Clinical Confirmation of Pan-Amyloid Reactivity of Radioiodinated Peptide 124I-p5+14 (AT-01) in Patients with Diverse Types of Systemic Amyloidosis Demonstrated by PET/CT Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
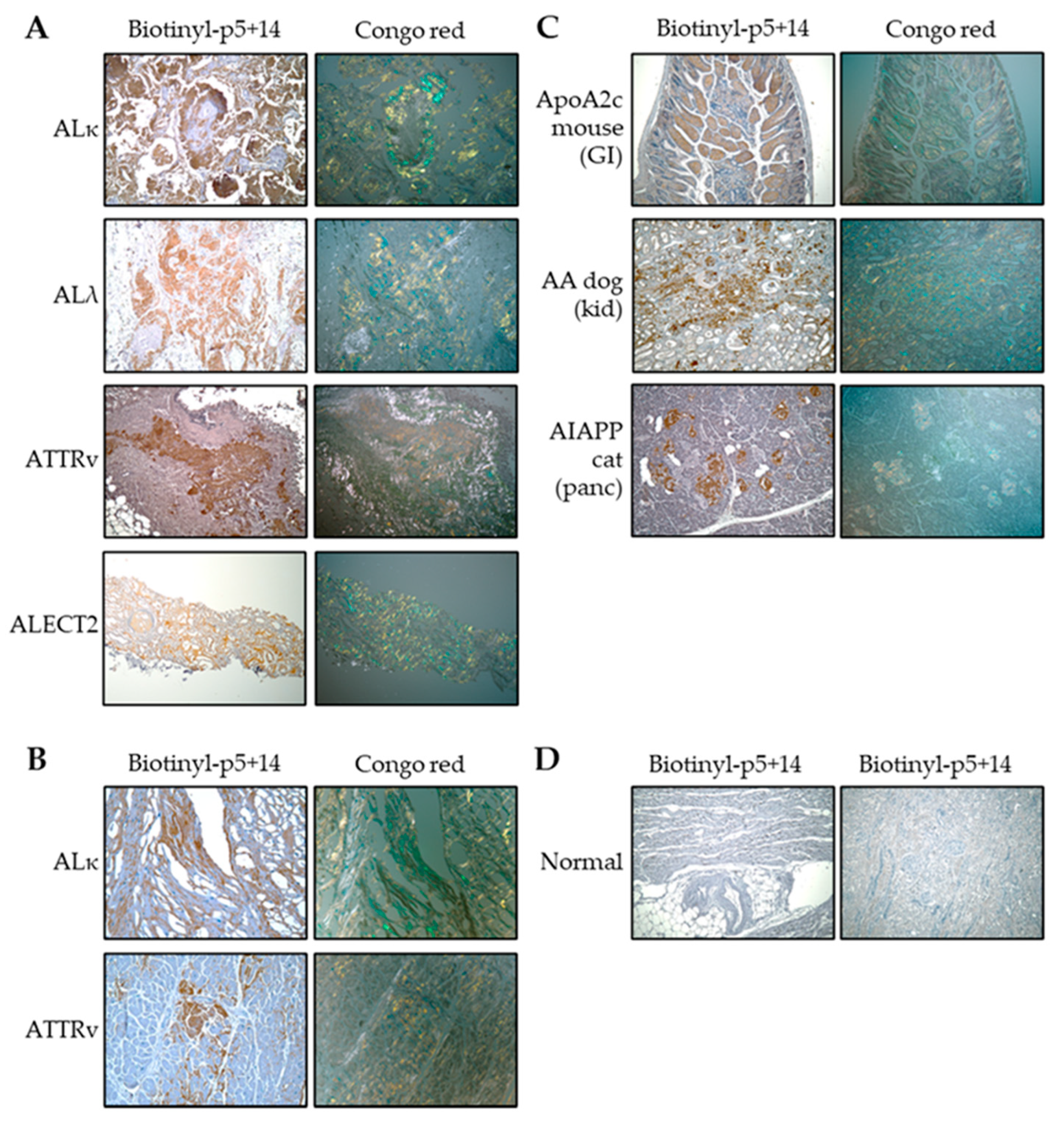
2.1. Peptide Histochemistry
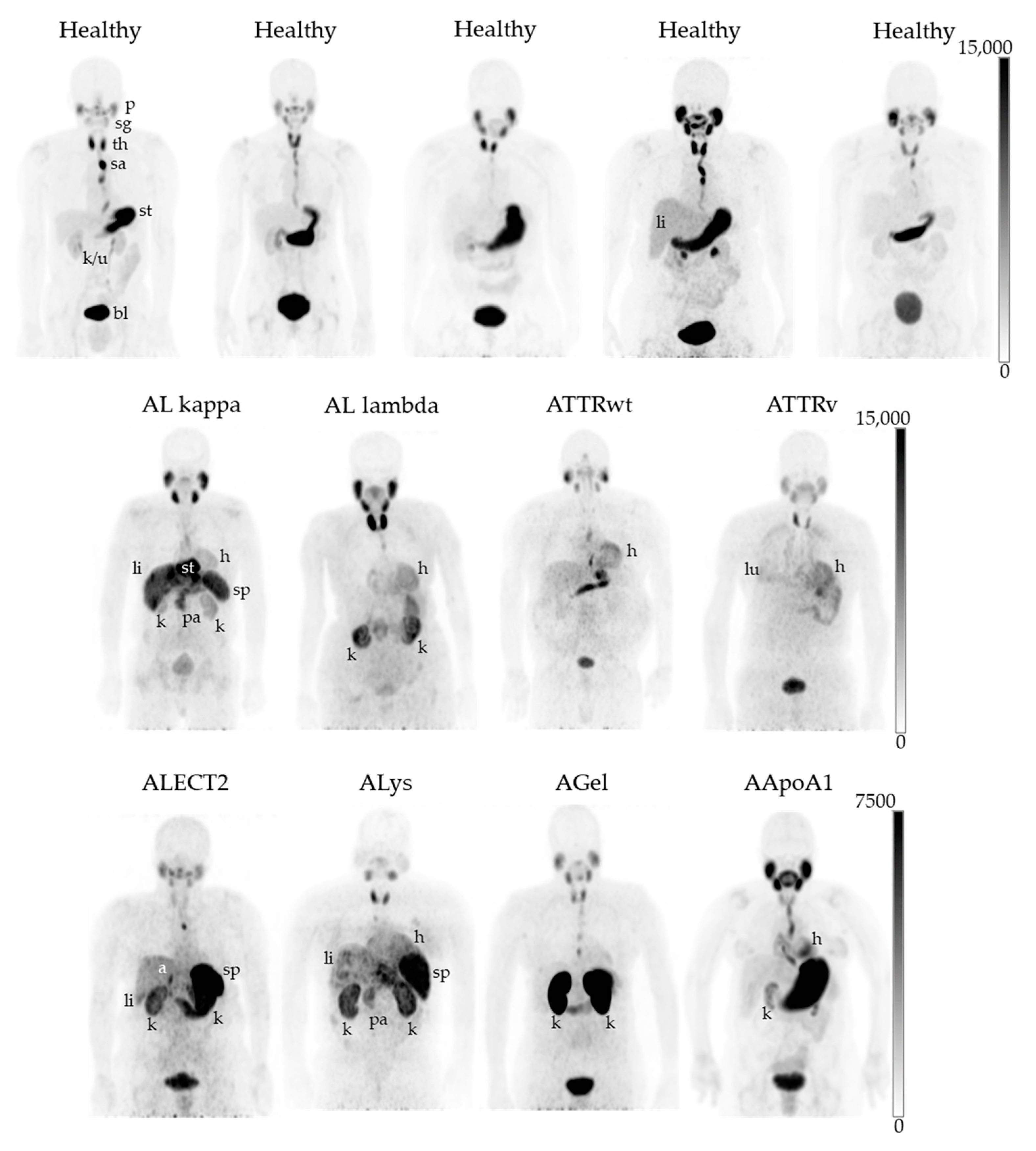
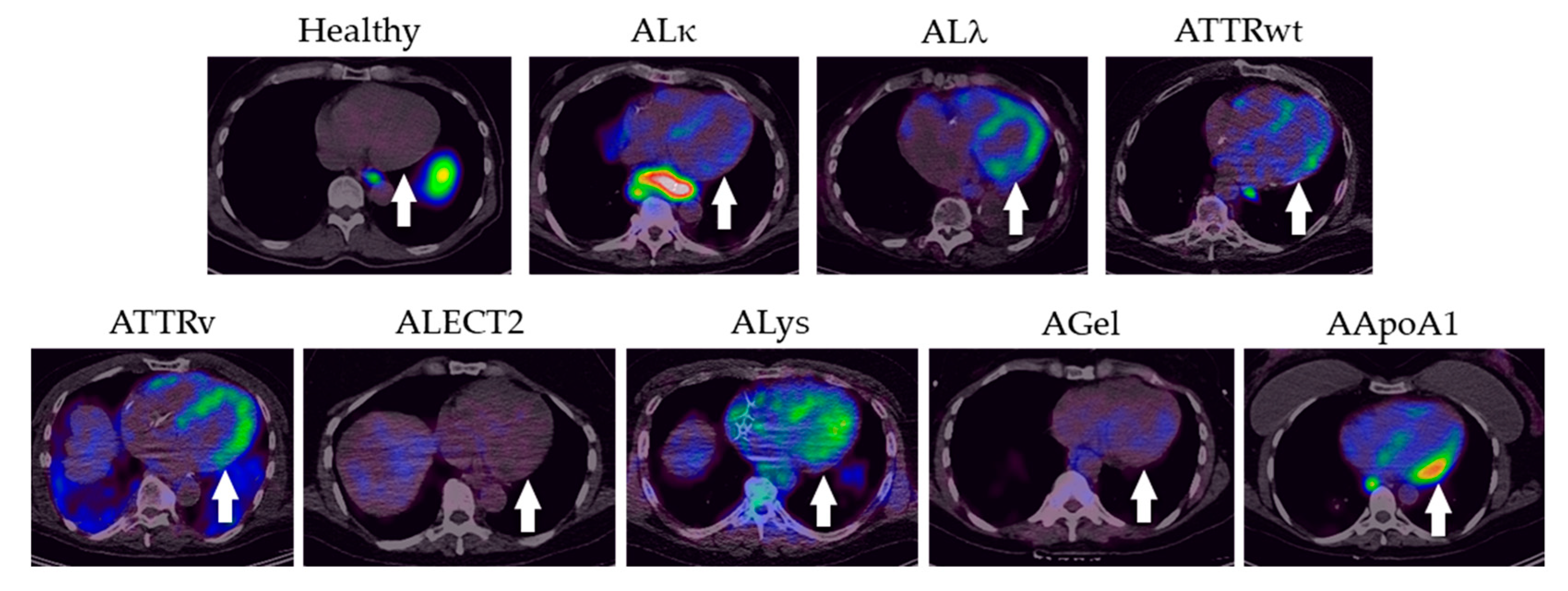
2.2. PET/CT Imaging with 124I-p5+14
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Peptide Histochemistry and Congo Red Staining
4.2. Study Participants
4.3. Peptide and Radiolabeling
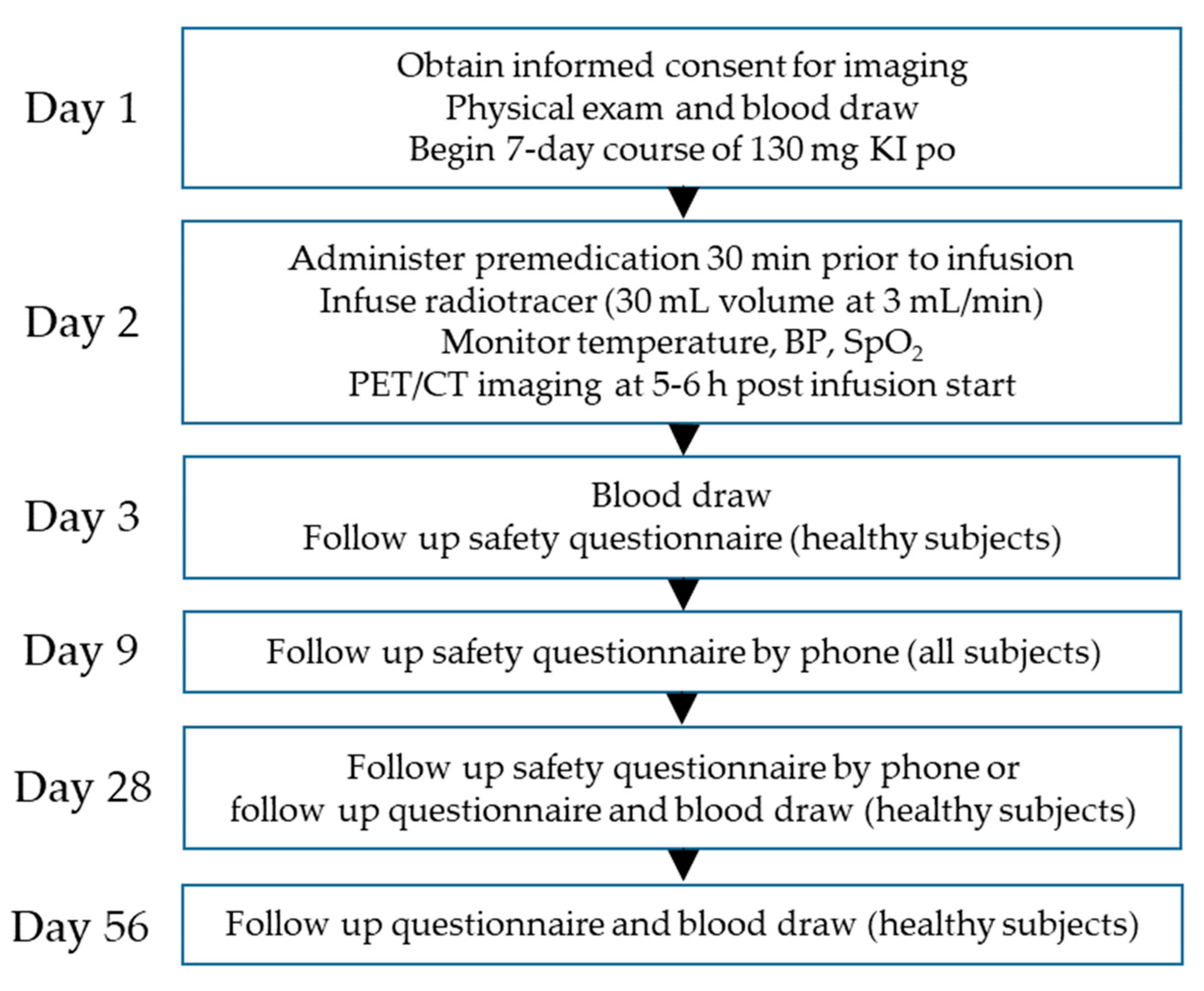
4.4. Study Design
4.5. Image Acquisition
4.6. Image Analysis
4.7. Study Oversight
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muchtar, E.; Dispenzieri, A.; Magen, H.; Grogan, M.; Mauermann, M.; McPhail, E.D.; Kurtin, P.J.; Leung, N.; Buadi, F.K.; Dingli, D.; et al. Systemic amyloidosis from A (AA) to T (ATTR): A review. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 289, 268–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxbaum, J.N.; Dispenzieri, A.; Eisenberg, D.S.; Fandrich, M.; Merlini, G.; Saraiva, M.J.M.; Sekijima, Y.; Westermark, P. Amyloid nomenclature 2022: Update, novel proteins, and recommendations by the International Society of Amyloidosis (ISA) Nomenclature Committee. Amyloid 2022, 29, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrana, J.A.; Theis, J.D.; Dasari, S.; Mereuta, O.M.; Dispenzieri, A.; Zeldenrust, S.R.; Gertz, M.A.; Kurtin, P.J.; Grogg, K.L.; Dogan, A. Clinical diagnosis and typing of systemic amyloidosis in subcutaneous fat aspirates by mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Haematologica 2014, 99, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezk, T.; Lachmann, H.J.; Fontana, M.; Naharro, A.M.; Sachchithanantham, S.; Mahmood, S.; Petrie, A.; Whelan, C.J.; Pinney, J.H.; Foard, D.; et al. Cardiorenal AL amyloidosis: Risk stratification and outcomes based upon cardiac and renal biomarkers. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 186, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittrich, T.; Kimmich, C.; Hegenbart, U.; Schonland, S.O. Prognosis and Staging of AL Amyloidosis. Acta Haematol. 2020, 143, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, S.; Chen, W.; Zeng, C.; Liu, Z. The clinical features and outcomes of systemic AL amyloidosis: A cohort of 231 Chinese patients. Clin. Kidney J. 2015, 8, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchtar, E.; Dispenzieri, A.; Leung, N.; Lacy, M.Q.; Buadi, F.K.; Dingli, D.; Grogan, M.; Hayman, S.R.; Kapoor, P.; Hwa, Y.L.; et al. Depth of organ response in AL amyloidosis is associated with improved survival: Grading the organ response criteria. Leukemia 2018, 32, 2240–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidana, S.; Milani, P.; Binder, M.; Basset, M.; Tandon, N.; Foli, A.; Dispenzieri, A.; Gertz, M.A.; Hayman, S.R.; Buadi, F.K.; et al. A validated composite organ and hematologic response model for early assessment of treatment outcomes in light chain amyloidosis. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lousada, I.; Comenzo, R.L.; Landau, H.; Guthrie, S.; Merlini, G. Light Chain Amyloidosis: Patient Experience Survey from the Amyloidosis Research Consortium. Adv. Ther. 2015, 32, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, P.N.; Lavender, J.P.; Pepys, M.B. Evaluation of systemic amyloidosis by scintigraphy with 123I-labeled serum amyloid P component. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 323, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, P.L.; Hazenberg, B.P.; Franssen, E.J.; Limburg, P.C.; van Rijswijk, M.H.; Piers, D.A. Kinetic studies with iodine-123-labeled serum amyloid P component in patients with systemic AA and AL amyloidosis and assessment of clinical value. J. Nucl. Med. 1998, 39, 699–706. [Google Scholar]
- Bokhari, S.; Shahzad, R.; Castano, A.; Maurer, M.S. Nuclear imaging modalities for cardiac amyloidosis. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2014, 21, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorbala, S.; Cuddy, S.; Falk, R.H. How to Image Cardiac Amyloidosis: A Practical Approach. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, 1368–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorbala, S.; Kijewski, M.F.; Park, M.A. Quantitative Bone-Avid Tracer SPECT/CT for Cardiac Amyloidosis: A Crucial Step Forward. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, 1364–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, J.S.; Martin, E.B.; Richey, T.; Stuckey, A.C.; Macy, S.; Wooliver, C.; Williams, A.; Foster, J.S.; McWilliams-Koeppen, P.; Uberbacher, E.; et al. Preclinical Validation of the Heparin-Reactive Peptide p5+14 as a Molecular Imaging Agent for Visceral Amyloidosis. Molecules 2015, 20, 7657–7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennel, S.J.; Stuckey, A.; McWilliams-Koeppen, H.P.; Richey, T.; Wall, J.S. Tc-99m Radiolabeled Peptide p5 + 14 is an Effective Probe for SPECT Imaging of Systemic Amyloidosis. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2016, 18, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, E.B.; Kennel, S.J.; Richey, T.; Wooliver, C.; Osborne, D.; Williams, A.; Stuckey, A.; Wall, J.S. Dynamic PET and SPECT imaging with radioiodinated, amyloid-reactive peptide p5 in mice: A positive role for peptide dehalogenation. Peptides 2014, 60, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, E.B.; Williams, A.; Richey, T.; Stuckey, A.; Heidel, R.E.; Kennel, S.J.; Wall, J.S. Comparative evaluation of p5+14 with SAP and peptide p5 by dual-energy SPECT imaging of mice with AA amyloidosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wall, J.S.; Kennel, S.J.; Martin, E.B. Dual-Energy SPECT and the Development of Peptide p5+14 for Imaging Amyloidosis. Mol. Imaging 2017, 16, 1536012117708705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.; Polydefkis, M.; Gonzalez-Duarte, A.; Wixner, J.; Kristen, A.V.; Schmidt, H.H.; Berk, J.L.; Losada Lopez, I.A.; Dispenzieri, A.; Quan, D.; et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of patisiran for hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis with polyneuropathy: 12-month results of an open-label extension study. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, M.D.; Waddington-Cruz, M.; Berk, J.L.; Polydefkis, M.; Dyck, P.J.; Wang, A.K.; Plante-Bordeneuve, V.; Barroso, F.A.; Merlini, G.; Obici, L.; et al. Inotersen Treatment for Patients with Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, P.; Drachman, B.M.; Gottlieb, S.S.; Hoffman, J.E.; Hummel, S.L.; Lenihan, D.J.; Ebede, B.; Gundapaneni, B.; Li, B.; Sultan, M.B.; et al. Long-Term Survival With Tafamidis in Patients With Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Heart Fail. 2022, 15, e008193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, M.S.; Schwartz, J.H.; Gundapaneni, B.; Elliott, P.M.; Merlini, G.; Waddington-Cruz, M.; Kristen, A.V.; Grogan, M.; Witteles, R.; Damy, T.; et al. Tafamidis Treatment for Patients with Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapezzi, C.; Elliott, P.; Damy, T.; Nativi-Nicolau, J.; Berk, J.L.; Velazquez, E.J.; Boman, K.; Gundapaneni, B.; Patterson, T.A.; Schwartz, J.H.; et al. Efficacy of Tafamidis in Patients With Hereditary and Wild-Type Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy: Further Analyses From ATTR-ACT. JACC Heart Fail. 2021, 9, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladini, G.; Merlini, G. How I treat AL amyloidosis. Blood 2022, 139, 2918–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thelander, U.; Westermark, G.T.; Antoni, G.; Estrada, S.; Zancanaro, A.; Ihse, E.; Westermark, P. Cardiac microcalcifications in transthyretin (ATTR) amyloidosis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2022, 352, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehman, E.C.; El-Sady, M.S.; Kijewski, M.F.; Khor, Y.M.; Jacob, S.; Ruberg, F.L.; Sanchorawala, V.; Landau, H.; Yee, A.J.; Bianchi, G.; et al. Early Detection of Multiorgan Light-Chain Amyloidosis by Whole-Body (18)F-Florbetapir PET/CT. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 1234–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoni, G.; Lubberink, M.; Estrada, S.; Axelsson, J.; Carlson, K.; Lindsjo, L.; Kero, T.; Langstrom, B.; Granstam, S.O.; Rosengren, S.; et al. In vivo visualization of amyloid deposits in the heart with 11C-PIB and PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2013, 54, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, I.; Pereira, P.J.; Damas, A.M.; Saraiva, M.J. Aprotinin binding to amyloid fibrils. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 2307–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Chong, V.; Murray, T.; McDonagh, T.; Hunter, J.; Poon, F.W.; Gray, H.W.; Neilly, J.B. Preliminary experience of 99mTc-Aprotinin scintigraphy in amyloidosis. Eur. J. Haematol. 2007, 79, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, C.; Bereza, M.; Kumar, S.T.; Kieninger, B.; Morgado, I.; Hortschansky, P.; Fritz, G.; Rocken, C.; Horn, U.; Fandrich, M. Pattern recognition with a fibril-specific antibody fragment reveals the surface variability of natural amyloid fibrils. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 408, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haupt, C.; Morgado, I.; Kumar, S.T.; Parthier, C.; Bereza, M.; Hortschansky, P.; Stubbs, M.T.; Horn, U.; Fandrich, M. Amyloid fibril recognition with the conformational B10 antibody fragment depends on electrostatic interactions. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 405, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennel, S.J.; Williams, A.; Stuckey, A.; Richey, T.; Wooliver, C.; Chazin, W.; Stern, D.A.; Martin, E.B.; Wall, J.S. The pattern recognition reagents RAGE VC1 and peptide p5 share common binding sites and exhibit specific reactivity with AA amyloid in mice. Amyloid 2016, 23, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizumoto, S.; Sugahara, K. Glycosaminoglycans are functional ligands for receptor for advanced glycation end-products in tumors. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 2462–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocken, C.; Kientsch-Engel, R.; Mansfeld, S.; Stix, B.; Stubenrauch, K.; Weigle, B.; Buhling, F.; Schwan, M.; Saeger, W. Advanced glycation end products and receptor for advanced glycation end products in AA amyloidosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 162, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adumeau, P.; Davydova, M.; Zeglis, B.M. Thiol-Reactive Bifunctional Chelators for the Creation of Site-Selectively Modified Radioimmunoconjugates with Improved Stability. Bioconjug Chem. 2018, 29, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, S.; Fontana, M.; Gillmore, J.D. Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment of Cardiac and Renal Amyloidosis. Cardiol. Clin. 2021, 39, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.Y.; Rowe, S.P.; Jain, S.K.; Schon, L.C.; Yung, R.C.; Nayfeh, T.A.; Bingham, C.O., 3rd; Foss, C.A.; Nimmagadda, S.; Pomper, M.G. Evaluation of Musculoskeletal and Pulmonary Bacterial Infections with [(124)I]FIAU PET/CT. Mol. Imaging 2020, 19, 1536012120936876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divgi, C.R.; Uzzo, R.G.; Gatsonis, C.; Bartz, R.; Treutner, S.; Yu, J.Q.; Chen, D.; Carrasquillo, J.A.; Larson, S.; Bevan, P.; et al. Positron emission tomography/computed tomography identification of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Results from the REDECT trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foss, C.A.; Plyku, D.; Ordonez, A.A.; Sanchez-Bautista, J.; Rosenthal, H.B.; Minn, I.; Lodge, M.A.; Pomper, M.G.; Sgouros, G.; Jain, S.K. Biodistribution and Radiation Dosimetry of (124)I-DPA-713, a PET Radiotracer for Macrophage-Associated Inflammation. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 1751–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, G.A.H.; Liang, C.; Mukherjee, J. [(124)I]IBETA: A New Abeta Plaque Positron Emission Tomography Imaging Agent for Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules 2022, 27, 4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Lin, Q.; Si, Z.; Fu, W.; Yang, T.; Shi, H.; Cheng, D. (124)I-Labeled Immuno-PET Targeting hTREM2 for the Diagnosis of Gastric Carcinoma. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 2235–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, H.; Ding, J.; Wang, F.; Meng, X.; Ding, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; Yao, S.; Sheng, X.; et al. Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of Programmed Death 1 Expression in Cancer Patients Using 124I-Labeled Toripalimab: A Pilot Clinical Translation Study. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 46, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Xie, J.; Chen, X. Peptide-based probes for targeted molecular imaging. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 1364–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, M.; Eriksson, L. Physics of pure and non-pure positron emitters for PET: A review and a discussion. EJNMMI Phys. 2016, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kertesz, H.; Conti, M.; Panin, V.; Cabello, J.; Bharkhada, D.; Beyer, T.; Papp, L.; Jentzen, W.; Cal-Gonzalez, J.; Herraiz, J.L.; et al. Positron range in combination with point-spread-function correction: An evaluation of different implementations for [124I]-PET imaging. EJNMMI Phys. 2022, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, T.; Page, J.; Burniston, M.; Skillen, A.; Ross, J.C.; Manwani, R.; McCool, D.; Hawkins, P.N.; Wechalekar, A.D. Extracardiac (18)F-florbetapir imaging in patients with systemic amyloidosis: More than hearts and minds. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, H.; Kiuchi, T.; Iijima, M.; Ueda, M.; Ando, Y.; Morozumi, S.; Tomita, M.; Kawagashira, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Katsuno, M.; et al. Systemic but asymptomatic transthyretin amyloidosis 8 years after domino liver transplantation. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2011, 82, 1287–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledesma, F.L.; Castelli, J.B. Autopsy findings in a patient with primary systemic AL (kappa light chain) amyloidosis. Autops. Case Rep. 2021, 11, e2021273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateishi, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Katsuki, M.; Nagata, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Kohashi, K.; Koga, Y.; Hashisako, M.; Kiyozawa, D.; Mori, T.; et al. Pathological review of cardiac amyloidosis using autopsy cases in a single Japanese institution. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2021, 227, 153635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, J.S.; Martin, E.B.; Endsley, A.; Stuckey, A.C.; Williams, A.D.; Powell, D.; Whittle, B.; Hall, S.; Lambeth, T.R.; Julian, R.R.; et al. First in Human Evaluation and Dosimetry Calculations for Peptide (124)I-p5+14-a Novel Radiotracer for the Detection of Systemic Amyloidosis Using PET/CT Imaging. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2022, 24, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Subject | Amyloid Type | Sex | Age (y) | Time from Diagnosis (y) | Injected Dose (MBq) | Injected Peptide (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P05 | ALECT2 | F | 63 | 6 | 38.5 1 | 1.30 |
| P07 | ALκ | M | 72 | 3 | 74.4 | 1.37 |
| P16 | ALλ | F | 79 | 5 | 74.4 | 1.34 |
| P23 | ALys | M | 45 | 4 | 74.9 | 1.10 |
| P24 | AGel | F | 63 | 16 | 72.5 | 1.52 |
| P26 | ATTRwt | M | 77 | 2 | 73.4 | 1.48 |
| P30 | AApoA1 | F | 49 | 5 | 75.9 | 1.27 |
| P32 | ATTRv | M | 75 | 2 | 76.2 | 1.20 |
| P43 | HV | M | 68 | NA | 74.5 | 1.40 |
| P44 | HV | F | 52 | NA | 74.8 | 1.40 |
| P45 | HV | F | 47 | NA | 73.6 | 1.62 |
| P47 | HV | F | 60 | NA | 74.0 | 1.52 |
| P54 | HV | M | 61 | NA | 73.3 | 1.63 |
| Organ | AL kappa | AL lambda | ATTRwt | ATTRv | ALECT2 | ALys | AGel | AApoA1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C 1 | I | C | I | C | I | C | I | C | I | C | I | C | I | C | I | |
| Heart | ✓ 2 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Lung | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Liver | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||
| Spleen | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||
| Kidney | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martin, E.B.; Stuckey, A.; Powell, D.; Lands, R.; Whittle, B.; Wooliver, C.; Macy, S.; Foster, J.S.; Guthrie, S.; Kennel, S.J.; et al. Clinical Confirmation of Pan-Amyloid Reactivity of Radioiodinated Peptide 124I-p5+14 (AT-01) in Patients with Diverse Types of Systemic Amyloidosis Demonstrated by PET/CT Imaging. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040629
Martin EB, Stuckey A, Powell D, Lands R, Whittle B, Wooliver C, Macy S, Foster JS, Guthrie S, Kennel SJ, et al. Clinical Confirmation of Pan-Amyloid Reactivity of Radioiodinated Peptide 124I-p5+14 (AT-01) in Patients with Diverse Types of Systemic Amyloidosis Demonstrated by PET/CT Imaging. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(4):629. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040629
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartin, Emily B., Alan Stuckey, Dustin Powell, Ronald Lands, Bryan Whittle, Craig Wooliver, Sallie Macy, James S. Foster, Spencer Guthrie, Stephen J. Kennel, and et al. 2023. "Clinical Confirmation of Pan-Amyloid Reactivity of Radioiodinated Peptide 124I-p5+14 (AT-01) in Patients with Diverse Types of Systemic Amyloidosis Demonstrated by PET/CT Imaging" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 4: 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040629
APA StyleMartin, E. B., Stuckey, A., Powell, D., Lands, R., Whittle, B., Wooliver, C., Macy, S., Foster, J. S., Guthrie, S., Kennel, S. J., & Wall, J. S. (2023). Clinical Confirmation of Pan-Amyloid Reactivity of Radioiodinated Peptide 124I-p5+14 (AT-01) in Patients with Diverse Types of Systemic Amyloidosis Demonstrated by PET/CT Imaging. Pharmaceuticals, 16(4), 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040629









