How to Treat Today? Oral and Facial Cancer-Associated Venous Thromboembolism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
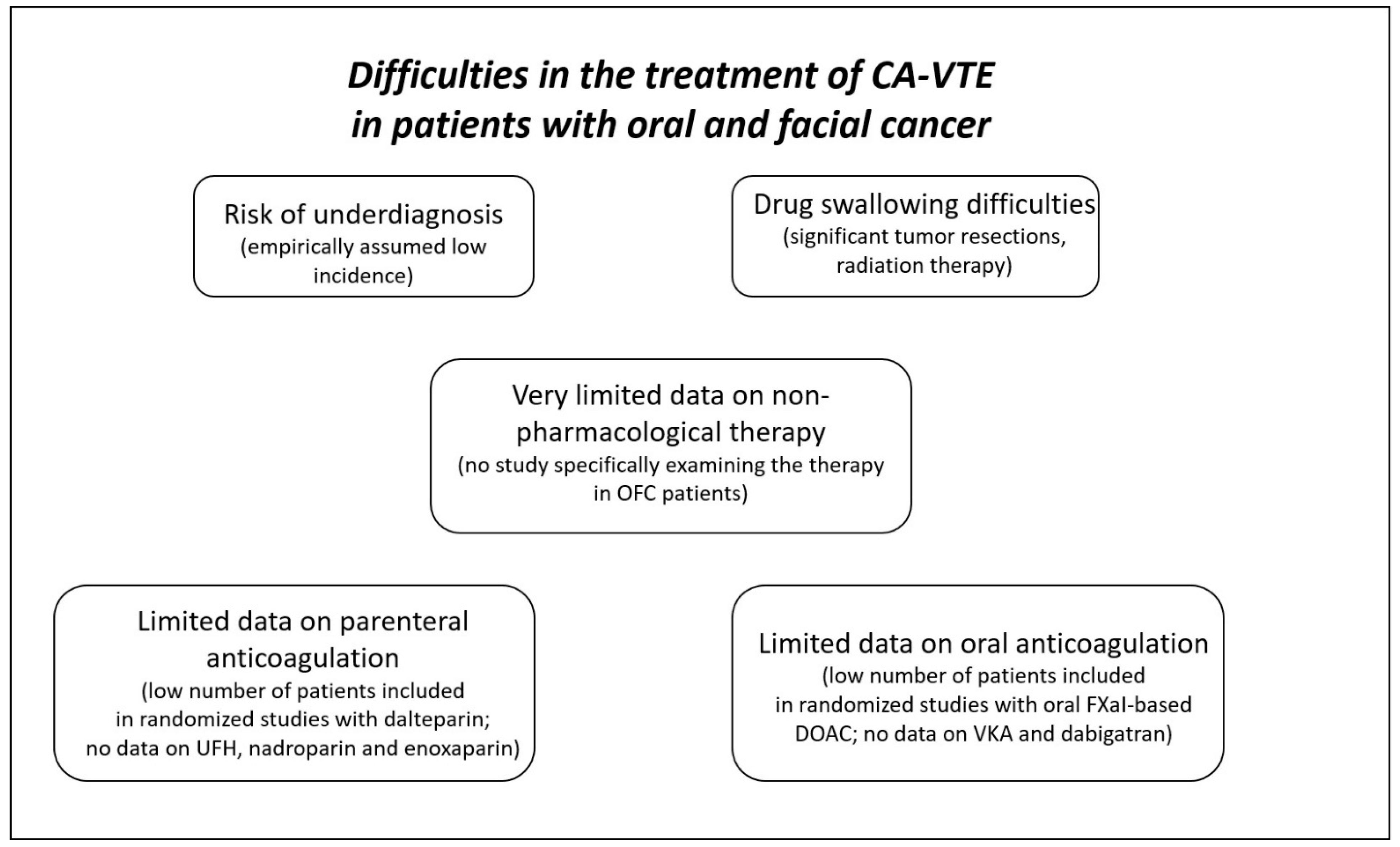
3. CA-VTE in Patients with OFC
4. Current Recommendations on Treatment of CA-VTE
5. Pharmacological Treatment of CA-VTE
6. Parenteral Anticoagulation in Patients with OFC
7. Oral anticoagulation in Patients with OFC
8. Non-Pharmacological Treatment of CA-VTE in Patients with OFC
9. How to Treat CA-VTE in Patients with OFC?
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khorana, A.A.; Mackman, N.; Falanga, A.; Pabinger, I.; Noble, S.; Ageno, W.; Moik, F.; Lee, A.Y.Y. Cancer-associated venous thromboembolism. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2022, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdol Razak, N.B.; Jones, G.; Bhandari, M.; Berndt, M.C.; Metharom, P. Cancer-Associated Thrombosis: An Overview of Mechanisms, Risk Factors, and Treatment. Cancers 2018, 10, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanfilippo, K.M.; Wang, T.F. Prevention and Treatment of Cancer-Associated Venous Thromboembolism: A Review. Curr. Treat. Options Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 21, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gennaro, L.; De Cristofaro, R.; Ferretti, A.; Basso, M.; Riccio, C.; Cordaro, M.; Lajolo, C. Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma-Associated Thrombosis: What Evidence? Cancers 2022, 14, 5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canonico, M.E.; Santoro, C.; Avvedimento, M.; Giugliano, G.; Mandoli, G.E.; Prastaro, M.; Franzone, A.; Piccolo, R.; Ilardi, F.; Cameli, M.; et al. Venous Thromboembolism and Cancer: A Comprehensive Review from Pathophysiology to Novel Treatment. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, A.; Kiss, K.; Lelkaitis, G.; Juhl, K.; Persson, M.; Charabi, B.W.; Mortensen, J.; Forman, J.L.; Sørensen, A.L.; Jensen, D.H.; et al. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR), tissue factor (TF) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR): Tumor expression patterns and prognostic value in oral cancer. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, W.; Edgington, T.S. Structural biology of tissue factor, the initiator of thrombogenesis in vivo. FASEB J. 1994, 8, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adesanya, M.A.; Maraveyas, A.; Madden, L.A. Cancer microvesicles induce tissue factor-related procoagulant activity in endothelial cells in vitro. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2017, 28, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.G.; Man, Q.W.; Zhang, W.; Li, C.; Xiong, X.P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Wang, W.M.; Sun, Z.J.; Jia, J.; Zhang, W.F.; et al. Elevated Level of Circulating Platelet-derived Microparticles in Oral Cancer. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisma, R.J.; Spiro, J.D.; Kreutzer, D.L. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Surg. 1997, 174, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotman, G.J. Plasma thromboxane A2 and prostacyclin concentrations in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J. Surg. Oncol. 1988, 38, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, J.D.; Killion, K.M.; Pruet, C.F.; Spaulding, M.B. von Willebrand factor in head and neck cancer. Cancer 1990, 66, 2387–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, A.T.; Gorzelanny, C.; Gebhardt, C.; Pantel, K.; Schneider, S.W. Interplay between coagulation and inflammation in cancer: Limitations and therapeutic opportunities. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2022, 102, 102322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hisada, Y.; Mackman, N. Cancer-associated pathways and biomarkers of venous thrombosis. Blood 2017, 130, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar]
- Santoro, C.; Capone, V.; Canonico, M.E.; Gargiulo, G.; Esposito, R.; Sanna, G.D.; Parodi, G.; Esposito, G. Single, Dual, and Triple Antithrombotic Therapy in Cancer Patients with Coronary Artery Disease: Searching for Evidence and Personalized Approaches. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2021, 47, 950–961. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khorana, A.A.; Francis, C.W.; Culakova, E.; Kuderer, N.M.; Lyman, G.H. Thromboembolism is a leading cause of death in cancer patients receiving outpatient chemotherapy. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 632–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppelt, P.; Betbadal, A.; Nayak, L. Approach to chemotherapy-associated thrombosis. Vasc. Med. 2015, 20, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, A.; Yamachika, E.; Mizutani, M.; Matsubara, M.; Moritani, N.; Nakatsuji, K.; Iida, S. Rapid occurrence of left ventricular thrombus associated with platinum-based chemotherapy plus cetuximab for the treatment of metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: A case report. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 7, 833–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai, L.; McCarn, K.; Stott, W.; Watts, T.; Wax, M.K.; Andersen, P.E.; Gross, N.D. Venous thromboembolism in patients with head and neck cancer after surgery. Head. Neck 2013, 35, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto, Y.; Yamashita, Y.; Kim, K.; Morimoto, T.; Saga, S.; Amano, H.; Takase, T.; Hiramori, S.; Oi, M.; Akao, M.; et al. Risk Factors for Major Bleeding During Anticoagulation Therapy in Cancer-Associated Venous Thromboembolism—From the COMMAND VTE Registry. Circ. J. 2020, 84, 2006–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søgaard, M.; Nielsen, P.B.; Skjøth, F.; Kjaeldgaard, J.N.; Larsen, T.B. Risk of recurrence and bleeding in patients with cancer-associated venous thromboembolism treated with rivaroxaban: A nationwide cohort study. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakai, N.A.; Walker, R.F.; MacLehose, R.F.; Adam, T.J.; Alonso, A.; Lutsey, P.L. Impact of anticoagulant choice on hospitalized bleeding risk when treating cancer-associated venous thromboembolism. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 2403–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frere, C.; Wahl, C.; Rueda-Camino, J.A.; Crichi, B.; Prata, P.H.; Marjanovic, Z.; Farge, D. A review of latest clinical practice guidelines for the management of cancer-associated thrombosis. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2022, 35, 101348. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Farge, D.; Frere, C.; Connors, J.M.; Ay, C.; Khorana, A.A.; Munoz, A.; Brenner, B.; Kakkar, A.; Rafii, H.; Solymoss, S.; et al. International Initiative on Thrombosis and Cancer (ITAC) advisory panel. 2019 international clinical practice guidelines for the treatment and prophylaxis of venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, e566–e581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Key, N.S.; Khorana, A.A.; Kuderer, N.M.; Bohlke, K.; Lee, A.Y.Y.; Arcelus, J.I.; Wong, S.L.; Balaban, E.P.; Flowers, C.R.; Francis, C.W.; et al. Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis and Treatment in Patients With Cancer: ASCO Clinical Practice Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 496–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyman, G.H.; Carrier, M.; Ay, C.; Di Nisio, M.; Hicks, L.K.; Khorana, A.A.; Leavitt, A.D.; Lee, A.Y.Y.; Macbeth, F.; Morgan, R.L.; et al. American Society of Hematology 2021 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: Prevention and treatment in patients with cancer. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 927–974. [Google Scholar]
- Streiff, M.B.; Holmstrom, B.; Angelini, D.; Ashrani, A.; Elshoury, A.; Fanikos, J.; Fertrin, K.Y.; Fogerty, A.E.; Gao, S.; Goldhaber, S.Z.; et al. Cancer-Associated Venous Thromboembolic Disease, Version 2.2021, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2021, 19, 1181–1201. [Google Scholar]
- Falanga, A.; Ay, C.; Di Nisio, M.; Gerotziafas, G.; Jara-Palomares, L.; Langer, F.; Lecumberri, R.; Mandala, M.; Maraveyas, A.; Pabinger, I.; et al. Venous thromboembolism in cancer patients: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 452–467. [Google Scholar]
- Khorana, A.A.; Noble, S.; Lee, A.Y.Y.; Soff, G.; Meyer, G.; O’Connell, C.; Carrier, M. Role of direct oral anticoagulants in the treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism: Guidance from the SSC of the ISTH. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 1891–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, S.; Lee, A.Y.Y.; Carrier, M.; Feugère, G.; Abreu, P.; Heissler, J. Low-molecular-weight-heparin versus a coumarin for the prevention of recurrent venous thromboembolism in high- and low-risk patients with active cancer: A post hoc analysis of the CLOT Study. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2019, 47, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, C.W.; Kessler, C.M.; Goldhaber, S.Z.; Kovacs, M.J.; Monreal, M.; Huisman, M.V.; Bergqvist, D.; Turpie, A.G.; Ortel, T.L.; Spyropoulos, A.C.; et al. Treatment of venous thromboembolism in cancer patients with dalteparin for up to 12 months: The DALTECAN Study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesavento, R.; Amitrano, M.; Trujillo-Santos, J.; Di Micco, P.; Mangiacapra, S.; López-Jiménez, L.; Falgá, C.; García-Bragado, F.; Piovella, C.; Prandoni, P.; et al. Fondaparinux in the initial and long-term treatment of venous thromboembolism. Thromb. Res. 2015, 135, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bauersachs, R.M. Fondaparinux Sodium: Recent Advances in the Management of Thrombosis. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 28, 10742484221145010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raskob, G.E.; van Es, N.; Verhamme, P.; Carrier, M.; Di Nisio, M.; Garcia, D.; Grosso, M.A.; Kakkar, A.K.; Kovacs, M.J.; Mercuri, M.F.; et al. Edoxaban for the Treatment of Cancer-Associated Venous Thromboembolism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.M.; Marshall, A.; Thirlwall, J.; Chapman, O.; Lokare, A.; Hill, C.; Hale, D.; Dunn, J.A.; Lyman, G.H.; Hutchinson, C.; et al. Comparison of an Oral Factor Xa Inhibitor With Low Molecular Weight Heparin in Patients With Cancer With Venous Thromboembolism: Results of a Randomized Trial (SELECT-D). J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2017–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBane, R.D., 2nd; Wysokinski, W.E.; Le-Rademacher, J.G.; Zemla, T.; Ashrani, A.; Tafur, A.; Perepu, U.; Anderson, D.; Gundabolu, K.; Kuzma, C.; et al. Apixaban and dalteparin in active malignancy-associated venous thromboembolism: The ADAM VTE trial. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planquette, B.; Bertoletti, L.; Charles-Nelson, A.; Laporte, S.; Grange, C.; Mahé, I.; Pernod, G.; Elias, A.; Couturaud, F.; Falvo, N.; et al. Rivaroxaban vs Dalteparin in Cancer-Associated Thromboembolism: A Randomized Trial. Chest 2022, 161, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnelli, G.; Becattini, C.; Meyer, G.; Muñoz, A.; Huisman, M.V.; Connors, J.M.; Cohen, A.; Bauersachs, R.; Brenner, B.; Torbicki, A.; et al. Apixaban for the Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism Associated with Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1599–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrag, D.; Uno, H.; Greenerger Rosovsky, R.P.; Rutherford, C.; Sanfilippo, K.M.; Villano, J.L.; Drescher, M.R.; Jayaram, N.H.; Holmes, C.E.; Feldman, L.E.; et al. The comparative effectiveness of direct oral anti-coagulants and low molecular weight heparins for prevention of recurrent venous thromboembolism in cancer: The CANVAS pragmatic randomized trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39 (Suppl. S15), 12020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klamroth, R.; Sinn, M.; Pollich, C.; Bischoff, S.; Lohneis, A.; Orlovic, A.M.; Wisłocka, L.; Habbel, P.; de Wit, M.; Späth-Schwalbe, E.; et al. Anticoagulation Practice in Patients with Cancer-Associated Thrombosis: Insights from GeCAT, a German Prospective Registry Study. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2022, 45, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.; Tang, H.; Hughes, R. Vena caval filters for the prevention of pulmonary embolism. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, 2010, CD006212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brailovsky, Y.; Yeung, H.M.; Lakhter, V.; Zack, C.J.; Zhao, H.; Bashir, R. In-hospital outcomes of catheter-directed thrombolysis versus anticoagulation in cancer patients with proximal deep venous thrombosis. J. Vasc. Surg. Venous Lymphat. Disord. 2020, 8, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selten, K.; Durak, K.; Kersten, A.; Kalverkamp, S. First Ultrasound-Assisted Thrombolysis for Pulmonary Embolism after Lung Surgery. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. Rep. 2023, 12, e14–e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Qin, J.; Xu, Y.Z.; Li, X.; Li, F.; Wang, X.; Hu, B.; Chu, H.; et al. The removal of floating right heart thrombi and pulmonary embolus using AngioJet device and venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: A case report. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, M.; Fu, G.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, B.; Kong, J.; He, X.; Gu, J. Angiojet pharmacomechanical thrombectomy versus anticoagulant therapy alone in massive cancer-associated thrombosis: A single centre retrospective cohort study. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2023, 55, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Heparin (Unfractionated) | Dalteparin | Enoxaparin | Nadroparin | Fondaparinux | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target factor | IIa (indirectly—trough antithrombin III) Xa (indirectly) | Xa (indirectly) | Xa (indirectly) | Xa (indirectly) | Xa (indirectly) |
| Indication for treatment of DVT and PE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Way of administration | Intravenous (bolus + continuous infusion) subcutaneous (multiple daily doses needed) | subcutaneous (once or twice daily) | subcutaneous (twice daily) | subcutaneous (twice daily) | subcutaneous (once daily) |
| Data for CA-VTE | No | Yes (as comparator) | No | No | No |
| Risk of HIT | High | Low | Low | Low | Extremely low |
| Liver metabolism or elimination | No | No | Yes | No | No |
| Kidney elimination | No | Yes | Low | Yes | Yes |
| Half-life | One hour (intravenous) 2 h (subcutaneous) | 3–4 h | 3–5 h | 3.5 h | 17 h |
| Test for drug levels assessment | ACT APTT | Anti-Xa activity | Anti-Xa activity | Anti-Xa activity | Anti-Xa activity (drug-specific) |
| Apixaban | Dabigatran | Edoxaban | Rivaroxaban | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target factor | Xa | IIa (thrombin) | Xa | Xa |
| Indication for treatment of DVT and PE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Drug form | Directly-acting | Prodrug (dabigatran-etexilate) | Directly-acting | Directly-acting |
| Data for CA-VTE | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Need for pre-treatment with parenteral anticoagulation | No (higher dose first 7 days recommended) | Yes | Yes | No (higher dose first 21 days recommended) |
| Liver metabolism | Yes (CYP3A4/5, CYP21A2, CYPSC8, CYP2C9/19, CYP2J2) | No | Yes (carboxylesterase 1, CYP3A4/5) | Yes (CYP3A4, CYP2J2) |
| Kidney elimination | 25–30% | 75–80% | 45–50% | 60–65% |
| Protein binding | 87% | 35% | 20% | 95% |
| Half-life | 8–15 h | 12–17 h | 8–10 h | 9–13 h |
| Onset of action | 1–3 h | 0.5–2 h | 1–2 h | 2–4 h |
| Test for drug levels assessment | Anti-Xa activity (drug-specific) LC-MS | Diluted thrombin time ecarin time LC-MS | Anti-Xa activity (drug-specific) LC-MS | Anti-Xa activity (drug-specific) LC-MS |
| Apixaban | Edoxaban | Rivaroxaban * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drug dosing | 10 mg b.i.d. for first 7 days followed by 5 mg b.i.d. (2.5 mg b.i.d. for reduced dosing) | 60 mg q.d. (30 mg q.d. for reduced dosing) | 15 mg b.i.d. first 21 days followed by 20 mg q.d. (15 mg q.d. for reduced dosing) |
| Pill drug dosage | 5 mg 2.5 mg | 60 mg 30 mg | 20 mg 15 mg |
| Pill design | Film-coated tablet | Film-coated tablet | Film-coated tablet |
| Pill shape | Oval (5 mg) Round (2.5 mg) | Round | Round biconvex |
| Pill dimension | 9.73 x 5.16 mm (5 mg) 5.95 mm + (2.5 mg) | 10.5 mm + (60 mg) 8.5 mm + (30 mg) | 6 mm + 9 mm ++ |
| Granules for oral suspension | No | Yes | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Janíčková, M.; Bolek, T.; Stančiaková, L.; Nagy, N.; Mokáň, M.; Samoš, M. How to Treat Today? Oral and Facial Cancer-Associated Venous Thromboembolism. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071011
Janíčková M, Bolek T, Stančiaková L, Nagy N, Mokáň M, Samoš M. How to Treat Today? Oral and Facial Cancer-Associated Venous Thromboembolism. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(7):1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071011
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaníčková, Mária, Tomáš Bolek, Lucia Stančiaková, Norbert Nagy, Marián Mokáň, and Matej Samoš. 2023. "How to Treat Today? Oral and Facial Cancer-Associated Venous Thromboembolism" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 7: 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071011
APA StyleJaníčková, M., Bolek, T., Stančiaková, L., Nagy, N., Mokáň, M., & Samoš, M. (2023). How to Treat Today? Oral and Facial Cancer-Associated Venous Thromboembolism. Pharmaceuticals, 16(7), 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071011







