In-Silico Mining of the Toxins Database (T3DB) towards Hunting Prospective Candidates as ABCB1 Inhibitors: Integrated Molecular Docking and Lipid Bilayer-Enhanced Molecular Dynamics Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. In-Silico Protocol Validation
2.2. Virtual Screening of the T3DB Database
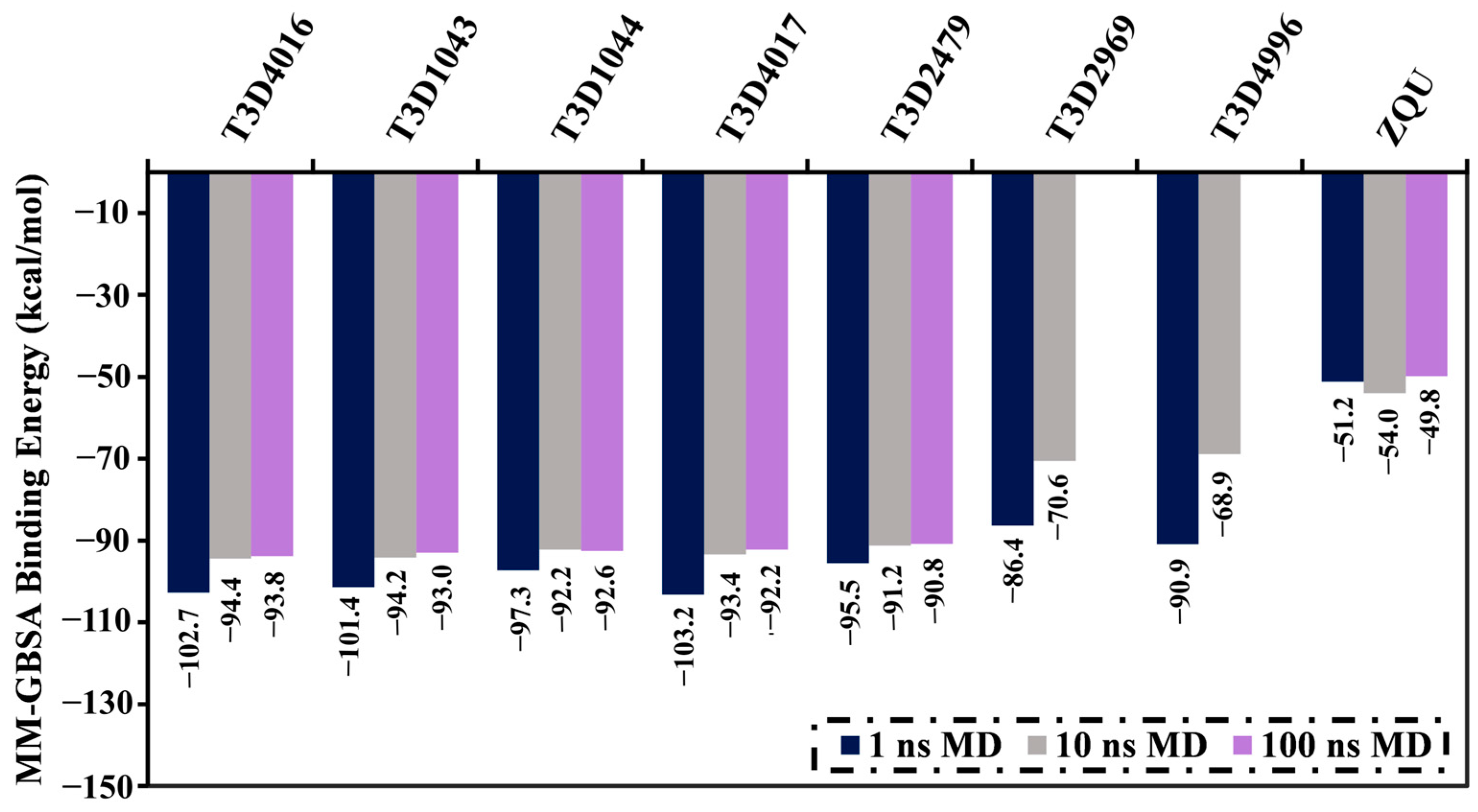
2.3. Molecular Dynamics
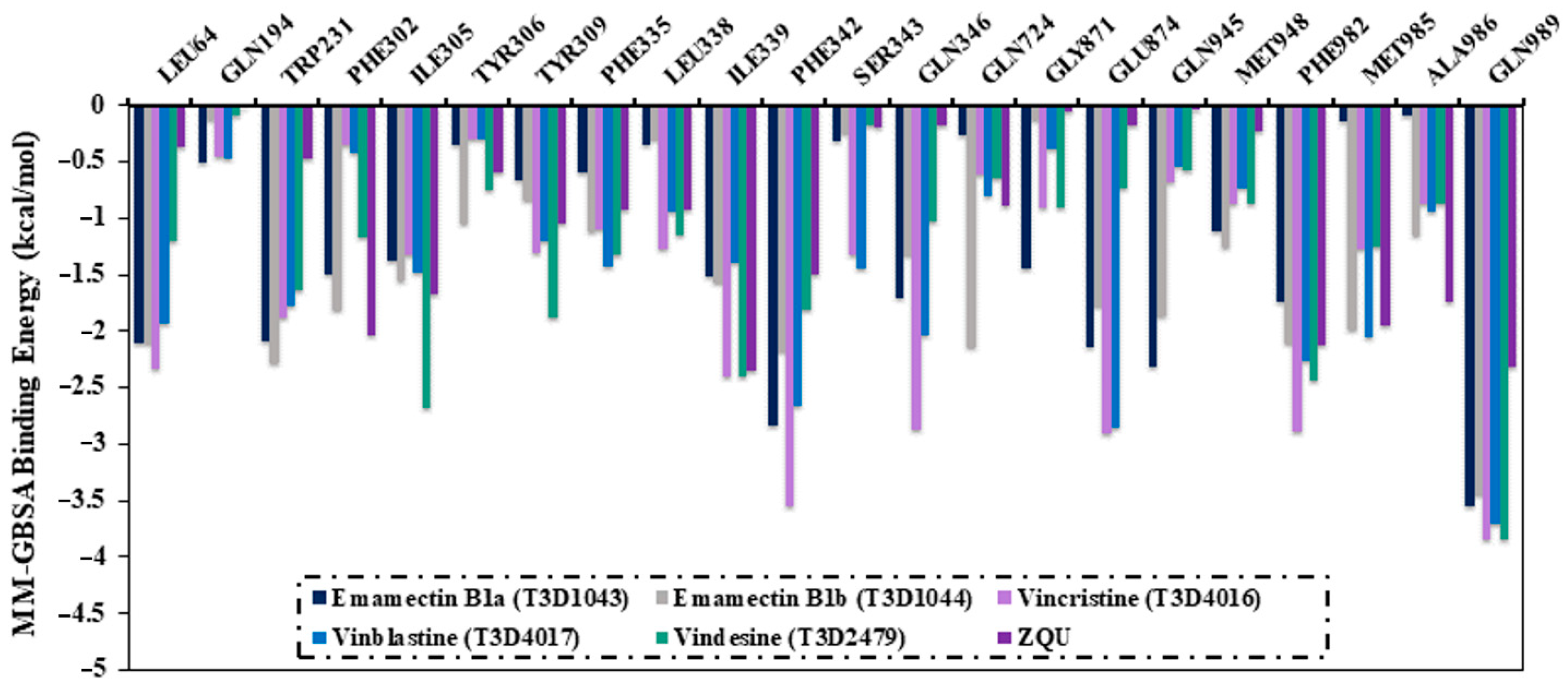
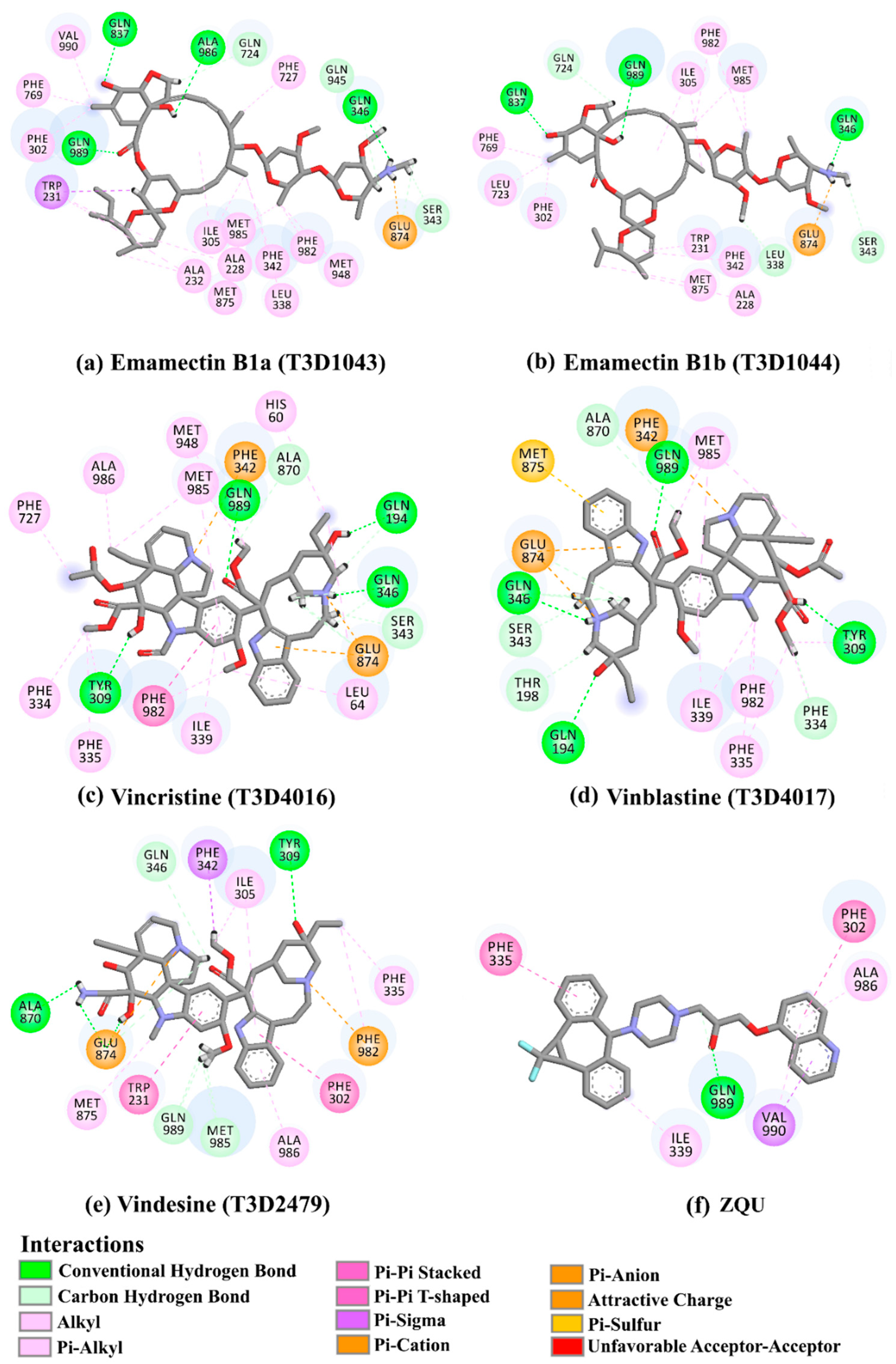
2.4. Post-Dynamics Analyses
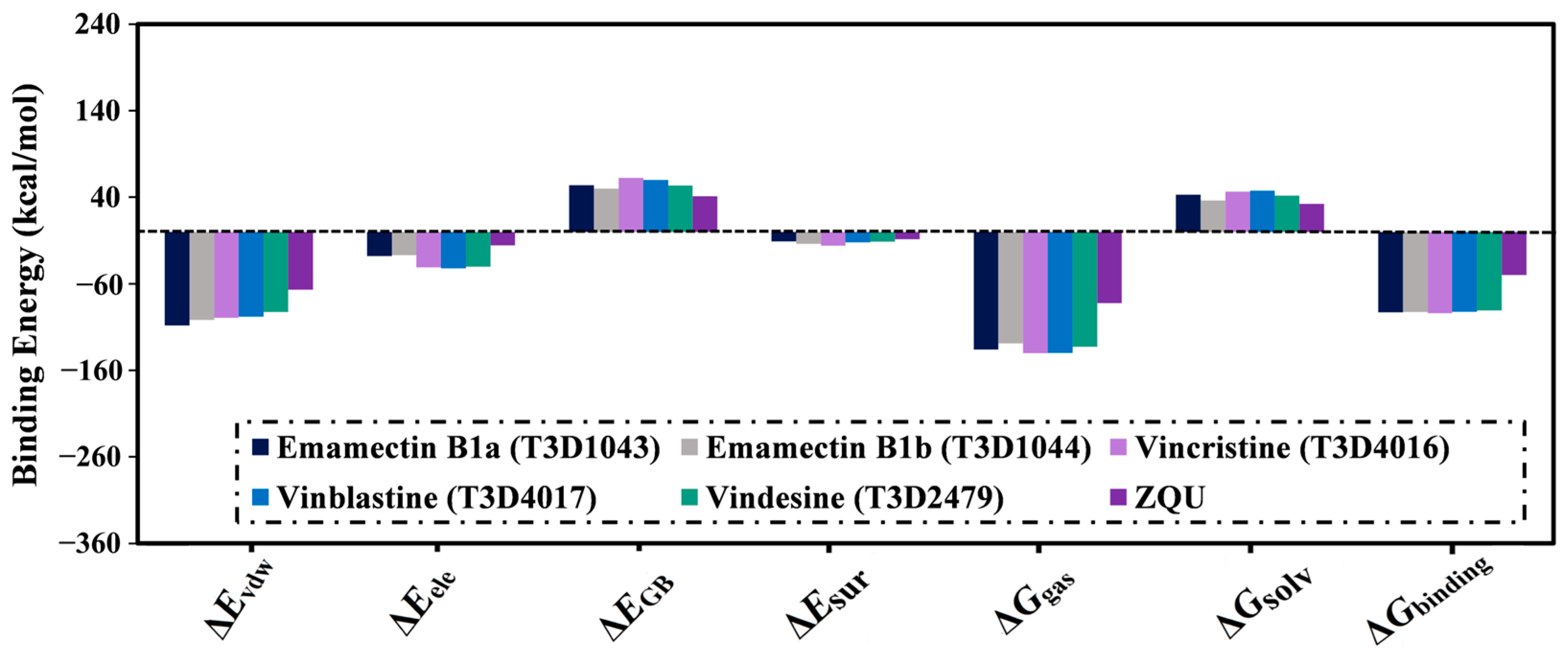
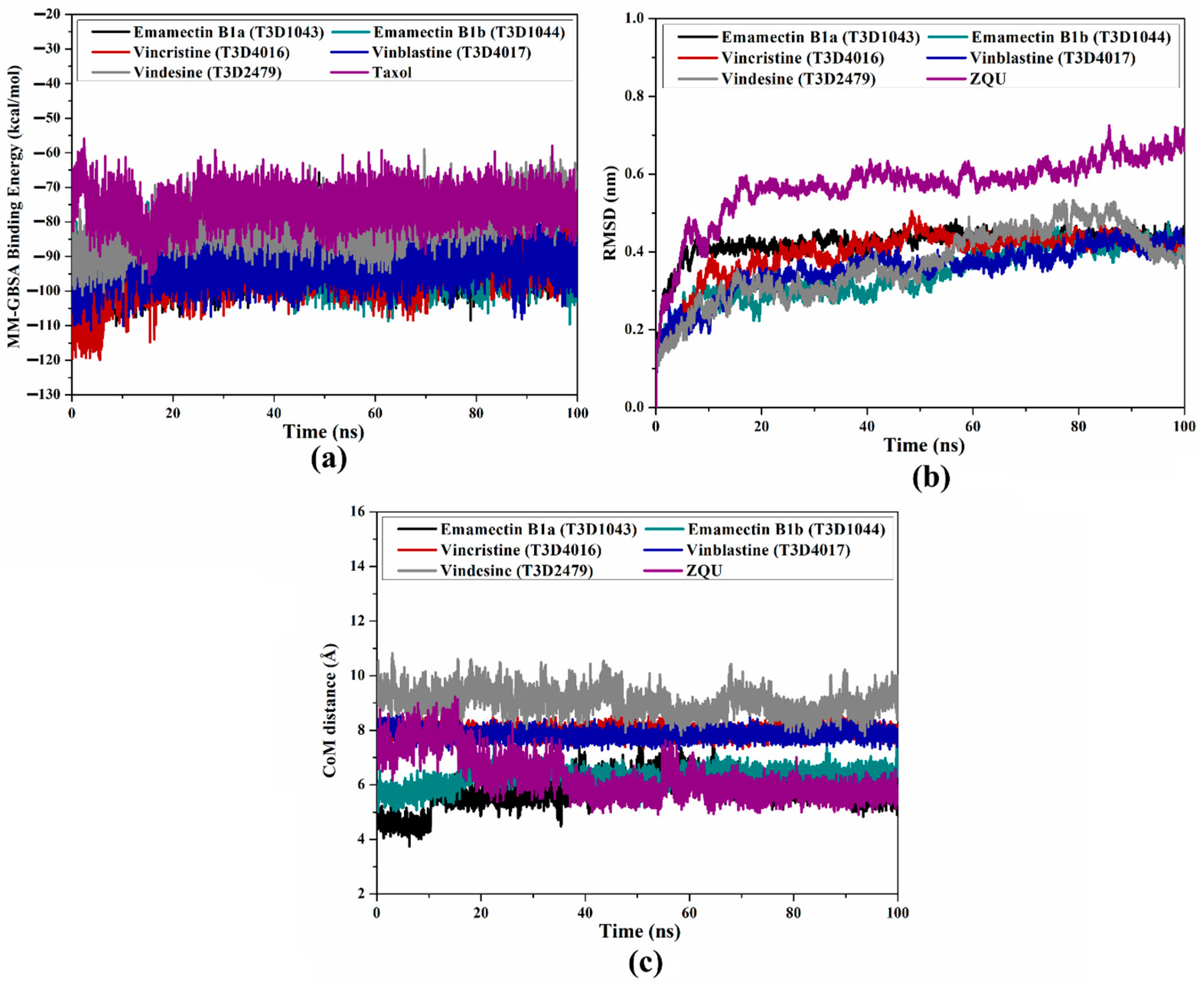
2.4.1. Binding Energy Per-Trajectory
2.4.2. Root-Mean-Square Deviation (RMSD)
2.4.3. Center-of-Mass (CoM) Distance
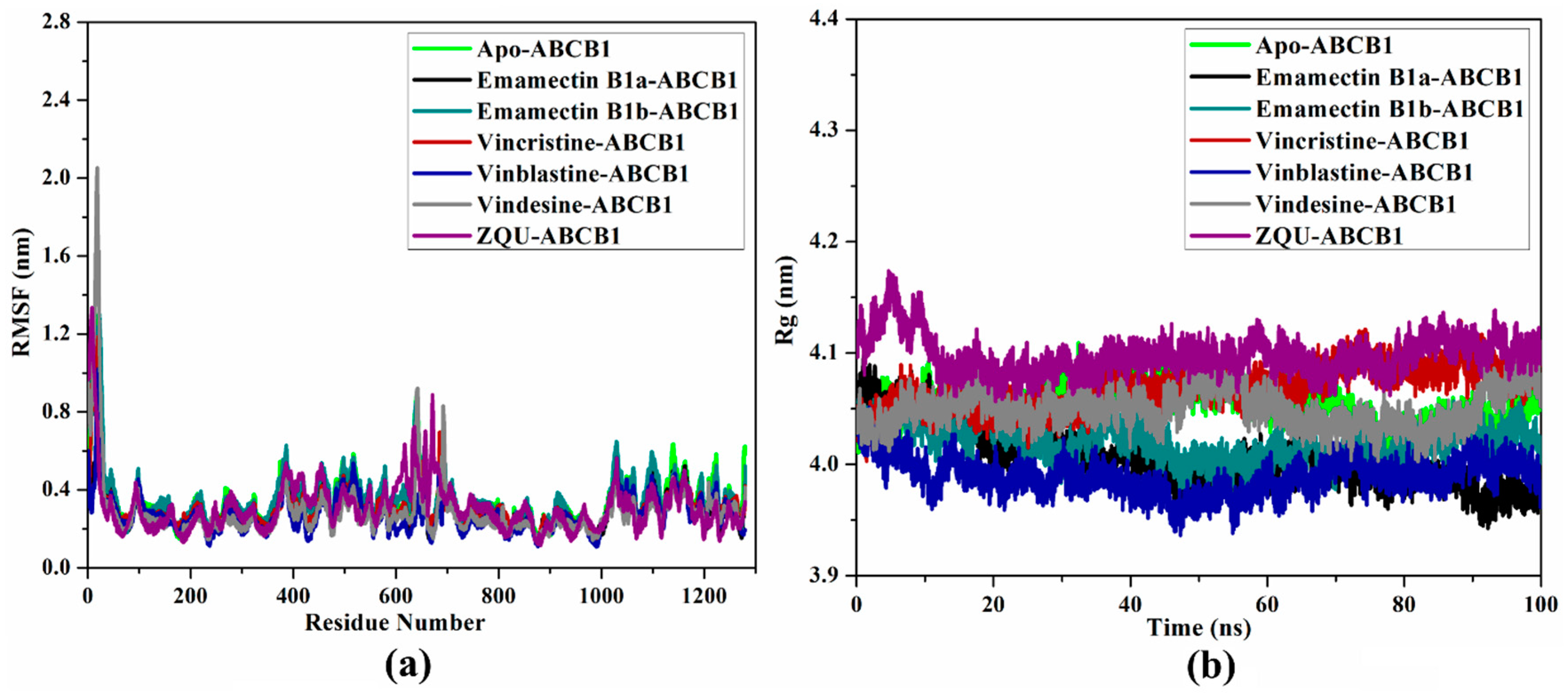
2.4.4. Root-Mean-Square Fluctuations (RMSF)
2.4.5. Radius of Gyration (Rg)
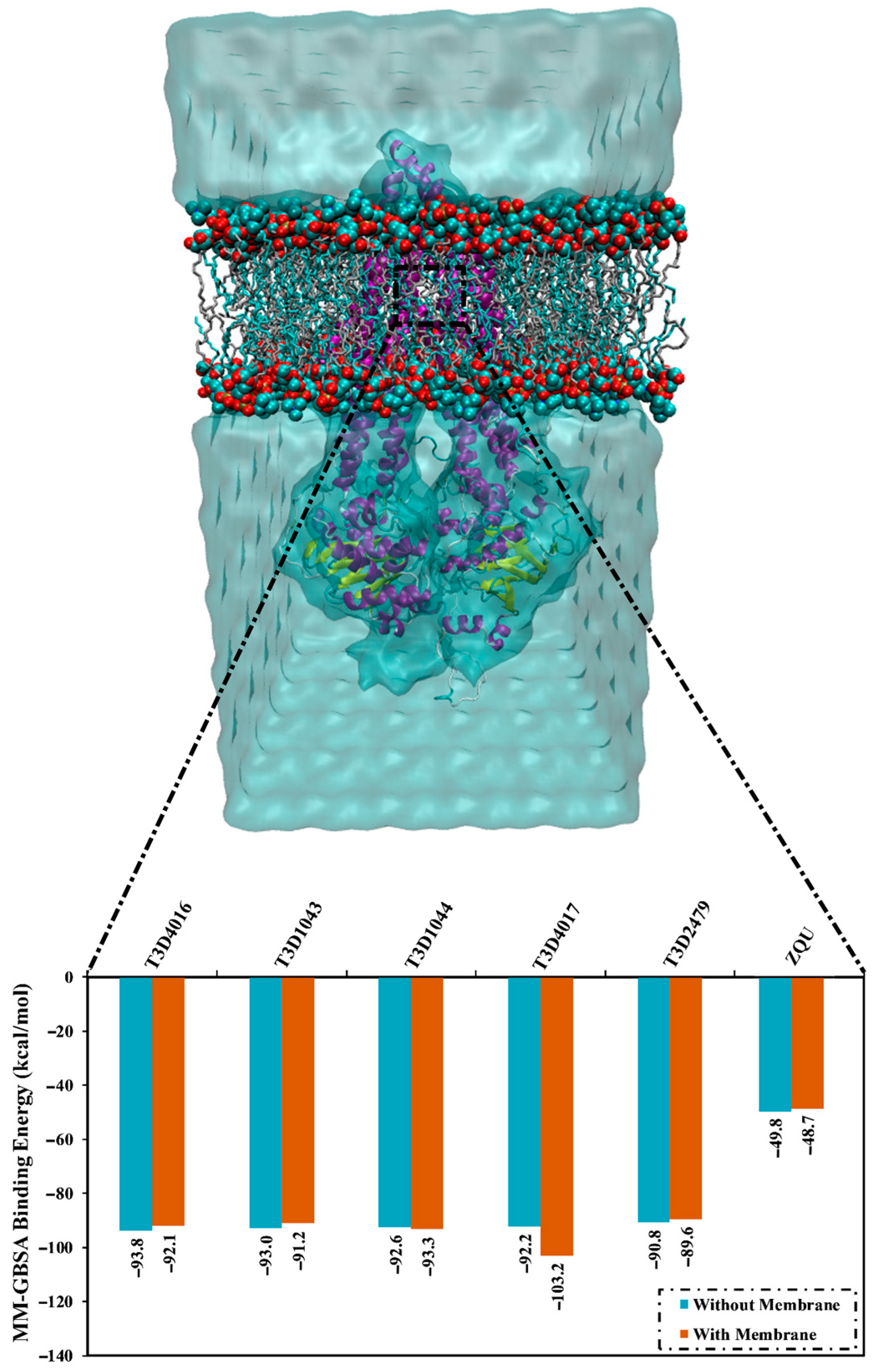
2.5. Lipid Bilayer-Enhanced MD
3. Computational Methods
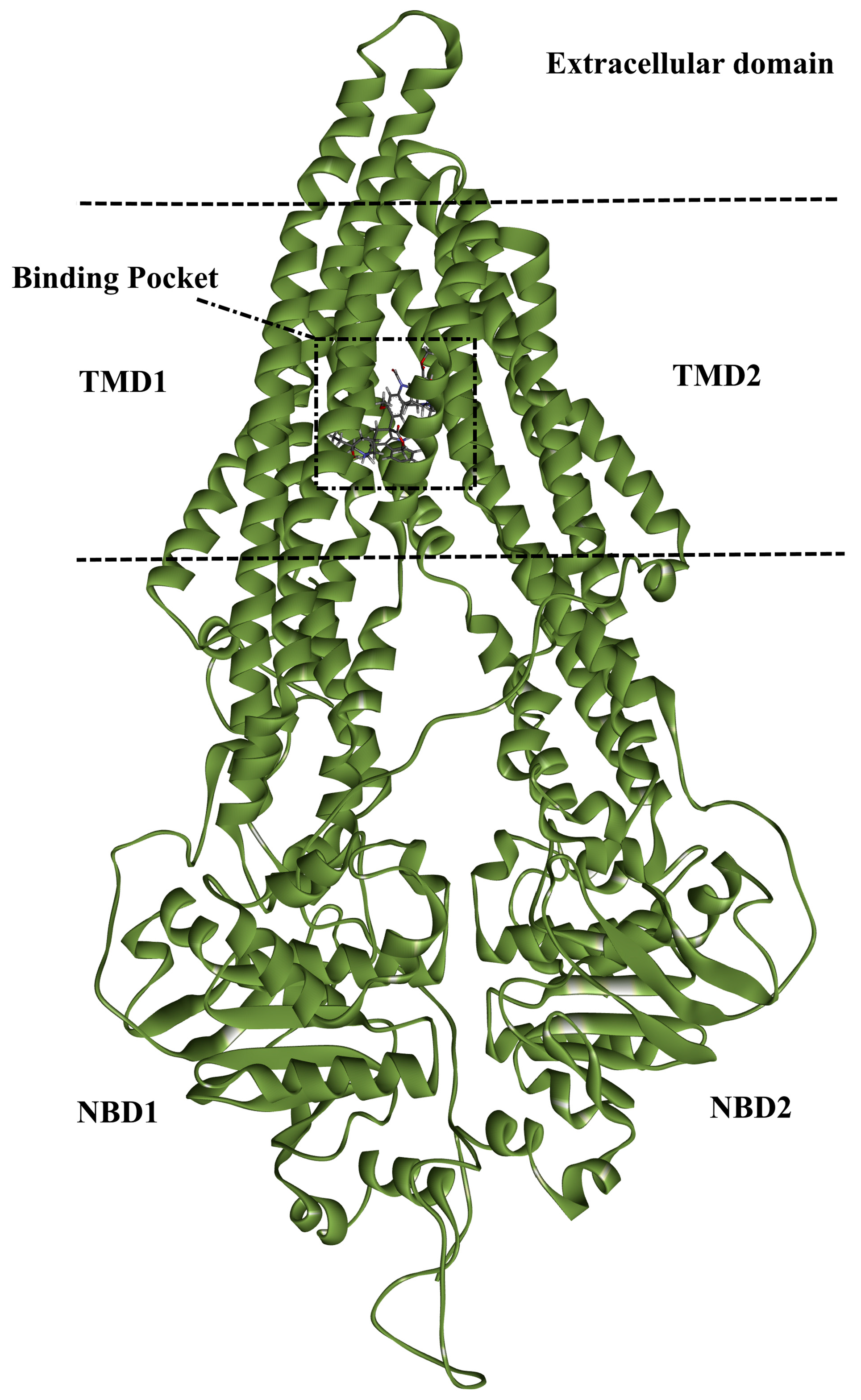
3.1. ABCB1 Preparation
3.2. T3DB Database Preparation
3.3. Molecular Docking
3.4. Molecular Dynamics
3.5. Lipid Bilayer-Enhanced MD
3.6. MM-GBSA Binding Energy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Debela, D.T.; Muzazu, S.G.; Heraro, K.D.; Ndalama, M.T.; Mesele, B.W.; Haile, D.C.; Kitui, S.K.; Manyazewal, T. New approaches and procedures for cancer treatment: Current perspectives. SAGE Open Med. 2021, 9, 20503121211034366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottesman, M.M.; Ling, V. The molecular basis of multidrug resistance in cancer: The early years of P-glycoprotein research. FEBS J. 2006, 580, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Nie, Y.; Shi, Y.; Fan, D. Multi-drug resistance in cancer chemotherapeutics: Mechanisms and lab approaches. Cancer Lett. 2014, 347, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckford, P.D.; Sharom, F.J. ABC efflux pump-based resistance to chemotherapy drugs. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 2989–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szakacs, G.; Paterson, J.K.; Ludwig, J.A.; Booth-Genthe, C.; Gottesman, M.M. Targeting multidrug resistance in cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, M.; Annilo, T. Evolution of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily in vertebrates. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2005, 6, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ween, M.P.; Armstrong, M.A.; Oehler, M.K.; Ricciardelli, C. The role of ABC transporters in ovarian cancer progression and chemoresistance. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2015, 96, 220–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharom, F.J. ABC multidrug transporters: Structure, function and role in chemoresistance. Pharmacogenomics 2008, 9, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage, H. An overview of cancer multidrug resistance: A still unsolved problem. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 3145–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.G.; Sikic, B.I. Molecular pathways: Regulation and therapeutic implications of multidrug resistance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1863–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliano, R.L.; Ling, V. A surface glycoprotein modulating drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1976, 455, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiebaut, F.; Tsuruo, T.; Hamada, H.; Gottesman, M.M.; Pastan, I.; Willingham, M.C. Cellular localization of the multidrug-resistance gene product P-glycoprotein in normal human tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 7735–7738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutmann, D.A.; Ward, A.; Urbatsch, I.L.; Chang, G.; van Veen, H.W. Understanding polyspecificity of multidrug ABC transporters: Closing in on the gaps in ABCB1. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010, 35, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.P.; Calcagno, A.M.; Ambudkar, S.V. Reversal of ABC drug transporter-mediated multidrug resistance in cancer cells: Evaluation of current strategies. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 1, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, E.; McDevitt, C.A.; Callaghan, R. Generating Inhibitors of P-Glycoprotein: Where to, Now? In Multi-Drug Resistance in Cancer; Zhou, J., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 405–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.L. Toxins and drug discovery. Toxicon 2014, 92, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordon, K.C.F.; Cologna, C.T.; Fornari-Baldo, E.C.; Pinheiro-Junior, E.L.; Cerni, F.A.; Amorim, F.G.; Anjolette, F.A.P.; Cordeiro, F.A.; Wiezel, G.A.; Cardoso, I.A.; et al. From Animal Poisons and Venoms to Medicines: Achievements, Challenges and Perspectives in Drug Discovery. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1132–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, S.; Dubey, A.; Kamboj, N.K.; Sahoo, A.K.; Kang, S.G.; Yadava, U. Drug repurposing for ligand-induced rearrangement of Sirt2 active site-based inhibitors via molecular modeling and quantum mechanics calculations. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, M.O.; Ciftci, H.I.; Ali, T.F.S.; Ellakwa, D.E.; Koga, R.; Tateishi, H.; Nakata, A.; Ito, A.; Yoshida, M.; Okamoto, Y.; et al. Antiproliferative S-Trityl-l-Cysteine-Derived Compounds as SIRT2 Inhibitors: Repurposing and Solubility Enhancement. Molecules 2019, 24, 3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.; Arndt, D.; Pon, A.; Sajed, T.; Guo, A.C.; Djoumbou, Y.; Knox, C.; Wilson, M.; Liang, Y.; Grant, J.; et al. T3DB: The toxic exposome database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D928–D934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.; Kowal, J.; Broude, E.; Roninson, I.; Locher, K.P. Structural insight into substrate and inhibitor discrimination by human P-glycoprotein. Science 2019, 363, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralj, S.; Jukič, M.; Bren, U. Comparative Analyses of Medicinal Chemistry and Cheminformatics Filters with Accessible Implementation in Konstanz Information Miner (KNIME). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesnik, S.; Jukic, M.; Bren, U. Mechanistic Insights of Polyphenolic Compounds from Rosemary Bound to Their Protein Targets Obtained by Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Free-Energy Calculations. Foods 2023, 12, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burg, R.W.; Miller, B.M.; Baker, E.E.; Birnbaum, J.; Currie, S.A.; Hartman, R.; Kong, Y.L.; Monaghan, R.L.; Olson, G.; Putter, I.; et al. Avermectins, new family of potent anthelmintic agents: Producing organism and fermentation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1979, 15, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martino, E.; Casamassima, G.; Castiglione, S.; Cellupica, E.; Pantalone, S.; Papagni, F.; Rui, M.; Siciliano, A.M.; Collina, S. Vinca alkaloids and analogues as anti-cancer agents: Looking back, peering ahead. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 2816–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-W.; Kong, X.-Y.; Wang, J.-H.; Du, G.-H. Vinblastine and Vincristine. In Natural Small Molecule Drugs from Plants; Du, G.-H., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 551–557. [Google Scholar]
- Nosol, K.; Romane, K.; Irobalieva, R.N.; Alam, A.; Kowal, J.; Fujita, N.; Locher, K.P. Cryo-EM structures reveal distinct mechanisms of inhibition of the human multidrug transporter ABCB1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 26245–26253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stansfeld, P.J.; Sansom, M.S. Molecular simulation approaches to membrane proteins. Structure 2011, 19, 1562–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti-Renom, M.A.; Stuart, A.C.; Fiser, A.; Sanchez, R.; Melo, F.; Sali, A. Comparative protein structure modeling of genes and genomes. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2000, 29, 291–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.C.; Myers, J.B.; Folta, T.; Shoja, V.; Heath, L.S.; Onufriev, A. H++: A server for estimating pKas and adding missing hydrogens to macromolecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W368–W371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, S.R.; McNaught, A.; Pletnev, I.; Stein, S.; Tchekhovskoi, D. InChI, the IUPAC International Chemical Identifier. J. Cheminformatics 2015, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OMEGA, version 2.5.1.4; OpenEye Scientific Software: Santa Fe, NM, USA, 2013.
- Hawkins, P.C.; Skillman, A.G.; Warren, G.L.; Ellingson, B.A.; Stahl, M.T. Conformer generation with OMEGA: Algorithm and validation using high quality structures from the Protein Databank and Cambridge Structural Database. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SZYBKI, version 1.9.0.3; OpenEye Scientific Software: Santa Fe, NM, USA, 2016.
- Halgren, T.A. MMFF VI. MMFF94s option for energy minimization studies. J. Comput. Chem. 1999, 20, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QUACPAC, version 1.7.0.2; OpenEye Scientific Software: Santa Fe, NM, USA, 2016.
- Gasteiger, J.; Marsili, M. Iterative partial equalization of orbital electronegativity—A rapid access to atomic charges. Tetrahedron 1980, 36, 3219–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forli, S.; Huey, R.; Pique, M.E.; Sanner, M.F.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. Computational protein-ligand docking and virtual drug screening with the AutoDock suite. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, D.A.; Betz, R.M.; Cerutti, D.S.; Cheatham, T.E.; Darden, T.A.; Duke, R.E.; Giese, T.J.; Gohlke, H.; Goetz, A.W.; Homeyer, N.; et al. AMBER; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Abdeljawaad, K.A.A.; Abdelrahman, A.H.M.; Jaragh-Alhadad, L.A.; Oraby, H.F.; Elkaeed, E.B.; Mekhemer, G.A.H.; Gabr, G.A.; Shawky, A.M.; Sidhom, P.A.; et al. Exploring natural product activity and species source candidates for hunting ABCB1 transporter inhibitors: An in silico drug discovery study. Molecules 2022, 27, 3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Abdelrahman, A.H.M.; Badr, E.A.A.; Almansour, N.M.; Alzahrani, O.R.; Ahmed, M.N.; Soliman, M.E.S.; Naeem, M.A.; Shawky, A.M.; Sidhom, P.A.; et al. Naturally occurring plant-based anticancerous candidates as prospective ABCG2 inhibitors: An in silico drug discovery study. Mol. Divers. 2022, 26, 3255–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Badr, E.A.A.; Abdelrahman, A.H.M.; Almansour, N.M.; Mekhemer, G.A.H.; Shawky, A.M.; Moustafa, M.F.; Atia, M.A.M. In Silico targeting human multidrug transporter ABCG2 in breast cancer: Database screening, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics study. Mol. Inform. 2022, 41, e2060039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Abdelrahman, A.H.M.; Jaragh-Alhadad, L.A.; Atia, M.A.M.; Alzahrani, O.R.; Ahmed, M.N.; Moustafa, M.S.; Soliman, M.E.S.; Shawky, A.M.; Pare, P.W.; et al. Exploring Toxins for Hunting SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors: Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics, Pharmacokinetic Properties, and Reactome Study. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K.E.; Simmerling, C. ff14SB: Improving the accuracy of protein side chain and backbone parameters from ff99SB. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Development and testing of a general amber force field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayly, C.I.; Cieplak, P.; Cornell, W.D.; Kollman, P.A. A well-behaved electrostatic potential based method using charge restraints for deriving atomic charges—The RESP model. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 10269–10280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.T.G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision E01; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, S.; Kollman, P.A. Settle—An Analytical Version of the Shake and Rattle Algorithm for Rigid Water Models. J. Comput. Chem. 1992, 13, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaguirre, J.A.; Catarello, D.P.; Wozniak, J.M.; Skeel, R.D. Langevin stabilization of molecular dynamics. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 114, 2090–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Postma, J.P.M.; Vangunsteren, W.F.; Dinola, A.; Haak, J.R. Molecular-dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassault Systèmes. Dassault Systèmes BIOVIA, Discovery Studio Visualize, version 2019; Dassault Systèmes: San Diego, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, S.; Kim, T.; Iyer, V.G.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI: A web-based graphical user interface for CHARMM. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, C.J.; Madej, B.D.; Skjevik, A.A.; Betz, R.M.; Teigen, K.; Gould, I.R.; Walker, R.C. Lipid14: The amber lipid force field. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2014, 10, 865–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massova, I.; Kollman, P.A. Combined molecular mechanical and continuum solvent approach (MM-PBSA/GBSA) to predict ligand binding. Perspect. Drug Discov. 2000, 18, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onufriev, A.; Bashford, D.; Case, D.A. Exploring protein native states and large-scale conformational changes with a modified generalized born model. Proteins 2004, 55, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, W. Assessing the performance of the molecular mechanics/Poisson Boltzmann surface area and molecular mechanics/generalized Born surface area methods. II. The accuracy of ranking poses generated from docking. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 866–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Sun, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.Z.H.; Hou, T. End-point binding free energy calculation with MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA: Strategies and applications in drug design. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 9478–9508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| No. | Compound Name/Code | Origin a | miLog P | Two-Dimensional Chemical Structures | Docking Score (kcal/mol) | Binding Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZQU | ------ | 4.9 |  | −8.4 | PHE302 (Pi-Pi T-shaped, 5.07 Å), PHE335 (Pi-Pi T-shaped, 5.27 Å), GLN989 (Carbon H-bond, 2.72 Å) | |
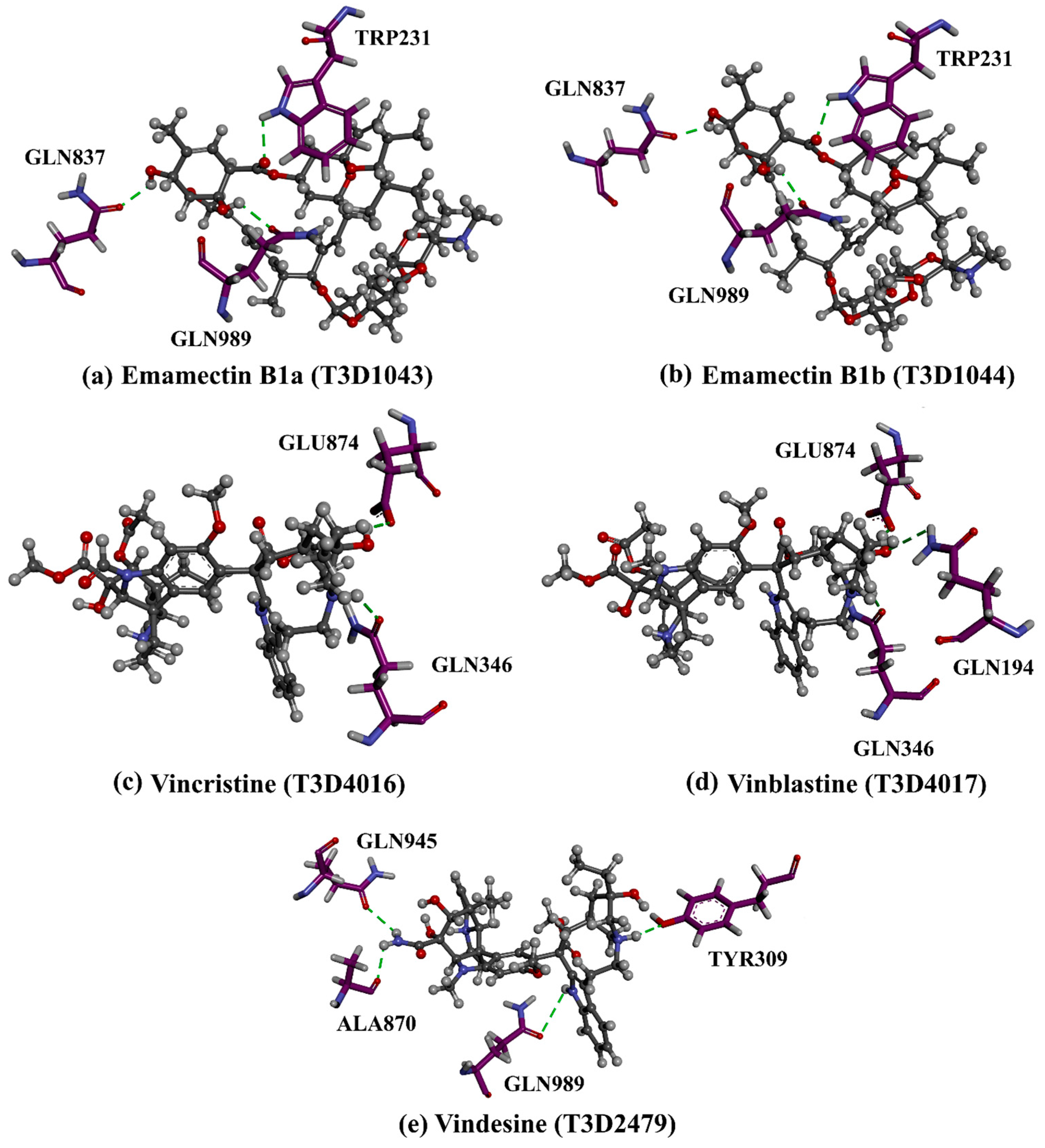
| 1 | T3D1044 (Emamectin B1b) | Bacterial toxin (Streptomyces avermitilis) | 2.3 | 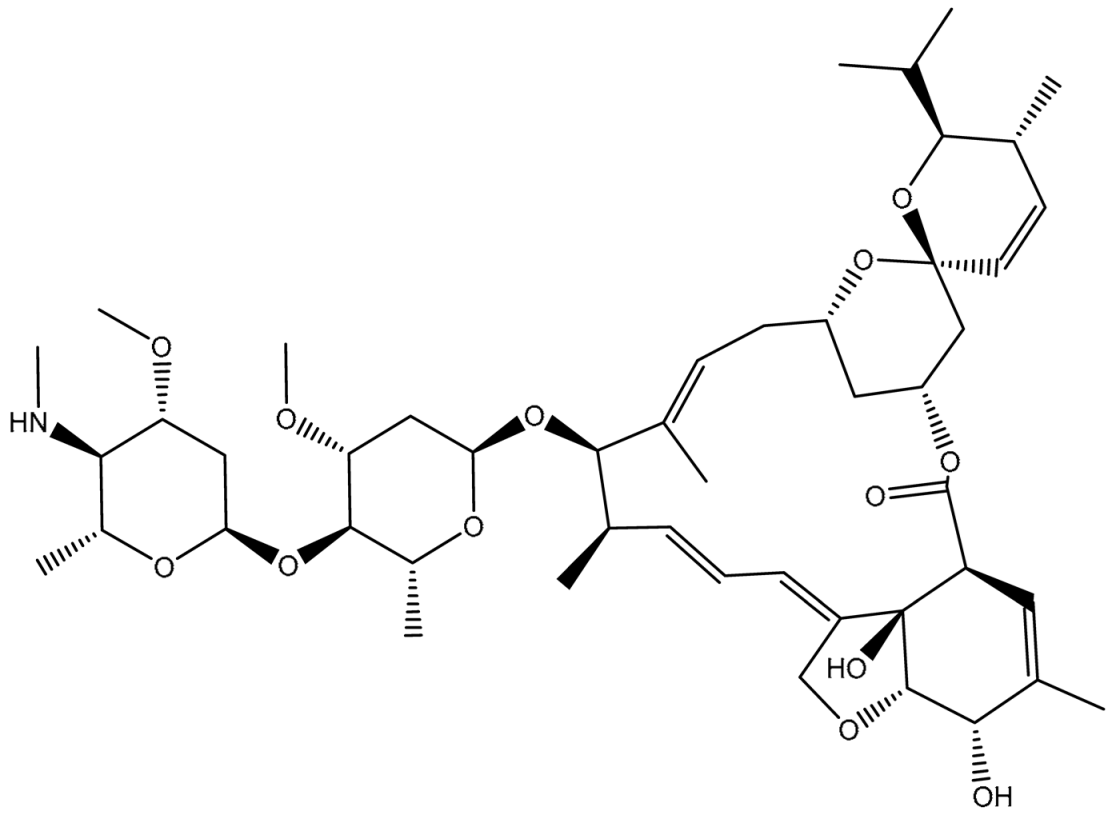 | −12.0 | TRP231 (Conventional H-bond, 2.32 Å; Pi-Sigma, 2.72 Å), TYR309 (Carbon H-bond, 2.97 Å), ILE339 (Carbon H-bond, 2.97, 3.26 Å), SER343 (Carbon H-bond, 2.61 Å), GLN837 (Conventional H-bond, 2.00 Å), GLN989 (Conventional H-bond, 2.14 Å; Carbon H-bond, 2.62 Å) |
| 2 | T3D1043 (Emamectin B1a) | Bacterial toxin (Streptomyces avermitilis) | 2.8 | 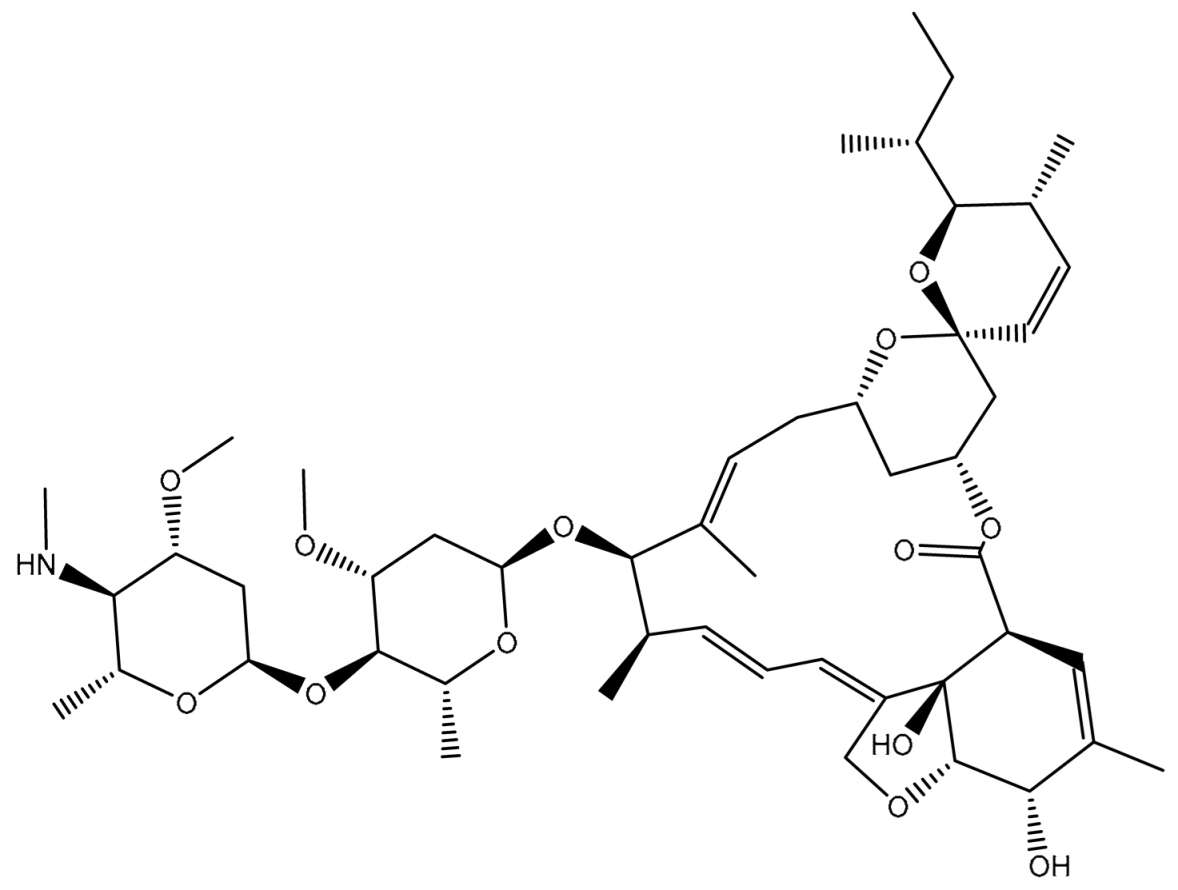 | −11.8 | TRP231 (Conventional H-bond, 2.30 Å; Pi-Sigma, 2.70 Å), GLN837 (Conventional H-bond, 2.04 Å), GLN989 (Conventional H-bond, 2.16 Å; Carbon H-bond, 2.67 Å), SER343 (Carbon H-bond, 2.34 Å), ILE339 (Carbon H-bond, 2.70, 2.80 Å) |
| 3 | T3D4017 (Vinblastine) | Synthetic compound (treatment of breast cancer) | 5.6 |  | −10.0 | GLN194 (Conventional H-bond, 3.20 Å), TRP231 (Pi-Pi Stacked, 4.64 Å), PHE342 (Pi-Pi Stacked, 4.58, 5.88 Å), GLN346 (Conventional H-bond, 2.05 Å; Carbon H-bond, 2.91 Å), GLU874 (Conventional H-bond, 2.00 Å; Carbon H-bond, 2.46, 3.06, 3.11 Å; Attractive charge, 4.26 Å) |
| 4 | T3D4016 (Vincristine) | Synthetic compound (treatment of acute lymphocytic leukemia) | 4.9 | 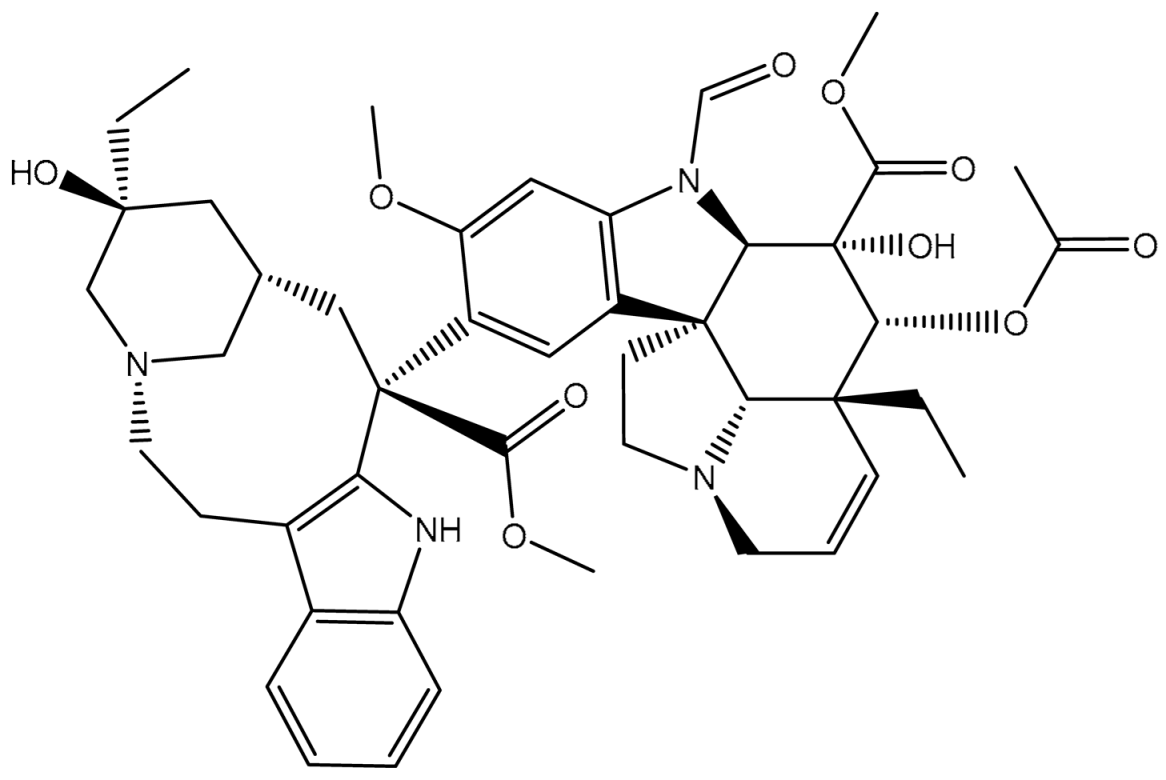 | −9.9 | TRP231 (Pi-Pi Stacked, 4.62 Å), PHE342 (Pi-Pi Stacked, 4.49, 5.71 Å), SER343 (Carbon H-bond, 2.49 Å), GLN346 (Conventional H-bond, 2.03 Å; Carbon H-bond, 2.93 Å), GLU874 (Conventional H-bond, 2.09 Å; Carbon H-bond, 2.61, 2.86 Å; Attractive charge, 4.38 Å) |
| 5 | T3D2479 (Vindesine) | Synthetic compound (antineoplastic agent) | 3.7 | 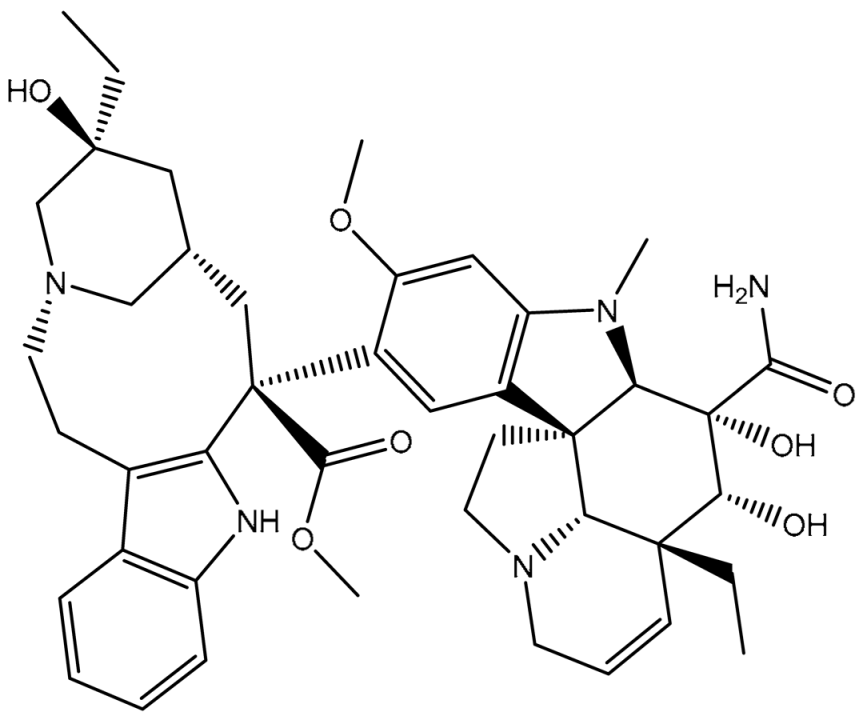 | −8.9 | TYR309 (Conventional H-bond, 2.16 Å), ALA870 (Conventional H-bond, 2.13 Å), GLY871 (Carbon H-bond, 2.99 Å), GLU874 (Carbon H-bond, 1.85, 2.74 Å; Attractive charge, 3.57 Å), GLN945 (Conventional H-bond, 2.41 Å), MET985 (Carbon H-bond, 2.83 Å), GLN989 (Conventional H-bond, 3.26 Å) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Abdeljawaad, K.A.A.; Abdelrahman, A.H.M.; Sidhom, P.A.; Tawfeek, A.M.; Mekhemer, G.A.H.; Abd El-Rahman, M.K.; Dabbish, E.; Shoeib, T. In-Silico Mining of the Toxins Database (T3DB) towards Hunting Prospective Candidates as ABCB1 Inhibitors: Integrated Molecular Docking and Lipid Bilayer-Enhanced Molecular Dynamics Study. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071019
Ibrahim MAA, Abdeljawaad KAA, Abdelrahman AHM, Sidhom PA, Tawfeek AM, Mekhemer GAH, Abd El-Rahman MK, Dabbish E, Shoeib T. In-Silico Mining of the Toxins Database (T3DB) towards Hunting Prospective Candidates as ABCB1 Inhibitors: Integrated Molecular Docking and Lipid Bilayer-Enhanced Molecular Dynamics Study. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(7):1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071019
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbrahim, Mahmoud A. A., Khlood A. A. Abdeljawaad, Alaa H. M. Abdelrahman, Peter A. Sidhom, Ahmed M. Tawfeek, Gamal A. H. Mekhemer, Mohamed K. Abd El-Rahman, Eslam Dabbish, and Tamer Shoeib. 2023. "In-Silico Mining of the Toxins Database (T3DB) towards Hunting Prospective Candidates as ABCB1 Inhibitors: Integrated Molecular Docking and Lipid Bilayer-Enhanced Molecular Dynamics Study" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 7: 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071019
APA StyleIbrahim, M. A. A., Abdeljawaad, K. A. A., Abdelrahman, A. H. M., Sidhom, P. A., Tawfeek, A. M., Mekhemer, G. A. H., Abd El-Rahman, M. K., Dabbish, E., & Shoeib, T. (2023). In-Silico Mining of the Toxins Database (T3DB) towards Hunting Prospective Candidates as ABCB1 Inhibitors: Integrated Molecular Docking and Lipid Bilayer-Enhanced Molecular Dynamics Study. Pharmaceuticals, 16(7), 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071019









