Spasmolytic and Uroprotective Effects of Apigenin by Downregulation of TGF-β and iNOS Pathways and Upregulation of Antioxidant Mechanisms: In Vitro and In Silico Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
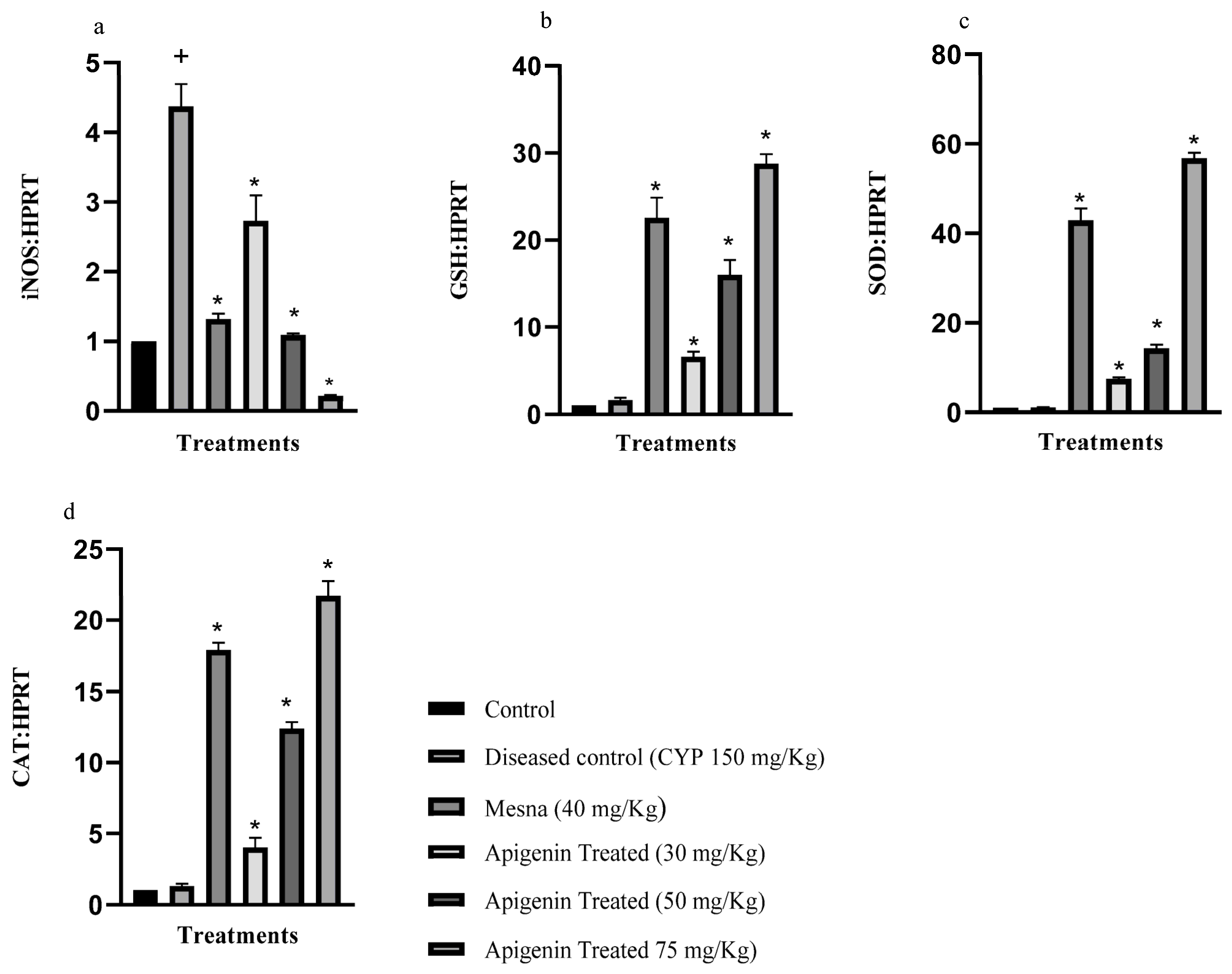
2.1. Effect of Apigenin on the Expression of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (iNOS), Glutathione Reductase (GSH), Superoxide Dismutase (SOD), and Catalase (CAT)
2.2. Effect of Apigenin on the Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Interleukin-6 (IL-6), Transforming Growth Factor 1-β (TGF 1-β), and Tissue Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α)
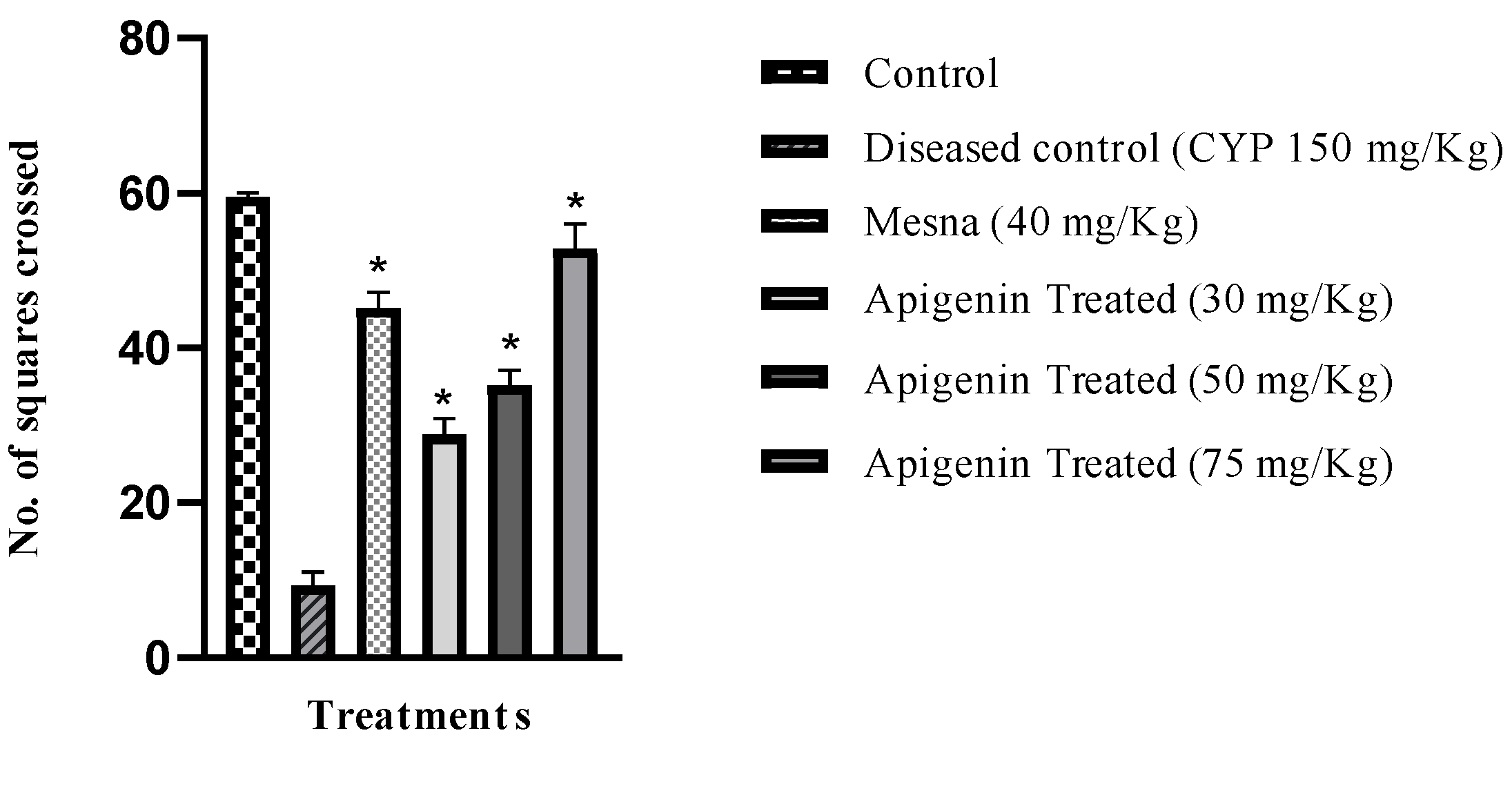
2.3. Effect of Apigenin on Nociception
2.4. Macroscopic Analysis
2.4.1. Effect of Apigenin on Bladder Weight
2.4.2. Effect of Apigenin on Hemorrhage and Edema
2.5. Effect of Apigenin on Vascular Permeability
2.6. Histopathological Studies
2.7. Molecular Docking
2.8. Effect of Apigenin on Isolated Rat Bladder Strips
2.8.1. Carbachol Contraction Response in Isolated Bladder Strips
2.8.2. Relaxant Response of Apigenin against Carbachol-Induced Contractions
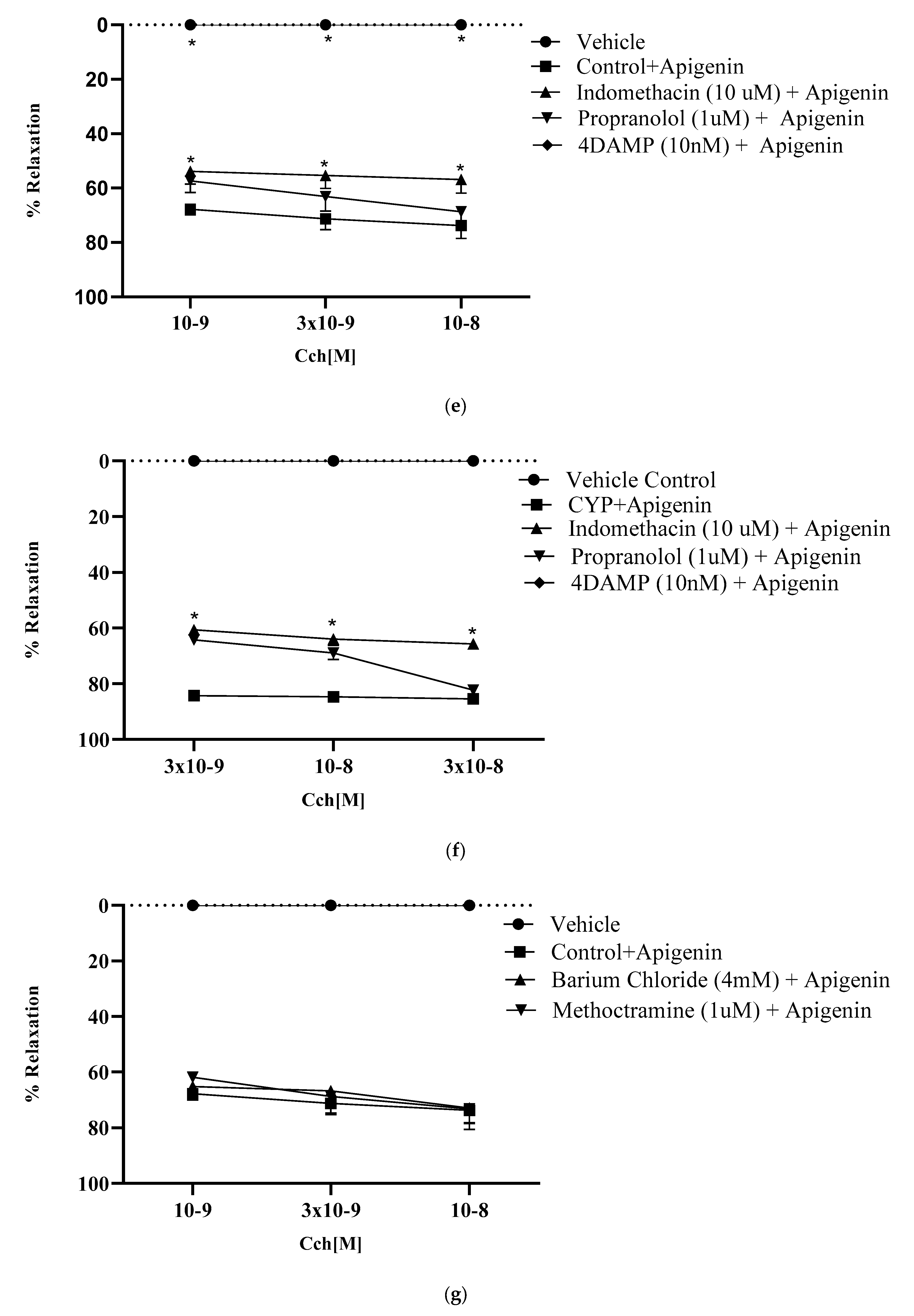
2.8.3. Effect of Muscarinic Receptors on Relaxant Potential of Apigenin
2.8.4. Effect of Nifedipine on Relaxant Potential of Apigenin
2.8.5. Role of KATP Channel Blocker in Relaxant Effect of Apigenin
2.8.6. Role of KIR Channels in Relaxant Effect of Apigenin
2.8.7. Involvement of β- Adrenergic Receptors in Relaxant Effect of Apigenin
2.8.8. Role of Prostaglandins in Relaxant Effect of Apigenin
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals Used
4.2. Animals Used
4.3. Cyclophosphamide-Induced Interstitial Cystitis
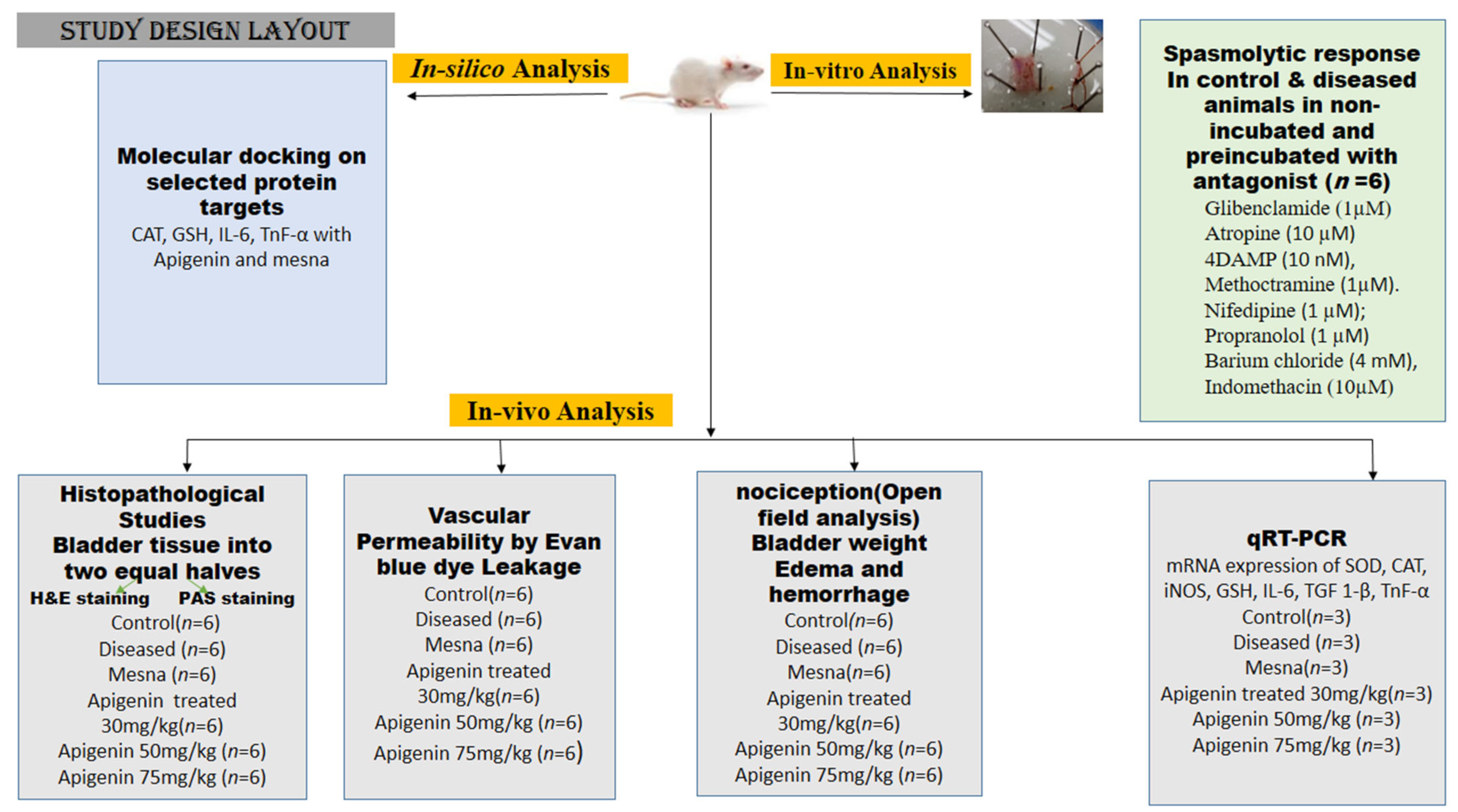
4.4. Study Design
4.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis for Measuring mRNA Expression of SOD, CAT, iNOS, GSH, IL-6, TGF 1-β, TNF-α
4.6. Assessment of Nociception
4.7. Assessment of Bladder Edema and Hemorrhage
4.8. Evaluation of Vascular Protein Leakage by the Evans Blue Dye Technique
4.9. Histologic Analysis
4.10. Molecular Docking
4.10.1. Ligand Selection
4.10.2. Characterization of Receptor
4.10.3. Docking Studies
4.10.4. Model Validation
4.11. In-Vitro Activity on Isolated Rat Bladder Strips
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smaldone, M.C.; Vodovotz, Y.; Tyagi, V.; Barclay, D.; Philips, B.J.; Yoshimura, N.; Tyagi, P. Multiplex analysis of urinary cytokine levels in rat model of cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis. Urology 2009, 73, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.W.; Chun, S.Y.; Lee, E.H.; Ha, Y.S.; Lee, J.N.; Song, P.H.; Yoo, E.S.; Kwon, T.G.; Chung, S.K.; Kim, B.S. Verification of mesenchymal stem cell injection therapy for interstitial cystitis in a rat model. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, D.R.; Chen, C.S.; Lin, W.Y.; Chang, P.J.; Huang, Y.C. Effect of hyaluronic acid on urine nerve growth factor in cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis. Int. J. Urol. 2011, 18, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kageyama, A.; Fujino, T.; Taki, Y.; Kato, Y.; Nozawa, Y.; Ito, Y.; Yamada, S. Alteration of muscarinic and purinergic receptors in urinary bladder of rats with cyclophosphamide-induced interstitial cystitis. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 436, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, M.; Anjum, I.; Abdullah, A.; Abid, S.Z.; Malik, M.N.H. Boswellic Acids, Pentacyclic Triterpenes, Attenuate Oxidative Stress, and Bladder Tissue Damage in Cyclophosphamide-Induced Cystitis. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 13697–13703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, P.; Tyagi, V.; Yoshimura, N.; Witteemer, E.; Barclay, D.; Loughran, P.A.; Zamora, R.; Vodovotz, Y. Gender-based reciprocal expression of transforming growth factor-β1 and the inducible nitric oxide synthase in a rat model of cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis. J. Inflamm. 2009, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, S.; Dru, C.; Bhowmick, N.A. Mechanisms of hemorrhagic cystitis. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Urol. 2014, 2, 199. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, R.A.; Lima-Junior, R.C.; Leite, C.A.V.G.; Mota, J.M.S.C.; Macedo, F.Y.; Lima, M.V.; Brito, G.A. Chemotherapy-induced hemorrhagic cystitis: Pathogenesis, pharmacological approaches and new insights. J. Exp. Integr. Med. 2012, 2, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrin, S.; Masuda, E.; Kugaya, H.; Ito, Y.; Yamada, S. Improvement by phytotherapeutic agent of detrusor overactivity, down-regulation of pharmacological receptors and urinary cytokines in rats with cyclophosphamide induced cystitis. J. Urol. 2013, 189, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, P.; Srivastava, A.; Watson, L.; Quinlan, L.R.; Pandit, A. Hyaluronic acid decreases IL-6 and IL-8 secretion and permeability in an inflammatory model of interstitial cystitis. Acta Biomater. 2015, 19, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Song, Y.J.; Song, B.; Huang, C.B.; Ling, Q.; Yu, X. TGF-β/MAPK signaling mediates the effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on urinary control and interstitial cystitis after urinary bladder transplantation. Am. J. Transl.Res. 2017, 9, 1193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, Y.Q.; Zhang, W.T.; Shi, C.H.; Wang, F.M.; Tian, X.J.; Ma, L.L. Phloroglucinol protects the urinary bladder via inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation in a rat model of cyclophosphamide-induced interstitial cystitis. Chin. Med. J. 2015, 128, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, M.; Aronsson, P.; Doufish, D.; Lampert, A.; Tobin, G. Muscarinic receptor subtypes involved in urothelium-derived relaxatory effects in the inflamed rat urinary bladder. Auton. Neurosci. 2012, 170, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, I.; Denizalti, M.; Kandilci, H.B.; Durlu-Kandilci, N.T.; Sahin-Erdemli, I. Enhancement of S1P-induced contractile response in detrusor smooth muscle of rats having cystitis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 814, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, S.Ç.; Keskin, C.; Şahintürk, V.; Ayhanci, A. Investigation of uroprotective effects of seed methanol extracts of Hypericum triquetrifolium Turra. on cyclophosphamide-induced bladder hemorrhagic cystitis and nephrotoxicity in Wistar albino rats. Çukurova Med. J. 2020, 45, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.L.G.; Cunha, F.V.M.; Sousa-Neto, B.P.S.; Oliveira, L.S.A.; Lopes, M.E.; Rezende, D.C.; Oliveira, F.D.A. α-Phellandrene attenuates tissular damage, oxidative stress, and TNF-α levels on acute model ifosfamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis in mice. Naunyn-Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol. 2020, 393, 1835–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopoldini, M.; Pitarch, I.P.; Russo, N.; Toscano, M. Structure, conformation, and electronic properties of apigenin, luteolin, and taxifolin antioxidants. A first principle theoretical study. J. Phys. Chem. 2004, 108, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Yi, W.J.; Tan, L.; Zhang, J.H.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, R. Apigenin attenuates streptozotocin-induced pancreatic β cell damage by its protective effects on cellular antioxidant defense. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2017, 53, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.P.V.; Selvendiran, K.; Banu, S.M.; Padmavathi, R.; Sakthisekaran, D. Protective role of Apigenin on the status of lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defense against hepatocarcinogenesis in Wistar albino rats. Phytomedicine 2004, 11, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Kandhare, A.; Mukherjee-Kandhare, A.; Bodhankar, S.L. Apigenin attenuated ethylene glycol induced urolithiasis in uninephrectomized hypertensive rats: A possible role of bikunin, BMP-2/4, and osteopontin. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2020, 16, 455. [Google Scholar]
- Altuntas, C.Z.; Daneshgari, F.; Sakalar, C.; Goksoy, E.; Gulen, M.F.; Kavran, M.; Qin, J.; Li, X.; Tuohy, V.K. Autoimmunity to uroplakin II causes cystitis in mice: A novel model of interstitial cystitis. Eur. Urol. 2012, 61, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera, P.L.; Iczkowski, K.A.; Wang, X.; Meyer-Siegler, K.L. Cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis increases bladder CXCR4 expression and CXCR4-macrophage migration inhibitory factor association. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkmaz, A.; Topal, T.; Oter, S. Pathophysiological aspects of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide induced hemorrhagic cystitis; implication of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species as well as PARP activation. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2007, 23, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, F.; Zhou, R.; Song, X.; Xie, M. Apigenin: A current review on its beneficial biological activities. J. Food Biochem. 2017, 41, e12376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toklu, H.; Alican, I.; Ercan, F.; Sener, G. The beneficial effect of resveratrol on rat bladder contractility and oxidant damage following ischemia/reperfusion. Pharmacology 2006, 78, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishijima, S.; Sugaya, K.; Kadekawa, K.; Ashitomi, K.; Ueda, T.; Yamamoto, H. High-dose tranilast administration to rats creates interstitial cystitis-like symptoms with increased vascular permeability. Life Sci. 2013, 93, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabbir, U.; Anjum, I.; Naveed Mushtaq, M.; Nasir Hayat Malik, M.; Ismail, S.; Javed, J.; Rehman, Z.U. Uroprotective and Hepatoprotective Potential of Anagallis arvensis against the Experimental Animal Model. J. Trop. Med. 2022, 2022, 7241121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assreuy, A.M.S.; Martins, G.J.; Moreira, M.E.F.; Brito, G.A.C.; Cavada, B.S.; Ribeiro, R.A.; Flores, C.A. Prevention of cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis by glucose-mannose binding plant lectins. J. Urol. 1999, 161, 1988–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgür, A.; Önol, F.F.; Ercan, F.; Tarcan, T. Prophylactic role of oral L-Arginine on histological and contractile changes in a rat chronic bladder injury model. Urol. Int. 2008, 81, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyathi, B.; Bvunzawabaya, J.T.; Mudawarima, C.V.P.; Manzombe, E.; Tsotsoro, K.; Selemani, M.A.; Munyuki, G.; Rwere, F. Antidiabetic and in silico molecular docking of Xeroderris stuhlmannii (Taub.) Mendonca EP Sousa phytochemical compounds on human α-glucosidases. bioRxiv 2022, 19, 116501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Dixit, S.; Mittal, A. In silico target identification and validation for antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of selective phytochemicals. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2019, 62, 20219915158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yende, S.R.; Shah, S.K.; Arora, S.K.; Moharir, K.S.; Lohiya, G.K. In silico prediction of phytoconstituents from Ehretia laevis targeting TNF-α in arthritis. Digit. Chin. Med. 2021, 4, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahran, E.M.; Abdel-Maqsoud, N.M.; Tammam, O.Y.; Abdel-Rahman, I.M.; Elrehany, M.A.; Bakhsh, H.T.; Altemani, F.H.; Algehainy, N.A.; Alzubaidi, M.A.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; et al. Scabicidal Potential of Coconut Seed Extract in Rabbits via Downregulating Inflammatory/Immune Cross Talk: A Comprehensive Phytochemical/GC-MS and In Silico Proof. Antibiotics 2022, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.H.; Biswas, P.; Dey, D.; Hannan, M.A.; Sahabuddin, M.; Araf, Y.; Kwon, Y.; Emran, T.B.; Ali, M.S.; Uddin, M.J. An In-Silico Identification of Potential Flavonoids against Kidney Fibrosis Targeting TGFβR-1. Life 2022, 12, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, D.; Ryberg, A.T.; To, K.; Delbro, D.S.; Tobin, G. Altered muscarinic receptor subtype expression and functional responses in cyclophosphamide induced cystitis in rats. Auton. Neurosci. 2005, 122, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, S.S.; Eglen, R.M. Muscarinic receptor subtypes modulating smooth muscle contractility in the urinary bladder. Life Sci. 1999, 64, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonev, A.D.; Nelson, M.T. ATP-sensitive potassium channels in smooth muscle cells from guinea pig urinary bladder. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 1993, 264, C1190–C1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dela Peña, I.C.; Yoon, S.Y.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, G.S.; Ryu, J.H.; Park, C.S.; Kim, Y.C.; Cheong, J.H. Bladder-relaxant properties of the novel benzofuroindole analogue LDD175. Pharmacology 2009, 83, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darblade, B.; Behr-Roussel, D.; Oger, S.; Hieble, J.P.; Lebret, T.; Gorny, D.; Benoit, G.; Alexandre, L.; Giuliano, F. Effects of potassium channel modulators on human detrusor smooth muscle myogenic phasic contractile activity: Potential therapeutic targets for overactive bladder. Urology 2006, 68, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishii, K.I.; Hisayama, T.; Takayanagi, I. Comparison of contractile mechanisms by carbachol and ATP in detrusor strips of rabbit urinary bladder. JJP 1992, 58, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, M.C. β-Adrenergic receptor subtypes in the urinary tract. Urin. Tract 2011, 202, 307–318. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, K.E.; Forman, A. Effects of prostaglandins on the smooth muscle of the urinary tract. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1978, 43, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabbir, R.; Hayat Malik, M.N.; Zaib, M.; Alamgeer; Jahan, S.; Khan, M.T. Amino Acid Conjugates of 2-Mercaptobenzimidazole Ameliorates High-Fat Diet-Induced Hyperlipidemia in Rats via Attenuation of HMGCR, APOB, and PCSK9. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 40502–40511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open Babel: An open chemical toolbox. J. Cheminform. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najm, S.; Naureen, H.; Sultana, K.; Anwar, F.; Rehman, S.; Arshad, S.; Khan, M.M. In-silico computational analysis of [6-(2, 3-Dichlorophenyl)-1, 2, 4-Triazine-3, 5-Diamine] metal complexes on voltage gated sodium channel and dihydrofolate reductase enzyme. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 33, 1779–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Roy, A.; Zhang, Y. Protein–ligand binding site recognition using complementary binding-specific substructure comparison and sequence profile alignment. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2588–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimipour, S.Y.; Sheikhshoaie, I.; Castro, J.; Dušek, M.; Tohidiyan, Z.; Eigner, V.; Khaleghi, M. Synthesis, spectral characterization, structural studies, molecular docking and antimicrobial evaluation of new dioxidouranium (VI) complexes incorporating tetradentate N 2 O 2 Schiff base ligands. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 95104–95117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, W.H.; Deghadi, R.G.; Mohamed, G.G. Metal complexes of ferrocenyl-substituted Schiff base: Preparation, characterization, molecular structure, molecular docking studies, and biological investigation. J. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 917, 121113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullmann, F.A.; Daugherty, S.L.; de Groat, W.C.; Birder, L.A. Bladder smooth muscle strip contractility as a method to evaluate lower urinary tract pharmacology. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 90, e51807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Groups | Bladder Weight (mg) Mean ± SEM | Nociception Mean ± SEM | Edema Mean ± SEM | Hemorrhage Mean ± SEM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 9.0 ± 0.36 * | 0 ± 0.001 * | 0 ± 0.01 * | 0 ± 0.001 * |
| Diseased control (CYP 150 mg/kg) | 17.16 ± 0.40 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ± 0.01 | 3+ ± 0.001 | 3+ ± 0.01 |
| Mesna (40 mg/kg) | 11.40 ± 0.51 * | 1 ± 0.001 * | 1+ ± 0.01 * | 0 ± 0.001 * |
| Apigenin Treated (30 mg/kg) | 13.00 ± 0.36 * | 1, 2 ± 0.02 * | 2+ ± 0.02 * | 3+ ± 0.01 * |
| Apigenin Treated (50 mg/kg) | 10.50 ± 0.34 * | 1 ± 0.04 * | 1+ ± 0.02 * | 2+ ± 0.02 * |
| Apigenin Treated (75 mg/kg) | 9.16 ± 0.30 * | 0 ± 0.01 * | 1+ ± 0.01 * | 1+ ± 0.02 * |
| Receptor | Active Compound | PDB ID | Binding Energy (Kcal/mol) | Inhibition Constant (ki) (nM) | Torsional Energy | No of Hydrogen Bonds | Interacting Residues |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalase-Apigenin | CAT(antioxidant) | 1DGB | −6.9 | 8.28 | 1.19 | 2 | THR239, PRO241, LEU245, TYR246, ASP238, TYR246 |
| Glutathione- Apigenin | GSH(antioxidant) | 3DK4 | −9.44 | 121.2 | 1.19 | 2 | TRP70, VAL74, GLU77, PRO373, HIS374, LEU438, GLY439, ASP441 |
| Cytokine- Apigenin | IL-6 (pro-inflammatory) | 4ZS7 | −7.49 | 3.25 | 1.19 | 1 | VAL2, GLN3, LEU4, ARG99, VAL24, TYR111, TRP112, GLN114 |
| Tumor necrosis factor- Apigenin | TNF-α (pro-inflammatory) | 4TWT | −8.77 | 375.5 | 1.19 | 1 | GLN61, LYS98, ILE116, PRO117, TYR119 |
| Catalase-Mesna | CAT (antioxidant) | 1DGB | −4.51 | 496.9 | 0.3 | 1 | LEU26, PRO78, THR79, LEU80, VAL132, LEU134 |
| Glutathione- Mesna | GSH (antioxidant) | 3DK4 | −5.01 | 210.95 | 0.3 | 2 | GLY29, SER30, GLY56, THR57, CYS58, THR339 |
| Cytokine- Mesna | IL-6 (pro-inflammatory) | 4ZS7 | −4.87 | 270.44 | 0.3 | 1 | LEU47, GLU48, TRP49, ARG94, ALA99, VAL100, PHE101S |
| Tumor necrosis factor- Mesna | TNF-α (pro-inflammatory) | 4TWT | −4.67 | 379.61 | 0.3 | 2 | VAL17, PHE144, GLU146, GLY148, GLN149, VAL150, TYR151 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saima; Anjum, I.; Mobashar, A.; Jahan, S.; Najm, S.; Nafidi, H.-A.; Bin Jardan, Y.A.; Bourhia, M. Spasmolytic and Uroprotective Effects of Apigenin by Downregulation of TGF-β and iNOS Pathways and Upregulation of Antioxidant Mechanisms: In Vitro and In Silico Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16060811
Saima, Anjum I, Mobashar A, Jahan S, Najm S, Nafidi H-A, Bin Jardan YA, Bourhia M. Spasmolytic and Uroprotective Effects of Apigenin by Downregulation of TGF-β and iNOS Pathways and Upregulation of Antioxidant Mechanisms: In Vitro and In Silico Analysis. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(6):811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16060811
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaima, Irfan Anjum, Aisha Mobashar, Shah Jahan, Saima Najm, Hiba-Allah Nafidi, Yousef A. Bin Jardan, and Mohammed Bourhia. 2023. "Spasmolytic and Uroprotective Effects of Apigenin by Downregulation of TGF-β and iNOS Pathways and Upregulation of Antioxidant Mechanisms: In Vitro and In Silico Analysis" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 6: 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16060811
APA StyleSaima, Anjum, I., Mobashar, A., Jahan, S., Najm, S., Nafidi, H.-A., Bin Jardan, Y. A., & Bourhia, M. (2023). Spasmolytic and Uroprotective Effects of Apigenin by Downregulation of TGF-β and iNOS Pathways and Upregulation of Antioxidant Mechanisms: In Vitro and In Silico Analysis. Pharmaceuticals, 16(6), 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16060811







