Abstract
Continuous evaluation of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccine effectiveness in hemodialysis (HD) patients is critical in this immunocompromised patient group with higher mortality rates due to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. The response towards vaccination in HD patients has been studied weeks after their first and second SARS-CoV-2 vaccination dose administration, but no further studies have been developed in a long-term manner, especially including both the humoral and cellular immune response. Longitudinal studies that monitor the immune response to COVID-19 vaccination in individuals undergoing HD are therefore necessary to prioritize vaccination strategies and minimize the pathogenic effects of SARS-CoV-2 in this high-risk group of patients. We followed up HD patients and healthy volunteers (HV) and monitored their humoral and cellular immune response three months after the second (V2+3M) and after the third vaccination dose (V3+3M), taking into consideration previous COVID-19 infections. Our cellular immunity results show that, while HD patients and HV individuals secrete comparable levels of IFN-γ and IL-2 in ex vivo stimulated whole blood at V2+3M in both naïve and COVID-19-recovered individuals, HD patients secrete higher levels of IFN-γ and IL-2 than HV at V3+3M. This is mainly due to a decay in the cellular immune response in HV individuals after the third dose. In contrast, our humoral immunity results show similar IgG binding antibody units (BAU) between HD patients and HV individuals at V3+3M, independently of their previous infection status. Overall, our results indicate that HD patients maintain strong cellular and humoral immune responses after repeated 1273-mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccinations over time. The data also highlights significant differences between cellular and humoral immunity after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, which emphasizes the importance of monitoring both arms of the immune response in the immunocompromised population.
1. Introduction
End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) patients undergoing hemodialysis (HD) are considered immunocompromised due to their vulnerability to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection and their increased risk of COVID-19 mortality [1]. Vaccine effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 is crucial for the protection of HD patients [2], especially after the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron) variant, which partially escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies [3,4] and has been reported to increase the number of hospitalizations among vaccinated adults [5]. Several reports have determined the ability of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines to generate immunity in HD patients and recommend implementing booster doses from highest to lowest priority-use groups [6,7,8].
Previous studies demonstrated a substantial increase in the antibody levels of naïve and COVID-19-recovered HD patients shortly after the second and third vaccine dose [9,10]. Others investigated the dynamics of post-vaccination antibody and T-cell responses for up to two months to determine the most appropriate timing for delivery of a booster dose. Results demonstrated comparable levels of total RBD antibodies and T-cells fifteen days and three months after the second vaccine dose between HD and HV [11]. This research group also investigated the immune response in HD patients, 90% without previous infection, and observed a booster effect on anti-RBD and neutralizing antibodies to different variants and a significant increase in SARS-CoV-2-S-IFN-γ-producing T-cells 46 days after receiving the third homologous mRNA vaccine dose [12]. More recent studies compared the immune response of non-infected naïve HD patients, who received four vaccine doses, with COVID-19-recovered HD patients, who only received three doses of the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine. The results indicated that, while there were no differences in the production of the proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-2 (IL-2) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) by T-cells, better humoral immunity was observed in the convalescent-vaccinated compared to vaccinated-only HD patients [13]. These results suggest that the cellular and humoral immune responses provide different information regarding the immunological status of vaccinated HD patients that do not necessarily correlate with each other. Table 1 summarizes some of the most relevant and related studies.

Table 1.
Summary of studies evaluating the humoral and cellular immune response in HD patients.
Here, we monitored the long-term effects of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in both, the cellular and humoral immune response in HD patients. Specifically, we evaluated the production of IFN-γ and IL-2 in the whole blood after stimulation with SARS-CoV-2 peptide pools and the IgG directed against Spike glycoprotein in HD patients and Healthy Volunteers (HV) with (COVID-19 recovered individuals) or without (naïve individuals) previous infection of SARS-CoV-2. Our results indicate that both naïve and COVID-19-recovered HD patients mount cellular and humoral immune responses comparable with HV individuals after the second and third dose of the 1273-mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.
2. Results
We first monitored the cellular immune response in naïve subjects without previous SARS-CoV-2 infection by evaluating the production of IFN-γ in the whole blood after spike-specific peptide pool stimulation. Comparing the production of IFN-γ between HD patients and HV individuals, we observed a similar IFN-γ production between these two groups at both time points, V2+3M (p = 0.35) and V3+3M (p = 0.73) (Figure 1A). However, when comparing the production of IFN-γ between the two time points, we observed a significant decrease at V3+3M in HV individuals (p = 0.008). This suggests that the durability of cellular immunity decreases more rapidly in healthy individuals without previous SARS-CoV-2 infection after a booster dose.
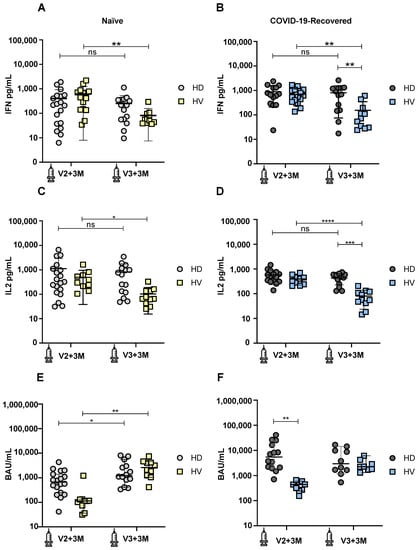
Figure 1.
Development of cellular and humoral immune responses after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in COVID-19-recovered and naïve hemodialysis (HD) patients and healthy volunteers (HV) 3 months after second (V2+3M) and 3 months after third (V3+3M) vaccination dose. (A) IFN-γ production in naïve HD patients (light grey symbols) and HV individuals (yellow symbols) at V2+3M and V3+3M. (B) IFN-γ production in COVID-19-recovered HD patients (dark grey symbols) and HV individuals (blue symbols) at V2+3M and V3+3M. (C) IL-2 production in naïve HD patients and HV individuals at V2+3M and V3+3M (D). IL-2 production in COVID-19-recovered HD patients and HV individuals at V2+3M and V3+3M. (E) SARS-CoV-2 spike-specific IgG serum levels in naïve HD patients and HV individuals at V2+3M and V3+3M. (F) Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 spike-specific IgG binding antibody units (BAU) in COVID-19-recovered HD patients and HV individuals at V2+3M and V3+3M. Values higher than 33.8 BAU/mL were considered positive. <0.05 (*), <0.005 (**), <0.0005 (***), and <0.0001 (****). Data are shown as mean ± SEM.
We next measured the production of IFN-γ in COVID-19-recovered subjects. Comparing the production of IFN-γ between HD patients and HV individuals, we observed that, while similar amounts of IFN-γ were produced between these groups at V2+3M (p = 0.69), there was a significant IFN-γ decrease in HV individuals compared to HD patients at V3+3M (p = 0.003) (Figure 1B). When comparing the production of IFN-γ between the two time points, we also observed a significant decrease at V3+3M in HV individuals (p = 0.001). This suggests that the durability of cellular immunity is maintained in HD patients with a previous SARS-CoV-2 infection after a booster dose.
Next, we measured the production of IL-2 in naïve subjects. Comparing the production of IL-2 between HD patients and HV individuals, we observed a similar IL-2 production between these two groups at both time points, V2+3M and V3+3M (p = 0.33). However, when comparing the production of IL-2 between the two time points, we observed a significant decrease at V3+3M in HV individuals (p = 0.011) (Figure 1C). These results are consistent with data from Figure 1A, suggesting a decrease in the durability of the cellular immunity in healthy individuals without a previous SARS-CoV-2 infection after a booster dose.
Finally, we compared the production of IL-2 in COVID-19-recovered subjects. Comparing the production of IL-2 between HD patients and HV individuals, we observed that, while similar amounts of IL-2 were produced between these groups at V2+3M (p = 0.15), there was a significant IL-2 decrease in HV individuals compared to HD patients at V3+3M (p = 0.0008) (Figure 1D). When comparing the production of IL-2 between the two time points, we also observed a significant decrease at V3+3M in HV individuals (p ≤ 0.0001). Overall, the cellular immunity results indicate that HD patients are able to mount and maintain a robust cellular immune response over time, while HV individuals decrease their ability to secrete both IFN-γ and IL-2 after a booster dose.
We also monitored the humoral immune response in naïve subjects without previous SARS-CoV-2 infection by measuring IgG binding antibody units specific against the Spike glycoprotein (Figure 1E,F). Comparing the IgG levels between naïve HD patients and HV individuals, we observed a similar antibody production between these two groups at both time points, V2+3M (p = 0.43) and V3+3M (p = 0.72) (Figure 1E). However, when comparing the IgG levels at the two time points, we observed a significant increase in antibody production from V2+3M to V3+3M in both HD patients (p = 0.045) and HV individuals (p = 0.002). This suggests that booster doses significantly increase the cumulative antibody responses after repeated vaccinations. Comparing the IgG levels between previously infected HD patients and HV individuals, we observed that HD patients show significantly higher IgG levels compared to HV individuals at V2+3M (p = 0.009). However, these differences were not significant at V3+3M between both groups (p = 0.63), indicating that both COVID-19-recovered HD patients and HV individuals maintain their humoral response long-term after boosting (Figure 1F).
3. Discussion
In this study, we examined the effects of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination on the humoral and cellular specific immune responses in HD patients compared to HV individuals with (COVID-19-recovered) or without (naïve) previous SARS-CoV-2 infection, three months after the second (V2+3M) and after the third (V3+3M) vaccination dose. Our results indicate that both naïve and COVID-19-recovered HD patients maintain strong cellular and humoral immune responses after receiving a third dose (booster), which is comparable or higher (significant increased at V3+3M for IFN-γ and IL-2) to HV individuals.
Several studies have described that most HD patients can mount competitive immune responses [7,14,15]. Considering the humoral immune response alone, a recent cohort study reported the induction of robust and durable humoral immune response three months after receiving the BNT162b2 vaccine in naïve HD patients, following a two-dose immunization scheme [10]. Previous studies from David Navarro’s laboratory evaluated both the T-cell and Spike-specific reactive antibody responses in HD patients fifteen days and three months after two doses of mRNA vaccines (mRNA-123 and BNT162b2). In line with our results, they observed that HD patients develop SARS-CoV-2 antibody responses comparable to healthy controls (HC) (i.e., 95% rate of HD patient responders at 3M vs. 100% of HC responders at 3M) [9]. In addition, no differences between CD4+ or CD8+ T-cell responses were observed across groups, although we reported higher IFN-γ and IL-2 production in HD patients with previous SARS-CoV-2 infection compared to controls at V3+3M. It is likely that differences across studies regarding the clinical characteristics of patients, the time points under study, and the methodological approaches to evaluate T-cell immunity may, in part, explain the discrepancy. More recent data from Navarro’s laboratory confirmed the ability of HD patients to produce high levels of IgG production 46 days after the booster (anti-RBD antibodies were detected in 39/40 HD patients). Furthermore, SARS-CoV-2 specific-IFN-γ-producing CD8+ and CD4+ T-cell responses were detected in 35 and 36/37 of HD patients, respectively, indicating that mRNA COVID-19 vaccines induce a booster effect on both humoral and cellular immune responses in this immunocompromised group [12]. Similarly, Anft and colleagues recently described a stable cellular immunity with no differences in the production of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-2 and TNF) between four times vaccinated, non-infected HD patients compared to three times vaccinated, infected HD patients. However, a significant fade of neutralizing antibodies after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in naïve HD patients (25%) compared to COVID-19-recovered HD patients (62.5%) was observed [13]. These results indicate significant differences between the humoral and cellular immune responses and highlight the importance of measuring both arms of the immune response in HD patients. Our results are consistent with these studies that report potent humoral and cellular immune responses in HD patients but further extend those findings, comparing HD data with HV and differentiating between patients with/without previous SARS-CoV-2 infection.
A limitation of our study is the small sample size and the differences in vaccines between groups; HD patients were vaccinated with mRNA-1273 (Moderna), while HV individuals were vaccinated with BNT162b2 (Pfizer). Several studies have described that BNT162b2 vaccination induces diminished seroconversion compared to mRNA-1273 vaccination [7,16,17]. Nevertheless, the absolute indicators of the cellular and humoral immunity in HD and HV are comparable in our study, as we used the same methodological approaches to obtain the data.
We conclude that HD patients develop potent cellular and humoral immune responses after COVID-19 vaccination over time, which is critical to lower the rate of COVID-19-related hospitalizations in this vulnerable group of patients [18]. While the precise mechanisms behind the robust immune response induced by SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, we hypnotize that trained immunity, which has previously been associated with COVID-19 vaccination and infection [19,20], may be responsible, in part, to the delicate balance between the protective and the inflammatory state of HD patients [21]. Although further studies are required to demonstrate the relationship between protection and specific T-cell or serological immune responses, the development of strong cellular and humoral immune responses reported here may help guide future vaccination strategies in immunocompromised groups of patients.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Design
In this study, peripheral blood from HD patients was drawn before hemodialysis (n = 38), while in HV individuals (n = 30) it was prospectively collected. The second vaccination dose of HD patients and Healthy Volunteers occurred in May 2021. The third vaccination dose of HD patients and Healthy Volunteers occurred in October 2021. All blood extractions were performed approximately 90 days after second vaccination dose and 90 days after third vaccination dose. All individuals were based in the Comunidad de Madrid, Spain. Healthy volunteers were obtained from Hospital Universitario La Paz in Madrid and HD patients were obtained from Hospital Universitario Puerta de Hierro in Madrid. Blood extractions from HD patients [Naïve (n = 19), COVID-19-recovered patients (n = 19)], HV individuals [naïve (n = 15), and COVID-19-recovered HV (n = 15)] were collected three months after the second (V2+3M) and three months after the third vaccine dose (V3+3M). Table 2 and Table 3 summarize HD patient and HV individuals’ characteristics.

Table 2.
Naïve and COVID-19 recovered HD patients’ characteristics.

Table 3.
Naïve and COVID-19 recovered HV individuals’ characteristics.
4.2. SARS-CoV-2 Peptide Pools and Whole-Blood Culture Assays
Lithium-heparinized blood samples were collected before the start of dialysis. On the same day, 320 µL of whole blood was mixed with 80µL of RPMI and stimulated with PepTivator ® SARS-CoV-2 Peptide Pools (S; 2 µg/mL, M; 2 µg/mL) or a DMSO control. After 16–20 h of culture, supernatant (plasma) was collected and stored at −20 °C for further cytokine quantification, as previously reported [14]. For previous SARS-CoV-2 infection detection, whole blood cultures were incubated with a peptide pool against SARS-CoV-2 membrane (M) protein (2 μg/mL).
4.3. Spike-Specific IgG Quantification and Analysis
To study the specific serologic response against SARS-CoV-2, plasma from HD patients and HV was collected. The Liaison ® SARS-CoV-2 TrimetricS IgG assay (Diasorin, Stillwater, MN, USA) was used for semiquantitative detection of IgG directed against the Spike glycoprotein. Values over 33.8 BAU/mL were considered positive.
4.4. Cytokine Quantification and Analysis
Cytokine concentrations in the supernatants (plasma) were quantified using ELLA with microfluidic multiplex cartridges measuring IFN-γ and IL-2 release following the manufacturer’s instructions (ProteinSimple, San Jose, CA, USA). The cytokine levels present in plasma stimulated with DMSO were subtracted from the corresponding Peptide-pool stimulated samples, as previously reported [22].
4.5. Statistics
Statistical analyses were performed by Two-Way ANOVA and Šídák’s multiple comparison tests. Normality of data was tested using D’Agostino and Pearson tests for normal distribution. Paired t test and unpaired t test were also used as appropriate, using Graphpad PRISM 9.01 (Graphpad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA).
Author Contributions
M.G.-P., P.C., J.B. and M.J.B.-B. performed cellular assays. M.P.-O. performed humoral assays. M.G.-P. and D.L.-O. organized the database and performed the statistical analysis C.C., M.d.R.L.-C., E.G.-P., P.P., A.O., J.P. and J.O. contributed to conception and design of the study. M.G.-P., J.B. and D.L.-O. performed writing review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding was obtained from Instituto de Salud Carlos III (ISCIII) RICORS program to RICORS2040 (RD21/0005/0001), FEDER funds; Acción Estratégica en Salud Intramural (AESI), Instituto de Salud Carlos III, grant number AESI PI21CIII_00022 to PP and Healthstar-plus -REACT-UE Grant through Segovia Arana Research Institute Puerta de Hierro Majadahonda-IDIPHIM. J.O. is a member of VACCELERATE (European Corona Vaccine Trial Accelerator Platform) Network under grant agreement Nº101037867, which aims to facilitate and accelerate the design and implementation of COVID-19 phase 2 and 3 vaccine trials. J.O. is a member of the INsTRuCT under the MSC grant agreement Nº860003 (Innovative Training in Myeloid Regulatory Cell Therapy) Consortium, a network of European scientists from academia and industry focused on developing innovative immunotherapies.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical approval of the study was obtained from the relevant authority—the Internal Review Board of Hospital Puerta de Hierro and Fundación Jimenez Diaz.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to starting the study. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Data Availability Statement
The original data contribution presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Sim, J.J.; Huang, C.W.; Selevan, D.C.; Chung, J.; Rutkowski, M.P.; Zhou, H. COVID-19 and Survival in Maintenance Dialysis. Kidney Med. 2021, 3, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, K.; Nangaku, M.; Ryuzaki, M.; Yamakawa, T.; Yoshihiro, O.; Hanafusa, N.; Sakai, K.; Kanno, Y.; Ando, R.; Shinoda, T.; et al. Effectiveness of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines on hemodialysis patients in Japan: A nationwide cohort study. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2022, 27, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; St Denis, K.J.; Hoelzemer, A.; Lam, E.C.; Nitido, A.D.; Sheehan, M.L.; Berrios, C.; Ofoman, O.; Chang, C.C.; Hauser, B.M.; et al. mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine boosters induce neutralizing immunity against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant. Cell 2022, 185, 457–466.e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jian, F.; Xiao, T.; Song, W.; Yisimayi, A.; Huang, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; An, R.; et al. Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies. Nature 2022, 602, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havers, F.P.; Pham, H.; Taylor, C.A.; Whitaker, M.; Patel, K.; Anglin, O.; Kambhampati, A.K.; Milucky, J.; Zell, E.; Chai, S.J.; et al. COVID-19-Associated Hospitalizations among Vaccinated and Unvaccinated Adults 18 Years or Older in 13 US States, January 2021 to April 2022. JAMA Intern. Med. 2022, 182, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paal, M.; Arend, F.M.; Lau, T.; Hasmann, S.; Soreth-Rieke, D.; Sorodoc-Otto, J.; Beuthien, W.; Krappe, J.; Toepfer, M.; Gersdorff, G.V.; et al. Antibody response to mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in haemodialysis patients. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, 2234–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumpf, J.; Siepmann, T.; Lindner, T.; Karger, C.; Schwöbel, J.; Anders, L.; Faulhaber-Walter, R.; Schewe, J.; Martin, H.; Schirutschke, H.; et al. Humoral and cellular immunity to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in renal transplant versus dialysis patients: A prospective, multicenter observational study using mRNA-1273 or BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2021, 9, 100178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Perez, M.; Montes-Casado, M.; Conde, P.; Cervera, I.; Baranda, J.; Berges-Buxeda, M.J.; Perez-Olmeda, M.; Sanchez-Tarjuelo, R.; Utrero-Rico, A.; Lozano-Ojalvo, D.; et al. Development of Potent Cellular and Humoral Immune Responses in Long-Term Hemodialysis Patients After 1273-mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 845882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensouna, I.; Caudwell, V.; Kubab, S.; Acquaviva, S.; Pardon, A.; Vittoz, N.; Bozman, D.F.; Hanafi, L.; Faucon, A.L.; Housset, P. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response after a Third Dose of the BNT162b2 Vaccine in Patients Receiving Maintenance Hemodialysis or Peritoneal Dialysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 79, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirioglu, S.; Kazancioglu, R.; Cebeci, E.; Eren, N.; Sakaci, T.; Alagoz, S.; Tugcu, M.; Tuglular, S.; Sumbul, B.; Seyahi, N.; et al. Humoral Response to BNT162b2 and CoronaVac in Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis: A Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study. Nephron 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizo, N.; Albert, E.; Giménez-Civera, E.; Puchades, M.J.; D’Marco, L.; Gandía-Salmerón, L.; Giménez, E.; Torre, I.; Sancho, A.; Gavela, E.; et al. Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2-Spike-reactive antibody and T-cell responses in chronic kidney disease patients within 3 months after COVID-19 full vaccination. Clin. Kidney J. 2022, 15, 1562–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizo, N.; Giménez, E.; Albert, E.; Zulaica, J.; Rodríguez-Moreno, A.; Rusu, L.; Giménez-Civera, E.; Puchades, M.J.; D’Marco, L.; Gandía-Salmerón, L.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-Spike Antibody and T-Cell Responses Elicited by a Homologous Third mRNA COVID-19 Dose in Hemodialysis and Kidney Transplant Recipients. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anft, M.; Skrzypczyk, S.; Frahnert, M.; Fricke, L.; Zapka, J.; Kühn, D.; Koos, B.; Adamzik, M.; Pfaender, S.; Stervbo, U.; et al. Significant fade of neutralizing antibodies and stable cellular immunity in 4 times COVID-19 vaccinated non-infected compared to COVID-19 convalescent and 3 times vaccinated hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. Rep. 2023, 8, 685–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broseta, J.J.; Rodríguez-Espinosa, D.; Rodríguez, N.; Mosquera, M.D.M.; Marcos, M.; Egri, N.; Pascal, M.; Soruco, E.; Bedini, J.L.; Bayés, B.; et al. Humoral and Cellular Responses to mRNA-1273 and BNT162b2 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines Administered to Hemodialysis Patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 78, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zitt, E.; Davidovic, T.; Schimpf, J.; Abbassi-Nik, A.; Mutschlechner, B.; Ulmer, H.; Benda, M.A.; Sprenger-Mähr, H.; Winder, T.; Lhotta, K. The Safety and Immunogenicity of the mRNA-BNT162b2 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in Hemodialysis Patients. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 704773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, P.; Anand, S.; Han, J.; Montez-Rath, M.E.; Sun, S.; Shang, T.; Parsonnet, J.; Chertow, G.M.; Schiller, B.; Abra, G. COVID-19 Vaccine Type and Humoral Immune Response in Patients Receiving Dialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 33, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, R.A.; Haller, M.C.; Apfalter, P.; Kerschner, H.; Cejka, D. Comparison of BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNtech) and mRNA-1273 (Moderna) SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine immunogenicity in dialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 697–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosconi, G.; Fantini, M.; Righini, M.; Flachi, M.; Semprini, S.; Hu, L.; Chiappo, F.; Veterani, B.; Ambri, K.; Ferrini, F.; et al. Efficacy of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Dialysis Patients: Epidemiological Analysis and Evaluation of the Clinical Progress. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Netea, M.G. Trained Innate Immunity, Epigenetics, and COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1078–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netea, M.G.; Joosten, L.A. Beyond adaptive immunity: Induction of trained immunity by COVID-19 adenoviral vaccines. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e166467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, K.L.; Chonchol, M. Does inflammation affect outcomes in dialysis patients? Semin. Dial. 2018, 31, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano-Ojalvo, D.; Camara, C.; Lopez-Granados, E.; Nozal, P.; Del Pino-Molina, L.; Bravo-Gallego, L.Y.; Paz-Artal, E.; Pion, M.; Correa-Rocha, R.; Ortiz, A.; et al. Differential effects of the second SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine dose on T cell immunity in naive and COVID-19 recovered individuals. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).