A Systematic Review of In Vivo Studies of the Efficacy of Herbal Medicines for Anti-Aging in the Last Five Years
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Collection Process
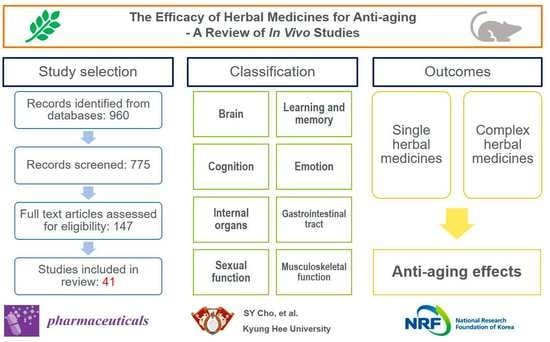
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Characteristics of Included Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Endocrinology, T.L.D. Opening the door to treating ageing as a disease. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, E.; Park, S.-Y.; Yin, C.S.; Kim, H.-T.; Kim, Y.M.; Yi, T.H. Antiaging effects of the mixture of Panax ginseng and Crataegus pinnatifida in human dermal fibroblasts and healthy human skin. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.H.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Rodriguez, I.; Nuankaew, W.; Bhawal, U.K.; Na Hong, B.; Kang, T.H. Anti-aging effects of Korean Red Ginseng (KRG) in differentiated embryo chondrocyte (DEC) knockout mice. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Sun, C.; Pei, Z.; Yun, T.; Fan, S.; Long, S.; Wu, T.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Xu, F. Liangyi Gao extends lifespan and exerts an antiaging effect in Caenorhabditis elegans by modulating DAF-16/FOXO. Biogerontology 2019, 20, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.-Y.; Jiang, J.-G.; Yang, L.; Wang, D.-W.; Zhu, W. Anti-ageing active ingredients from herbs and nutraceuticals used in traditional Chinese medicine: Pharmacological mechanisms and implications for drug discovery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1395–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.J.; Choi, B.T.; Shin, H.K.; Shin, B.C.; Han, Y.K.; Baek, J.U. Establishment of a comprehensive list of candidate antiaging medicinal herb used in Korean medicine by text mining of the classical Korean medical literature, “dongeuibogam,” and preliminary evaluation of the antiaging effects of these herbs. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 873185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phu, H.T.; Thuan, D.T.B.; Nguyen, T.H.D.; Posadino, A.M.; Eid, A.H.; Pintus, G. Herbal Medicine for Slowing Aging and Aging-associated Conditions: Efficacy, Mechanisms and Safety. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2020, 18, 369–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Ding, Q.; Feng, S.; Liu, Z.; Shi, Y. Antioxidant mechanism of modified Qiongyu paste against aging based on network pharmacology and experimental validation. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Sci. 2022, 9, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, B.; Xia, B.; Zhu, R.; Liu, Y.; Dai, X.; Ye, Z.; Zhao, D.; Mo, F.; et al. BaZiBuShen alleviates cognitive deficits and regulates Sirt6/NRF2/HO-1 and Sirt6/P53-PGC-1α-TERT signaling pathways in aging mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 282, 114653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.-H.; Huang, N.-K.; Shiao, Y.-J.; Lu, C.-K.; Chao, Y.-M.; Huang, Y.-J.; Yeh, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-L. Gastrodiae rhizoma attenuates brain aging via promoting neuritogenesis and neurodifferentiation. Phytomedicine 2021, 87, 153576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-Salinas, A.K.; Vázquez-Roque, R.A.; Díaz, A.; Pulido, G.; Treviño, S.; Floran, B.; Flores, G. The treatment of Goji berry (Lycium barbarum) improves the neuroplasticity of the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus in aged rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 83, 108416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumiyoshi, E.; Hashimoto, M.; Hossain, S.; Matsuzaki, K.; Islam, R.; Tanabe, Y.; Maruyama, K.; Kajima, K.; Arai, H.; Ohizumi, Y.; et al. Anredera cordifolia extract enhances learning and memory in senescence-accelerated mouse-prone 8 (SAMP8) mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 3992–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, M.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Sui, X.; Lin, J.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.; et al. Microbiome-Metabolomics Reveals Endogenous Alterations of Energy Metabolism by the Dushen Tang to Attenuate D-Galactose-Induced Memory Impairment in Rats. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6649085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Yu, R.; Wang, X.; Wei, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, A.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ji, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. Role of Eclipta prostrata extract in improving spatial learning and memory deficits in D-galactose-induced aging in rats. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2019, 39, 649–657. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.-J.; Liu, X.-J.; Tian, J.-S.; Gao, X.-X.; Liu, H.-L.; Du, G.-H.; Qin, X.-M. Effects of Guilingji on Aging Rats and Its Underlying Mechanisms. Rejuvenation Res. 2020, 23, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Chang, Y.; Gao, L.; Qin, X.; Du, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y. Protective effects of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi extract on D-galactose induced aging rats. Metab. Brain Dis. 2018, 33, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, N.E.; Zweig, J.A.; Caruso, M.; Martin, M.D.; Zhu, J.Y.; Quinn, J.F.; Soumyanath, A. Centella asiatica increases hippocampal synaptic density and improves memory and executive function in aged mice. Brain Behav. 2018, 8, e01024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainanta, T.; Jaroenporn, S.; Wititsuwankul, P.; Malaivijitnond, S. Comparison of neuroprotective effects of dihydrotestosterone, 17β-estradiol, and Pueraria mirifica herb extract on cognitive impairment in androgen deficient male rats. Horm. Behav. 2022, 143, 105198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Tang, X.; Gong, D.; Xia, P.; Wang, F.; Xu, S. Bungeanum Improves Cognitive Dysfunction and Neurological Deficits in D-Galactose-Induced Aging Mice via Activating PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, N.; Maruko, A.; Oshima, K.; Yoshida, M.; Honma, K.; Sugiyama, C.; Nagai, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Odaguchi, H.; Okada, N. Kampo formulas alleviate aging-related emotional disturbances and neuroinflammation in male senescence-accelerated mouse prone 8 mice. Aging 2022, 14, 109–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-M.; Shibu, M.A.; Chen, C.-S.; Tamilselvi, S.; Tsai, C.-T.; Tsai, C.-C.; Kumar, K.A.; Lin, H.-J.; Mahalakshmi, B.; Kuo, W.-W.; et al. Adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells along with Alpinia oxyphylla extract alleviate mitochondria-mediated cardiac apoptosis in aging models and cardiac function in aging rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 264, 113297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-M.; Tamilselvi, S.; Lin, H.-J.; Tsai, C.-C.; Lin, Y.-M.; Day, C.H.; Viswanadha, V.P.; Chang, H.-N.; Kuo, W.-W.; Huang, C.-Y. Alpinia oxyphylla Miq extract ameliorates cardiac fibrosis associated with D-galactose induced aging in rats. Environ. Toxicol. 2019, 34, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, J.-Z.; Lin, Z.-X.; Yuan, Q.-J.; Li, Y.-C.; Liang, J.-L.; Zhan, J.Y.-X.; Xie, Y.-L.; Su, Z.-R.; Liu, Y.-H. Ameliorative effect of supercritical fluid extract of Chrysanthemum indicum Linnén against D-galactose induced brain and liver injury in senescent mice via suppression of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 234, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Bae, H.-M.; Baik, I. Potential Antiaging and Hepatoprotective Effects of Acanthopanax senticosus Extracts in Adult Rat Models. Rejuvenation Res. 2023; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, D.; Jóźwik, A.; Łysek-Gładysińska, M.; Grzybek, W.; Adamus-Białek, W.; Bicki, J.; Strzałkowska, N.; Kamińska, A.; Horbańczuk, O.; Atanasov, A. Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) Seeds Dietary Supplementation Regulates Liver Antioxidant Defense Systems in Aging Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Z.-Z.; Lin, Z.-X.; Su, Z.-R.; Zheng, L.; Li, H.-L.; Xie, J.-H.; Xian, Y.-F.; Yi, T.-G.; Huang, S.-Q.; Chen, J.-P. Angelica sinensis Supercritical Fluid CO2 Extract Attenuates D-Galactose-Induced Liver and Kidney Impairment in Mice by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. J. Med. Food 2018, 21, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, D.; Kang, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, D.; Duan, Y.; Wang, J. Integration of lncRNA and mRNA profiles to reveal the protective effects of Codonopsis pilosula extract on the gastrointestinal tract of mice subjected to D-galactose-induced aging. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 47, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenghua, P.; Ziqin, Z.; Shuyu, T.; Huixia, Z.; Xianglu, R.; Jiao, G. An integrated fecal microbiome and metabolome in the aged mice reveal anti-aging effects from the intestines and biochemical mechanism of FuFang zhenshu TiaoZhi(FTZ). Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Ning, S.; Yang, X.; Shi, J.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, A.; Gao, X.; Tian, J.; Zhang, B.; Qin, X. Brain and testicular metabonomics revealed the protective effects of Guilingji on senile sexual dysfunction rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 290, 115047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.-J.; Tian, J.-S.; Tai, G.; Gao, X.-X.; Liu, H.-L.; Du, G.-H.; Liu, X.-J.; Qin, X.-M. 1H NMR-based metabolomics revealed the protective effects of Guilingji on the testicular dysfunction of aging rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 238, 111839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, J.Y.; Park, M.J.; Park, H.J.; Park, N.C.; Joo, B.S. Combination of Korean Red Ginseng Extract and Hydrogen-Rich Water Improves Spermatogenesis and Sperm Motility in Male Mice. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2020, 26, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Ma, N.; Liu, Z.; Wang, T.; Yuan, C.; He, Y.; Dun, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yuan, D.; Zhang, C. Protective effect of Wuzi Yanzong recipe on testicular dysfunction through inhibition of germ cell apoptosis in ageing rats via endoplasmic reticulum stress. Andrologia 2019, 51, e13181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.-A.; Oh, K.-N.; Choi, E.J.; Oh, D.-R.; Kim, Y.J.; Bae, D.; Hong, J.A.; Pan, S.; Kim, K.M.; Kim, D.-W.; et al. In vitro and in vivo androgen regulation of Dendropanax morbiferus leaf extract on late-onset hypogonadism. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2018, 64, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.C.; Jeon, S.H.; Qun, Z.G.; Bashraheel, F.; Choi, S.W.; Kim, S.J.; Bae, W.J.; Cho, H.J.; Ha, U.-S.; Hong, S.H.; et al. Lycium chinense Mill improves hypogonadism via anti-oxidative stress and anti-apoptotic effect in old aged rat model. Aging Male 2020, 23, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.W.; Jeon, S.H.; Kwon, E.B.; Zhu, G.Q.; Lee, K.W.; Choi, J.B.; Jeong, H.C.; Kim, K.S.; Bae, S.R.; Bae, W.J.; et al. Effect of Korean Herbal Formula (Modified Ojayeonjonghwan) on Androgen Receptor Expression in an Aging Rat Model of Late Onset Hypogonadism. World J. Men’s Health 2019, 37, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chu, N.; Qiu, X.-M.; Tang, W.; Gober, H.-J.; Li, D.-J.; Wang, L. Effects of Heyan Kuntai Capsule on Follicular Development and Oocyte Cohesin Levels in Aged Mice. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2018, 24, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; You, S. Effect of samul-tang on female fertility via RAS signaling pathway in ovaries of aged mice. Aging 2021, 13, 14829–14842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wei, M.-L.; Dong, X.-Y. Effects of Yu Linzhu on ovarian function and oocyte mitochondria in natural aging mice. Aging 2021, 13, 23328–23337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, B.; Zhu, R.; Li, R.; Tian, Y.; Liu, C.; Jia, Q.; Wang, L.; Tang, J.; Zhao, D.; et al. Fructus Ligustri Lucidi preserves bone quality through the regulation of gut microbiota diversity, oxidative stress, TMAO and Sirt6 levels in aging mice. Aging 2019, 11, 9348–9368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, Y.; Ishida, T.; Morisawa, S.; Jobu, K.; Ou, Y.; Fujita, H.; Hanazaki, K.; Miyamura, M. Juzentaihoto Suppresses Muscle Atrophy and Decreased Motor Function in SAMP8 Mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 44, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amitani, H.; Chiba, S.; Amitani, M.; Michihara, S.; Takemoto, R.; Han, L.; Fujita, N.; Takahashi, R.; Inui, A. Impact of Ninjin’yoeito on frailty and short life in klotho-hypomorphic (kl/kl) mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 973897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orita, K.; Yamate, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Hiramoto, K. Ameliorative Effect of Hochu-ekki-to on Natural Skin Aging. Pharmacology 2020, 105, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiramoto, K.; Orita, K.; Yamate, Y.; Kobayashi, H. Role of Momordica charantia in preventing the natural aging process of skin and sexual organs in mice. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e14243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Komatsu, T.; Ohata, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Yoshii, Y.; Park, S.; Mori, R.; Satou, M.; Kondo, Y.; et al. Effects of rikkunshito supplementation on resistance to oxidative stress and lifespan in mice. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2020, 20, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, Y.; Miyama, Y.; Imai, R.; Oizumi, H.; Miyazaki, S.; Haneda, E.; Mizuno, K.; Omiya, Y.; Ikeda, Y.; Mizoguchi, K. Ninjin’yoeito, a traditional Japanese medicine, attenuates age-related deficits of muscle performance, self-care motivation, and body temperature in C57BL/6 mice. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2022, 86, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Chen, K.; Li, J.; Fang, Z.; Pang, H.; Yin, Y.; Rong, X.; Guo, J. Gut microbiota combined with metabolomics reveals the metabolic profile of the normal aging process and the anti-aging effect of FuFang Zhenshu TiaoZhi(FTZ) in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Gao, L.; Qin, X.; Du, G.; Zhou, Y. The intervention effect of licorice in d-galactose induced aging rats by regulating the taurine metabolic pathway. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 4814–4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, W.; Song, N.; Yan, Q.; Liang, H.; Zhang, W. The analysis of the effects of Liuwei Dihuang decoction on aging-related metabolites and metabolic pathways in naturally aging mice by ultra-performance liquid chromatography quadruple time-of-light mass spectrometry. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021, 72, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ai, J.; Mao, H.; Gao, X. Effects of Eclipta prostrata on gut microbiota of SAMP6 mice with osteoporosis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 402–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Guo, P.; Jin, Y.; Li, M.; Hu, X.; Wang, W.; Wei, X.; Qi, S. Momordica charantia polysaccharide ameliorates D-galactose-induced aging through the Nrf2/β-Catenin signaling pathway. Metab. Brain Dis. 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Peng, M.; Meng, H.; Ma, H.; Cai, P.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Si, G. A Review on Central Nervous System Effects of Gastrodin. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, F.; Chen, Z. Lycium Barbarum: A Traditional Chinese Herb and A Promising Anti-Aging Agent. Aging Dis. 2017, 8, 778–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.; Ye, J.; Gao, L.; Liu, Y. The main bioactive compounds of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. for alleviation of inflammatory cytokines: A comprehensive review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Yang, L.; Gao, L.; Du, G.; Qin, X.; Zhou, Y. The leaves of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi attenuate brain aging in D-galactose-induced rats via regulating glutamate metabolism and Nrf2 signaling pathway. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 170, 111978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shengkai, D.; Qianqian, L.; Yazhen, S. The Effects and Regulatory Mechanism of Flavonoids from Stems and Leaves of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi in Promoting Neurogenesis and Improving Memory Impairment Mediated by the BDNF-ERK-CREB Signaling Pathway in Rats. CNS Neurol. Disord.-Drug Targets 2022, 21, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shengkai, D.; Yazhen, S. Flavonoids from Stems and Leaves of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi Regulate the Brain Tau Hyperphosphorylation at Multiple Sites Induced by Composited Aβ in Rats. CNS Neurol. Disord.-Drug Targets 2022, 21, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-H.; Lee, R.; Nam, S.M.; Kim, D.-G.; Cho, I.-H.; Kim, H.-C.; Cho, Y.; Rhim, H.; Nah, S.-Y. Ginseng gintonin, aging societies, and geriatric brain diseases. Integr. Med. Res. 2021, 10, 100450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Du, Q.; Li, N.; Du, S.; Sun, Z. Alpiniae oxyphyllae Fructus and Alzheimer’s disease: An update and current perspective on this traditional Chinese medicine. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 135, 111167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Chen, B.; Niu, K.; Long, Z.; Yang, F.; Xie, Y. Alpiniae oxyphylla fructus extract promotes longevity and stress resistance of C. elegans via DAF-16 and SKN-1. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1034515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, J.; Pan, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L.; Sun, G. Analysis of Chemical Constituents of Chrysanthemum morifolium Extract and Its Effect on Postprandial Lipid Metabolism in Healthy Adults. Molecules 2023, 28, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.-L.; Zeng, R.; Gu, C.-M.; Qu, Y.; Huang, L.-F. Angelica sinensis in China-A review of botanical profile, ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and chemical analysis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 190, 116–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Khan, T.; Fatima, K.; Ali, Q.U.A.; Ovais, M.; Khalil, A.T.; Ullah, I.; Raza, A.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Idrees, M. Selected hepatoprotective herbal medicines: Evidence from ethnomedicinal applications, animal models, and possible mechanism of actions. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojcikowski, K.; Johnson, D.; Gobe, G. Herbs or natural substances as complementary therapies for chronic kidney disease: Ideas for future studies. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 2006, 147, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, F.; Ji, Y.; Peng, L.; Liu, Q.; Cao, H.; Yang, Y.; He, X.; Zeng, N. Extraction, purification, structural characteristics and biological properties of the polysaccharides from Codonopsis pilosula: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 261, 117863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.P.; Shi, X.; Kong, G.W.S.; Wang, C.C.; Wu, J.C.Y.; Lin, Z.X.; Li, T.C.; Chan, D.Y.L. The Therapeutic Effects of a Traditional Chinese Medicine Formula Wuzi Yanzong Pill for the Treatment of Oligoasthenozoospermia: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 2968025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.; Park, S.J.; Hwang, M. Effectiveness a herbal medicine (Sipjeondaebo-tang) on adults with chronic fatigue syndrome: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Integr. Med. Res. 2021, 10, 100664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qiu, H.; Li, C.; Cai, P.; Qi, F. The positive role of traditional Chinese medicine as an adjunctive therapy for cancer. Biosci. Trends 2021, 15, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Classification | Study (Author, year) | Country | Herbal Medicine (Part) | Herbal Extraction | Route of Administration | Dosage (Day) | Treatment Period | Animal Model (Age) | Induced Way | Sex | n/ Group | Outcomes and Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brain | ||||||||||||
| Xie et al., 2022 [8] | China | Modified Qiongyu paste | N/R | oral | 0.3 g/kg, 0.6 g/kg, 1.2 g/kg | 6 w | C57BL/6N mice (6–8 w) | D-gal (150 mg/kg/day for 6 w) | M | 10 | SOD (brain cortex) ↑ TNF-α (serum) ↓ IL-6 (serum) ↓ | |
| Li et al., 2022 [9] | China | BaZiBuShen | water | oral | 0.7 g/kg, 1.4 g/kg, 2.8 g/kg | 65 d | ICR mice (8 w) | D-gal (120 mg/kg/day) and NaNO2 (90 mg/kg/day) for 3 m | M | 14 | memory and cognitive deficits ↓ motor function and grip strength ↑ GSH/GSSG, MDA, and TAC (brain) ↑ preserved mitochondrial function in cerebral cortex maintained telomerase activity and telomere length P53, caspase-3, Bax expressions ↓ Sirt6, p–HO–1, p-NRF2, PGC-1α, and Bcl-2 expressions↑ | |
| Hsu et al., 2021 [10] | Taiwan | Gastrodiae Rhizoma (rhizome) | ethanol | intragastric | 5 mg/kg, 20 mg/kg, 50 mg/kg | 8 w | C57BL/6 mice (6 w) | D-gal (200 mg/kg/day for 8 w) | M | 6 | learning and memory abilities (nesting and burrowing test, and Morris water maze test) ↑ reversed the decreased CAT and SOD (brain) GSH-Px activity (the cortex and hippocampus) ↑ MDA ↓ hippocampal neurogenesis ↑ regulated the SH2B1-Akt pathway | |
| Ruíz-Salinas et al., 2020 [11] | Mexico | Lycium barbarum (fruits) | N/R | N/R | 3 g/kg | 60 d | Sprague-Dawley rats (18 m) | N/R | M | 15 | dendritic morphology in the PFC and hippocampus neurons ↑ Synaptophysin↑ Caspase 3 ↓ 3-nitrotyrosine ↓ Nrf2 ↓ ROS (PFC and hippocampus) ↓ | |
| Learning and memory | ||||||||||||
| Sumiyoshi et al., 2021 [12] | Japan | Anredera cordifolia (leaves) | methanol | oral | N/R | 31 w | SAMP8 mice (15 w) | N/R | M | 9 or 10 | faster acquisition and better retention in the Morris water maze task neuronal plasticity-related protein (hippocampal BDNF, NMDAR subunit, postsynaptic density protein-95, pCREB/CREB) ↑ | |
| Wang et al., 2021 [13] | China | Dushen Tang | water | oral | 0.3 g/kg | N/R | Sprague-Dawley rats (6 w) | D-gal (500 mg/kg/day for 7 w) | M | 10 | the spatial memory and learning abilities (Morris water maze test) ↑ neuronal damage in the hippocampus ↓ regulated the structure of the gut microbiota | |
| Xia et al., 2019 [14] | China | Eclipta prostrata (leaves) | water | oral | 50 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg, 200 mg/kg | 3 w | Sprague-Dawley rats (30 w) | D-gal (100 mg/kg/day for 6 w) | M | 10 | the spatial memory and learning abilities (Morris water maze test) ↑ neuronal damage in the hippocampus↓ SOD, CAT, GSH-Px, GR ↑ iNOS, NO ↓ dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin (5-HT) ↑ | |
| Zhao et al., 2020 [15] | China | Guilingji | suspension | oral | 37.5 mg/kg, 75 mg/kg, 150 mg/kg | 4 w | Sprague-Dawley rats (23 m) | N/R | M | 10 | the spatial memory and learning abilities (Morris water maze test) ↑ SOD, CAT and GSH-Px ↑ MDA ↓ Ach ↑ AchE ↓ 1H-NMR-based serum metabolomics | |
| Zhao et al., 2018 [16] | China | Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi (root) | ethanol | oral | 100 mg/kg/, 200 mg/kg | 10 w | Sprague-Dawley rats | D-gal (100 mg/kg/day for 10 w) | M | 10 | the spatial and learning memory (open-field test and Morris water maze test) ↑ SOD, CAT, GPx ↑ MDA ↓ histological abnormalities of hippocampus neurons ↓ | |
| Cognition | ||||||||||||
| Gray et al., 2018 [17] | USA | Centella asiatica (leaves) | water | oral | 2 g/L | 2 w | CB6F1 mice (20 m) | N/R | M, F | 18 (M + F) | performance in the Object Location Memory task ↑ performance in the Novel Object Recognition Task ↑ synaptic density in the hippocampus ↑ | |
| Fainanta et al., 2022 [18] | Thailand | Pueraria mirifica (N/R) | ethanol | oral | 100 mg/kg | 2 m | Sprague-Dawley rats (androgen-deficient, 2 m) | orchidectomized | M | 13 | impairment of spatial learning behavior and memory capacity was prevented maintain synaptic function and structure and suppress neurofibrillary tangles mitigated the increased Tau3 and Tau4 mRNA levels | |
| Zhao et al., 2020 [19] | China | Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim (N/R) | water or volatile oil | oral | 450 mg/kg | 48 d | Kunming mice | D-gal (500 mg/kg) | M | 10 | impaired memory was alleviated prevented hippocampal neuron damage MDA (brain) ↓ upregulated Nrf2 and HO-1 the expression ratio of Bcl2/Bax ↑ | |
| Emotion | ||||||||||||
| Ito et al., 2022 [20] | Japan | Kososan, Hachimijiogan | water | oral | 1.0 g/kg | 13 w | SAMP8 mice (7 w) | N/R | M | N/R | depression-like behaviors (the tail suspension test, sucrose preference test, and open field test) ↓ hippocampal neuroinflammation ↓ tau accumulation ↓ IL-6 and MCP-1 ↓ | |
| Internal organs | ||||||||||||
| Heart | Chang et al., 2021 [21] | Taiwan | Alpinia oxyphylla Miq. (fruits) | water | oral | 100 mg/kg | 4 w | Wistar-Kyoto rats (20 w) | D-gal (150 mg kg/day for 8 w) | M | 6 | aging associated cardiac damages ↓ cardiac performance ↑ |
| Heart | Chang et al., 2019 [22] | Taiwan | Alpinia oxyphylla Miq. (fruits) | water | oral | 50 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg, 150 mg/kg | 8 w | Sprague-Dawley rats (8 w) | D-gal (150 mg kg/day for 8 w) | M | N/R | collagen deposition and cardiac fibrosis ↓ |
| Liver and brain | Zhang et al., 2019 [23] | China | Chrysanthemum indicum Linne (flowers and buds) | carbon dioxide fluid | oral | 100 mg/kg, 150 mg/kg, 300 mg/kg | 8 w | Kunming mice (N/R) | D-gal (200 mg/kg) | M | 10 | body weight ↑ attenuated the decline of thymus and spleen indexes elevated levels of ALT and AST ↓ alleviated abnormal alterations in structure and function of brain and liver ↓ renewing normal antioxidant enzymes activities (SOD, CAT, GSH-Px) MDA accumulation ↓ IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α ↓ attenuated the increase of Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and cleaved caspase-3 activation in the liver and brain |
| Liver | Kim et al., 2023 [24] | Korea | Acanthopanax senticosus (stem and root) | ethanol | oral | 7 mg | 24 w | Sprague-Dawley rats (24 w) | N/R | M | 10 | leukocyte telomere length ↑ AST, ALT ↓ |
| Liver | Tewari et al., 2020 [25] | Poland | Trigonella foenum-graecum L. (seeds) | N/R | oral | 0.125 g, 0.250 g | 4 w | Swiss mice (12 m) | N/R | M | 6 | SOD ↑ glutathione reductase ↓ GSH-Px ↓ total polyphenols↑ free radical scavenging properties↑ |
| Liver and kidney | Mo et al., 2018 [26] | China | Angelica sinensis (root) | carbon dioxide fluid | oral | 20 mg/kg, 40 mg/kg, 80 mg/kg | 8 w | Kunming strain mice (8 w) | D-gal (200 mg/kg/day for 8 w) | M | N/R | the organ index ↑ functional parameters ↑ the hepatic and renal MD ↓ gene expressions of hepatic and renal Cu, Zn-SOD, CAT, and GPx ↑ iNOS, COX-2, IκBα, p-IκBα, and p65 ↓ IκBα ↑ ameliorated the histological deterioration |
| Gastrointestinal tract | ||||||||||||
| Meng et al., 2021 [27] | China | Codonopsis pilosula (root) | water | intragastric | 5 g/kg, 10 g/kg, 15 g/kg | 6 w | Kunming mice (2 m) | D-gal (50 g/kg/day) | M, F | 20 | weight and thymus index ↑ D-xylose absorption ↑ motilin secretion ↑ reversed the changes of gastric histomorphology | |
| Piao et al., 2020 [28] | China | Fufang Zhenzhu Tiao Zhi | alcohol and water | oral | 1.0 g/kg | 12 w | C57BL/6J mice (22 m) | naturally aging | F | 6 | intestinal inflammation ↓ telomerase activity ↑ partially reversed the fecal metabolites abnormalities restored the disorders of intestinal flora | |
| Sexual function | ||||||||||||
| Ding et al., 2022 [29] | China | Guilingji | suspension | intragastric | 37.5 mg/kg, 75 mg/kg, 150 mg/kg | 8 w | Sprague-Dawley rats (6 w) | D-gal (300 mg/kg/day for 8 w) | M, F | 6 | the mount and ejaculation latency levels ↑ testicular morphology improved GnRH and LH levels improved | |
| testicular function | Zhao et al., 2019 [30] | China | Guilingji | suspension | intragastric | 37.5 mg/kg, 75 mg/kg, 150 mg/kg | 4 w | Sprague-Dawley rats (23 m) | naturally aging | M | 10 | Weights of the testicles ↑ T concentration ↑ Morphologic abnormality of testicular tissues: improved Urinary levels of alanine, pantothenate, phenylalanine, β-hydroxybutyrate and pyruvate ↓ |
| Ku et al., 2020 [31] | Korea | Korean Red Ginseng (root) | water | oral | 50 mg/kg | 4 w | C57BL/b inbred mice (12 m) | N/R | M | 10 | sperm production and sperm motility ↑ testosterone and FSH (serum) ↑ VEGF ↑ spermatogenesis-related genes (inhibin-α, nectin-2, and CREB) ↑ | |
| Zhao et al., 2019 [32] | China | Wuzi Yanzong recipe | N/R | oral | 1 g/kg, 4 g/kg | 4 m | Sprague-Dawley rats (16 m) | N/R | M | 10 | the testicular weight and index ↑ sperm count and viability ↑ testosterone ↑ estradiol ↓ activated the onset of ERS germ cell apoptosis ↓ | |
| hypogonadism | Jung et al., 2018 [33] | Korea | Dendropanax morbiferus H.Lév (leaves) | water | oral | 50 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg, 200 mg/kg | 4 w | Sprague-Dawley rats (6–7 m) | N/R | M | 5 | improved physical tests (rotarod, treadmill, and swimming tests) testosterone, LH ↑ TG and LDL cholesterol ↓ testicular spermatogenesis ↑ |
| Jeong et al., 2020 [34] | Korea | Lycium chinense P. Mill (fruits) | ethanol | oral | 150 mg/kg, 300mg/kg | 6 w | Sprague-Dawley rats (18 m) | N/R | M | 6 | sperm counts and motility testosterone ↑ androgen receptor expression (testis and prostate) ↑ SOD ↑ 8-OHdG ↓ Bcl-2 ↑ apoptotic activator (BAX) ↓ phosphorylated Akt and ERK ↑ | |
| Choi et al., 2019 [35] | Korea | Modified Ojayeonjonghwan | ethanol | oral | 200 mg/kg, 400 mg/kg | 4 w | Sprague-Dawley rats (18 m) | N/R | M | 6 | the weights of testis and epididymis ↑ testosterone (serum) ↑ SOD ↑ 8-OHdG ↓ upregulated androgen receptor expression in testicular tissue | |
| ovarian function | Zhang et al., 2018 [36] | China | Heyan Kuntai Capsule | N/R | intragastric | 0.3 g/kg, 0.9 g/kg, 2.7 g/kg | 4 w | C57BL/6J mice (11 m) | naturally aging | F | 5 | the total number of follicles ↑ the number of primordial and primary follicles ↑ suppressed the apoptosis of follicles did not alter serum estrogen concentrations |
| Kim et al., 2021 [37] | Korea | Samul-tang | N/R | oral | 2.5 g/kg 5 times per week | 4 w | BALB/c mice (40 w) | N/R | F | 7 | AMH and FSH (serum) ↑ prevented age-related ovarian follicle loss Quality of oocytes and blastocysts were enhanced reversed aged-induced changes in mRNA expression (ovary) triggered changes in aging-related genes | |
| Yang et al., 2021 [38] | China | Yu Linzhu | N/R | intragastric | 0.3 mL | 6 w | BALB/c mice (9 m) | naturally aging | F | 10 | the ovarian area recovered the ovarian blood flow improved the ovarian volume ↑ the degree of adhesion ↓ the infiltration of ovarian interstitial lymphocytes ↓ the zona pellucida recovered FSH and LH ↓ E2 and AMH ↑ ROS, MDA ↓ GSH-Px ↑ mitochondrial function of oocytes improved | |
| Musculoskeletal function | ||||||||||||
| Bone | Li et al., 2019 [39] | China | Fructus Ligustri Lucidi (fruits) | water | intragastric | 4.9 g/kg/day | 65 d | ICR mice | D-gal (120 mg/kg/day) and NaNO2 (90 mg/kg/day) for 3 m | M | 10 | revealed a non-osteoporotic bone phenotype the memory and cognitive function ↑ MDA, 8-OH-dG, Nox4 ↓ TAC, GSH/GSSG ↑ the regulation of gut microbiota diversity |
| muscle and motor | Morita et al., 2021 [40] | Japan | Juzentaihoto | water | oral | 4% | 18 w | SAMP8 mice (18 w) | N/R | M | 6, 7 | gastrocnemius muscle and extensor digitorum longus weights ↑ gastrocnemius muscle fiber cross-sectional areas ↑ motor function (Rota-rod test) ↑ IGF-1(serum), mRNA Sirt1 ↑ TNF-α, IL-6 ↓ mRNA levels of Atrogin1 and MuRF1 (gastrocnemius) ↓ |
| muscle and motor | Amitani et al., 2022 [41] | Japan | Ninjin’yoeito | N/R | oral | 3%, 5% | 30 d | klotho-hypomorphic (kl/kl) mice (4 w) | N/R | M | 11 | survival rate ↑ free walking, rotarod, and spontaneous activity test ↑ triceps surae muscles weight ↑ bone strength ↑ telomere content ↑ age-related histological declines in heart, lung, thymus, testis, bone tissue, muscles and age-related motor dysfunction were improved |
| Others | ||||||||||||
| Skin | Orita et al., 2020 [42] | Japan | Hochu-ekki-to | water | oral | 1.0 g/kg, 3 times per week | 2 y | hairless mice (8 w) | naturally aging | N/R | 10 | moisture retention, skin hydration, and the generation of wrinkles: improved vitamin A, vitamin C, collagen type I, collagen type III, fibroblasts, and hyaluronic acid levels in the skin ↑ ROS ↓ |
| Skin and sexual organs | Hiramoto et al., 2020 [43] | Japan | Momordica charantia (fruits) | water | oral | 50 mg/kg, 3 times per week | 2 y | bred hairless mice (8 w) | naturally aging | M, F | 10 | improved moisture retention, hydration, thickness, and reduced wrinkle score cell apoptosis (ovaries and testes) ↓ MMP-1 and hyaluronidase 2 (skin) ↓ IL-33 ↑ |
| Lifespan extension | Wang et al., 2019 [44] | Japan | Rikkunshito | N/R | oral | N/R | ① 12 w ② 14 w ③ 15 w | ① wild-type and NPY knockout mice (82–89 w) ② inbred C57BL/6 mice (14–16 w) ③ C57BL/6 mice (16–18 w) | ① N/R ② 3-nitropropionic acid injection to induce oxidative stress ③ doxorubicin injection to induce oxidative stress | M, F | ① 19, 20 ② 18, 19 ③ 13, 14 | ① no significant effect on lifespan body weight, white adipose tissue weight and brown adipose tissue weight ↓ ghrelin levels ↑ ② upregulated anti-oxidative gene expression in the liver ③ plasma ghrelin concentration ↑ |
| Physiology (geriatric syndromes) | Matsubara et al, 2022 [45] | Japan | Ninjin’yoeito | water | oral | 1%, 3% | 11 w | C57BL/6 mice (88 w) | N/R | M | 10–15 | rectal temperature ↑ forelimb grip strength ↑ self-care motivation (sucrose splash test) ↑ |
| Gut microbiota and the metabolome | Luo et al., 2020 [46] | China | FuFang Zhenshu TiaoZhi | N/R | oral | 1.0 g kg | 12 w | C57BL/6JNarl mice (20 m) | N/R | N/R | 6 | the autonomous activity and the motor coordination ability ↑ glucose, lipids ↓ TNF-α, IL-6 ↓ the diversity and abundance of gut microbiota ↑ regulate the structure of gut microbiota |
| Metabolomic Analysis | Zhao et al., 2018 [47] | China | Glycyrrhiza glabra (Licorice) (root) | water | oral | 1 g/kg, 10 g/kg | 7 w | Sprague-Dawley rats (7 w) | D-gal (300 mg/kg/day for 7 w) | M | 10 | taurine metabolic pathway was significantly correlated with the ageing process taurine, CDO1 and CSAD ↑ |
| Metabolomic Analysis | Xi et al., 2021 [48] | China | Liuwei Dihuang decoction | water | oral | 9.75 g/kg | 30 d | ICR mice (20 m) | naturally aging | M | 10 | the organ index ↑ weight-bearing swimming time ↑ regulated the expression level of 11 aging-associated metabolites |
| Study (Author, Year) | Herbal Prescriptions | Components |
|---|---|---|
| Xie et al., 2022 [8] | Modified Qiongyu paste | Panax ginseng, Poria cocos, Rehmannia glutinosa, Cistanche deserticola, Salvia miltiorrhiza. |
| Li et al., 2022 [9] | BaZiBuShen | Cuscuta chinensis Lam., Lycium barbarum L., Epimedium brevicornu Maxim., Schisandra sphenanthera Rehder & E.H. Wilson, Cnidium monnieri (L.) Cuss, Rosa laevigata Michx., Rubus idaeus L., Allium tuberosum Rottler ex Spreng., Morinda officinalis F.C. How, Cistanche deserticola Y.C. Ma, Rehmannia glutinosa (Gaertn.) DC., Cyathula officinalis K.C. Kuan, Panax ginseng C. A. Mey., Young unossified hairy antler of male Cervus, Nippon Temminck or. Cervus elaphus Linnaeus (Cervidae)., Marine teleost fish, Melia azedarach L. |
| Wang et al., 2021 [13] | Dushen Tang | Panax ginseng C.A. Mey |
| Zhao et al., 2020 [15] Ding et al., 2022 [29] Zhao et al., 2019 [30] | Guilingji | Ginseng Radix et Rhizoma Rubra, Cervi Cornu Pantotrichum, Hippocampus, Lycii Fructus, Caryophylli Flos, Manis Squama, Passeris Meddula Achyranthis Bidentatae Radix, Cynomorii Herba, Rehmanniae Radix Praeparata, Psoraleae Frutus, Cuscutae Semen, Eucommiae Cortex, Spirferis Fossilia, Cistanches Herba, Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma, Asparagi Radix, Epimedii Folium, Halitum and Amomi Fructus |
| Ito et al., 2022 [20] | Kososan | Cyperus rhizome, Perilla herb, Citrus unshiu peel, Glycyrrhiza, Ginger |
| Ito et al., 2022 [20] | Hachimijiogan | Rehmannia root, Alisma rhizome, Poria sclerotium, Dioscorea rhizome, Cornus fruit, Moutan bark, Cinnamon bark, Aconite root |
| Piao et al., 2020 [28] Luo et al., 2020 [46] | Fufang Zhenzhu Tiao Zhi | Citri sarcodactylis fructus, Ligustri lucidi fructus, Salviae miltiorrhizae radix et rhizoma, Notoginseng radix et rhizoma, Coptidis rhizoma, Atractylodis macrocephalae rhizoma, Cirsii japonici herba et radix, Eucommiae cortex |
| Zhao et al., 2019 [32] | Wuzi Yanzong recipe | Plantaginis semen, Rubi fructus, Schisandrae chinensis fructus, Lycii fructus, Cuscutae semen |
| Choi et al., 2019 [35] | Modified Ojayeonjonghwan | Cornus officinalis Sieb. et Zucc., Lycium chinense Miller, Rubus coreanus Miquel, Cuscuta chinensis Lam, Schisandra chinensis Baillon |
| Zhang et al., 2018 [36] | Heyan Kuntai Capsule | Radix Rehmanniae praeparata, Radix Paeoniae Alba, Colla Corii Asini, Rhizoma Coptidis, Radix Scutellariae, Poria |
| Kim et al., 2021 [37] | Samul-tang | Paeonia lactiflora, Liqusticum striatum, Rehmannia glutinosa, Angelica gigas. |
| Yang et al., 2021 [38] | Yu Linzhu | Rehmanniae Radix Preparata, Cuscutae Semen, Gingseng Radix, Atractylodis Rhizoma alba, Poria cocos, Paeoniae Radix, Eucommiae Cortex, Cervi Cornus Colla., Angelicae Gigantis Radix, Cnidium officinale, Glycyrrhizae Radix |
| Morita et al., 2021 [40] | Juzentaihoto | Astragali Radix, Atractylodis Lanceae Rhizoma, Cinnamomi Cortex, Angelica Radix, Rehmanniae Radix, Ginseng Radix, Paeoniae Radix, Poria, Cnidii Rhizoma, Glycyrrhizae Radix |
| Amitani et al., 2022 [41] Matsubara et al., 2022 [45] | Ninjin’yoeito | Rehmannia root, Japanese angelica root, Atractylodes rhizome, Poria sclerotium, Ginseng, Cinnamon bark, Polygala root, Peony root, Citrus unshiu peel, Astragalus root, Glycyrrhiza, Schisandra fruit |
| Orita et al., 2020 [42] | Hochu-ekki-to | Astragali Radix, Astractylodis Rhizoma, Ginseng Radix, Angelicae Radix, Bupleuri Radix, Zizyphi Fructus, Auranti Nobilis Pericarpium, Glycyrrhizae Radix, Cimcifugae Rhizoma, Zingiberis Rhizoma |
| Wang et al., 2019 [44] | Rikkunshito | Atractylodes lancea rhizome, ginseng, pinellia tuber, Poria sclerotium, jujube, citrus unshiu peel, Glycyrrhiza and ginger |
| Xi et al., 2021 [48] | Liuwei Dihuang decoction | Rehmannia glutinosa, Cornus officinalis, Chinese yam, Poria cocos, Moutan bark, Alisma |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, S.-Y.; Lee, H.-G.; Kwon, S.; Park, S.-U.; Jung, W.-S.; Moon, S.-K.; Park, J.-M.; Ko, C.-N. A Systematic Review of In Vivo Studies of the Efficacy of Herbal Medicines for Anti-Aging in the Last Five Years. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030448
Cho S-Y, Lee H-G, Kwon S, Park S-U, Jung W-S, Moon S-K, Park J-M, Ko C-N. A Systematic Review of In Vivo Studies of the Efficacy of Herbal Medicines for Anti-Aging in the Last Five Years. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(3):448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030448
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Seung-Yeon, Han-Gyul Lee, Seungwon Kwon, Seong-Uk Park, Woo-Sang Jung, Sang-Kwan Moon, Jung-Mi Park, and Chang-Nam Ko. 2023. "A Systematic Review of In Vivo Studies of the Efficacy of Herbal Medicines for Anti-Aging in the Last Five Years" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 3: 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030448
APA StyleCho, S.-Y., Lee, H.-G., Kwon, S., Park, S.-U., Jung, W.-S., Moon, S.-K., Park, J.-M., & Ko, C.-N. (2023). A Systematic Review of In Vivo Studies of the Efficacy of Herbal Medicines for Anti-Aging in the Last Five Years. Pharmaceuticals, 16(3), 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030448