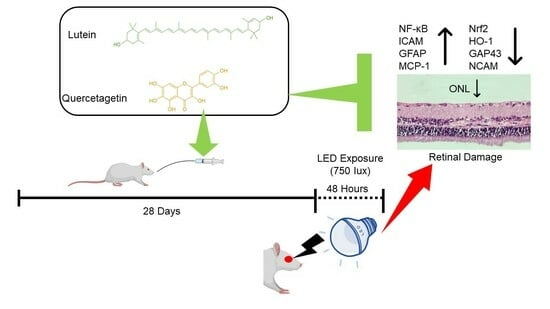
Lutein/Zeaxanthin Isomers and Quercetagetin Combination Safeguards the Retina from Photo-Oxidative Damage by Modulating Neuroplasticity Markers and the Nrf2 Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
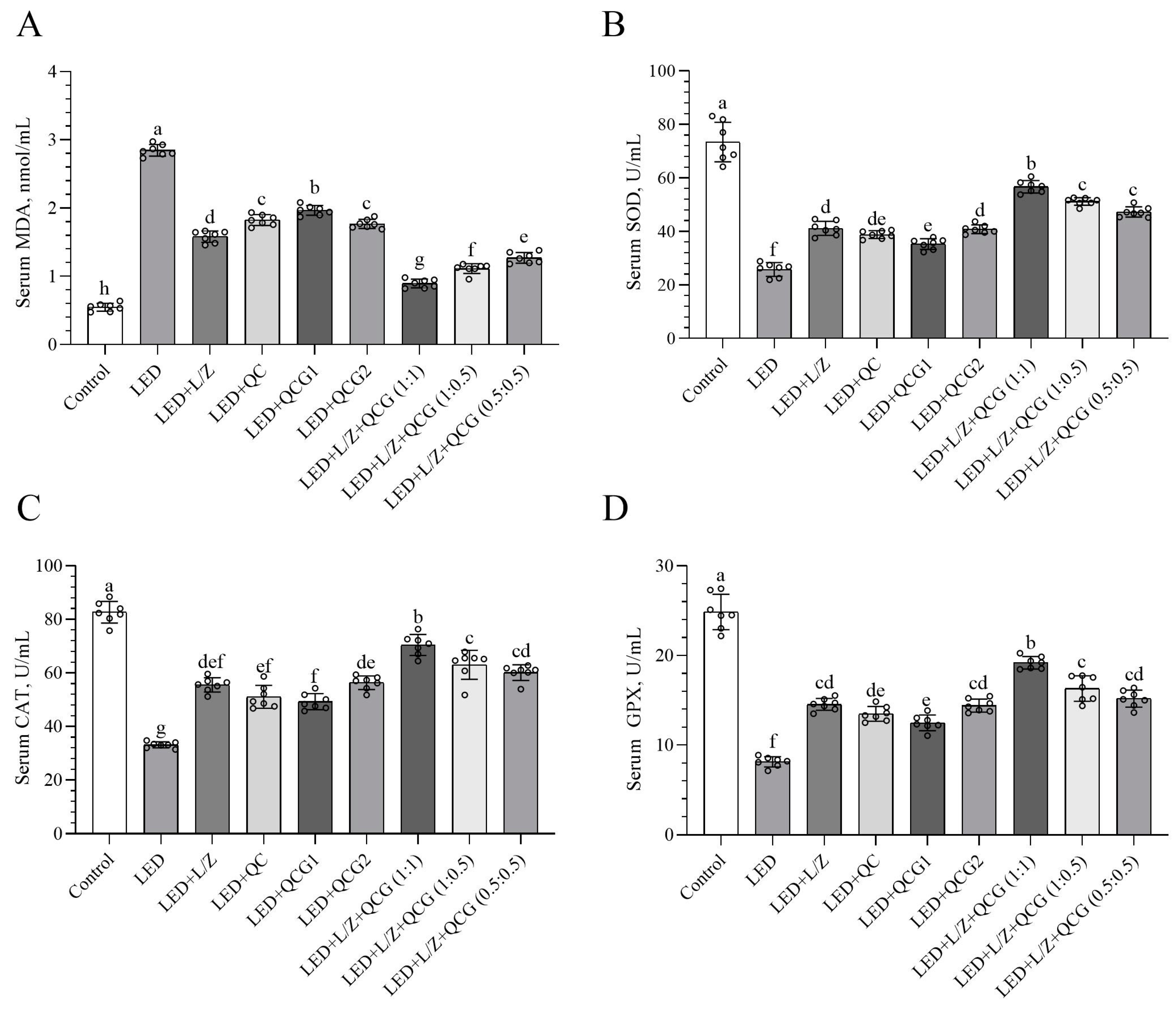
2.1. Serum Malondialdehyde (MDA) and Antioxidant Enzyme Levels
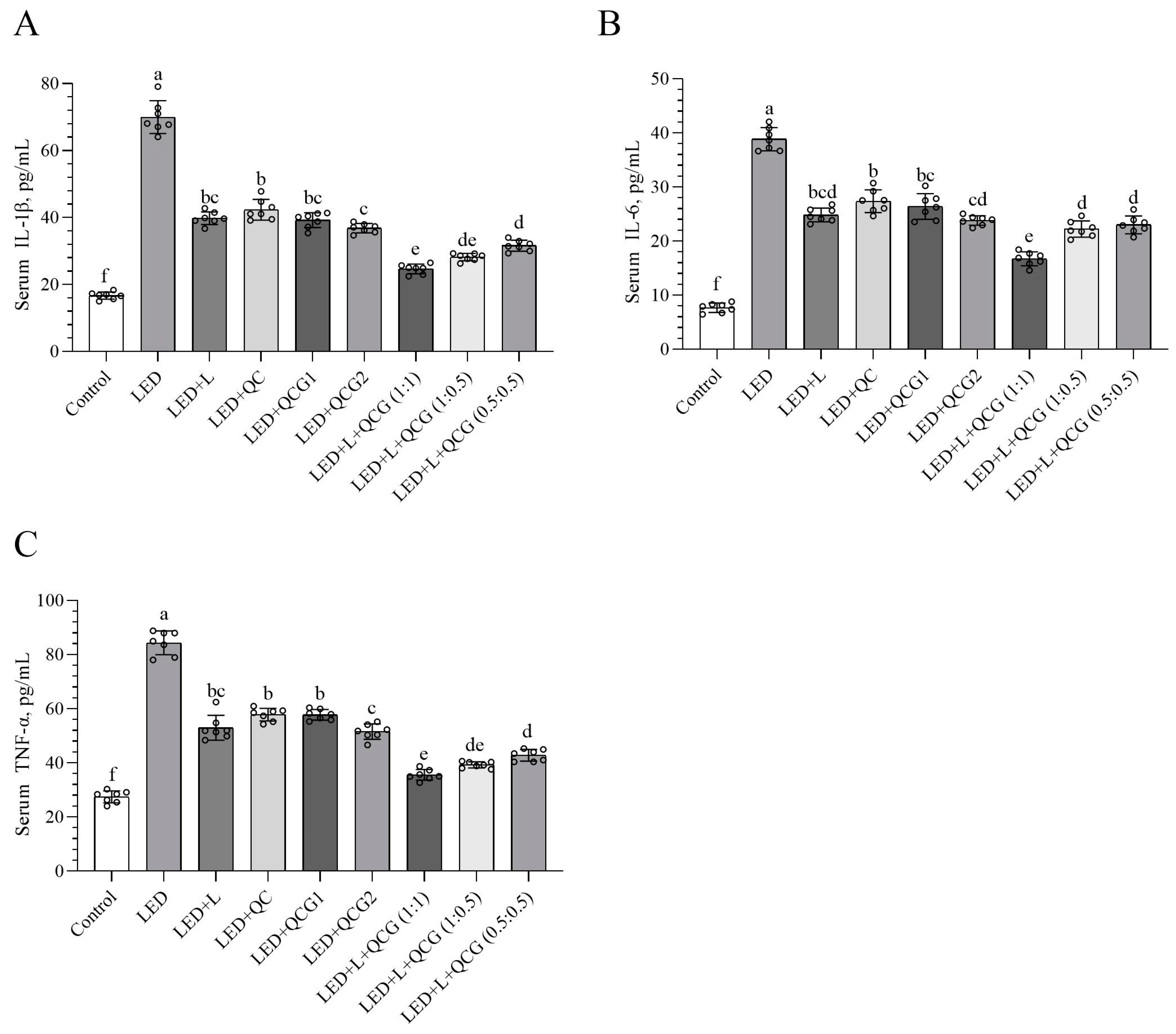
2.2. Serum Inflammatory Cytokine Levels
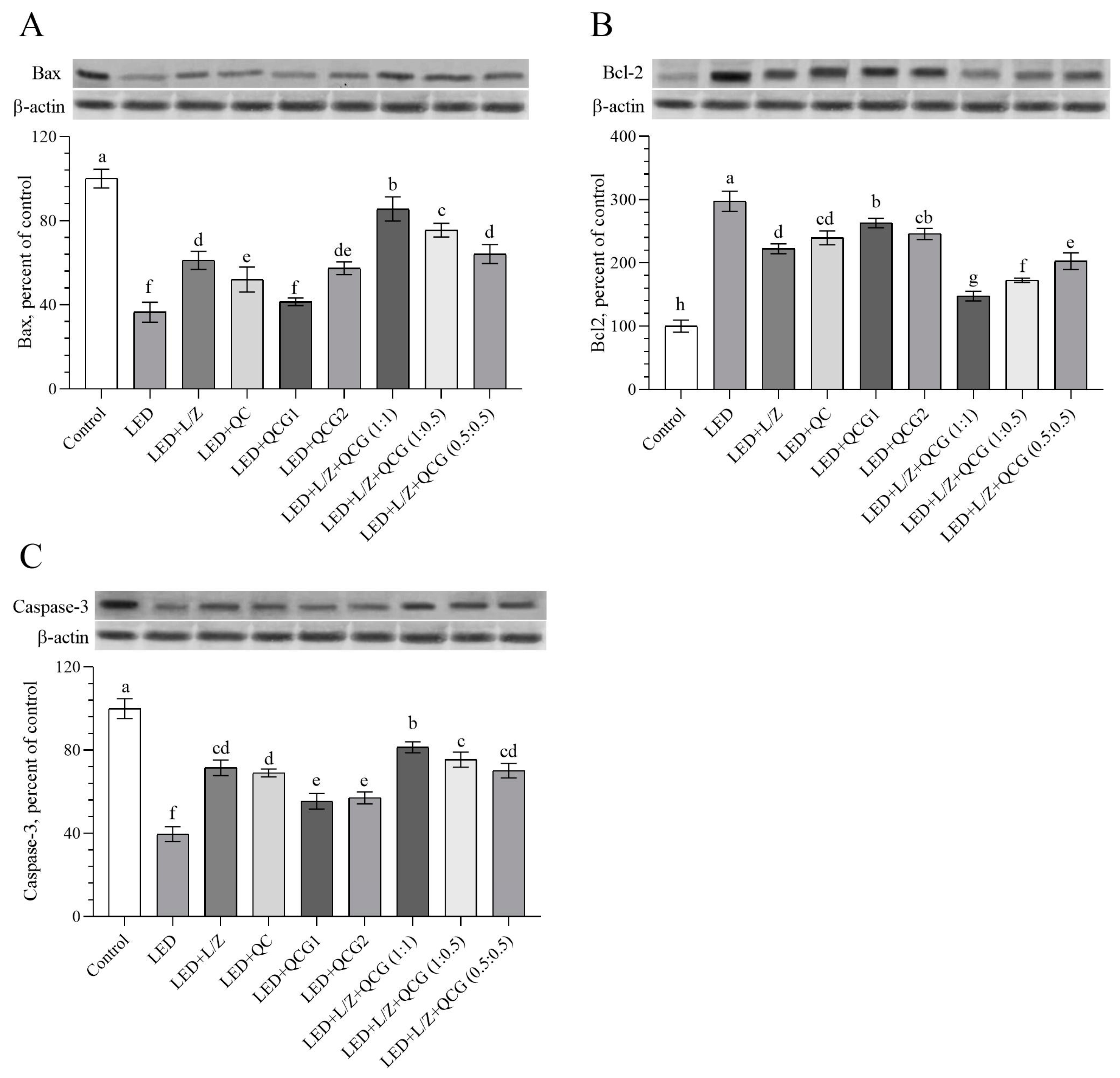
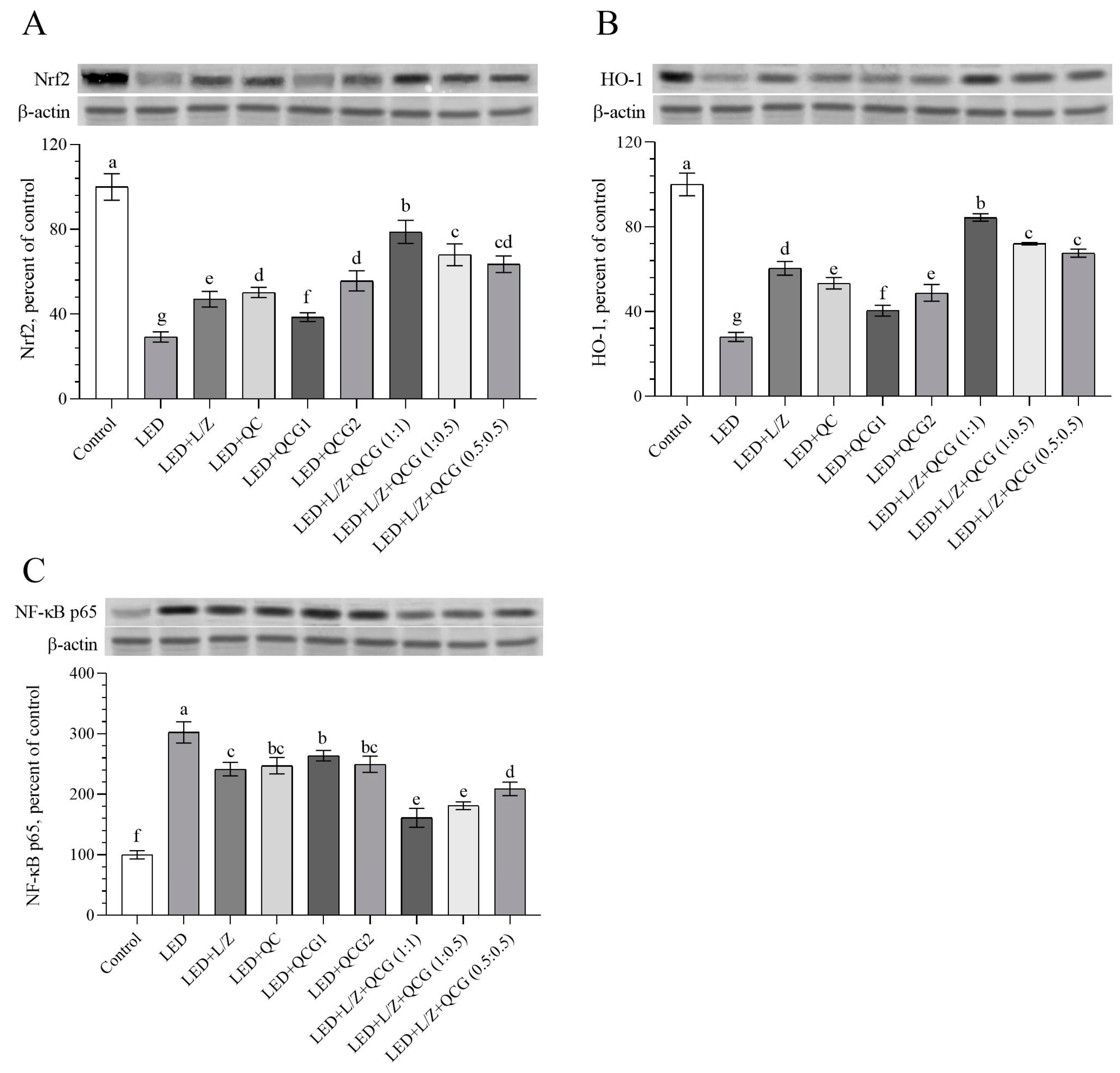
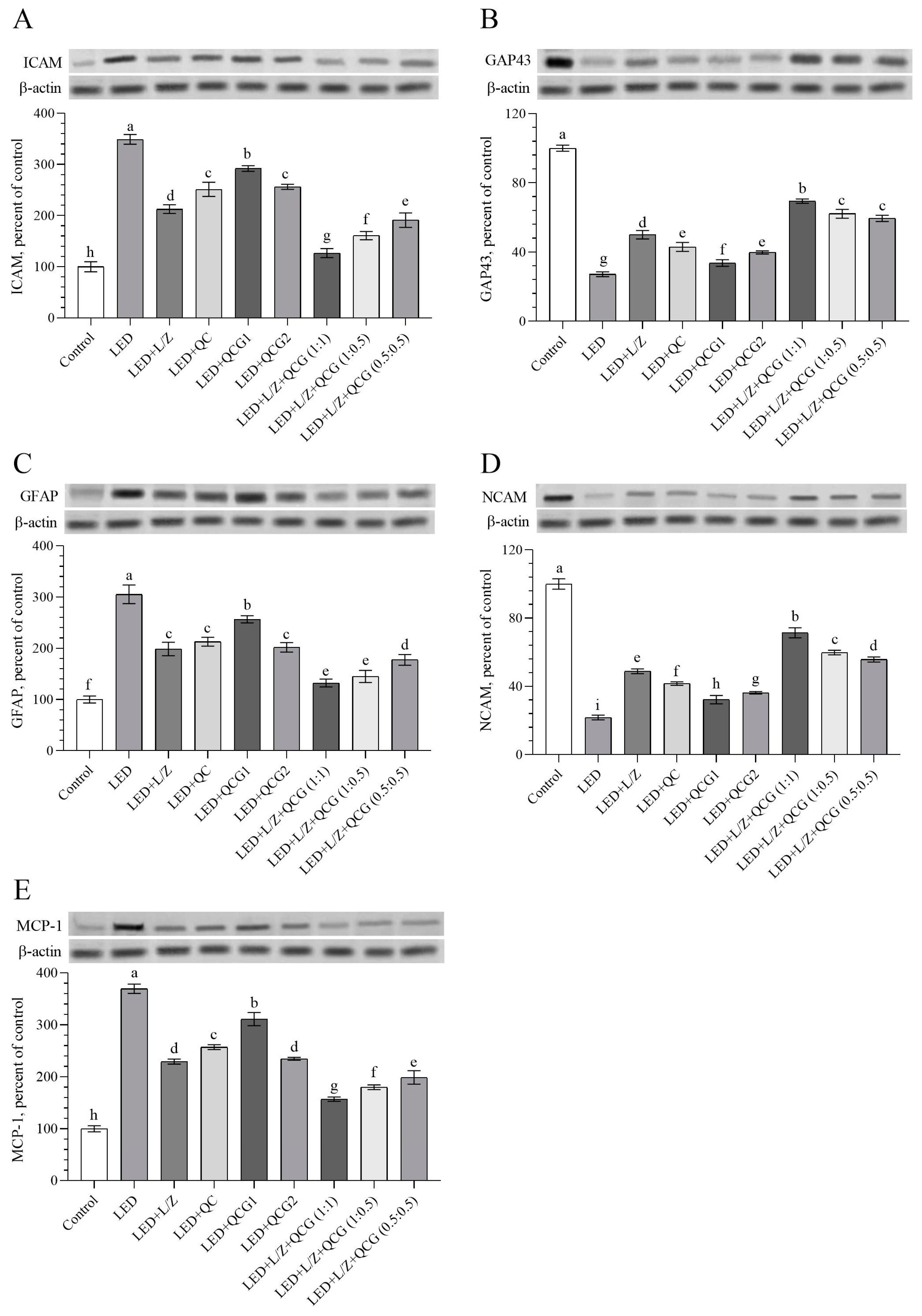
2.3. Retinal Protein Levels
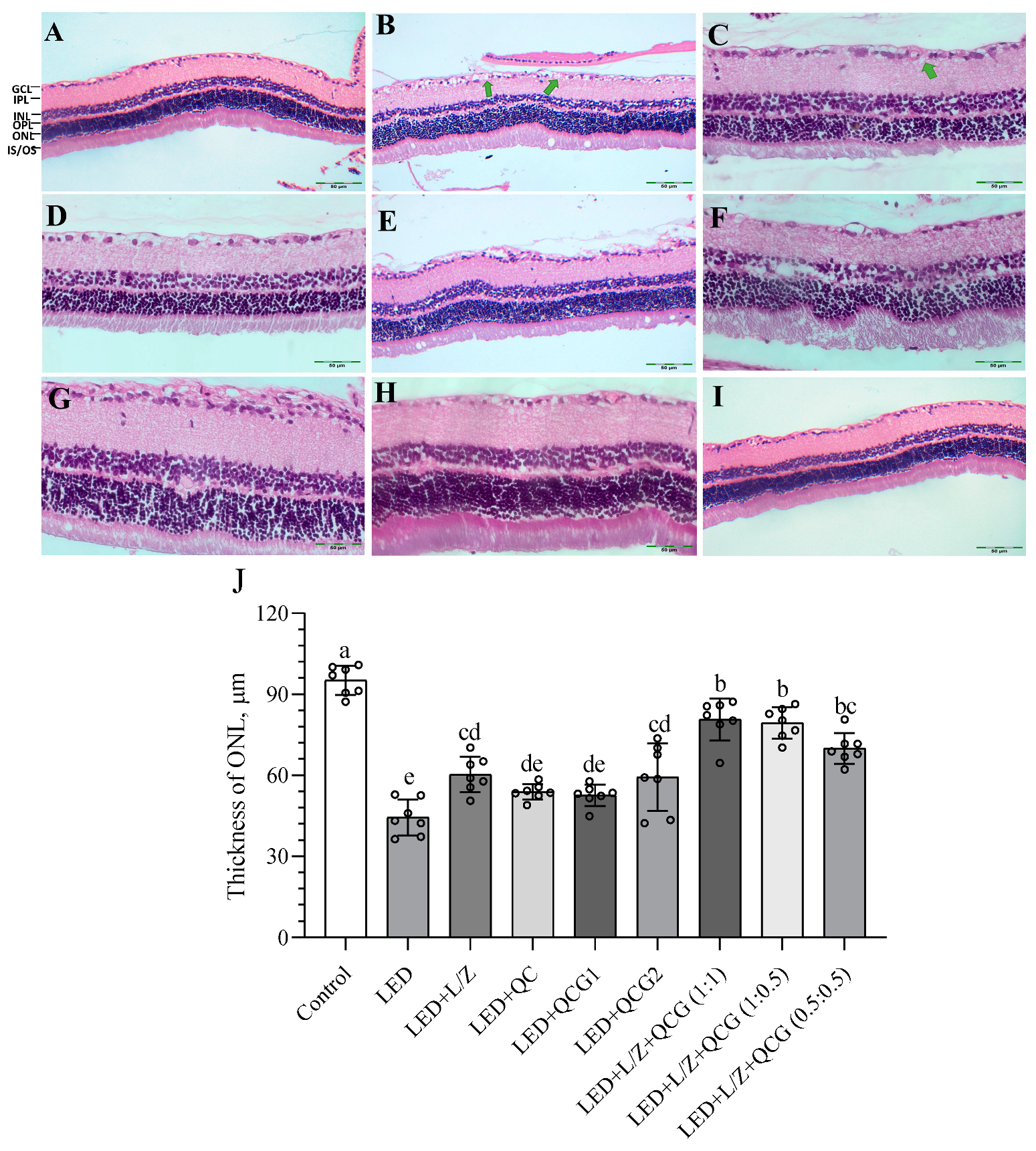
2.4. Retinal Histopathology
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Experimental Procedures
4.2. Experimental Procedures
4.3. Biochemical Analyses
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Histopathological Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaadane, I.; Boulenguez, P.; Chahory, S.; Carré, S.; Savoldelli, M.; Jonet, L.; Behar Cohen, F.; Martinsons, C.; Torriglia, A. Retinal damage induced by commercial light emitting diodes (LEDs). Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 84, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaadane, I.; Villalpando Rodriguez, G.E.; Boulenguez, P.; Chahory, S.; Carre, S.; Savoldelli, M.; Jonet, L.; Behar-Cohen, F.; Martinsons, C.; Torriglia, A. Effects of white light-emitting diode (LED) exposure on retinal pigment epithelium in vivo. Cell Commun. Signal. 2017, 21, 3453–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orhan, C.; Tuzcu, M.; Gencoglu, H.; Sahin, E.; Sahin, N.; Ozercan, I.H.; Namjoshi, T.; Srivastava, V.; Morde, A.; Rai, D.; et al. Different Doses of β-Cryptoxanthin May Secure the Retina from Photo-oxidative Injury Resulted from Common LED Sources. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6672525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, K.; Gencoglu, H.; Akdemir, F.; Orhan, C.; Tuzcu, M.; Sahin, N.; Yilmaz, I.; Juturu, V. Lutein and zeaxanthin isomers may attenuate photo-oxidative retinal damage via modulation of G protein-coupled receptors and growth factors in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 516, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M.; Yuki, K.; Kurihara, T.; Miyake, S.; Noda, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Ishida, S.; Tsubota, K.; Ozawa, Y. Biological role of lutein in the light-induced retinal degeneration. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liao, Z.; Aihemaitijiang, S.; Hou, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Xie, K.; Zhang, Z. Lutein protected the retina from light induced retinal damage by inhibiting increasing oxidative stress and inflammation. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 73, 104107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.J.; Kim, H. Lutein as a Modulator of Oxidative Stress-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Liu, X.B.; Chen, X.M.; Kong, Q.H.; Liu, Y.S.; So, K.F.; Chen, J.S.; Xu, Y.; Mi, X.S.; Tang, S.B. Lutein delays photoreceptor degeneration in a mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 1596–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cho, E.; Willett, W.C.; Sastry, S.M.; Schaumberg, D.A. Intakes of lutein, zeaxanthin, and other carotenoids and age-related macular degeneration during 2 decades of prospective follow-up. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2015, 133, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, Y.; Kaidzu, S.; Kim, Y.C.; Matsuoka, Y.; Ishihara, T.; Ohira, A.; Tanito, M. Suppression of Light-Induced Retinal Degeneration by Quercetin via the AP-1 Pathway in Rats. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.C.; Wu, Y.H.; Huang, W.C.; Pang, J.H.S.; Huang, T.H.; Cheng, C.Y. Anti-inflammatory property of quercetin through downregulation of ICAM-1 and MMP-9 in TNF-α-activated retinal pigment epithelial cells. Cytokine 2019, 116, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saviranta, N.M.M.; Veeroos, L.; Granlund, L.J.; Hassinen, V.H.; Kaarniranta, K.; Karjalainen, R.O. Plant flavonol quercetin and isoflavone biochanin A differentially induce protection against oxidative stress and inflammation in ARPE-19 cells. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Gupta, S.K.; Nag, T.C.; Srivastava, S.; Saxena, R.; Jha, K.A.; Srinivasan, B.P. Retinal neuroprotective effects of quercetin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Exp. Eye Res. 2014, 125, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, C.; Hu, J.; Guo, X.; Zhang, D.; Wu, W.; Zhou, F.; Ji, B. Protective effect of quercetin and chlorogenic acid, two polyphenols widely present in edible plant varieties, on visible light-induced retinal degeneration in vivo. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 33, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, O.; Deniz Yilmaz, M. Concise synthesis of quercetagetin (3,3′,4′,5,6,7-hexahydroxyflavone) with antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Results Chem. 2021, 3, 100255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.J.; Han, S.C.; Ock, J.W.; Kang, H.K.; Yoo, E.S. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Quercetagetin, an Active Component of Immature Citrus unshiu, in HaCaT Human Keratinocytes. Biomol. Ther. 2013, 21, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, H.H.; Galano, J.M.; Crauste, C.; Durand, T.; Lee, J.C.Y. Combination of Lutein and Zeaxanthin, and DHA Regulated Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Oxidation in H2O2-Stressed Retinal Cells. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, C.; Gencoglu, H.; Tuzcu, M.; Sahin, N.; Ozercan, I.H.; Morde, A.A.; Padigaru, M.; Sahin, K. Allyl isothiocyanate attenuates LED light-induced retinal damage in rats: Exploration for the potential molecular mechanisms. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2021, 40, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, R.; Canovai, A.; Melecchi, A.; Pezzino, S.; Corsaro, R.; Dal Monte, M.; Rusciano, D.; Bagnoli, P.; Cammalleri, M. Dietary Supplementation of Antioxidant Compounds Prevents Light-Induced Retinal Damage in a Rat Model. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, T.; Sheng, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, F.; Zhu, J.; Ding, M. Lotus Seedpod Proanthocyanidins Protect Against Light-Induced Retinal Damage via Antioxidative Stress, Anti-Apoptosis, and Neuroprotective Effects. Med. Sci. Monit. 2021, 27, e935000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; He, M. Protective effect of lutein on oxidative stress damage caused by acute PM2.5 exposure in rats. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2020, 9, 2028–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuzcu, M.; Orhan, C.; Muz, O.E.; Sahin, N.; Juturu, V.; Sahin, K. Lutein and zeaxanthin isomers modulates lipid metabolism and the inflammatory state of retina in obesity-induced high-fat diet rodent model. BMC Ophthalmol. 2017, 17, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nir, I.; Kedzierski, W.; Chen, J.; Travis, G.H. Expression of Bcl-2 protects against photoreceptor degeneration in retinal degeneration slow (rds) mice. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 2150–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Godley, B.F.; Jin, G.-F.; Guo, Y.-S.; Hurst, J.S. Bcl-2 Overexpression Increases Survival in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells Exposed to H2O2. Exp. Eye Res. 2002, 74, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dlugosz, P.J.; Billen, L.P.; Annis, M.G.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, J.; Leber, B.; Andrews, D.W. Bcl-2 changes conformation to inhibit Bax oligomerization. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 2287–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangdehi, S.R.M.; Moghaddam, A.H.; Ranjbar, M. Anti-apoptotic effect of silymarin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles on hippocampal caspase-3 and Bcl-2 expression following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int. J. Neurosci. 2022, 132, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Liu, M.; He, Y.; Yang, B. Quercetin protect cigarette smoke extracts induced inflammation and apoptosis in RPE cells. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 2010–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Kang, S.M.; Jeon, B.T.; Kim, Y.D.; Ha, J.H.; Kim, Y.T.; Jeon, Y.J. Isolation and identification of an antioxidant flavonoid compound from citrus-processing by-product. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 1925–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, B.; Du, F.; Hu, C.; Li, H.; Feng, Y.; Zhu, R.; Mo, M.; Cao, Y.; et al. 17β-Estradiol up-regulates Nrf2 via PI3K/AKT and estrogen receptor signaling pathways to suppress light-induced degeneration in rat retina. Neuroscience 2015, 304, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivarudrappa, A.H.; Ponesakki, G. Lutein reverses hyperglycemia-mediated blockage of Nrf2 translocation by modulating the activation of intracellular protein kinases in retinal pigment epithelial (ARPE-19) cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 14, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunal, M.Y.; Sakul, A.A.; Caglayan, A.B.; Erten, F.; Kursun, O.E.D.; Kilic, E.; Sahin, K. Protective Effect of Lutein/Zeaxanthin Isomers in Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice. Neurotox. Res. 2021, 39, 1543–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Wei, Z.; Han, S.; Chen, B. Effects of dietary supplementation with quercetagetin on nutrient digestibility, intestinal morphology, immunity, and antioxidant capacity of broilers. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 106014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.; Kang, N.J.; Popowicz, G.M.; Arciniega, M.; Jung, S.K.; Byun, S.; Song, N.R.; Heo, Y.S.; Kim, B.Y.; Lee, H.J.; et al. Structural and Functional Analysis of the Natural JNK1 Inhibitor Quercetagetin. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.W.; Yang, C.M.; Yang, C.H. Effects of the Emitted Light Spectrum of Liquid Crystal Displays on Light-Induced Retinal Photoreceptor Cell Damage. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 20, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Tsujikawa, M.; Itabe, H.; Du, Z.J.; Xie, P.; Matsumura, N.; Fu, X.; Zhang, R.; Sonoda, K.H.; Egashira, K.; et al. Chronic photo-oxidative stress and subsequent MCP-1 activation as causative factors for age-related macular degeneration. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 2407–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, K.A.; Nag, T.C.; Wadhwa, S.; Roy, T.S. Immunohistochemical Localization of GFAP and Glutamate Regulatory Proteins in Chick Retina and Their Levels of Expressions in Altered Photoperiods. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 37, 1029–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, K.; Akdemir, F.; Orhan, C.; Tuzcu, M.; Gencoglu, H.; Sahin, N.; Ozercan, I.H.; Ali, S.; Yilmaz, I.; Juturu, V. (3R, 3’R)-zeaxanthin protects the retina from photo-oxidative damage via modulating the inflammation and visual health molecular markers. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2019, 38, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapfhammer, J.P.; Christ, F.; Schwab, M.E. The growth-associated protein GAP-43 is specifically expressed in tyrosine hydroxylase-positive cells of the rat retina. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 1997, 101, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, M.P.S.; LeVatte, T.L.; O’Reilly, A.M.; Smith, B.J.; Tremblay, F.; Brown, R.E.; Clarke, D.B. Effect of NCAM on aged-related deterioration in vision. Neurobiol. Aging 2016, 41, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.C.; Huang, W.C.; Pang, J.H.S.; Wu, Y.H.; Cheng, C.Y. Quercetin Inhibits the Production of IL-1β-Induced Inflammatory Cytokines and Chemokines in ARPE-19 Cells via the MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikrishnan, R.; Rusia, S.; Ilamurugan, G.; Salunkhe, U.; Deshpande, J.; Shankaranarayanan, J.; Shankaranarayana, M.L.; Soni, M.G. Safety assessment of lutein and zeaxanthin (Lutemax™ 2020): Subchronic toxicity and mutagenicity studies. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 2841–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Wu, J.; Cheng, X.; Qian, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Lian, Y. A research of marigold flavonoids from marigold residues. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 191, 115898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefil, F.; Kahraman, I.; Dokuyucu, R.; Gokce, H.; Ozturk, A.; Tutuk, O.; Aydin, M.; Ozkan, U.; Pinar, N. Ameliorating effect of quercetin on acute pentylenetetrazole induced seizures in rats. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 2471–2477. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Collier, R.J.; Wang, Y.; Smith, S.S.; Martin, E.; Ornberg, R.; Rhoades, K.; Romano, C. Complement Deposition and Microglial Activation in the Outer Retina in Light-Induced Retinopathy: Inhibition by a 5-HT1A Agonist. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 8108–8116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Groups | Treatments |
|---|---|
| Control | Not exposed to intense LED light and administered with 0.5 mL vehicle (corn oil) |
| LED | Exposed to intense LED light and administered with 0.5 mL of vehicle |
| LED + L/Z | Exposed to intense LED light and administered with 20 mg/kg BW of L/Z |
| LED + QC | Exposed to intense LED light and administered with 20 mg/kg BW of quercetin |
| LED + QCG1 | Exposed to intense LED light and administered with 10 mg/kg BW of quercetagetin |
| LED + QCG2 | Exposed to intense LED light and administered with 20 mg/kg BW of quercetagetin |
| LED + L/Z + QCG (1:1) | Exposed to intense LED light and administered with 20 mg/kg BW of L/Z & Quercetagetin at a 1:1 ratio |
| LED + L/Z + QCG (1:0.5) | Exposed to intense LED light and administered with 20 mg/kg BW of L/Z & Quercetagetin at a 1:0.5 ratio |
| LED + L/Z + QCG (0.5:0.5) | Exposed to intense LED light and administered with 20 mg/kg BW of L/Z & Quercetagetin at a 0.5:0.5 ratio |
| Product | Batch No | Total Xanthophyll | Lutein | Zeaxanthin | Quercetagetin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lutemax 2020 (Free L/Z OS 20%/SF/IN-802) | 0000090850 | 26.06 | 22.05 | 4.01 | - |
| Quercetagetin | ND-93-111 | - | - | - | 80.92 |
| Lutemax 2020 OS & Quercetagetin ratio 1:1 | ND-93-139 | 28.51 | 22.93 | 5.14 | 26.69 |
| Lutemax 2020 OS & Quercetagetin ratio 1:0.5 | ND-93-141 | 28.86 | 23.27 | 5.16 | 12.52 |
| Lutemax 2020 OS & Quercetagetin ratio 0.5:0.5 | ND-93-140 | 16.34 | 13.14 | 2.88 | 11.56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sahin, E.; Orhan, C.; Sahin, N.; Padigaru, M.; Morde, A.; Lal, M.; Dhavan, N.; Erten, F.; Bilgic, A.A.; Ozercan, I.H.; et al. Lutein/Zeaxanthin Isomers and Quercetagetin Combination Safeguards the Retina from Photo-Oxidative Damage by Modulating Neuroplasticity Markers and the Nrf2 Pathway. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16111543
Sahin E, Orhan C, Sahin N, Padigaru M, Morde A, Lal M, Dhavan N, Erten F, Bilgic AA, Ozercan IH, et al. Lutein/Zeaxanthin Isomers and Quercetagetin Combination Safeguards the Retina from Photo-Oxidative Damage by Modulating Neuroplasticity Markers and the Nrf2 Pathway. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(11):1543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16111543
Chicago/Turabian StyleSahin, Emre, Cemal Orhan, Nurhan Sahin, Muralidhara Padigaru, Abhijeet Morde, Mohan Lal, Nanasaheb Dhavan, Fusun Erten, Ahmet Alp Bilgic, Ibrahim Hanifi Ozercan, and et al. 2023. "Lutein/Zeaxanthin Isomers and Quercetagetin Combination Safeguards the Retina from Photo-Oxidative Damage by Modulating Neuroplasticity Markers and the Nrf2 Pathway" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 11: 1543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16111543
APA StyleSahin, E., Orhan, C., Sahin, N., Padigaru, M., Morde, A., Lal, M., Dhavan, N., Erten, F., Bilgic, A. A., Ozercan, I. H., & Sahin, K. (2023). Lutein/Zeaxanthin Isomers and Quercetagetin Combination Safeguards the Retina from Photo-Oxidative Damage by Modulating Neuroplasticity Markers and the Nrf2 Pathway. Pharmaceuticals, 16(11), 1543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16111543