Targeting SIRT1/FoxO3a/Nrf2 and PI3K/AKT Pathways with Rebamipide Attenuates Acetic Acid-Induced Colitis in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of Rebamipide on the Severity of Colitis and Colonic Macroscopic Pathological Changes in Rats Exposed to Acetic Acid-Induced Colitis
2.2. Effect of Rebamipide on the Colonic Histopathological Damage and Microscopical Damage Scores in Rats Exposed to Acetic Acid-Induced Colitis
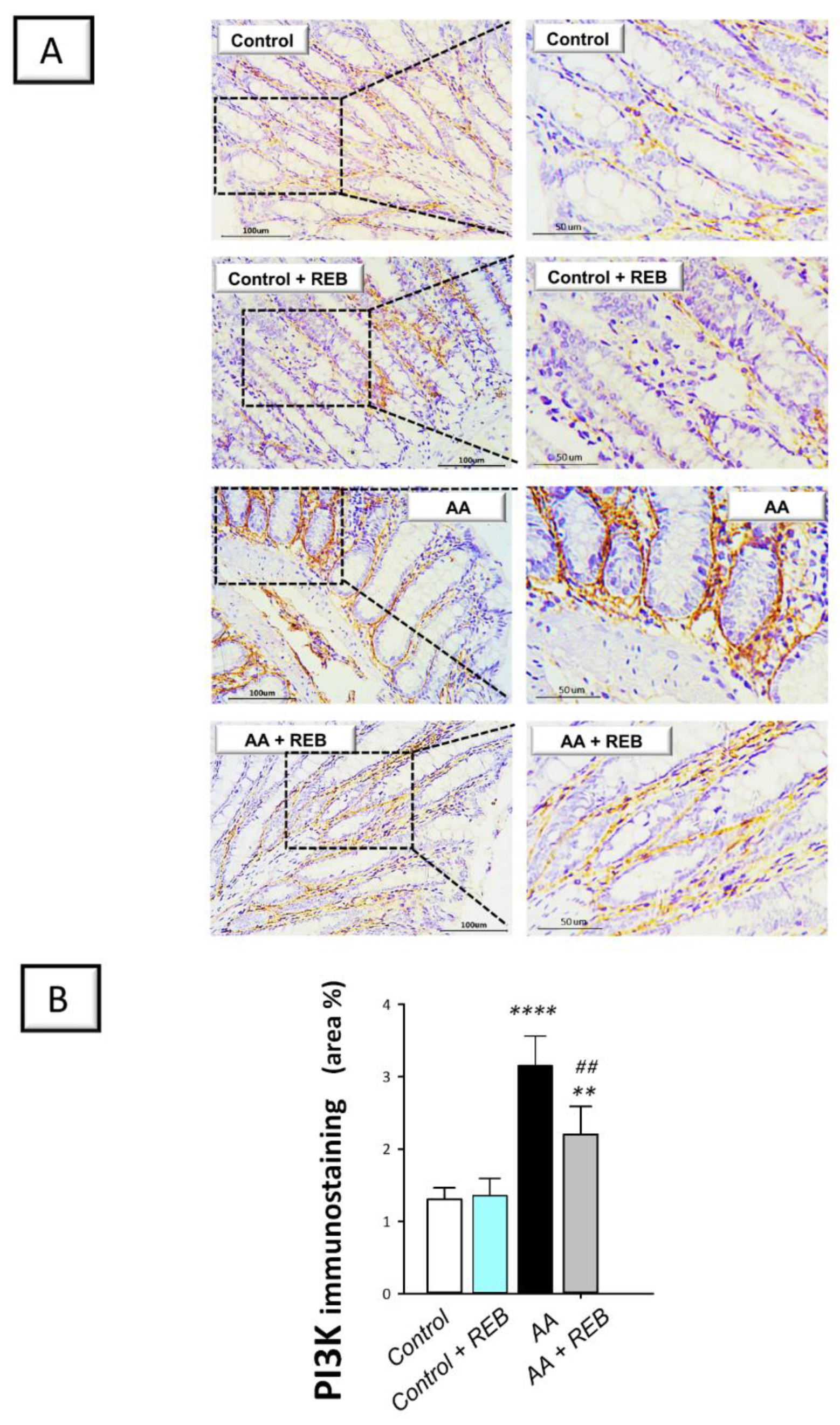
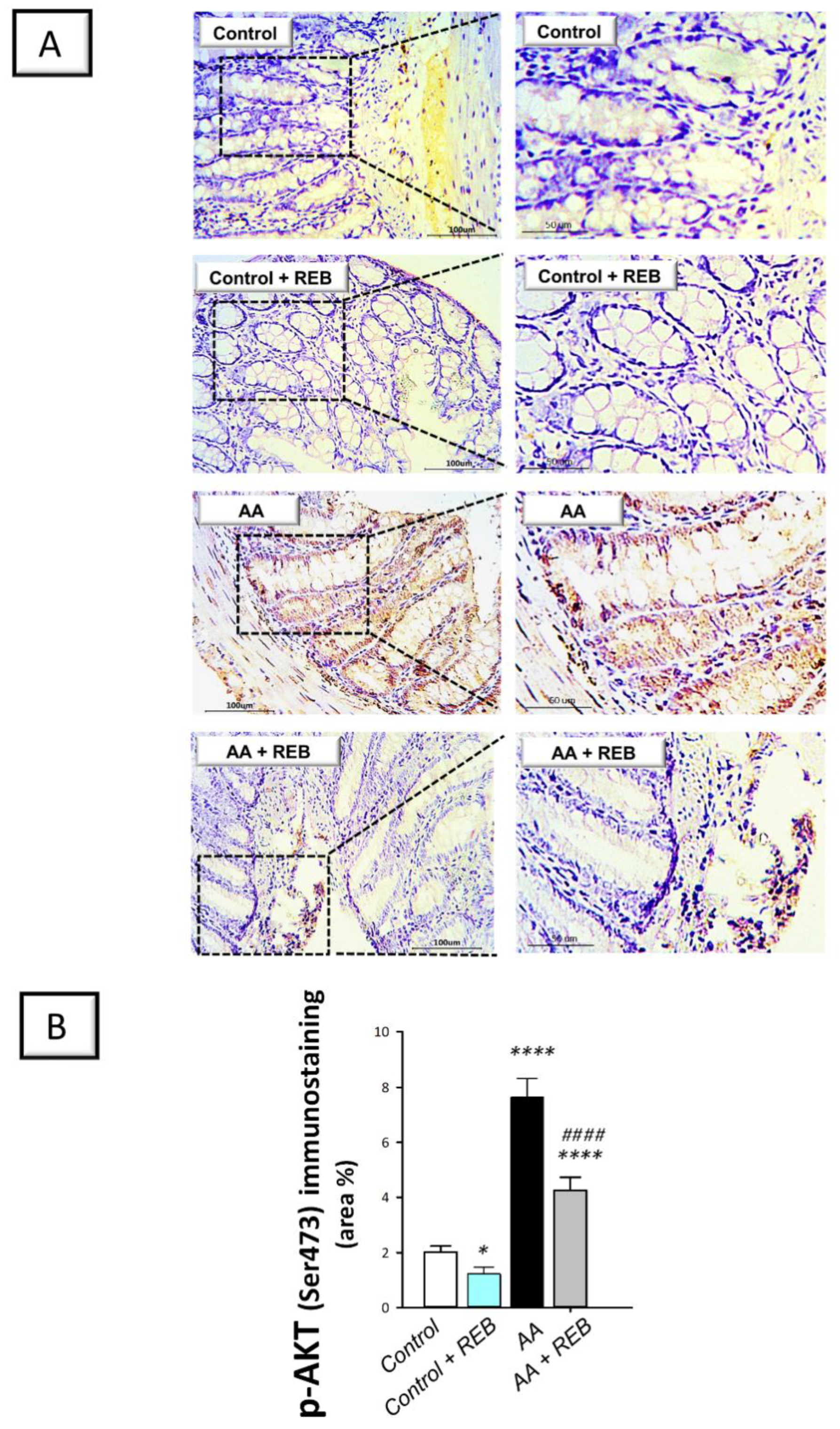
2.3. Effect of Rebamipide on the Inflammatory Signals and Colonic PI3K/AKT Pathway in Rats Exposed to Acetic Acid-Induced Colitis
2.4. Effect of Rebamipide on the Colonic Oxidative Stress Markers and Antioxidant Defenses in Rats Exposed to Acetic Acid-Induced Colitis
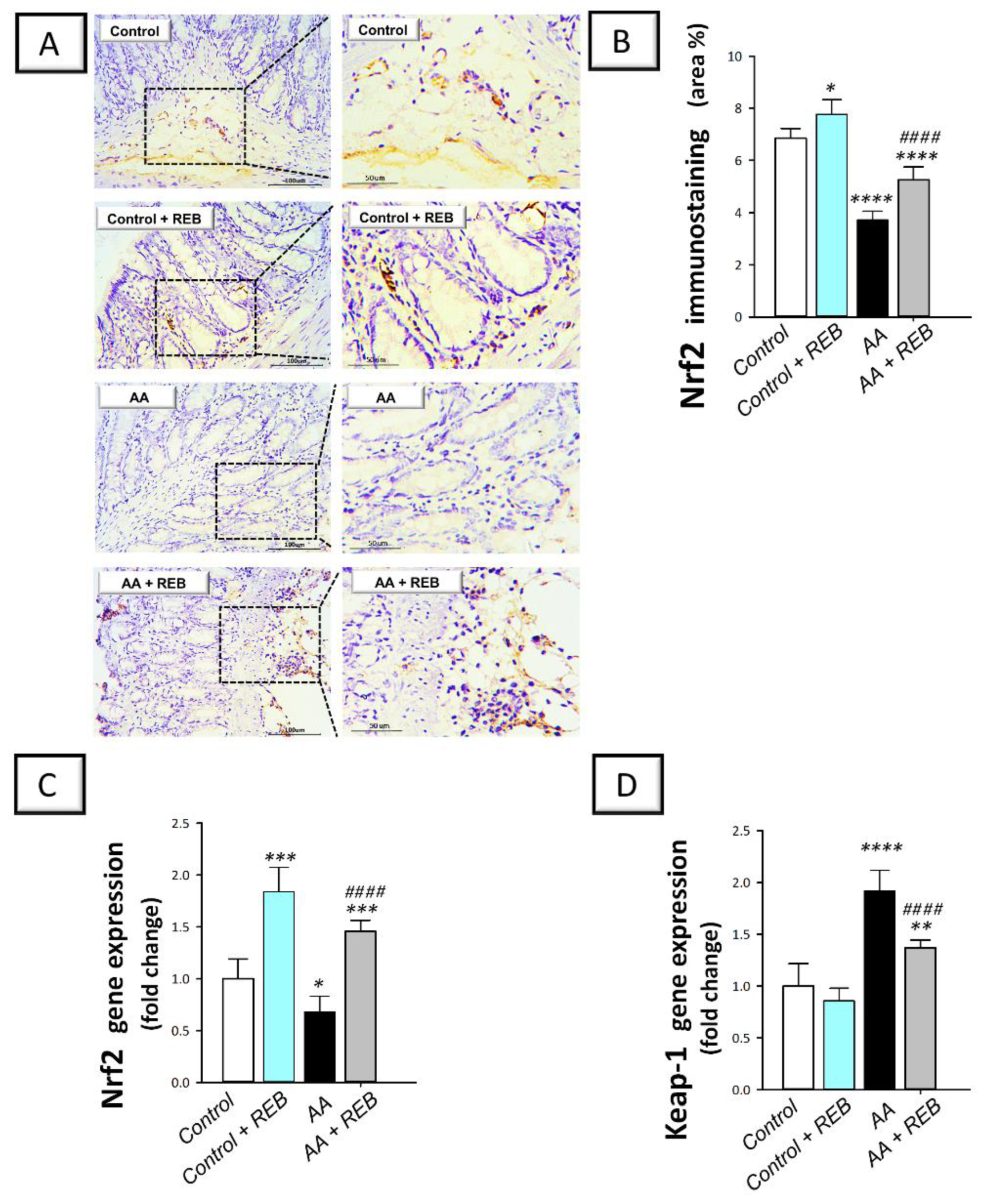
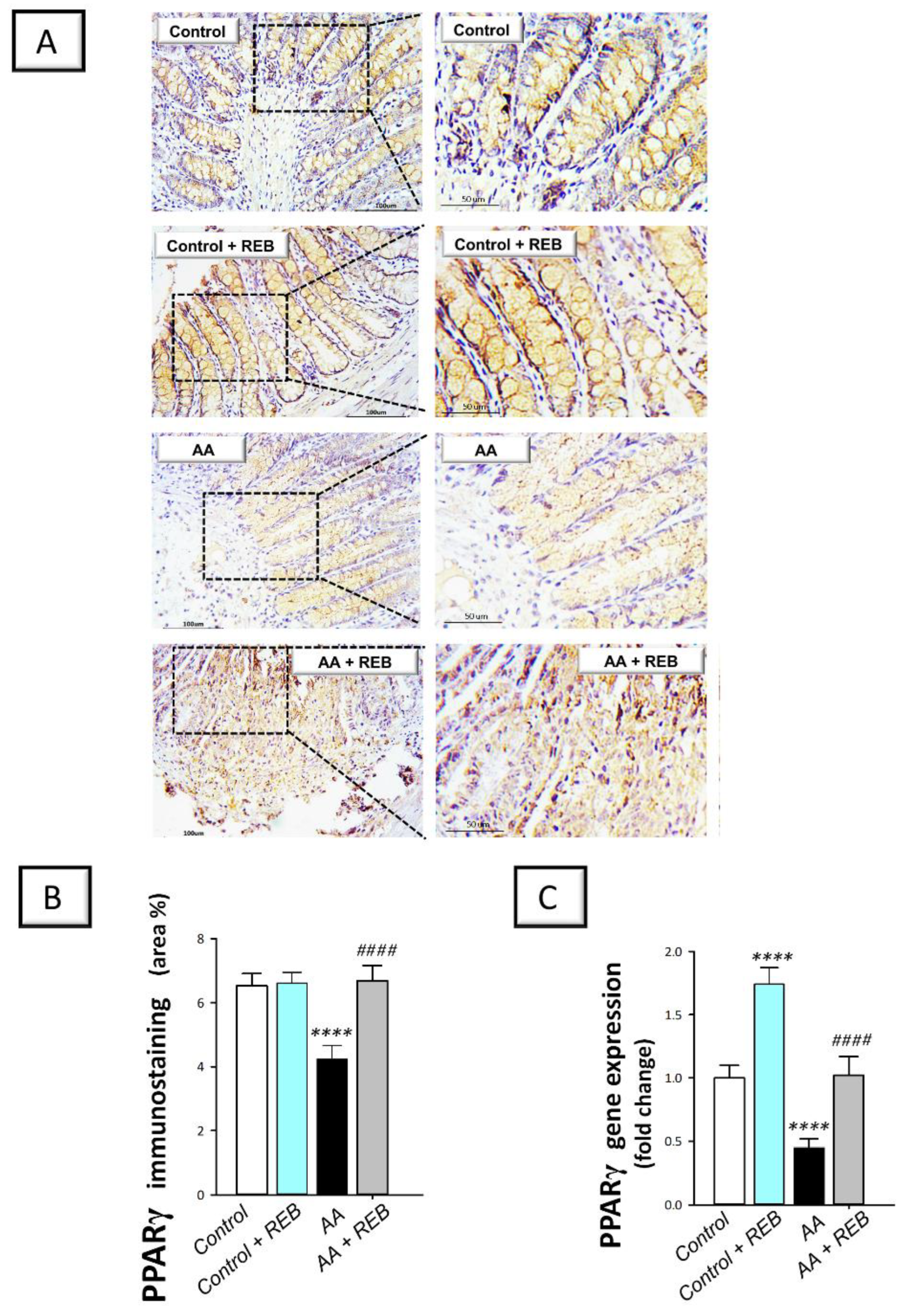
2.5. Effect of Rebamipide on the Colonic Antioxidant Nrf2/Keap-1 Pathway and the Cytoprotective Signal PPAR-γ in Rats Exposed to Acetic Acid-Induced Colitis
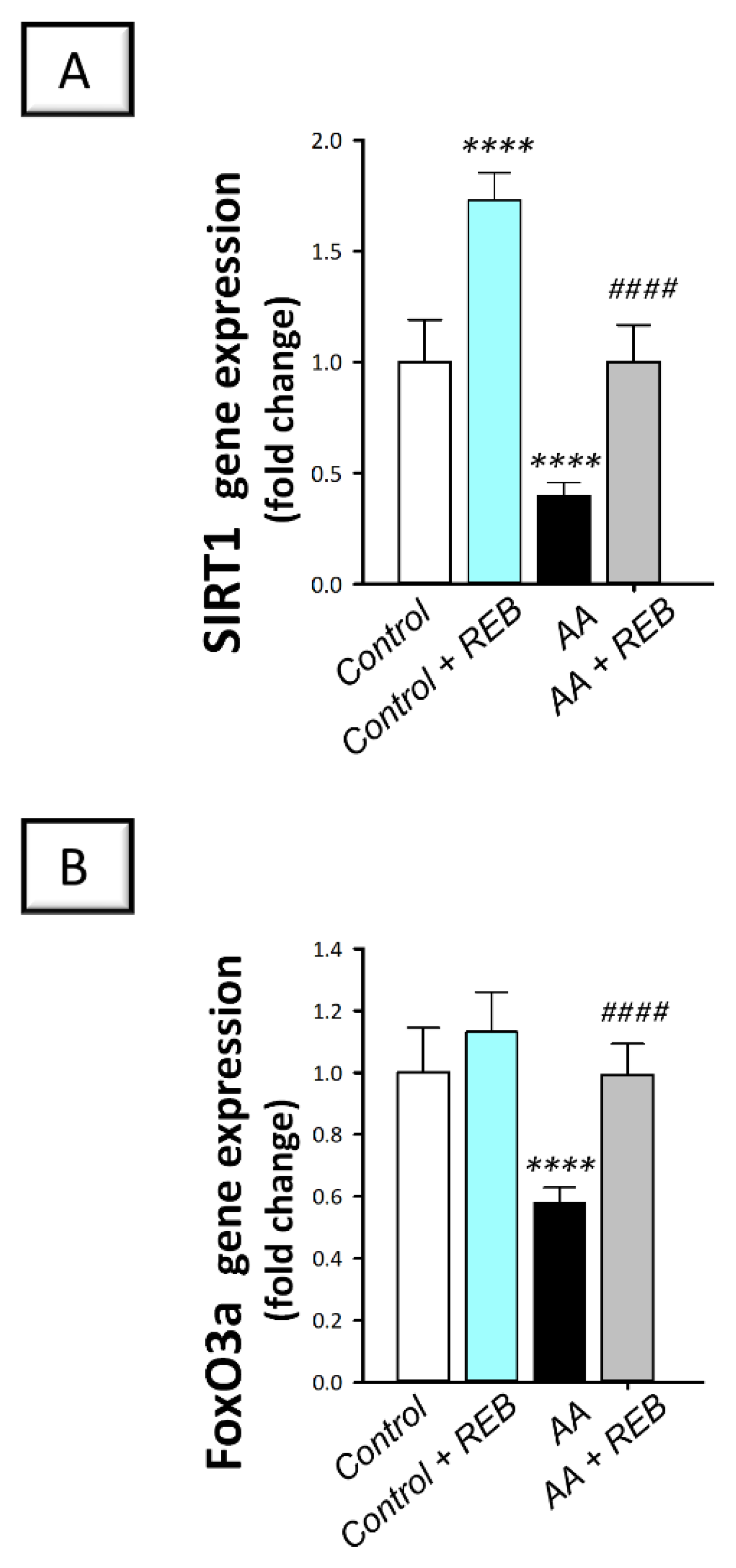
2.6. Effect of Rebamipide on the Colonic Antioxidant SIRT1/FoxO3a Pathway in Rats Exposed to Acetic Acid-Induced Colitis
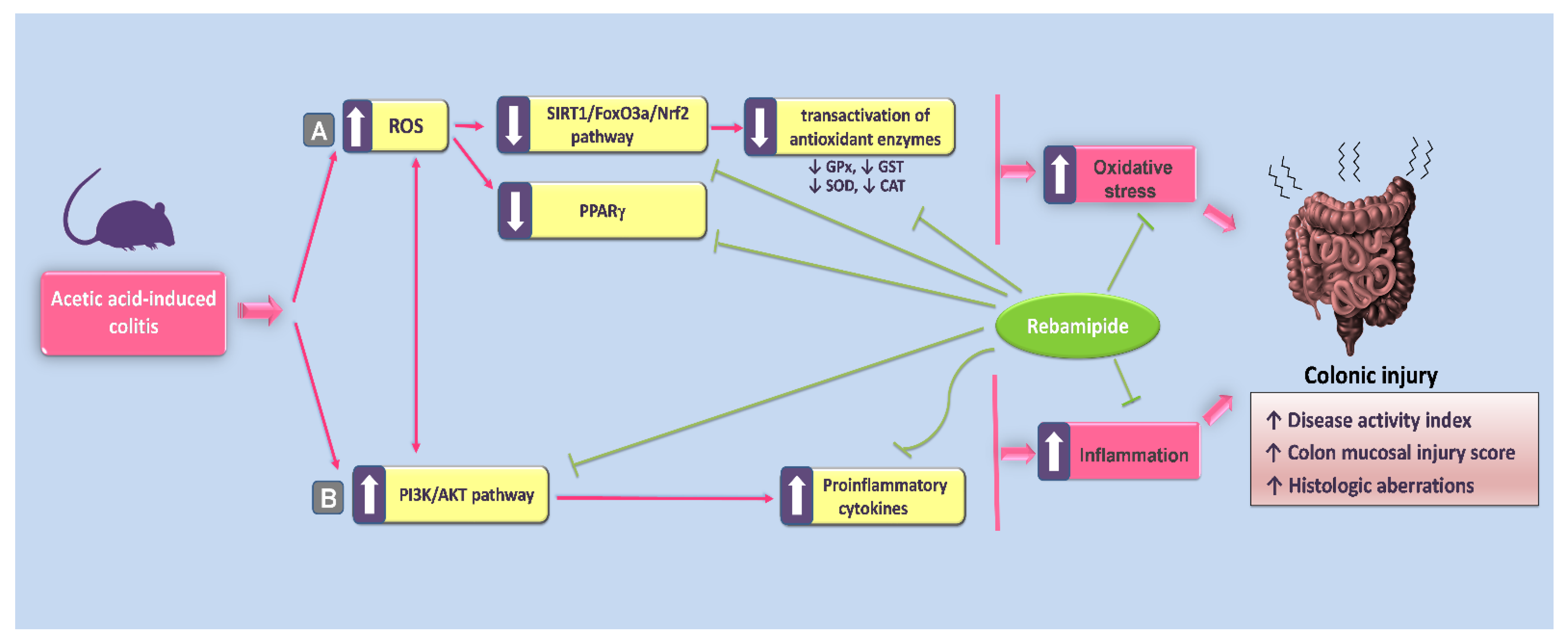
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Experimental Animals
4.3. Induction of Colitis
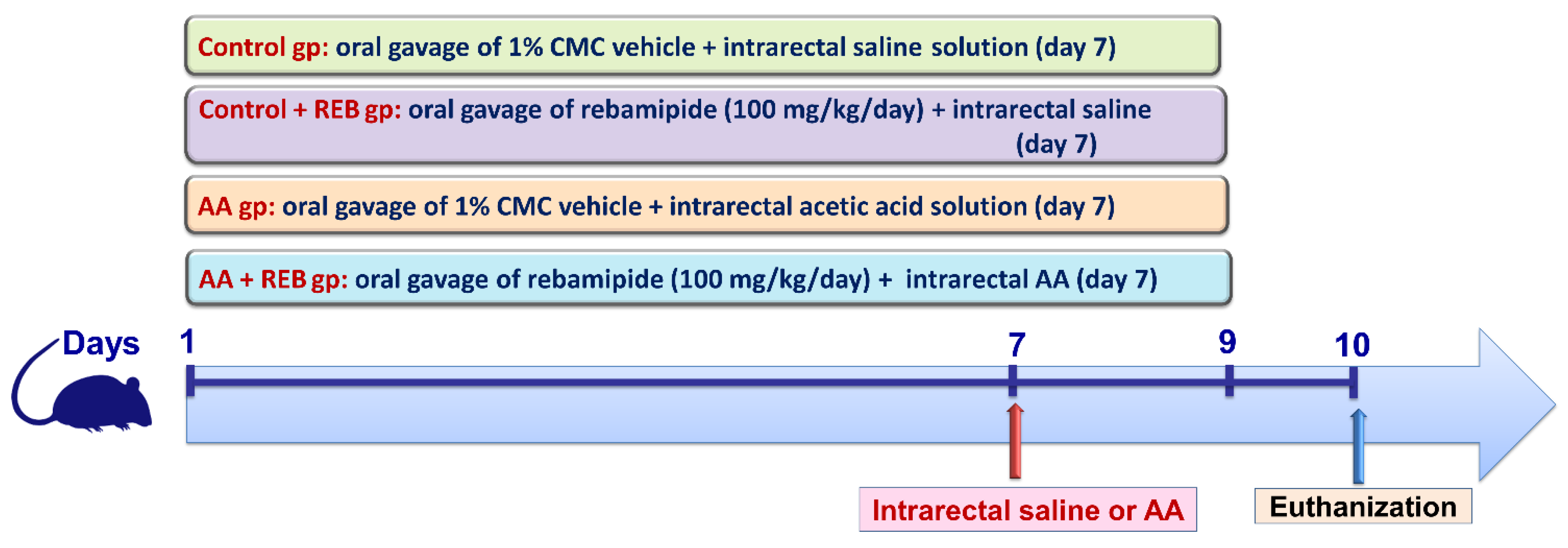
4.4. Experimental Design
4.5. Sample Preparation
4.6. Disease Activity Index (DAI) and Macroscopic Damage Scoring
4.7. Histopathology and Microscopical Damage Scores
4.8. Measurement of TNF-α, IL-6, and CRP
4.9. Assessment of Colon Oxidative Stress Markers
4.10. Immunohistochemical Analysis
4.11. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gajendran, M.; Loganathan, P.; Jimenez, G.; Catinella, A.P.; Ng, N.; Umapathy, C.; Ziade, N.; Hashash, J.G. A comprehensive review and update on ulcerative colitis. Dis. Mon. 2019, 65, 100851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, G.; Trivedi, P.P.; Sandala, B. Oxidative stress in ulcerative colitis: An old concept but a new concern. Free Radic. Res. 2012, 46, 1339–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, M.R.; Salama, R.M.; Zaki, H.F.; El-Sahar, A.E. Vildagliptin attenuates acetic acid-induced colitis in rats via targeting PI3K/Akt/NFkappaB, Nrf2 and CREB signaling pathways and the expression of lncRNA IFNG-AS1 and miR-146a. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 92, 107354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, H.H.; Salama, S.A.; Eid, A.H.; Omar, H.A.; Arafael, S.A.; Maghrabi, I.A. Camel’s milk ameliorates TNBS-induced colitis in rats via downregulation of inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 69, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Sun, W.; Zhou, X.; Gong, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, D.; Xiang, F. Dihydroartemisinin Protects against Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice through Inhibiting the PI3K/AKT and NF-kappaB Signaling Pathways. Biomed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 1415809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Piao, X.; Niu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, C.; Wu, T.; Gu, Q.; Cui, T.; Li, S. Kuijieyuan Decoction Improved Intestinal Barrier Injury of Ulcerative Colitis by Affecting TLR4-Dependent PI3K/AKT/NF-kappaB Oxidative and Inflammatory Signaling and Gut Microbiota. Front. Pharm. 2020, 11, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, T.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z.; Cao, J.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Y. Melatonin-mediated MT2 attenuates colitis induced by dextran sodium sulfate via PI3K/AKT/Nrf2/SIRT1/RORalpha/NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 96, 107779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshazly, S.M.; Elhassanny, A.E.M.; Mahmoud, N.M. Cilostazol protects against acetic acid-induced colitis in rats: Possible role for cAMP/SIRT1 pathway. Eur. J. Pharm. 2020, 881, 173234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Li, Y.; She, Y.; Wu, M.; Hu, Y.; Qin, K.; Li, L.; Yu, H.; Zhao, Q.; Jin, Z.; et al. Renshen Baidu powder protects ulcerative colitis via inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Front. Pharm. 2022, 13, 880589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Banerjee, N.; Barnes, R.C.; Pfent, C.M.; Talcott, S.T.; Dashwood, R.H.; Mertens-Talcott, S.U. Mango polyphenolics reduce inflammation in intestinal colitis-involvement of the miR-126/PI3K/AKT/mTOR axis in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Carcinog. 2017, 56, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rejaie, S.S.; Abuohashish, H.M.; Al-Enazi, M.M.; Al-Assaf, A.H.; Parmar, M.Y.; Ahmed, M.M. Protective effect of naringenin on acetic acid-induced ulcerative colitis in rats. World J. Gasteroenterol. 2013, 19, 5633–5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, S.; Khalil, R.M.; Abdo, W.S.; Nassif, D.; El-Ahwany, E. Olmesartan ameliorates chemically-induced ulcerative colitis in rats via modulating NFκB and Nrf-2/HO-1 signaling crosstalk. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2019, 364, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Z.; Han, C.; Zhang, W.; Xu, M.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, M.; Sun, H.; Xie, H. Systematic understanding of the mechanism and effects of Arctigenin attenuates inflammation in dextran sulfate sodium-induced acute colitis through suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome by SIRT1. Am. J. Trans. Res. 2019, 11, 3992. [Google Scholar]
- Arab, H.H.; Al-Shorbagy, M.Y.; Saad, M.A. Activation of autophagy and suppression of apoptosis by dapagliflozin attenuates experimental inflammatory bowel disease in rats: Targeting AMPK/mTOR, HMGB1/RAGE and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2021, 335, 109368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Yamamoto, M. Molecular mechanisms activating the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway of antioxidant gene regulation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2005, 7, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabel, A.M.; Atef, A.; Borg, H.M.; El-Sheikh, A.A.K.; Al Khabbaz, H.J.; Arab, H.H.; Estfanous, R.S. Perindopril/Ambrosin Combination Mitigates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice: Crosstalk between Toll-Like Receptor 4, the Pro-Inflammatory Pathways, and SIRT1/PPAR-gamma Signaling. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, A.M.; Abdel-Fattah, M.M.; Arab, H.H.; Mohamed, W.R.; Hassanein, E.H.M. Targeting inflammation and redox aberrations by perindopril attenuates methotrexate-induced intestinal injury in rats: Role of TLR4/NF-kappaB and c-Fos/c-Jun pro-inflammatory pathways and PPAR-gamma/SIRT1 cytoprotective signals. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 351, 109732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertin, B.; Dubuquoy, L.; Colombel, J.F.; Desreumaux, P. PPAR-gamma in ulcerative colitis: A novel target for intervention. Curr. Drug Targets 2013, 14, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Deng, W.; Li, F.; Xiang, L.; Lv, P.; Chen, Y. Treatment with butyrate alleviates dextran sulfate sodium and Clostridium difficile-induced colitis by preventing activity of Th17 cells via regulation of SIRT1/mTOR in mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2023, 111, 109155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa Melo, N.M.; Almeida, M.V.S.; de Oliveira Campos, D.M.; de Oliveira, C.B.S.; Oliveira, J.I.N. Animal models for inducing inflammatory bowel diseases: Integrative review. Health Sci. J. 2021, 11, 80–87. [Google Scholar]
- Zaghloul, M.S.; Elshal, M.; Abdelmageed, M.E. Preventive empagliflozin activity on acute acetic acid-induced ulcerative colitis in rats via modulation of SIRT-1/PI3K/AKT pathway and improving colon barrier. Environ. Toxicol. Pharm. 2022, 91, 103833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuralay, F.; Yildiz, C.; Ozutemiz, O.; Islekel, H.; Caliskan, S.; Bingol, B.; Ozkal, S. Effects of trimetazidine on acetic acid-induced colitis in female Swiss rats. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2003, 66, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelsameea, A.A.; Alsemeh, A.E.; Alabassery, N.; Samy, W.; Fawzy, A.; Abbas, N.A.T. Icosapent ethyl alleviates acetic acid-induced ulcerative colitis via modulation of SIRT1 signaling pathway in rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 115, 109621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Yoshikawa, T.; Tarnawski, A. Rebamipide: Overview of its mechanisms of action and efficacy in mucosal protection and ulcer healing. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1998, 43, 5s–13s. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hagiwara, T.; Mukaisho, K.; Ling, Z.Q.; Sakano, T.; Sugihara, H.; Hattori, T. Rebamipide contributes to reducing adverse effects of long-term administration of omeprazole in rats. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2007, 52, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.S.; Lim, J.Y.; Chun, H.J.; Lee, M.; Kim, E.S.; Keum, B.; Seo, Y.S.; Jeen, Y.T.; Um, S.H.; Lee, H.S.; et al. The effect of polaprezinc on gastric mucosal protection in rats with ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage: Comparison study with rebamipide. Life Sci. 2013, 93, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, Y.; Matsui, H.; Muramatsu, M.; Shimokawa, O.; Shibahara, T.; Yanaka, A.; Nakahara, A.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Tanaka, N.; Nakamura, Y. Rebamipide significantly inhibits indomethacin-induced mitochondrial damage, lipid peroxidation, and apoptosis in gastric epithelial RGM-1 cells. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2005, 50, S76–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmansy, R.A.; Seleem, H.S.; Mahmoud, A.R.; Hassanein, E.H.M.; Ali, F.E.M. Rebamipide potentially mitigates methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity via inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation: A molecular and histochemical study. Anat. Rec. (Hoboken) 2021, 304, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wahab, B.A.; Ali, F.E.M.; Alkahtani, S.A.; Alshabi, A.M.; Mahnashi, M.H.; Hassanein, E.H.M. Hepatoprotective effect of rebamipide against methotrexate-induced hepatic intoxication: Role of Nrf2/GSK-3β, NF-κβ-p65/JAK1/STAT3, and PUMA/Bax/Bcl-2 signaling pathways. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2020, 42, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Krishnamurthy, S. Rebamipide Mitigates Impairments in Mitochondrial Function and Bioenergetics with alpha-Synuclein Pathology in 6-OHDA-Induced Hemiparkinson’s Model in Rats. Neurotox Res. 2019, 35, 542–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, T.; Maeda, T.; Nagamoto, H.; Kumakura, T.; Takai, M.; Mori, T. Rebamipide enema is effective for treatment of experimental dextran sulfate sodium induced colitis in rats. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2005, 50 (Suppl. S1), S124–S131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogasawara, N.; Sasaki, M.; Itoh, Y.; Tokudome, K.; Kondo, Y.; Ito, Y.; Tanida, S.; Kamiya, T.; Kataoka, H.; Joh, T.; et al. Rebamipide suppresses TLR-TBK1 signaling pathway resulting in regulating IRF3/7 and IFN-alpha/beta reduction. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2011, 48, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, K.A.; Jurenka, J.S. Inflammatory bowel disease Part 1: Ulcerative colitis--pathophysiology and conventional and alternative treatment options. Altern. Med. Rev. 2003, 8, 247–283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arab, H.H.; Eid, A.H.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Senousy, M.A. Linagliptin mitigates experimental inflammatory bowel disease in rats by targeting inflammatory and redox signaling. Life Sci. 2021, 273, 119295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shen, L.; Lv, T.; Wang, R.; Zhang, N.; Peng, H.; Diao, W. Salidroside attenuates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice via SIRT1/FoxOs signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharm. 2019, 861, 172591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arafa, E.A.; Mohamed, W.R.; Zaher, D.M.; Omar, H.A. Gliclazide attenuates acetic acid-induced colitis via the modulation of PPARgamma, NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2020, 391, 114919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arab, H.H.; Ashour, A.M.; Gad, A.M.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Kabel, A.M. Activation of AMPK/mTOR-driven autophagy and inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome by saxagliptin ameliorate ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage. Life Sci. 2021, 280, 119743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, H.H.; Al-Shorbagy, M.Y.; Abdallah, D.M.; Nassar, N.N. Telmisartan attenuates colon inflammation, oxidative perturbations and apoptosis in a rat model of experimental inflammatory bowel disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.D.; Hong, K.W. Preventive effect of rebamipide on gastric lesions induced by ischemia-reperfusion in the rat. J. Pharm. Exp. 1995, 275, 340–344. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, T.; Zinchuk, V.S.; Garcia del Saz, E.; Jiang, F.; Yamasaki, Y.; Kataoka, S.; Okada, T.; Tsunawaki, S.; Seguchi, H. Suppressive effect of rebamipide, an antiulcer agent, against activation of human neutrophils exposed to formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine. Histol. Histopathol. 2000, 15, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhonde, M.R.; Gupte, R.D.; Dadarkar, S.D.; Jadhav, M.G.; Tannu, A.A.; Bhatt, P.; Bhatia, D.R.; Desai, N.K.; Deore, V.; Yewalkar, N.; et al. A novel mTOR inhibitor is efficacious in a murine model of colitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008, 295, G1237–G1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuzun, A.; Erdil, A.; Inal, V.; Aydin, A.; Bagci, S.; Yesilova, Z.; Sayal, A.; Karaeren, N.; Dagalp, K. Oxidative stress and antioxidant capacity in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Biochem. 2002, 35, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.C.; Park, H.J.; Lee, K.M.; Shin, D.G. Free radical scavenger effect of rebamipide in sperm processing and cryopreservation. Asian J. Androl. 2003, 5, 195–201. [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai, K.; Osaka, T.; Yamasaki, K. Protection by rebamipide against acetic acid-induced colitis in rats: Relationship with its antioxidative activity. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1998, 43, 125S–133S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Naito, Y.; Tanigawa, T.; Kondo, M. Free radical scavenging activity of the novel anti-ulcer agent rebamipide studied by electron spin resonance. Arzneimittelforschung 1993, 43, 363–366. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, J.W.; Yao, H.; Caito, S.; Sundar, I.K.; Rahman, I. Redox regulation of SIRT1 in inflammation and cellular senescence. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 61, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardizzone, A.; Filippone, A.; Mannino, D.; Scuderi, S.A.; Casili, G.; Lanza, M.; Cucinotta, L.; Campolo, M.; Esposito, E. Ulva pertusa, a Marine Green Alga, Attenuates DNBS-Induced Colitis Damage via NF-kappaB/Nrf2/SIRT1 Signaling Pathways. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardyn, J.D.; Ponsford, A.H.; Sanderson, C.M. Dissecting molecular cross-talk between Nrf2 and NF-kappaB response pathways. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2015, 43, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Ubaid, S.J. Role of silent information regulator 1 (SIRT1) in regulating oxidative stress and inflammation. Inflammation 2020, 43, 1589–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, F.; Hoberg, J.E.; Ramsey, C.S.; Keller, M.D.; Jones, D.R.; Frye, R.A.; Mayo, M.W. Modulation of NF-kappaB-dependent transcription and cell survival by the SIRT1 deacetylase. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 2369–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korbecki, J.; Bobinski, R.; Dutka, M. Self-regulation of the inflammatory response by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Inflamm. Res. 2019, 68, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wahab, B.A.; Alkahtani, S.A.; Alqahtani, A.A.; Hassanein, E.H.M. Umbelliferone ameliorates ulcerative colitis induced by acetic acid via modulation of TLR4/NF-κB-p65/iNOS and SIRT1/PPARγ signaling pathways in rats. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 37644–37659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurata, S.; Nakashima, T.; Osaki, T.; Uematsu, N.; Shibamori, M.; Sakurai, K.; Kamiya, S. Rebamipide protects small intestinal mucosal injuries caused by indomethacin by modulating intestinal microbiota and the gene expression in intestinal mucosa in a rat model. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2015, 56, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Q.; Xu, J.M.; Xiang, L.; Hu, Y.M.; Hu, X.P.; Xu, Z.W. Change of nitric oxide in experimental colitis and its inhibition by melatonin in vivo and in vitro. Postgrad. Med. J. 2005, 81, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, S.A.; Arab, H.H.; Hassan, M.H.; Maghrabi, I.A. Cadmium-induced hepatocellular injury: Modulatory effects of γ-glutamyl cysteine on the biomarkers of inflammation, DNA damage, and apoptotic cell death. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2019, 52, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvez, J.; Coelho, G.; Crespo, M.E.; Cruz, T.; Rodriguez-Cabezas, M.E.; Concha, A.; Gonzalez, M.; Zarzuelo, A. Intestinal anti-inflammatory activity of morin on chronic experimental colitis in the rat. Aliment. Pharm. 2001, 15, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihara, M.; Uchiyama, M. Determination of malonaldehyde precursor in tissues by thiobarbituric acid test. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 86, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, R.A.; Burk, R.F. Glutathione peroxidase activity in selenium-deficient rat liver. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1976, 71, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keen, J.H.; Habig, W.H.; Jakoby, W.B. Mechanism for the several activities of the glutathione S-transferases. J. Biol. Chem. 1976, 251, 6183–6188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.K. Colorimetric assay of catalase. Anal. Biochem. 1972, 47, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fikry, E.M.; Gad, A.M.; Eid, A.H.; Arab, H.H. Caffeic acid and ellagic acid ameliorate adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats via targeting inflammatory signals, chitinase-3-like protein-1 and angiogenesis. Biomed. Pharm. 2019, 110, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, H.H.; Eid, A.H.; El-Sheikh, A.A.K.; Arafa, E.A.; Ashour, A.M. Irbesartan reprofiling for the amelioration of ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury in rats: Role of inflammation, apoptosis, and autophagy. Life Sci. 2022, 308, 120939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanein, E.H.M.; Shalkami, A.S.; Khalaf, M.M.; Mohamed, W.R.; Hemeida, R.A.M. The impact of Keap1/Nrf2, P(38)MAPK/NF-κB and Bax/Bcl2/caspase-3 signaling pathways in the protective effects of berberine against methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity. Biomed. Pharm. 2019, 109, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
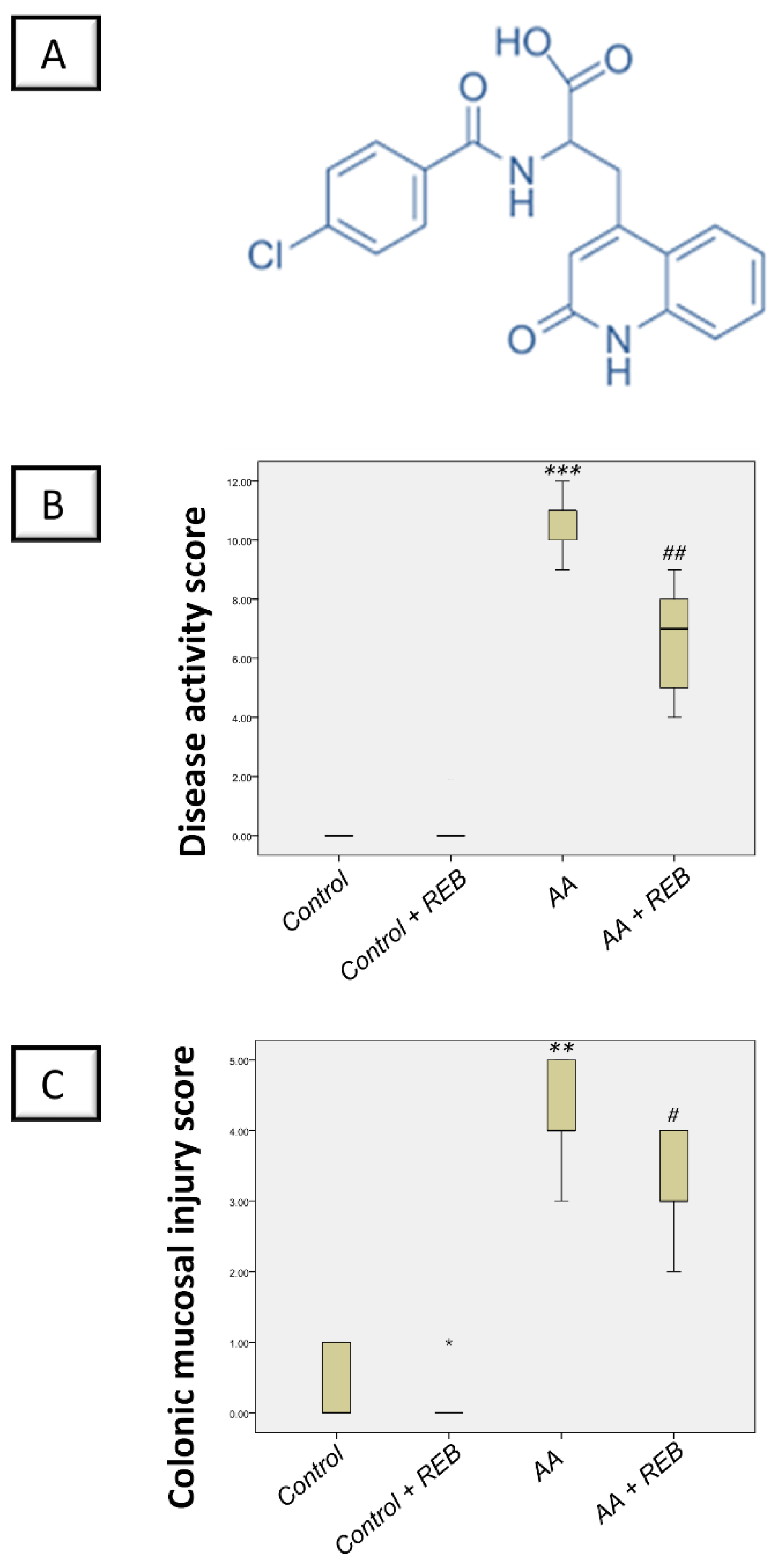
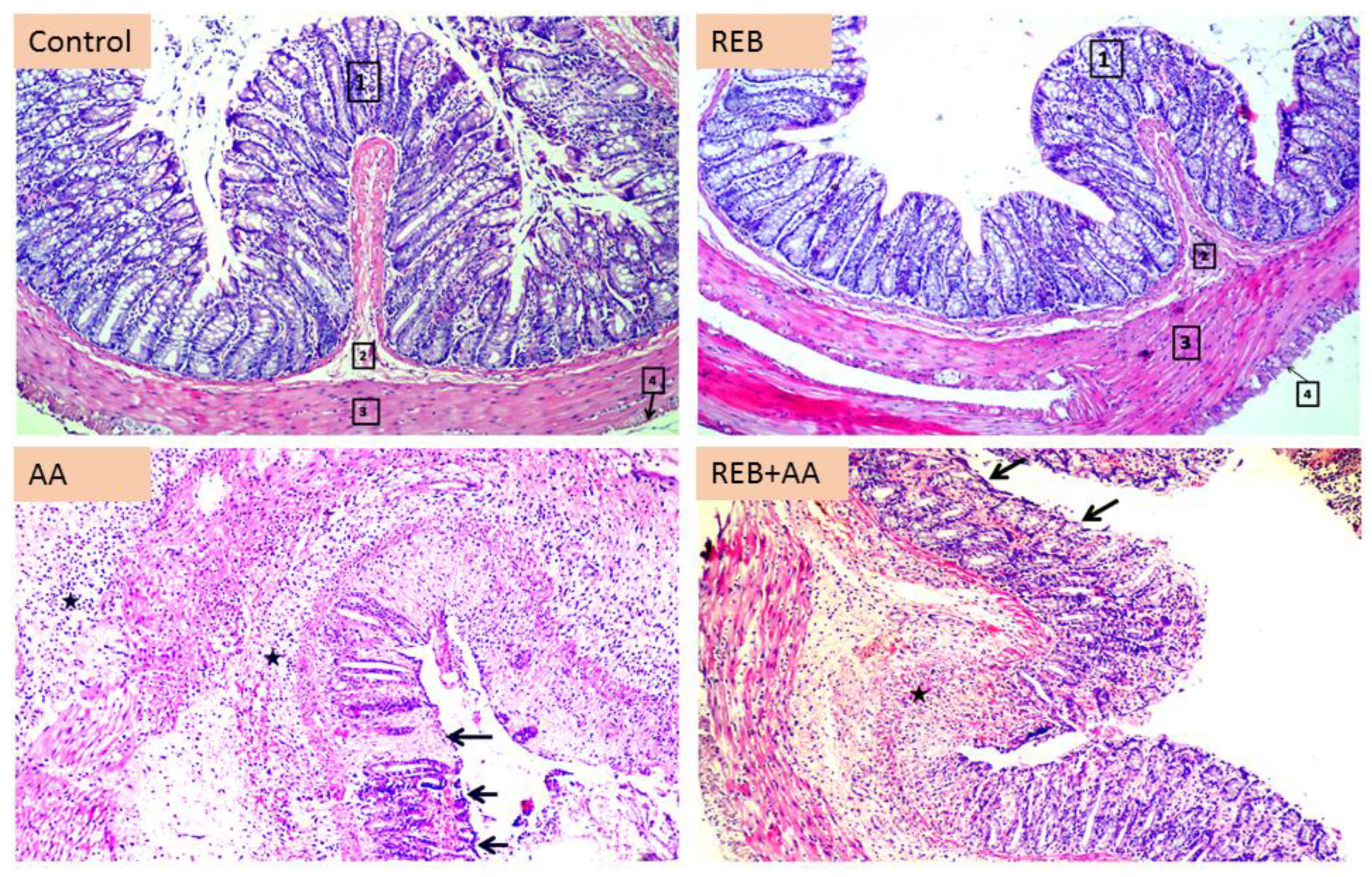
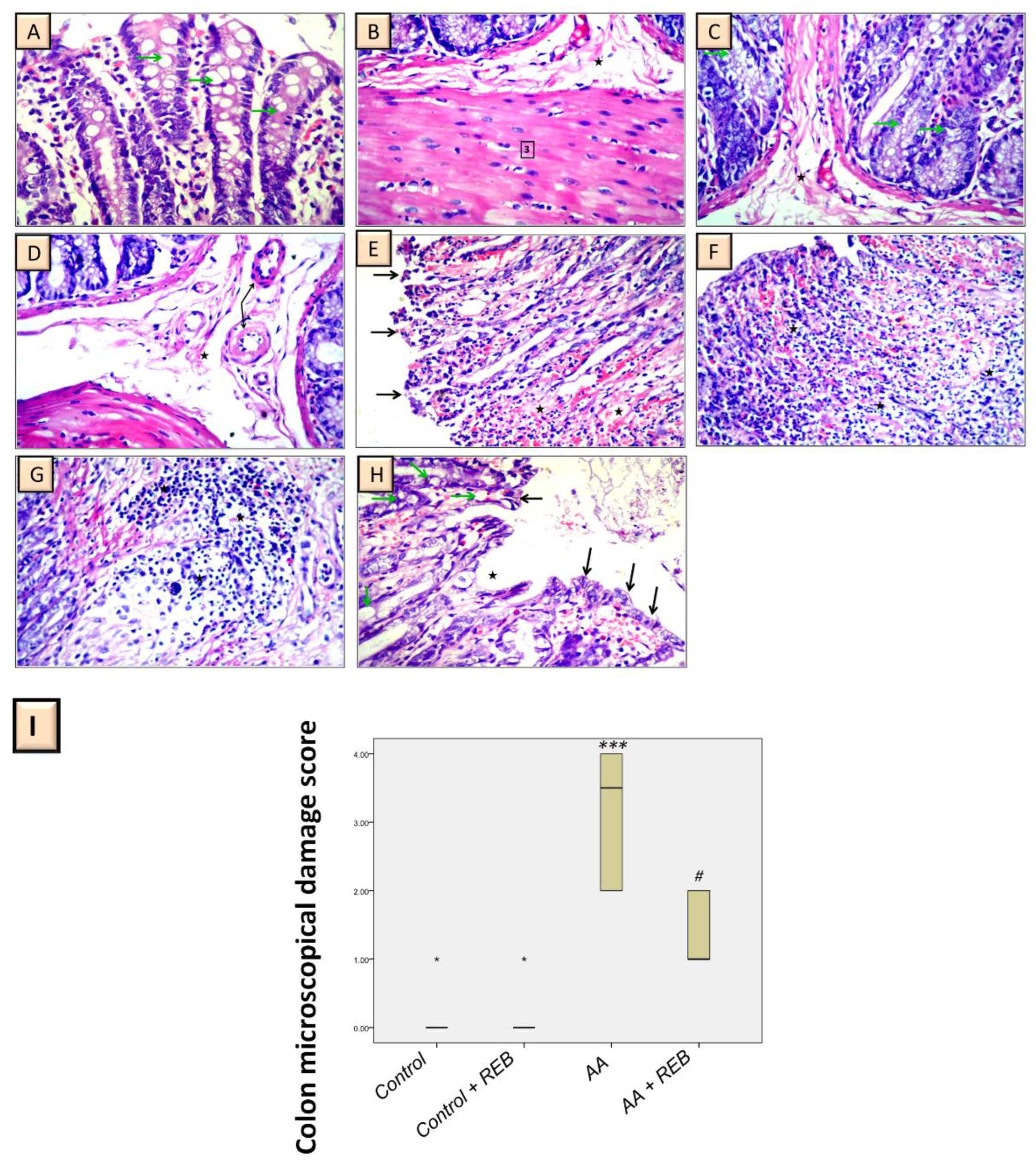
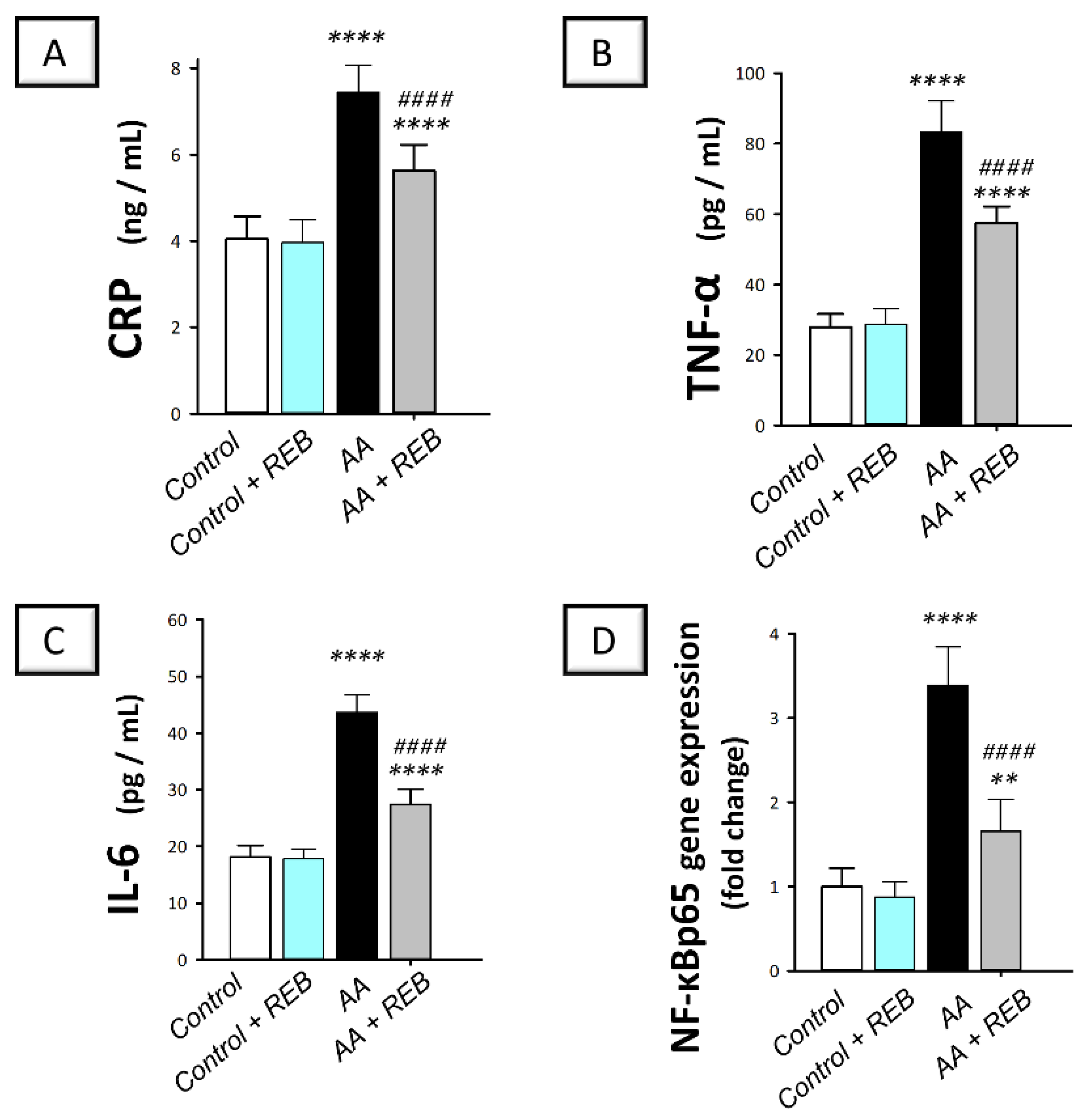

| Score | Criterion |
|---|---|
| 0 | No injury |
| 1 | Mild hyperemia with a tiny portion of edema and no erosion or ulceration |
| 2 | Moderate hyperemia with moderate edema and one erosion site |
| 3 | Moderate hyperemia with moderate edema and two erosion sites |
| 4 | Severe hyperemia with severe edema, and inflammation covering the mucosal layer, and with major inflammation not exceeding 1 cm in diameter |
| 5 | Severe hyperemia with severe edema, swelling, bleeding, and inflammation covering the mucosal layer, and with major inflammation measuring more than 1 cm in diameter. |
| Target Gene | Gene Accession Number | The Nucleotide Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| NF-κB | XM_006233360.4 | F: TGGGACGACACCTCTACACA R: GGAGCTCATCTCATAGTTGTCC |
| Nrf2 | NM_001399173.1 | F: ATTGCTGTCCATCTCTGTCAG R: GCTATTTTCCATTCCCGAGTTAC |
| Keap-1 | XM_006242591.3 | F: TCAGCTAGAGGCGTACTGGA R: TTCGGTTACCATCCTGCGAG |
| PPAR-γ | NM_001145367.1 | F: GGGACGCTGAAGAAGAGACCTG R: CACAGTCCGGTCAGAAAGTGA |
| SIRT1 | NM_001414959.1 | F: CGGTCTGTCAGCATCATCTTCC R: CGCCTTATCCTCTAGTTCCTGTG |
| FOXO-3 | NM_001106395.1 | F: GCCTCATCTCAAAGCTGGGT R: AGTTCTGCTCCACGGGAAAG |
| GAPDH | NM_017008.4 | F: TGCTGGTGCTGAGTATGTCG R: TTGAGAGCAATGCCAGCC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdel-Fattah, M.M.; Hassanein, E.H.M.; Sayed, A.M.; Alsufyani, S.E.; El-Sheikh, A.A.K.; Arab, H.H.; Mohamed, W.R. Targeting SIRT1/FoxO3a/Nrf2 and PI3K/AKT Pathways with Rebamipide Attenuates Acetic Acid-Induced Colitis in Rats. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040533
Abdel-Fattah MM, Hassanein EHM, Sayed AM, Alsufyani SE, El-Sheikh AAK, Arab HH, Mohamed WR. Targeting SIRT1/FoxO3a/Nrf2 and PI3K/AKT Pathways with Rebamipide Attenuates Acetic Acid-Induced Colitis in Rats. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(4):533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040533
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdel-Fattah, Maha M., Emad H. M. Hassanein, Ahmed M. Sayed, Shuruq E. Alsufyani, Azza A. K. El-Sheikh, Hany H. Arab, and Wafaa R. Mohamed. 2023. "Targeting SIRT1/FoxO3a/Nrf2 and PI3K/AKT Pathways with Rebamipide Attenuates Acetic Acid-Induced Colitis in Rats" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 4: 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040533
APA StyleAbdel-Fattah, M. M., Hassanein, E. H. M., Sayed, A. M., Alsufyani, S. E., El-Sheikh, A. A. K., Arab, H. H., & Mohamed, W. R. (2023). Targeting SIRT1/FoxO3a/Nrf2 and PI3K/AKT Pathways with Rebamipide Attenuates Acetic Acid-Induced Colitis in Rats. Pharmaceuticals, 16(4), 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040533






