Role of MicroRNA-502-3p in Human Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
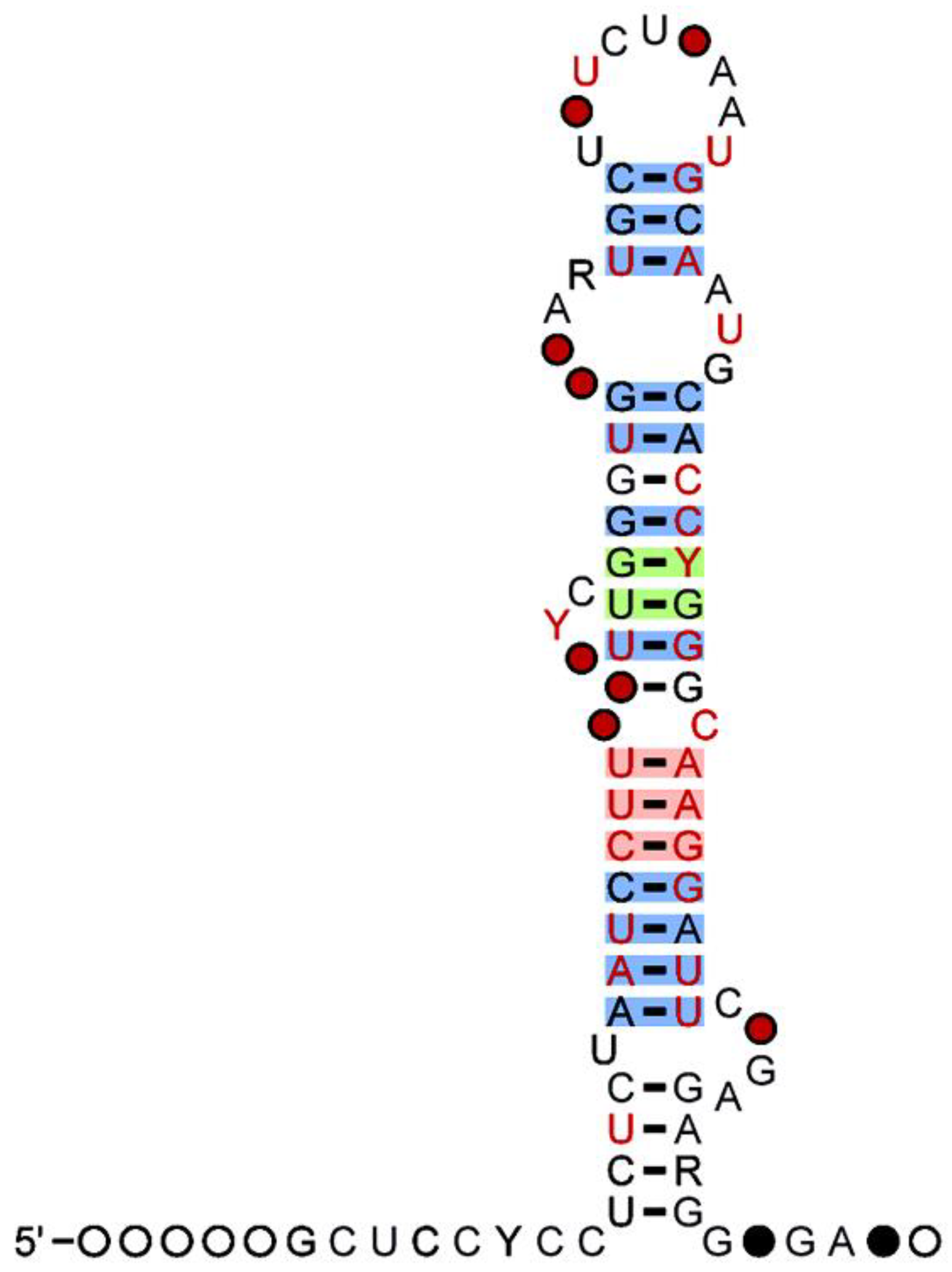
2. MicroRNAs
3. MiR-500 Family
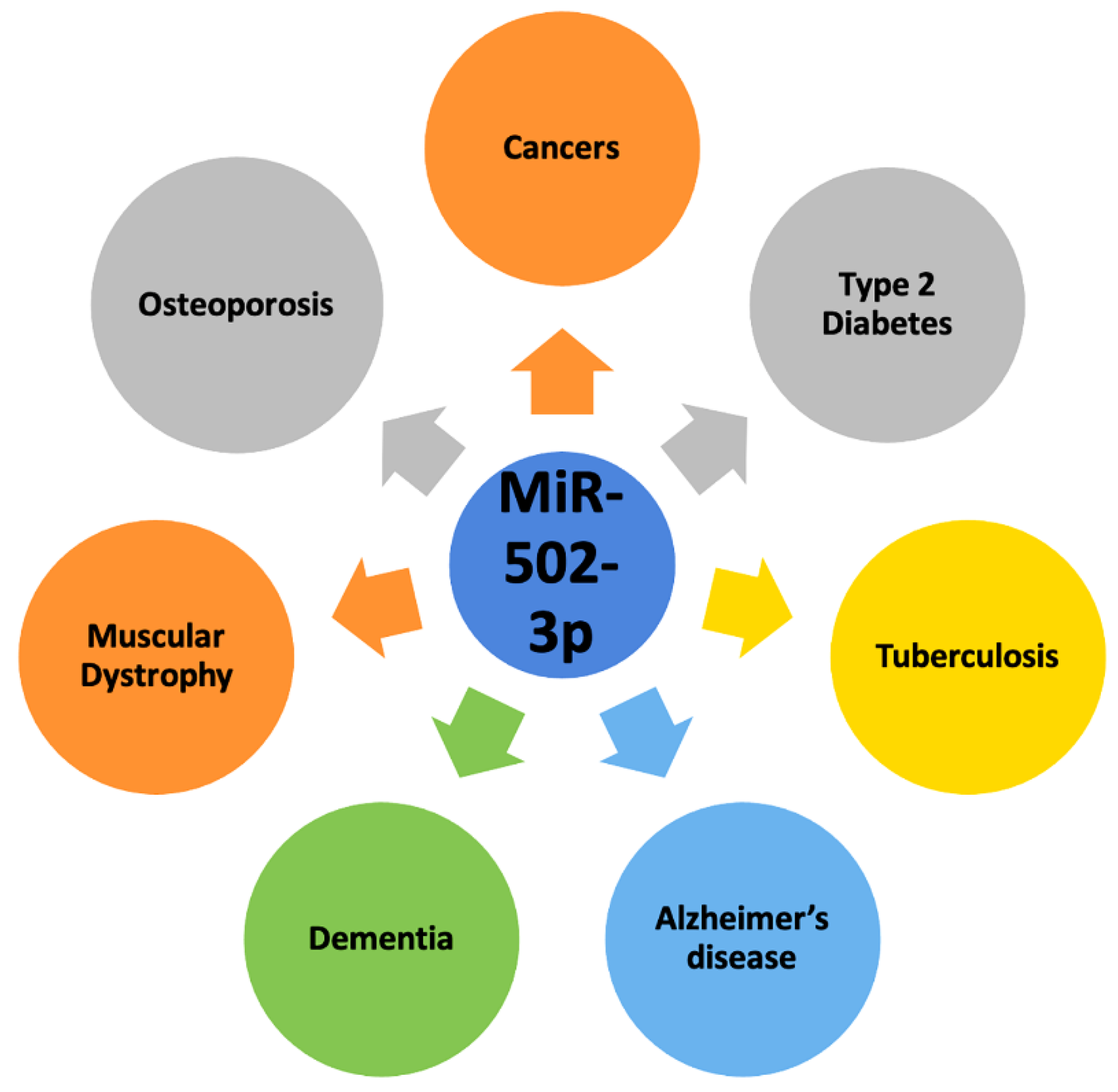
4. MiR-502-3p and Human Diseases
4.1. Osteoporotic Fractures
4.2. Diabetes
4.3. Tuberculosis
4.4. Other Human Diseases
5. MiR-502-3p and Human Cancers
5.1. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
5.2. Invasive Pituitary Adenoma
5.3. Colorectal Cancer
5.4. Gallbladder Cancer
5.5. Lung Cancer
5.6. Pancreatic Cancer
5.7. Stomach Cancer
5.8. Other Cancers
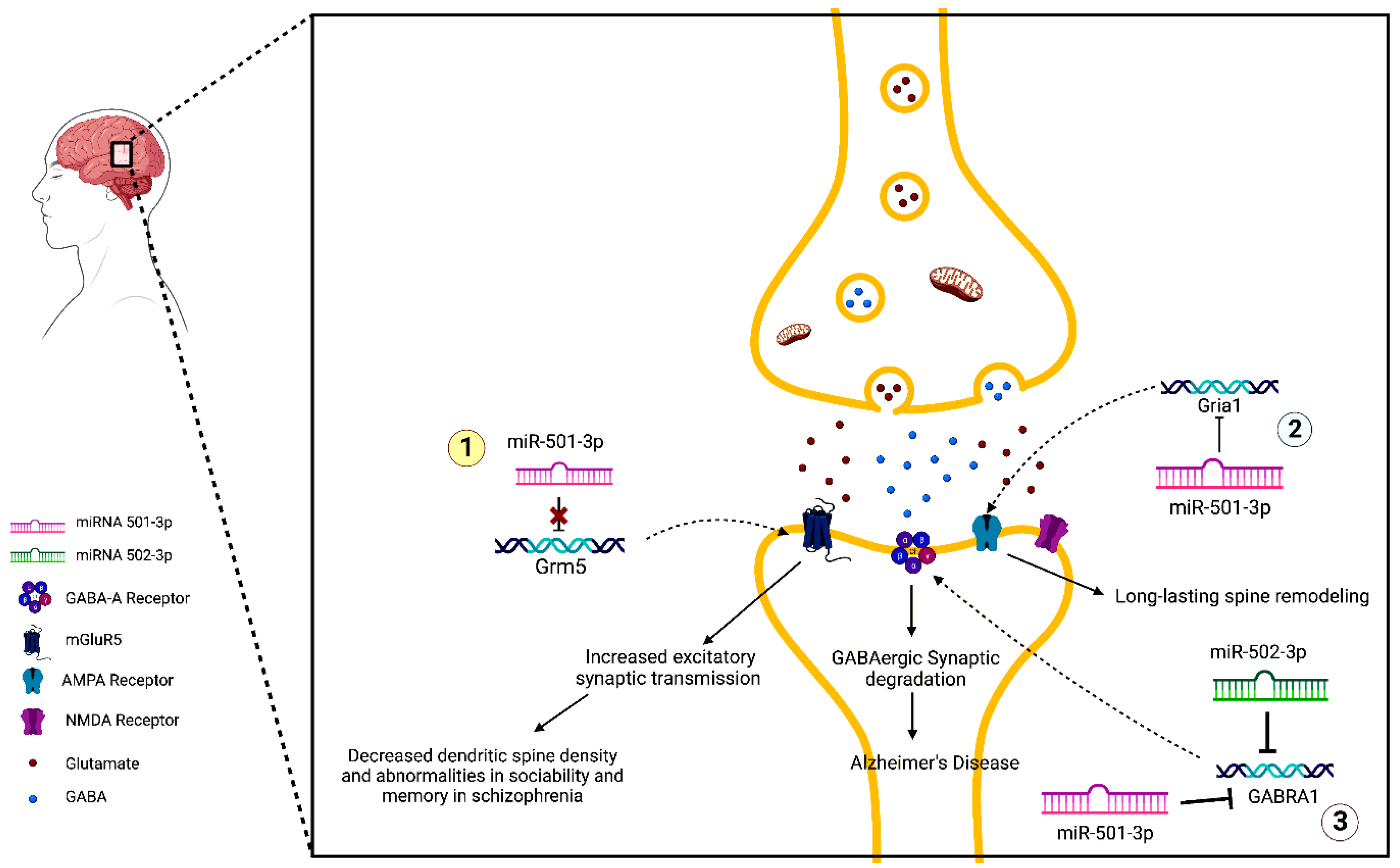
6. MiR-502-3p and Neurodegenerative Disease
7. MiR-501-3p and Neurodegenerative Disease
7.1. Schizophrenia
7.2. Cognition and Memory
7.3. Alzheimer’s Disease
8. MiR-502-3p and Alzheimer’s Disease
9. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patterson, C. World Alzheimer Report 2018. The State of the Art of Dementia Research: New Frontiers; Alzheimer’s Disease International: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Alzheimer’s Association. Facts and Figures. 2022. Available online: https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/facts-figures (accessed on 3 November 2022).
- National Institute of Aging. Alzheimer’s Disease Fact Sheet. 2022. Available online: https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/alzheimers-disease-fact-sheet (accessed on 3 November 2022).
- Kowal, P.; Goodkind, D.; He, W. An Aging World: 2015, International Population Reports; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- Kasper, D.L.; Fauci, A.S.; Hauser, S.L.; Longo, D.L.; Lameson, J.L.; Loscalzo, J. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Barve, K.H.; Kumar, M.S. Recent Advancements in Pathogenesis, Diagnostics and Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2020, 18, 1106–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayodele, T.; Rogaeva, E.; Kurup, J.T.; Beecham, G.; Reitz, C. Early-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease: What Is Missing in Research? Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2021, 21, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.S.; Hasana, S.; Hossain, M.F.; Islam, M.S.; Behl, T.; Perveen, A.; Hafeez, A.; Ashraf, G.M. Molecular Genetics of Early- and Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Gene Ther. 2021, 21, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nikolac Perkovic, M.; Pivac, N. Genetic Markers of Alzheimer’s Disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1192, 27–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.; Lee, B.Y.; Hane, F.T. Recent Progress in Alzheimer’s Disease Research, Part 2: Genetics and Epidemiology. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 57, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, P.; Reddy, P.H.; Kumar, S. Deregulated mitochondrial microRNAs in Alzheimer’s disease: Focus on synapse and mitochondria. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 73, 101529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Place, R.F.; Li, L.C.; Pookot, D.; Noonan, E.J.; Dahiya, R. MicroRNA-373 induces expression of genes with complementary promoter sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1608–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Chawla, Y.K.; Ghosh, S.; Chakraborti, A. Severity of hepatitis C virus (genotype-3) infection positively correlates with circulating microRNA-122 in patients sera. Dis. Markers Vol. 2014, 2014, 435476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Vijayan, M.; Bhatti, J.S.; Reddy, P.H. MicroRNAs as Peripheral Biomarkers in Aging and Age-Related Diseases. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2017, 146, 47–94. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Reddy, P.H. A New Discovery of MicroRNA-455-3p in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 72, S117–S130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, J.; Gangwani, L.; Kumar, S. Mitochondria Localized microRNAs: An Unexplored miRNA Niche in Alzheimer’s Disease and Aging. Cells 2023, 12, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Croce, C.M. The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2016, 1, 15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macfarlane, L.A.; Murphy, P.R. MicroRNA: Biogenesis, Function and Role in Cancer. Curr. Genom. 2010, 11, 537–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Sen, S. MicroRNA as Biomarkers and Diagnostics. J. Cell Physiol. 2016, 231, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupaimoole, R.; Slack, F.J. MicroRNA therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takousis, P.; Sadlon, A.; Schulz, J.; Wohlers, I.; Dobricic, V.; Middleton, L.; Lill, C.M.; Perneczky, R.; Bertram, L. Differential expression of microRNAs in Alzheimer’s disease brain, blood, and cerebrospinal fluid. Alzheimers Dement. 2019, 15, 1468–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Reddy, P.H. Are circulating microRNAs peripheral biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1862, 1617–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, H.S.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.J.; Min, J.W.; Iwatsubo, T.; Teunissen, C.E.; Cho, H.J.; Ryu, J.H. Targeting MicroRNA-485-3p Blocks Alzheimer’s Disease Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Vijayan, M.; Reddy, P.H. MicroRNA-455-3p as a potential peripheral biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 3808–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Reddy, P.H. MicroRNA-455-3p as a Potential Biomarker for Alzheimer’s Disease: An Update. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Reddy, P.H. Elevated levels of MicroRNA-455-3p in the cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer’s patients: A potential biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2021, 1867, 166052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Morton, H.; Sawant, N.; Orlov, E.; Bunquin, L.E.; Pradeepkiran, J.A.; Alvir, R.; Reddy, P.H. MicroRNA-455-3p improves synaptic, cognitive functions and extends lifespan: Relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. Redox. Biol. 2021, 48, 102182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Orlov, E.; Gowda, P.; Bose, C.; Swerdlow, R.H.; Lahiri, D.K.; Reddy, P.H. Synaptosome microRNAs regulate synapse functions in Alzheimer’s disease. NPJ Genom. Med. 2022, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, M.S.; Kim, A.S.; Prasad, N.; Levy, S.E.; Zhang, H.; Andl, T. Characterization of the Merkel Cell Carcinoma miRNome. J. Skin Cancer 2014, 2014, 289548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamichhane, A.P. Osteoporosis-an update. JNMA J. Nepal Med. Assoc. 2005, 44, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; Lu, L. Systemic immune-inflammation index acts as a novel diagnostic biomarker for postmenopausal osteoporosis and could predict the risk of osteoporotic fracture. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Sun, Z.; Wang, L. Study on Omentin-1 and miR-502-3p in osteoporotic fracture. J. Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2021, 21, 308–316. [Google Scholar]
- Centers of Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report. 2022. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html (accessed on 17 November 2022).
- Papatheodorou, K.; Banach, M.; Edmonds, M.; Papanas, N.; Papazoglou, D. Complications of Diabetes. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 189525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayfield, J. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus: New criteria. Am. Fam. Physician 1998, 58, 1355–1362+1369–1370. [Google Scholar]
- Galicia-Garcia, U.; Benito-Vicente, A.; Jebari, S.; Larrea-Sebal, A.; Siddiqi, H.; Uribe, K.B.; Ostolaza, H.; Martín, C. Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montastier, E.; Beuzelin, D.; Martins, F.; Mir, L.; Marqués, M.A.; Thalamas, C.; Iacovoni, J.; Langin, D.; Viguerie, N. Niacin induces miR-502-3p expression which impairs insulin sensitivity in human adipocytes. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 1485–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natarajan, A.; Beena, P.M.; Devnikar, A.V.; Mali, S. A systemic review on tuberculosis. Indian J. Tuberc. 2020, 7, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Dong, Z.; Lin, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y. MicroRNA-502-3p promotes Mycobacterium tuberculosis survival in macrophages by modulating the inflammatory response by targeting ROCK1. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvius, N.; Bonne, G.; Straatman, K.; Reddy, T.; Gant, T.W.; Shackleton, S. MicroRNA expression profiling in patients with lamin A/C-associated muscular dystrophy. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 3966–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, D.; Chandrasekaran, S.P.; Ramachandran, V.; Kalaivanan, K.; Carani Venkatraman, A. Evaluation of Serum miRNA-24, miRNA-29a and miRNA-502-3p Expression in PCOS Subjects: Correlation with Biochemical Parameters Related to PCOS and Insulin Resistance. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2020, 35, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallek, M.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Eichhorst, B. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Lancet 2018, 391, 1524–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dancescu, M.; Rubio-Trujillo, M.; Biron, G.; Bron, D.; Delespesse, G.; Sarfati, M. Interleukin 4 protects chronic lymphocytic leukemic B cells from death by apoptosis and upregulates Bcl-2 expression. J. Exp. Med. 1992, 176, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Lafuente, N.; Alcaraz-García, M.J.; Sebastián-Ruiz, S.; García-Serna, A.M.; Gómez-Espuch, J.; Moraleda, J.M.; Minguela, A.; García-Alonso, A.M.; Parrado, A. IL-4 Up-Regulates MiR-21 and the MiRNAs Hosted in the CLCN5 Gene in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, M.G.; Krook, L.S.; Cruz, S.V. Pituitary adenomas: An overview. Am. Fam. Physician 2013, 88, 319–327. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, W.; Qiao, Y.; Song, H.; Li, L.; Guo, J.; Lu, D.; Deng, X. LncRNA LINC00473 is involved in the progression of invasive pituitary adenoma by upregulating KMT5A via ceRNA-mediated miR-502-3p evasion. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Abak, A.; Hussen, B.M.; Taheri, M.; Sharifi, G. The Emerging Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Pituitary Gland Tumors and Meningioma. Cancers 2021, 13, 5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Goding Sauer, A.; Fedewa, S.A.; Butterly, L.F.; Anderson, J.C.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.S. Intramucosal Carcinoma. Available online: https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/colontumorintramucosal.html (accessed on 26 December 2022).
- Sugai, T.; Osakabe, M.; Niinuma, T.; Sugimoto, R.; Eizuka, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Yanagawa, N.; Otsuka, K.; Sasaki, A.; Matsumoto, T.; et al. Genome-Wide Analysis of microRNA and mRNA Expression in Colorectal Intramucosal Neoplasia and Colorectal Cancer with a Microsatellite-Stable Phenotype Based on Adenoma-Carcinoma Sequences. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 831100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Chen, S.; Yang, Y.; Miao, H.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Ma, J.; Zhang, T.; Ren, T.; Li, Y.; et al. Long-term exposure to genistein inhibits the proliferation of gallbladder cancer by downregulating the MCM complex. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.P.; Jin, Y.P.; Wu, X.S.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.S.; Li, H.F.; Xiang, S.S.; Song, X.L.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Y.J.; et al. LncRNA-HGBC stabilized by HuR promotes gallbladder cancer progression by regulating miR-502-3p/SET/AKT axis. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, A.; Hino, T.; Yanagawa, M.; Nishino, M.; Hida, T.; Hunninghake, G.M.; Tomiyama, N.; Christiani, D.C.; Hatabu, H. Interstitial Lung Abnormalities at CT: Subtypes, Clinical Significance, and Associations with Lung Cancer. Radiographics 2022, 42, 1925–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Quintero, B.; Buendía-Roldán, I.; Ramírez-Salazar, E.G.; Balderas-Martínez, Y.I.; Ramírez-Rodríguez, S.L.; Martínez-Espinosa, K.; Selman, M. Circulating microRNA Signature Associated to Interstitial Lung Abnormalities in Respiratory Asymptomatic Subjects. Cells 2020, 9, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelsson, G.T.; Putman, R.K.; Aspelund, T.; Gudmundsson, E.F.; Hida, T.; Araki, T.; Nishino, M.; Hatabu, H.; Gudnason, V.; Hunninghake, G.M.; et al. The associations of interstitial lung abnormalities with cancer diagnoses and mortality. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 1902154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Treatment Centers of America. Adenocarcinoma of the Lung. 2022. Available online: https://www.cancercenter.com/cancer-types/lung-cancer/types/adenocarcinoma-of-the-lung (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- Subat, S.; Inamura, K.; Ninomiya, H.; Nagano, H.; Okumura, S.; Ishikawa, Y. Unique MicroRNA and mRNA Interactions in EGFR-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Govindan, R.; Wang, L.; Liu, P.Y.; Goodgame, B.; Wen, W.; Sezhiyan, A.; Pfeifer, J.; Li, Y.F.; Hua, X.; et al. MicroRNA profiling and prediction of recurrence/relapse-free survival in stage I lung cancer. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.T.; Qin, H.; Man Cheung, F.K.; Su, J.; Zhang, D.D.; Liu, S.Y.; Li, X.F.; Qin, J.; Lin, J.T.; Jiang, B.Y.; et al. Plasma extracellular vesicle microRNAs for pulmonary ground-glass nodules. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1663666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, B.; Cui, M.; Yang, G.; Wang, H.; Feng, M.; You, L.; Zhao, Y. Tumor microenvironment participates in metastasis of pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Zhou, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Gao, F.; Li, H. Differential expression profiles of microRNAs in highly and weakly invasive/metastatic pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 6026–6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Gong, Y.; Ma, J.; Gong, X. Overexpressed circ-RPL15 predicts poor survival and promotes the progression of gastric cancer via regulating miR-502-3p/OLFM4/STAT3 pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 127, 110219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Bae, W.J.; Ahn, J.M.; Heo, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Choi, K.W.; Sung, C.O.; Lee, D. MicroRNA signatures associated with lymph node metastasis in intramucosal gastric cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2021, 34, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, A.C. Conjunctival malignant melanoma in Denmark: Epidemiology, treatment and prognosis with special emphasis on tumorigenesis and genetic profile. Acta Ophthalmol. 2016, 94, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, Q.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, S.; Fan, J.; Wang, J. Comparing MicroRNA Profilings of Purified HER-2-Negative and HER-2-Positive Cells Validates miR-362-5p/Sema3A as Characteristic Molecular Change in Triple-Negative Breast Cancers. Dis. Markers 2019, 6057280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Corrigan-Cummins, M.; Hudson, J.; Maric, I.; Simakova, O.; Neelapu, S.S.; Kwak, L.W.; Janik, J.E.; Gause, B.; Jaffe, E.S.; et al. MicroRNA profiling of follicular lymphoma identifies microRNAs related to cell proliferation and tumor response. Haematologica 2012, 97, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Han, X.; Xing, X. Bioinformatics Methods Reveal the Biomarkers and the miRNA-mRNA Network in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Healthc. Eng. 2022, 2022, 9963096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wach, S.; Nolte, E.; Theil, A.; Stöhr, C.; T Rau, T.; Hartmann, A.; Ekici, A.; Keck, B.; Taubert, H.; Wullich, B. MicroRNA profiles classify papillary renal cell carcinoma subtypes. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassan, M.; Realdon, S.; Cascione, L.; Hahne, J.C.; Munari, G.; Guzzardo, V.; Arcidiacono, D.; Lampis, A.; Brignola, S.; Dal Santo, L.; et al. Circulating microRNA expression profiling revealed miR-92a-3p as a novel biomarker of Barrett’s carcinogenesis. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, M.; Piscopo, P.; Talarico, G.; Ricci, L.; Crestini, A.; Tosto, G.; Gasparini, M.; Bruno, G.; Denti, M.A.; Confaloni, A. Plasma microRNA profiling distinguishes patients with frontotemporal dementia from healthy subjects. Neurobiol. Aging 2019, 84, 240.e1–240.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, P.; Chandra, S.R.; Christopher, R. Circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for the identification of vascular dementia due to cerebral small vessel disease. Age Ageing 2017, 46, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, J.; Kino, Y.; Niida, S. MicroRNA-Seq Data Analysis Pipeline to Identify Blood Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease from Public Data. Biomark. Insights 2015, 10, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winship, I.R.; Dursun, S.M.; Baker, G.B.; Balista, P.A.; Kandratavicius, L.; Maia-de-Oliveira, J.P.; Hallak, J.; Howland, J.G. An Overview of Animal Models Related to Schizophrenia. Can. J. Psychiatry. 2019, 64, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Fact Sheets—Schizophrenia. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/schizophrenia (accessed on 17 January 2023).
- Liang, W.; Hou, Y.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Huang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, F.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Loss of schizophrenia-related miR-501-3p in mice impairs sociability and memory by enhancing mGluR5-mediated glutamatergic transmission. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn7357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.; O`connell, T.; Johnson, S.; Cline, S.; Merikle, E.; Martenyi, F.; Simpson, K.N. Estimating Alzheimer’s Disease Progression Rates from Normal Cognition Through Mild Cognitive Impairment and Stages of Dementia. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2018, 15, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, N.; Kikuchi, M.; Miyashita, A.; Hatsuta, H.; Saito, Y.; Kasuga, K.; Murayama, S.; Ikeuchi, T.; Kuwano, R. Serum microRNA miR-501-3p as a potential biomarker related to the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2017, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullett, J.M.; Chen, Z.; O’Shea, A.; Akbar, M.; Bian, J.; Rani, A.; Porges, E.C.; Foster, T.C.; Woods, A.J.; Modave, F.; et al. MicroRNA predicts cognitive performance in healthy older adults. Neurobiol. Aging 2020, 95, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, M.; Islam, M.R.; Kerimoglu, C.; Lancelin, C.; Gisa, V.; Burkhardt, S.; Krüger, D.M.; Marquardt, T.; Malchow, B.; Schmitt, A.; et al. Exercise as a model to identify microRNAs linked to human cognition: A role for microRNA-409 and microRNA-501. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyama, K.; Spin, J.M.; Deng, A.C.; Huang, T.T.; Wei, K.; Wagenhäuser, M.U.; Yoshino, T.; Nguyen, H.; Mulorz, J.; Kundu, S.; et al. MicroRNA-Mediated Therapy Modulating Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption Improves Vascular Cognitive Impairment. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 1392–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.K.; Verbich, D.; McKinney, R.A. AMPA receptors as drug targets in neurological disease—Advantages, caveats, and future outlook. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2012, 35, 1908–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Hu, T.; Luo, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, Z. miR-501-3p mediates the activity-dependent regulation of the expression of AMPA receptor subunit GluA1. J. Cell. Biol. 2015, 208, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. Synaptosome microRNAs: Emerging synapse players in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 1275–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Johnson, J.J.; Stack, M.S. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization for MicroRNA Detection in Archived Oral Cancer Tissues. J. Oncol. 2012, 2012, 903581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| MiRNA-502-3p and Human Diseases | |||||
| Disease | miR-502-3p | Target Gene | Signaling Pathway | Purpose | Reference |
| Osteoporosis | Downregulated | Biomarker | Zhang et al., 2021 | ||
| Diabetes Type 2 | Upregulated | Therapeutic | Montastier et al., 2019 | ||
| Tuberculosis | Upregulated | ROCK1 | TLR4/NF-κB | Detrimental | Liu et al., 2021 |
| Lamin A/C-associated Muscular Dystrophy | Upregulated | Sylvius et al., 2011 | |||
| MiRNA-502-3p and Human Cancers | |||||
| Disease | miR-502-3p | Target Gene | Signaling Pathway | Purpose | Reference |
| Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia | Upregulated | IL-4 pathway | Therapeutic | Ruiz-Lafuente et al., 2015 | |
| Invasive Pituitary Adenoma | Downregulated | KMT5A | LINC00473/miR-502-3p/KMT5A Axis | Li et al., 2021 | |
| Colorectal Cancer | Upregulated | OLFM4 | Detrimental | Sugai et al., 2022 | |
| Gallbladder Cancer | Downregulated | SET | LncRNA-HGBC/miR-502-3p/SET/AKT Axis | Hu et al., 2019 | |
| Interstitial Lung Abnormality | Upregulated | p53 Signaling Pathway | Biomarker | Ortiz-Quintero et al., 2020 | |
| Lung Adenocarcinoma | Upregulated | MUC4 | Detrimental | Subat et al., 2018 | |
| Pulmonary Ground-Glass Nodules | Upregulated | Prognostic | Zhang et al., 2019 | ||
| Pancreatic Cancer | Downregulated | Various | Tan et al., 2018 | ||
| Stomach Cancer | Downregulated | OLFM4 | circ-RPL15/miR-502-3p/OLFM4/STAT3 | Kim et al., 2021 | |
| Merkel Cell Carcinoma | Upregulated | Ning et al., 2014 | |||
| Conjunctival Malignant Melanoma | Upregulated | Larsen et al., 2016 | |||
| Triple Negative Breast Cancer | Upregulated | Zhang et al., 2019 | |||
| Follicular Lymphoma | Upregulated | Wang et al., 2012 | |||
| Hepatocellular Carcinoma | Detrimental | Liu et al., 2022 | |||
| Renal Cell Carcinoma | Downregulated | Diagnostic | Wach et al., 2013 | ||
| Esophageal Adenocarcinoma | Downregulated | Fassan et al., 2020 | |||
| MiRNA-502-3p and Neurodegenerative Disorders | |||||
| Disease | miR-502-3p | Target Gene | Signaling Pathway | Proposed Benefit | Reference |
| Frontotemporal Dementia | Downregulated | Biomarker | Grasso et al., 2019 | ||
| Vascular Dementia | Upregulated | Biomarker | Prabhakar et al., 2017 | ||
| Alzheimer’s Disease | Downregulated | Biomarker | Satoh et al., 2015 | ||
| Alzheimer’s Disease | Upregulated (Synapse) | GABRA1 | GABAergic synapse | Therapeutic | Kumar et al., 2022 |
| MiRNA-501-3p and Neurodegenerative Disorders | |||||
| Disease | miR-501-3p | Target Gene | Signaling Pathway | Proposed Benefit | Reference |
| Schizophrenia | Downregulated | Grm5 | Therapeutic | Liang et al., 2022 | |
| Cognition | Negatively Correlated | Predictive | Gullett et al., 2020 | ||
| Memory | Upregulated | Therapeutic | Goldberg et al., 2021 | ||
| Vascular Dementia | Upregulated | ZO-1 | TNFα/miR-501-3p/ZO-1 axis | Therapeutic | Toyama et al., 2018 |
| Alzheimer’s Disease | Downregulated (serum), Upregulated (brain) | Hara et al., 2017 | |||
| AMPAR Degradation | Upregulated | Gria1 | Hu et al., 2015 | ||
| Alzheimer’s Disease | Upregulated (Synapse) | GABRA1 | Therapeutic | Kumar et al., 2022 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Devara, D.; Choudhary, Y.; Kumar, S. Role of MicroRNA-502-3p in Human Diseases. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040532
Devara D, Choudhary Y, Kumar S. Role of MicroRNA-502-3p in Human Diseases. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(4):532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040532
Chicago/Turabian StyleDevara, Davin, Yashmit Choudhary, and Subodh Kumar. 2023. "Role of MicroRNA-502-3p in Human Diseases" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 4: 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040532
APA StyleDevara, D., Choudhary, Y., & Kumar, S. (2023). Role of MicroRNA-502-3p in Human Diseases. Pharmaceuticals, 16(4), 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040532










