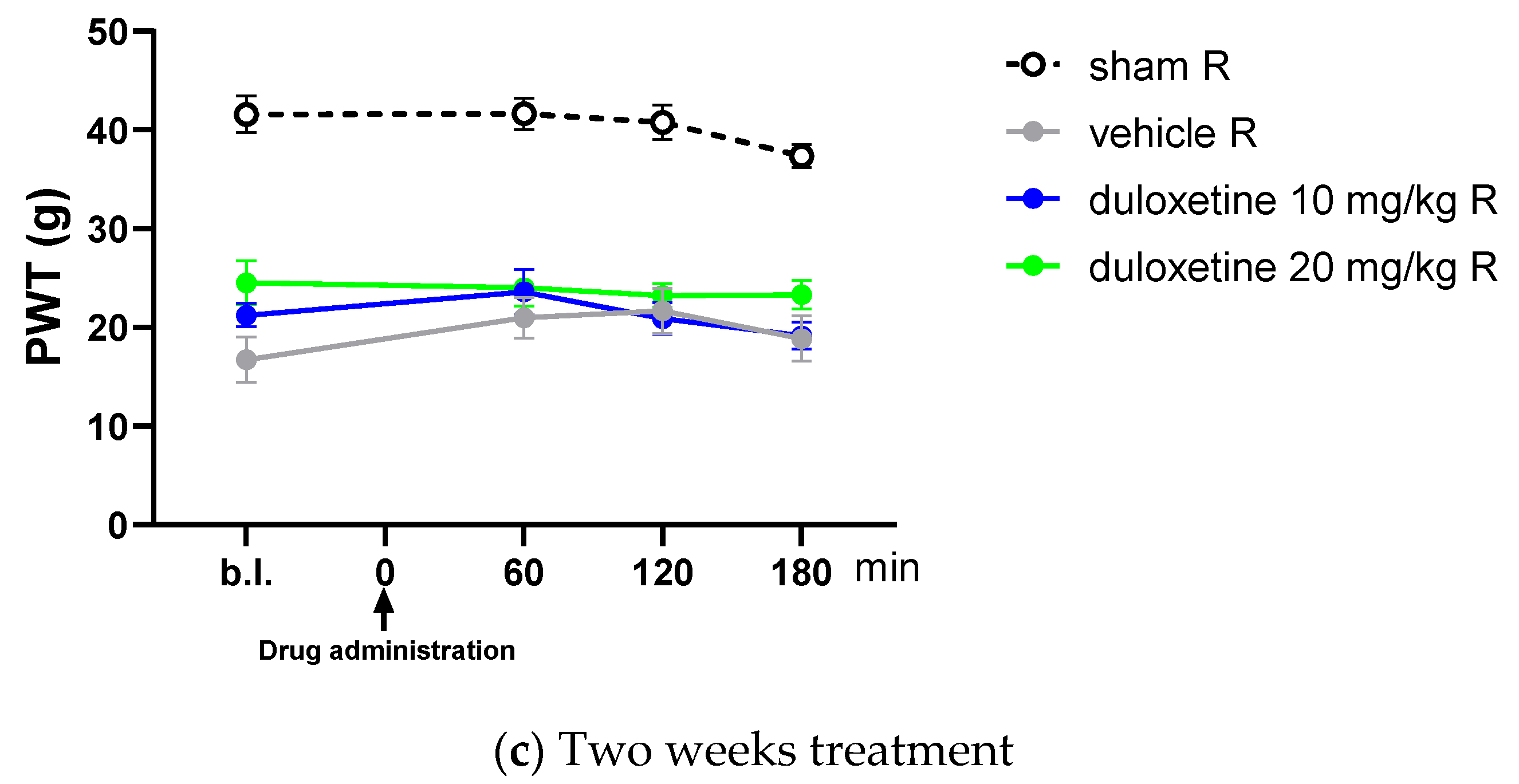
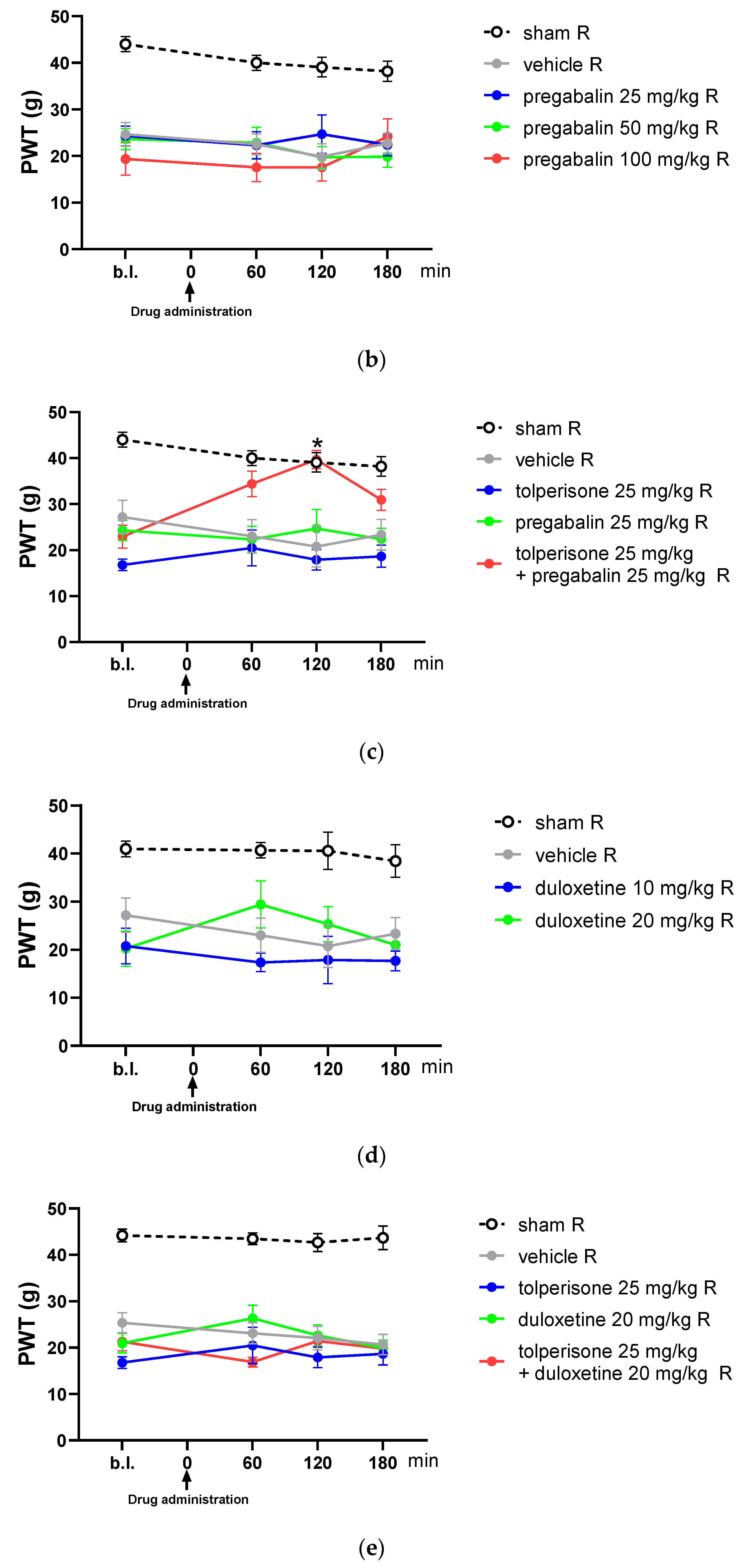
2.2. Acute Oral Co-Administration of Tolperisone with Pregabalin but Not Duloxetine Alleviates Tactile Allodynia of Rats with Neuropathic Pain Evoked by pSNL
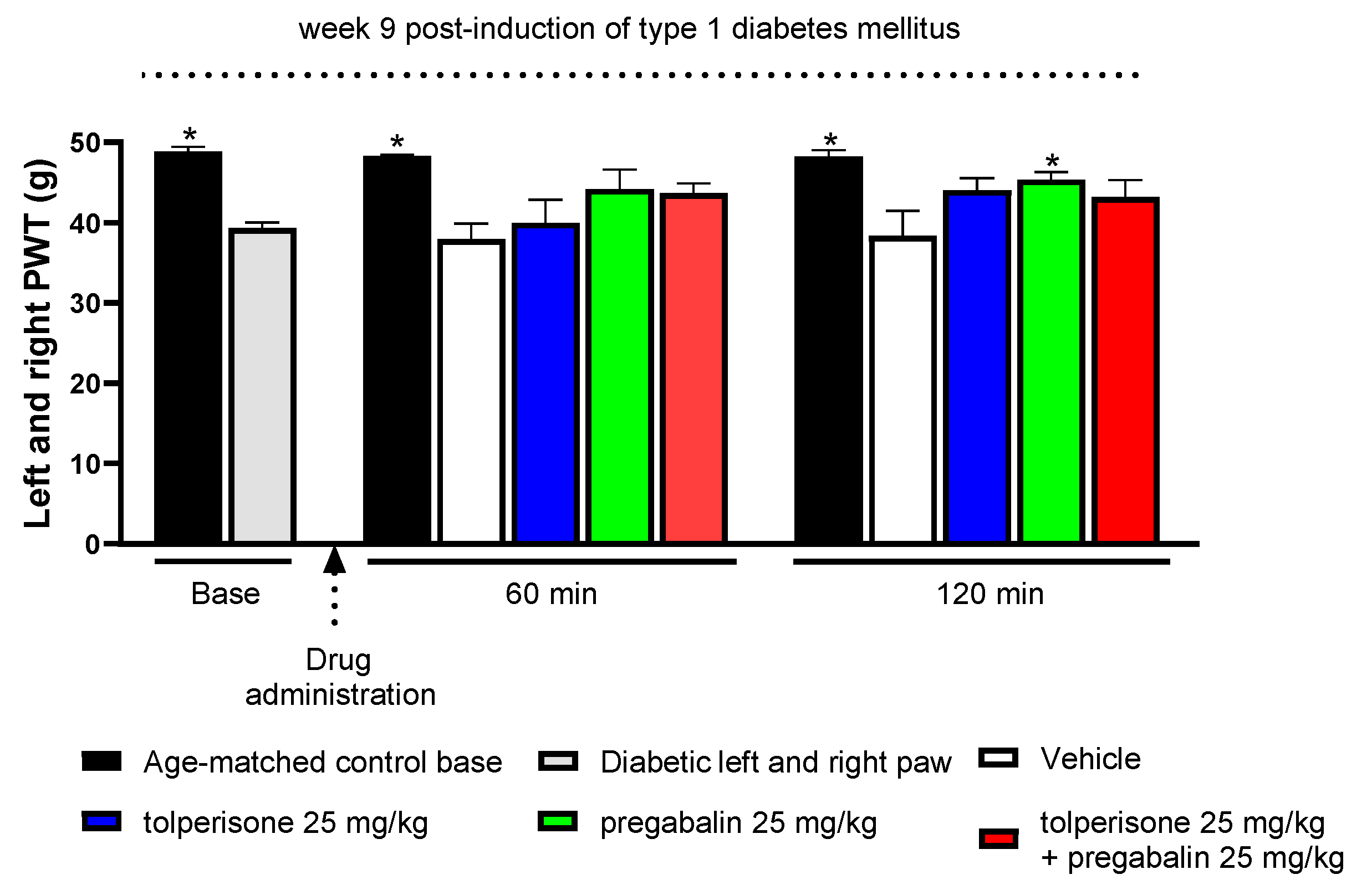
2.3. The Impact of Pregabalin and Tolperisone on Peripheral Neuropathic Pain of Diabetic Rats after Acute Administration
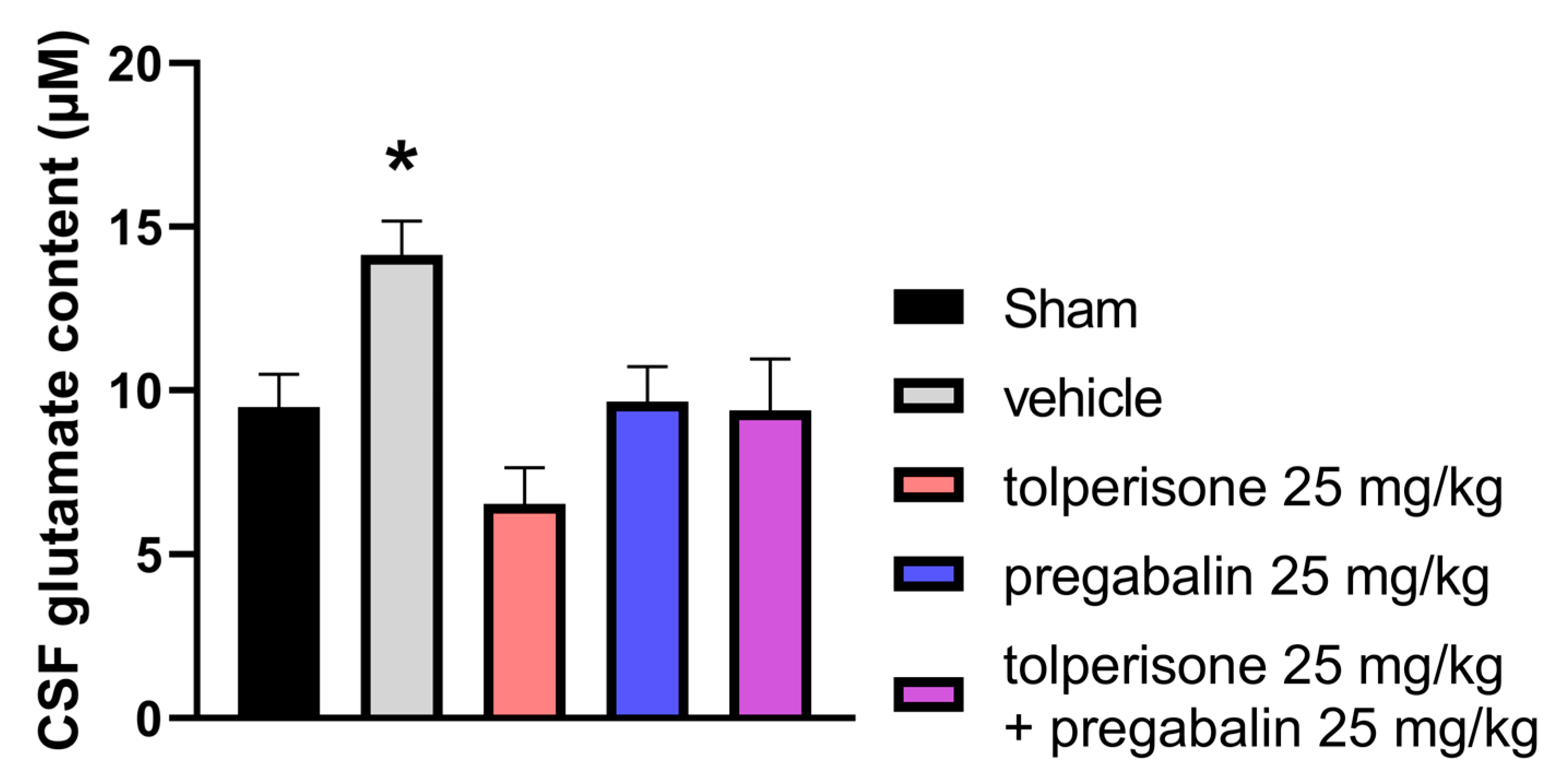
2.4. Effects of Acute Treatment with Tolperisone, Pregabalin, or their Combination on CSF Glutamate Content in Rats with pSNL-Induced Neuropathic Pain
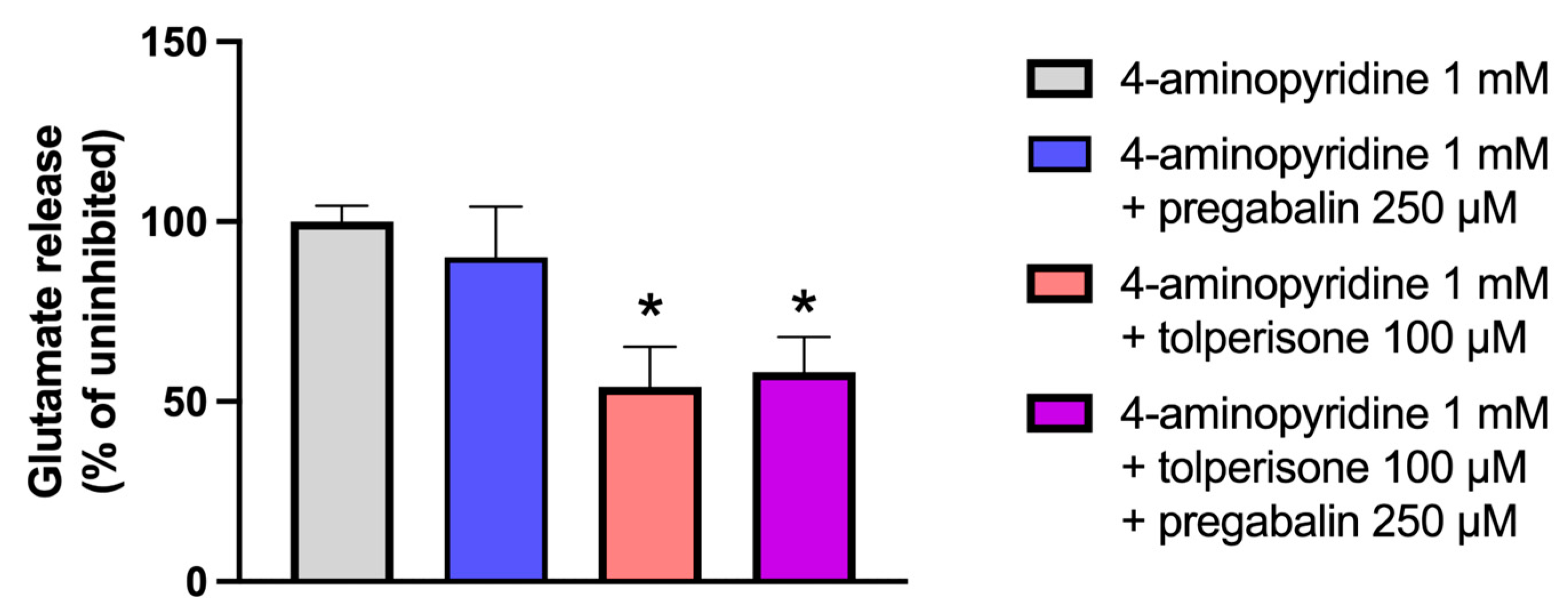
2.5. Effects of Treatment with Tolperisone, Pregabalin, or Their Combination on 4-Aminopyridine-Induced Glutamate Release from Rat Synaptosomes
2.6. The Impact of Pregabalin, Tolperisone, and Pregabalin/Tolperisone Combination on Motor Dysfunction and Coordination Imbalance in Naïve Rats
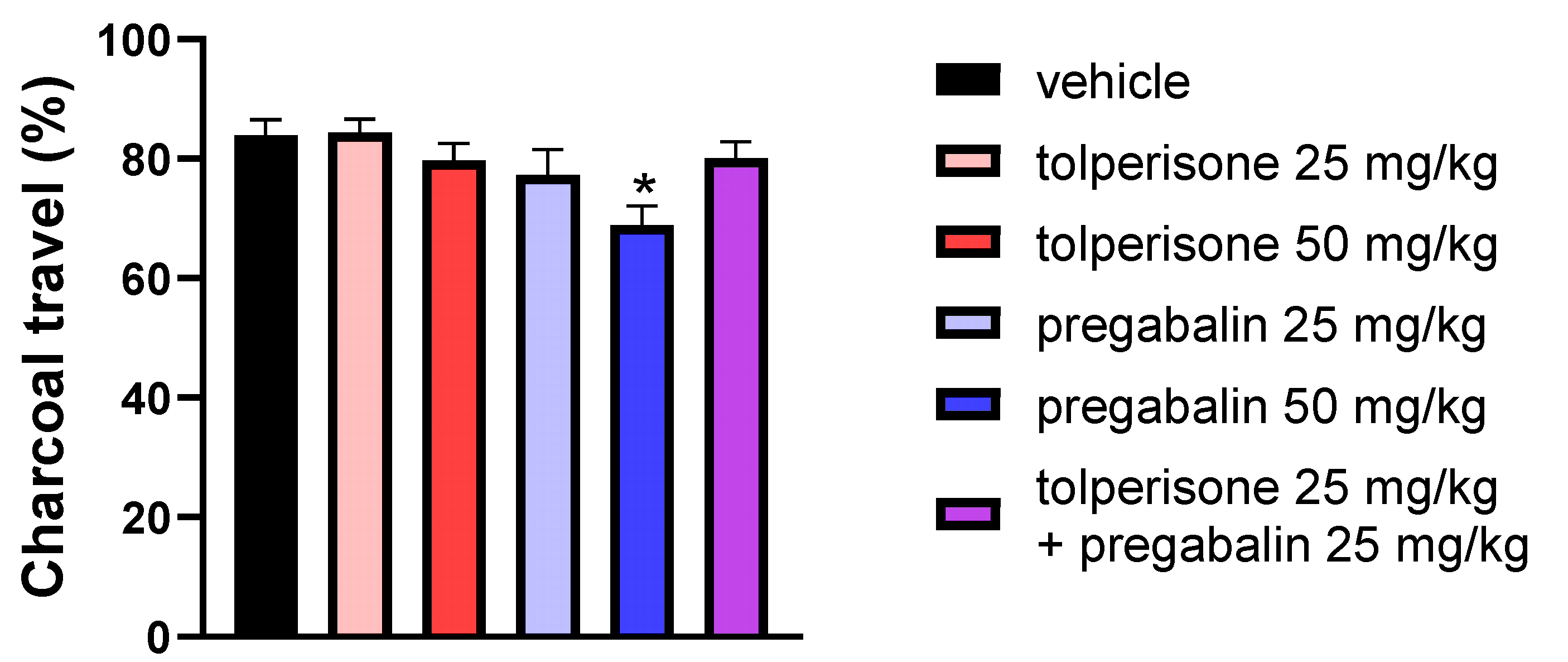
2.7. The Impact of Pregabalin, Tolperisone, and Pregabalin/Tolperisone Combination on Gastrointestinal (GI) Transit in Naïve Rats
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Chemicals
4.3. Experimental Protocols of the Animal Study
4.4. Partial Sciatic Nerve Ligation (pSNL)
4.5. Assessment of Mechanical Allodynia
4.6. Treatment of Neuropathic Animals
4.7. Motor Function Test
4.8. Determination of GastroIntestinal Peristalsis in Rats
4.9. Animal Model of Type 1 Diabetes-Induced Polyneuropathic Pain
4.10. Capillary Electrophoresis Analysis of CSF Glutamate Content
4.11. Glutamate Release from Synaptosomes
4.12. Enzyme-Linked Fluorescent Assay of Glutamate Released from Synaptosomes
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

Appendix B
References
- Al-Khrasani, M.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Balogh, M.; Király, K.; Barsi, S.; Hajnal, B.; Köles, L.; Zádori, Z.S.; Harsing, L.G., Jr. Glycine transporter inhibitors: A new avenue for managing neuropathic pain. Brain. Res. Bull. 2019, 152, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Sindrup, S.H.; Jensen, T.S. The evidence for pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain. Pain 2010, 150, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attal, N. Pharmacological treatments of neuropathic pain: The latest recommendations. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 175, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alles, S.R.A.; Cain, S.M.; Snutch, T.P. Pregabalin as a Pain Therapeutic: Beyond Calcium Channels; Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience; Frontiers Media S.A.: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 14. [Google Scholar]
- Kremer, M.; Yalcin, I.; Goumon, Y.; Wurtz, X.; Nexon, L.; Daniel, D.; Megat, S.; Ceredig, R.A.; Ernst, C.; Turecki, G.; et al. A dual noradrenergic mechanism for the relief of neuropathic allodynia by the antidepressant drugs duloxetine and amitriptyline. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 9934–9954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Attal, N.; Haroutounian, S.; McNicol, E.; Baron, R.; Dworkin, R.H.; Gilron, I.; Haanpää, M.; Hansson, P.; Jensen, T.S.; et al. Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickering, G.; Martin, E.; Tiberghien, F.; Delorme, C.; Mick, G. Localized neuropathic pain: An expert consensus on local treatments. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 2709–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meacham, K.; Shepherd, A.; Mohapatra, D.P.; Haroutounian, S. Neuropathic Pain: Central vs. Peripheral Mechanisms. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2017, 21, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffa, R.B.; Pergolizzi, J.V.; Tallarida, R.J. The Determination and Application of Fixed-Dose Analgesic Combinations for Treating Multimodal Pain. J. Pain 2010, 11, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadzadeh, A.; Lakatos, P.P.; Balogh, M.; Zádor, F.; Karádi, D.; Zádori, Z.S.; Király, K.; Galambos, A.R.; Barsi, S.; Riba, P. Pharmacological Evidence on Augmented Antiallodynia Following Systemic Co-Treatment with GlyT-1 and GlyT-2 Inhibitors in Rat Neuropathic Pain Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffa, R.B.; Clark-Vetri, R.; Tallarida, R.J.; Wertheimer, A.I. Combination strategies for pain management. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2003, 4, 1697–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffa, R.B. Pharmacology of oral combination analgesics: Rational therapy for pain. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2001, 26, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilron, I.; Bailey, J.M.; Tu, D.; Holden, R.R.; Jackson, A.C.; Houlden, R.L. Nortriptyline and gabapentin, alone and in combination for neuropathic pain: A double-blind, randomised controlled crossover trial. Lancet 2009, 374, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, V.; Singh, N.; Singh Jaggi, A. Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net Pregabalin in Neuropathic Pain: Evidences and Possible Mechanisms. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2014, 12, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, M.J.; Cox, P.J.; Stott, E.; Melrose, H.; Offord, J.; Su, T.Z.; Bramwell, S.; Corradini, L.; England, S.; Winks, J.; et al. Identification of the α2-δ-1 subunit of voltage-calcium calcium channels as a molecular target for pain mediating the analgesic actions of pregabalin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17537–17542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilron, I.; Bailey, J.M.; Tu, D.; Holden, R.R.; Weaver, D.F.; Houlden, R.L. Morphine, gabapentin, or their combination for neuropathic pain. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1324–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, M.; O’Brien, C.; Wilson, M.C. Prolonged-release oxycodone enhances the effects of existing gabapentin therapy in painful diabetic neuropathy patients. Eur. J. Pain. 2008, 12, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zin, C.S.; Nissen, L.M.; O’Callaghan, J.P.; Duffull, S.B.; Smith, M.T.; Moore, B.J. A randomized, controlled trial of oxycodone versus placebo in patients with postherpetic neuralgia and painful diabetic neuropathy treated with pregabalin. J. Pain. 2010, 11, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, E.A.; Dickenson, A.H. A Combination of Gabapentin and Morphine Mediates Enhanced Inhibitory Effects on Dorsal Horn Neuronal Responses in a Rat Model of Neuropathy. Anesthesiology 2002, 96, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahm, T.S.; Ahn, H.J.; Ryu, S.; Gwak, M.S.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, J.K.; Yu, J.M. Combined carbamazepine and pregabalin therapy in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Br. J. Anaesth. 2012, 109, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balanaser, M.; Carley, M.; Baron, R.; Finnerup, N.B.; Moore, R.A.; Rowbotham, M.C.; Chaparro, L.E.; Gilron, I. Combination pharmacotherapy for the treatment of neuropathic pain in adults: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain 2022, 164, 230–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratzel, H.G.; Alken, R.-G.; Ramm, S. Efficacy and tolerance of repeated oral doses of tolperisone hydrochloride in the treatment of painful reflex muscle spasm: Results of a prospective placebo-controlled double-blind trial. Pain 1996, 67, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimamoto, K. Glutamate transporter blockers for elucidation of the function of excitatory neurotransmission systems. Chem. Rec. 2008, 8, 182–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, D.; Lohberger, B.; Steinecker, B.; Schmidt, K.; Quasthoff, S.; Schreibmayer, W. A comparative study of the action of tolperisone on seven different voltage dependent sodium channel isoforms. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 538, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novales-Li, P.; Sun, X.-P.; Takeuchi, H. Suppression of calcium current in a snail neurone by eperisone and its analogues. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1989, 168, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quasthoff, S.; Pojer, C.; Mori, A.; Hofer, D.; Liebmann, P.; Kieseier, B.C.; Schreibmayer, W. No blocking effects of the pentapeptide QYNAD on Na+ channel subtypes expressed in Xenopus oocytes or action potential conduction in isolated rat sural nerve. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 352, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakatos, P.P.; Karádi, D.; Galambos, A.R.; Essmat, N.; Király, K.; Laufer, R.; Geda, O.; Zádori, Z.S.; Tábi, T.; Al-Khrasani, M.; et al. The Acute Antiallodynic Effect of Tolperisone in Rat Neuropathic Pain and Evaluation of Its Mechanism of Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, M.; Zádor, F.; Zádori, Z.S.; Shaqura, M.; Király, K.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Varga, B.; Lázár, B.; Mousa, S.A.; Hosztafi, S.; et al. Efficacy-Based Perspective to Overcome Reduced Opioid Analgesia of Advanced Painful Diabetic Neuropathy in Rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thesleff, S. Aminopyridines and Synaptic Transmission. Neuroscience 1980, 5, 1413–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Prieto, J.; Budd, D.C.; Herrero, I.; Vázquez, E.; Nicholls, D.G. Presynaptic receptors and the control of glutamate exocytosis. Trends Neurosci. 1996, 19, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.P. What is new in neuropathic pain? Support. Care Cancer 2006, 15, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilron, I.; Max, M.B. Combination pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain: Current evidence and future directions. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2005, 5, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seltzer, Z.; Dubner, R.; Shir, Y. A novel behavioral model of neuropathic pain disorders produced in rats by partial sciatic nerve injury. Pain 1990, 43, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.L.; Eisenach, J.C.; Chen, S.R. Gabapentin Suppresses Ectopic Nerve Discharges and Reverses Allodynia in Neuropathic Rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 288, 1026–1030. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, R.; Podestá, M.; Boralli, V. Animal Study Investigation of the Combination of Pregabalin with Duloxetine or Amitriptyline on the Pharmacokinetics and Antiallodynic Effect during Neuropathic Pain in Rats [Internet]. Available online: www.painphysicianjournal.com (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Sharma, U.; Griesing, T.; Emir, B.; Young, J.P. Time to Onset of Neuropathic Pain Reduction: A Retrospective Analysis of Data From Nine Controlled Trials of Pregabalin for Painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy and Postherpetic Neuralgia [Internet]. Available online: www.americantherapeutics.com (accessed on 1 November 2010).
- Santos-Nogueira, E.; Castro, E.R.; Mancuso, R.; Navarro, X.; TenBroek, E.M.; Yunker, L.; Nies, M.F.; Bendele, A.M.; Pottabathini, R.; Kumar, A.; et al. Randall-Selitto Test: A New Approach for the Detection of Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2012, 29, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Király, K.; Kozsurek, M.; Lukácsi, E.; Barta, B.; Alpár, A.; Balázsa, T.; Fekete, C.; Szabon, J.; Helyes, Z.; Bölcskei, K.; et al. Glial cell type-specific changes in spinal dipeptidyl peptidase 4 expression and effects of its inhibitors in inflammatory and neuropatic pain. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, R.; Mayoral, V.; Leijon, G.; Binder, A.; Steigerwald, I.; Serpell, M. Efficacy and safety of combination therapy with 5% lidocaine medicated plaster and pregabalin in post-herpetic neuralgia and diabetic polyneuropathy. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2009, 25, 1677–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, S.; Wilhelm, S.; Lledo, A.; Schacht, A.; Tölle, T.; Bouhassira, D.; Cruccu, G.; Skljarevski, V.; Freynhagen, R. Duloxetine and pregabalin: High-dose monotherapy or their combination? The “cOMBO-DN study”—A multinational, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group study in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. Pain 2013, 154, 2616–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, A.; Gentry, C.; Patel, S.; Kesingland, A.; Bevan, S. Comparative activity of the anti-convulsants oxcarbazepine, carbamazepine, lamotrigine and gabapentin in a model of neuropathic pain in the rat and guinea-pig. Pain 2003, 105, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chincholkar, M. Analgesic mechanisms of gabapentinoids and effects in experimental pain models: A narrative review. Br. J. Anaesth. 2018, 120, 1315–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, M.; Yalcin, I.; Nexon, L.; Wurtz, X.; Ceredig, R.A.; Daniel, D.; Hawkes, R.A.; Salvat, E.; Barrot, M. The antiallodynic action of pregabalin in neuropathic pain is independent from the opioid system. Mol. Pain 2016, 12, 1744806916633477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, G.; Florian, J.A.; Bramwell, S.; Field, M.J.; Tan, K.K.C.; Marshall, S.; DeJongh, J.; Bies, R.R.; Danhof, M. Pharmacokinetic–Pharmacodynamic Analysis of the Static Allodynia Response to Pregabalin and Sildenafil in a Rat Model of Neuropathic Pain. Experiment 2010, 334, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Suto, T.; Saito, S.; Obata, H. Repeated Administration of Duloxetine Suppresses Neuropathic Pain by Accumulating Effects of Noradrenaline in the Spinal Cord. Obstet. Anesth. Dig. 2018, 126, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanenberg, R.J.; Irving, G.A.; Risser, R.C.; Ahl, J.; Robinson, M.J.; Skljarevski, V.; Malcolm, S.K. Duloxetine, Pregabalin, and Duloxetine Plus Gabapentin for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain Management in Patients with Inadequate Pain Response to Gabapentin: An Open-Label, Randomized, Noninferiority Comparison. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2011, 86, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-S.; Jun, I.-G.; Kim, S.-H.; Park, J.Y. Intrathecal Gabapentin Increases Interleukin-10 Expression and Inhibits Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine in a Rat Model of Neuropathic Pain. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2013, 28, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.J.; Joo, H.S.; Chang, H.W.; Lee, J.Y.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, Y.; Moon, D.E. Attenuation of neuropathy-induced allodynia following intraplantar injection of pregabalin. Can. J. Anaesth. 2010, 57, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freynhagen, R.; Strojek, K.; Griesing, T.; Whalen, E.; Balkenohl, M. Efficacy of pregabalin in neuropathic pain evaluated in a 12-week, randomised, double-blind, multicentre, placebo-controlled trial of flexible- and fixed-dose regimens. Pain 2005, 115, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatowski, R.; Gálvez, R.; Cherry, D.A.; Jacquot, F.; Vincent, E.; Maisonobe, P.; Versavel, M. Pregabalin reduces pain and improves sleep and mood disturbances in patients with post-herpetic neuralgia: Results of a randomised, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Pain 2004, 109, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangaiarkkarasi, A.; Rameshkannan, S.; Meher Ali, R. Effect of gabapentin and pregabalin in rat model of taxol induced neuropathic pain. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2015, 9, FF11–FF14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, W.; Suzuki, R.; Webber, M.; Hunt, S.P.; Dickenson, A.H. Depletion of endogenous spinal 5-HT attenuates the behavioural hypersensitivity to mechanical and cooling stimuli induced by spinal nerve ligation. Pain 2006, 123, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Rahman, W.; Hunt, S.P.; Dickenson, A.H. Descending facilitatory control of mechanically evoked responses is enhanced in deep dorsal horn neurones following peripheral nerve injury. Brain Res. 2004, 1019, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, C.S.; Nieto-Rostro, M.; Rahman, W.; Tran-Van-Minh, A.; Ferron, L.; Douglas, L.; Kadurin, I.; Ranjan, Y.S.; Fernandez-Alacid, L.; Millar, N.S.; et al. The increased trafficking of the calcium channel subunit α2δ-l to presynaptic terminals in neuropathic pain is inhibited by the α2δ ligand pregabalin. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 4076–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dib-Hajj, S.D.; Fjell, J.; Cummins, T.R.; Zheng, Z.; Fried, K.; LaMotte, R.; Black, J.A.; Waxman, S.G. Plasticity of sodium channel expression in DRG neurons in the chronic constriction injury model of neuropathic pain. Pain 1999, 83, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, N.; Sekizawa, T.; Gotoh, T.; Watabiki, T.; Takahashi, M.; Kakimoto, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Iino, M.; Nagakura, Y. Spontaneous and evoked pain-associated behaviors in a rat model of neuropathic pain respond differently to drugs with different mechanisms of action. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2016, 141, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pancrazio, J.J.; Kamatchi, G.L.; Roscoe, A.K.; Lynch, C., III. Inhibition of Neuronal Na Channels by Antidepressant Drugs. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 284, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jo, S.; Bean, B.P. Sidedness of carbamazepine accessibility to voltage-gated sodium channels. Mol. Pharmacol. 2014, 85, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Larsen, A.; Sopelana, D.; Diaz-Maroto, I.; Perona-Moratalla, A.; Gracia-Gil, J.; García-Muñozguren, S.; Palazón-García, E.; Segura, T. Assessment of efficacy and safety of eslicarbazepine acetate for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Eur. J. Pain 2018, 22, 1080–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chogtu, B.; Dhar, S.; Himabindu, P.; Bairy, K. Comparing the efficacy of carbamazepine, gabapentin and lamotrigine in chronic constriction injury model of neuropathic pain in rats. Int. J. Nutr. Pharmacol. Neurol. Dis. 2013, 3, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mahmood, S.M.A.; Abdullah, S.T.B.C.; Ahmad, N.N.F.N.; Bin Mohamed, A.H.; Razak, T.A. Analgesic synergism of gabapentin and carbamazepine in rat model of diabetic neuropathic pain. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2016, 15, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnus, L. Nonepileptic uses of gabapentin. Epilepsia 1999, 40 (Suppl. 6), S66–S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obermann, M.; Yoon, M.S.; Sensen, K.; Maschke, M.; Diener, H.; Katsarava, Z. Efficacy of Pregabalin in the Treatment of Trigeminal Neuralgia. Cephalalgia 2007, 28, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.C.; Brauer, S.; Espir, M.L.E. Long-term treatment of trigeminal neuralgia with carbamazepine. Postgrad. Med. J. 1981, 57, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taheri, A.; Marani, S.F.; Khoshbin, M.; Beygi, M. A retrospective review of efficacy of combination therapy with pregabalin and carbamazepine versus pregabalin and amitriptyline in treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Anaesth. Pain Intensive Care 2019, 19, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Prisco, L.; Ganau, M.; Bigotto, F.; Zornada, F. Trigeminal neuralgia: Successful antiepileptic drug combination therapy in three refractory cases. Drug Health Patient Saf. 2011, 3, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooch, C.; Podwall, D. The diabetic neuropathies. Neurologist 2004, 10, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Mello, R.; Dickenson, A.H. Spinal cord mechanisms of pain. Br. J. Anaesth. 2008, 101, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.R.; Samoriski, G.; Pan, H.L. Antinociceptive effects of chronic administration of uncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonists in a rat model of diabetic neuropathic pain. Neuropharmacology 2009, 57, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaplan, S.R.; Malmberg, A.B.; Yaksh, T.L. Efficacy of Spinal NMDA Receptor Antagonism in Formalin Hyperalgesia and Nerve Injury Evoked Allodynia in the Rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 280, 829–838. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg, E.; Lacross, S.; Strassman, A.M. The clinically tested N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist memantine blocks and reverses thermal hyperalgesia in a rat model of painful mono-neuropathy. Neurosci. Lett. 1995, 187, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Price, D.D.; Hayes, R.L.; Lu, J.; Mayer, D.J.; Frenk, H. Intrathecal treatment with dextrorphan or ketamine potently reduces pain-related behaviors in a rat model of peripheral mononeuropathy. Brain Res. 1993, 605, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Matthews, E.A.; Dickenson, A.H. Comparison of the Effects of MK-801, Ketamine and Memantine on Responses of Spinal Dorsal Horn Neurones in a Rat Model of Mononeuropathy [Internet]. Available online: www.elsevier.nl/locate/pain (accessed on 1 March 2001).
- Richter, R.W.; Portenoy, R.; Sharma, U.; Lamoreaux, L.; Bockbrader, H.; Knapp, L.E. Relief of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy with pregabalin: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J. Pain 2005, 6, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesser, H.; Sharma, U.; LaMoreaux, L.; Poole, R.M. Pregabalin relieves symptoms of painful diabetic neuropathy: A randomized controlled trial. Neurology 2004, 63, 2104–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, X.; Lu, X.; Zhang, C.; Shi, Q.; Feng, L. Pregabalin treatment of peripheral nerve damage in a murine diabetic peripheral neuropathy model. Acta Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balogh, M.; Varga, B.K.; Karádi, D.; Riba, P.; Puskár, Z.; Kozsurek, M.; Al-Khrasani, M.; Király, K. Similarity and dissimilarity in antinociceptive effects of dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 inhibitors, Diprotin A and vildagliptin in rat inflammatory pain models following spinal administration. Brain Res. Bull. 2019, 147, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanlon, K.E.; Vanderah, T.W. Constitutive Activity at the Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor and Behavioral Responses. Methods Enzym. 2010, 484, 3–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zádor, F.; Balogh, M.; Váradi, A.; Zádori, Z.S.; Király, K.; Szűcs, E.; Varga, B.; Lázár, B.; Hosztafi, S.; Riba, P.; et al. 14-O-Methylmorphine: A Novel Selective Mu-Opioid Receptor Agonist with High Efficacy and Affinity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 814, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courteix, C.; Bardin, M.; Chantelauze, C.; Lavarenne, J.; Eschalier, A. Study of the sensitivity of the diabetes-induced pain model in rats to a range of analgesics. Pain 1994, 57, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaei, Z.; Hadjzadeh, M.-A.; Nemati, H.; Hosseini, M.; Ahmadi, M.; Shafiee, S. Antihyperglycemic and Antioxidant Activity of Crocin in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. J. Med. Food 2013, 16, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courteix, C.; Eschalier, A.; Lavarenne, J. Streptozocin-induced diabetic rats: Behavioural evidence for a model of chronic pain. Pain 1993, 53, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakó, T.; Szabó, E.; Tábi, T.; Zachar, G.; Csillag, A.; Szökő, E. Chiral analysis of amino acid neurotransmitters and neuromodulators in mouse brain by CE-LIF. Electrophoresis 2014, 35, 2870–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, J.; Prentice, H.; Wu, J.-Y. Preparation, Stimulation and Other Uses of Adult Rat Brain Synaptosomes. Bio-Protocol 2017, 7, e2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Essmat, N.; Galambos, A.R.; Lakatos, P.P.; Karádi, D.Á.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Abbood, S.K.; Geda, O.; Laufer, R.; Király, K.; Riba, P.; et al. Pregabalin–Tolperisone Combination to Treat Neuropathic Pain: Improved Analgesia and Reduced Side Effects in Rats. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081115
Essmat N, Galambos AR, Lakatos PP, Karádi DÁ, Mohammadzadeh A, Abbood SK, Geda O, Laufer R, Király K, Riba P, et al. Pregabalin–Tolperisone Combination to Treat Neuropathic Pain: Improved Analgesia and Reduced Side Effects in Rats. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(8):1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081115
Chicago/Turabian StyleEssmat, Nariman, Anna Rita Galambos, Péter P. Lakatos, Dávid Árpád Karádi, Amir Mohammadzadeh, Sarah Kadhim Abbood, Orsolya Geda, Rudolf Laufer, Kornél Király, Pál Riba, and et al. 2023. "Pregabalin–Tolperisone Combination to Treat Neuropathic Pain: Improved Analgesia and Reduced Side Effects in Rats" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 8: 1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081115
APA StyleEssmat, N., Galambos, A. R., Lakatos, P. P., Karádi, D. Á., Mohammadzadeh, A., Abbood, S. K., Geda, O., Laufer, R., Király, K., Riba, P., Zádori, Z. S., Szökő, É., Tábi, T., & Al-Khrasani, M. (2023). Pregabalin–Tolperisone Combination to Treat Neuropathic Pain: Improved Analgesia and Reduced Side Effects in Rats. Pharmaceuticals, 16(8), 1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081115








