Investigation of Novel Benzoxazole-Oxadiazole Derivatives as Effective Anti-Alzheimer’s Agents: In Vitro and In Silico Approaches
Abstract
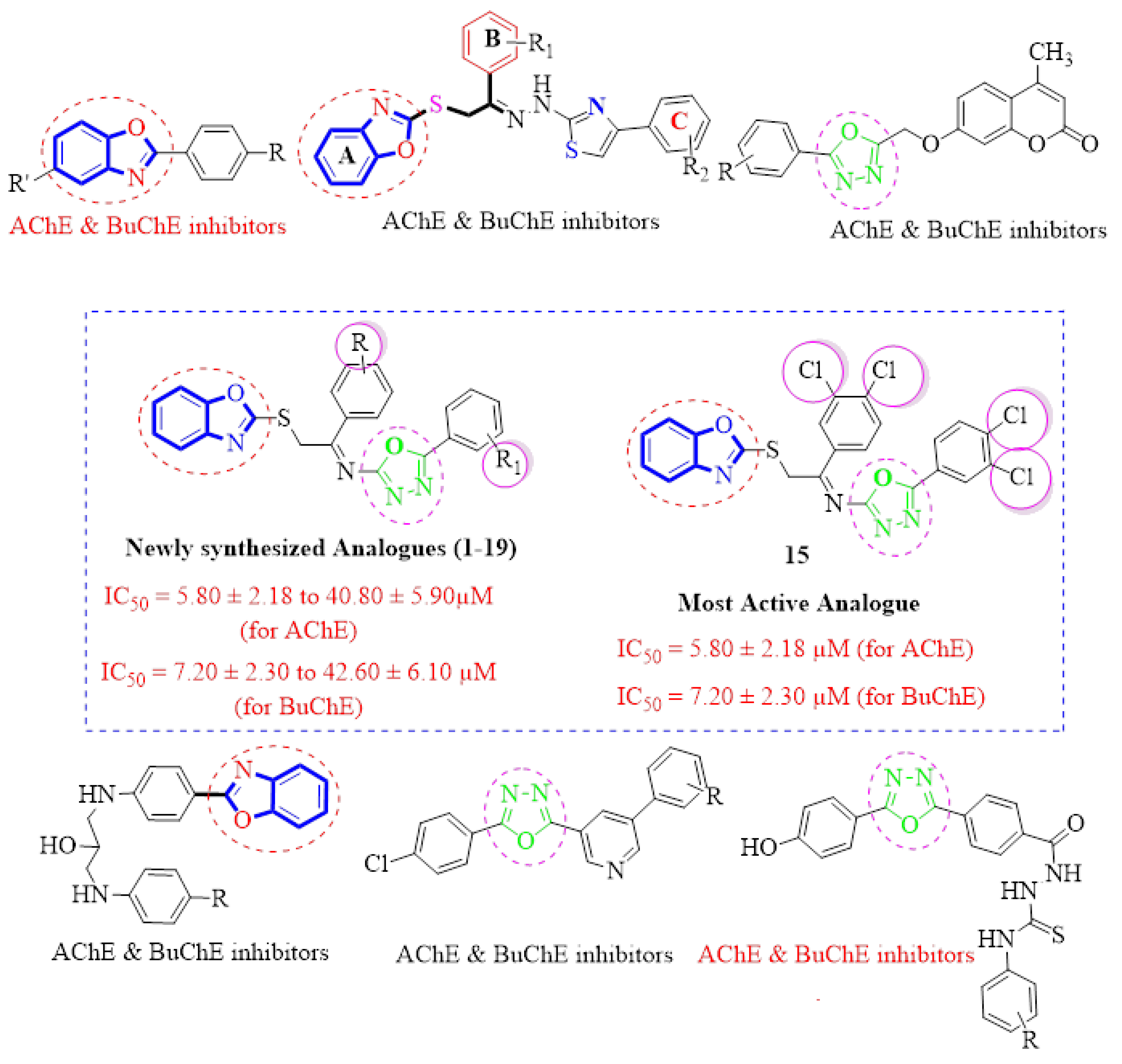
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
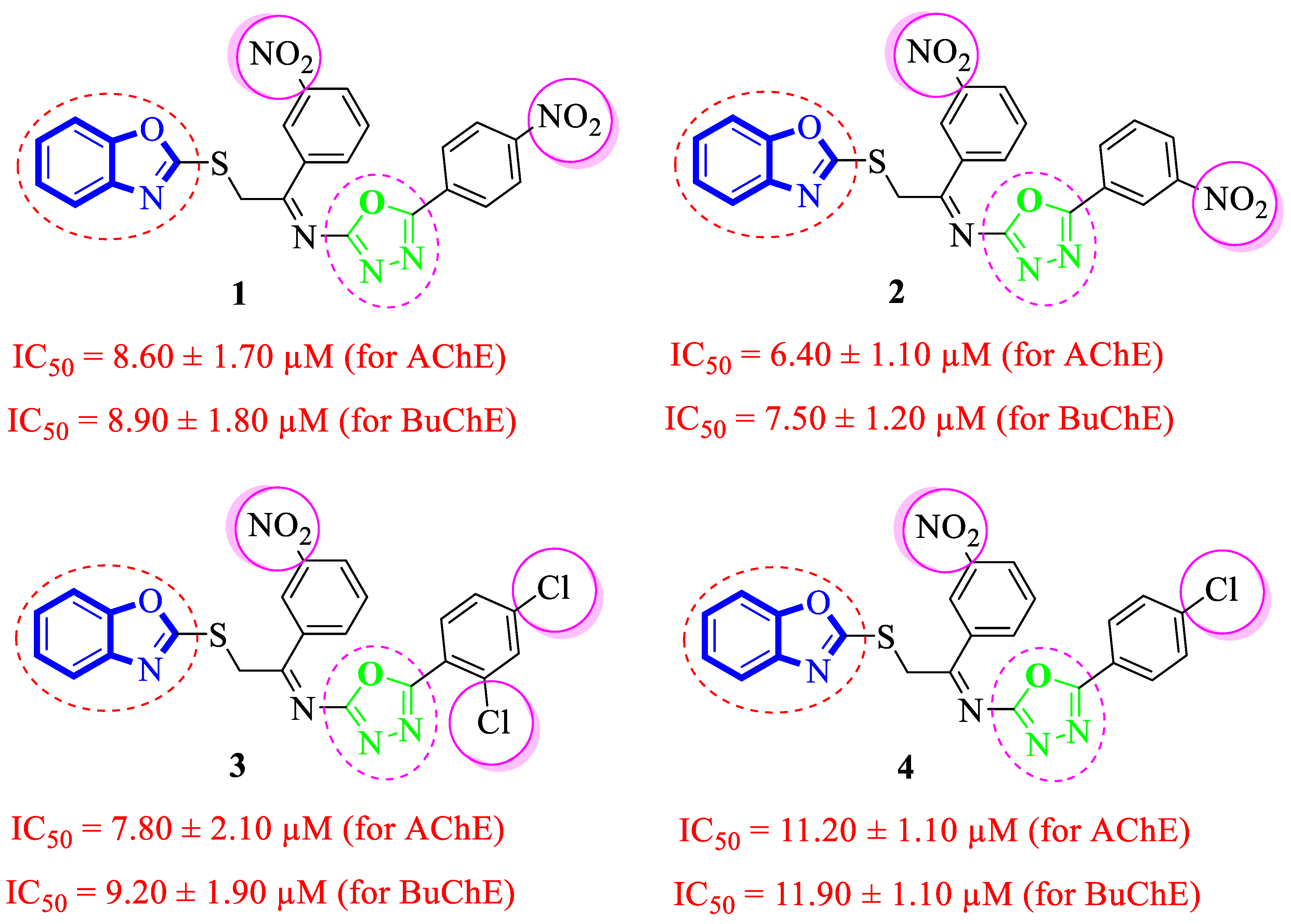
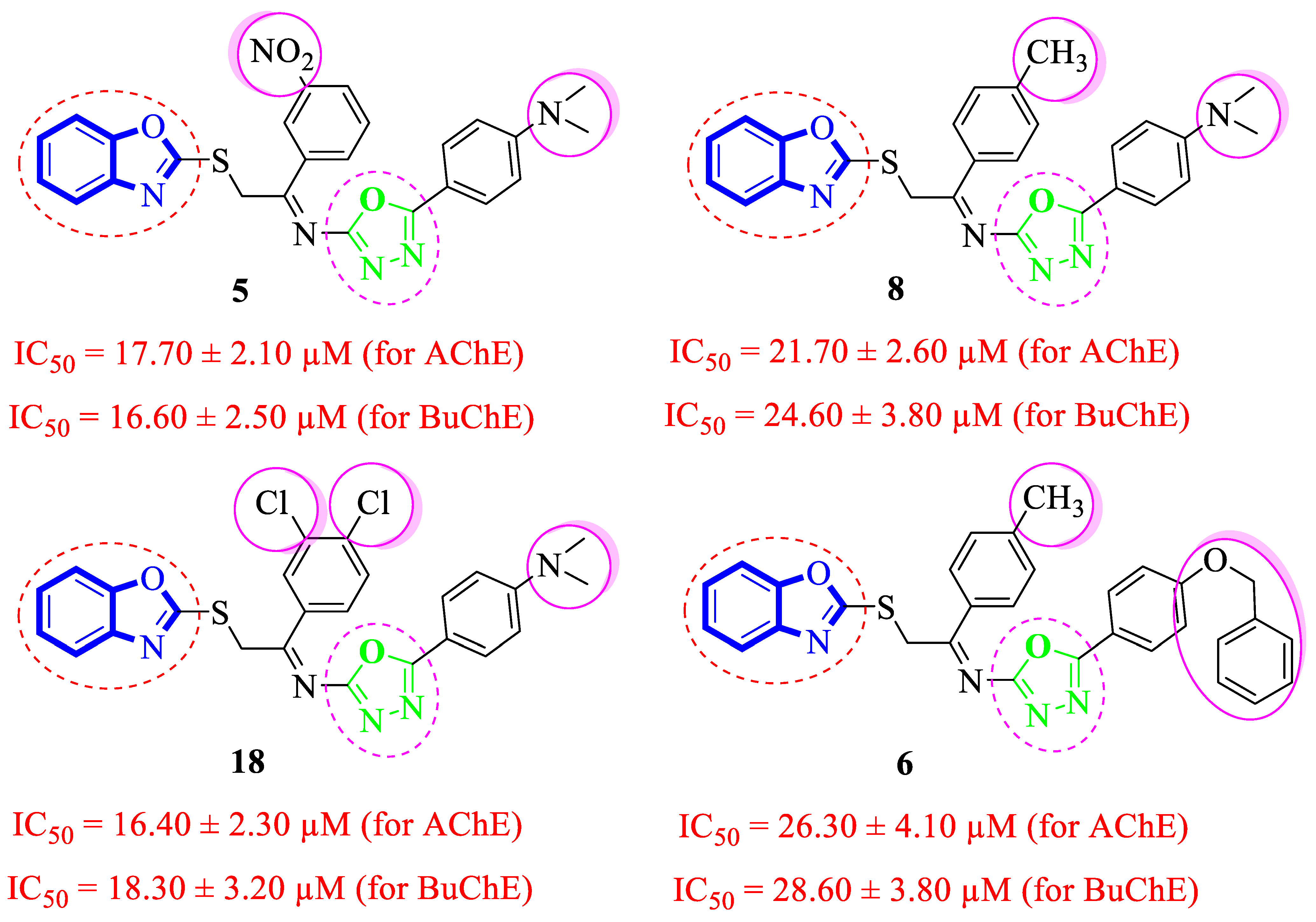
2.2. In Vitro Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and Butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE) Inhibitory Activities
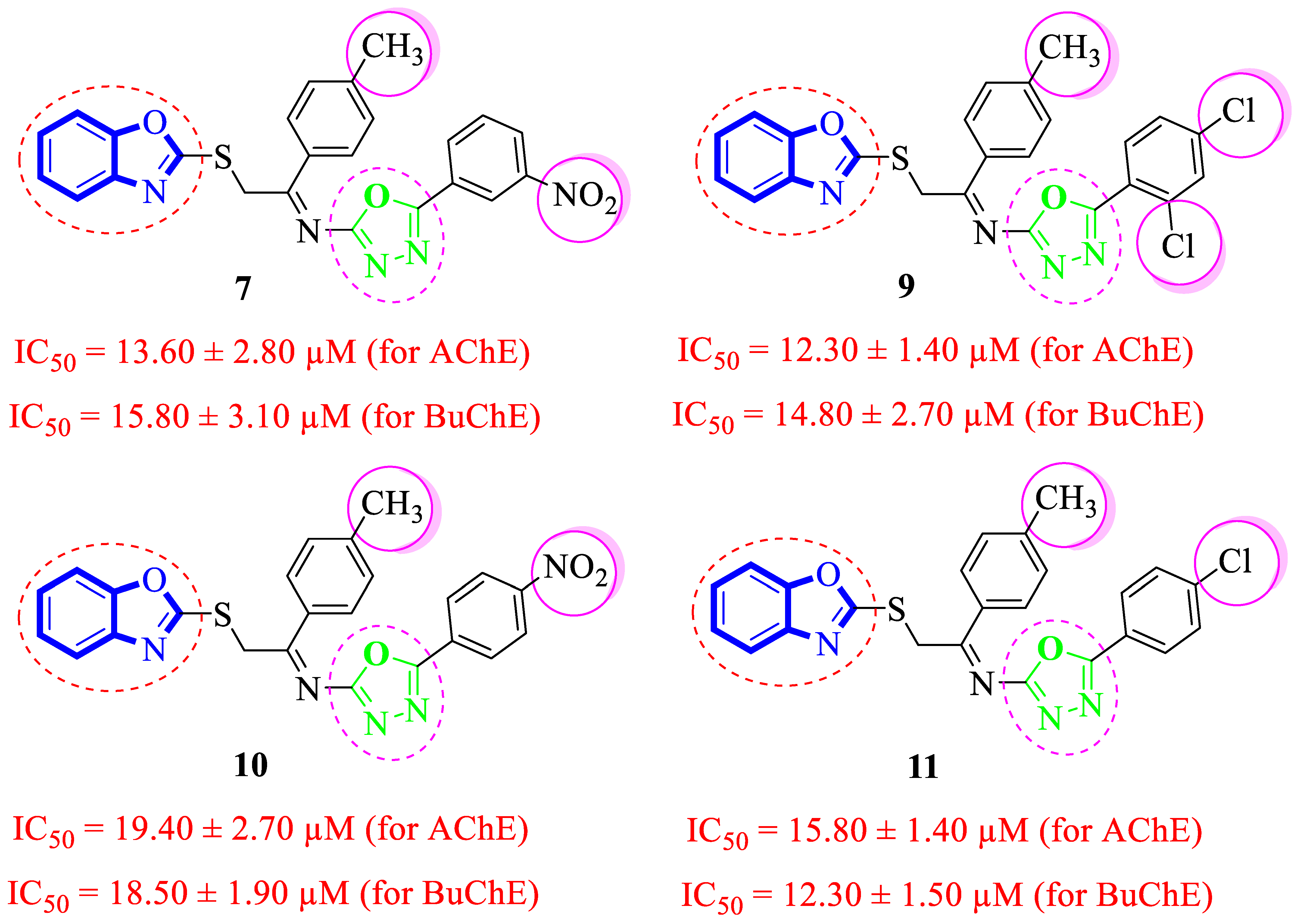
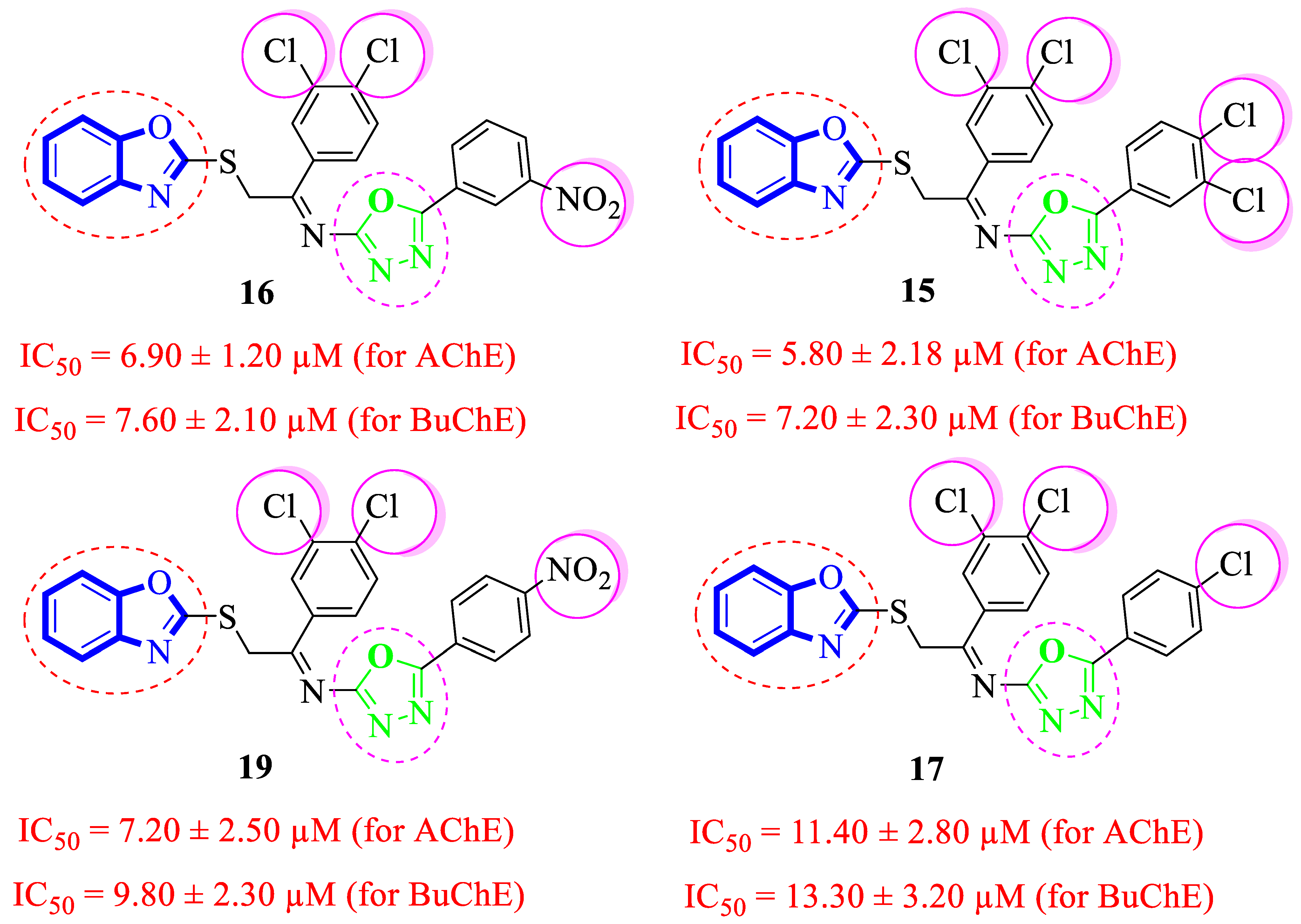
Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR) Studies for Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and Butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE) Inhibitory Activities
2.3. Molecular Docking Study
2.4. Computational Details
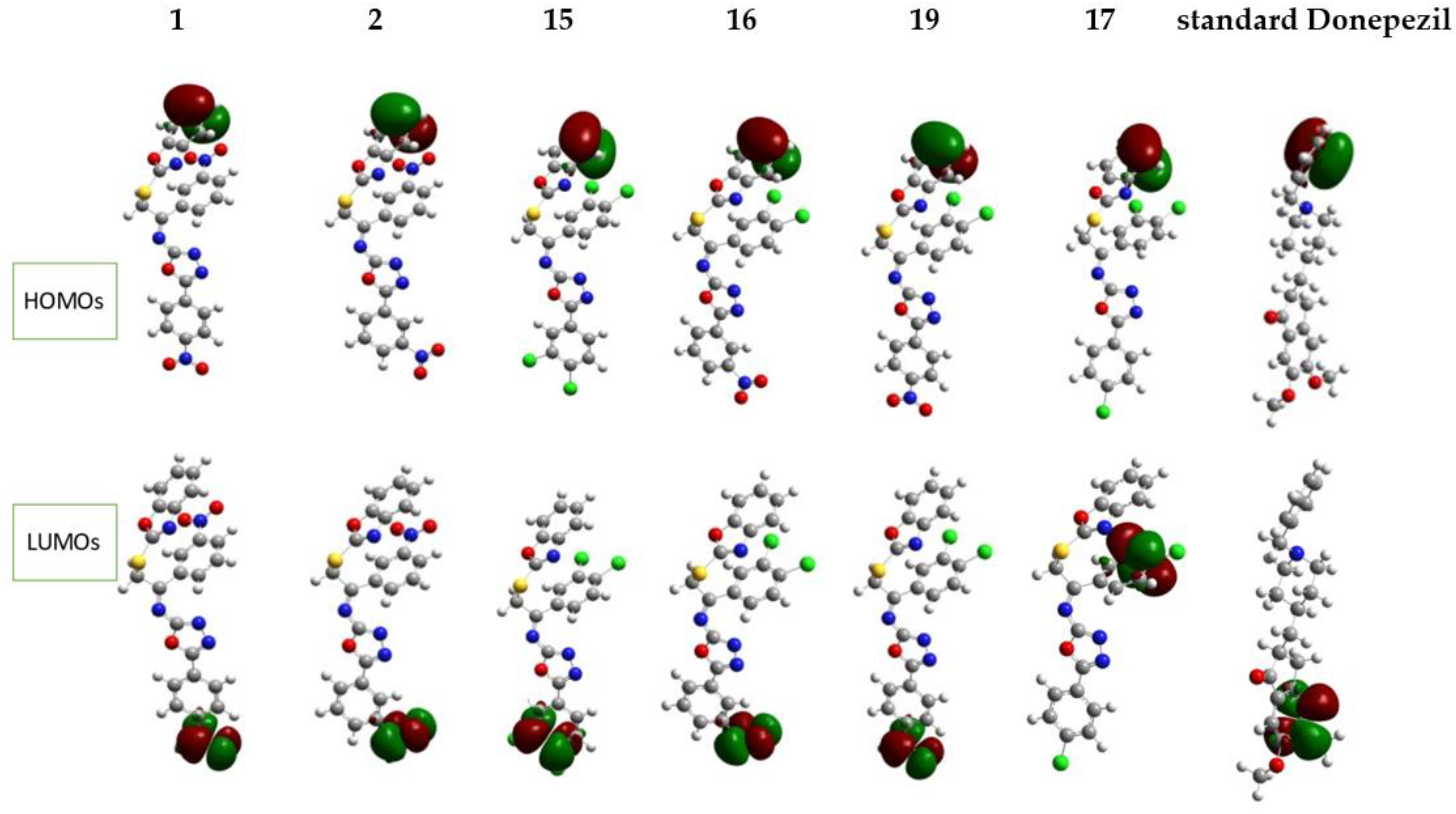
2.4.1. Frontier Molecular Orbital (FMO) Analysis
2.4.2. Reactivity Descriptor Parameters
2.4.3. Non-Linear Optical (NLO) Properties
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Methods
3.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Benzoxazole-Based Oxadiazole Analogues (1–19)
3.2.1. Synthesis of Substituted 2-(Benzo[d]oxazol-2-ylthio)-1-phenylethan-1-one Intermediate (III)
3.2.2. Synthesis of Substituted 5-Phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-amine Intermediate (VI)
3.2.3. Synthesis of Targeted Benzoxazole-Based Oxadiazole Scaffolds (1–19)
3.3. Spectral Analysis
3.3.1. (E)-2-(Benzo[d]oxazol-2-ylthio)-1-(3-nitrophenyl)-N-(5-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)ethan-1-imine (1)
3.3.2. (E)-2-(Benzo[d]oxazol-2-ylthio)-1-(3-nitrophenyl)-N-(5-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)ethan-1-imine (2)
3.3.3. (E)-2-(Benzo[d]oxazol-2-ylthio)-N-(5-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-1-(3-nitrophenyl)ethan-1-imine (3)
3.3.4. (E)-2-(Benzo[d]oxazol-2-ylthio)-N-(5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-1-(3-nitrophenyl)ethan-1-imine (4)
3.3.5. (E)-4-(5-((2-(Benzo[d]oxazol-2-ylthio)-1-(3-nitrophenyl)ethylidene)amino)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (5)
3.3.6. (E)-2-(Benzo[d]oxazol-2-ylthio)-N-(5-(4-(benzyloxy)phenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-1-(p-tolyl)ethan-1-imine (6) (Figures S1 and S2)
3.3.7. (E)-2-(Benzo[d]oxazol-2-ylthio)-N-(5-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-1-(p-tolyl)ethan-1-imine (7)
3.3.8. (E)-4-(5-((2-(Benzo[d]oxazol-2-ylthio)-1-(p-tolyl)ethylidene)amino)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (8) (Figures S3 and S4)
3.3.9. (E)-2-(Benzo[d]oxazol-2-ylthio)-N-(5-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-1-(p-tolyl)ethan-1-imine (9) (Figures S5 and S6)
3.3.10. (E)-2-(Benzo[d]oxazol-2-ylthio)-N-(5-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-1-(p-tolyl)ethan-1-imine (10)
3.3.11. (E)-2-(Benzo[d]oxazol-2-ylthio)-N-(5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-1-(p-tolyl)ethan-1-imine (11)
3.3.12. (E)-4-(5-((2-(Benzo[d]oxazol-2-ylthio)-1-(p-tolyl)ethylidene)amino)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)benzaldehyde (12)
3.3.13. (E)-2-(Benzo[d]oxazol-2-ylthio)-N-(5-(4-(benzyloxy)phenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-1-(m-tolyl)ethan-1-imine (13)
3.3.14. (E)-2-(Benzo[d]oxazol-2-ylthio)-N-(5-(naphthalen-2-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-1-(p-tolyl)ethan-1-imine (14)
3.3.15. (E)-2-(Benzo[d]oxazol-2-ylthio)-1-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-N-(5-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)ethan-1-imine (15)
3.3.16. (E)-2-(Benzo[d]oxazol-2-ylthio)-1-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-N-(5-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)ethan-1-imine (16)
3.3.17. (E)-2-(Benzo[d]oxazol-2-ylthio)-N-(5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-1-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)ethan-1-imine (17)
3.3.18. (E)-4-(5-((2-(Benzo[d]oxazol-2-ylthio)-1-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)ethylidene)amino)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (18)
3.3.19. (E)-2-(Benzo[d]oxazol-2-ylthio)-1-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-N-(5-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)ethan-1-imine (19)
3.4. Assay Protocol for Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition
3.5. Assay Protocol for Molecular Docking
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berman, H.A.; Yguerabide, J.; Taylor, P. Fluorescence energy transfer on acetylcholinesterase: Spatial relationship between peripheral site and active center. Biochemistry 1980, 19, 2226–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayeux, R. Epidemiology of neurodegeneration. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 26, 81–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skovronsky, D.M.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Neurodegenerative diseases: New concepts of pathogenesis and their therapeutic implications. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2006, 1, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pievani, M.; de Haan, W.; Wu, T.; Seeley, W.W.; Frisoni, G.B. Functional network disruption in the degenerative dementias. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budimir, A. Metal ions, Alzheimer’s disease and chelation therapy. Acta. Pharm. 2011, 61, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafii, M.S.; Aisen, P.S. Advances in Alzheimer’s disease drug development. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimo, A.; Jonsson, L.; Bond, J.; Prince, M.; Winblad, B.I. Alzheimer Disease International The worldwide economic impact of dementia 2010. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2013, 9, 1–11.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.; Bogdanovic, N.; Winblad, B.; Portelius, E.; Andreasen, N.; Cedazo-Minguez, A.; Zetterberg, H. Pathways to Alzheimer’s disease. J. Int. Med. 2014, 275, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, A.; Estrada, M.; Perez, C.; Rodriguez-Franco, M.I.; Iriepa, I.; Moraleda, I.; Chioua, M.; Marco-Contelles, J. Pyridonepezils, new dual AChE inhibitors as potential drugs for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: Synthesis, biological assessment, and molecular modeling. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 57, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akasofu, S.; Kimura, M.; Kosasa, T.; Sawada, K.; Ogura, H. Study of neuroprotection of donepezil, a therapy for Alzheimer’s disease. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2008, 175, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvesh, S.; Hopkins, D.A.; Geula, C. Neurobiology of butyrylcholinesterase. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Bachiller, M.I.; Perez, C.; Gonzalez-Munoz, G.C.; Conde, S.; Lopez, M.G.; Villarroya, M.; Garcia, A.G.; Rodriguez-Franco, M.I. Novel tacrine-8-hydroxyquinoline hybrids as multifunctional agents for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, with neuroprotective, cholinergic, antioxidant, and copper-complexing properties. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 4927–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzgrabe, U.; Kapkova, P.; Alptuzun, V.; Scheiber, J.; Kugelmann, E. Targeting acetylcholinesterase to treat neurodegeneration. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets. 2007, 11, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreiras, M.; Mendes, E.; Perry, M.; Francisco, A.; Marco-Contelles, J. The multifactorial nature of Alzheimer’s disease for developing potential therapeutics. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1745–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolognesi, M.L.; Rosini, M.; Andrisano, V. MTDL design strategy in the context of Alzheimeir’s disease: From lipocrine to memoquin and beyond. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockwood, K.; Mintzer, J.; Truyen, L.; Wessel, T.; Wilkinson, D. Effects of a flexible galantamine dose in Alzheimer’s disease: A randomised, controlled trial. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 2001, 71, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, P.S.; Almeida, R.C.; Schneider, K.; Beil, W.; Süssmuth, R.D.; Fiedler, H.P. Nataxazole, a New Benzoxazole Derivative with Antitumor Activity Produced by Streptomyces Sp. Tü 6176. J. Antibiot. 2008, 61, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Jacob, M.R.; Reynolds, M.B.; Kerwin, S.M. Synthesis and Evaluation of Anticancer Benzoxazoles and Benzimidazoles Related to UK-1. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2002, 10, 3997–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Manjunath, B.; Ghorai, S.; Sasmal, S. Benzoxazole Alkaloids: Occurrence, Chemistry, and Biology. Alkaloids Chem. Biol. 2018, 79, 71–137. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Huang, J.; Kurtán, T.; Mándi, A.; Jia, H.; Cheng, W.; Lin, W. Aaptodines A-D, Spiro Naphthyridine-Furooxazoloquinoline Hybrid Alkaloids from the Sponge AaptosSuberitoides. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 8215–8218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Madono, T.; Shigemori, H. Nakijinol, a Novel Sesquiterpenoid Containing a Benzoxazole Ring from an Okinawan Sponge. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 5589–5590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fang, X.; Xu, M.; Lei, Y.; Wu, Z.; Hu, X. Enantioselective Total Synthesis of Pseudopteroxazole and Ileabethoxazole. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7845–7849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Don, M.J.; Shen, C.C.; Lin, Y.L.; Syu, W.J.; Ding, Y.H.; Sun, C.M. Nitrogen-Containing Compounds from Salvia Miltiorrhiza. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1066–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Su, F.; Liu, C.; Yuan, H.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, Z.; Quan, T.; Luo, T. Enantioselective Total Syntheses of Various Amphilectane and Serrulatane Diterpenoids via Cope Rearrangements. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 6261–6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.Z.; Mulholland, N.; Beattie, D.; Irwin, D.; Gu, Y.C.; Chen, Q.; Yang, G.F.; Clough, J. Synthesis and antifungal activity of 3-(1,3,4-oxadiazol-5-yl) -indoles and 3-(1,3,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)methyl-indoles. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 63, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahsan, M.J.; Choupra, A.; Sharma, R.K.; Jadav, S.S.; Padmaja, P.; Hassan, M.Z.; al-Tamimi, A.B.S.; Geesi, M.H.; Bakht, M.A. Rationale Design, Synthesis, Cytotoxicity Evaluation, and Molecular Docking Studies of 1,3,4-oxadiazole Analogues. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Zhai, Z.W.; Wedge, D.E.; Duke, S.O.; Wu, H.K.; Weng, J.Q.; Tan, C.X.; Zhang, Y.G.; Liu, X.H. Synthesis and biological activity of novel 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives containing a pyrazole moiety. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2019, 45, 5989–6001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhu, X.L.; Jiang, L.L.; Liu, Z.M.; Yang, G.F. Synthesis, antifungal activity and CoMFA analysis of novel 1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 43, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.B.; Li, P.; He, Y.J.; Luo, J.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Y.H.; Chen, L.T. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel pyrethrin derivatives containing 1,3,4-oxadiazole and thioether moieties as active insecticidal agents. Chem. Pap. 2020, 74, 1621–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajik, H.; Dadras, A. Synthesis and herbicidal activity of novel 5-chloro-3-fluoro-2-phenoxypyridines with a 1,3,4-oxadiazole ring. J. Pestic. Sci. 2011, 36, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.N.; Gao, M.N.; Tu, H.; Ouyang, G.P. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of novel substituted purine derivatives. J. Heterocyclic Chem. 2016, 53, 2042–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.T.; Zhang, T.T.; Wang, P.Y.; Wu, Z.B.; Zhou, L.; Ye, Y.Q.; Zhou, X.; He, M.; Yang, S. Synthesis and bioactivities of novel 2-(thioether/sulfone)-5-pyrazolyl-1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2017, 28, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.H.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liao, G.P.; Shi, L.; Yang, X. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel sulfone derivatives containing 1,3,4-oxadiazole moiety. World J. Org. Chem. 2014, 2, 18–27. [Google Scholar]
- Rani, A.; Singh, A.; Kaur, J.; Singh, G.; Bhatti, R.; Gumede, N.; Kisten, P.; Singh, P.; and Kumar, V. 1H-1, 2, 3-triazole grafted tacrine-chalcone conjugates as potential cholinesterase inhibitors with the evaluation of their behavioral tests and oxidative stress in mice brain cells. Bioorganic Chem. 2021, 114, 105053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temiz-Arpaci, O.; Arisoy, M.; Sac, D.; Doganc, F.; Tasci, M.; Senol, F.S.; and Orhan, I.E. Biological evaluation and docking studies of some benzoxazole derivatives as inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase. Z. Nat. C 2016, 71, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, P.; Tripathi, P.N.; Sharma, P.; Rai, S.N.; Singh, S.P.; Srivastava, R.K.; Shankar, S.; and Shrivastava, S.K. Design and development of some phenyl benzoxazole derivatives as a potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitor with antioxidant property to enhance learning and memory. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 163, 116–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmaniye, D.; Çelikateş, B.K.; Sağlık, B.N.; Levent, S.; Çevik, U.A.; Çavuşoğlu, B.K.; Ilgın, S.; Özkay, Y.; Kaplancıklı, Z.A. Synthesis of some new benzoxazole derivatives and investigation of their anticancer activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 210, 112979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, N.; Al Sabahi, B.; AbuKhader, M.; Al Balushi, K.; Akhtar, M.J.; Khan, S.A. Design, synthesis and in vitro biological activities of coumarin linked 1, 3, 4-oxadiazole hybrids as potential multi-target directed anti-Alzheimer agents. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2022, 34, 101977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elghazawy, N.H.; Zaafar, D.; Hassan, R.R.; Mahmoud, M.Y.; Bedda, L.; Bakr, A.F.; Arafa, R.K. Discovery of new 1, 3, 4-oxadiazoles with dual activity targeting the cholinergic pathway as effective anti-Alzheimer agents. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 13, 1187–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, M.; Kilic, B.; Sagkan, R.I.; Aksakal, F.; Ercetin, T.; Gulcan, H.O.; Dogruer, D.S. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of new benzoxazolone/benzothiazolone derivatives as multi-target agents against Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 212, 113124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S.; Antony, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Krieg, H. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 154104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimme, S.; Ehrlich, S.; Goerigk, L. Effect of the damping function in dispersion corrected density functional theory. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoosefian, M.; Etminan, N. The role of solvent polarity in the electronic properties, stability and reactivity trend of a tryptophane/Pd doped SWCNT novel nanobiosensor from polar protic to non-polar solvents. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 64818–64825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayade, R.P.; Sekar, N. Benzimidazole-thiazole based NLOphoric styryl dyes with solid state emission–Synthesis, photophysical, hyperpolarizability and TD-DFT studies. Dye Pigment. 2016, 128, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, R.G.; Elantabli, F.M.; Aziz, A.A.A.; Moustafa, H.; El-Medani, S.M. Synthesis, characterization, NLO properties, antimicrobial, CT-DNA binding and DFT modeling of Ni (II), Pd (II), Pt (II), Mo (IV) and Ru (I) complexes with NOS Schiff base. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1176, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israr, H.; Rasool, N.; Rizwan, K.; Hashmi, M.A.; Mahmood, T.; Rashid, U.; Hussein, M.Z.; Akhtar, M.N. Synthesis and reactivities of triphenyl acetamide analogs for potential nonlinear optical material uses. Symmetry 2019, 11, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, K.; Rasool, N.; Hashmi, M.A.; Noreen, S.; Zubair, M.; Arshad, M.; Shah, S.A.A. Palladium (0) Catalyzed Synthesis of (E)-4-Bromo-N-((3-bromothiophen-2-yl) methylene)-2-methylaniline Derivatives via Suzuki Cross-Coupling Reaction: An Exploration of Their Non-Linear Optical Properties, Reactivity and Structural Features. Molecules 2021, 26, 5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suman, G.R.; Bubbly, S.G.; Gudennavar, S.B.; Muthu, S.; Roopashree, B.; Gayatri, V.; Gowda, N.N. Structural investigation, spectroscopic and energy level studies of Schiff base: 2-[(3′-N-salicylidenephenyl) benzimidazole] using experimental and DFT methods. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1139, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, M.; Rasool, N.; Ahmad, G.; Kosar, N.; Rashid, U. N-Arylation of Protected and Unprotected 5-Bromo-2-aminobenzimidazole as Organic Material: Non-Linear Optical (NLO) Properties and Structural Feature Determination through Computational Approach. Molecules 2021, 26, 6920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Li, D.; Zhang, A.-L.; Gao, J.-M. Synthesis, Antifungal Activities and Molecular Docking Studies of Benzoxazole and Benzothiazole Derivatives. Molecules 2018, 23, 2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, S.K.; Sinha, S.K.; Srivastava, P.; Tripathi, P.N.; Sharma, P.; Tripathi, M.K.; Tripathi, A.; Choubey, P.K.; Waiker, D.K.; Aggarwal, L.M.; et al. Design and development of novel p-aminobenzoic acid derivatives as potential cholinesterase inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorganic Chem. 2019, 82, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Ullah, H.; Hussain, R.; Khan, Y.; Khan, M.U.; Khan, M.; Sattar, A.; Khan, M.S. Synthesis, in vitro bio-evaluation, and molecular docking study of thiosemicarbazone-based isatin/bis-Schiff base hybrid analogues as effective cholinesterase inhibitors. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1284, 135351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-R.; Ren, S.-T.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.-X.; Liu, S.-H.; Liu, W.-W.; Shi, D.-H.; Cao, Z.-L. Synthesis and anticholinesterase activities of novel glycosyl benzoxazole derivatives. J. Chem. Res. 2020, 44, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Y.; Rehman, W.; Hussain, R.; Khan, S.; Malik, A.; Khan, M.; Liaqat, A.; Rasheed, L.; Begum, F.; Fazil, S.; et al. New biologically potent benzimidazole-based-triazole derivatives as acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors along with molecular docking study. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2022, 59, 2225–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



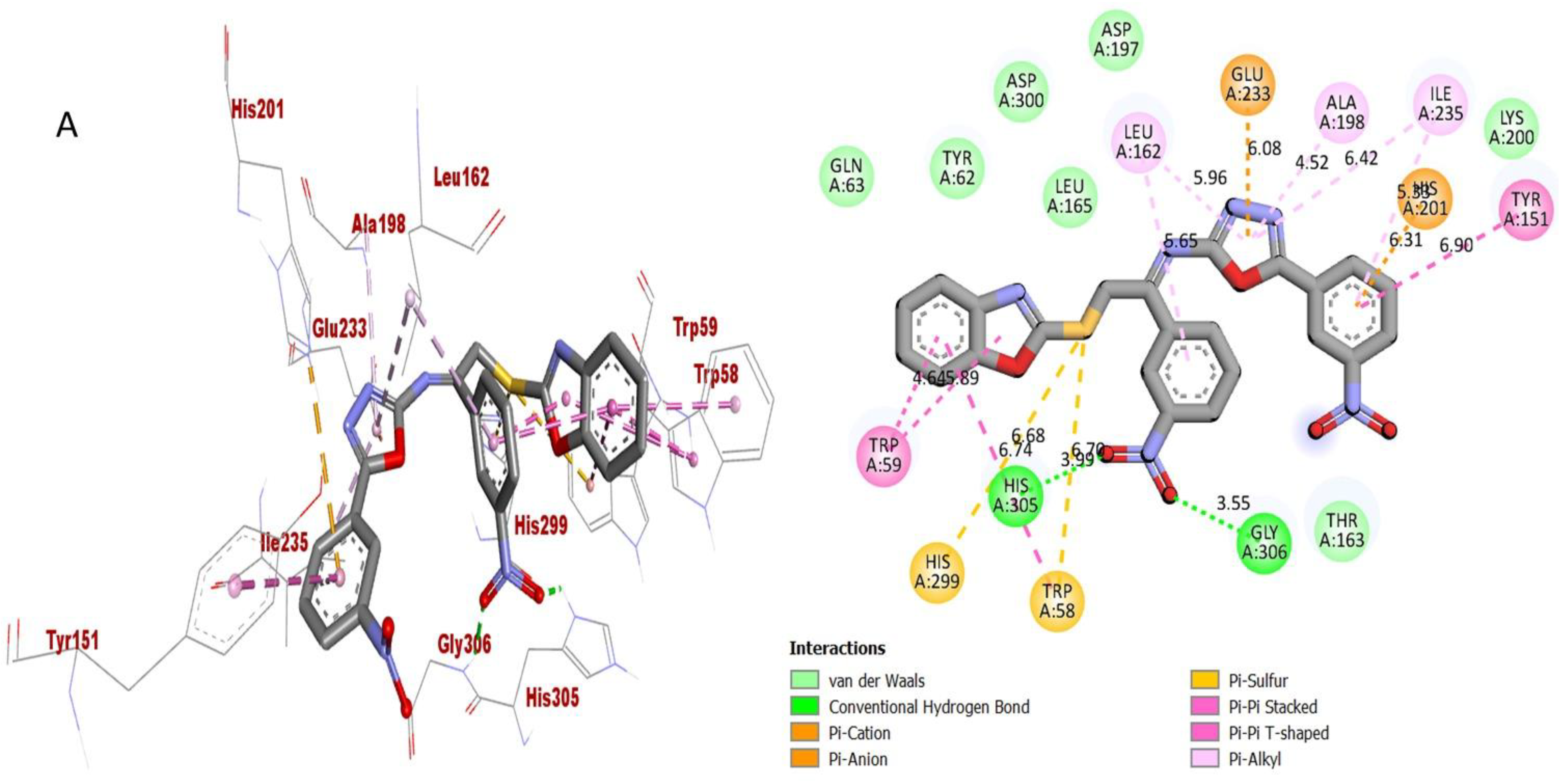
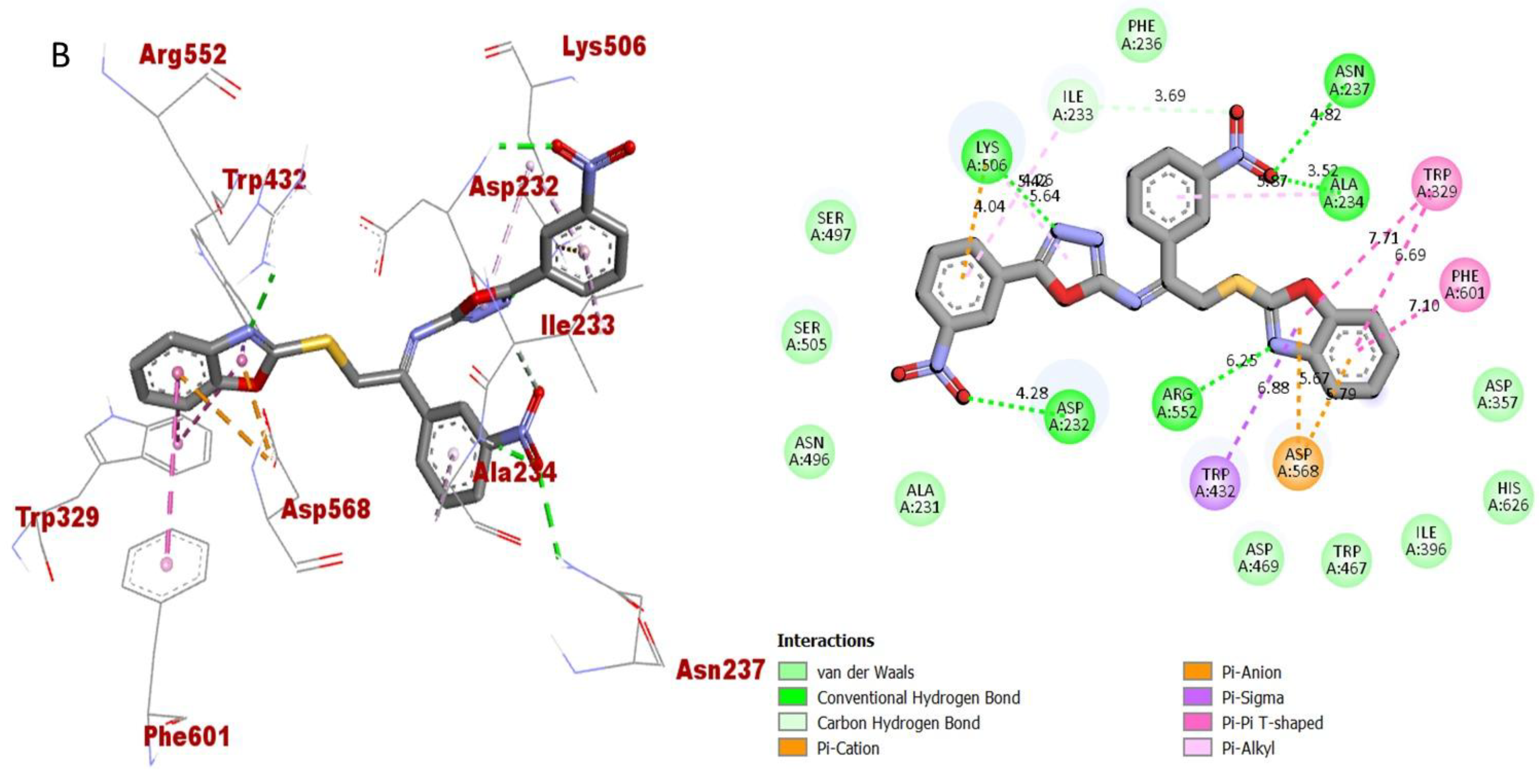




| Active Analogues | Receptor | Types of Interactions | Distance (Ao) | Docking Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analogue-2 (A) in AChE complex | TRP-A-58 | Pi-S | 6.70 | −12.83 |
| TRP-A-58 | Pi-Pi Stacked | 6.74 | ||
| HIS-A-305 | H-B | 3.99 | ||
| HIS-A-299 | Pi-S | 6.68 | ||
| TRP-A-59 | Pi-Pi Stacked | 5.89 | ||
| TRP-A-59 | Pi-Pi Stacked | 4.64 | ||
| LEU-A-162 | Pi-R | 5.65 | ||
| LEU-A-162 | Pi-R | 5.96 | ||
| GLU-A-233 | Pi-S | 6.08 | ||
| ALA-A-198 | Pi-R | 4.52 | ||
| ILE-A-235 | Pi-R | 6.42 | ||
| ILE-A-235 | Pi-R | 5.33 | ||
| HIS-A-201 | Pi-S | 6.31 | ||
| TYR-A-151 | Pi-Pi Stacked | 6.90 | ||
| GLY-A-306 | H-B | 3.55 | ||
| Analogue-2 (B) in BuChE complex | ASP-A-232 | H-B | 4.28 | −12.43 |
| LYS-A-506 | Pi-Anion | 4.04 | ||
| LYS-A-506 | Pi-R | 5.64 | ||
| LYS-A-506 | H-B | 5.26 | ||
| ILE-A-233 | Pi-R | 5.22 | ||
| ILE-A-233 | C-H | 3.69 | ||
| ASN-A-237 | H-B | 4.82 | ||
| ALA-A-234 | H-B | 3.52 | ||
| ALA-A-234 | Pi-R | 5.87 | ||
| TRP-A-329 | Pi-Pi T-Shaped | 7.71 | ||
| TRP-A-329 | Pi-Pi T-Shaped | 6.69 | ||
| PHE-A-601 | Pi-Pi T-Shaped | 7.10 | ||
| ASP-A-568 | Pi-Anion | 5.79 | ||
| ASP-A-568 | Pi-Anion | 5.67 | ||
| TRP-A-432 | Pi-Sigma | 6.88 | ||
| ARG-A-552 | H-B | 6.25 | ||
| Analogue-15 (C) in AChE complex | HIS-A-305 | Pi-R | 3.97 | −11.87 |
| LEU-A-162 | Pi-R | 5.29 | ||
| LEU-A-162 | Pi-R | 6.14 | ||
| LEU-A-162 | Pi-Sigma | 7.29 | ||
| LEU-A-162 | Pi-R | 7.09 | ||
| HIS-A-101 | Pi-S | 5.47 | ||
| LYS-A-200 | Pi-R | 4.16 | ||
| HIS-A-201 | Pi-S | 5.49 | ||
| ILE-A-235 | Pi-Sigma | 4.02 | ||
| ALA-A-198 | Pi-R | 5.61 | ||
| ALA-A-198 | Pi-R | 5.13 | ||
| ALA-A-198 | Pi-R | 6.82 | ||
| GLU-A-233 | Pi-S | 4.60 | ||
| GLN-A-63 | H-B | 4.58 | ||
| LEU-A-165 | Pi-R | 5.50 | ||
| TRP-A-59 | Pi-Pi Stacked | 3.97 | ||
| TRP-A-59 | Pi-R | 6.04 | ||
| TRP-A-59 | Pi-R | 5.96 | ||
| Analogue-15 (D) in BChE complex | ARG-A-552 | H-B | 6.01 | −11.25 |
| PHE-A-476 | Pi-S | 6.26 | ||
| ASP-A-568 | Pi-Anion | 5.57 | ||
| ASP-A-568 | Pi-Anion | 6.42 | ||
| ASP-A-568 | Pi-Anion | 6.01 | ||
| TRP-A-432 | Pi-R | 7.68 | ||
| PHE-A-601 | Pi-R | 5.63 | ||
| ALA-A-602 | Pi-R | 4.70 | ||
| ALA-A-628 | Pi-R | 4.51 | ||
| LEU-A-240 | Pi-R | 5.85 | ||
| ILE-A-233 | Pi-R | 4.16 | ||
| ILE-A-233 | Pi-R | 4.66 | ||
| ALA-A-234 | Pi-R | 4.32 | ||
| ALA-A-234 | H-B | 3.28 | ||
| ALA-A-234 | Pi-R | 5.35 | ||
| Analogue-16 (E) in AChE complex | LEU-A-162 | Pi-R | 5.60 | −10.96 |
| LEU-A-162 | Pi-R | 5.80 | ||
| LEU-A-162 | Pi-R | 6.22 | ||
| LYS-A-200 | Pi-R | 5.57 | ||
| HIS-A-201 | Pi-Anion | 5.55 | ||
| HIS-A-201 | Pi-Anion | 6.45 | ||
| ILE-A-235 | Pi-Sigma | 5.17 | ||
| ALA-A-198 | Pi-R | 4.44 | ||
| ALA-A-198 | Pi-R | 6.70 | ||
| GLN-A-63 | H-B | 4.32 | ||
| LEU-A-165 | Pi-Sigma | 5.37 | ||
| TRP-A-59 | Pi-Pi Stacked | 4.17 | ||
| TRP-A-59 | H-B | 4.64 | ||
| HIS-A-305 | Pi-R | 3.93 | ||
| Analogue-16 (F) in BuChE complex | PHE-A-601 | Pi-Pi Stacked | 7.18 | −10.16 |
| TRP-A-329 | Pi-Pi Stacked | 6.82 | ||
| ASP-A-568 | Pi-Anion | 5.75 | ||
| ASP-A-568 | Pi-Anion | 5.71 | ||
| TRP-A-432 | Pi-Sigma | 6.88 | ||
| ARG-A-552 | H-B | 6.41 | ||
| ASP-A-232 | H-B | 3.39 | ||
| LYS-A-506 | Pi-Anion | 4.44 | ||
| PHE-A-476 | Pi-R | 4.78 | ||
| LYS-A-506 | Pi-Anion | 5.26 | ||
| ILE-A-233 | Pi-R | 6.06 | ||
| PHE-A-476 | Pi-R | 5.19 | ||
| PHE-A-476 | Pi-Pi Stacked | 4.28 |
| Synthesized Compounds | R | R1 | AChE Inhibition IC50 ± SEM a [µM] | BuChE Inhibition IC50 ± SEM a [µM] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 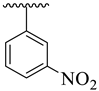 | 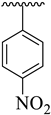 | 8.60 ± 1.70 | 8.90 ± 1.80 |
| 2 | 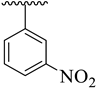 | 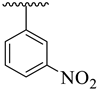 | 6.40 ± 1.10 | 7.50 ± 1.20 |
| 3 | 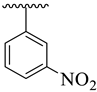 | 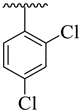 | 7.80 ± 2.10 | 9.20 ± 1.90 |
| 4 | 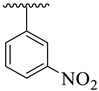 | 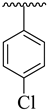 | 11.20 ± 1.10 | 11.90 ± 1.10 |
| 5 | 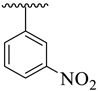 | 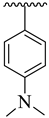 | 17.70 ± 2.10 | 16.60 ± 2.50 |
| 6 | 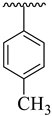 | 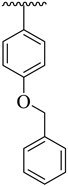 | 26.30 ± 4.10 | 28.60 ± 3.80 |
| 7 |  | 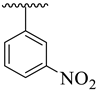 | 13.60 ± 2.80 | 15.80 ± 3.10 |
| 8 | 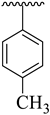 | 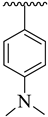 | 21.70 ± 2.60 | 24.60 ± 3.80 |
| 9 | 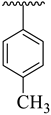 | 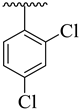 | 12.30 ± 1.40 | 14.80 ± 2.70 |
| 10 | 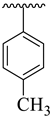 | 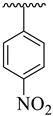 | 19.40 ± 2.70 | 18.50 ± 1.90 |
| 11 | 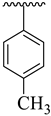 | 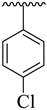 | 15.80 ± 1.40 | 12.30 ± 1.50 |
| 12 | 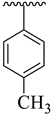 | 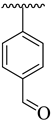 | 25.70 ± 2.60 | 28.70 ± 3.90 |
| 13 | 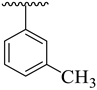 | 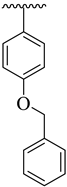 | 27.90 ± 5.60 | 31.50 ± 4.90 |
| 14 | 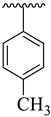 | 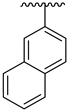 | 40.80 ± 5.90 | 42.60 ± 6.10 |
| 15 | 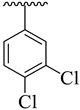 | 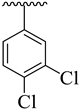 | 5.80 ± 2.18 | 7.20 ± 2.30 |
| 16 | 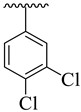 | 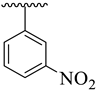 | 6.90 ± 1.20 | 7.60 ± 2.10 |
| 17 | 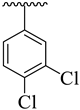 | 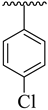 | 11.40 ± 2.80 | 13.30 ± 3.20 |
| 18 | 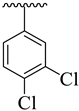 | 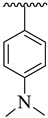 | 16.40 ± 2.30 | 18.30 ± 3.20 |
| 19 | 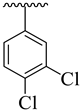 | 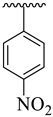 | 7.20 ± 2.50 | 9.80 ± 2.30 |
| Standard Donepezil b drug | 33.65 ± 3.50 | 35.80 ± 4.60 | ||
1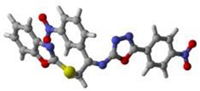 | 2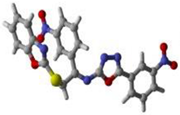 | 15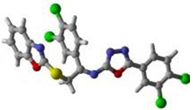 | Standard Donepezil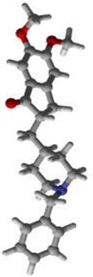 |
16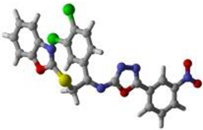 | 19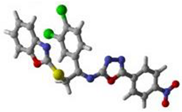 | 17 |
| Compounds | EHOMO (eV) | ELUMO (eV) | ΔH-L (eV) | μο (Debye) | βο (e.s.u.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −6.69 | −2.83 | 3.86 | 4.73 | 6.91 × 10−29 |
| 2 | −6.68 | −2.60 | 4.08 | 7.62 | 1.23 × 10−29 |
| 15 | −6.69 | −2.26 | 4.42 | 3.90 | 1.83 × 10−29 |
| 16 | −6.70 | −2.59 | 4.10 | 10.01 | 2.23 × 10−29 |
| 19 | −6.70 | −2.82 | 3.88 | 6.81 | 8.03 × 10−29 |
| 17 | −6.65 | −2.25 | 4.40 | 5.21 | 2.83 × 10−29 |
| Standard Donepezil | −5.84 | −1.23 | 4.61 | 7.61 | 1.65 × 10−29 |
| Compounds | I (eV) | EA (eV) | η (eV) | µ (eV) | ω (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.69 | 2.83 | −1.93 | 4.76 | −5.87 |
| 2 | 6.68 | 2.60 | −2.04 | 4.64 | −5.28 |
| 15 | 6.69 | 2.26 | −2.21 | 4.48 | −4.53 |
| 16 | 6.70 | 2.59 | −2.05 | 4.64 | −5.26 |
| 19 | 6.70 | 2.82 | −1.94 | 4.76 | −5.84 |
| 17 | 6.65 | 2.25 | −2.20 | 4.45 | −4.50 |
| Standard Donepezil | 5.84 | 1.23 | −2.30 | 3.53 | −2.71 |
| Compounds | αο (a.u.) | βο (a.u.) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 538.88 | 8005.45 |
| 2 | 530.58 | 1429.40 |
| 15 | 558.30 | 2129.64 |
| 16 | 542.47 | 2588.09 |
| 19 | 553.44 | 9302.00 |
| 17 | 544.45 | 3278.25 |
| Standard Donepezil | 429.28 | 1919.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anwar, S.; Rehman, W.; Hussain, R.; Khan, S.; Alanazi, M.M.; Alsaif, N.A.; Khan, Y.; Iqbal, S.; Naz, A.; Hashmi, M.A. Investigation of Novel Benzoxazole-Oxadiazole Derivatives as Effective Anti-Alzheimer’s Agents: In Vitro and In Silico Approaches. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16070909
Anwar S, Rehman W, Hussain R, Khan S, Alanazi MM, Alsaif NA, Khan Y, Iqbal S, Naz A, Hashmi MA. Investigation of Novel Benzoxazole-Oxadiazole Derivatives as Effective Anti-Alzheimer’s Agents: In Vitro and In Silico Approaches. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(7):909. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16070909
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnwar, Saeed, Wajid Rehman, Rafaqat Hussain, Shoaib Khan, Mohammed M. Alanazi, Nawaf A. Alsaif, Yousaf Khan, Shahid Iqbal, Adeela Naz, and Muhammad Ali Hashmi. 2023. "Investigation of Novel Benzoxazole-Oxadiazole Derivatives as Effective Anti-Alzheimer’s Agents: In Vitro and In Silico Approaches" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 7: 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16070909
APA StyleAnwar, S., Rehman, W., Hussain, R., Khan, S., Alanazi, M. M., Alsaif, N. A., Khan, Y., Iqbal, S., Naz, A., & Hashmi, M. A. (2023). Investigation of Novel Benzoxazole-Oxadiazole Derivatives as Effective Anti-Alzheimer’s Agents: In Vitro and In Silico Approaches. Pharmaceuticals, 16(7), 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16070909