Comparative Assessment and High-Throughput Drug-Combination Profiling of TEAD-Palmitoylation Inhibitors in Hippo Pathway Deficient Mesothelioma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
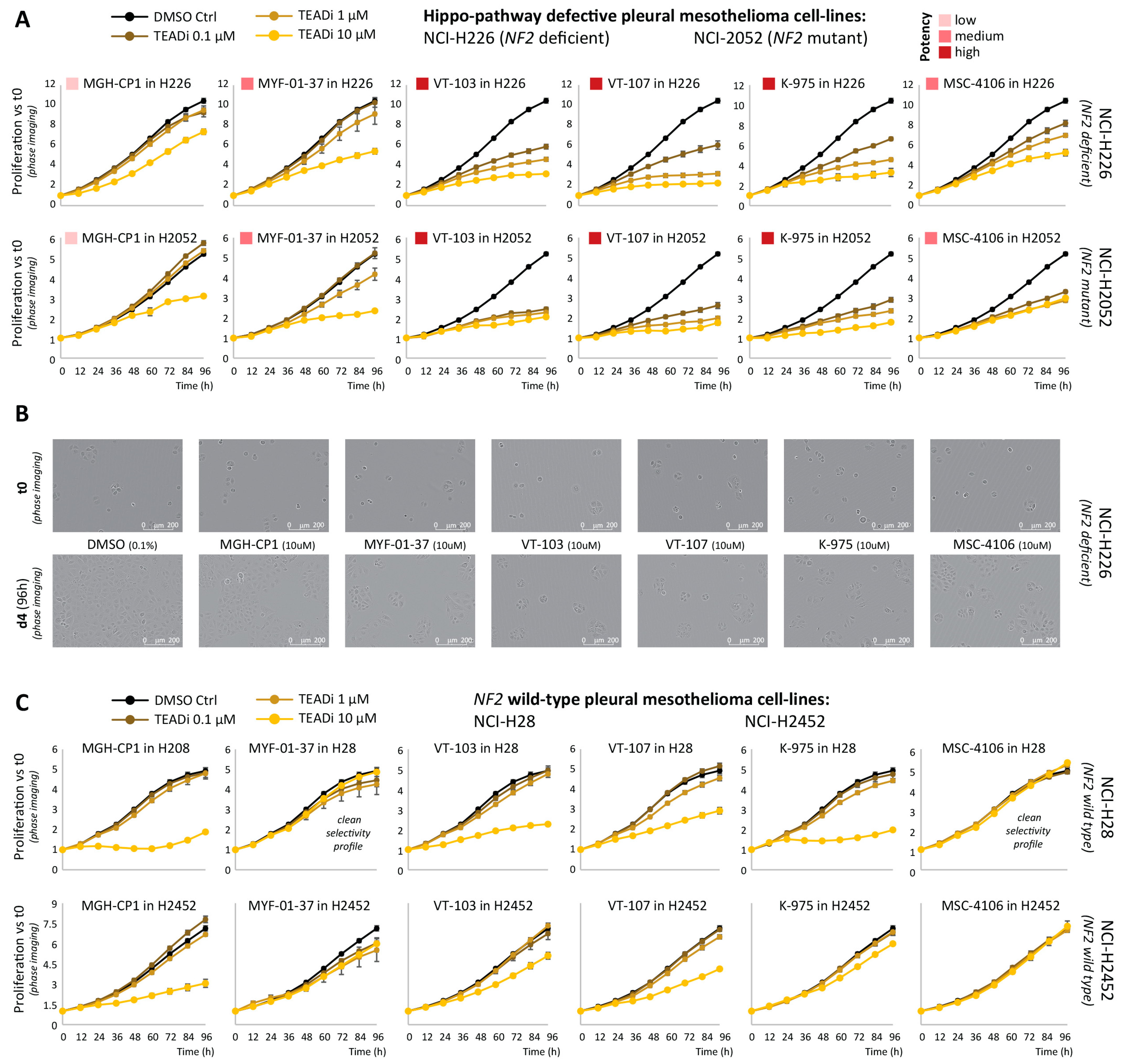
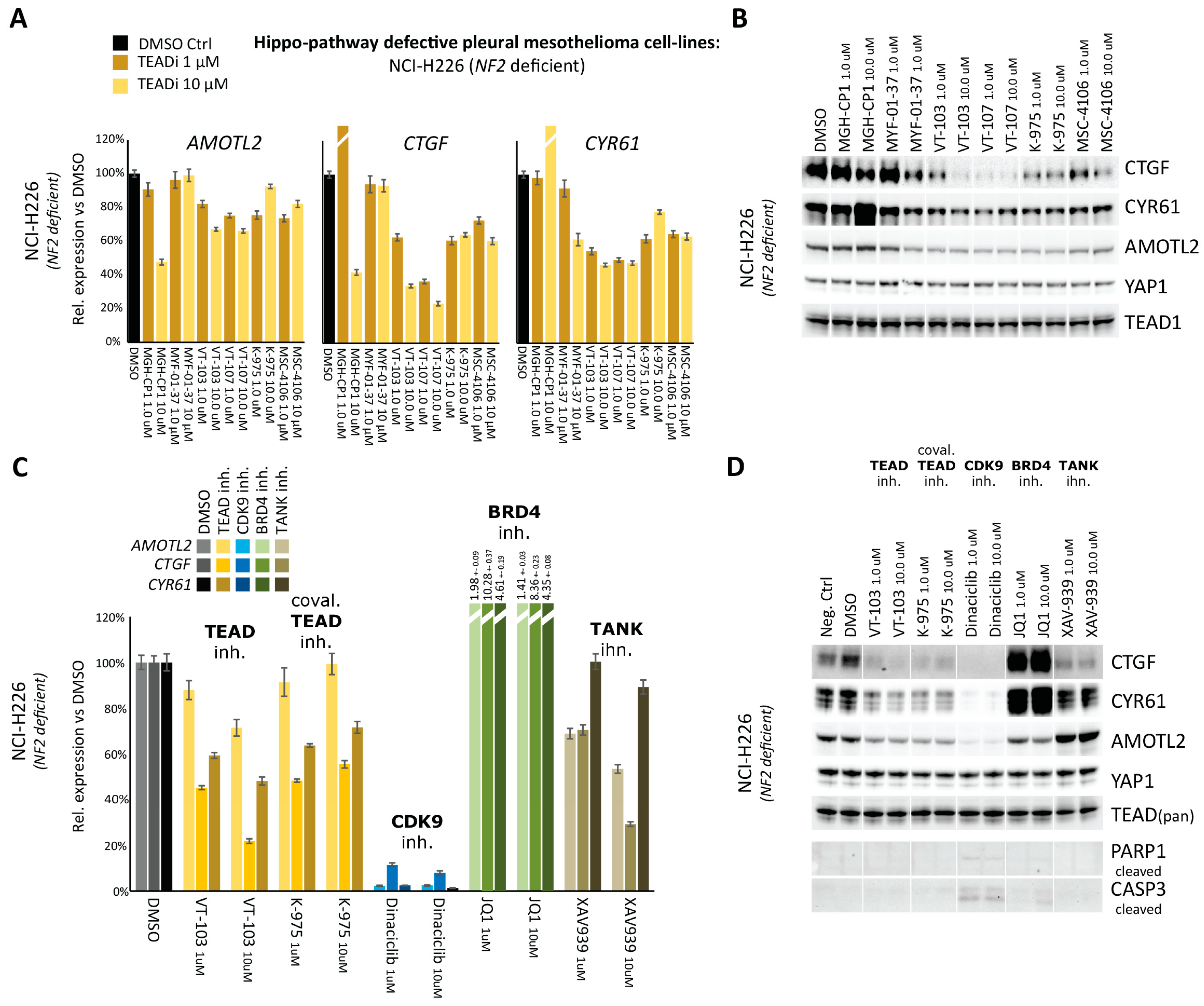
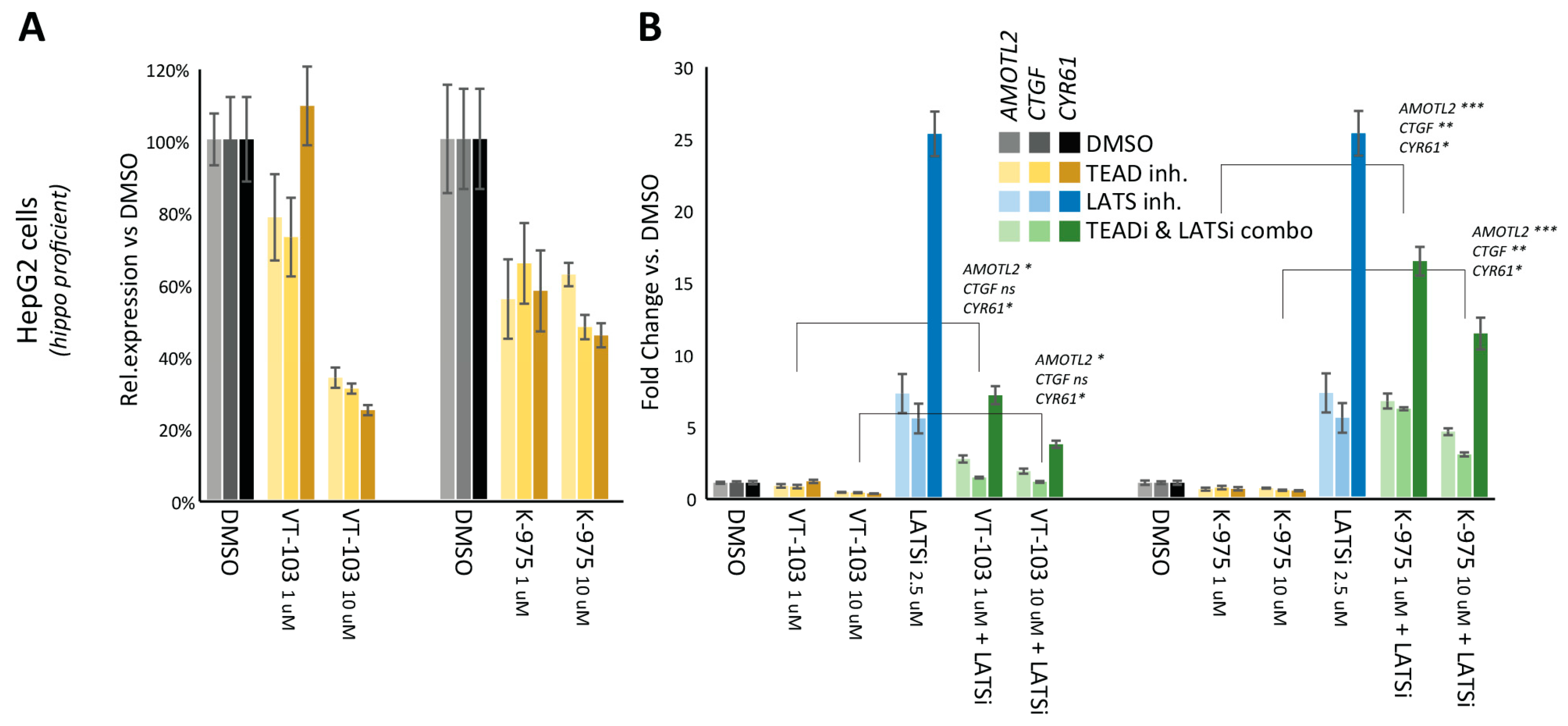
2.1. Comparative Assessment of TEAD-Palmitoylation Inhibitors in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
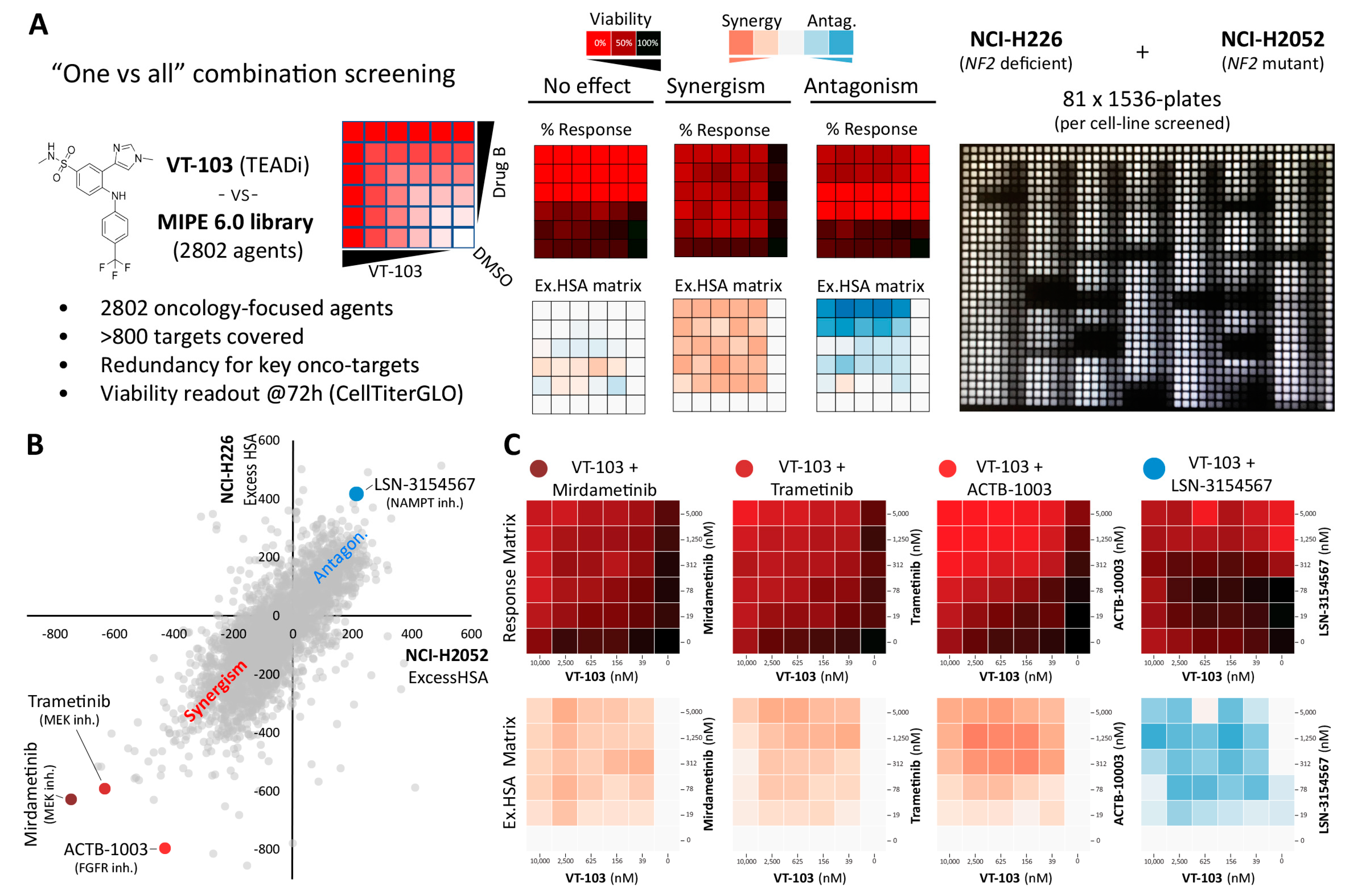
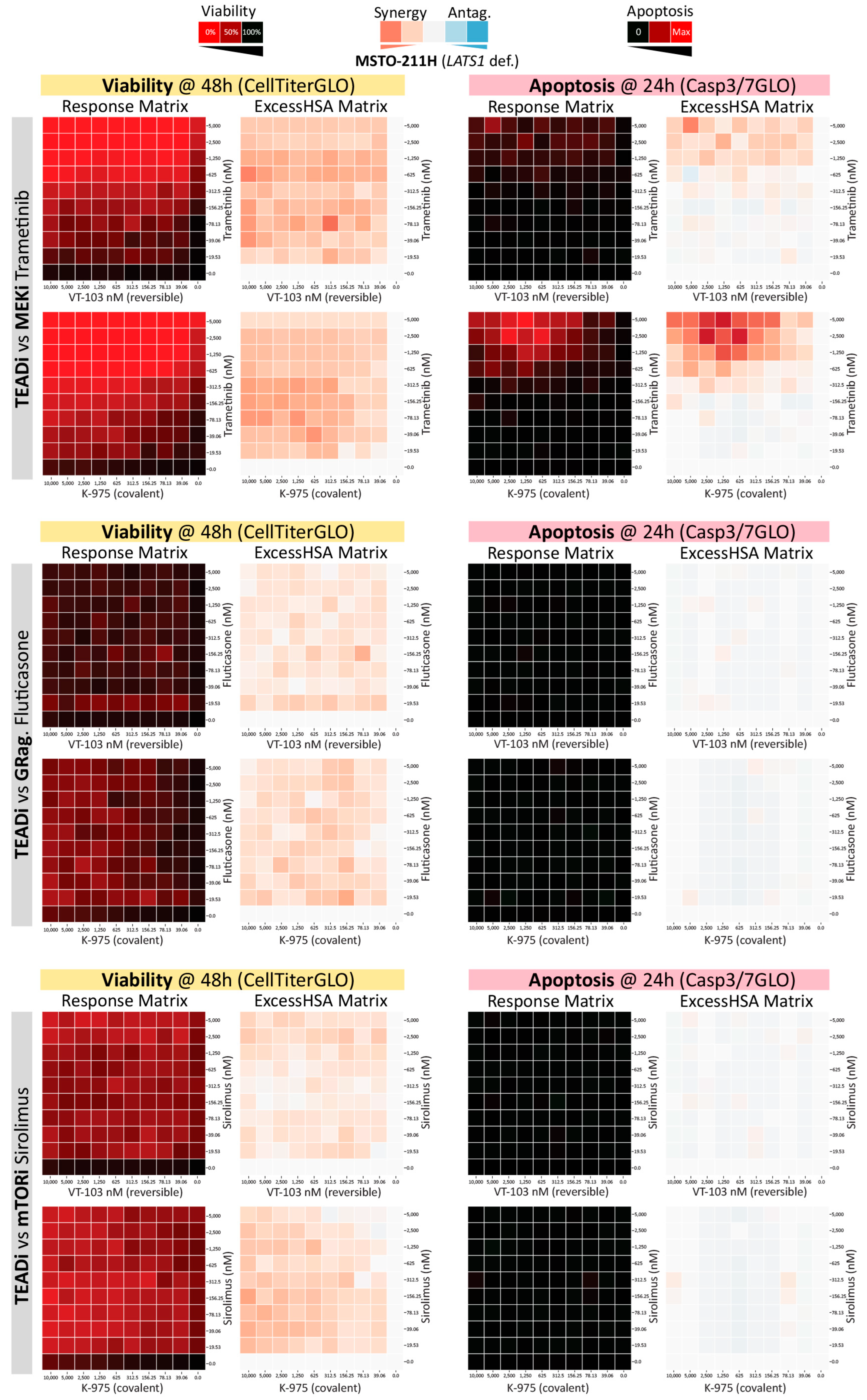
2.2. High-Throughput Mapping of TEAD-Palmitoylation Inhibitors Drug-Combination Landscape
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Drugs
4.3. RNA Extraction and RT-QPCR
4.4. Western Blot
4.5. Incucyte Live-Cell Proliferation Assays
4.6. End-Point Proliferation Assays
4.7. Quantitative High-Throughput Combination Screening (qHTCS)
4.8. Drug-Target Set Enrichment Analysis (DTSEA)
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, F.X.; Zhao, B.; Guan, K.L. Hippo Pathway in Organ Size Control, Tissue Homeostasis, and Cancer. Cell 2015, 163, 811–828. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.X.; Zhao, B.; Panupinthu, N.; Jewell, J.L.; Lian, I.; Wang, L.H.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, H.; Tumaneng, K.; Li, H.; et al. Regulation of the Hippo-YAP pathway by G-protein-coupled receptor signaling. Cell 2012, 150, 780–791. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.Y.; Yu, J.; Guan, K.L. Cell detachment activates the Hippo pathway via cytoskeleton reorganization to induce anoikis. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 54–68. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Wei, X.; Li, W.; Udan, R.S.; Yang, Q.; Kim, J.; Xie, J.; Ikenoue, T.; Yu, J.; Li, L.; et al. Inactivation of YAP oncoprotein by the Hippo pathway is involved in cell contact inhibition and tissue growth control. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 2747–2761. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Li, L.; Tumaneng, K.; Wang, C.Y.; Guan, K.L. A coordinated phosphorylation by Lats and CK1 regulates YAP stability through SCF(beta-TRCP). Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Maglic, D.; Dill, M.T.; Mojumdar, K.; Ng, P.K.; Jeong, K.J.; Tsang, Y.H.; Moreno, D.; Bhavana, V.H.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of the Hippo Signaling Pathway in Cancer. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 1304–1317.e1305. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, A.; Chang, M.T.; Vissers, J.H.A.; Dey, A.; Harvey, K.F. The Hippo Pathway as a Driver of Select Human Cancers. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 781–796. [Google Scholar]
- Faraji, F.; Ramirez, S.I.; Anguiano Quiroz, P.Y.; Mendez-Molina, A.N.; Gutkind, J.S. Genomic Hippo Pathway Alterations and Persistent YAP/TAZ Activation: New Hallmarks in Head and Neck Cancer. Cells 2022, 11, 1370. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, F.; Yu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, N.; Pan, D. Spatial organization of Hippo signaling at the plasma membrane mediated by the tumor suppressor Merlin/NF2. Cell 2013, 154, 1342–1355. [Google Scholar]
- Sekido, Y.; Sato, T. NF2 alteration in mesothelioma. Front. Toxicol. 2023, 5, 1161995. [Google Scholar]
- Pobbati, A.V.; Han, X.; Hung, A.W.; Weiguang, S.; Huda, N.; Chen, G.Y.; Kang, C.; Chia, C.S.; Luo, X.; Hong, W.; et al. Targeting the Central Pocket in Human Transcription Factor TEAD as a Potential Cancer Therapeutic Strategy. Structure 2015, 23, 2076–2086. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chan, P.; Han, X.; Zheng, B.; DeRan, M.; Yu, J.; Jarugumilli, G.K.; Deng, H.; Pan, D.; Luo, X.; Wu, X. Autopalmitoylation of TEAD proteins regulates transcriptional output of the Hippo pathway. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 282–289. [Google Scholar]
- Noland, C.L.; Gierke, S.; Schnier, P.D.; Murray, J.; Sandoval, W.N.; Sagolla, M.; Dey, A.; Hannoush, R.N.; Fairbrother, W.J.; Cunningham, C.N. Palmitoylation of TEAD Transcription Factors Is Required for Their Stability and Function in Hippo Pathway Signaling. Structure 2016, 24, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.G.; Gumbiner, B.M. Cell contact and Nf2/Merlin-dependent regulation of TEAD palmitoylation and activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 9877–9882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesrouze, Y.; Aguilar, G.; Meyerhofer, M.; Bokhovchuk, F.; Zimmermann, C.; Fontana, P.; Vissieres, A.; Voshol, H.; Erdmann, D.; Affolter, M.; et al. The role of lysine palmitoylation/myristoylation in the function of the TEAD transcription factors. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4984. [Google Scholar]
- Noritsugu, K.; Suzuki, T.; Dodo, K.; Ohgane, K.; Ichikawa, Y.; Koike, K.; Morita, S.; Umehara, T.; Ogawa, K.; Sodeoka, M.; et al. Lysine long-chain fatty acylation regulates the TEAD transcription factor. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112388. [Google Scholar]
- Holden, J.K.; Crawford, J.J.; Noland, C.L.; Schmidt, S.; Zbieg, J.R.; Lacap, J.A.; Zang, R.; Miller, G.M.; Zhang, Y.; Beroza, P.; et al. Small Molecule Dysregulation of TEAD Lipidation Induces a Dominant-Negative Inhibition of Hippo Pathway Signaling. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107809. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneda, A.; Seike, T.; Danjo, T.; Nakajima, T.; Otsubo, N.; Yamaguchi, D.; Tsuji, Y.; Hamaguchi, K.; Yasunaga, M.; Nishiya, Y.; et al. The novel potent TEAD inhibitor, K-975, inhibits YAP1/TAZ-TEAD protein-protein interactions and exerts an anti-tumor effect on malignant pleural mesothelioma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 4399–4415. [Google Scholar]
- Kurppa, K.J.; Liu, Y.; To, C.; Zhang, T.; Fan, M.; Vajdi, A.; Knelson, E.H.; Xie, Y.; Lim, K.; Cejas, P.; et al. Treatment-Induced Tumor Dormancy through YAP-Mediated Transcriptional Reprogramming of the Apoptotic Pathway. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 104–122.e112. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Sun, Y.; Jarugumilli, G.K.; Liu, S.; Dang, K.; Cotton, J.L.; Xiol, J.; Chan, P.Y.; DeRan, M.; Ma, L.; et al. Lats1/2 Sustain Intestinal Stem Cells and Wnt Activation through TEAD-Dependent and Independent Transcription. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 26, 675–692.e678. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.; Li, Y.; Lu, W.; Spitters, T.; Fang, X.; Wang, J.; Cai, S.; Gao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Duan, Z.; et al. Discovery of a subtype-selective, covalent inhibitor against palmitoylation pocket of TEAD3. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 3206–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.T.; Konradi, A.W.; Feng, Y.; Peng, X.; Ma, M.; Li, J.; Yu, F.X.; Guan, K.L.; Post, L. Small Molecule Inhibitors of TEAD Auto-palmitoylation Selectively Inhibit Proliferation and Tumor Growth of NF2-deficient Mesothelioma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, M.; Lu, W.; Che, J.; Kwiatkowski, N.P.; Gao, Y.; Seo, H.S.; Ficarro, S.B.; Gokhale, P.C.; Liu, Y.; Geffken, E.A.; et al. Covalent disruptor of YAP-TEAD association suppresses defective Hippo signaling. Elife 2022, 11, e78810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gridnev, A.; Maity, S.; Misra, J.R. Structure-based discovery of a novel small-molecule inhibitor of TEAD palmitoylation with anticancer activity. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1021823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Sun, Y.; Liu, S.; Erb, H.; Singh, A.; Mao, J.; Luo, X.; Wu, X. Discovery of a new class of reversible TEA domain transcription factor inhibitors with a novel binding mode. Elife 2022, 11, e78810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Ning, C.; Yue, J.; Zhang, C.; He, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z. Discovering inhibitors of TEAD palmitate binding pocket through virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulation. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2022, 98, 107648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hu, L.; Tao, Z.; Jarugumilli, G.K.; Erb, H.; Singh, A.; Li, Q.; Cotton, J.L.; Greninger, P.; Egan, R.K.; et al. Pharmacological blockade of TEAD-YAP reveals its therapeutic limitation in cancer cells. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Fan, M.; Ji, W.; Tse, J.; You, I.; Ficarro, S.B.; Tavares, I.; Che, J.; Kim, A.Y.; Zhu, X.; et al. Structure-Based Design of Y-Shaped Covalent TEAD Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 4617–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pobbati, A.V.; Kumar, R.; Rubin, B.P.; Hong, W. Therapeutic targeting of TEAD transcription factors in cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2023, 48, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, I.A.M.; Gopalakrishnan, R.; Mercan, S.; Mourikis, T.P.; Martin, T.; Wengert, S.; Sheng, C.; Ji, F.; Lopes, R.; Knehr, J.; et al. Cancer lineage-specific regulation of YAP responsive elements revealed through large-scale functional epigenomic screens. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, T.; Peterson, C.; Schneider, R.; Garg, S.; Schwarz, D.; Gunera, J.; Seshire, A.; Kotzner, L.; Schlesiger, S.; Musil, D.; et al. Optimization of TEAD P-Site Binding Fragment Hit into In Vivo Active Lead MSC-4106. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 9206–9229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, G.G.; Carrara, M.; Yuan, W.C.; Valdes-Quezada, C.; Gurung, B.; Pepe-Mooney, B.; Zhang, T.; Geeven, G.; Gray, N.S.; de Laat, W.; et al. YAP Drives Growth by Controlling Transcriptional Pause Release from Dynamic Enhancers. Mol. Cell 2015, 60, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Wu, T.; Gutman, O.; Lu, H.; Zhou, Q.; Henis, Y.I.; Luo, K. Phase separation of TAZ compartmentalizes the transcription machinery to promote gene expression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanconato, F.; Battilana, G.; Forcato, M.; Filippi, L.; Azzolin, L.; Manfrin, A.; Quaranta, E.; Di Biagio, D.; Sigismondo, G.; Guzzardo, V.; et al. Transcriptional addiction in cancer cells is mediated by YAP/TAZ through BRD4. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, N.; Li, X.; Tran, M.K.; Han, X.; Chen, J. Tankyrase Inhibitors Target YAP by Stabilizing Angiomotin Family Proteins. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceribelli, D.D.M.; Hoyt, S.; Morris, P.; Tosto, F.A.; Thomas, C.J. LATS Inhibitors and Uses. Thereof. Patent No. PCT/US23/24589, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.L.; Wilson, K.M.; Ceribelli, M.; Stanton, B.Z.; Woo, P.J.; Kreimer, S.; Qin, E.Y.; Zhang, X.; Lennon, J.; Nagaraja, S.; et al. Therapeutic strategies for diffuse midline glioma from high-throughput combination drug screening. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaaw0064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mott, B.T.; Eastman, R.T.; Guha, R.; Sherlach, K.S.; Siriwardana, A.; Shinn, P.; McKnight, C.; Michael, S.; Lacerda-Queiroz, N.; Patel, P.R.; et al. High-throughput matrix screening identifies synergistic and antagonistic antimalarial drug combinations. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foucquier, J.; Guedj, M. Analysis of drug combinations: Current methodological landscape. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2015, 3, e00149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyanaga, A.; Masuda, M.; Tsuta, K.; Kawasaki, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Sakuma, T.; Asamura, H.; Gemma, A.; Yamada, T. Hippo pathway gene mutations in malignant mesothelioma: Revealed by RNA and targeted exon sequencing. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Solimini, N.L.; Elledge, S.J. Principles of cancer therapy: Oncogene and non-oncogene addiction. Cell 2009, 136, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henley, M.J.; Koehler, A.N. Advances in targeting ‘undruggable’ transcription factors with small molecules. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 669–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagiel, B.; Melnyk, P.; Cotelle, P. Progress with YAP/TAZ-TEAD inhibitors: A patent review (2018-present). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2022, 32, 899–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, J.J.; Bronner, S.M.; Zbieg, J.R. Hippo pathway inhibition by blocking the YAP/TAZ-TEAD interface: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2018, 28, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pobbati, A.V.; Mejuch, T.; Chakraborty, S.; Karatas, H.; Bharath, S.R.; Gueret, S.M.; Goy, P.A.; Hahne, G.; Pahl, A.; Sievers, S.; et al. Identification of Quinolinols as Activators of TEAD-Dependent Transcription. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 2909–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.H.; Hagenbeek, T.J.; Lee, H.J.; Li, J.; Rose, C.M.; Lin, E.; Yu, M.; Martin, S.E.; Piskol, R.; Lacap, J.A.; et al. Machine-Learning and Chemicogenomics Approach Defines and Predicts Cross-Talk of Hippo and MAPK Pathways. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 778–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Bivona, T.G. The Hippo effector YAP regulates the response of cancer cells to MAPK pathway inhibitors. Mol. Cell Oncol. 2016, 3, e1021441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Sabnis, A.J.; Chan, E.; Olivas, V.; Cade, L.; Pazarentzos, E.; Asthana, S.; Neel, D.; Yan, J.J.; Lu, X.; et al. The Hippo effector YAP promotes resistance to RAF- and MEK-targeted cancer therapies. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, B.A.; El-Deiry, W.S. Targeting apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 395–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furet, P.; Bordas, V.; Le Douget, M.; Salem, B.; Mesrouze, Y.; Imbach-Weese, P.; Sellner, H.; Voegtle, M.; Soldermann, N.; Chapeau, E.; et al. The First Class of Small Molecules Potently Disrupting the YAP-TEAD Interaction by Direct Competition. ChemMedChem 2022, 17, e202200303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmelzle, T.; Chapeau, E.; Bauer, D.; Chene, P.; Faris, J.; Fernandez, C.; Furet, P.; Galli, G.; Gong, J.; Harlfinger, S.; et al. IAG933, a selective and orally efficacious YAP1/WWTR1(TAZ)-panTEAD protein-protein interaction inhibitor with pre-clinical activity in monotherapy and combinations. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, LB319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenbeek, T.J.; Zbieg, J.R.; Hafner, M.; Mroue, R.; Lacap, J.A.; Sodir, N.M.; Noland, C.L.; Afghani, S.; Kishore, A.; Bhat, K.P.; et al. An allosteric pan-TEAD inhibitor blocks oncogenic YAP/TAZ signaling and overcomes KRAS G12C inhibitor resistance. Nat. Cancer 2023, 4, 812–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.C.; Moroishi, T.; Meng, Z.; Jeong, H.S.; Plouffe, S.W.; Sekido, Y.; Han, J.; Park, H.W.; Guan, K.L. Regulation of Hippo pathway transcription factor TEAD by p38 MAPK-induced cytoplasmic translocation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.C.; Park, H.W.; Guan, K.L. Regulation of the Hippo Pathway Transcription Factor TEAD. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2017, 42, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Evsen, L.; Morris, P.J.; Thomas, C.J.; Ceribelli, M. Comparative Assessment and High-Throughput Drug-Combination Profiling of TEAD-Palmitoylation Inhibitors in Hippo Pathway Deficient Mesothelioma. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16121635
Evsen L, Morris PJ, Thomas CJ, Ceribelli M. Comparative Assessment and High-Throughput Drug-Combination Profiling of TEAD-Palmitoylation Inhibitors in Hippo Pathway Deficient Mesothelioma. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(12):1635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16121635
Chicago/Turabian StyleEvsen, Lale, Patrick J. Morris, Craig J. Thomas, and Michele Ceribelli. 2023. "Comparative Assessment and High-Throughput Drug-Combination Profiling of TEAD-Palmitoylation Inhibitors in Hippo Pathway Deficient Mesothelioma" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 12: 1635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16121635
APA StyleEvsen, L., Morris, P. J., Thomas, C. J., & Ceribelli, M. (2023). Comparative Assessment and High-Throughput Drug-Combination Profiling of TEAD-Palmitoylation Inhibitors in Hippo Pathway Deficient Mesothelioma. Pharmaceuticals, 16(12), 1635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16121635






