Meloxicam Targets COX-2/NOX1/NOX4/Nrf2 Axis to Ameliorate the Depression-like Neuropathology Induced by Chronic Restraint Stress in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
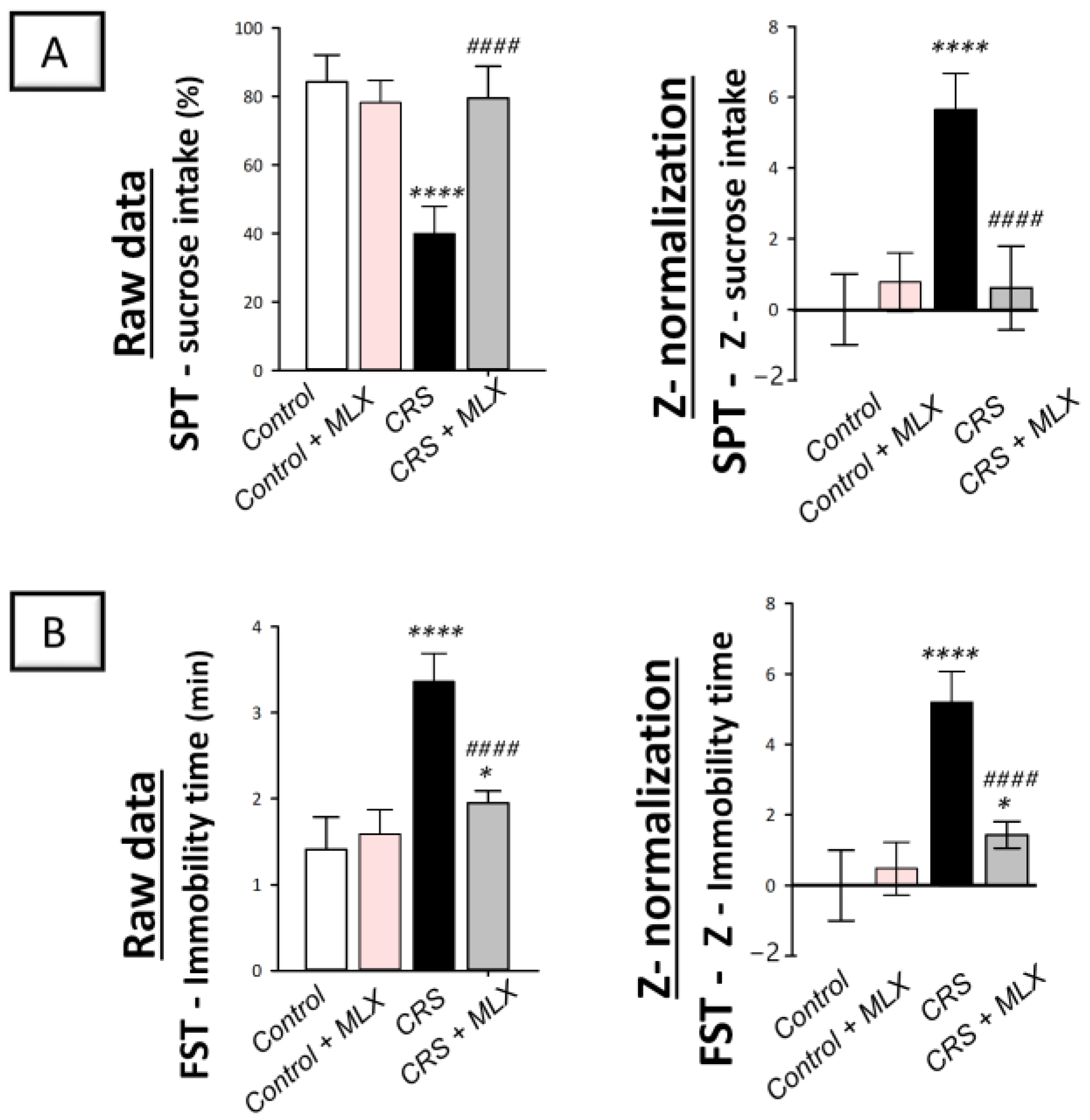
2.1. Meloxicam Improves CRS-Evoked Depression-like Behavior
2.2. Meloxicam Counteracts CRS-Induced Decline in Movement Activity
2.3. Meloxicam Attenuates CRS-Induced Histopathological Aberrations in the Brain Cortex and Hippocampus
2.4. Meloxicam Lowers CRS-Induced Spike in Serum Corticosterone
2.5. Meloxicam Counteracts CRS-Induced Decline in Hippocampal Monoamine Neurotransmitters
2.6. Meloxicam Suppresses Hippocampal NOX1/NOX4 Pro-Oxidant Signals and Enhances the Antioxidant Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway in Rats Exposed to CRS
2.7. Meloxicam Inhibits Hippocampal Pro-Inflammatory Signals and COX-2/PGE2 in Rats Exposed to CRS
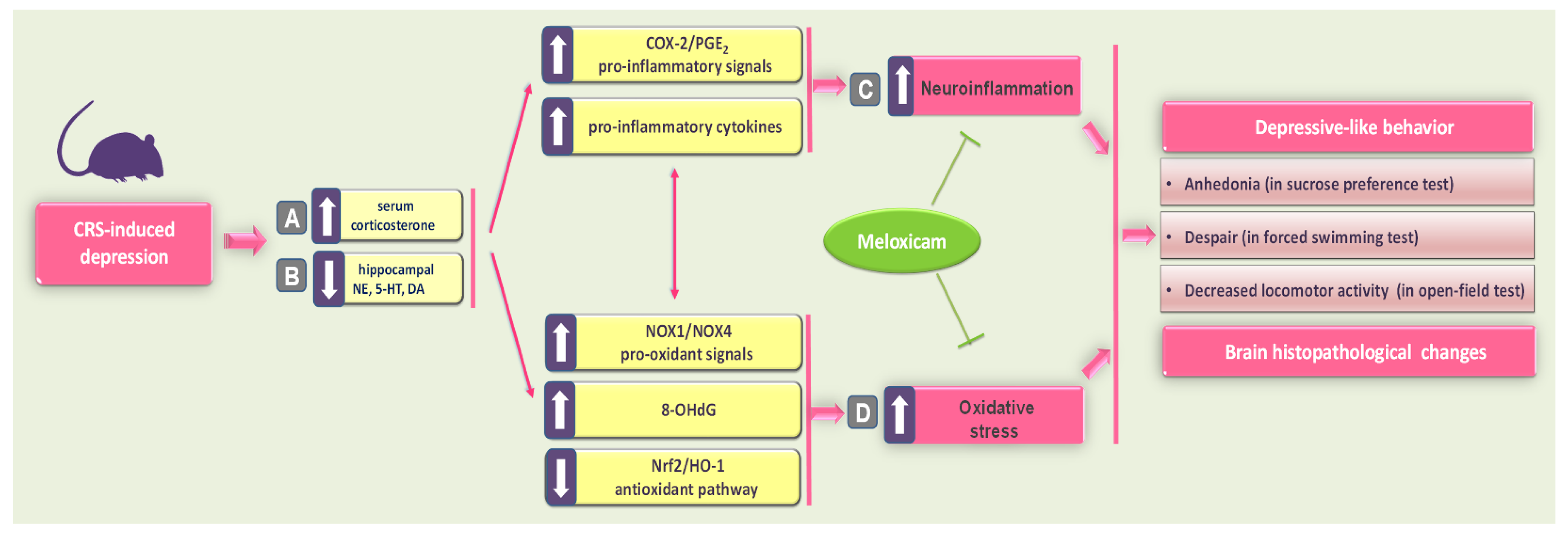
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Animals
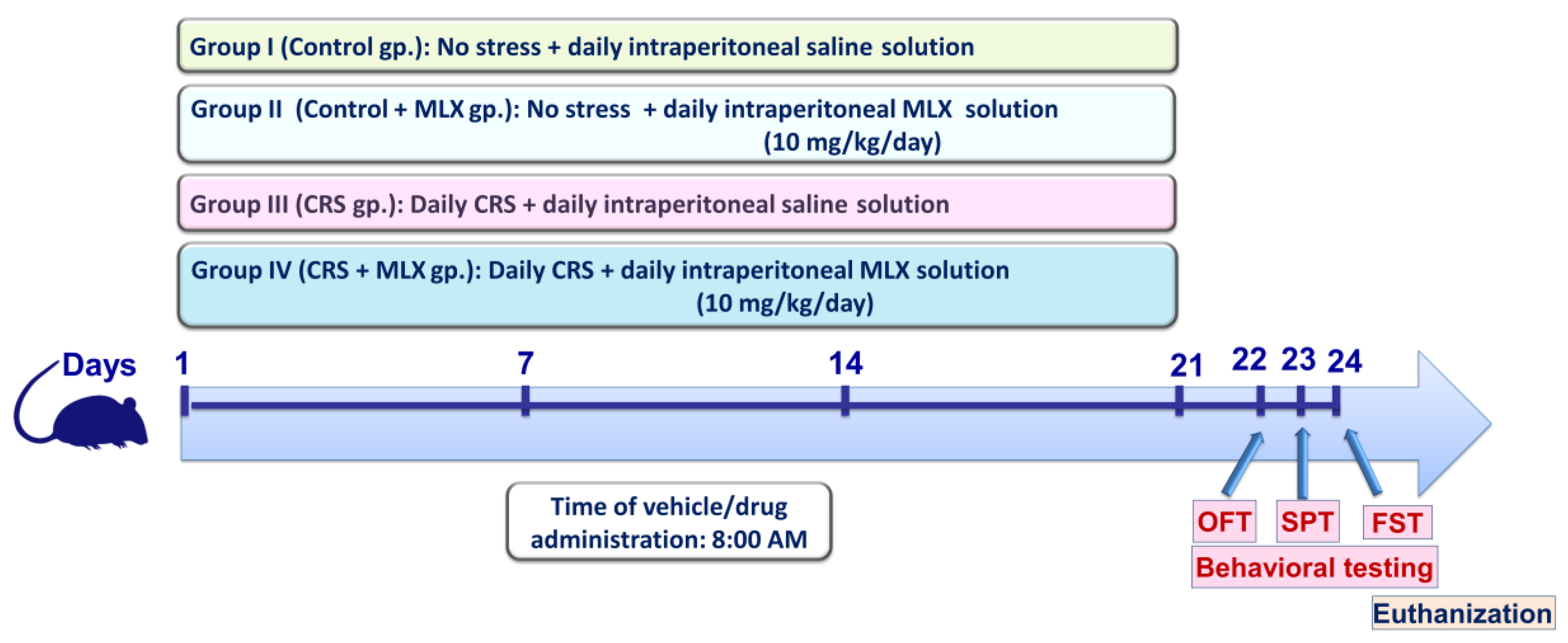
4.3. Experimental Protocol
4.4. Procedures of the CRS
4.5. Behavioral Outcomes
4.5.1. Sucrose Preference Test (SPT)
4.5.2. Forced Swimming Test (FST)
4.5.3. Open-Field Test (OFT)
4.5.4. Sequence of the Behavioral Tests
4.5.5. Normalization of Z-Scores
4.6. Histopathology and Neuropathological Scoring
4.7. Serum Corticosterone
4.8. Hippocampal Neurotransmitters
4.9. Measurement of 8-OHdG
4.10. Immunoblotting
4.11. Pro-Inflammatory Signals
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benazzi, F. Various forms of depression. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 8, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, D.R.; Yoo, J.S.; Kim, Y.; Kang, H.; Lee, H.; Lm, S.J.; Choi, E.J.; Jung, M.A.; Bae, D.; Oh, K.N.; et al. Vaccinium bracteatum Leaf Extract Reverses Chronic Restraint Stress-Induced Depression-like Behavior in Mice: Regulation of Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis, Serotonin Turnover Systems, and ERK/Akt Phosphorylation. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jangra, A.; Sriram, C.S.; Dwivedi, S.; Gurjar, S.S.; Hussain, M.I.; Borah, P.; Lahkar, M. Sodium Phenylbutyrate and Edaravone Abrogate Chronic Restraint Stress-Induced Behavioral Deficits: Implication of Oxido-Nitrosative, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Cascade, and Neuroinflammation. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 37, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jangra, A.; Dwivedi, S.; Sriram, C.S.; Gurjar, S.S.; Kwatra, M.; Sulakhiya, K.; Baruah, C.C.; Lahkar, M. Honokiol abrogates chronic restraint stress-induced cognitive impairment and depressive-like behaviour by blocking endoplasmic reticulum stress in the hippocampus of mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 770, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo-Payet, N.; Battista, M.C. Steroidogenesis-adrenal cell signal transduction. Compr. Physiol. 2014, 4, 889–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamon, M.; Blier, P. Monoamine neurocircuitry in depression and strategies for new treatments. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 45, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabel, A.M.; Arab, H.H.; Atef, A.; Estfanous, R.S. Omarigliptin/galangin combination mitigates lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation in rats: Involvement of glucagon-like peptide-1, toll-like receptor-4, apoptosis and Akt/GSK-3beta signaling. Life Sci. 2022, 295, 120396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-L.; Wu, H.-R.; Zhang, S.-S.; Xiao, H.-L.; Yu, J.; Ma, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Liu, Q. Catalpol ameliorates depressive-like behaviors in CUMS mice via oxidative stress-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome and neuroinflammation. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, M.A.; Al-Shorbagy, M.Y.; Arab, H.H. Targeting the TLR4/NF-kappaBeta Axis and NLRP1/3 Inflammasomes by Rosuvastatin: A Role in Impeding Ovariectomy-Induced Cognitive Decline Neuropathology in Rats. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 4562–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haile, M.; Boutajangout, A.; Chung, K.; Chan, J.; Stolper, T.; Vincent, N.; Batchan, M.; D’Urso, J.; Lin, Y.; Kline, R.; et al. The Cox-2 Inhibitor Meloxicam Ameliorates Neuroinflammation and Depressive Behavior in Adult Mice after Splenectomy. J. Neurophysiol. Neurol. Disord. 2016, 3, 101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arab, H.H.; Khames, A.; Alsufyani, S.E.; El-Sheikh, A.A.; Gad, A.M. Targeting the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Linked PERK/GRP78/CHOP Pathway with Magnesium Sulfate Attenuates Chronic-Restraint-Stress-Induced Depression-like Neuropathology in Rats. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwatra, M.; Ahmed, S.; Gawali, B.; Panda, S.R.; Naidu, V. Hesperidin alleviates chronic restraint stress and lipopolysaccharide-induced Hippocampus and Frontal cortex damage in mice: Role of TLR4/NF-kappaB, p38 MAPK/JNK, Nrf2/ARE signaling. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 140, 104835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sani, G.; Margoni, S.; Brugnami, A.; Ferrara, O.M.; Bernardi, E.; Simonetti, A.; Monti, L.; Mazza, M.; Janiri, D.; Moccia, L.; et al. The Nrf2 Pathway in Depressive Disorders: A Systematic Review of Animal and Human Studies. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tossetta, G.; Marzioni, D. Targeting the NRF2/KEAP1 pathway in cervical and endometrial cancers. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 941, 175503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibi, M.; Liu, J.; Arakawa, N.; Kitaoka, S.; Kawaji, A.; Matsuda, K.I.; Iwata, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Katsuyama, M.; Zhu, K.; et al. Depressive-like Behaviors Are Regulated by NOX1/NADPH Oxidase by Redox Modification of NMDA Receptor 1. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 4200–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, R.; Dhandapani, K.M.; Vadlamudi, R.K.; Brann, D.W. NADPH oxidase in brain injury and neurodegenerative disorders. Mol. Neurodegener. 2017, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, K.; Posternak, M.; Jonathan, E.A. Toward achieving optimal response: Understanding and managing antidepressant side effects. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 10, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, C.L.; Kelley, M.E.; Dunlop, B.W.; Holtzheimer, P.E., 3rd; Craighead, W.E.; Mayberg, H.S. Pretreatment brain states identify likely nonresponse to standard treatments for depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 76, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strekalova, T.; Pavlov, D.; Trofimov, A.; Anthony, D.C.; Svistunov, A.; Proshin, A.; Umriukhin, A.; Lyundup, A.; Lesch, K.P.; Cespuglio, R. Hippocampal Over-Expression of Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) Is Associated with Susceptibility to Stress-Induced Anhedonia in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, M.; Uchimura, K.; Zhu, R.L.; Nagayama, T.; Rose, M.E.; Stetler, R.A.; Isakson, P.C.; Chen, J.; Graham, S.H. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition prevents delayed death of CA1 hippocampal neurons following global ischemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 10954–10959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Famitafreshi, H.; Karimian, M. Prostaglandins as the agents that modulate the course of brain disorders. Degener. Neurol. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.; Wang, X.; Pace, T.W.; Wu, H.; Miller, A.H. Inhibition of COX-2 by celecoxib enhances glucocorticoid receptor function. Mol. Psychiatry 2005, 10, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aid, S.; Langenbach, R.; Bosetti, F. Neuroinflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide is exacerbated in mice genetically deficient in cyclooxygenase-2. J. Neuroinflamm. 2008, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkey, C.J. COX-2 inhibitors. Lancet 1999, 353, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugidos, I.F.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, P.; Santos-Galdiano, M.; Font-Belmonte, E.; Anuncibay-Soto, B.; Perez-Rodriguez, D.; Gonzalo-Orden, J.M.; Fernandez-Lopez, A. Neuroprotective effects of meloxicam on transient brain ischemia in rats: The two faces of anti-inflammatory treatments. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 1961–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohn, C.; Lomniczi, A.; Faletti, A.; Scorticati, C.; Elverdin, J.C.; McCann, S.M.; Rettori, V. Effects of aminoguanidine and meloxicam on nitric oxide and prostaglandin E production induced by lipopolysaccharide in the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary of the rat. Neuroimmunomodulation 2001, 9, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novakova, I.; Subileau, E.A.; Toegel, S.; Gruber, D.; Lachmann, B.; Urban, E.; Chesne, C.; Noe, C.R.; Neuhaus, W. Transport rankings of non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs across blood-brain barrier in vitro models. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Luo, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, L.; Hu, C.; Chen, Q.; Yang, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Xia, H. Meloxicam improves cognitive impairment of diabetic rats through COX2-PGE2-EPs-cAMP/pPKA pathway. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 4121–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goverdhan, P.; Sravanthi, A.; Mamatha, T. Neuroprotective effects of meloxicam and selegiline in scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment and oxidative stress. Int. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2012, 2012, 974013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, K.R.; Fauerby, N.; Raida, Z.; Kalliokoski, O.; Hau, J.; Johansen, F.F.; Abelson, K.S. Effects of buprenorphine and meloxicam analgesia on induced cerebral ischemia in C57BL/6 male mice. Comp. Med. 2013, 63, 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- Tasaki, Y.; Yamamoto, J.; Omura, T.; Sakaguchi, T.; Kimura, N.; Ohtaki, K.; Ono, T.; Suno, M.; Asari, M.; Ohkubo, T.; et al. Meloxicam ameliorates motor dysfunction and dopaminergic neurodegeneration by maintaining Akt-signaling in a mouse Parkinson’s disease model. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 521, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartha, S.; Weisshaar, C.L.; Philips, B.H.; Winkelstein, B.A. Pre-treatment with Meloxicam Prevents the Spinal Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in DRG Neurons that Accompany Painful Cervical Radiculopathy. Neuroscience 2018, 388, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, C.L.; Glasper, E.R.; Harrell, C.S.; Malviya, S.A.; Otis, J.S.; Neigh, G.N. Meloxicam blocks neuroinflammation, but not depressive-like behaviors, in HIV-1 transgenic female rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; Huang, H.; Li, S.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Z.; Huang, R.; Liao, W.; Xie, P.; Zhou, J. Hippocampal proteomic changes of susceptibility and resilience to depression or anxiety in a rat model of chronic mild stress. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheggi, S.; De Montis, M.G.; Gambarana, C. Making Sense of Rodent Models of Anhedonia. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018, 21, 1049–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porsolt, R.D.; Bertin, A.; Jalfre, M. Behavioral despair in mice: A primary screening test for antidepressants. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 1977, 229, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arab, H.H.; Safar, M.M.; Shahin, N.N. Targeting ROS-Dependent AKT/GSK-3beta/NF-kappaB and DJ-1/Nrf2 Pathways by Dapagliflozin Attenuates Neuronal Injury and Motor Dysfunction in Rotenone-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Rat Model. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 689–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amarat, W.; Abukhalil, M.H.; Althunibat, O.Y.; Alfwuaires, M.A.; Alnamshan, M.M.; Alqosaibi, A.I.; Ahmeda, A.F.; Kamel, E.M.; Arab, H.H.; Mahmoud, A.M. Galangin Attenuates Liver Injury, Oxidative Stress and Inflammation, and Upregulates Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Processes 2021, 9, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, H.H.; Eid, A.H.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Senousy, M.A. Linagliptin mitigates experimental inflammatory bowel disease in rats by targeting inflammatory and redox signaling. Life Sci. 2021, 273, 119295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, H.H.; Abd El-Aal, S.A.; Eid, A.H.; Arafa, E.A.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Ashour, A.M. Targeting inflammation, autophagy, and apoptosis by troxerutin attenuates methotrexate-induced renal injury in rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 103, 108284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Feng, Y.B.; Wang, L.; Shen, J.; Li, Y.; Fan, C.; Wang, P.; Yu, S.Y. COX-2 inhibition rescues depression-like behaviors via suppressing glial activation, oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis in rats. Neuropharmacology 2019, 160, 107779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troubat, R.; Barone, P.; Leman, S.; Desmidt, T.; Cressant, A.; Atanasova, B.; Brizard, B.; El Hage, W.; Surget, A.; Belzung, C.; et al. Neuroinflammation and depression: A review. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 53, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gałecki, P.; Talarowska, M. Inflammatory theory of depression. Psychiatr. Pol. 2018, 52, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Jiang, M.; Gu, S.; Wang, F.; Yuan, B. Early Life Stress Induced DNA Methylation of Monoamine Oxidases Leads to Depressive-like Behavior. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 582247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teismann, P.; Ferger, B. Inhibition of the cyclooxygenase isoenzymes COX-1 and COX-2 provide neuroprotection in the MPTP-mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Synapse 2001, 39, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, K.A.; Dion-Albert, L.; Kaufmann, F.N.; Tuck, E.; Lebel, M.; Menard, C. Neurobiology of resilience in depression: Immune and vascular insights from human and animal studies. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 53, 183–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Han, X.; Yang, J.; Bao, J.; Di, X.; Zhang, G.; Liu, H. Magnesium Sulfate Provides Neuroprotection in Eclampsia-like Seizure Model by Ameliorating Neuroinflammation and Brain Edema. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 7938–7948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er, A.; Coskun, D.; Bahcivan, E.; Dik, B. Effect of doxycycline and meloxicam on cytokines, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, matrix metalloproteinase-3, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 and cyclooxygenase-2 in brain. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2020, 23, 1328. [Google Scholar]
- Kalonia, H.; Kumar, A. Suppressing inflammatory cascade by cyclo-oxygenase inhibitors attenuates quinolinic acid induced Huntington’s disease-like alterations in rats. Life Sci. 2011, 88, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgarhi, R.; Shehata, M.M.; Abdelsameea, A.A.; Salem, A.E. Effects of Diclofenac Versus Meloxicam in Pentylenetetrazol-Kindled Mice. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 1913–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, J.; Molotkov, A.; Mintz, A.; Mann, J.J. Progress in PET Imaging of Neuroinflammation Targeting COX-2 Enzyme. Molecules 2021, 26, 3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, B.Y.; Xie, C.N.; Xie, J.Y.; Gao, Z.W.; Fei, X.W.; Hong, E.H.; Chen, W.J.; Chen, Y.Z. Knockdown of NADPH oxidase 4 reduces mitochondrial oxidative stress and neuronal pyroptosis following intracerebral hemorrhage. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 1734–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, R.N.; Ahmed, L.A.; Abdul Salam, R.M.; Ahmed, K.A.; Attia, A.S. Crosstalk Among NLRP3 Inflammasome, ET(B)R Signaling, and miRNAs in Stress-Induced Depression-like Behavior: A Modulatory Role for SGLT2 Inhibitors. Neurotherapeutics 2021, 18, 2664–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, H.H.; Abd El Aal, H.A.; Alsufyani, S.E.; El-Sheikh, A.A.K.; Arafa, E.A.; Ashour, A.M.; Kabel, A.M.; Eid, A.H. Topiramate Reprofiling for the Attenuation of Cadmium-Induced Testicular Impairment in Rats: Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome and AMPK/mTOR-Linked Autophagy. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safar, M.M.; Arab, H.H.; Rizk, S.M.; El-Maraghy, S.A. Bone Marrow-Derived Endothelial Progenitor Cells Protect Against Scopolamine-Induced Alzheimer-like Pathological Aberrations. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 1403–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Yang, R.R.; Zhang, J.L.; Wang, P.; Gong, Y.; Hu, W.F.; Wu, Y.; Gao, M.H.; Huang, C. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid produces antidepressant-like effects in a chronic unpredictable stress model of depression via attenuation of neuroinflammation, oxido-nitrosative stress, and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 32, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilloux, J.P.; Seney, M.; Edgar, N.; Sibille, E. Integrated behavioral z-scoring increases the sensitivity and reliability of behavioral phenotyping in mice: Relevance to emotionality and sex. J. Neurosci. Methods 2011, 197, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, H.H.; Eid, A.H.; El-Sheikh, A.A.K.; Arafa, E.A.; Ashour, A.M. Irbesartan reprofiling for the amelioration of ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury in rats: Role of inflammation, apoptosis, and autophagy. Life Sci. 2022, 308, 120939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoresen, M.; Bagenholm, R.; Loberg, E.M.; Apricena, F.; Kjellmer, I. Posthypoxic cooling of neonatal rats provides protection against brain injury. Arch. Dis. Child.-Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1996, 74, F3–F9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, N.N.; Al-Shorbagy, M.Y.; Arab, H.H.; Abdallah, D.M. Saxagliptin: A novel antiparkinsonian approach. Neuropharmacology 2015, 89, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, H.H.; Abd El-Aal, S.A.; Ashour, A.M.; El-Sheikh, A.A.K.; Al Khabbaz, H.J.; Arafa, E.A.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Kabel, A.M. Targeting inflammation and redox perturbations by lisinopril mitigates Freund’s adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats: Role of JAK-2/STAT-3/RANKL axis, MMPs, and VEGF. Inflammopharmacology 2022, 30, 1909–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, K.M.; Gad, A.M.; Mansour, S.M.; Safar, M.M.; Fawzy, H.M. Venlafaxine alleviates complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats: Modulation of STAT-3/IL-17/RANKL axis. Life Sci. 2019, 226, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, A.; Tam, W.W.; Zhang, M.W.; Ho, C.S.; Husain, S.F.; McIntyre, R.S.; Ho, R.C. IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α and CRP in elderly patients with depression or Alzheimer’s disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arab, H.H.; Khames, A.; Mohammad, M.K.; Alsufyani, S.E.; Ashour, A.M.; El-Sheikh, A.A.K.; Darwish, H.W.; Gad, A.M. Meloxicam Targets COX-2/NOX1/NOX4/Nrf2 Axis to Ameliorate the Depression-like Neuropathology Induced by Chronic Restraint Stress in Rats. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16060848
Arab HH, Khames A, Mohammad MK, Alsufyani SE, Ashour AM, El-Sheikh AAK, Darwish HW, Gad AM. Meloxicam Targets COX-2/NOX1/NOX4/Nrf2 Axis to Ameliorate the Depression-like Neuropathology Induced by Chronic Restraint Stress in Rats. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(6):848. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16060848
Chicago/Turabian StyleArab, Hany H., Ali Khames, Mostafa K. Mohammad, Shuruq E. Alsufyani, Ahmed M. Ashour, Azza A. K. El-Sheikh, Hany W. Darwish, and Amany M. Gad. 2023. "Meloxicam Targets COX-2/NOX1/NOX4/Nrf2 Axis to Ameliorate the Depression-like Neuropathology Induced by Chronic Restraint Stress in Rats" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 6: 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16060848
APA StyleArab, H. H., Khames, A., Mohammad, M. K., Alsufyani, S. E., Ashour, A. M., El-Sheikh, A. A. K., Darwish, H. W., & Gad, A. M. (2023). Meloxicam Targets COX-2/NOX1/NOX4/Nrf2 Axis to Ameliorate the Depression-like Neuropathology Induced by Chronic Restraint Stress in Rats. Pharmaceuticals, 16(6), 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16060848





