Meroterpenoids from Gongolaria abies-marina against Kinetoplastids: In Vitro Activity and Programmed Cell Death Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
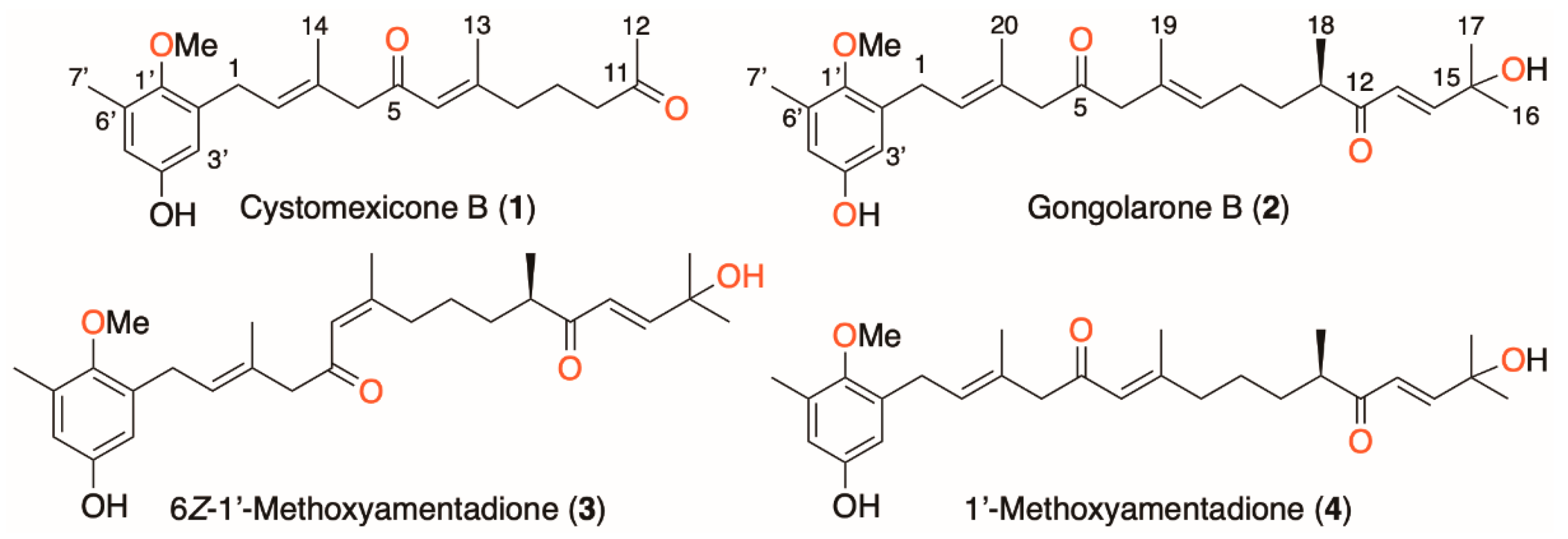
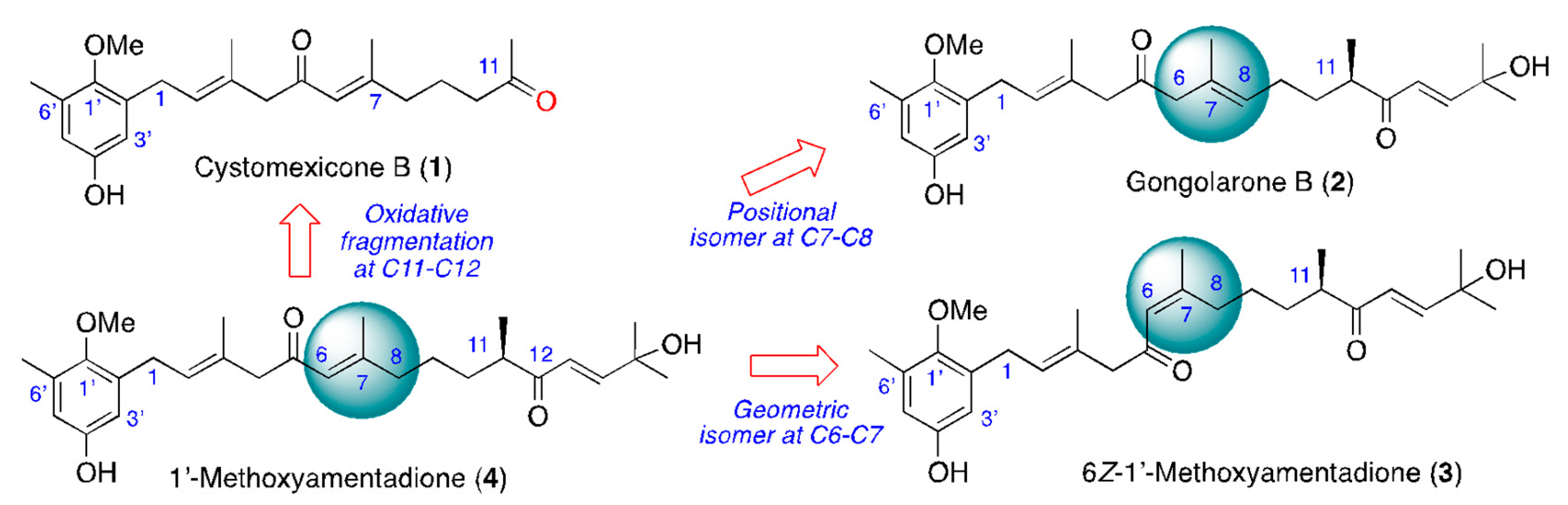
2.1. Isolation and Chemical Characterization of Meroterpenoids of Gongolaria abies-marina
2.2. Antiparasitic Activity
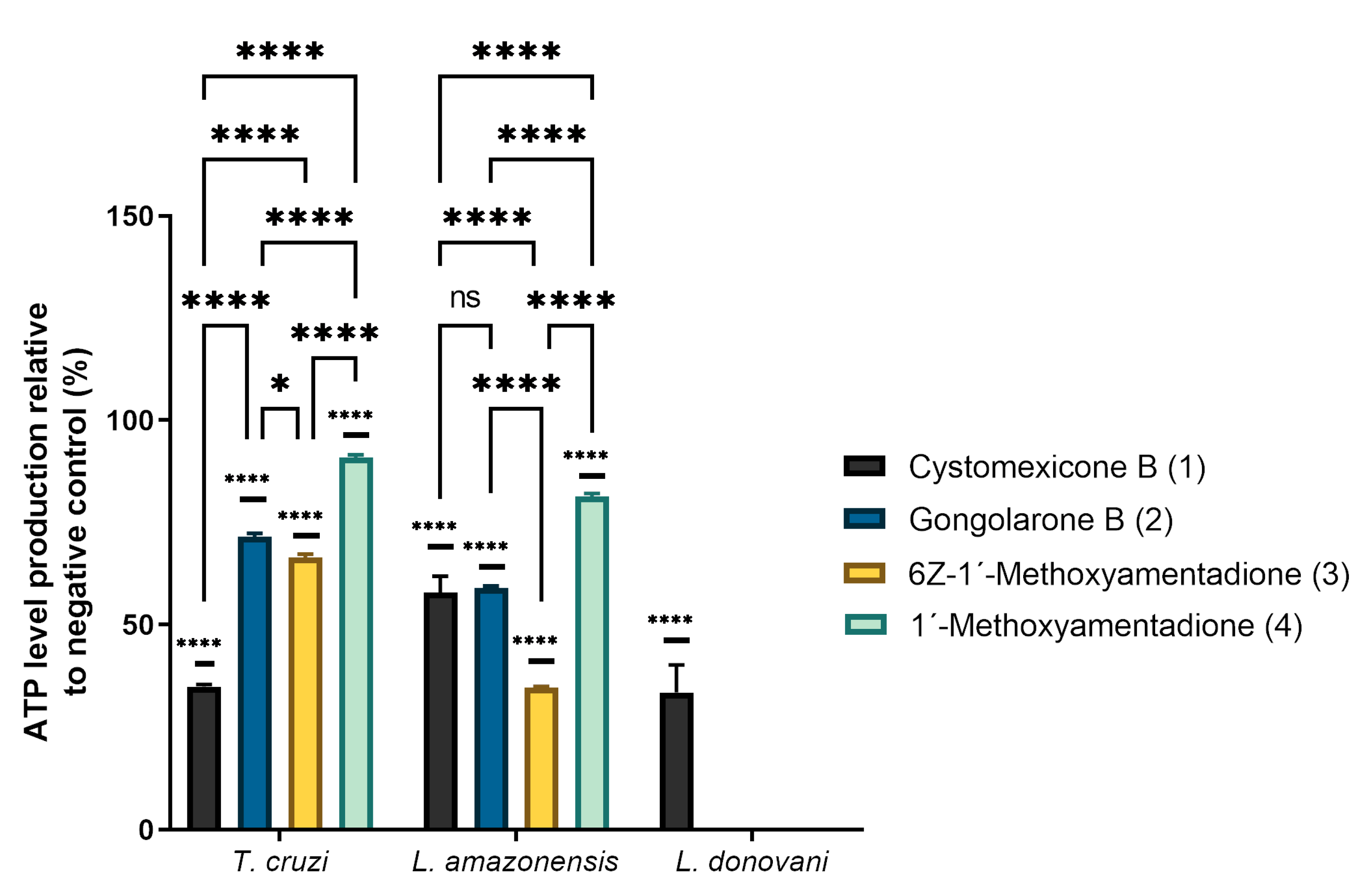
2.3. ATP Level Analysis
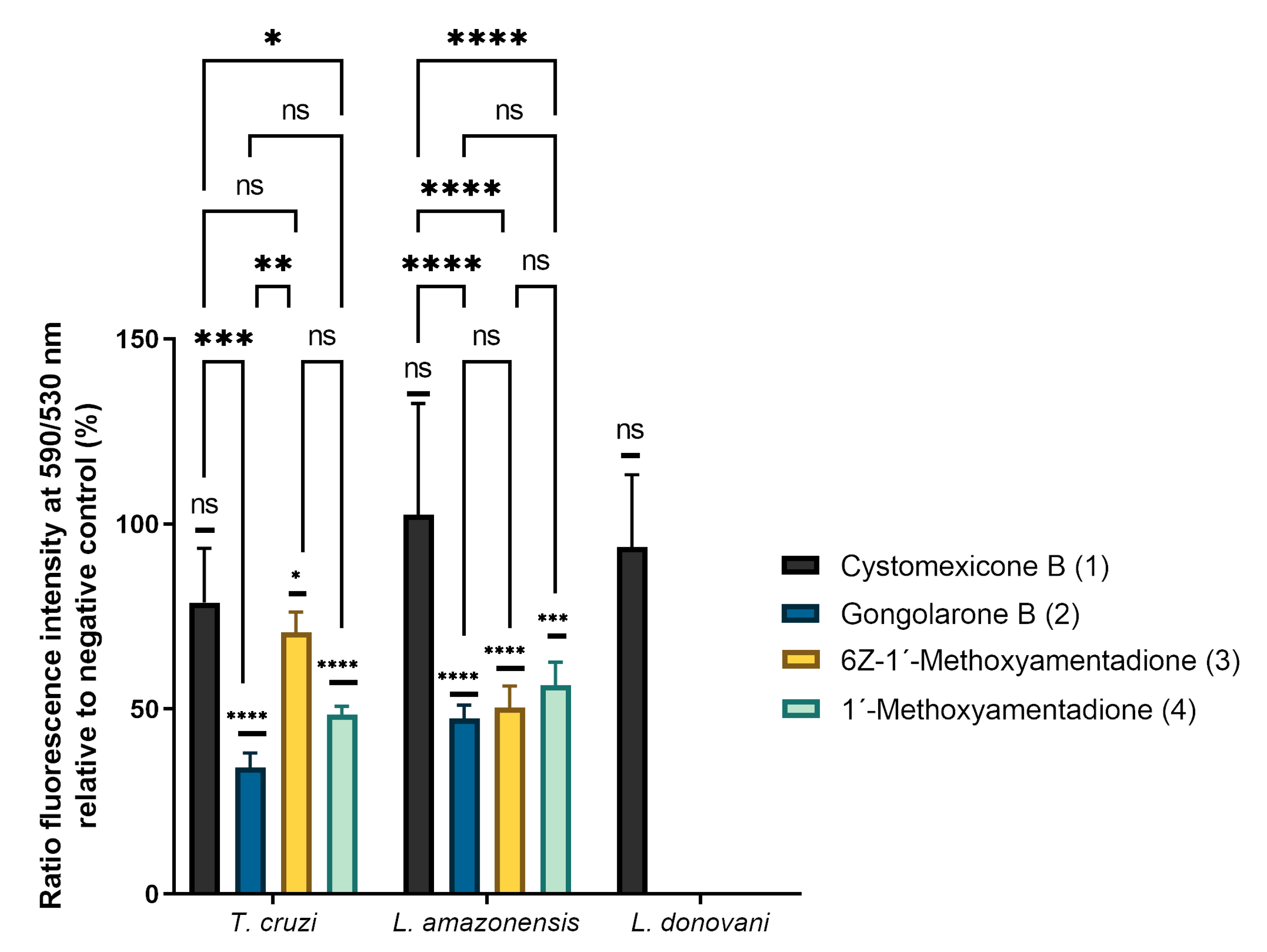
2.4. Analysis of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Changes
2.5. Plasmatic Membrane Permeability Assay and Chromatin Condensation Analysis
2.6. Analysis of Reactive Oxygen Species
2.7. Immunofluorescence Analysis of Actin
2.8. Immunofluorescence Analysis of Tubulin
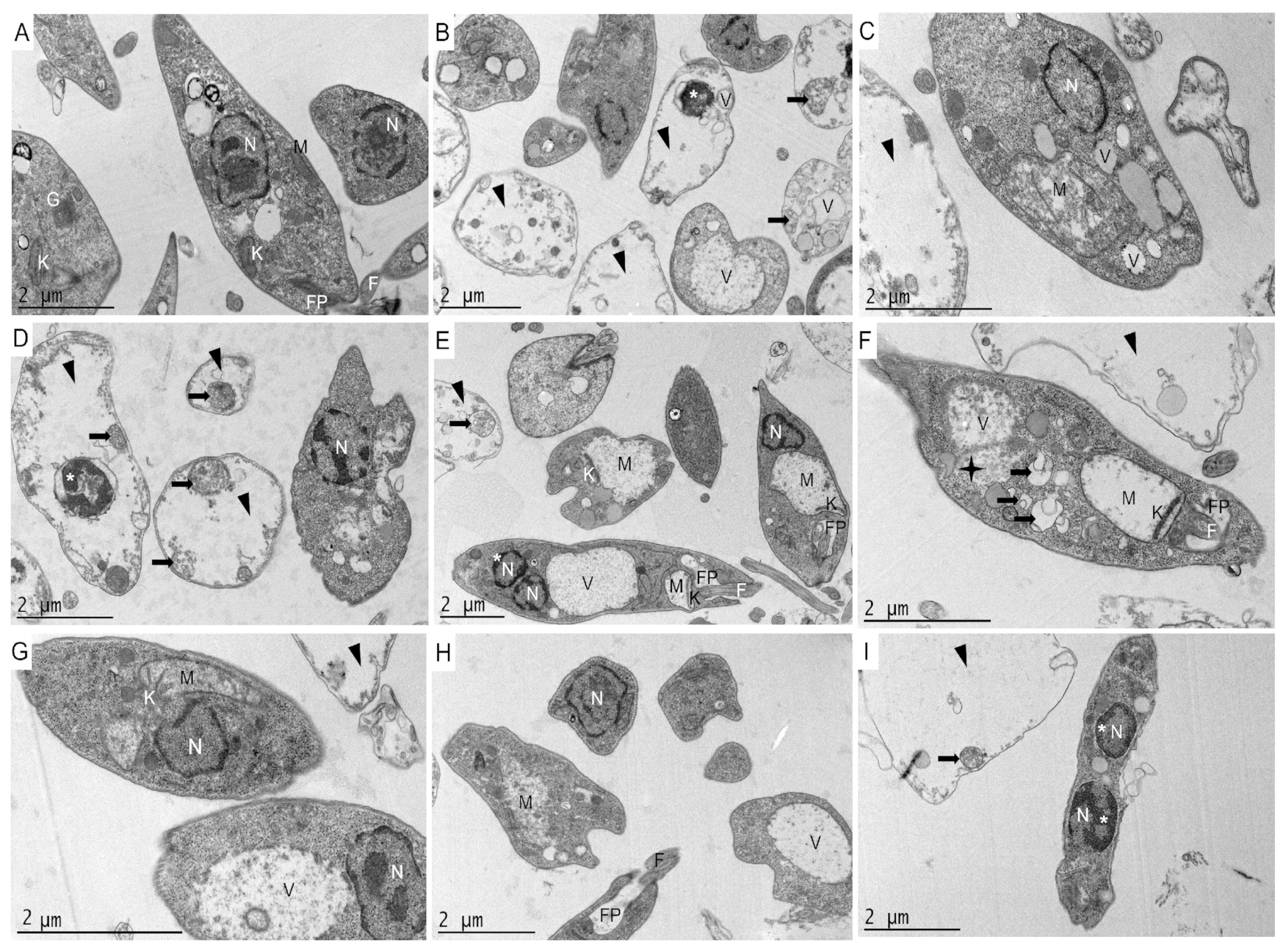
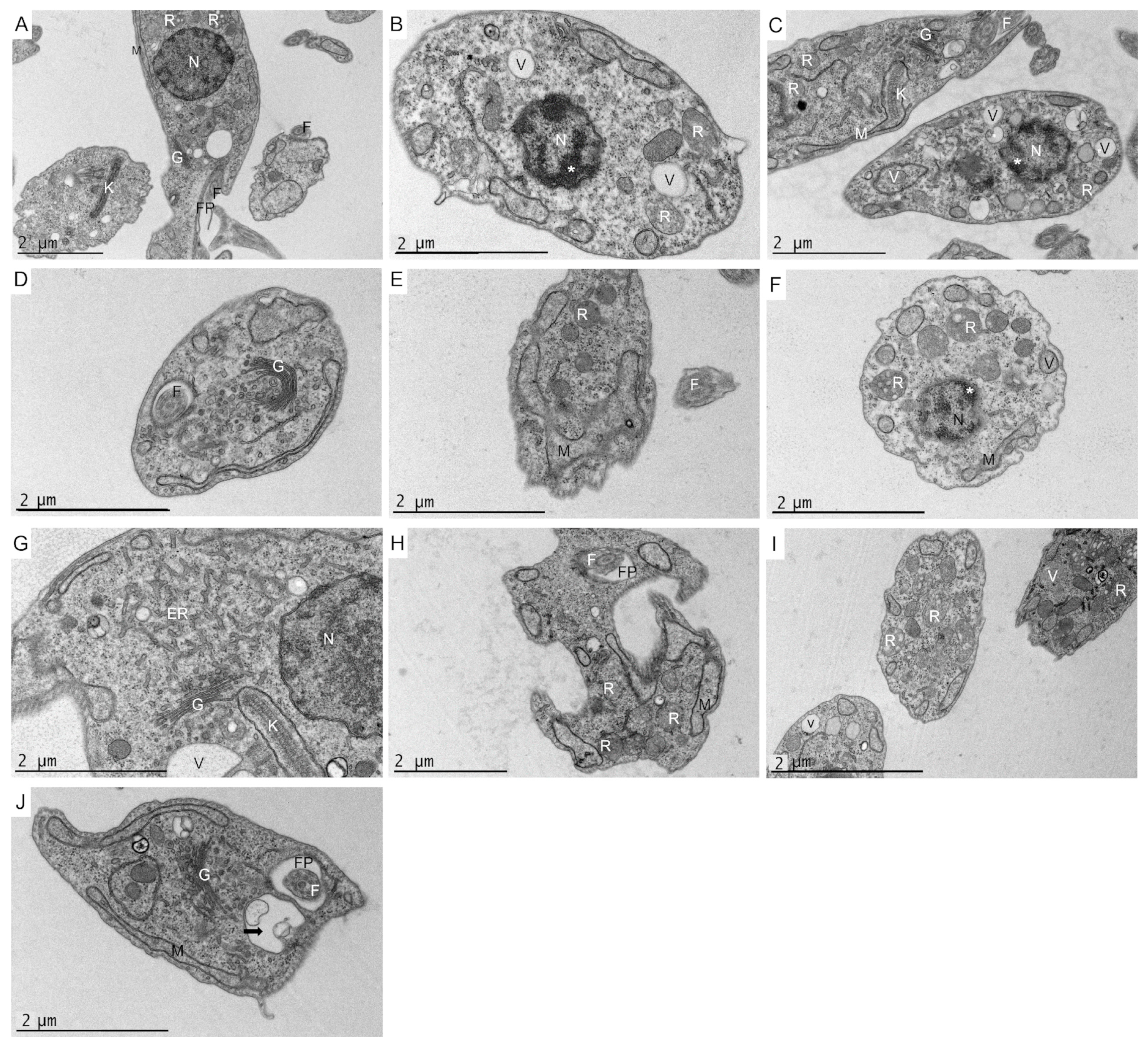
2.9. Ultrastructural Effects on L. amazonensis Promastigotes and T. cruzi Epimastigotes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Chemical Methods and Procedures
4.2. Algae Material
4.3. Extraction and Bio-Guided Fractionation: Isolation of Compounds 1–4
4.3.1. Cystomexicone B (1)
4.3.2. Gongolarone B (2)
4.3.3. 6Z-1′-Methoxyamentadione (3)
4.3.4. 1′-Methoxyamentadione (4)
4.4. Cultures
4.5. Leishmanicidal and Trypanocidal Activity Assay
4.6. In Vitro Effect against Amastigote Stage of Leishmania amazonensis
4.7. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.8. Study of the Mechanism of Cell Death in the Parasites
4.8.1. Analysis of ATP Levels
4.8.2. Analysis of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
4.8.3. Analysis of Plasma Membrane Permeability
4.8.4. Chromatin Condensation Determination
4.8.5. Analysis of Reactive Oxygen Species
4.8.6. Immunofluorescence Analysis of Actin
4.8.7. Immunofluorescence Analysis of Tubulin
4.9. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Neglected Tropical Diseases. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/q-a-detail/neglected-tropical-diseases (accessed on 7 January 2023).
- WHO. Leishmaniasis. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/leishmaniasis (accessed on 7 January 2023).
- WHO. Chagas Disease (American Trypanosomiasis). Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/chagas-disease#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 7 January 2023).
- Moretti, N.S.; Mortara, R.A.; Schenkman, S. Trypanosoma cruzi. Trends Parasitol. 2020, 36, 404–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangenito, L.S.; da Silva Santos, V.; d’Avila-Levy, C.M.; Branquinha, M.H.; Souza Dos Santos, A.L.; de Oliveira, S. Leishmaniasis and Chagas disease—Neglected tropical diseases: Treatment updates. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reece, S.E.; Pollitt, L.C.; Colegrave, N.; Gardner, A. The meaning of death: Evolution and ecology of apoptosis in protozoan parasites. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menna-Barreto, R. Cell death pathways in pathogenic trypanosomatids: Lessons of (over) kill. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nweze, J.A.; Mbaoji, F.N.; Li, Y.M.; Yang, L.Y.; Huang, S.S.; Chigor, V.N.; Eze, E.A.; Pan, L.X.; Zhang, T.; Yang, D.F. Potentials of marine natural products against malaria, leishmaniasis, and trypanosomiasis parasites: A review of recent articles. Infect. Dis. Poverty. 2021, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlgaeBase. Available online: http://www.algaebase.org (accessed on 19 January 2023).
- Mhadhebi, L.; Laroche-Clary, A.; Robert, J.; Bouraoui, A. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiproliferative activities of organic fractions from the Mediterranean brown seaweed Cystoseira sedoides. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2011, 89, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanavi, M.; Nabavi, M.; Sadati, N.; Shams Ardekani, M.; Sohrabipour, J.; Nabavi, S.M.; Ghaeli, P.; Ostad, S.N. Cytotoxic activity of some marine brown algae against cancer cell lines. Biol. Res. 2010, 43, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, G.; Pinto, E.; Andrade, P.B.; Valentão, P. Antifungal activity of phlorotannins against dermatophytes and yeasts: Approaches to the mechanism of action and influence on Candida albicans virulence factor. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno de Sousa, C.; Gangadhar, K.N.; Morais, T.R.; Conserva, G.A.; Vizetto-Duarte, C.; Pereira, H.; Laurenti, M.D.; Campino, L.; Levy, D.; Uemi, M.; et al. Antileishmanial activity of meroditerpenoids from the macroalgae Cystoseira baccata. Exp. Parasitol. 2017, 174, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibraheem, I.B.M.; Abdel-Raouf, N.; Abdel-Hameed, M.S.; Kel-yamany, K. Antimicrobial and antiviral activities against Newcastle disease virus (NDV) from marine algae isolated from Qusier and Marsa-Alam seashore (Red Sea). Egypt. Afr. J. Biotech. 2012, 11, 8332–8340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spavieri, J.; Allmendinger, A.; Kaiser, M.; Casey, R.; Hingley-Wilson, S.; Lalvani, A.; Guiry, M.D.; Blunden, G.; Tasdemir, D. Antimycobacterial, antiprotozoal and cytotoxic potential of twenty-one brown algae (Phaeophyceae) from British and Irish Waters. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 1724–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Expósito, R.L.; San Nicolás-Hernández, D.; Sifaoui, I.; Cuadrado, C.; Salazar-Villatoro, L.; Reyes-Batlle, M.; Hernández-Daranas, A.; Omaña-Molina, M.; Fernández, J.J.; Díaz-Marrero, A.R.; et al. Gongolarones as antiamoeboid chemical scaffold. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 158, 114185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiboub, O.; Sifaoui, I.; Lorenzo-Morales, J.; Abderrabba, M.; Mejri, M.; Fernández, J.J.; Piñero, J.E.; Díaz-Marrero, A.R. Spiralyde A, an antikinetoplastid dolabellane from the brown alga Dictyota spiralis. Mar. Drugs. 2019, 17, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo-Morales, J.; Díaz-Marrero, A.R.; Cen-Pacheco, F.; Sifaoui, I.; Reyes-Batlle, M.; Souto, M.L.; Hernández Daranas, A.; Piñero, J.E.; Fernández, J.J. Evaluation of oxasqualenoids from the red alga Laurencia viridis against Acanthamoeba. Mar. Drugs. 2019, 17, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazir, M.; Saleem, M.; Tousif, M.I.; Anwar, M.A.; Surup, F.; Ali, I.; Wang, D.; Mamadalieva, N.Z.; Alshammari, E.; Ashour, M.L.; et al. Meroterpenoids: A comprehensive update insight on structural diversity and biology. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbakh, H.; Zubía, E.; Reyes, C.L.; Calderón-Montaño, J.M.; Motilva, V. Anticancer activities of meroterpenoids isolated from the brown alga Cystoseira usneoides against the human colon cancer cells HT-29. Foods. 2020, 9, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suffness, M.; Pezzuto, J.M. Assays related to cancer drug discovery. In Methods in Plant Biochemistry: Assays for Bioactivity, 6th ed.; Hostettmann, K., Ed.; Academic Press Ltd.: London, UK, 1991; Volume 6, pp. 71–133. [Google Scholar]
- Salomão, K.; de Souza, E.M.; Henriques-Pons, A.; Barbosa, H.S.; de Castro, S.L. Brazilian green propolis: Effects in vitro and in vivo on Trypanosoma cruzi. J. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 2011, 185918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno de Sousa, C.; Lago, J.H.G.; Macridachis, J.; Oliveira, M.; Brito, L.; Vizetto-Duarte, C.; Florindo, C.; Hendrickx, S.; Maes, L.; Morais, T.; et al. Report of in vitro antileishmanial properties of Iberian macroalgae. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 1778–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, P.; Marín, C.; Rodríguez-González, I.; Hitos, A.B.; Rosales, M.J.; Reina, M.; Díaz, J.G.; González-Coloma, A.; Sánchez- Moreno, M. In vitro activity of C20-diterpenoid alkaloid derivatives in promastigotes and intracellular amastigotes of Leishmania infantum. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2005, 25, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, P.A.; Gomes, P.S.; Midlej, V.; Coimbra, E.S.; de Matos Guedes, H.L. PF-429242, a subtilisin inhibitor, is effective in vitro against Leishmania infantum. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 583834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombaça, A.C.S.; Dossow, D.V.; Barbosa, J.M.C.; Paz, C.; Burgos, V.; Menna-Barreto, R.F.S. Trypanocidal activity of natural sesquiterpenoids involves mitochondrial dysfunction, ROS production and autophagic phenotype in Trypanosoma cruzi. Molecules 2018, 23, 2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, L.S.; Moreira, C.S.; Calvet, C.M.; Lechuga, G.C.; Souza, R.S.; Bourguignon, S.C.; Ferreira, V.F.; Rocha, D.; Pereira, M.C.S. Efficacy of 2-hydroxy-3-phenylsulfanylmethyl-[1,4]-naphthoquinone derivatives against different Trypanosoma cruzi discrete type units: Identification of a promising hit compound. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 144, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiboub, O.; Sifaoui, I.; Abderrabba, M.; Mondher, M.; Fernández, J.J.; Díaz-Marrero, A.R.; Lorenzo-Morales, J.; Piñero, J.E. Apoptosis-like cell death upon kinetoplastid induction by compounds isolated from the brown algae Dictyota spiralis. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, C.M.; Ambaru, B.; Bajaj, R. Emerging functions of actins and actin binding proteins in trypanosomatids. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 587685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ângelo de Souza, L.; Silva E Bastos, M.; de Melo Agripino, J.; Souza Onofre, T.; Apaza Calla, L.F.; Heimburg, T.; Ghazy, E.; Bayer, T.; Ferraz da Silva, V.H.; Dutra Ribeiro, P.; et al. Histone deacetylases inhibitors as new potential drugs against Leishmania braziliensis, the main causative agent of new world tegumentary leishmaniasis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 180, 114191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, A.N.; de Graffenried, C.L. More than microtubules: The structure and function of the subpellicular array in trypanosomatids. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 760–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, J.C.; Doyle, P.S.; Palmer, J.; Hsieh, I.; Bainton, D.F.; McKerrow, J.H. Cysteine protease inhibitors alter Golgi complex ultrastructure and function in Trypanosoma cruzi. J. Cell Sci. 1998, 111, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Saha, S.; BoseDasgupta, S. The ultimate fate determinants of drug induced cell-death mechanisms in Trypanosomatids. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2021, 15, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.J.; Navarro, G.; Norte, M. Novel metabolites from the brown alga Cystoseira abies-marina. Nat. Prod. Lett. 1998, 12, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethencourt-Estrella, C.J.; Delgado-Hernández, S.; López-Arencibia, A.; San Nicolás-Hernández, D.; Sifaoui, I.; Tejedor, D.; García-Tellado, F.; Lorenzo-Morales, J.; Piñero, J.E. Acrylonitrile derivatives against Trypanosoma cruzi: In vitro activity and programmed cell death study. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Arencibia, A.; Martín-Navarro, C.; Sifaoui, I.; Reyes-Batlle, M.; Wagner, C.; Lorenzo-Morales, J.; Maciver, S.K.; Piñero, J.E. Perifosine mechanisms of action in Leishmania species. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02127-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartuche, L.; Sifaoui, I.; López-Arencibia, A.; Bethencourt-Estrella, C.J.; San Nicolás-Hernández, D.; Lorenzo-Morales, J.; Piñero, J.E.; Díaz-Marrero, A.R.; Fernández, J.J. Antikinetoplastid activity of indolocarbazoles from Streptomyces sanyensis. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Arencibia, A.; Bethencourt-Estrella, C.J.; Freijo, M.B.; Reyes-Batlle, M.; Sifaoui, I.; Nicolás-Hernández, D.S.; McNaughton-Smith, G.; Lorenzo-Morales, J.; Abad-Grillo, T.; Piñero, J.E. New phenalenone analogues with improved activity against Leishmania species. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Arencibia, A.; San Nicolás-Hernández, D.; Bethencourt-Estrella, C.J.; Sifaoui, I.; Reyes-Batlle, M.; Rodríguez-Expósito, R.L.; Rizo-Liendo, A.; Lorenzo-Morales, J.; Bazzocchi, I.L.; Piñero, J.E.; et al. Withanolides from Withania aristata as antikinetoplastid agents through induction of programmed cell death. Pathogens 2019, 8, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Arencibia, A.; Reyes-Batlle, M.; Freijo, M.B.; Sifaoui, I.; Bethencourt-Estrella, C.J.; Rizo-Liendo, A.; Chiboub, O.; McNaughton-Smith, G.; Lorenzo-Morales, J.; Abad-Grillo, T.; et al. In vitro activity of 1H-phenalen-1-one derivatives against Leishmania spp. and evidence of programmed cell death. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeouk, I.; Sifaoui, I.; López-Arencibia, A.; Reyes-Batlle, M.; Bethencourt-Estrella, C.; Bazzocchi, I.L.; Bekhti, K.; Lorenzo-Morales, J.; Jiménez, I.A.; Piñero, J.E. Sesquiterpenoids and flavonoids from Inula viscosa induce programmed cell death in kinetoplastids. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelan-Ramírez, I.; Salazar-Villatoro, L.; Chávez-Munguía, B.; Salinas-Lara, C.; Sánchez-Garibay, C.; Flores-Maldonado, C.; Hernández-Martínez, D.; Anaya-Martínez, V.; Ávila-Costa, M.R.; Méndez-Cruz, A.R.; et al. Schwann Cell autophagy and necrosis as mechanisms of cell death by Acanthamoeba. Pathogens 2020, 9, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifaoui, I.; Díaz-Rodríguez, P.; Rodríguez-Exposito, R.L.; Reyes-Batlle, M.; Lopez-Arencibia, A.; Salazar Villatoro, L.; Castelan-Ramírez, I.; Omana-Molina, M.; Oliva, A.; Pinero, J.E.; et al. Pitavastatin loaded nanoparticles: A suitable ophthalmic treatment for Acanthamoeba keratitis inducing cell death and autophagy in Acanthamoeba polyphaga. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022, 180, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compounds | L. amazonensis | L. donovani | T. cruzi | Murine Macrophages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cystomexicone B (1) | 36.65 ± 4.24 (7.61) a | 248.27 ± 0.94 (1.12) a | 19.19 ± 2.62 (14.53) a | >278.96 |
| Gongolarone B (2) | 6.45 ± 0.44 (3.79) a | - | 2.92 ± 0.25 (8.36) a | 24.41 ± 3.98 |
| 6Z-1′-Methoxyamentadione (3) | 4.88 ± 0.33 (5.49) a | 97.94 ± 5.32 (0.27) a | 3.26 ± 0.11 (8.19) a | 26.80 ± 4.06 |
| 1′-Methoxyamentadione (4) | 4.88 ± 0.86 (5.41) a | 126.51 ± 1.15 (0.21) a | 4.93 ± 0.55 (5.36) a | 26.42 ± 2.27 |
| Miltefosine * | 6.48 ± 0.10 (11.10) a | 3.31 ± 0.11 (21.80) a | - | 72.18 ± 1.25 |
| Benznidazole * | - | - | 6.95 ± 0.50 (57.51) a | 399.91 ± 1.04 |
| Compounds | L. amazonensis |
|---|---|
| Cystomexicone B (1) | 24.55 ± 0.83 (11.36) a |
| Gongolarone B (2) | 16.23 ± 1.90 (1.50) a |
| 6Z-1′-Methoxyamentadione (3) | 16.17 ± 2.61 (1.66) a |
| 1′-Methoxyamentadione (4) | 27.59 ± 1.68 (0.96) a |
| Miltefosine * | 3.12 ± 0.12 (23.16) a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nicolás-Hernández, D.S.; Rodríguez-Expósito, R.L.; López-Arencibia, A.; Bethencourt-Estrella, C.J.; Sifaoui, I.; Salazar-Villatoro, L.; Omaña-Molina, M.; Fernández, J.J.; Díaz-Marrero, A.R.; Piñero, J.E.; et al. Meroterpenoids from Gongolaria abies-marina against Kinetoplastids: In Vitro Activity and Programmed Cell Death Study. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040476
Nicolás-Hernández DS, Rodríguez-Expósito RL, López-Arencibia A, Bethencourt-Estrella CJ, Sifaoui I, Salazar-Villatoro L, Omaña-Molina M, Fernández JJ, Díaz-Marrero AR, Piñero JE, et al. Meroterpenoids from Gongolaria abies-marina against Kinetoplastids: In Vitro Activity and Programmed Cell Death Study. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(4):476. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040476
Chicago/Turabian StyleNicolás-Hernández, Desirée San, Rubén L. Rodríguez-Expósito, Atteneri López-Arencibia, Carlos J. Bethencourt-Estrella, Ines Sifaoui, Lizbeth Salazar-Villatoro, Maritza Omaña-Molina, José J. Fernández, Ana R. Díaz-Marrero, José E. Piñero, and et al. 2023. "Meroterpenoids from Gongolaria abies-marina against Kinetoplastids: In Vitro Activity and Programmed Cell Death Study" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 4: 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040476
APA StyleNicolás-Hernández, D. S., Rodríguez-Expósito, R. L., López-Arencibia, A., Bethencourt-Estrella, C. J., Sifaoui, I., Salazar-Villatoro, L., Omaña-Molina, M., Fernández, J. J., Díaz-Marrero, A. R., Piñero, J. E., & Lorenzo-Morales, J. (2023). Meroterpenoids from Gongolaria abies-marina against Kinetoplastids: In Vitro Activity and Programmed Cell Death Study. Pharmaceuticals, 16(4), 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040476













