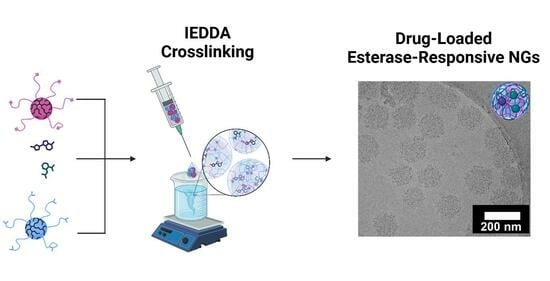
Esterase-Responsive Polyglycerol-Based Nanogels for Intracellular Drug Delivery in Rare Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
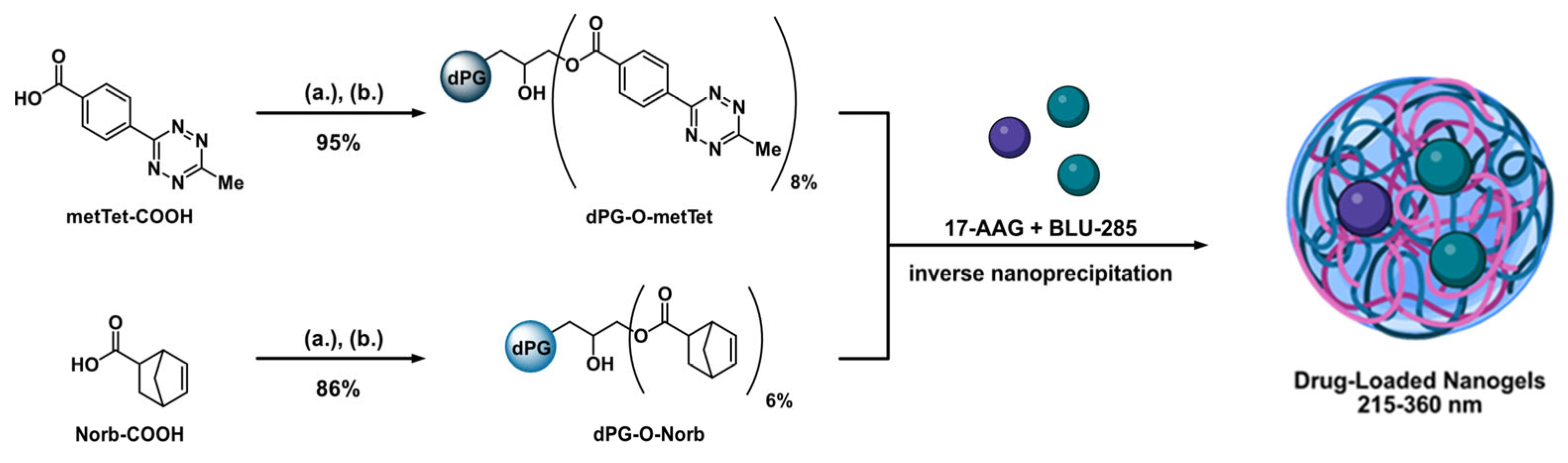
2.1. Macromonomer Synthesis
2.2. Nanogel Formation and Drug Loading
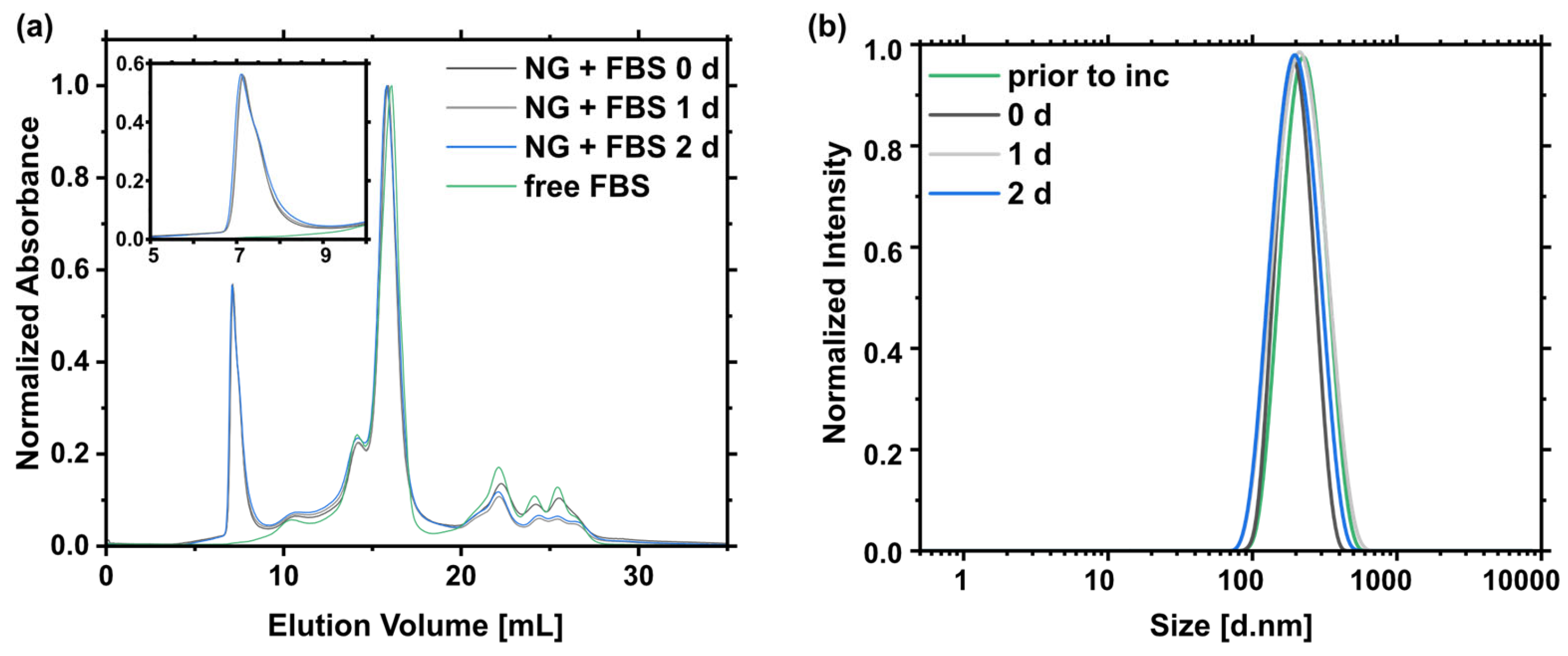
2.3. Nanogel Degradation
2.4. Compatibility Studies
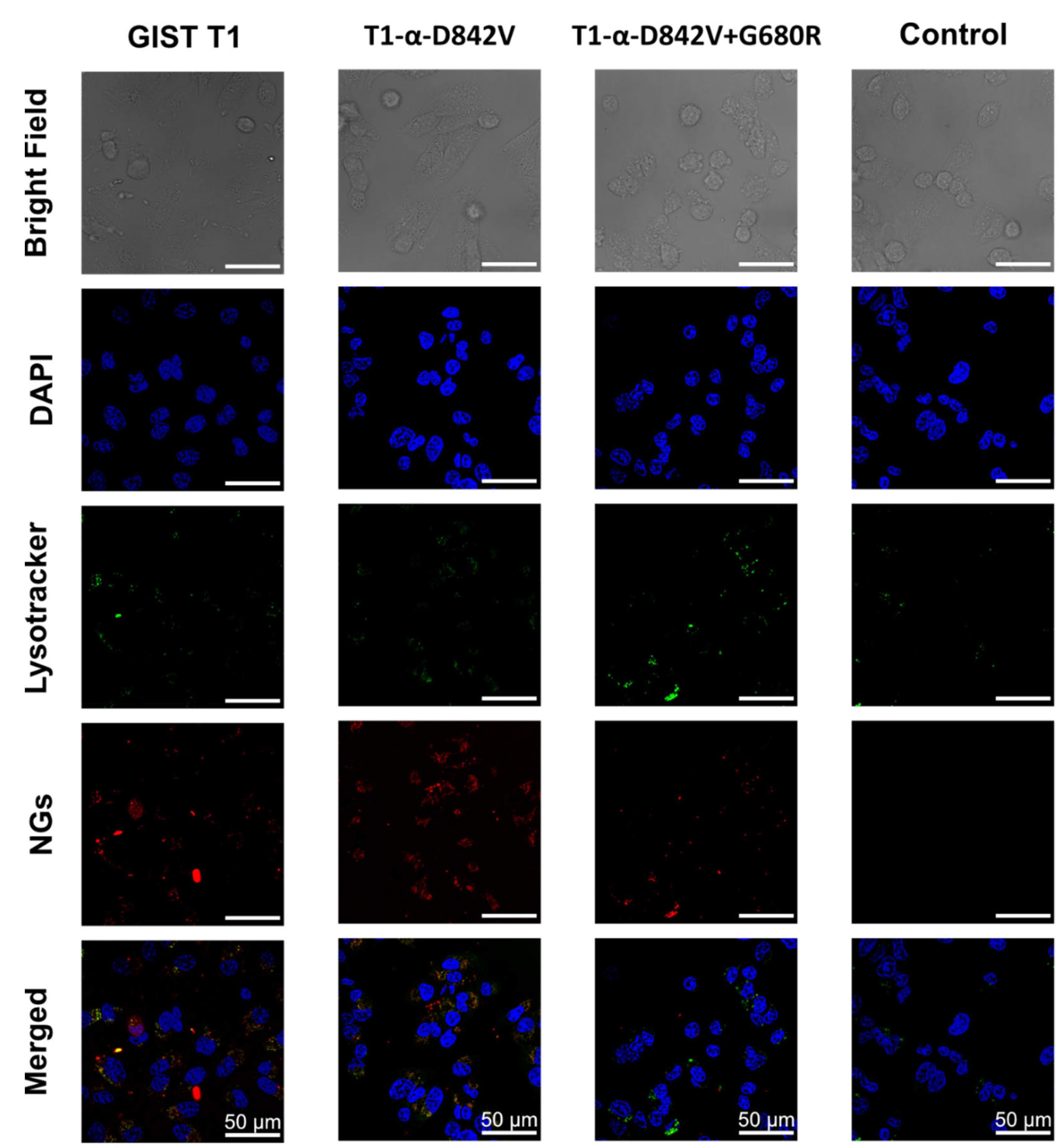
2.5. Cellular Uptake
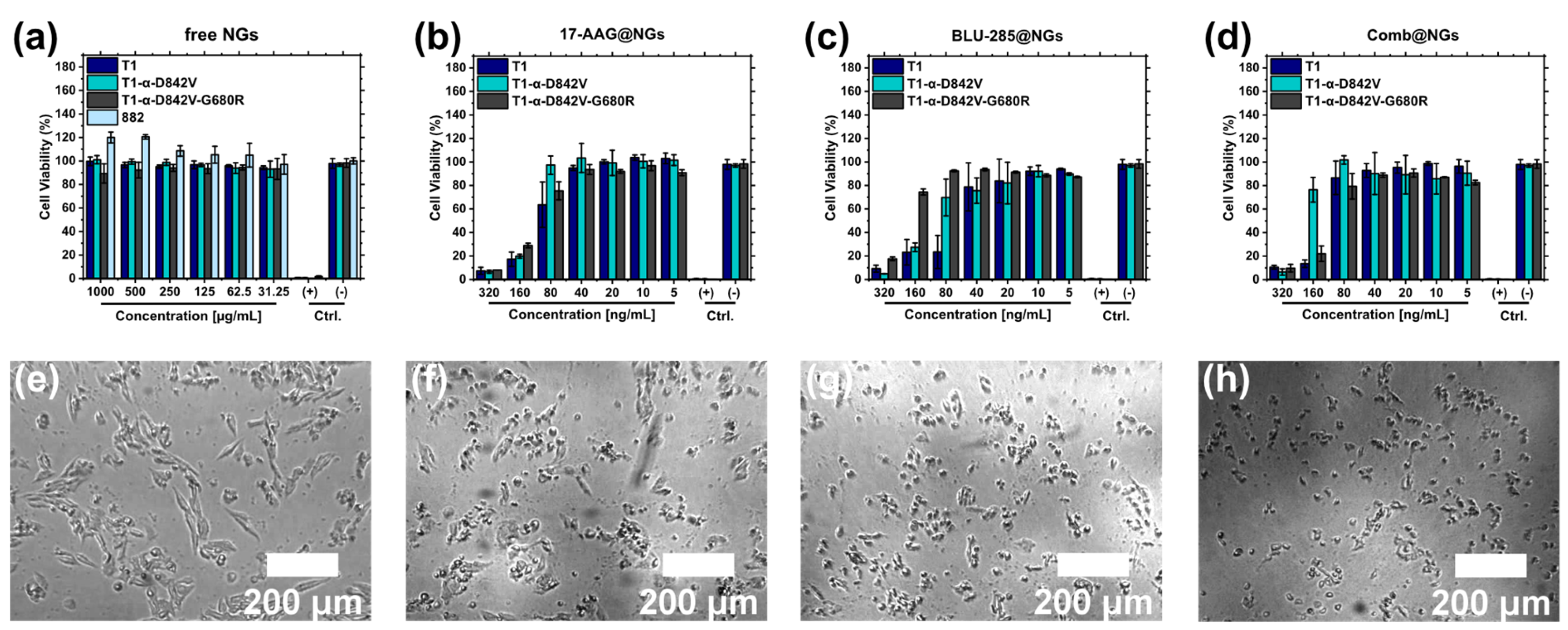
2.6. Cell Viability Studies
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. NMR
4.3. GPC
4.4. Synthesis of Materials
- Synthesis of metTet-COOH, Cy5-Norb, and dPG-OH
- Synthesis of dPG-O-metTet
- Synthesis of dPG-O-Norb
- Cy5-Labeling of dPG-O-metTet
- Cy5-Labeling of NGs
4.5. Procedures
4.5.1. NG Formation
4.5.2. Cryo-TEM
4.5.3. Drug Encapsulation
4.5.4. Macromonomer Degradation
4.5.5. NG Degradation
4.5.6. Serum Stability
4.5.7. Ex vivo Red Blood Cell Hemolysis Assay
4.5.8. Cell Lines and Cultivation
4.5.9. Cellular Uptake Studies
4.5.10. Cell Viability
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pogorzelski, M.; Falkenhorst, J.; Bauer, S. Molecular subtypes of gastrointestinal stromal tumor requiring specific treatments. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2016, 28, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, K.W.; Leabu, M. Interstitial Cells of Cajal (ICC) and Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST): Facts, speculations, and myths. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2006, 10, 995–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, T.; Goto, O.; Raut, C.P.; Yahagi, N. Diagnostic and treatment strategy for small gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Cancer 2016, 122, 3110–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunewald, S.; Klug, L.R.; Mühlenberg, T.; Lategahn, J.; Falkenhorst, J.; Town, A.; Ehrt, C.; Wardelmann, E.; Hartmann, W.; Schildhaus, H.-U.; et al. Resistance to Avapritinib in PDGFRA-Driven GIST Is Caused by Secondary Mutations in the PDGFRA Kinase Domain. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 108–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rammohan, A.; Sathyanesan, J.; Rajendran, K.; Pitchaimuthu, A.; Perumal, S.K.; Srinivasan, U.; Ramasamy, R.; Palaniappan, R.; Govindan, M. A gist of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: A review. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2013, 5, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miettinen, M.; Sarlomo-Rikala, M.; Sobin, L.H.; Lasota, J. Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors and Leiomyosarcomas in the Colon: A Clinicopathologic, Immunohistochemical, and Molecular Genetic Study of 44 Cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2000, 24, 1339–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tworek, J.A.; Appelman, H.D.; Singleton, T.P.; Greenson, J.K. Stromal tumors of the jejunum and ileum. Mod. Pathol. 1997, 10, 200–209. [Google Scholar]
- Tworek, J.A.; Goldblum, J.R.; Weiss, S.W.; Greenson, J.K.; Appelman, H.D. Stromal Tumors of the Anorectum: A Clinicopathologic Study of 22 Cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1999, 23, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tworek, J.A.; Goldblum, J.R.; Weiss, S.W.; Greenson, J.K.; Appelman, H.D. Stromal Tumors of the Abdominal Colon: A Clinicopathologic Study of 20 Cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1999, 23, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brainard, J.A.; Goldblum, J.R. Stromal Tumors of the Jejunum and Ileum: A Clinicopathologic Study of 39 Cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1997, 21, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.; Dean, P.J. Stromal neoplasms of the rectum and anal canal. Hum. Pathol. 1992, 23, 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, M.; Sarlomo-Rikala, M.; Sobin, L.H.; Lasota, J. Esophageal Stromal Tumors: A Clinicopathologic, Immunohistochemical, and Molecular Genetic Study of 17 Cases and Comparison with Esophageal Leiomyomas and Leiomyosarcomas. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2000, 24, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Hidalgo, C.; Bojorge, B.d.L.; Albores-Saavedra, J. Stromal Tumor of the Gallbladder with Phenotype of Interstitial Cells of Cajal: A Previously Unrecognized Neoplasm. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2000, 24, 1420–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reith, J.D.; Goldblum, J.R.; Lyles, R.H.; Weiss, S.W. Extragastrointestinal (Soft Tissue) Stromal Tumors: An Analysis of 48 Cases with Emphasis on Histologic Predictors of Outcome. Mod. Pathol. 2000, 13, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, M.; Lasota, J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors—Definition, clinical, histological, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic features and differential diagnosis. Virchows Arch. 2001, 438, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corless, C.L.; Fletcher, J.A.; Heinrich, M.C. Biology of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 3813–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunio, M.A.; Al Asiri, M.; Saleh, R.M.; Akbar, S.A.; Ali, N.M.; Senosy Hassan, M.A. Obstructive Small Bowel Metastasis from Uterine Leiomyosarcoma: A Case Report. Case Rep. Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 2014, 603097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaat, B.E.C.; Hollema, H.; Molenaar, W.M.; Broers, G.H.T.; Pijpe, J.; Mastik, M.F.; Hoekstra, H.J.; Berg, E.v.d.; Scheper, R.J.; Graaf, W.T.A.v.d. Soft Tissue Leiomyosarcomas and Malignant Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors: Differences in Clinical Outcome and Expression of Multidrug Resistance Proteins. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 3211–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, T.O.; West, R.B.; Linn, S.C.; Alter, O.; Knowling, M.A.; O’Connell, J.X.; Zhu, S.; Fero, M.; Sherlock, G.; Pollack, J.R.; et al. Molecular characterisation of soft tissue tumours: A gene expression study. Lancet 2002, 359, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, M.C.; Corless, C.L.; Demetri, G.D.; Blanke, C.D.; Mehren, M.v.; Joensuu, H.; McGreevey, L.S.; Chen, C.-J.; Abbeele, A.D.V.d.; Druker, B.J.; et al. Kinase Mutations and Imatinib Response in Patients with Metastatic Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 4342–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, G.P.; Guida, T.; Alfano, L.; Avilla, E.; Santoro, M.; Carlomagno, F.; Melillo, R.M. Molecular Mechanism of 17-Allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin (17-AAG)-induced AXL Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 17481–17494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talaei, S.; Mellatyar, H.; Asadi, A.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Sheervalilou, R.; Zarghami, N. Spotlight on 17-AAG as an Hsp90 inhibitor for molecular targeted cancer treatment. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2019, 93, 760–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, D.; Shen, Z.; Wang, W.; Ning, G.; Zhu, Y. The HSP90 inhibitor 17-AAG exhibits potent antitumor activity for pheochromocytoma in a xenograft model. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 5103–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, L.M.; Jayanthan, A.A.; Narendran, A. Effects of 17-Allylamino-17-Demethoxygeldanamycin (17-AAG) on Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) with Respect to Bcr-Abl Status and Imatinib Mesylate Sensitivity. Pediatr. Res. 2005, 57, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Soni, K.S.; Desale, S.S.; Bronich, T.K. Nanogels: An overview of properties, biomedical applications and obstacles to clinical translation. J. Control Release 2016, 240, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karg, M.; Pich, A.; Hellweg, T.; Hoare, T.; Lyon, L.A.; Crassous, J.J.; Suzuki, D.; Gumerov, R.A.; Schneider, S.; Potemkin, I.I.; et al. Nanogels and Microgels: From Model Colloids to Applications, Recent Developments, and Future Trends. Langmuir 2019, 35, 6231–6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackiewicz, M.; Romanski, J.; Krug, P.; Mazur, M.; Stojek, Z.; Karbarz, M. Tunable environmental sensitivity and degradability of nanogels based on derivatives of cystine and poly(ethylene glycols) of various length for biocompatible drug carrier. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 118, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legros, C.; Wirotius, A.-L.; De Pauw-Gillet, M.-C.; Tam, K.C.; Taton, D.; Lecommandoux, S. Poly(2-oxazoline)-Based Nanogels as Biocompatible Pseudopolypeptide Nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Achazi, K.; Haag, R. Boronate Cross-linked ATP- and pH-Responsive Nanogels for Intracellular Delivery of Anticancer Drugs. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2015, 4, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, N.; Esrafili, A.; Esfandiari, B.; Abednezhad, A.; Naghizadeh, M.; Arasteh, J. Synthesis of pH-sensitive hyaluronic acid nanogels loaded with paclitaxel and interferon gamma: Characterization and effect on the A549 lung carcinoma cell line. Colloids Surf. B 2021, 205, 111845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Pang, L.; Cong, H.; Shen, Y.; Yu, B. Application and design of esterase-responsive nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Drug Deliv. 2019, 26, 416–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, P.; Gangapurwala, G.; Pretzel, D.; Leiske, M.N.; Wang, L.; Hoeppener, S.; Schubert, S.; Brendel, J.C.; Schubert, U.S. Smart pH-Sensitive Nanogels for Controlled Release in an Acidic Environment. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.H.W.; Song, I.-S.; Hossain, A.; Choi, M.-K.; Yamane, Y.; Liang, Z.D.; Lu, J.; Wu, L.Y.-H.; Siddik, Z.H.; Klomp, L.W.J.; et al. Elevated Glutathione Levels Confer Cellular Sensitization to Cisplatin Toxicity by Up-Regulation of Copper Transporter hCtr1. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 74, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhilber, D.; Witting, M.; Zhang, X.; Staegemann, M.; Paulus, F.; Friess, W.; Küchler, S.; Haag, R. Surfactant free preparation of biodegradable dendritic polyglycerol nanogels by inverse nanoprecipitation for encapsulation and release of pharmaceutical biomacromolecules. J. Control Release 2013, 169, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kainthan, R.K.; Brooks, D.E. In vivo biological evaluation of high molecular weight hyperbranched polyglycerols. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4779–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegers, C.; Biesalski, M.; Haag, R. Self-Assembled Monolayers of Dendritic Polyglycerol Derivatives on Gold That Resist the Adsorption of Proteins. Chem. Eur. J. 2004, 10, 2831–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bewersdorff, T.; Vonnemann, J.; Kanik, A.; Haag, R.; Haase, A. The influence of surface charge on serum protein interaction and cellular uptake: Studies with dendritic polyglycerols and dendritic polyglycerol-coated gold nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 2001–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, B.C.; Nelson, C.E.; Yu, S.S.; Beavers, K.R.; Kim, A.J.; Li, H.; Nelson, H.M.; Giorgio, T.D.; Duvall, C.L. Ex Vivo Red Blood Cell Hemolysis Assay for the Evaluation of pH-responsive Endosomolytic Agents for Cytosolic Delivery of Biomacromolecular Drugs. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 73, e50166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schötz, S.; Reisbeck, F.; Schmitt, A.-C.; Dimde, M.; Quaas, E.; Achazi, K.; Haag, R. Tunable Polyglycerol-Based Redox-Responsive Nanogels for Efficient Cytochrome C Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehrl, A.; Schötz, S.; Haag, R. Systematic Screening of Different Polyglycerin-Based Dienophile Macromonomers for Efficient Nanogel Formation through IEDDA Inverse Nanoprecipitation. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2020, 41, 1900510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
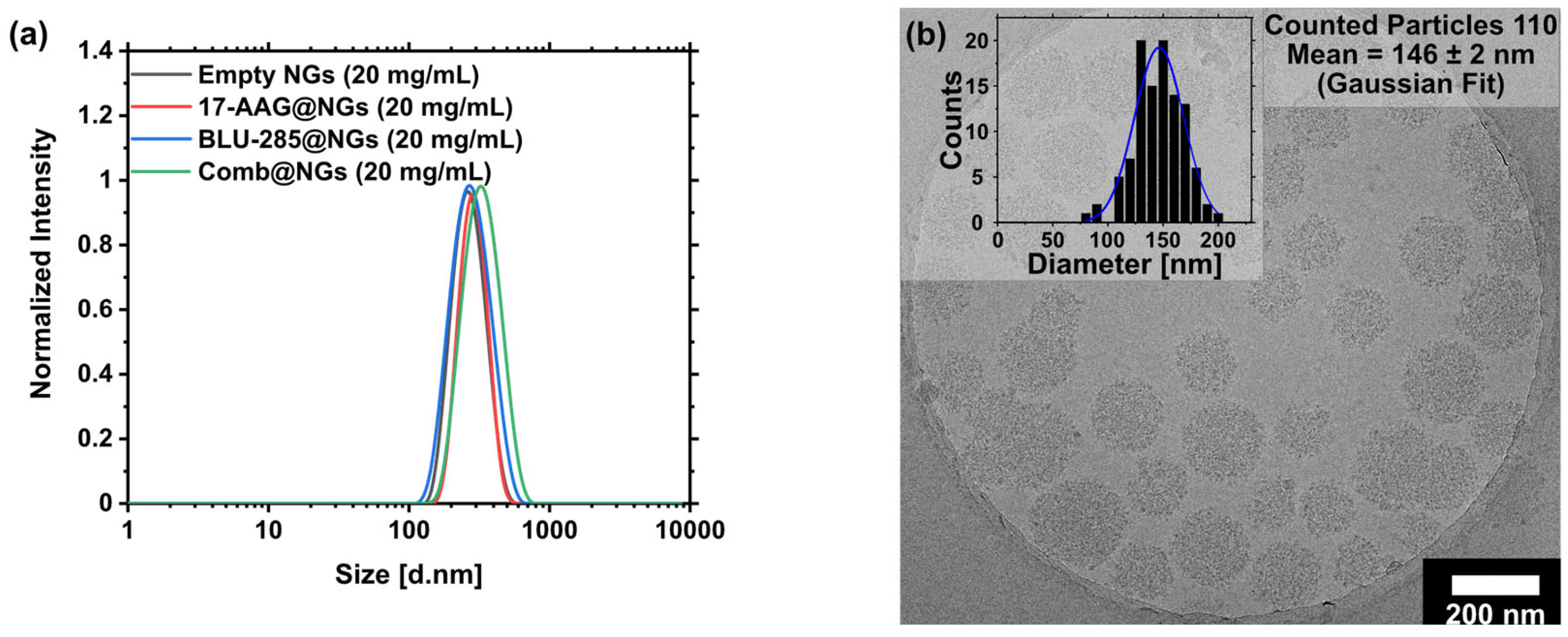

| Entry | Name | DLC [wt%]theo | DLC [wt%]calc 1 | ee (%) | Size [d.nm] 2 | PDI 2 | ζ—Potential [mV] 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Empty NGs | - | - | - | 257 ± 7 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | −0.6 | |
| 2 | 17-AAG@NGs | 5 | 4.95 | 99 | 276 ± 4 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 1.9 | |
| 3 | BLU-285@NGs | 5 | 4.95 | 99 | 272 ± 12 | 0.10 ± 0.04 | 3.9 | |
| 4 | Comb@NGs | 17-AAG | 5 | 5.00 | Quant. | 361 ± 18 | 0.21 ± 0.05 | 3.8 |
| BLU-285 | 5 | 3.10 | 62 |
| Time | NG Area (%) 1 | Size [d.nm] 2 | PDI 2 | Ζ—Potential [mV]2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prior to inc. | - | 215 ± 1 | 0.10 ± 0.10 | −0.6 ± 0.5 |
| 0 day | 100.00 ± 0.71 | 189 ± 3 | 0.03 ± 0.06 | −2.26 ± 0.5 |
| 1 day | 104.48 ± 0.67 | 198 ± 4 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | −2.08 ± 0.4 |
| 2 days | 99.77 ± 0.74 | 182 ± 2 | 0.15 ± 0.02 | −1.94 ± 0.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schötz, S.; Griepe, A.K.; Goerisch, B.B.; Kortam, S.; Vainer, Y.S.; Dimde, M.; Koeppe, H.; Wedepohl, S.; Quaas, E.; Achazi, K.; et al. Esterase-Responsive Polyglycerol-Based Nanogels for Intracellular Drug Delivery in Rare Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16111618
Schötz S, Griepe AK, Goerisch BB, Kortam S, Vainer YS, Dimde M, Koeppe H, Wedepohl S, Quaas E, Achazi K, et al. Esterase-Responsive Polyglycerol-Based Nanogels for Intracellular Drug Delivery in Rare Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(11):1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16111618
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchötz, Sebastian, Adele K. Griepe, Björn B. Goerisch, Sally Kortam, Yael Shammai Vainer, Mathias Dimde, Hanna Koeppe, Stefanie Wedepohl, Elisa Quaas, Katharina Achazi, and et al. 2023. "Esterase-Responsive Polyglycerol-Based Nanogels for Intracellular Drug Delivery in Rare Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 11: 1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16111618
APA StyleSchötz, S., Griepe, A. K., Goerisch, B. B., Kortam, S., Vainer, Y. S., Dimde, M., Koeppe, H., Wedepohl, S., Quaas, E., Achazi, K., Schroeder, A., & Haag, R. (2023). Esterase-Responsive Polyglycerol-Based Nanogels for Intracellular Drug Delivery in Rare Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors. Pharmaceuticals, 16(11), 1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16111618