Discovery of RC-752, a Novel Sigma-1 Receptor Antagonist with Antinociceptive Activity: A Promising Tool for Fighting Neuropathic Pain
Abstract
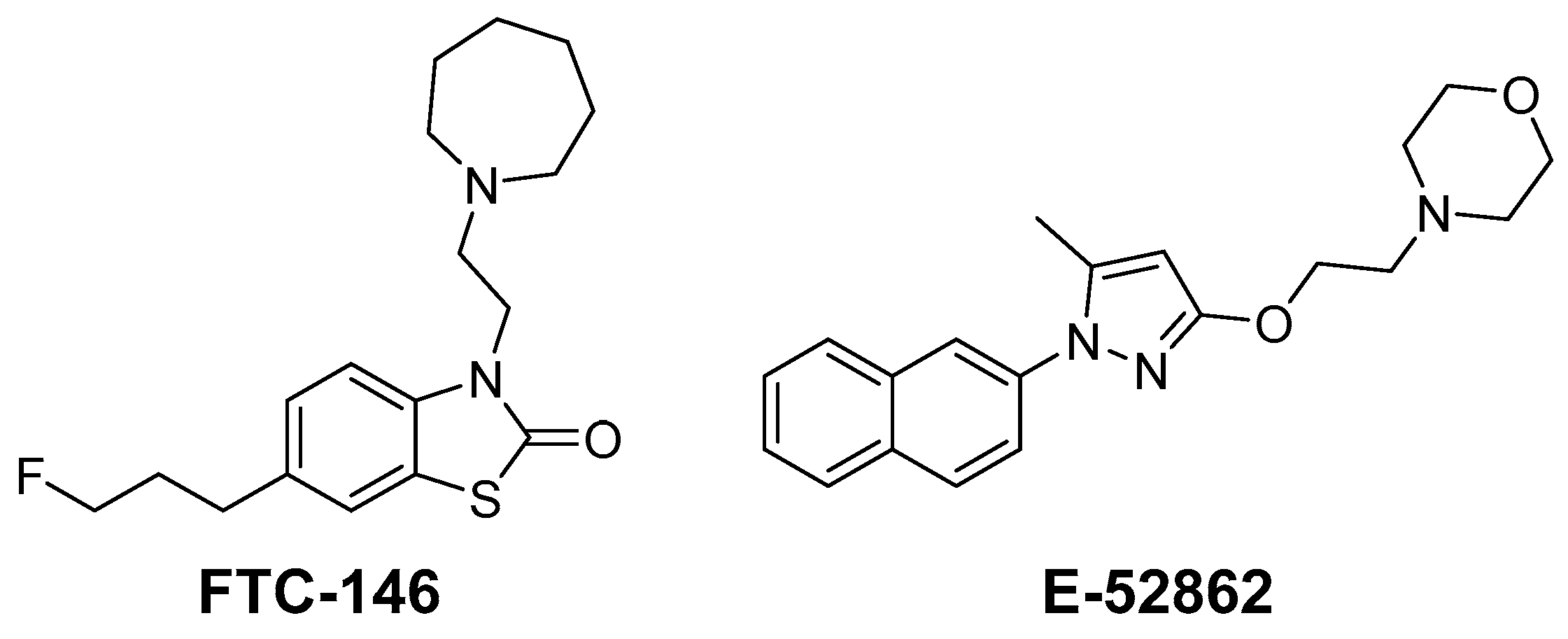
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
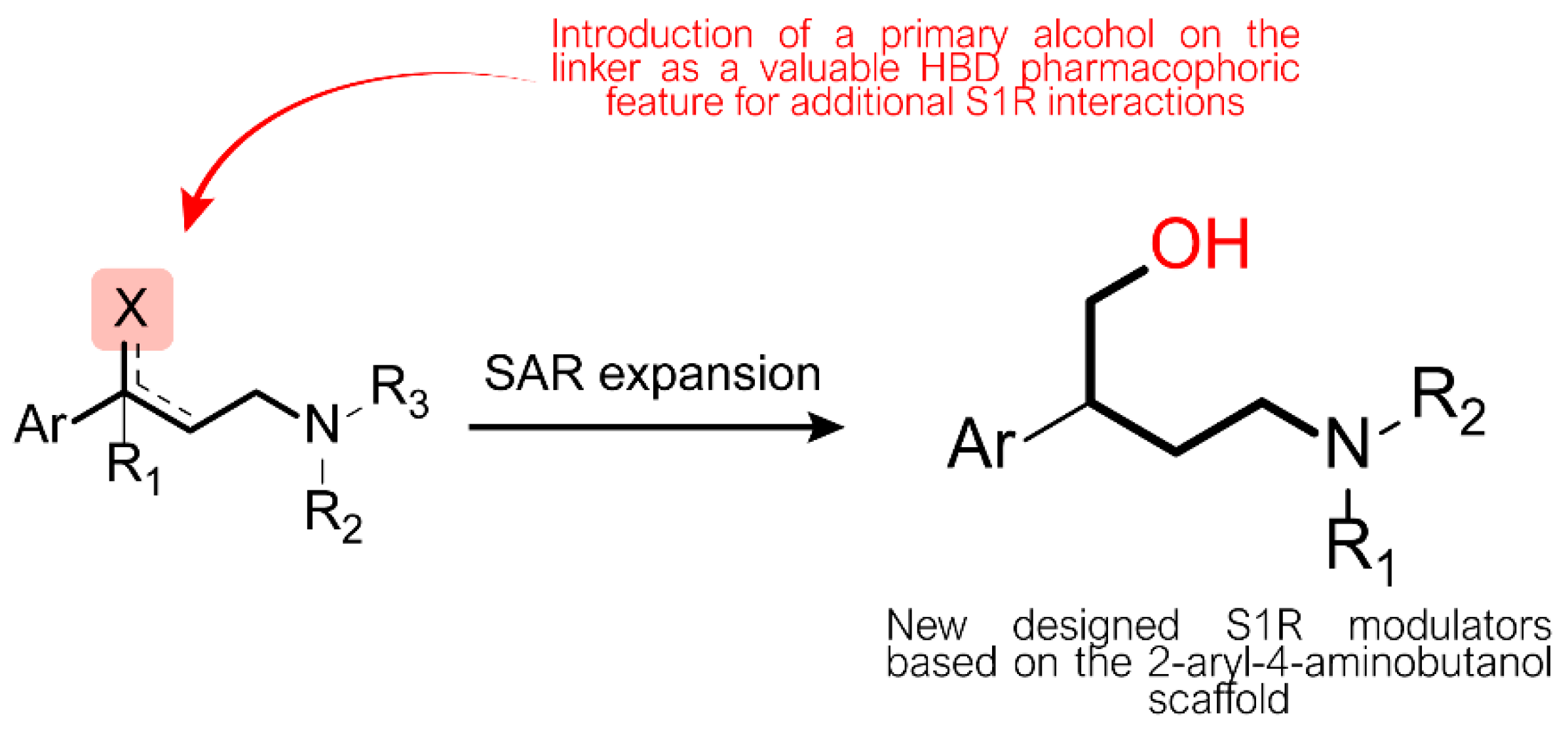
2.1. Design and Synthesis
2.2. Binding Affinity
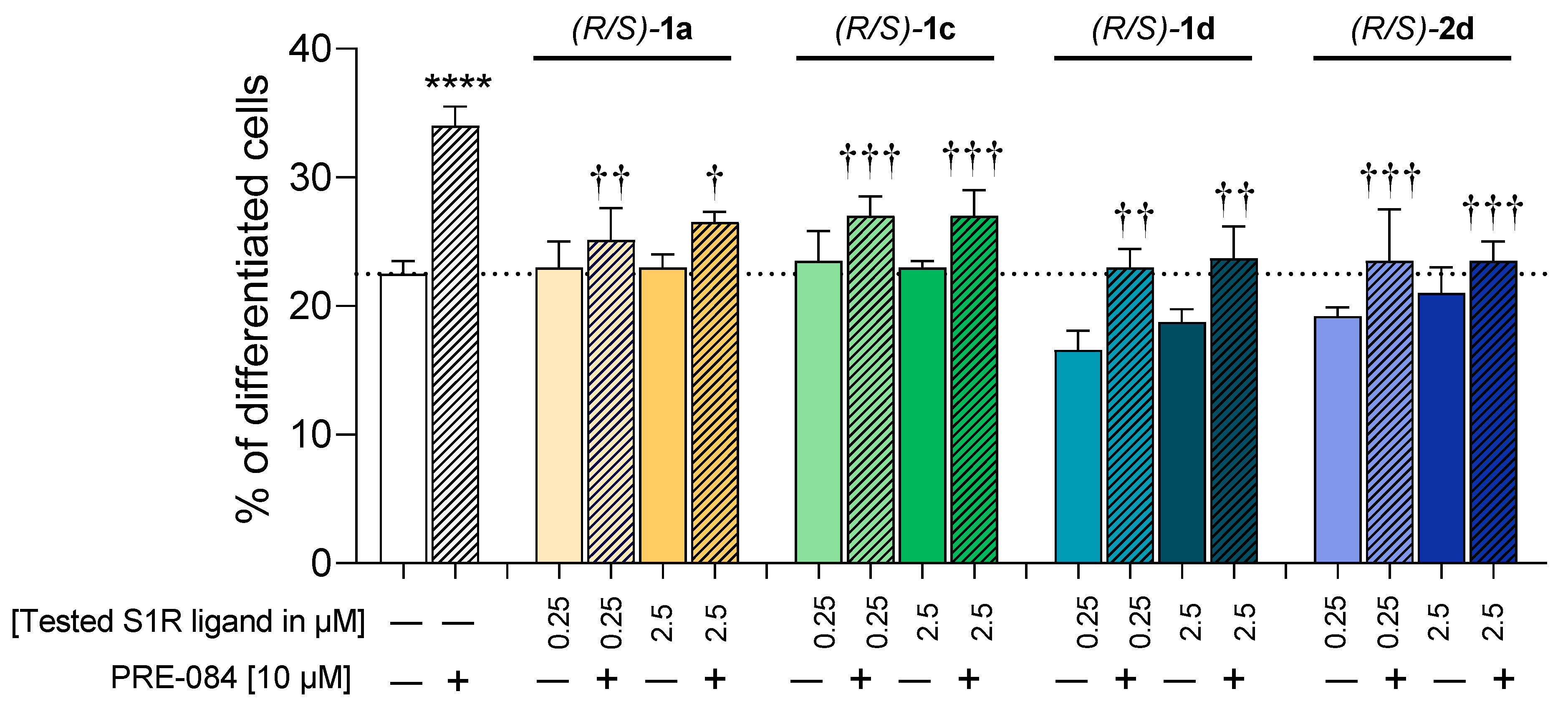
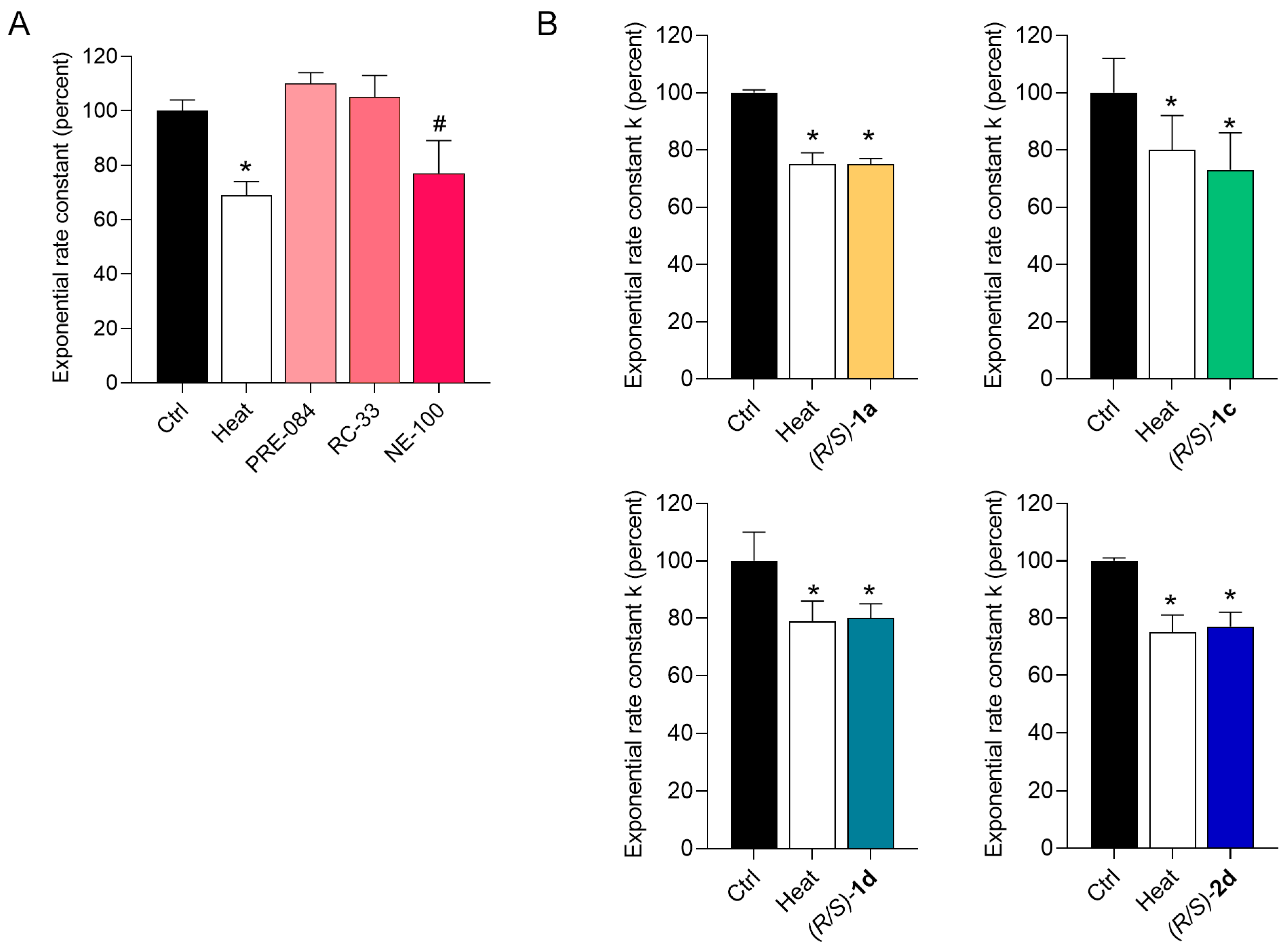
2.3. Functional Profiling
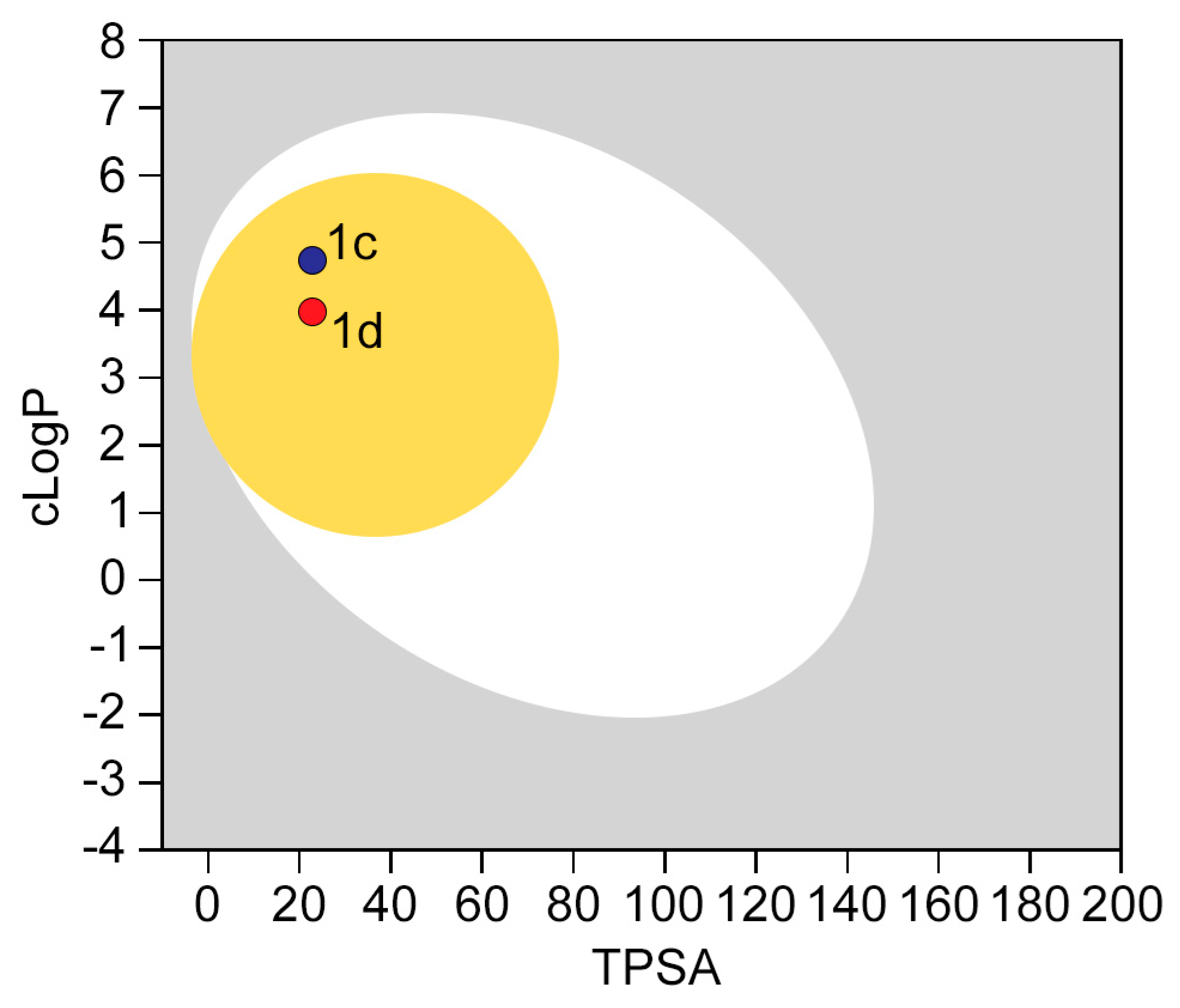
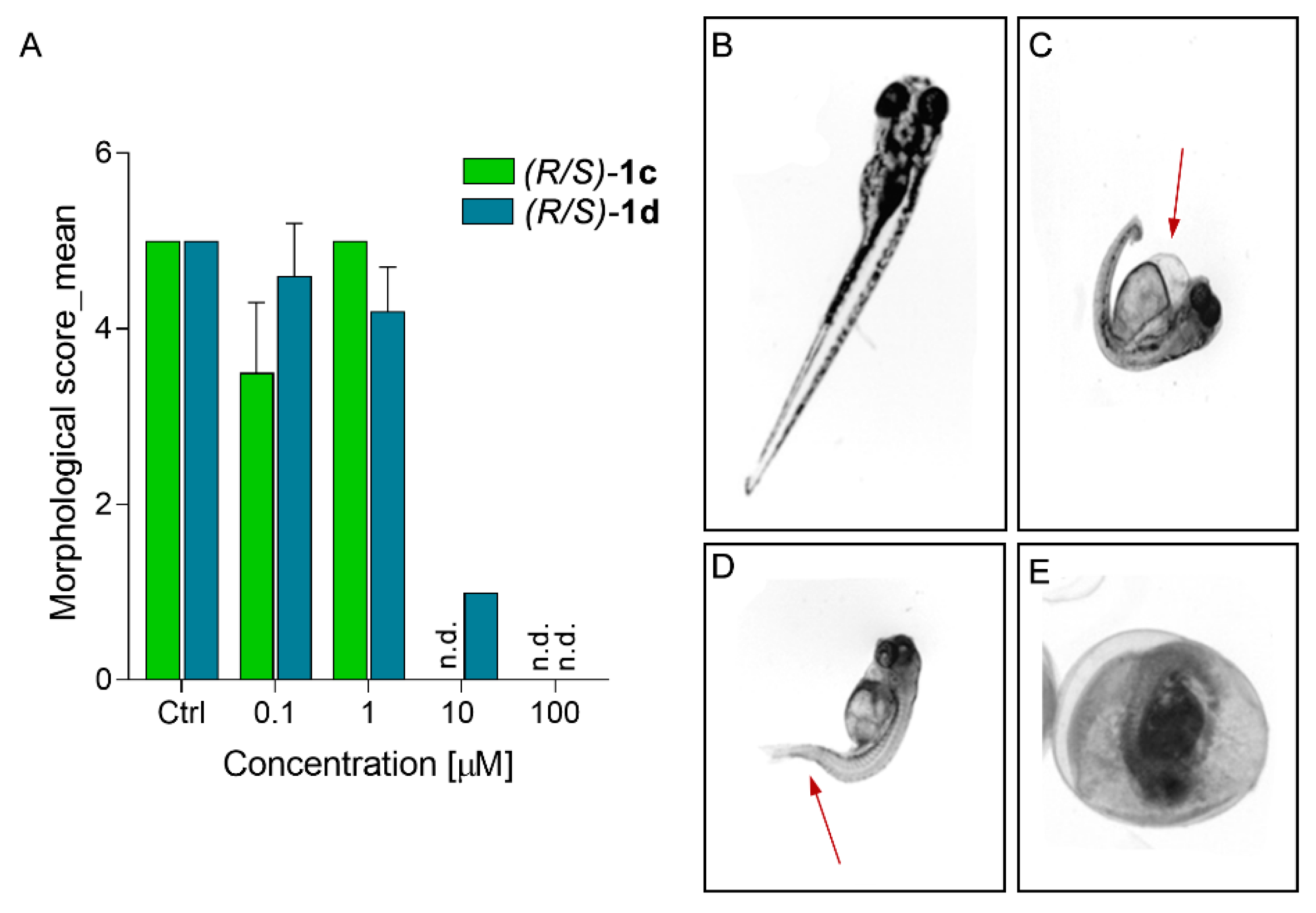
2.4. In Silico Developability and Early Toxicity Studies
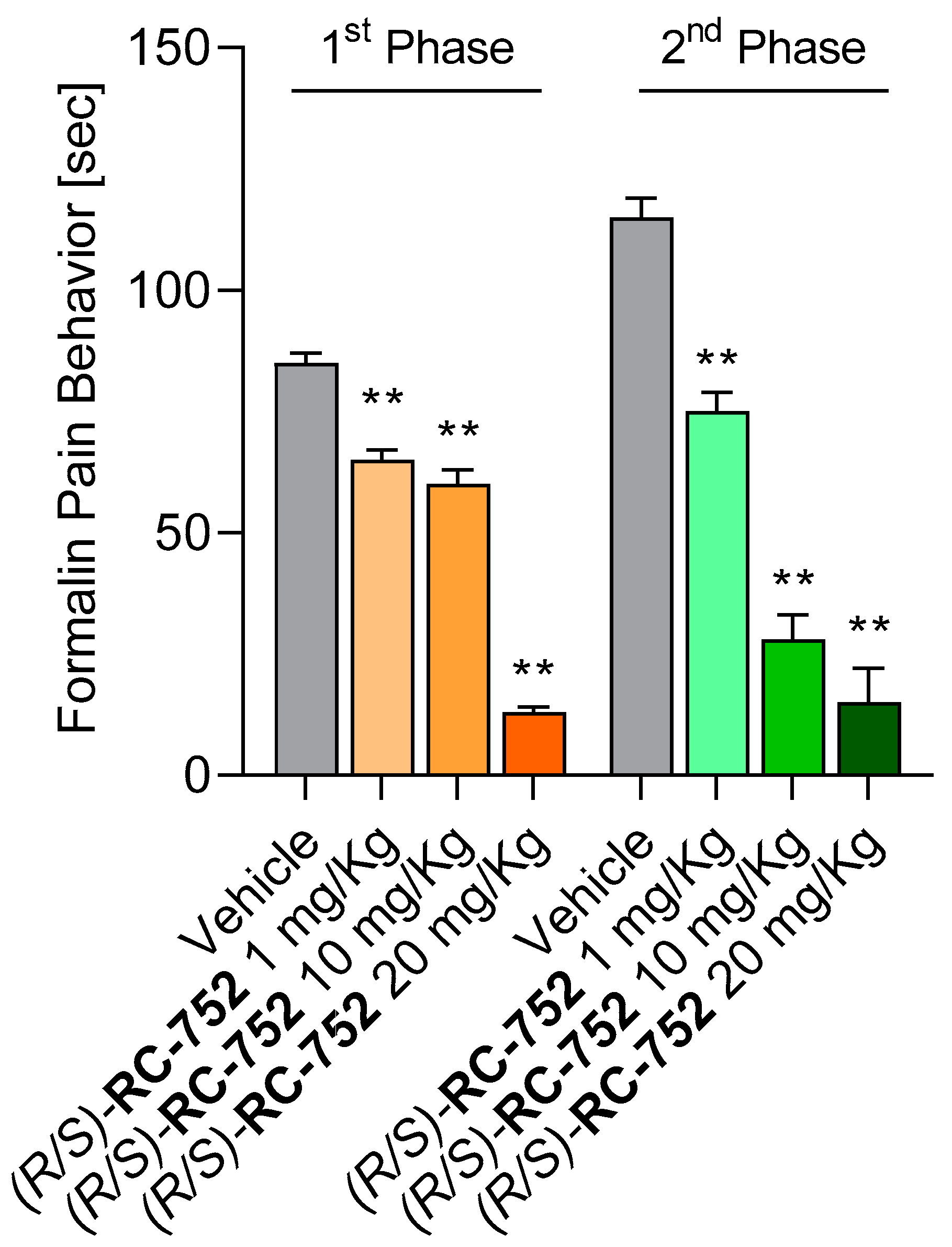
2.5. In Vivo Antinociceptive Studies
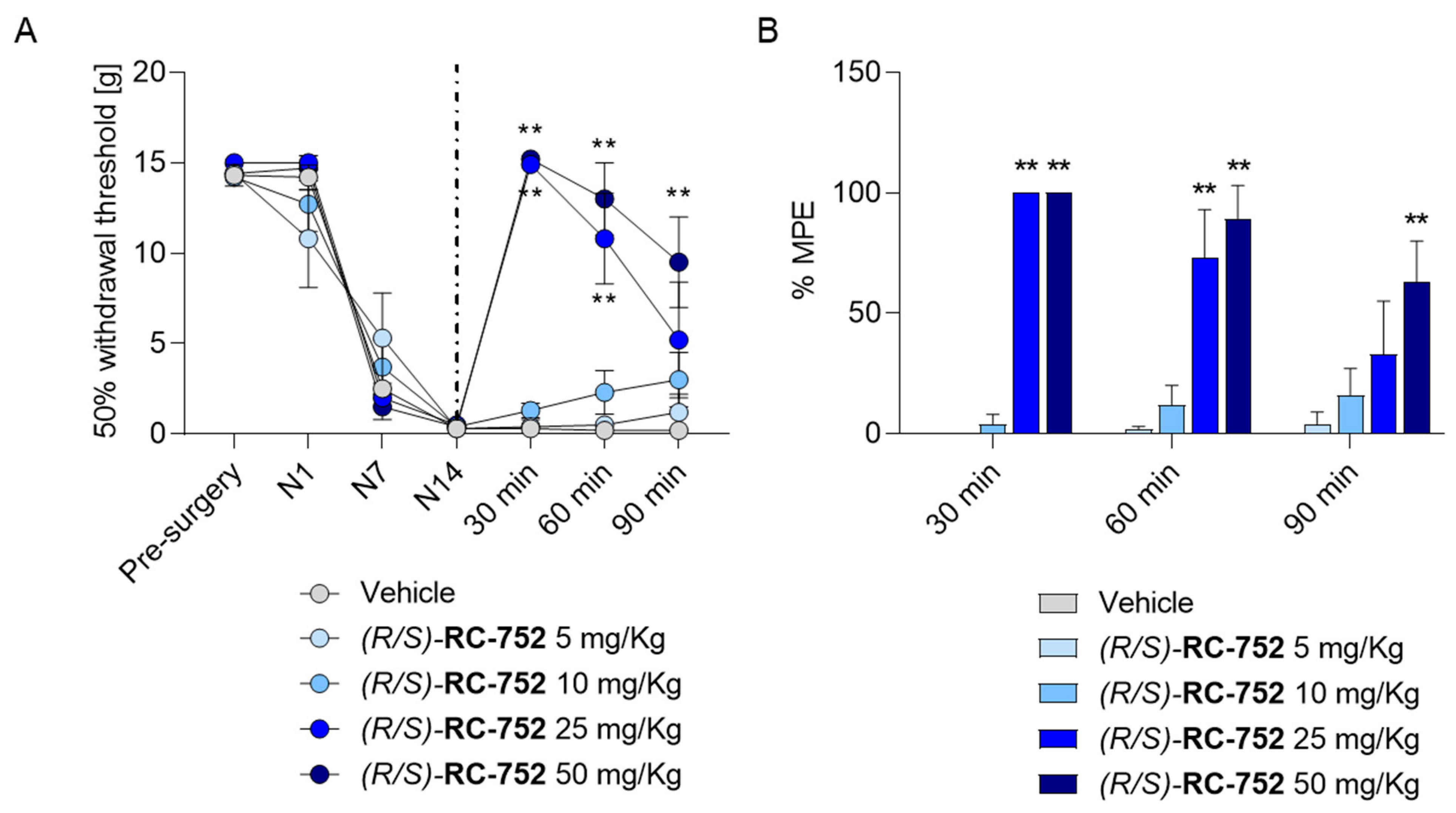
2.5.1. Assessment of the Antinociceptive Activity in the Formalin Test
2.5.2. Assessment of the Antinociceptive Activity in Chung’s Neuropathic Pain Model
3. Conclusions
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Chemistry
General procedures
General Procedure for the Synthesis of 4–6
Synthesis of ethyl (E)-3-([1,1’-biphenyl]-4-yl)but-2-enoate (4)
Synthesis of ethyl (E)-3-(naphthalen-2-yl)but-2-enoate (5)
Synthesis of ethyl (E)-3-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)but-2-enoate (6)
General Procedure for the Synthesis of 7–9
Synthesis of 4-([1,1’-biphenyl]-4-yl)furan-2(5H)-one (7)
Synthesis of 4-(naphthalen-2-yl)furan-2(5H)-one (8)
Synthesis of 4-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)furan-2(5H)-one (9)
General Procedure for the Synthesis of 10–12
Synthesis of 4-([1,1’-biphenyl]-4-yl)dihydrofuran-2(3H)-one (10)
Synthesis of 4-(naphthalen-2-yl)dihydrofuran-2(3H)-one (11)
Synthesis of 4-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)dihydrofuran-2(3H)-one (12)
General Procedure for the Synthesis of 13a–15d
Synthesis of 3-([1,1’-biphenyl]-4-yl)-4-hydroxy-1-morpholinobutan-1-one (13a)
Synthesis of 3-([1,1’-biphenyl]-4-yl)-N,N-diethyl-4-hydroxybutanamide (13b)
Synthesis of 3-([1,1’-biphenyl]-4-yl)-N-benzyl-4-hydroxy-N-methylbutanamide (13c)
Synthesis of 3-([1,1’-biphenyl]-4-yl)-4-hydroxy-1-(piperidin-1-yl)butan-1-one (13d)
Synthesis of 4-hydroxy-1-morpholino-3-(naphthalen-2-yl)butan-1-one (14a)
Synthesis of N,N-diethyl-4-hydroxy-3-(naphthalen-2-yl)butanamide (14b)
Synthesis of N-benzyl-4-hydroxy-N-methyl-3-(naphthalen-2-yl)butanamide (14c)
Synthesis of 4-hydroxy-3-(naphthalen-2-yl)-1-(piperidin-1-yl)butan-1-one (14d)
Synthesis of 4-hydroxy-3-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)-1-morpholinobutan-1-one (15a)
Synthesis of N,N-diethyl-4-hydroxy-3-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)butanamide (15b)
Synthesis of N-benzyl-4-hydroxy-3-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)-N-methylbutanamide (15c)
Synthesis of 4-hydroxy-3-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)-1-(piperidin-1-yl)butan-1-one (15d)
General Procedure for the Synthesis of 1a–3e
Synthesis of 2-([1,1’-biphenyl]-4-yl)-4-morpholinobutan-1-ol (1a)
Synthesis of 2-([1,1’-biphenyl]-4-yl)-4-(diethylamino)butan-1-ol (1b)
Synthesis of 3-([1,1’-biphenyl]-4-yl)-N-benzyl-4-hydroxy-N-methylbutanamine (1c)
Synthesis of 2-([1,1’-biphenyl]-4-yl)-4-(piperidin-1-yl)butan-1-ol (1d)
Synthesis of 2-([1,1’-biphenyl]-4-yl)-4-(4-benzylpiperidin-1-yl)butan-1-ol (1e)
Synthesis of 4-morpholino-2-(naphthalen-2-yl)butan-1-ol (2a)
Synthesis of 4-(diethylamino)-2-(naphthalen-2-yl)butan-1-ol (2b)
Synthesis of 4-(benzyl(methyl)amino)-2-(naphthalen-2-yl)butan-1-ol (2c)
Synthesis of 2-(naphthalen-2-yl)-4-(piperidin-1-yl)butan-1-ol (2d)
Synthesis of 4-(4-benzylpiperidin-1-yl)-2-(naphthalen-2-yl)butan-1-ol (2e)
Synthesis of 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)-4-morpholinobutan-1-ol (3a)
Synthesis of 4-(diethylamino)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)butan-1-ol (3b)
Synthesis of 4-(benzyl(methyl)amino)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)butan-1-ol (3c)
Synthesis of 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)-4-(piperidin-1-yl)butan-1-ol (3d)
Synthesis of 4-(4-benzylpiperidin-1-yl)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)butan-1-ol (3e)
4.2. Receptor Binding Studies
4.2.1. Preparation of Membrane Homogenates from Guinea Pig Brain
4.2.2. S1R Binding Assay Protocol
4.3. NGF-Induced Neurite Outgrowth Assay in PC12 Cells
4.3.1. Cell Culture
4.3.2. Quantification of Neurite Outgrowth
4.4. Water Permeability Assay
4.5. In Vivo Toxicity
4.5.1. Animal Care and Maintenance
4.5.2. Toxicity Evaluation
4.6. In Vitro Metabolic Stability
LC–MS/MS Analytical Method
4.7. MTS Cytotoxicity Assay
Cell Proliferation Assay
4.8. In Vivo Assays
4.8.1. Animals
4.8.2. Formalin-Induced Licking Paw Test
4.8.3. Sciatic Nerve Ligation Model
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Finnerup, N.B.; Kuner, R.; Jensen, T.S. Neuropathic Pain: From Mechanisms to Treatment. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 259–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alles, S.R.A.; Smith, P.A. Etiology and Pharmacology of Neuropathic Pain. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 315–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierthmühlen, J.; Baron, R. Neuropathic Pain. Semin. Neurol. 2016, 36, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, R.; Binder, A.; Wasner, G. Neuropathic Pain: Diagnosis, Pathophysiological Mechanisms, and Treatment. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attal, N.; Martinez, V.; Bouhassira, D. Potential for Increased Prevalence of Neuropathic Pain after the COVID-19 Pandemic. Pain Rep. 2021, 6, e884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdy, R.; Eid, R.A.; Fathy, W.; Abdel-Aziz, M.M.; Ibrahim, R.E.; Yehia, A.; Sheemy, M.S.; Hussein, M. Characteristics and Risk Factors of Persistent Neuropathic Pain in Recovered COVID-19 Patients. Pain Med. 2022, 23, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarland, A.J.; Yousuf, M.S.; Shiers, S.; Price, T.J. Neurobiology of SARS-CoV-2 Interactions with the Peripheral Nervous System: Implications for COVID-19 and Pain. Pain Rep. 2021, 6, e885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellul, M.A.; Benjamin, L.; Singh, B.; Lant, S.; Michael, B.D.; Easton, A.; Kneen, R.; Defres, S.; Sejvar, J.; Solomon, T. Neurological Associations of COVID-19. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 767–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhassira, D. Neuropathic Pain: Definition, Assessment and Epidemiology. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 175, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Attal, N.; Haroutounian, S.; McNicol, E.; Baron, R.; Dworkin, R.H.; Gilron, I.; Haanpää, M.; Hansson, P.; Jensen, T.S.; et al. Pharmacotherapy for Neuropathic Pain in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humo, M.; Lu, H.; Yalcin, I. The Molecular Neurobiology of Chronic Pain–Induced Depression. Cell Tissue Res. 2019, 377, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherif, F.; Zouari, H.G.; Cherif, W.; Hadded, M.; Cheour, M.; Damak, R. Depression Prevalence in Neuropathic Pain and Its Impact on the Quality of Life. Pain Res. Manag. 2020, 2020, 7408508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieson, S.; Lin, C.-W.C.; Underwood, M.; Eldabe, S. Pregabalin and Gabapentin for Pain. BMJ 2020, 369, m1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senderovich, H.; Jeyapragasan, G. Is There a Role for Combined Use of Gabapentin and Pregabalin in Pain Control? Too Good to Be True? Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2018, 34, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duehmke, R.M.; Derry, S.; Wiffen, P.J.; Bell, R.F.; Aldington, D.; Moore, R.A. Tramadol for Neuropathic Pain in Adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 6, CD003726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freo, U.; Romualdi, P.; Kress, H.G. Tapentadol for Neuropathic Pain: A Review of Clinical Studies. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 1537–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, T.; Chen, J.; Wiffen, J.; Derry, S.; Carr, B.; Aldington, D.; Cole, P.; Moore, R. Morphine for Chronic Neuropathic Pain in Adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 5, CD011669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insights, Q.M. Non-Opioid Pain Treatment Market Size to Grow at a CAGR of 16.8% from 2021 to 2030. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/non-opioid-pain-treatment-market-report (accessed on 3 July 2023).
- Linciano, P.; Rossino, G.; Listro, R.; Rossi, D.; Collina, S. Sigma-1 Receptor Antagonists: Promising Players in Fighting Neuropathic Pain. Pharm. Pat. Anal. 2020, 9, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Cantero, M.C.; González-Cano, R.; Tejada, M.Á.; Santos-Caballero, M.; Perazzoli, G.; Nieto, F.R.; Cobos, E.J. Sigma-1 Receptor: A Drug Target for the Modulation of Neuroimmune and Neuroglial Interactions during Chronic Pain. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 163, 105339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, J.L.; Zamanillo, D.; Corbera, J.; Baeyens, J.M.; Maldonado, R.; Pericàs, M.A.; Vela, J.M.; Torrens, A. Selective Sigma-1 (Sigma1) Receptor Antagonists: Emerging Target for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Agents Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlos, M.; Romero, L.; Zamanillo, D.; Plata-Salamán, C.; Vela, J.M. Sigma-1 Receptor and Pain. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2017, 244, 131–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Caparros, I.; Ruiz-Cantero, M.C.; Perazzoli, G.; Cronin, S.J.F.; Vela, J.M.; Hamed, M.F.; Penninger, J.M.; Baeyens, J.M.; Cobos, E.J.; Nieto, F.R. Sigma-1 Receptors Control Neuropathic Pain and Macrophage Infiltration into the Dorsal Root Ganglion after Peripheral Nerve Injury. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2020, 34, 5951–5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Puente, B.; Zamanillo, D.; Romero, L.; Carceller, A.; Vela, J.M.; Merlos, M.; Portillo-Salido, E. Comprehensive Preclinical Assessment of Sensory, Functional, Motivational-Affective, and Neurochemical Outcomes in Neuropathic Pain: The Case of the Sigma-1 Receptor. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2022, 5, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, H.R.; Kruse, A.C. The Molecular Function of σ Receptors: Past, Present, and Future. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 40, 636–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Lázaro, S.L.; González-Ramírez, R.; Rosenbaum, T. Molecular Interplay Between the Sigma-1 Receptor, Steroids, and Ion Channels. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsson, A.; Ohsawa, M.; Hallberg, M.; Nyberg, F.; Kamei, J. Substance P(1-7) Induces Antihyperalgesia in Diabetic Mice through a Mechanism Involving the Naloxone-Sensitive Sigma Receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 626, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cendan, C.M.; Pujalte, J.M.; Portillo-Salido, E.; Montoliu, L.; Baeyens, J.M. Formalin-Induced Pain Is Reduced in Sigma(1) Receptor Knockout Mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 511, 73–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entrena, J.M.; Sánchez-Fernández, C.; Nieto, F.R.; González-Cano, R.; Yeste, S.; Cobos, E.J.; Baeyens, J.M. Sigma-1 Receptor Agonism Promotes Mechanical Allodynia After Priming the Nociceptive System with Capsaicin. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Caparrós, I.; Perazzoli, G.; Yeste, S.; Cikes, D.; Baeyens, J.M.; Cobos, E.J.; Nieto, F.R. Sigma-1 Receptor Inhibition Reduces Neuropathic Pain Induced by Partial Sciatic Nerve Transection in Mice by Opioid-Dependent and -Independent Mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gris, G.; Cobos, E.J.; Zamanillo, D.; Portillo-Salido, E. Sigma-1 Receptor and Inflammatory Pain. Inflamm. Res. 2015, 64, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, L.; Eans, S.; Ramadan-Siraj, I.; Modica, M.; Romeo, G.; Intagliata, S.; McLaughlin, J. Examination of the Novel Sigma-1 Receptor Antagonist, SI 1/28, for Antinociceptive and Anti-Allodynic Efficacy against Multiple Types of Nociception with Fewer Liabilities of Use. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, F.R.; Cendan, C.M.; Sanchez-Fernandez, C.; Cobos, E.J.; Entrena, J.M.; Tejada, M.A.; Zamanillo, D.; Vela, J.M.; Baeyens, J.M. Role of Sigma-1 Receptors in Paclitaxel-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Mice. J. Pain Off. J. Am. Pain Soc. 2012, 13, 1107–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavaletti, G.; Alberti, P.; Argyriou, A.A.; Lustberg, M.; Staff, N.P.; Tamburin, S.; on behalf of the Toxic Neuropathy Consortium of the Peripheral Nerve Society. Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neurotoxicity: A Multifaceted, Still Unsolved Issue. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2019, 24, S6–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argyriou, A.A.; Bruna, J.; Marmiroli, P.; Cavaletti, G. Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neurotoxicity (CIPN): An Update. Crit. Rev. Oncol. /Hematol. 2012, 82, 51–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Welsh, W.J. Novel Sigma 1 Receptor Antagonists as Potential Therapeutics for Pain Management. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 890–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesei, A.; Cortesi, M.; Pignatta, S.; Arienti, C.; Dondio, G.M.; Bigogno, C.; Malacrida, A.; Miloso, M.; Meregalli, C.; Chiorazzi, A.; et al. Anti-Tumor Efficacy Assessment of the Sigma Receptor Pan Modulator RC-106. A Promising Therapeutic Tool for Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortesi, M.; Zamagni, A.; Pignatta, S.; Zanoni, M.; Arienti, C.; Rossi, D.; Collina, S.; Tesei, A. Pan-Sigma Receptor Modulator RC-106 Induces Terminal Unfolded Protein Response In In Vitro Pancreatic Cancer Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatematteo, F.S.; Niso, M.; Lacivita, E.; Abate, C. Σ2 Receptor and Its Role in Cancer with Focus on a MultiTarget Directed Ligand (MTDL) Approach. Molecules 2021, 26, 3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, M.L.; Shen, B.; Zavaleta, C.L.; Nielsen, C.H.; Mesangeau, C.; Vuppala, P.K.; Chan, C.; Avery, B.A.; Fishback, J.A.; Matsumoto, R.R.; et al. New Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Radioligand for Imaging σ-1 Receptors in Living Subjects. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 8272–8282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, J.L.; Cuberes, R.; Berrocal, J.; Contijoch, M.; Christmann, U.; Fernández, A.; Port, A.; Holenz, J.; Buschmann, H.; Laggner, C.; et al. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of the 1-Arylpyrazole Class of Σ1 Receptor Antagonists: Identification of 4-{2-[5-Methyl-1- (Naphthalen-2-Yl)-1H-Pyrazol-3-Yloxy]Ethyl}morpholine (S1RA, E-52862). J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 8211–8224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AdisInsight Drugs E-52862. Available online: https://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800031669 (accessed on 7 April 2023).
- clinicaltrials.gov. [18F]FTC-146 PET/MRI in Healthy Volunteers and in CRPS and Sciatica. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02753101 (accessed on 7 April 2023).
- James, M.L.; Shen, B.; Nielsen, C.H.; Behera, D.; Buckmaster, C.L.; Mesangeau, C.; Zavaleta, C.; Vuppala, P.K.; Jamalapuram, S.; Avery, B.A.; et al. Evaluation of σ-1 Receptor Radioligand 18 F-FTC-146 in Rats and Squirrel Monkeys Using PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.; Park, J.H.; Hjørnevik, T.; Cipriano, P.W.; Yoon, D.; Gulaka, P.K.; Holly, D.; Behera, D.; Avery, B.A.; Gambhir, S.S.; et al. Radiosynthesis and First-In-Human PET/MRI Evaluation with Clinical-Grade [18F]FTC-146. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2017, 19, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruna, J.; Videla, S.; Argyriou, A.A.; Velasco, R.; Villoria, J.; Santos, C.; Nadal, C.; Cavaletti, G.; Alberti, P.; Briani, C.; et al. Efficacy of a Novel Sigma-1 Receptor Antagonist for Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathy: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase IIa Clinical Trial. Neurother. J. Am. Soc. Exp. NeuroTherapeutics 2018, 15, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weickhardt, A.; Wells, K.; Messersmith, W. Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathy in Colorectal Cancer. J. Oncol. 2011, 2011, 201593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gris, G.; Portillo-Salido, E.; Aubel, B.; Darbaky, Y.; Deseure, K.; Vela, J.M.; Merlos, M.; Zamanillo, D. The Selective Sigma-1 Receptor Antagonist E-52862 Attenuates Neuropathic Pain of Different Aetiology in Rats. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EU Clinical Trials Register. Clinical Trials for 2012-000398-21. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/search?query=2012-000398-21 (accessed on 7 April 2023).
- Rossino, G.; Rui, M.; Pozzetti, L.; Schepmann, D.; Wünsch, B.; Zampieri, D.; Pellavio, G.; Laforenza, U.; Rinaldi, S.; Colombo, G.; et al. Setup and Validation of a Reliable Docking Protocol for the Development of Neuroprotective Agents by Targeting the Sigma-1 Receptor (S1R). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, M.; Rossino, G.; Coniglio, S.; Monteleone, S.; Scuteri, A.; Malacrida, A.; Rossi, D.; Catenacci, L.; Sorrenti, M.; Paolillo, M.; et al. Identification of Dual Sigma1 Receptor Modulators/Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors with Antioxidant and Neurotrophic Properties, as Neuroprotective Agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 158, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, M.; Rossi, D.; Marra, A.; Paolillo, M.; Schinelli, S.; Curti, D.; Tesei, A.; Cortesi, M.; Zamagni, A.; Laurini, E.; et al. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of New Aryl-Alkyl(Alkenyl)-4-Benzylpiperidines, Novel Sigma Receptor (SR) Modulators, as Potential Anticancer-Agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 124, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Listro, R.; Stotani, S.; Rossino, G.; Rui, M.; Malacrida, A.; Cavaletti, G.; Cortesi, M.; Arienti, C.; Tesei, A.; Rossi, D.; et al. Exploring the RC-106 Chemical Space: Design and Synthesis of Novel (E)-1-(3-Arylbut-2-En-1-Yl)-4-(Substituted) Piperazine Derivatives as Potential Anticancer Agents. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, R.; Almansa, C.; Plata-Salamán, C.; Vela, J.M. A New Pharmacophore Model for the Design of Sigma-1 Ligands Validated on a Large Experimental Dataset. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagorce, D.; Sperandio, O.; Galons, H.; Miteva, M.A.; Villoutreix, B.O. FAF-Drugs2: Free ADME/Tox Filtering Tool to Assist Drug Discovery and Chemical Biology Projects. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagtap, S. Heck Reaction—State of the Art. Catalysts 2017, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loddo, G.; Azzolina, O.; Magnani, A.; Urbano, M.; Collina, S. Efficient Microwave and Phosphane-Free Synthesis of Trisubstituted Olefins via Heck Coupling. Lett. Org. Chem. 2006, 3, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Rui, M.; Di Giacomo, M.; Schepmann, D.; Wünsch, B.; Monteleone, S.; Liedl, K.R.; Collina, S. Gaining in Pan-Affinity towards Sigma 1 and Sigma 2 Receptors. SAR Studies on Arylalkylamines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishima, T.; Hashimoto, K. Potentiation of Nerve Growth Factor-Induced Neurite Outgrowth in PC12 Cells by Ifenprodil: The Role of Sigma-1 and IP3 Receptors. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takebayashi, M.; Hayashi, T.; Su, T.-P. Nerve Growth Factor-Induced Neurite Sprouting in PC12 Cells Involves ς-1 Receptors: Implications for Antidepressants. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 303, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, D.; Pedrali, A.; Urbano, M.; Gaggeri, R.; Serra, M.; Fernández, L.; Fernández, M.; Caballero, J.; Ronsisvalle, S.; Prezzavento, O.; et al. Identification of a Potent and Selective Σ1 Receptor Agonist Potentiating NGF-Induced Neurite Outgrowth in PC12 Cells. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6210–6224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motawe, Z.Y.; Abdelmaboud, S.S.; Cuevas, J.; Breslin, J.W. PRE-084 as a Tool to Uncover Potential Therapeutic Applications for Selective Sigma-1 Receptor Activation. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2020, 126, 105803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medraño-Fernandez, I.; Bestetti, S.; Bertolotti, M.; Bienert, G.P.; Bottino, C.; Laforenza, U.; Rubartelli, A.; Sitia, R. Stress Regulates Aquaporin-8 Permeability to Impact Cell Growth and Survival. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2016, 24, 1031–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellavio, G.; Rui, M.; Caliogna, L.; Martino, E.; Gastaldi, G.; Collina, S.; Laforenza, U. Regulation of Aquaporin Functional Properties Mediated by the Antioxidant Effects of Natural Compounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellavio, G.; Rossino, G.; Gastaldi, G.; Rossi, D.; Linciano, P.; Collina, S.; Laforenza, U. Sigma-1 Receptor Agonists Acting on Aquaporin-Mediated H2O2 Permeability: New Tools for Counteracting Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marra, A.; Rossi, D.; Pignataro, L.; Bigogno, C.; Canta, A.; Oggioni, N.; Malacrida, A.; Corbo, M.; Cavaletti, G.; Peviani, M.; et al. Toward the Identification of Neuroprotective Agents: G-Scale Synthesis, Pharmacokinetic Evaluation and CNS Distribution of (R)-RC-33, a Promising Sigma1 Receptor Agonist. Future Med. Chem. 2016, 8, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuyama, S.; Nakazato, A. NE-100: A Novel Sigma Receptor Antagonist. CNS Drug Rev. 1996, 2, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Lee, D.W.; Kang, B.C. The ‘R’ Principles in Laboratory Animal Experiments. Lab. Anim. Res. 2020, 36, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, D.; Tolba, R.H. Ethics in Animal-Based Research. Eur. Surg. Res. 2015, 55, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A Free Web Tool to Evaluate Pharmacokinetics, Drug-Likeness and Medicinal Chemistry Friendliness of Small Molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassar, S.; Adatto, I.; Freeman, J.L.; Gamse, J.T.; Iturria, I.; Lawrence, C.; Muriana, A.; Peterson, R.T.; Van Cruchten, S.; Zon, L.I. Use of Zebrafish in Drug Discovery Toxicology. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 33, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosszu, A.; Antal, Z.; Veres-Szekely, A.; Lenart, L.; Balogh, D.B.; Szkibinszkij, E.; Illesy, L.; Hodrea, J.; Banki, N.F.; Wagner, L.; et al. The Role of Sigma-1 Receptor in Sex-Specific Heat Shock Response in an Experimental Rat Model of Renal Ischaemia/Reperfusion Injury. Transpl. Int. 2018, 31, 1268–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Developmental Toxicology: Methods and Protocols; Harris, C., Hansen, J.M., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; Volume 889, ISBN 978-1-61779-866-5. [Google Scholar]
- Brannen, K.C.; Panzica-Kelly, J.M.; Danberry, T.L.; Augustine-Rauch, K.A. Development of a Zebrafish Embryo Teratogenicity Assay and Quantitative Prediction Model. Birth Defects Res. B Dev. Reprod Toxicol. 2010, 89, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, S.E.; Jeffrey, P. Utility of Metabolic Stability Screening: Comparison of in Vitro and in Vivo Clearance. Xenobiotica 2001, 31, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brian Houston, J. Utility of in Vitro Drug Metabolism Data in Predicting in Vivo Metabolic Clearance. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1994, 47, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, R.J.; McGinnity, D.F.; Austin, R.P. A Unified Model for Predicting Human Hepatic, Metabolic Clearance from in Vitro Intrinsic Clearance Data in Hepatocytes and Microsomes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2005, 33, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, B.; Morris, T. Physiological Parameters in Laboratory Animals and Humans. Pharm. Res. 1993, 10, 1093–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubuisson, D.; Dennis, S.G. The Formalin Test: A Quantitative Study of the Analgesic Effects of Morphine, Meperidine, and Brain Stem Stimulation in Rats and Cats. Pain 1977, 4, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho Kim, S.; Mo Chung, J. An Experimental Model for Peripheral Neuropathy Produced by Segmental Spinal Nerve Ligation in the Rat. Pain 1992, 50, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonin, R.P.; Bories, C.; De Koninck, Y. A Simplified Up-Down Method (SUDO) for Measuring Mechanical Nociception in Rodents Using von Frey Filaments. Mol. Pain 2014, 10, 1744-8069-10-26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

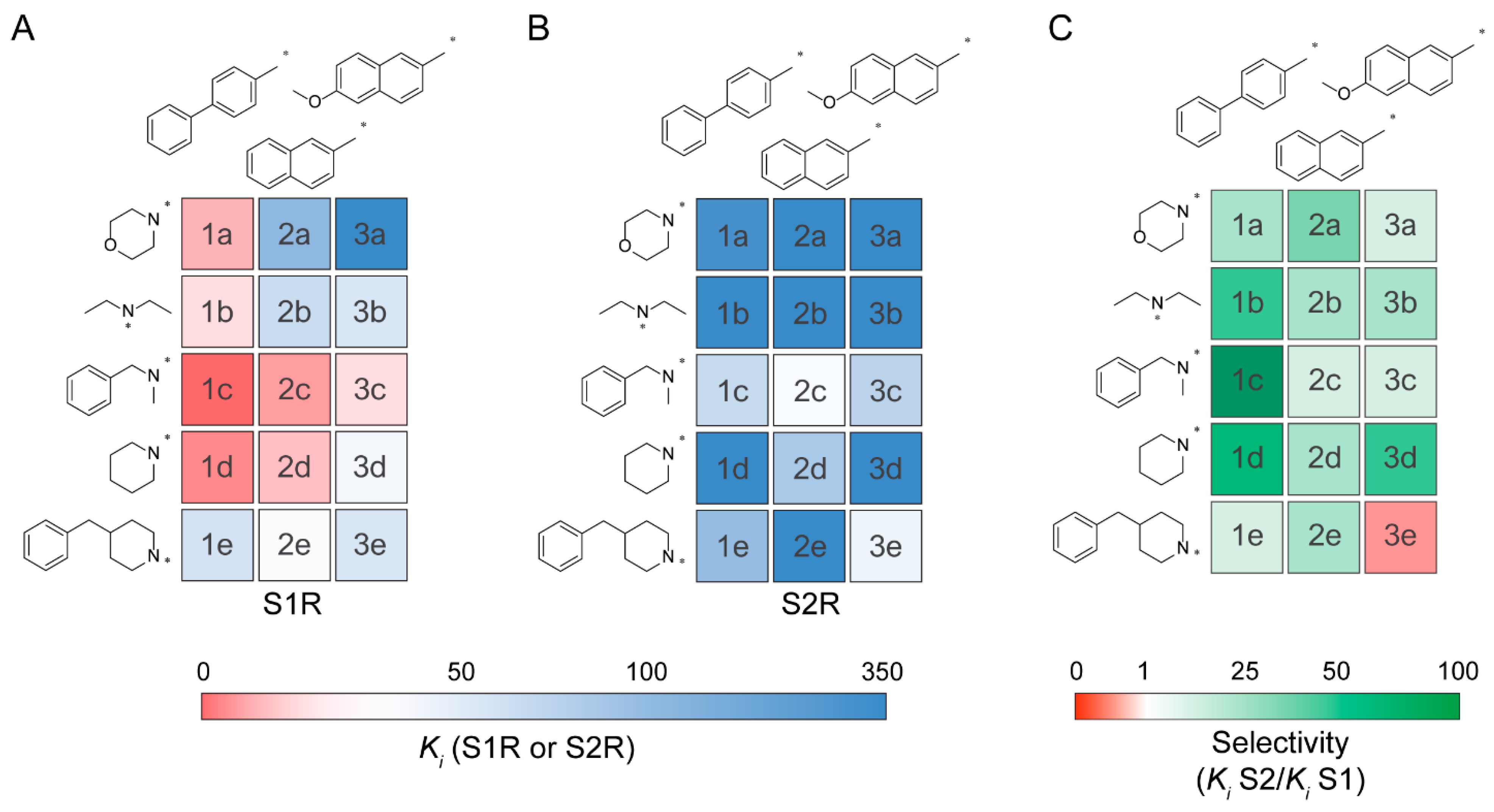
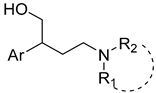 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmpd | Ar | R1 | R2 | S1R Ki (nM) | S2R Ki (nM) | Selectivity (Ki S2R/Ki S1R) |
| 1a | 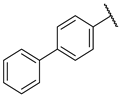 | -CH2CH2OCH2CH2- | 13 ± 3 | 310 | 24 | |
| 1b | CH3CH2- | CH3CH2- | 20 ± 4 | 677 | 34 | |
| 1c | CH3- | -Bn | 0.95 ± 0.08 | 121 | 127 | |
| 1d | -CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2- | 6.2 ± 0.9 | 360 | 58 | ||
| 1e | -CH2CH2CH(CH2Ph)CH2CH2- | 94 ± 12 | 197 | 2 | ||
| 2a | 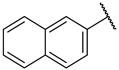 | -CH2CH2OCH2CH2- | 206 ± 37 | 6300 | 31 | |
| 2b | CH3CH2- | CH3CH2- | 110 ± 25 | 1100 | 10 | |
| 2c | CH3- | -Bn | 9.5 ± 1.8 | 35 ± 3 | 4 | |
| 2d | -CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2- | 15 ± 6 | 167 | 11 | ||
| 2e | -CH2CH2CH(CH2Ph)CH2CH2- | 25 ± 4 | 331 | 13 | ||
| 3a | 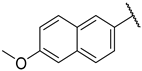 | -CH2CH2OCH2CH2- | 324 ± 10 | 1300 | 4 | |
| 3b | CH3CH2- | CH3CH2- | 87 ± 28 | 1200 | 14 | |
| 3c | CH3- | -Bn | 20 ± 3 | 138 | 7 | |
| 3d | -CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2- | 38 ± 9 | 1200 | 32 | ||
| 3e | -CH2CH2CH(CH2Ph)CH2CH2- | 85 ± 11 | 53 | 0.6 | ||
| Cli (µL/min/mg Protein) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Classification | Low Cli | Medium Cli | High Cli |
| Mouse | ≤2.5 | 2.5–66 | >66 |
| Compound | Parent Ion | Product Ion | DP (V) | CE (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-EC | 190.9 | 163.0 | 56 | 23 |
| Propranolol | 260.4 | 183.2 | 40 | 25 |
| Verapamil | 455.4 | 165.1 | 31 | 35 |
| (R/S)-1d | 310.4 | 179.3 | 66 | 45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rossino, G.; Marra, A.; Listro, R.; Peviani, M.; Poggio, E.; Curti, D.; Pellavio, G.; Laforenza, U.; Dondio, G.; Schepmann, D.; et al. Discovery of RC-752, a Novel Sigma-1 Receptor Antagonist with Antinociceptive Activity: A Promising Tool for Fighting Neuropathic Pain. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16070962
Rossino G, Marra A, Listro R, Peviani M, Poggio E, Curti D, Pellavio G, Laforenza U, Dondio G, Schepmann D, et al. Discovery of RC-752, a Novel Sigma-1 Receptor Antagonist with Antinociceptive Activity: A Promising Tool for Fighting Neuropathic Pain. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(7):962. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16070962
Chicago/Turabian StyleRossino, Giacomo, Annamaria Marra, Roberta Listro, Marco Peviani, Elena Poggio, Daniela Curti, Giorgia Pellavio, Umberto Laforenza, Giulio Dondio, Dirk Schepmann, and et al. 2023. "Discovery of RC-752, a Novel Sigma-1 Receptor Antagonist with Antinociceptive Activity: A Promising Tool for Fighting Neuropathic Pain" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 7: 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16070962
APA StyleRossino, G., Marra, A., Listro, R., Peviani, M., Poggio, E., Curti, D., Pellavio, G., Laforenza, U., Dondio, G., Schepmann, D., Wünsch, B., Bedeschi, M., Marino, N., Tesei, A., Ha, H.-J., Kim, Y.-H., Ann, J., Lee, J., Linciano, P., ... Collina, S. (2023). Discovery of RC-752, a Novel Sigma-1 Receptor Antagonist with Antinociceptive Activity: A Promising Tool for Fighting Neuropathic Pain. Pharmaceuticals, 16(7), 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16070962










