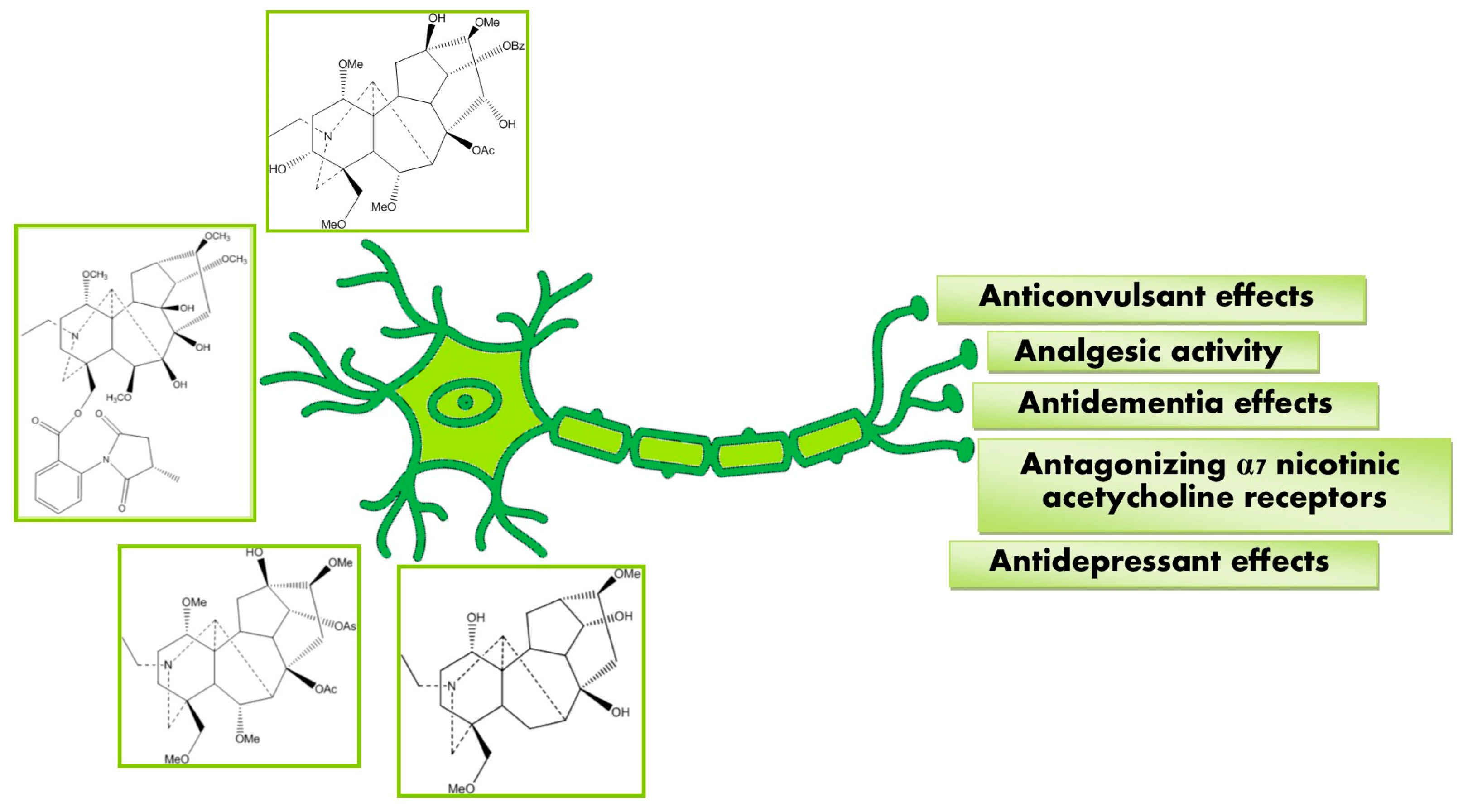
Neuropharmacological Potential of Diterpenoid Alkaloids
Abstract
1. Introduction
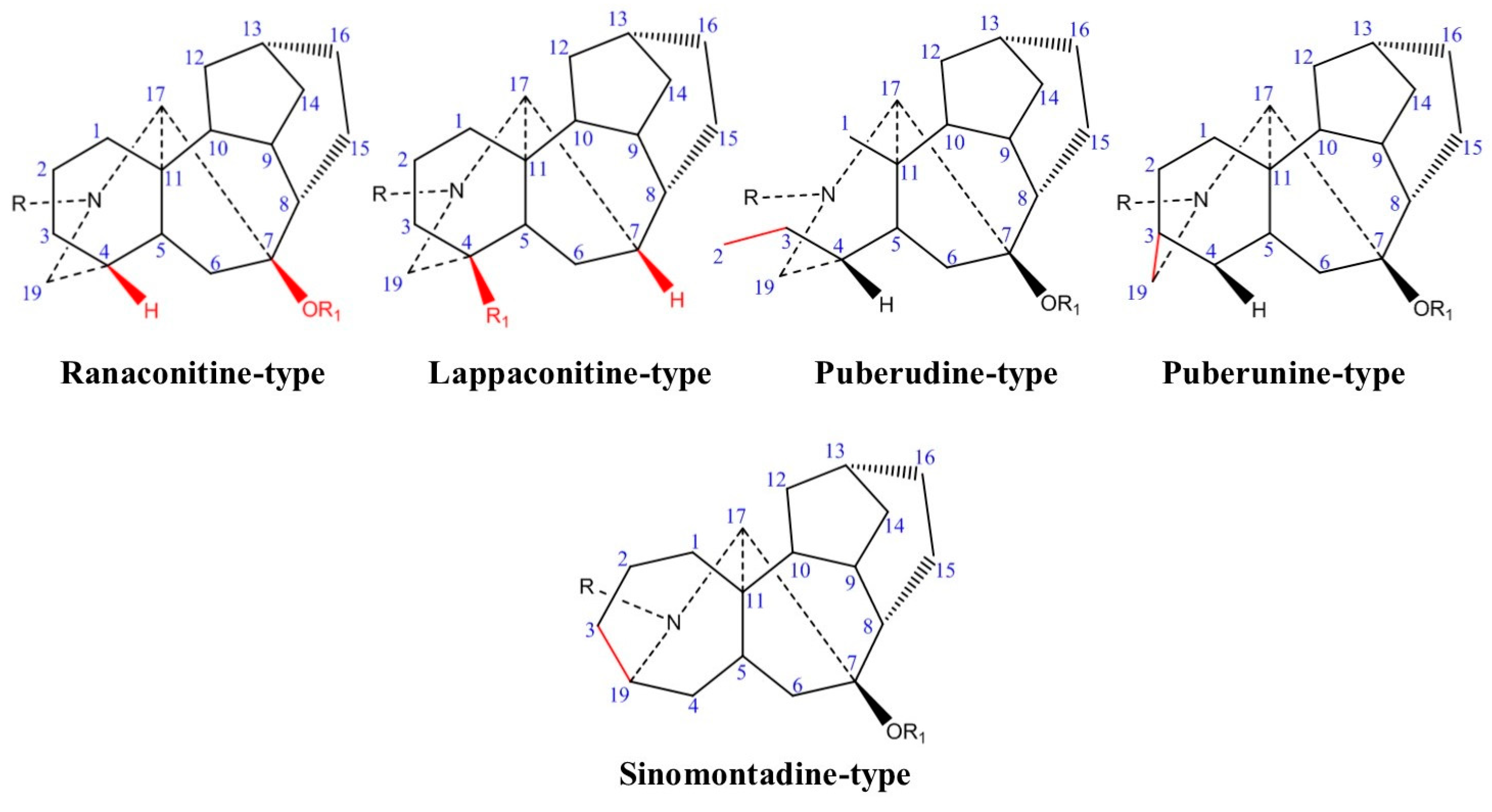
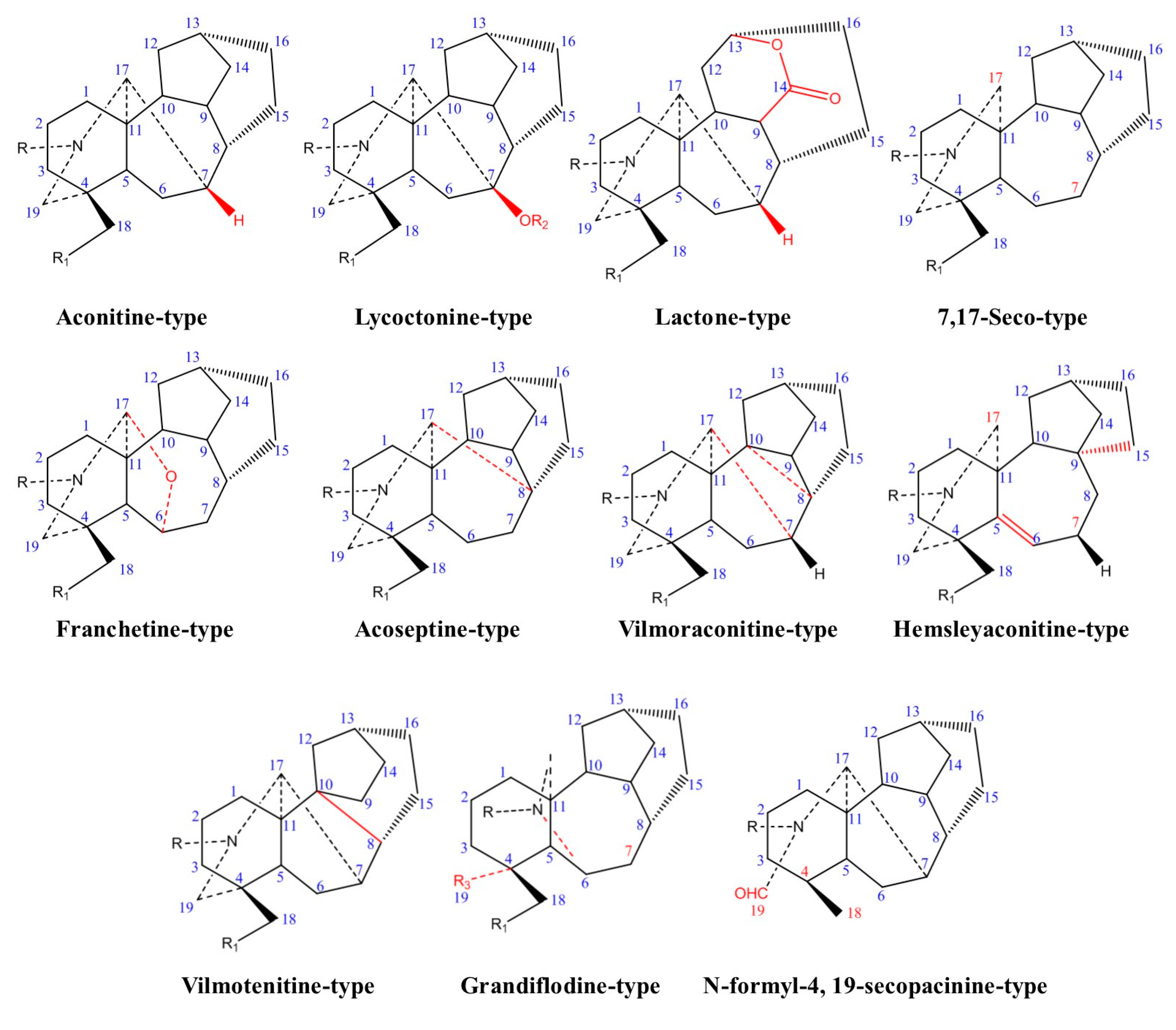
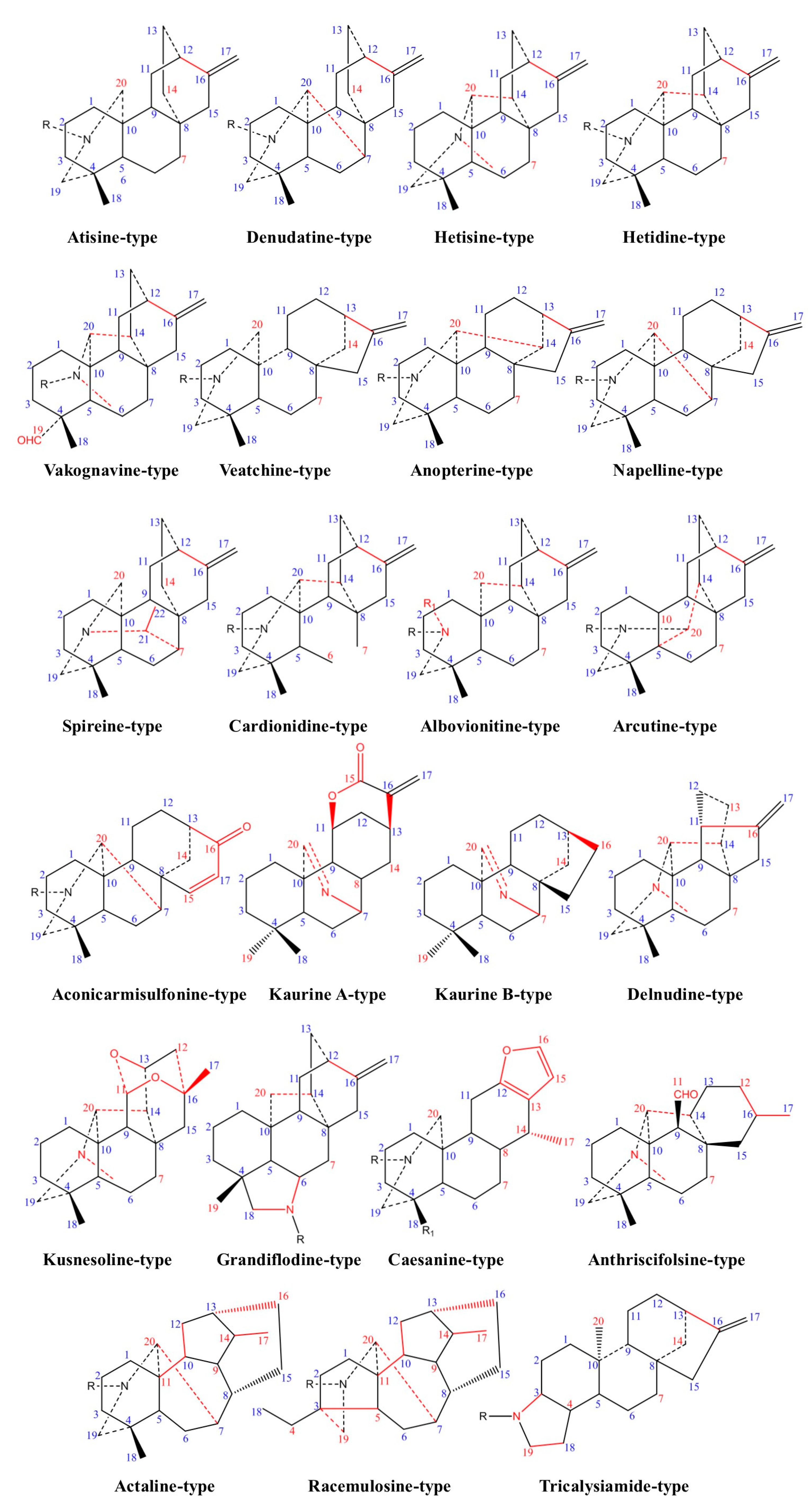
2. Chemistry and Biosynthetic Pathway
2.1. Chemical Classification
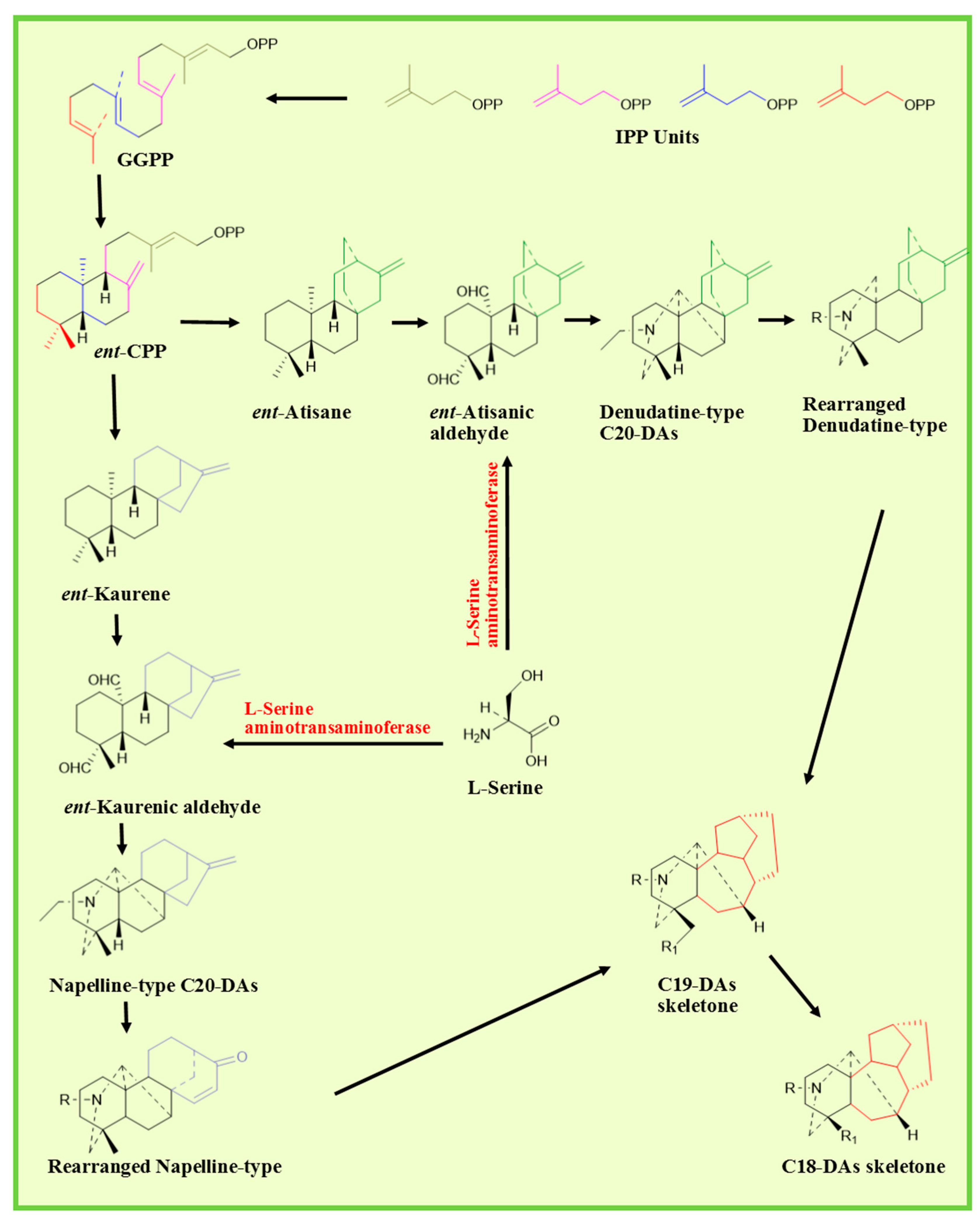
2.2. Biosynthetic Pathway
3. Pharmacological Activities
3.1. Anticonvulsant Effects
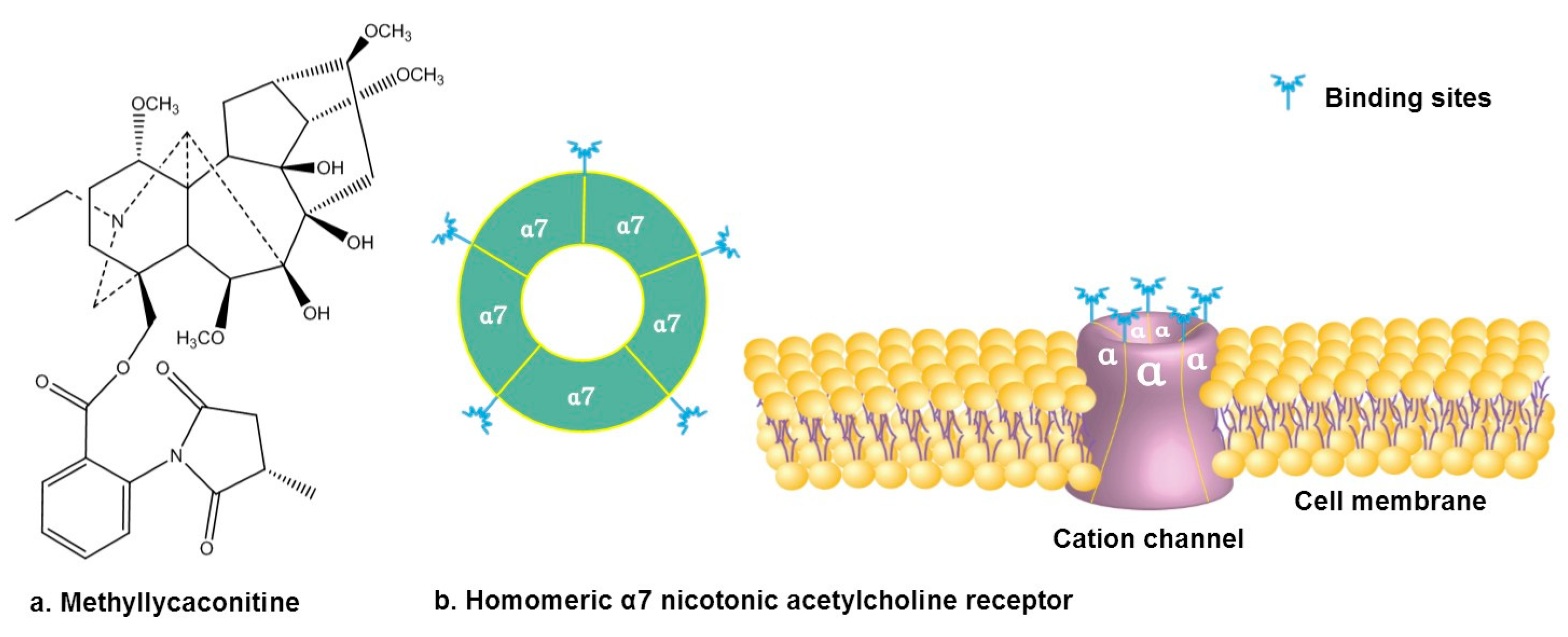
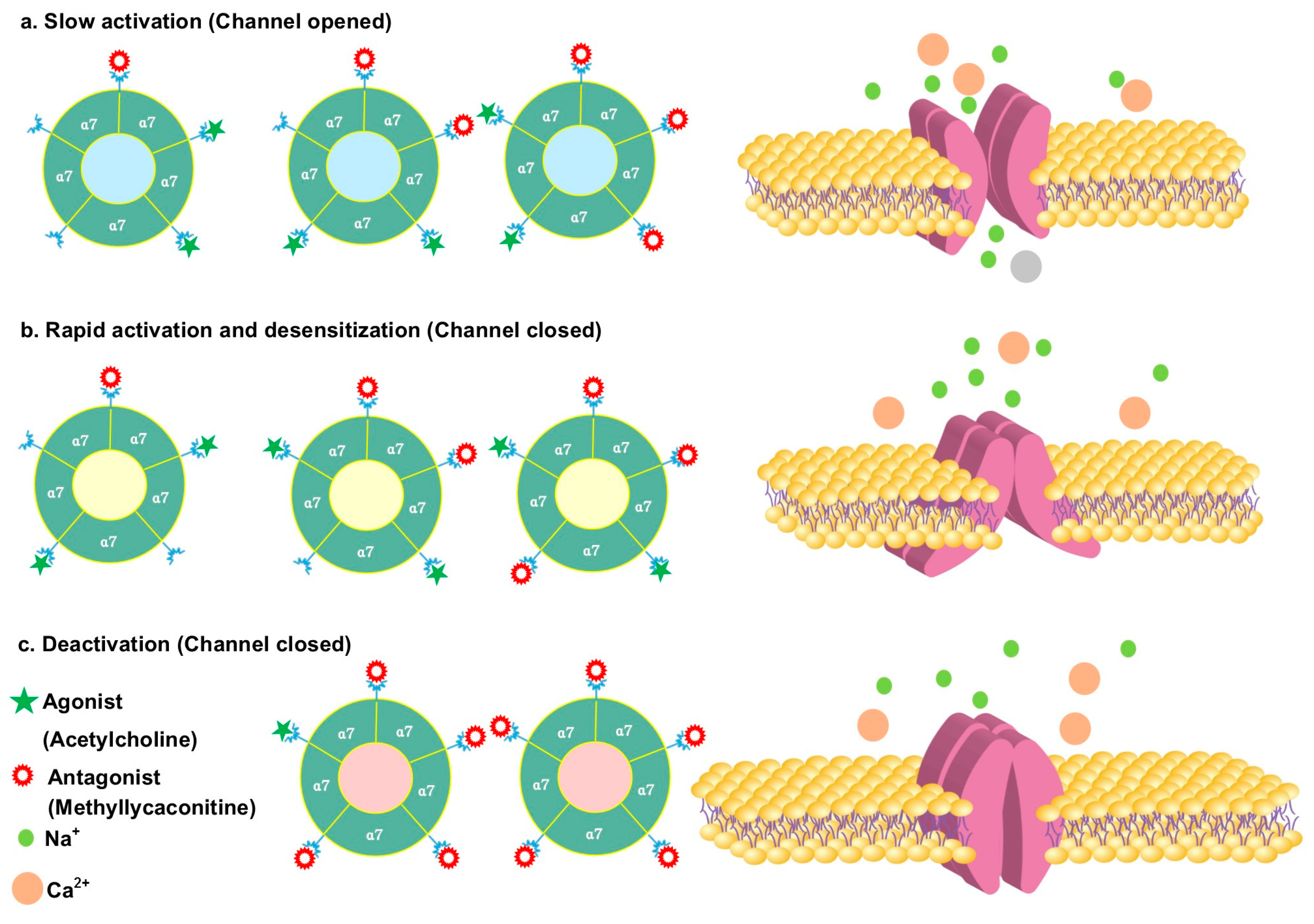
3.2. Antagonizing α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor
3.3. Analgesic Activity
| Plant | Used Part/Constituents | Biological Activity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aconitum episcopale | Episcopaline B (20) | Antinociceptive effect 2-fold lower than aspirin and acetaminophen | [101] |
| Aconitum pseudostapfianum | Pseudostapine C (21) | 2-fold more potent antinociceptive effect than aspirin and acetaminophen | [102] |
| Aconitum episcopale | Episcopine A (22) | 2-fold more potent antinociceptive effect than aspirin and acetaminophen | [103] |
| Aconitum carmichaelii | 18 | Antinociceptive effect | [98] |
| Aconitum carmichaeli | Plant extract and neoline (23) | Attenuated the mechanical hyperalgesia | [104] |
| Aconitum carmichaeli | Plant extract and 23 | Attenuated cold and mechanical hyperalgesia | [105] |
| Aconitum carmichaeli | Aqueous extracts | Antinociceptive activity | [106] |
| Aconitum carmichaeli | Processed aconitum tuber | High doses of processed Aconiti tuber inhibit the acute but potentiate the chronic antinociception of morphine | [107] |
| Delphinium denudatum | Aqueous root extract | Antinociceptive activity | [108] |
| Aconitum carmichaeli | Processed aconitum tuber and 8 | Antinociceptive activity of 8 was more potent than morphine | [109] |
| Aconitum sp. | 1 | Significant analgesic effects | [110] |
| Aconitum carmichaelii | Aconicatisulfonines A (24) and B (25) | Analgesic activities | [111] |
| Delphinium denudatum | Ethanolic extract and methanol fraction | Analgesic activity | [112] |
| Aconitum kusnezoffii | 23 | Analgesic activity | [113] |
| Aconitum carmichaelii | Aconicarmichosides E (26), F (27), H (28), I (29), and J (30) | Analgesic activity | [114] |
| Aconitum sp. | 3 | Relieves the pain | [82] |
| Aconitum baikalensis | Napelline (31), hypaconitine (32), 7, 8, 12-epinapelline N-oxide (33). | Analgesic activity comparable to that of sodium metamizole | [115] |
| Aconitum weixiense | Weisaconitines D (34) | Analgesic activity | [116] |
| Aconitum carmichaeli | Guiwuline (35) | Potential analgesic activity | [117] |
| Aconitum carmichaeli | 8-O-cinnamoylneoline (36) | Analgesic activity | [118] |
3.4. Antidementia Effect
| Plant | Used Part/Constituents | Biological Activity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aconitum hemsleyanum | Hemsleyaline (41) | Mild AChE inhibitory effect | [126] |
| Aconitum kirinense | Diterpenoid alkaloids | Moderate AChE inhibitory effect | [127] |
| Aconitum laeve | Diterpenoid alkaloids | Swatinine-C (42) and hohenackerine (43) competitively inhibited AChE and BChE Aconorine (44) and 3 noncompetitively inhibited AChE | [128] |
| Delphinium denudatum | Diterpenoid alkaloids | Jadwarine-A (45), 18, and dihydropentagynine (46) competitively inhibited AChE and BChE, while 1β-hydroxy,14β-acetyl condelphine (47) and jadwarine-B (48) showed non-competitive inhibition | [129] |
| Aconitum heterophyllum | Diterpenoid alkaloids | Compounds 6b-methoxy, 9b-dihydroxylheteratisine (49), 6,15b-dihydroxylhetisine (50), iso-atisine (51), heteratisine, 19-epi-isoatisine (52), and atidine (53) non-competitively inhibited AChE and BChE, while compounds 1a,11,13b-trihydroxylhetisine (54) and hetisinone (55) were determined as competitive inhibitors | [130] |
| Delphinium denudatum | Isotalatizidine (18) hydrate | Potent dual cholinesterase inhibitor | [131] |
| Aconitum heterophyllum | Heterophyllinine A(56) and B (57) | 56 and 57 inhibited AChE and BChE enzymes | [132] |
| Aconitum falconeri | Faleoconitine (58) and Pseudaconitine (59) | Moderate inhibitory activity on AChE | [133] |
3.5. Antidepressant Effects
3.6. Miscellaneous Effects
4. Clinical Trials
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
7. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kiss, T.; Cank, K.; Orbán-Gyapai, O.; Liktor-Busa, E.; Rutkovska, S.; Pučka, I.; Hohmann, J.; Csupor, D. Screening for diterpene alkaloids in the Spiraea genus. Planta Med. 2015, 81, PM_19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.P.; Chen, Q.H.; Liang, X.T. The C18-diterpenoid alkaloids. Alkaloids Chem. Biol. 2009, 67, 1–78. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.-P.; Chen, Q.-H.; Liu, X.-Y. Diterpenoid alkaloids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 529–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.-P.; Liang, X.-T. C20-diterpenoid alkaloids. Alkaloids Chem. Biol. 2002, 59, 1–280. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.-P.; Chen, Q.-H. The C19-diterpenoid alkaloids. Alkaloids Chem. Biol. 2010, 69, 1–577. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Liang, W.J.; Shi, Y.N.; Kennelly, E.J.; Zhao, D.K. Structural diversity, bioactivities, and biosynthesis of natural diterpenoid alkaloids†. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 763–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewick, P.M. Medicinal Natural Products: A Biosynthetic Approach; John Wiley & Sons: West Sussex, UK, 2002; pp. 385–388. [Google Scholar]
- Thawabteh, A.M.; Thawabteh, A.; Lelario, F.; Bufo, S.A.; Scrano, L. Classification, Toxicity and Bioactivity of Natural Diterpenoid Alkaloids. Molecules 2021, 26, 4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, A. The effects of Aconitum alkaloids on the central nervous system. Prog. Neurobiol. 1998, 56, 211–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, J.-F.; Chen, L.; Gao, F.; Zhou, X.-L. Diterpenoid alkaloids from Aconitum anthoroideum that offer protection against MPP+–Induced apoptosis of SH–SY5Y cells and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity. Phytochemistry 2020, 178, 112459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisset, N.G. Arrow poisons in China. part ii. Aconitum—Botany, chemistry, and pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1981, 4, 247–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.C. A revision of the genus Delphinium (Ranunculaceae) of China (I). Guihaia 2019, 39, 1425–1469. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, T.; Cai, L.; Ding, Z. A systematic review on the chemical constituents of the genus Consolida (Ranunculaceae) and their biological activities. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 35072–35089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitiş, L.; Süzgeç, S.; Mericli, F.; Özçelik, H.; Zapp, J.; Becker, H.; Meriçli, A.H. Alkaloids from Consolida olopetala. Pharm. Biol. 2006, 44, 244–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, T.; Cank, K.B.; Orban-Gyapai, O.; Liktor-Busa, E.; Zomborszki, Z.P.; Rutkovska, S.; Pučka, I.; Németh, A.; Csupor, D. Phytochemical and pharmacological investigation of Spiraea chamaedryfolia: A contribution to the chemotaxonomy of Spiraea genus. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Bin Bong, J.; Lee, C.-H.; Shin, B.-S.; Kang, H.G. Aconitine Neurotoxicity According to Administration Methods. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Gao, Y.; Luan, S. Two decades of advances in diterpenoid alkaloids with cytotoxicity activities. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 23937–23946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Cai, L.; Ding, Z. An overview of the chemical constituents from the genus Delphinium reported in the last four decades. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 13669–13686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, T.; Malhotra, N.; Chanumolu, S.K.; Chauhan, R.S. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) transcriptomes reveal association of multiple genes and pathways contributing to secondary metabolites accumulation in tuberous roots of Aconitum heterophyllum Wall. Planta 2015, 242, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranová, E.; Coman, D.; Gruissem, W. Structure and Dynamics of the Isoprenoid Pathway Network. Mol. Plant 2012, 5, 318–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkota, K.P.; Sewald, N. Terpenoid alkaloids derived by amination reaction. In Natural Products: Phytochemistry, Botany and Metabolism of Alkaloids, Phenolics and Terpenes; Ramawat, K.G., Mérillon, J.-M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 923–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.-J.; Gao, S.; Fan, L.-M.; Nie, J.-L.; He, H.-P.; Zeng, Y.; Shen, Y.-M.; Hao, X.-J. Approach to the Biosynthesis of Atisine-Type Diterpenoid Alkaloids. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrone, D.; Chen, X.; Coates, R.M.; Peters, R.J. Characterization of the kaurene oxidase CYP701A3, a multifunctional cytochrome P450 from gibberellin biosynthesis. Biochem. J. 2010, 431, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, M.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Song, H.; Zhang, D.; Wang, F.; Qin, Y. Synthesis of Atisine, Ajaconine, Denudatine, and Hetidine Diterpenoid Alkaloids by a Bioinspired Approach. Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 15896–15900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Shen, Y.; Shi, Y.; Shi, X.; Qiao, Q.; Zi, S.; Zhao, E.; Yu, D.; Kennelly, E.J. Probing the transcriptome of Aconitum carmichaelii reveals the candidate genes associated with the biosynthesis of the toxic aconitine-type C19-diterpenoid alkaloids. Phytochemistry 2018, 152, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, M.; Sato, F. Unusual P450 reactions in plant secondary metabolism. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 507, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Tang, L.; Zhou, X.; Wang, T.; Kou, Z.; Wang, Z. A review on phytochemistry and pharmacological activities of the processed lateral root of Aconitum carmichaelii Debeaux. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 160, 173–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, W.A. Characteristics of compounds that cross the blood-brain barrier. BMC Neurol. 2009, 9, S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turabekova, M.A.; Rasulev, B.F. QSAR Analysis of the Structure—Toxicity Relationship of Aconitum and Delphinium Diterpene Alkaloids. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2005, 41, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turabekova, M.A.; Rasulev, B.F.; Levkovich, M.G.; Abdullaev, N.D.; Leszczynski, J. Aconitum and Delphinium sp. alkaloids as antagonist modulators of voltage-gated Na+ channels: AM1/DFT electronic structure investigations and QSAR studies. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2008, 32, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshé, S.L.; Perucca, E.; Ryvlin, P.; Tomson, T. Epilepsy: New advances. Lancet 2015, 385, 884–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, D.I.; Isom, L.L.; Petrou, S. Role of Sodium Channels in Epilepsy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a022814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Tang, F.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Cui, R. Anticonvulsant Effects of Fuzi Total Alkaloid on Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Seizure in Mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 123, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, W.A. Structure and Function of Voltage-Sensitive Ion Channels. Science 1988, 242, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, W.A. Cellular and molecular biology of voltage-gated sodium channels. Physiol. Rev. 1992, 72, S15–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.E.; Olivera, B.M. Neurotoxins: Overview of an emerging research technology. Trends Neurosci. 1994, 17, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, H.; Doi, A.; Ishibashi, H.; Akaike, N. Aconitine facilitates spontaneous transmitter release at rat ventromedial hypothalamic neurons. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 135, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, A. Inhibition of rat hippocampal excitability by the plant alkaloid 3-acetylaconitine mediated by interaction with voltage-dependent sodium channels. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1997, 355, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, A.; Simmet, T. Antagonism of the aconitine-induced inexcitability by the structurally related Aconitum alkaloids, lappaconitine and ajacine. Brain Res. 1999, 842, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, A.; Shi, Q.; Aschoff, J.; Peters, T. Electrophysiological effects of aconitine in rat hippocampal slices. Neuropharmacology 1996, 35, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, U.; Ameri, A. Different Effects on [3H]Noradrenaline Uptake of the Aconitum Alkaloids Aconitine, 3-Acetylaconitine, Lappaconitine, and N-Desacetyllappaconitine in Rat Hippocampus. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1998, 55, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, L.J.; Voss, J.M.; McLeay, L.; Sleigh, J.W. Aconitine induces prolonged seizure-like events in rat neocortical brain slices. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 584, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.-Q.; Yang, H.-H.; Yue, J.-M.; Hu, G.-Y. Songorine, a diterpenoid alkaloid of the genus Aconitum, is a novel GABAA receptor antagonist in rat brain. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 337, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koszegi, Z.; Atlasz, T.; Csupor, D.; Hohmann, J.; Hernadi, I. Aconitum alkaloid songorine acts as a potent GABAA receptor agonist in the rat brain in vivo. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. Wars. 2007, 94, 367–368. [Google Scholar]
- Ameri, A. Effects of the Aconitum alkaloid mesaconitine in rat hippocampal slices and the involvement of α-and β-adrenoceptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 123, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.L.; Zeeshan, M.; Ahmad, M.; Shaheen, F.; Simjee, S.U. Anticonvulsant activity of DNS II fraction in the acute seizure models. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 128, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.; Zeeshan, M.; Ahmad, M.; Shaheen, F.; Simjee, S. Anticonvulsant activity of Aconitum violaceum against maximal electroshock induced seizure model. Behv Pharm. 2008, 19, 658–659. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, M.; Shaheen, F.; Choudhary, M.I.; Sombati, S.; Rahman, A.-U.; DeLorenzo, R.J. Inhibition of sustained repetitive firing in cultured hippocampal neurons by an aqueous fraction isolated from Delphinium denudatum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 90, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.; Shaheen, F.; Choudhary, M.I.; Rahman, A.-U.; Sombati, S.; DeLorenzo, R.J. In vitro inhibition of pentylenetetrazole and bicuculline-induced epileptiform activity in rat hippocampal pyramidal neurons by aqueous fraction isolated from Delphinium denudatum. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 333, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.; Shaheen, F.; Choudhary, M.I.; Sombati, S.; Rafiq, A.; Suria, A.; Rahman, A.-U.; DeLorenzo, R.J. Anticonvulsant activities of ethanolic extract and aqueous fraction isolated from Delphinium denudatum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2001, 78, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, A.; Zimmermann, T.; Simmet, T. Frequency- and structure-dependent inhibition of normal and epileptiform activity by 6-benzoyldeltamine in rat hippocampal slices. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 369, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, A.; Simmet, T. Interaction of the structurally related Aconitum alkaloids, aconitine and 6-benzyolheteratisine, in the rat hippocampus. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 386, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, A. Effects of the Aconitum alkaloid songorine on synaptic transmission and paired-pulse facilitation of CA1 pyramidal cells in rat hippocampal slices. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 125, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, A. Structure-dependent inhibitory action of the Aconitum alkaloids 14-benzoyltalitasamine and talitasamine in rat hippocampal slices. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1998, 357, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, A. Inhibition of stimulus-triggered and spontaneous epileptiform activity in rat hippocampal slices by the Aconitum alkaloid mesaconitine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 342, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, A.; Gleitz, J.; Peters, T. Inhibition of neuronal activity in rat hippocampal slices by Aconitum alkaloids. Brain Res. 1996, 738, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, A. Structure-dependent differences in the effects of the Aconitum alkaloids lappaconitine, N-desacetyllappaconitine and lappaconidine in rat hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1997, 769, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, A. Inhibition of rat hippocampal excitability by the Aconitum alkaloid, 1-benzoylnapelline, but not by napelline. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 335, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, A. Electrophysiological actions of the plant alkaloid 6-benzoylheteratisine in rat hippocampal slices. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1997, 355, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, A. Effects of the alkaloids 6-benzoylheteratisine and heteratisine on neuronal activity in rat hippocampal slices. Neuropharmacology 1997, 36, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, A.; Gleitz, J.; Peters, T. Aconitine inhibits epileptiform activity in rat hippocampal slices. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1996, 354, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.N.T.; Abraham, N.; Lewis, R.J. Structure-Function of Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Inhibitors Derived from Natural Toxins. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 609005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dineley, K.T.; Pandya, A.A.; Yakel, J.L. Nicotinic ACh receptors as therapeutic targets in CNS disorders. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Goethem, N.P.; Paes, D.; Puzzo, D.; Fedele, E.; Rebosio, C.; Gulisano, W.; Palmeri, A.; Wennogle, L.P.; Peng, Y.; Bertrand, D.; et al. Antagonizing α7 nicotinic receptors with methyllycaconitine (MLA) potentiates receptor activity and memory acquisition. Cell. Signal. 2019, 62, 109338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, A.S.; van Schalkwyk, G.I.; Bloch, M.H. Alpha-7 nicotinic agonists for cognitive deficits in neuropsychiatric disorders: A translational meta-analysis of rodent and human studies. Prog. Neuro Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 75, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennings, K.R.; Brown, D.G.; Wright, D.P. Methyllycaconitine, a naturally occurring insecticide with a high affinity for the insect cholinergic receptor. Experientia 1986, 42, 611–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, J.W. Nicotinic Agonists, Antagonists, and Modulators from Natural Sources. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2005, 25, 513–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.D.; Caldwell, D.P. Low-dose mecamylamine improves learning of rats in the radial-arm maze repeated acquisition procedure. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2006, 86, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, B.T.; Welch, K.D.; Cook, D.; Gardner, D.R. Potentiation of the actions of acetylcholine, epibatidine, and nicotine by methyllycaconitine at fetal muscle-type nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 662, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, B.; Shoaib, M.; Stolerman, I.P. Selective nicotinic receptor antagonists: Effects on attention and nicotine-induced attentional enhancement. Psychopharmacology 2011, 217, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, D.A.; Heshmati, P.; Kholdebarin, E.; Levin, E.D. Decreasing nicotinic receptor activity and the spatial learning impairment caused by the NMDA glutamate antagonist dizocilpine in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 741, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.D.; Cauley, M.; Rezvani, A.H. Improvement of attentional function with antagonism of nicotinic receptors in female rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 702, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.-X.; Zhu, H.-Q.; Pang, R.-P.; Wen, B.-T.; Liu, X.-G. Mechanisms for therapeutic effect of bulleyaconitine A on chronic pain. Mol. Pain 2018, 14, 1744806918797243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhuber, J.; Zhu, M.; Prinz, S.; Kopp, B. Aconitum in Traditional Chinese Medicine-A valuable drug or an unpredictable risk? J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 126, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Liu, W.-K.; Deng, L.; Tian, J.-X.; Tong, X.-L. Clinical Efficacy of Aconitum-Containing Traditional Chinese Medicine for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2014, 42, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-N.; Wei, J.; Huang, L.-T.; Ju, P.-J.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.-X. Bulleyaconitine A Inhibits Visceral Nociception and Spinal Synaptic Plasticity through Stimulation of Microglial Release of Dynorphin A. Neural Plast. 2020, 2020, 1484087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Ding, X.N.; Wang, Y.D. The clinical studies of BLA tablets to treat common chronic pain. Chin. J. Pain. Med. 2011, 17, 314–315. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.C.; Liu, X.J.; Lu, W.H.; Wang, M.D.; Li, A.L. Studies on the analgesic action and physical dependence of bulleyaconitine A. Yao Xue Xue Bao Acta Pharm. Sin. 1986, 21, 886–891. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.-F.; Fan, H.; Wang, Y.-X. Aconitum-Derived Bulleyaconitine A Exhibits Antihypersensitivity through Direct Stimulating Dynorphin A Expression in Spinal Microglia. J. Pain 2016, 17, 530–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.-X.; Yang, J.; Pang, R.-P.; Zeng, W.-A.; Ouyang, H.-D.; Liu, Y.Q.; Liu, X.-G. Bulleyaconitine A attenuates hyperexcitability of dorsal root ganglion neurons induced by spared nerve injury: The role of preferably blocking Nav1.7 and Nav1.3 channels. Mol. Pain 2018, 14, 1744806918778491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-F.; Gerner, P.; Schmidt, B.; Xu, Z.Z.; Nau, C.; Wang, S.-Y.; Ji, R.-R.; Wang, G.K. Use of Bulleyaconitine A as an Adjuvant for Prolonged Cutaneous Analgesia in the Rat. Anesth. Analg. 2008, 107, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.-Q.; Xu, J.; Shen, K.-F.; Pang, R.-P.; Wei, X.-H.; Liu, X.-G. Bulleyaconitine A depresses neuropathic pain and potentiation at C-fiber synapses in spinal dorsal horn induced by paclitaxel in rats. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 273, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyirimigabo, E.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Agyemang, K.; Zhang, Y. A review on phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology studies of Aconitum. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, M.; Satoh, T. Pharmacological studies of lappaconitine. Analgesic activities. Arzneimittelforschung 1988, 38, 892–895. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Q.-A.; Li, M. Effect of Lappaconitine on Postoperative Pain and Serum Complement 3 and 4 Levels of Cancer Patients Undergoing Rectum Surgery. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 2015, 35, 668–672. [Google Scholar]
- Ono, M.; Satoh, T. Pharmacological Studies on Lappaconitine: Possible Interaction with Endogenous Noradrenergic and Serotonergic Pathways to Induce Antinociception. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1992, 58, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, M.; Satoh, T. Pharmacological studies on lappaconitine: Antinociception and Inhibition of the Spinal Action of Substance P and Somatostatin. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1991, 55, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.-K.; Shi, X.-Q.; Zhang, L.-M.; Yang, D.-Q.; Guo, H.-C.; Chen, Y.-P.; Shen, Y. Four new diterpenoid alkaloids with antitumor effect from Aconitum nagarum var. heterotrichum. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2017, 28, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.L.; Wei, Z.R.; Zhang, T.H.; Zeng, X.Q.; Wu, B.H. Effects of lappaconitine on pain and inflammatory response of severely burned rats and the mechanism. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi Zhonghua Shaoshang Zazhi Chin. J. Burn. 2017, 33, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.; Zhao, Y.-D.; Xiao, Z.; Wen, H.-Z.; Cui, J.; Ruan, H.-Z. Effect of lappaconitine on neuropathic pain mediated by P2X3 receptor in rat dorsal root ganglion. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 58, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Zheng, Y.M.; Yu, Y.; Gan, Y.; Gao, Z.B. Inhibitory effects of lappaconitine on the neuronal isoforms of voltage-gated sodium channels. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.-L.; Ao, J.-P.; Wang, Y.-R.; Huang, Q.; Li, T.-F.; Li, X.-Y.; Wang, Y.-X. Lappaconitine, a C18-diterpenoid alkaloid, exhibits antihypersensitivity in chronic pain through stimulation of spinal dynorphin A expression. Psychopharmacology 2018, 235, 2559–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, M.; Satoh, T. Pharmacological studies of lappaconitine. Analgesia produced by intracerebroventricular, intracisternal and intrathecal injections. J. Pharm. Dyn. 1990, 13, 374–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murayama, M.; Ito, T.; Konno, C.; Hikino, H. Mechanism of analgesic action of mesaconitine. I. Relationship between analgesic effect and central monoamines or opiate receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1984, 101, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friese, J.; Gleitz, J.; Gutser, U.T.; Heubach, J.F.; Matthiesen, T.; Wilffert, B.; Selve, N. Aconitum sp. alkaloids: The modulation of voltage-dependent Na+ channels, toxicity and antinociceptive properties. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 337, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikino, H.; Murayama, M. Mechanism of the antinociceptive action of mesaconitine: Participation of brain stem and lumbar enlargement. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1985, 85, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Oyama, T.; Ishige, A.; Isono, T.; Asami, A.; Ikeda, Y.; Noguchi, M.; Omiya, Y. Antinociceptive Mechanism of the Actonitine Alkaloids Mesaconitine and Benzoylmesaconine. Planta Med. 1994, 60, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, S.; Xia, H.; Hu, M.; Chen, C.; Fu, J.; Shi, G.; Guo, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, W.; Shi, J.; et al. Isotalatizidine, a C19-diterpenoid alkaloid, attenuates chronic neuropathic pain through stimulating ERK/CREB signaling pathway-mediated microglial dynorphin A expression. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Mao, X.-F.; Wu, H.-Y.; Li, T.-F.; Sun, M.-L.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.-X. Bullatine A stimulates spinal microglial dynorphin A expression to produce anti-hypersensitivity in a variety of rat pain models. J. Neuroinflammation 2016, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Sun, M.-L.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.-Y.; Wang, Y.-X. Concurrent bullatine A enhances morphine antinociception and inhibits morphine antinociceptive tolerance by indirect activation of spinal κ-opioid receptors. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 196, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, J.X.; Li, Q.; Mao, X.; Peng, T.F.; Liu, H.Q.; Yin, S.; Yuan, H.J. Antinociceptive C19–diterpenoid alkaloids from the root of Aconitum episcopale. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 24, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, J.X.; Li, Q.; Mao, X.; Peng, T.F.; Jin, N.H.; Yin, S.; Tang, Y. Antinociceptive C19–diterpenoid alkaloids isolated from Aconitum pseudostapfianum. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 23, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, J.; Li, Q.; Mao, X.; Peng, T.; Jin, N.; Yin, S.; Shi, X.; Li, Y. Antinociceptive C19-Diterpenoid Alkaloids from Aconitum episcopale. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2021, 57, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimura, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Ishiuchi, K.; Ohsawa, M.; Makino, T. Neoline is the active ingredient of processed aconite root against murine peripheral neuropathic pain model, and its pharmacokinetics in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 241, 111859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Miyamoto, K.; Yokoyama, N.; Sugi, M.; Kagioka, A.; Kitao, Y.; Adachi, T.; Ohsawa, M.; Mizukami, H.; Makino, T. Processed aconite root and its active ingredient neoline may alleviate oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathic pain. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 186, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, M.C.; Liu, I.-M.; Liou, S.-S.; Chang, Y.-S. Mesaconitine plays the major role in the antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of Radix Aconiti Carmichaeli (Chuan Wu). J. Food Drug Anal. 2011, 19, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Hayashida, M.; Arita, H.; Huang, W.; Xiao, L.; Chiba, S.; Sekiyama, H.; Hanaoka, K. High doses of processed Aconiti tuber inhibit the acute but potentiate the chronic antinociception of morphine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 119, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, S.; Ahmad, M.A.; Siddiqui, T.A. Acute Toxicity and Antinociceptive Properties of Delphinium denudatum. Pharm. Biol. 2003, 41, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyama, T.; Isono, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Hayakawa, Y. Anti-nociceptive Effects of Aconiti Tuber and its Alkaloids. Am. J. Chin. Med. 1994, 22, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Han, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Qi, X.; Liu, Z.; Leung, E.L.-H.; Wang, D. Comparison of analgesic activities of aconitine in different mice pain models. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Shao, S.; Guo, Q.; Xu, C.; Xia, H.; Zhang, T.; Shi, J. Aconicatisulfonines A and B, Analgesic Zwitterionic C20-Diterpenoid Alkaloids with a Rearranged Atisane Skeleton from Aconitum carmichaelii. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 6850–6854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaheer, I.; Rahman, S.Z.; Khan, R.A.; Parveen, M.; Ahmad, M. Evaluation of analgesic activity of extracts of Delphinium denudatum in animal models: A dose dependent pre-clinical trial. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2018, 12, FC01–FC04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Sun, S.D.; Wang, M.Y.; Li, C.F.; Yuan, D.; Fu, H.Z. Chemical constituents and analgesic activity of Aconitum kusnezoffii Reichb. J. Chin. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 27, 855–863. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Xia, H.; Meng, X.; Shi, G.; Xu, C.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, T.; Shi, J. C19-Diterpenoid alkaloid arabinosides from an aqueous extract of the lateral root of Aconitum carmichaelii and their analgesic activities. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesterova, Y.V.; Povet’yeva, T.; Suslov, N.; Zyuz’kov, G.; Pushkarskii, S.; Aksinenko, S.; Schultz, E.; Kravtsova, S.; Krapivin, A. Analgesic Activity of Diterpene Alkaloids from Aconitum baikalensis. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 157, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.-K.; Ai, H.-L.; Zi, S.-H.; Zhang, L.-M.; Yang, S.-C.; Guo, H.-C.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Y.-P.; Chen, J.-J. Four new C 18 -diterpenoid alkaloids with analgesic activity from Aconitum weixiense. Fitoterapia 2013, 91, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.-P.; Lou, H.-Y.; Huang, L.; Hao, X.-J.; Liang, G.-Y.; Yang, Z.-C.; Pan, W.-D. A novel franchetine type norditerpenoid isolated from the roots of Aconitum carmichaeli Debx. with potential analgesic activity and less toxicity. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 4444–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taki, M.; Niitu, K.; Omiya, Y.; Noguchi, M.; Fukuchi, M.; Aburada, M.; Okada, M. 8-O-Cinnamoylneoline, a New Alkaloid from the Flower Buds of Aconitum carmichaeli and its Toxic and Analgesic Activities. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 800–803. [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.-K.; Liu, H.; Jiang, H.-L.; Yue, J.-M.; Hu, G.-Y.; Chen, H.-Z. Discovery of talatisamine as a novel specific blocker for the delayed rectifier K+ channels in rat hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience 2008, 155, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Song, M.; Tan, X.; Cheng, F.; Zheng, S.; Shen, J.; Luo, X.; Ji, R.; Yue, J. Structure-Based Discovery of Potassium Channel Blockers from Natural Products: Virtual Screening and Electrophysiological Assay Testing. Chem. Biol. 2003, 10, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.L.; Xie, Z.H.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wei, L.F.; Yang, H.; Yang, H.N.; Liu, Y.Q.; Bi, J.Z. Methyllycaconitine Alleviates Amyloid-β Peptides-Induced Cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.X.; Zhang, J.F.; Zhen, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Gao, F.; Zhou, X.L. Isolation, Structure Elucidation, Semi-Synthesis, and Structural Modification of C19-Diterpenoid Alkaloids from Aconitum apetalumand Their Neuroprotective Activities. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterova, Y.V.; Povet’eva, T.N.; Suslov, N.I.; Zyuz’kov, G.N.; Zhdanov, V.V.; Fedorova, Y.S.; Kul’pin, P.V.; Shaposhnikov, K.V. Correction of Cholinergic Abnormalities in Mnestic Processes with Diterpene Alkaloid Songorine. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 165, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zyuz’kov, G.N.; Suslov, N.I.; Losev, E.A.; Ermolaeva, L.A.; Zhdanov, V.V.; Udut, E.V.; Miroshnichenko, L.A.; Simanina, E.V.; Demkin, V.P.; Povet’eva, T.N. Cerebroprotective and Regenerative Effects of Alkaloid Z77 under Conditions of Brain Ischemia. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015, 158, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Yu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, S.; You, D.; Shi, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; et al. Aconiti lateralis Radix Praeparata inhibits Alzheimer’s disease by regulating the complex regulation network with the core of GRIN1 and MAPK1. Pharm. Biol. 2021, 59, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.-H.; Chen, Y.; Sun, X.-Y.; Fan, H.; Li, W.; Deng, L.; Yin, T.-P. A new diterpenoid alkaloid from Aconitum hemsleyanum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, G.-Y.; Qin, L.-L.; Gao, F.; Huang, S.; Zhou, X.-L. Fifteen new diterpenoid alkaloids from the roots of Aconitum kirinense Nakai. Fitoterapia 2020, 141, 104477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.; Ahmad, S.; Shah, S.A.A.; Khan, H.U.; Khan, F.A.; Ali, M.; Latif, A.; Shaheen, F.; Ahmad, M. Selective dual cholinesterase inhibitors from Aconitum laeve. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 20, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.; Ahmad, S.; Ali, M.; Latif, A.; Shah, S.A.A.; Naz, H.; Rahman, N.U.; Shaheen, F.; Wadood, A.; Khan, H.U.; et al. Norditerpenoid alkaloids of Delphinium denudatum as cholinesterase inhibitors. Bioorganic Chem. 2018, 78, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.; Ahmad, S.; Shah, S.A.A.; Latif, A.; Ali, M.; Khan, F.A.; Tahir, M.N.; Shaheen, F.; Wadood, A.; Ahmad, M. Antioxidant and anticholinesterase potential of diterpenoid alkaloids from Aconitum heterophyllum. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 3368–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.; Ahmad, S.; Khan, E.; Shahzad, A.; Ali, M.; Tahir, M.N.; Shaheen, F.; Ahmad, M. Isolation, crystal structure determination and cholinesterase inhibitory potential of isotalatizidine hydrate from Delphinium denudatum. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, M.; Obaidullah; Ahmad, M.; Wadood, N.; Lodhi, M.A.; Shaheen, F.; Choudhary, M.I. New diterpenoid alkaloids from Aconitum heterophyllum Wall: Selective butyrylcholinestrase inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2009, 24, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta-ur-Rahman; Fatima, N.; Akhtar, F.; Choudhary, M.I.; Khalid, A. New norditerpenoid alkaloids from Aconitum falconeri. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1393–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, J.T.; Olsen, G.M.; Wiborg, O.; Redrobe, J.P. Antidepressant-like effects of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonists, but not agonists, in the mouse forced swim and mouse tail suspension tests. J. Psychopharmacol. 2009, 23, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterova, Y.V.; Povetieva, T.N.; Suslov, N.I.; Semenov, A.A.; Pushkarskiy, S.V. Antidepressant Activity of Diterpene Alkaloids of Aconitum baicalense Turcz. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2011, 151, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Li, B.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Tang, F.; Shao, D.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, H.; Cui, R.; Li, Y. Antidepressant-like Effect of Fuzi Total Alkaloid on Ovariectomized Mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 120, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineur, Y.S.; Mose, T.N.; Blakeman, S.; Picciotto, M.R. Hippocampal α7 nicotinic ACh receptors contribute to modulation of depression-like behaviour in C57BL/6J mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 1903–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterova, Y.V.; Povet’eva, T.N.; Suslov, N.I.; Shults, E.E.; Ziuz’kov, G.N.; Aksinenko, S.G.; Afanas’eva, O.G.; Krapivin, A.V.; Kharina, T.G. Anxiolytic Activity of Diterpene Alkaloid Songorine. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015, 159, 620–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.; Yousuf, S.; Khan, M.B.; Ahmad, A.S.; Saleem, S.; Hoda, M.N.; Islam, F. Protective effects of ethanolic extract of Delphinium denudatum in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2006, 25, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.Y.; Qin, C.H.; Duan, B.L.; Huang, Y.Q.; Ma, K. Clinical efficacy of bulleyaconitine A combined with gabapentin on postherpetic neuralgia. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2021, 101, 3575–3580. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.G.; Wang, Q.H.; Lin, Y.B. Clinical study in epidural injection with lappaconitine for post-operative analgesia. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 1995, 15, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Clinical analgesic effect of lappaconitine in 56 patients after cholecystectomy. Chin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 15, 551. [Google Scholar]
- Dzhakhangirov, F.N.; Sultankhodzhaev, M.N.; Tashkhodzhaev, B.; Salimov, B.T. Diterpenoid alkaloids as a new class of antiarrhythmic agents. Structure-activity relationship. Chem. Nat. Compd. 1997, 33, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeev, A.E.; Verkhratskii, A.N.; Dzhakhangirov, F.N. Effects of allapinine on sodium currents in neurons isolated from the rat trigeminal ganglion and cardiomyocytes. Neurophysiology 1990, 22, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-L.; Shen, X.-L.; Chen, Q.-H.; Qi, G.; Wang, W.; Wang, F.-P. Structure-Analgesic Activity Relationship Studies on the C18- and C19-Diterpenoid Alkaloids. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 57, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panter, K.E.; Manners, G.D.; Stegelmeier, B.L.; Lee, S.; Gardner, D.R.; Ralphs, M.H.; Pfister, J.A.; James, L.F. Larkspur poisoning: Toxicology and alkaloid structure–activity relationships. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2002, 30, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.Y.K. Aconite poisoning. Clin. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, T.Y.K. Aconitum alkaloid content and the high toxicity of aconite tincture. Forensic Sci. Int. 2012, 222, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegelmeier, B.L.; Hall, J.O.; Gardner, D.R.; Panter, K.E. The toxicity and kinetics of larkspur alkaloid, methyllycaconitine, in mice. J. Anim. Sci. 2003, 81, 1237–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, Y.-T.; Wang, N.; Feng, Y. The toxicology and detoxification of Aconitum: Traditional and modern views. Chin. Med. 2021, 16, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csupor, D.; Wenzig, E.-M.; Zupkó, I.; Wölkart, K.; Hohmann, J.; Bauer, R. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of aconitine-type and lipo-alkaloids of Aconitum carmichaelii roots. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 2079–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
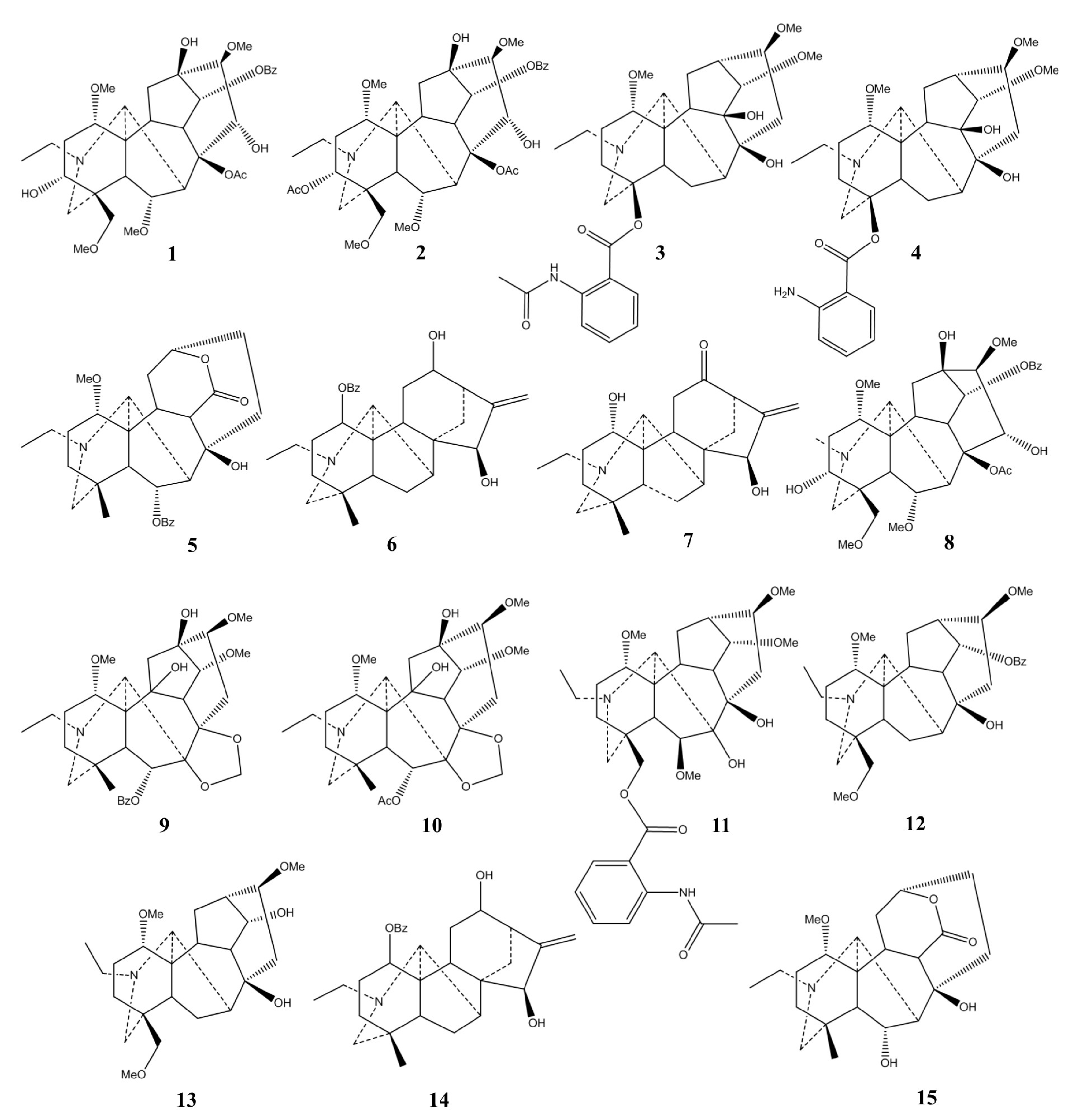
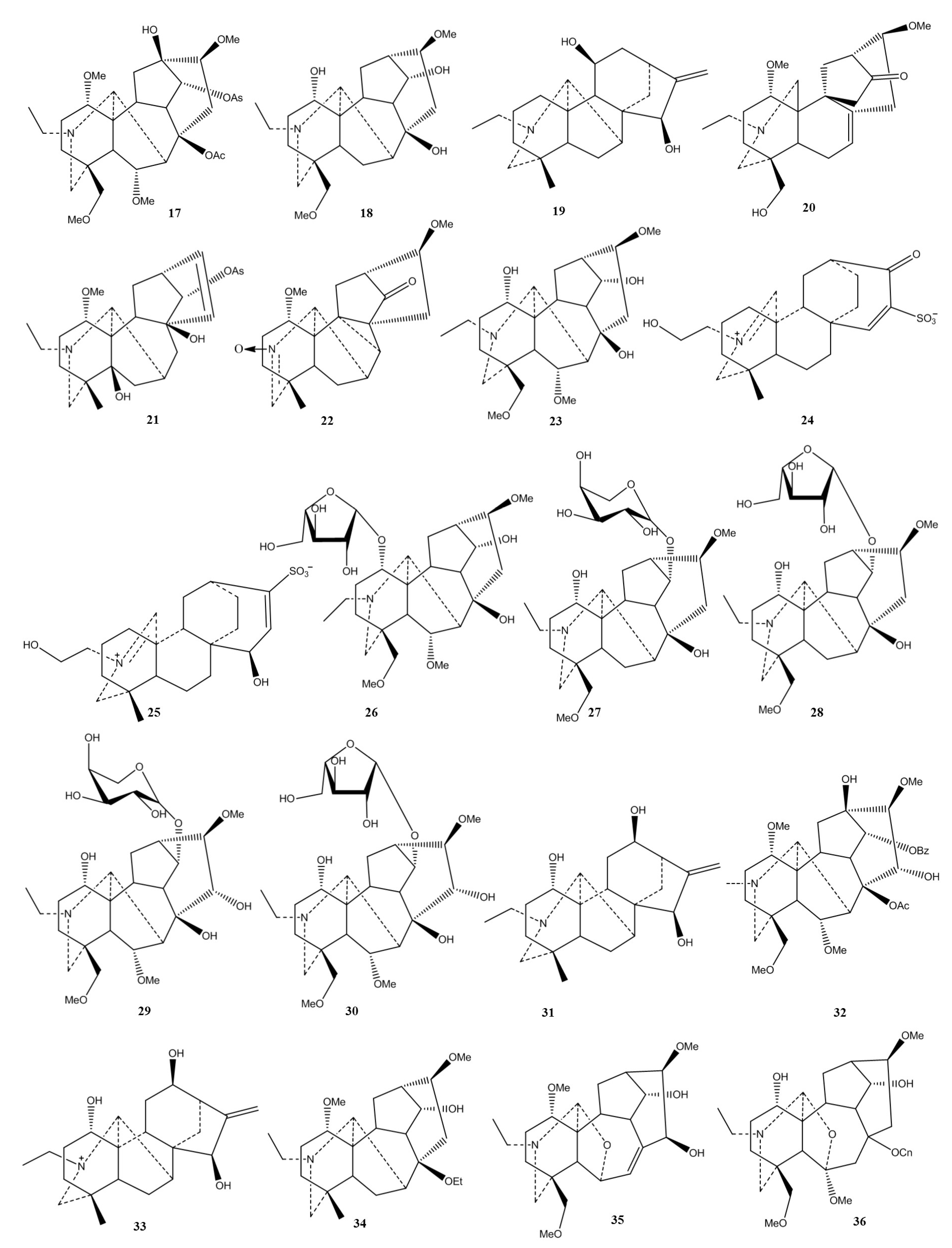
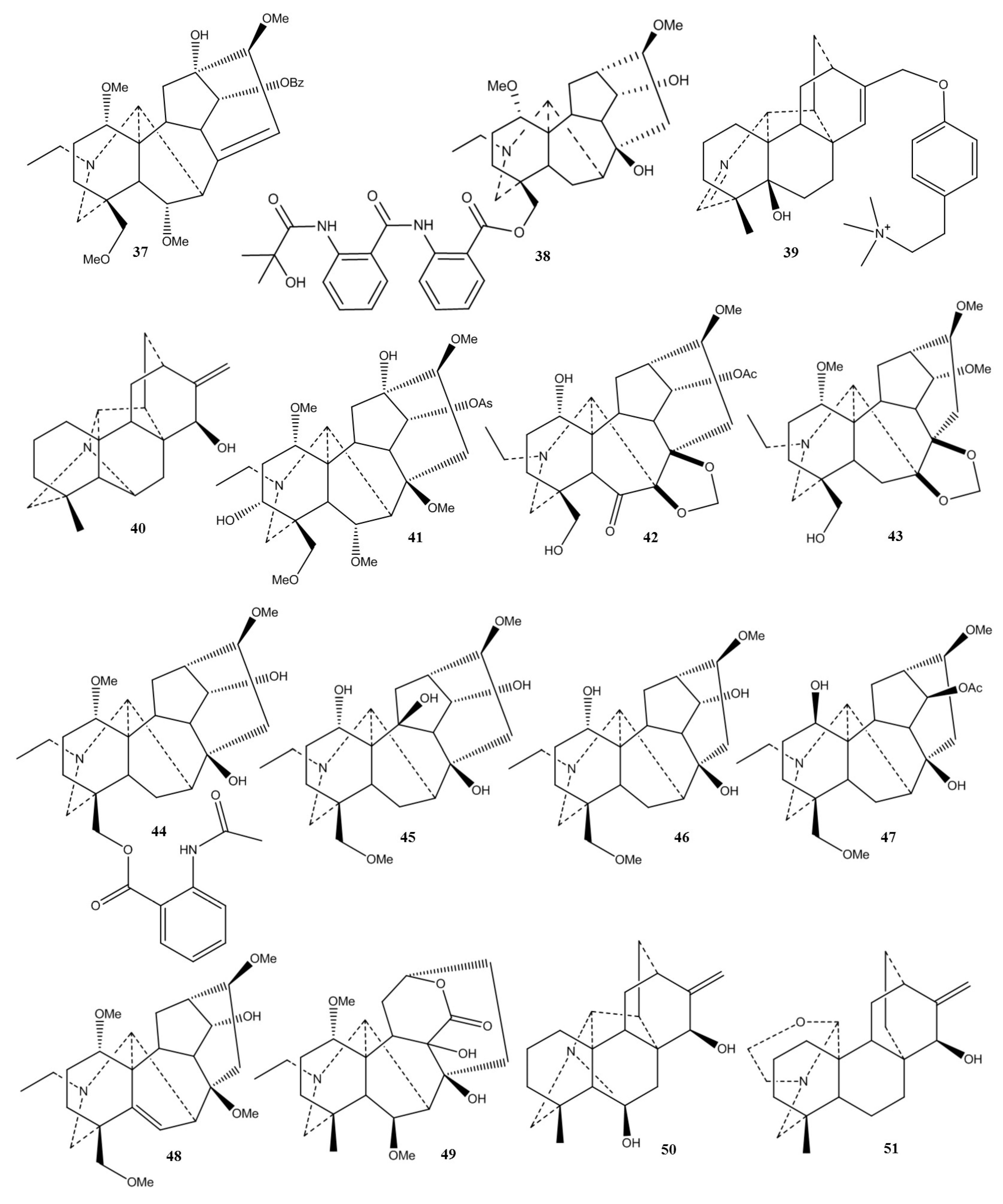
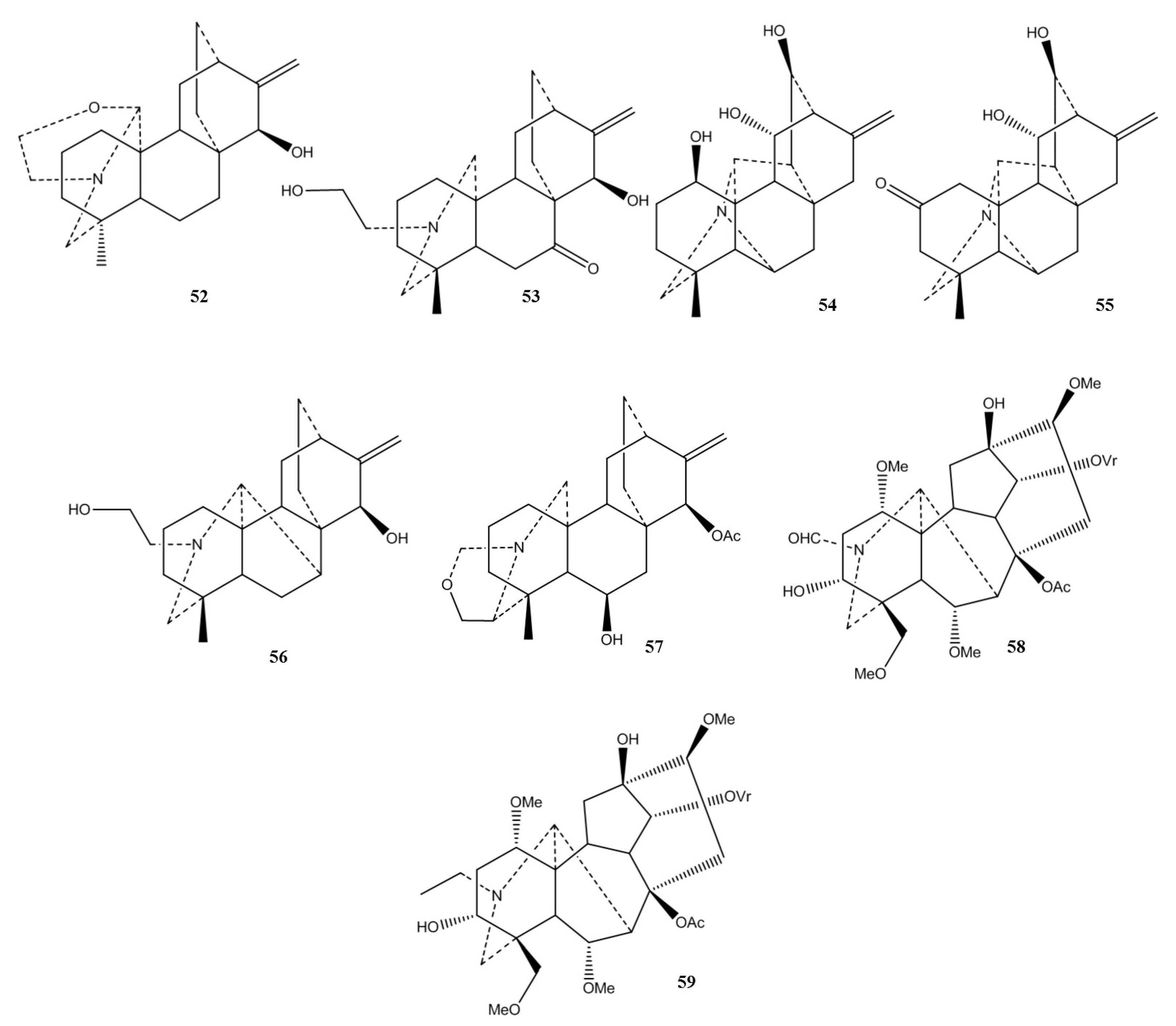
| Plant | Used Part/Constituents | Biological Activity | Affected In Vitro/In Vivo Model | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delphinium nordhagenii | Acetone fraction | Anticonvulsant activity | Mice | [46] |
| Aconitum violaceum | Various fractions | Anticonvulsant activity | Mice | [47] |
| Delphinium denudatum | Aqueous fraction | Antiepileptiform activity | Cultured rat hippocampal pyramidal neurons | [48] |
| Delphinium denudatum | Aqueous fraction of roots | Antiepileptiform activity | Primary hippocampal neuronal cultures | [49] |
| Delphinium denudatum | Ethanolic extract and the aqueous fraction of roots | Anticonvulsant activity | Mice | [50] |
| Aconitum carmichaeli | Fuzi total alkaloids | Increase the seizure latency and decrease the mortality | Mice | [33] |
| Aconitum sp. | 6-Benzoyl deltamine (9) and eldeline (10) | Antiepileptiform activity | Rat hippocampal slices | [51] |
| 1, 3, and ajacine (11) | Antiepileptiform activity | Rat hippocampal slices | [39] | |
| 5 | Antiepileptiform activity | Rat hippocampal slices | [52] | |
| 7 | Increasing excitability | Rat hippocampal slices | [53] | |
| 14-Benzoyl talatisamine (12) and talatisamine (13) | Antiepileptiform activity | Rat hippocampal slices | [54] | |
| 8 | Antiepileptiform activity | Rat hippocampal slices | [45] | |
| 8 | 10 nM evoked excitation 30–100 nM biphasic effect above 100 nM suppressed the orthodromic population spike | Rat hippocampal slices | [55] | |
| 1, 3, and 5 | Antiepileptiform activity | Rat hippocampal slices | [56] | |
| 3 and 4 | Antiepileptiform activity | Rat hippocampal slices | [57] | |
| 2 | Antiepileptiform activity | Rat hippocampal slices | [38] | |
| 1-Benzoyl napelline (14) | Antiepileptiform activity | Rat hippocampal slices | [58] | |
| 5 | Antiepileptiform activity | Rat hippocampal slices | [59] | |
| 5 and heteratisine (15) | Antiepileptiform activity | Rat hippocampal slices | [60] | |
| 1 | Antiepileptiform activity | Rat hippocampal slices | [61] | |
| 1 | Prolonged seizure-like activity | Neocortical slices from juvenile Sprague-Dawley rats | [42] |
| Biological Activities | Affected In Vitro/In Vivo Model | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Picomolar concentration of 16 potentiated α7 nAChR activity/improved memory acquisition processes. | Oocytes from mature Xenopus laevis females/rat | [64] |
| Nanomolar concentrations of 16 acted as a co-agonist to potentiate TE-671 cell responses to acetylcholine, epibatidine, nicotine, and neostigmine. | Rhabdomyosarcoma cell line TE-671 | [69] |
| 16 (0.4–1.3 mg/kg) improved response accuracy at low doses. | Rat model | [70] |
| 16 (1–4 mg/kg) significantly counteracted the learning impairment caused by dizocilpine. | Rat model | [71] |
| 16 (1 mg/kg) significantly improved attentional function. | Rat model | [72] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salehi, A.; Ghanadian, M.; Zolfaghari, B.; Jassbi, A.R.; Fattahian, M.; Reisi, P.; Csupor, D.; Khan, I.A.; Ali, Z. Neuropharmacological Potential of Diterpenoid Alkaloids. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16050747
Salehi A, Ghanadian M, Zolfaghari B, Jassbi AR, Fattahian M, Reisi P, Csupor D, Khan IA, Ali Z. Neuropharmacological Potential of Diterpenoid Alkaloids. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(5):747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16050747
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalehi, Arash, Mustafa Ghanadian, Behzad Zolfaghari, Amir Reza Jassbi, Maryam Fattahian, Parham Reisi, Dezső Csupor, Ikhlas A. Khan, and Zulfiqar Ali. 2023. "Neuropharmacological Potential of Diterpenoid Alkaloids" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 5: 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16050747
APA StyleSalehi, A., Ghanadian, M., Zolfaghari, B., Jassbi, A. R., Fattahian, M., Reisi, P., Csupor, D., Khan, I. A., & Ali, Z. (2023). Neuropharmacological Potential of Diterpenoid Alkaloids. Pharmaceuticals, 16(5), 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16050747








