A Window to the Brain: The Retina to Monitor the Progression and Efficacy of Saffron Repron® Pre-Treatment in an LPS Model of Neuroinflammation and Memory Impairment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
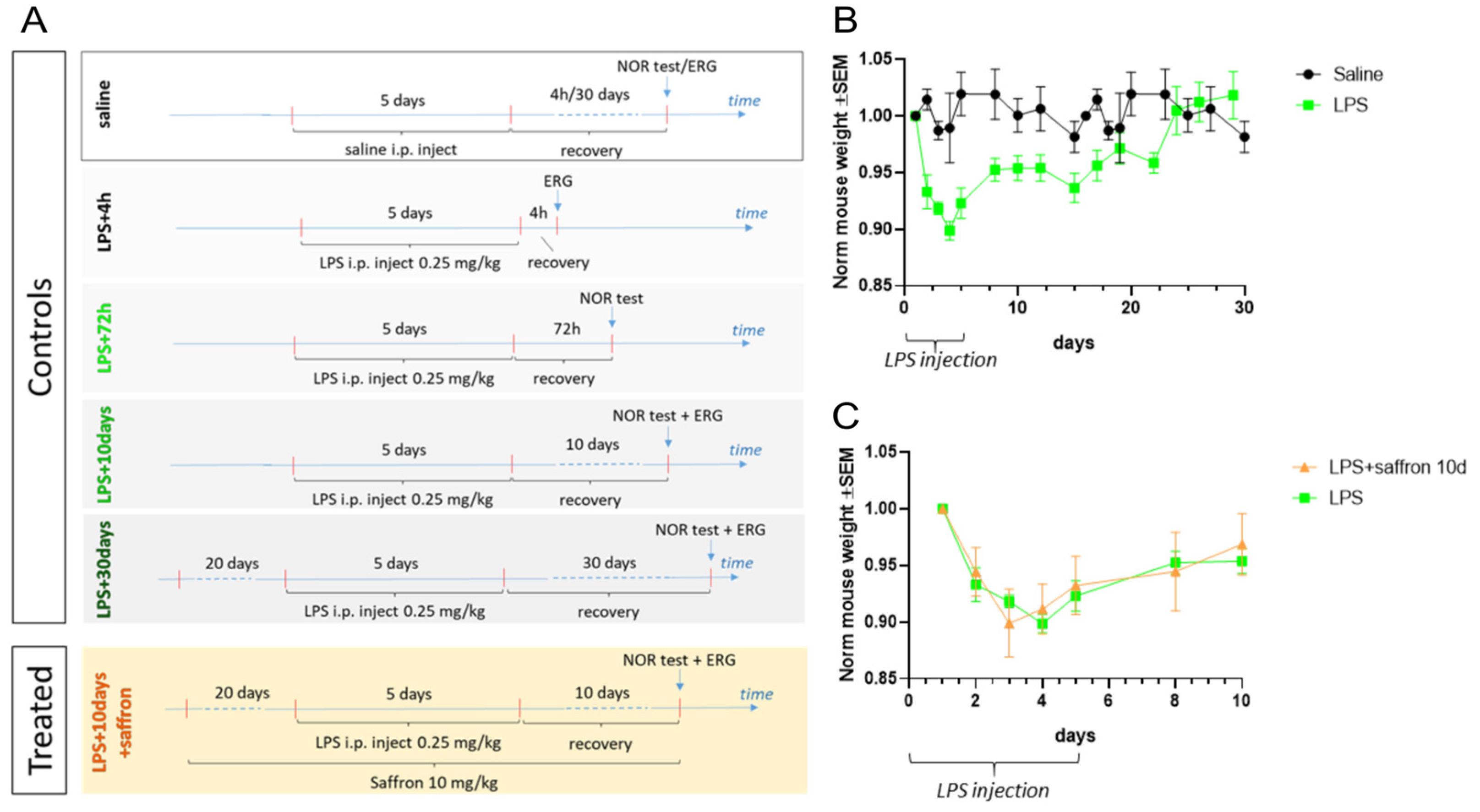
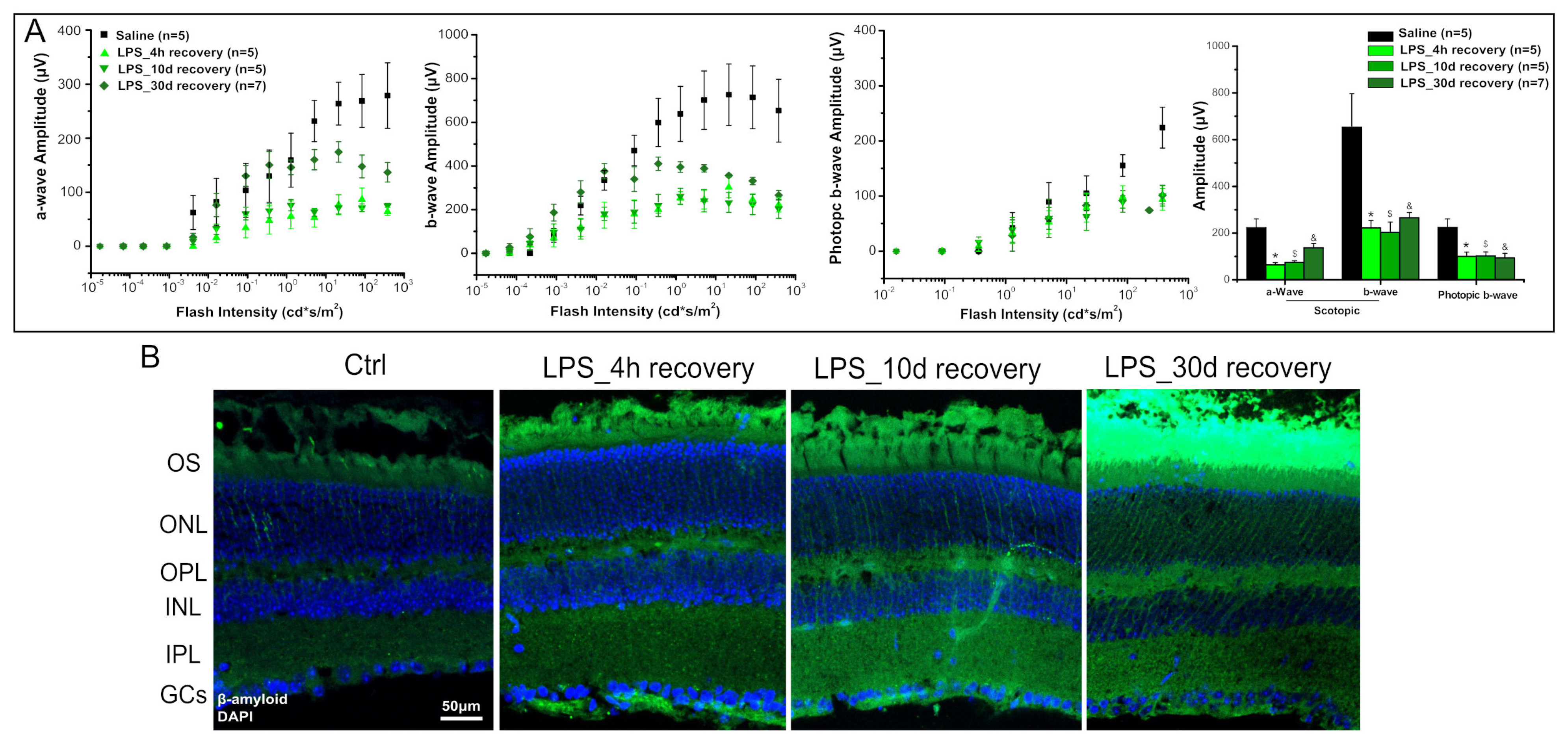
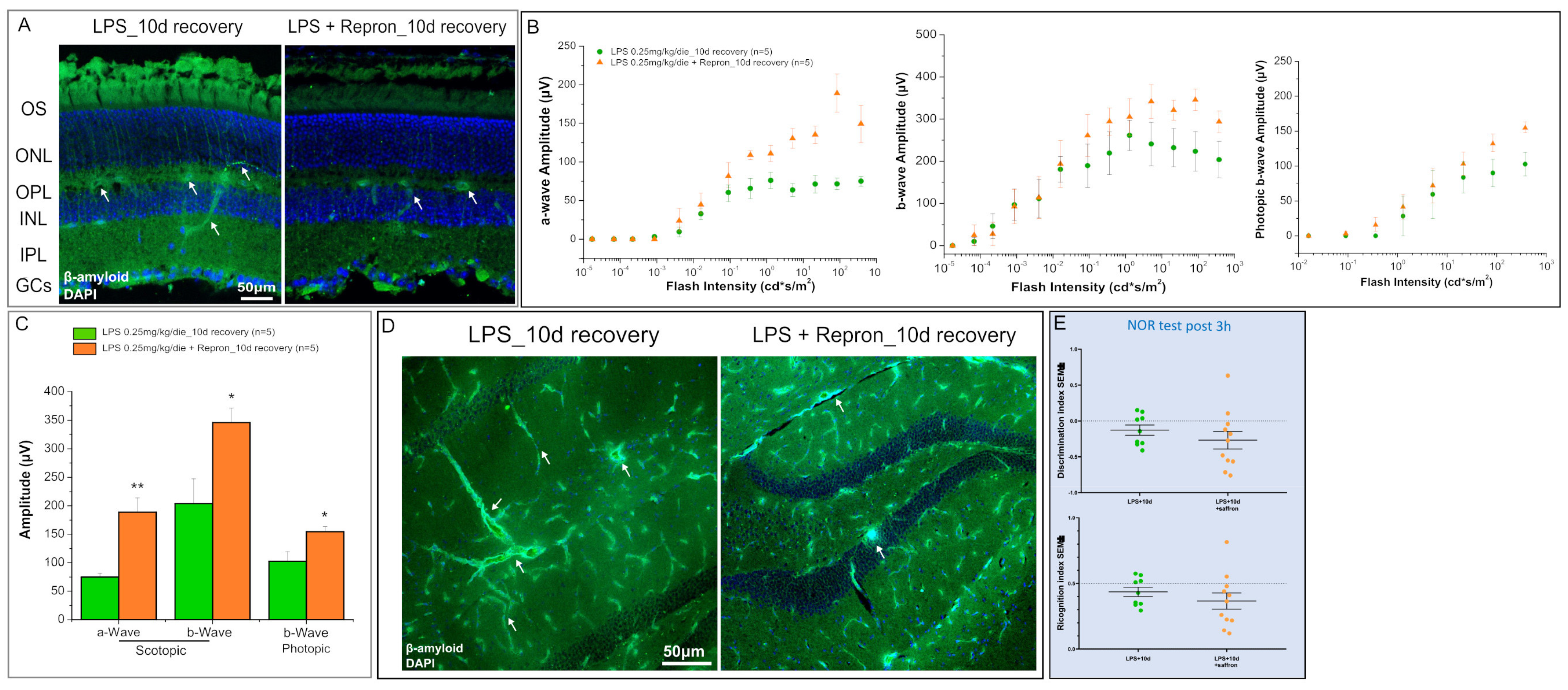
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice
4.2. Mouse Model of Neuroinflammation and Saffron Repron® Treatment
4.3. Novel Object Recognition (NOR) Test
- DI = 0 and RI = 0.5: Time (T) new object exploration = T familiar object exploration; the animal does not remember.
- DI > 0 and RI > 0.5: T new object exploration > T familiar object exploration, the animal remembers.
- DI < 0 and RI < 0.5: T new object exploration < T familiar object exploration, the animal does not remember or remembers and is afraid of the new object (is anxious/depressed).
4.4. Electroretinogram (ERG)
4.5. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
4.6. Western Blot
4.7. Immunohistochemistry
4.8. Statistic
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allison, D.J.; Ditor, D.S. The Common Inflammatory Etiology of Depression and Cognitive Impairment: A Therapeutic Target. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samadian, M.; Gholipour, M.; Hajiesmaeili, M.; Taheri, M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. The Eminent Role of MicroRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 641080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, R.; Rahmani, F.; Rezaei, N. MicroRNA in Alzheimer’s Disease Revisited: Implications for Major Neuropathological Mechanisms. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 29, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polymeropoulos, M.H.; Lavedan, C.; Leroy, E.; Ide, S.E.; Dehejia, A.; Dutra, A.; Pike, B.; Root, H.; Rubenstein, J.; Boyer, R.; et al. Mutation in the α-Synuclein Gene Identified in Families with Parkinson’s Disease. Science 1997, 276, 2045–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surmeier, D.J.; Obeso, J.A.; Halliday, G.M. Selective Neuronal Vulnerability in Parkinson Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Bi, W.; Xiao, S.; Lan, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Lu, D.; Wei, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Neuroinflammation Induced by Lipopolysaccharide Causes Cognitive Impairment in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransohoff, R.M. A Polarizing Question: Do M1 and M2 Microglia Exist? Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, M.L.; Zecca, L.; Hong, J.-S. Microglia-Mediated Neurotoxicity: Uncovering the Molecular Mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmani, F.; Rezaei, N. Therapeutic Targeting of Toll-like Receptors: A Review of Toll-like Receptors and Their Signaling Pathways in Psoriasis. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 12, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannarkat, G.T.; Boss, J.M.; Tansey, M.G. The Role of Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Park. Dis. 2013, 3, 493–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolós, M.; Perea, J.R.; Avila, J. Alzheimer’s Disease as an Inflammatory Disease. Biomol. Concepts 2017, 8, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venegas, C.; Heneka, M.T. Danger-Associated Molecular Patterns in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 101, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aarsland, D.; Bronnick, K.; Williams-Gray, C.; Weintraub, D.; Marder, K.; Kulisevsky, J.; Burn, D.; Barone, P.; Pagonabarraga, J.; Allcock, L.; et al. Mild Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson Disease: A Multicenter Pooled Analysis. Neurology 2010, 75, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blennow, K.; de Leon, M.J.; Zetterberg, H. Alzheimer’s Disease. Lancet 2006, 368, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeTure, M.A.; Dickson, D.W. The Neuropathological Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.B.; O’Callaghan, J.P. Biomarkers of Parkinson’s Disease: Present and Future. Metabolism 2015, 64, S40–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unschuld, P.G. Prevention of Alzheimer’s disease: Medical and lifestyle interventions. Rev. Med. Suisse 2021, 17, 1614–1616. [Google Scholar]
- Gelb, D.J.; Oliver, E.; Gilman, S. Diagnostic Criteria for Parkinson Disease. Arch. Neurol. 1999, 56, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veitch, D.P.; Weiner, M.W.; Aisen, P.S.; Beckett, L.A.; DeCarli, C.; Green, R.C.; Harvey, D.; Jack, C.R.; Jagust, W.; Landau, S.M.; et al. Using the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative to Improve Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022, 18, 824–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charles-Messance, H.; Blot, G.; Couturier, A.; Vignaud, L.; Touhami, S.; Beguier, F.; Siqueiros, L.; Forster, V.; Barmo, N.; Augustin, S.; et al. IL-1β Induces Rod Degeneration through the Disruption of Retinal Glutamate Homeostasis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romaus-Sanjurjo, D.; Regueiro, U.; López-López, M.; Vázquez-Vázquez, L.; Ouro, A.; Lema, I.; Sobrino, T. Alzheimer’s Disease Seen through the Eye: Ocular Alterations and Neurodegeneration. IJMS 2022, 23, 2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yue, Y.; Tian, T. Retinal Degeneration: A Window to Understand the Origin and Progression of Parkinson’s Disease? Front. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 799526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.F.; Chakarova, C.F.; Abd El-Aziz, M.M.; Bhattacharya, S.S. Photoreceptor Degeneration: Genetic and Mechanistic Dissection of a Complex Trait. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Jaber, V.R.; Pogue, A.I.; Sharfman, N.M.; Taylor, C.; Lukiw, W.J. Lipopolysaccharides (LPSs) as Potent Neurotoxic Glycolipids in Alzheimer’s Disease (AD). IJMS 2022, 23, 12671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christodoulou, E.; Kadoglou, N.P.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; Valsami, G. Saffron: A Natural Product with Potential Pharmaceutical Applications. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 1634–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- José Bagur, M.; Alonso Salinas, G.; Jiménez-Monreal, A.; Chaouqi, S.; Llorens, S.; Martínez-Tomé, M.; Alonso, G. Saffron: An Old Medicinal Plant and a Potential Novel Functional Food. Molecules 2017, 23, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poma, A.; Fontecchio, G.; Carlucci, G.; Chichiricco, G. Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Drugs from Saffron Crocus. Anti-Inflamm. Anti-Allergy Agents Med. Chem. 2012, 11, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Paolo, M.; Corsi, F.; Maggi, M.; Nardi, L.; Bisti, S.; Piano, I.; Gargini, C. Efficacy of Hydroponically Cultivated Saffron in the Preservation of Retinal Pigment Epithelium. Molecules 2023, 28, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, M.A.; Consonni, R.; Cagliani, L.R.; Prestipino, G.; Bisti, S.; Picco, C. Saffron and Retinal Neurodegenerative Diseases: Relevance of Chemical Composition. J. Anat. 2023, 243, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marco, S.; Carnicelli, V.; Franceschini, N.; Di Paolo, M.; Piccardi, M.; Bisti, S.; Falsini, B. Saffron: A Multitask Neuroprotective Agent for Retinal Degenerative Diseases. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falsini, B.; Piccardi, M.; Minnella, A.; Savastano, C.; Capoluongo, E.; Fadda, A.; Balestrazzi, E.; Maccarone, R.; Bisti, S. Influence of Saffron Supplementation on Retinal Flicker Sensitivity in Early Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maccarone, R.; Di Marco, S.; Bisti, S. Saffron Supplement Maintains Morphology and Function after Exposure to Damaging Light in Mammalian Retina. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marangoni, D.; Falsini, B.; Piccardi, M.; Ambrosio, L.; Minnella, A.; Savastano, M.; Bisti, S.; Maccarone, R.; Fadda, A.; Mello, E.; et al. Functional Effect of Saffron Supplementation and Risk Genotypes in Early Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Preliminary Report. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piano, I.; Di Paolo, M.; Corsi, F.; Piragine, E.; Bisti, S.; Gargini, C.; Di Marco, S. Retinal Neurodegeneration: Correlation between Nutraceutical Treatment and Animal Model. Nutrients 2021, 13, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccardi, M.; Fadda, A.; Martelli, F.; Marangoni, D.; Magli, A.; Minnella, A.M.; Bertelli, M.; Di Marco, S.; Bisti, S.; Falsini, B. Antioxidant Saffron and Central Retinal Function in ABCA4-Related Stargardt Macular Dystrophy. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccardi, M.; Marangoni, D.; Minnella, A.M.; Savastano, M.C.; Valentini, P.; Ambrosio, L.; Capoluongo, E.; Maccarone, R.; Bisti, S.; Falsini, B. A Longitudinal Follow-Up Study of Saffron Supplementation in Early Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Sustained Benefits to Central Retinal Function. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 429124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Z.; Yu, X.; Yin, Y.; Qian, S.; Wang, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, T.; et al. Quercitrin Rapidly Alleviated Depression-like Behaviors in Lipopolysaccharide-Treated Mice: The Involvement of PI3K/AKT/NF-ΚB Signaling Suppression and CREB/BDNF Signaling Restoration in the Hippocampus. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 3387–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Ali, T.; Rehman, S.U.; Khan, M.S.; Alam, S.I.; Ikram, M.; Muhammad, T.; Saeed, K.; Badshah, H.; Kim, M.O. Neuroprotective Effect of Quercetin Against the Detrimental Effects of LPS in the Adult Mouse Brain. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.O.; Chan, K.P.; Yip, Y.W.Y.; Chu, W.K.; Wang, C.C.; Pang, C.P. Systemic and Ocular Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms of Green Tea Extract on Endotoxin-Induced Ocular Inflammation. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 899271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoh Kam, J.; Lenassi, E.; Jeffery, G. Viewing Ageing Eyes: Diverse Sites of Amyloid Beta Accumulation in the Ageing Mouse Retina and the Up-Regulation of Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iseri, P.K.; Altinaş, Ö.; Tokay, T.; Yüksel, N. Relationship between Cognitive Impairment and Retinal Morphological and Visual Functional Abnormalities in Alzheimer Disease. J. Neuro-Ophthalmol. 2006, 26, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, K.; Chan, T.-F.; Wu, A.; Leung, I.Y.-P.; So, K.-F.; Chang, R.C.-C. Neurodegeneration of the Retina in Mouse Models of Alzheimer’s Disease: What Can We Learn from the Retina? Age 2012, 34, 633–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dajas, F.; Rivera-Megret, F.; Blasina, F.; Arredondo, F.; Abin-Carriquiry, J.A.; Costa, G.; Echeverry, C.; Lafon, L.; Heizen, H.; Ferreira, M.; et al. Neuroprotection by Flavonoids. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2003, 36, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scapagnini, G.; Sonya, V.; Nader, A.G.; Calogero, C.; Zella, D.; Fabio, G. Modulation of Nrf2/ARE Pathway by Food Polyphenols: A Nutritional Neuroprotective Strategy for Cognitive and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 44, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, F.; Sha, L.; Wang, S.; Tao, L.; Yao, L.; He, M.; Yao, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhu, Z.; et al. (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Ameliorates Learning and Memory Deficits by Adjusting the Balance of TrkA/P75NTR Signaling in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 49, 1350–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.; Kim, T.; Rehman, S.U.; Khan, M.S.; Amin, F.U.; Khan, M.; Ikram, M.; Kim, M.O. Natural Dietary Supplementation of Anthocyanins via PI3K/Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathways Mitigate Oxidative Stress, Neurodegeneration, and Memory Impairment in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 6076–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggi, M.A.; Bisti, S.; Picco, C. Saffron: Chemical Composition and Neuroprotective Activity. Molecules 2020, 25, 5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, H.; Nieus, T.; Lonardoni, D.; Maccione, A.; Berdondini, L. High-Resolution Bioelectrical Imaging of Aβ-Induced Network Dysfunction on CMOS-MEAs for Neurotoxicity and Rescue Studies. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koronyo, Y.; Rentsendorj, A.; Mirzaei, N.; Regis, G.C.; Sheyn, J.; Shi, H.; Barron, E.; Cook-Wiens, G.; Rodriguez, A.R.; Medeiros, R.; et al. Retinal Pathological Features and Proteome Signatures of Alzheimer’s Disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2023, 145, 409–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natoli, R.; Zhu, Y.; Valter, K.; Bisti, S.; Eells, J.; Stone, J. Gene and Noncoding RNA Regulation Underlying Photoreceptor Protection: Microarray Study of Dietary Antioxidant Saffron and Photobiomodulation in Rat Retina. Mol. Vis. 2010, 16, 1801–1822. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.; Mitrofanis, J.; Johnstone, D.M.; Falsini, B.; Bisti, S.; Adam, P.; Nuevo, A.B.; George-Weinstein, M.; Mason, R.; Eells, J. Acquired Resilience: An Evolved System of Tissue Protection in Mammals. Dose-Response 2018, 16, 155932581880342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, C.R.A.; Gomes, G.F.; Candelario-Jalil, E.; Fiebich, B.L.; de Oliveira, A.C.P. Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammation as a Bridge to Understand Neurodegeneration. IJMS 2019, 20, 2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibenhener, M.L.; Wooten, M.C. Use of the Open Field Maze to Measure Locomotor and Anxiety-like Behavior in Mice. JoVE 2015, 96, e52434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piano, I.; Novelli, E.; Gasco, P.; Ghidoni, R.; Strettoi, E.; Gargini, C. Cone Survival and Preservation of Visual Acuity in an Animal Model of Retinal Degeneration. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2013, 37, 1853–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsi, F.; Baglini, E.; Barresi, E.; Salerno, S.; Cerri, C.; Martini, C.; Da Settimo Passetti, F.; Taliani, S.; Gargini, C.; Piano, I. Targeting TSPO Reduces Inflammation and Apoptosis in an In Vitro Photoreceptor-Like Model of Retinal Degeneration. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 3188–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Antibody | Host | Company | Work Dilution | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-Beta-Amyloid 1–42 | Rabbit | Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MI, USA AB5078P | 1:500 | IHC |
| Anti-Iba1 | Mouse | Millipore, Temecula, CA, USA MABN92 | 1:1000 | WB |
| Anti-iNOS | Mouse | R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA MAB9502 | 1:500 | WB |
| Anti-rabbit Alexa Flour-488 | BioRad, Hercules, CA, USA | 1:500 | IHC | |
| Anti-mouse IgG HRP conjugated | Sigma-Aldrich | 1:5000 | WB |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Paolo, M.; Corsi, F.; Cerri, C.; Bisti, S.; Piano, I.; Gargini, C. A Window to the Brain: The Retina to Monitor the Progression and Efficacy of Saffron Repron® Pre-Treatment in an LPS Model of Neuroinflammation and Memory Impairment. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091307
Di Paolo M, Corsi F, Cerri C, Bisti S, Piano I, Gargini C. A Window to the Brain: The Retina to Monitor the Progression and Efficacy of Saffron Repron® Pre-Treatment in an LPS Model of Neuroinflammation and Memory Impairment. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(9):1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091307
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Paolo, Mattia, Francesca Corsi, Chiara Cerri, Silvia Bisti, Ilaria Piano, and Claudia Gargini. 2023. "A Window to the Brain: The Retina to Monitor the Progression and Efficacy of Saffron Repron® Pre-Treatment in an LPS Model of Neuroinflammation and Memory Impairment" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 9: 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091307
APA StyleDi Paolo, M., Corsi, F., Cerri, C., Bisti, S., Piano, I., & Gargini, C. (2023). A Window to the Brain: The Retina to Monitor the Progression and Efficacy of Saffron Repron® Pre-Treatment in an LPS Model of Neuroinflammation and Memory Impairment. Pharmaceuticals, 16(9), 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091307








