Abstract
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is one of the most common pathogens of healthcare-associated infections. Medicinal plants have long been used in the traditional treatment of diseases or syndromes worldwide. Combined use of plant extracts could improve the effectiveness of pharmacological action by obtaining synergism, acting on multiple targets simultaneously, reducing the doses of individual components, and minimizing side effects. We aimed to investigate the synergistic inhibitory effects of selected medicinal plants (Caesalpinia sappan L. (CS), Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. (GU), Sanguisorba officinalis L. (SO), and Uncaria gambir Roxb. (UG)) on the bacterial growth of MRSA and its clinical isolates. SO and UG extracts generated the best synergistic interaction as adjudged by checkerboard synergy assays. MICs of the individual extracts decreased 4-fold from 250 to 62.5 μg/mL, respectively. The SO + UG combination was further evaluated for its effects on bacterial growth inhibition, minimum bactericidal/inhibitory concentration (MBC/MIC) ratio, and time-kill kinetics. The results indicate that the SO + UG combination synergistically inhibited the bacterial growth of MRSA strains with bactericidal effects. SO + UG combination also exhibited more potent effects against clinical isolates. In multistep resistance selection experiments, both standard and isolates of MRSA showed no resistance to the SO + UG combination even after repeated exposure over fourteen passages. Our data suggest that using plant extract combinations could be a potential strategy to treat MRSA infections.
1. Introduction
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is one of the most prevalent pathogens of healthcare-associated (HA) infections [1]. MRSA has become a serious threat to global health and can cause mild to invasive, life-threatening infections. It is responsible for increased morbidity and mortality, length of stay, and economic burden [1,2,3]. The overall proportion of MRSA isolates exceeded 20% in all World Health Organization (WHO) regions, and even exceeded 80% in some reports [3]. In hospital settings, the prevalence of MRSA has been reported to be 70–80% in Asian countries, more than in Europe (25%) [4]. In particular, the proportion of MRSA in HA isolates was 73.3% in South Korea [5].
MRSA is a major threat among antibiotic-resistant agents, causing ~19,000 deaths with a healthcare cost of USD 3–4 billion annually in the US. [6]. The ability of MRSA to tolerate conventional antibiotics leads to difficult-to-treat infections and limits the therapeutic options available [4,7]. Methicillin resistance in Staphylococci is mediated by the mecA gene, which encodes a modified penicillin-binding protein 2a (PBP 2a) that results in resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics by causing a low binding affinity [8,9]. Furthermore, over time, MRSA has developed resistance to other antibiotic classes, including fluoroquinolone, macrolide, aminoglycoside, and clindamycin [10]. With the growing problem of antibiotic resistance, novel antibiotic agents with different mechanisms of action are urgently needed to control MRSA infections.
Many plant species found to possess medicinal values have long been used in the traditional treatment of diseases or syndromes worldwide [11,12]. Medicinal plants are still being provided as traditional medicines to 70–95% of the population in developing countries. They are also utilized, either directly or indirectly, in at least 25% of all modern medicines [13]. Medicinal plants have various bioactive compounds, such as alkaloids, flavonoids, phenolic compounds, steroids, tannins, terpenoids, and other secondary metabolites, which act remarkably on parasites and pathogens [12,14]. Plant-derived compounds possess unique pharmacological properties such as low cost, less toxicity, fewer side effects, and less likely to develop resistance [15,16,17].
Synergism is the interaction of two or more drugs that produces a greater influence than either individually [18]. Synergism is preferred to treat infections associated with multidrug-resistance (MDR) or those at risk of treatment failure with a single drug because plant extracts in combination provide more benefits than what is generally available alone [19,20]. Combined use of plant extracts could improve the effectiveness of pharmacological action by obtaining synergism, acting on multiple targets simultaneously, reducing the doses of individual extracts, and minimizing side effects [21,22]. However, it is important to know which of the four possible effects (synergism, partial synergism, addition, or antagonism) of a therapeutic or even toxic response leads to the combined effect of plant extracts and to optimize the appropriate proportion that produces a more effective therapeutic effect [23,24].
A previous study by our team has reported the inhibitory effects of medicinal plants on the bacterial growth of MRSA. We also selected four medicinal plants (Caesalpinia sappan L. (CS), Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. (GU), Sanguisorba officinalis L. (SO), and Uncaria gambir Roxb. (UG)) based on their potent effects in that study [25]. The present study aimed to investigate the synergistic effects of selected medicinal plants against MRSA strains, including clinical isolates. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report to investigate the synergistic inhibitory effects of selected medicinal plants on the bacterial growth of MRSA strains.
2. Results and Discussion
In this study, we confirmed the synergistic inhibitory effects of selected medicinal plants on the bacterial growth of MRSA and its clinical isolates. The selection of medicinal plants was established based on minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) for MRSA strains reported in our previous study [25]. MIC values of medicinal plants were determined using the broth microdilution method as follows: CS (62.5 μg/mL), GU (250 μg/mL), SO (250 μg/mL), and UG (250 μg/mL) [25]. Information on the plants and their pharmacological uses is presented in Table 1 [26,27,28,29,30].

Table 1.
List of medicinal plants used in the present study and their pharmacological uses in traditional medicines.
Based on the UPLC analysis, the major compounds of selected medicinal plants were tentatively identified. Representative chromatograms obtained from the UPLC analysis are shown in Figure 1. The chromatograms recorded at different detection wavelengths are presented in Figures S1–S4. For each peak, we tentatively identified five compounds as follows: Peak 1 (Brazilin, observed RT: 2.98 min; formula: C16H14O5; molecular weight: 286.28 g/mol), Peak 2 (Protosappanin B, observed RT: 3.10 min; formula: C16H16O6; molecular weight: 304.30 g/mol), Peak 3 (Liquiritin apioside, observed RT: 4.35 min; formula: C26H30O13; molecular weight: 550.51 g/mol), Peak 4 (Glycyrrhizin, observed RT: 9.48 min; formula: C42H62O16; molecular weight: 822.94 g/mol), and Peak 5 (Catechin, observed RT: 3.07 min; formula: C15H14O6; molecular weight: 290.27 g/mol). Table 2 summarizes detailed information on each compound identified or deduced based on data reported in the literature [31,32,33,34,35,36]. The chemical structures of these compounds are shown in Figure 2.
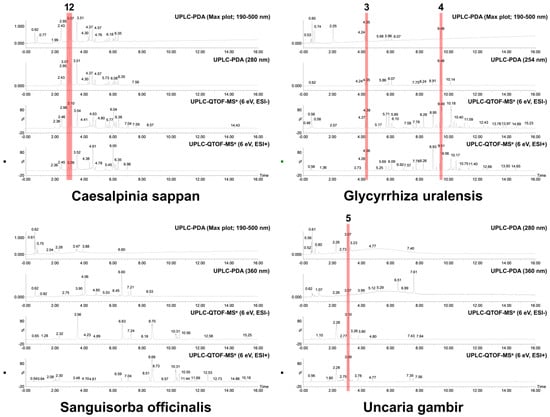
Figure 1.
Representative UPLC chromatograms of 70% ethanol extracts (3 mg/mL) from selected medicinal plants. The tentatively identified compounds are as follows: (1) brazilin; (2) protosappanin B; (3) liquiritin apioside; (4) glycyrrhizin; (5) catechin. The analysis conditions were set as follows: column, ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 1.7 μm column (2.1 × 100 mm); column temperature, 35 °C; flow rate, 0.4 mL/min; injection volume, 1 μL; detection wavelength, max plot (190–500 nm), 210 nm, 254 nm, 280 nm, and 360 nm. The mobile phase gradient conditions were set as described in Table S1.

Table 2.
Tentative identification of the major compounds in the plant extracts.
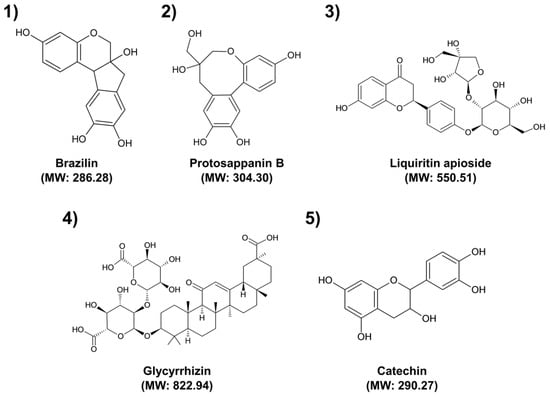
Figure 2.
Chemical structures of the tentatively identified major compounds. (1) Brazilin; (2) Protosappanin B; (3) Liquiritin apioside; (4) Glycyrrhizin; (5) Catechin. MW: Molecular weight.
The antimicrobial activities of medicinal plants are attributed to their ability to produce several secondary metabolites with antimicrobial properties [37]. These activities are dependent not only on the presence of secondary metabolites but also on their concentration and the possible interactions with other components [37,38]. Therefore, it is important to identify compounds involved in a specific pharmacological action and investigate their interactions with other compounds. Brazilin (Peak 1) and protosappanin B (Peak 2) have been reported as the major compounds in CS [32]. Protosappanin displayed antibacterial activities with MIC at 128 µg/mL against both S. aureus and MRSA [39]. Especially, brazilin showed remarkable activities against antibiotic-resistant bacteria, including MRSA, vancomycin-resistant enterococci, and multidrug resistant Burkholderia cepacia, with MIC values ranging from 4 to 32 µg/mL [38]. Liquiritin apioside (Peak 3) and glycyrrhizin (Peak 4) are the main bioactive components with major pharmacological activities in GU [40]. Glycyrrhizin inhibited the growth of clinical isolates of MRSA and MSSA, with MIC ranging from 32 to 512 μg/mL and 16 to 512 μg/mL, respectively [41]. Catechin (Peak 5) has been reported as the major compound in UG [42]. MIC values of catechin ranged from 78.1 to 156.2 μg/mL against clinical isolates of MRSA [43]. Flavonoids such as brazilin, protosappanin B, liquiritin apioside, and catechin can have various antibacterial mechanisms against bacteria. They inhibit biofilm formation, cell envelope synthesis, nucleic acid synthesis, and ATP synthesis and damage the bacterial respiratory chain, membrane bilayer, and membrane proteins [44]. As a terpenoid, glycyrrhizin’s antibacterial activity is due to the disruption of membranes, anti-quorum sensing, and inhibition of protein and ATP synthesis [45]. However, major active compounds involved in the antibacterial activity of SO extract were not identified [46]. This may be because the antibacterial effect of SO extract is not caused by a specific compound but rather by interactions between several compounds in the extract. Therefore, further studies are needed to identify unknown antibacterial compounds of SO extract and elucidate their antibacterial mechanism.
Antibacterial bioassays were conducted to evaluate the inhibitory effects of plant extracts alone and in combination. Two reference strains (MSSA and MRSA) and two clinical isolates (MDRSA and MRSA) were employed in these assays. Methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA; S. aureus ATCC 29,213) showed no resistance to 10 different antibiotic discs used in the antibiotic susceptibility testing: ampicillin (Amp; 10 µg), methicillin (Meth; 5 µg), penicillin G (Pen; 10 IU), kanamycin (Kan; 30 µg), gentamicin (Gen; 10 µg), streptomycin (Strep; 10 µg), tetracycline (Tet; 30 µg), erythromycin (Eryth; 15 µg), vancomycin (Van; 30 µg), and chloramphenicol (Chl; 30 µg) (Liofilchem, Teramo, Italy). The antibiotic resistance profiles of MRSA strains were as follows: MRSA (ATCC 33,591; Amp, Meth, Pen, Kan, Eryth, Strep, Tet, Gen, and Chl), MDRSA (CI-2; Amp, Meth, Pen, Kan, Eryth, Strep, Tet, and Gen), and MRSA (CI-21; Amp, Meth, Pen, Kan, Strep, and Gen) [25]. MDR was defined as strains resistant to at least one antibiotic in three or more different antibiotic classes [47]. All MRSA strains were resistant to antibiotics of beta-lactam and aminoglycoside classes. The most resistant isolate was CI-2, which was resistant to 8 out of 10 tested antibiotics and only sensitive to vancomycin and chloramphenicol. As most MDRSA isolates have been reported to be sensitive to chloramphenicol in the previous study [48], CI-2 was found to be susceptible to chloramphenicol.
MICs of individual extracts were determined by the broth microdilution method. According to Figure S5 and Table 3, the ethanol extracts of selected medicinal plants showed significant inhibitory effects with MIC values ranging from 62.5 to 250 μg/mL. Among the tested extracts, CS extract had the lowest MIC (62.5 μg/mL) value against all tested strains, while other tested extracts had equal MIC (250 μg/mL) values. The inhibitory effects of selected medicinal plants were relatively more potent than most plant extracts reported in large-scale screening studies [10,11,49]. Furthermore, the susceptibility of each tested strain to different extracts showed no significant differences. These results suggest that plant extracts could be active with different antibacterial mechanisms and target sites compared to conventional antibiotics toward bacterial strains regardless of their antibiotic resistance patterns [50].

Table 3.
Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values of selected medicinal plants against test bacterial strains.
Combined use of plant extracts can cause different interactions of natural compounds because each extract contains diverse types of compounds. The enhanced antibacterial activity of plant extract combinations is well-known, as has been reported in previous literature [12,23,51]. However, some interactions decrease the efficacy of plant extract combinations by neutralizing each other, forming inactive complexes, and/or acting competitively for the same molecular target [52,53,54]. Therefore, it is necessary to confirm the influence of the combination of plant extracts. Checkerboard synergy assays were performed to evaluate the synergistic effects of selected medicinal plants (Figure S6). Fractional inhibitory concentrations (FICs) and their interpretations are presented in Table 4. SO and UG extracts generated the best synergistic interactions (FICI = 0.5). Their MICs decreased 4-fold, respectively. On the other hand, the GU + SO combination showed additive effects (FICI = 1). Other tested combinations showed partial synergistic effects (FICI = 0.625). No antagonism was found in any plant extract combinations. Among individual extracts used in combination, the CS extract showed the highest MIC reduction with an 8-fold decrease (MIC = 7.81 μg/mL), but there was no highest synergistic effect (Table 4). These results suggest that the potent activity of one extract might not necessarily lead to a high synergy with another extract. Antibacterial mechanisms of plant extract combinations are not fully understood yet. Thus, we conducted further antibacterial analysis to elucidate the inhibitory effects of the SO + UG combination, showing the best synergism.

Table 4.
Fractional inhibitory concentration (FIC) values of selected medicinal plants in combination against test bacterial strains.
To assess the efficacy of the SO + UG combination in inhibiting MRSA strains, the results of checkerboard analysis are presented as heatmaps indicating the percentage of bacterial growth inhibition based on optical density at 595 nm (OD595) values (Figure 3a). Darker regions represent higher bacterial cell density. FICIs of SO and UG extracts were 0.5 for all tested strains (Table 4). These results indicate that their synergistic effects existed regardless of the different resistance patterns of the tested strains. According to cell viability assays performed in previous studies, SO and UG extracts showed no cytotoxicity and were safe [55,56]. However, further studies are needed on the influences of the combined effects of SO and UG extracts on toxicity.
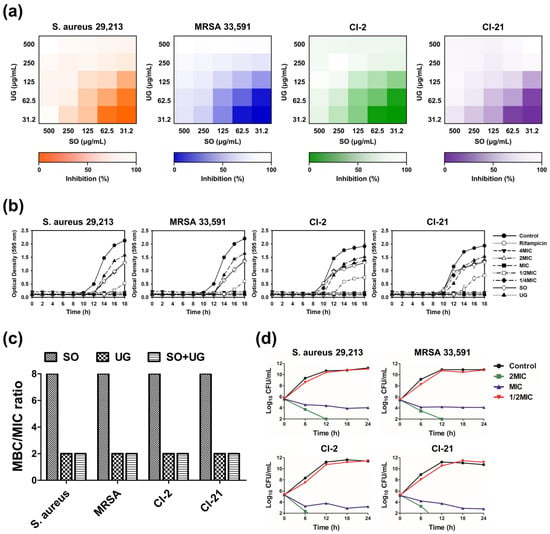
Figure 3.
The SO + UG combination synergistically inhibits bacterial growth of MRSA isolates. (a) Heatmaps of checkerboard synergy assays for the SO + UG combination. The results are presented as the percentage of bacterial growth inhibition based on OD595 values. Darker regions represent higher bacterial cell density. (b) Influences of the SO + UG combination on bacterial growth of MRSA strains. The concentration of the individual extracts was 125 μg/mL (sub-MIC). (c) MBC/MIC ratio of SO, UG extracts alone, or their combination. (d) Time-kill curves of the SO + UG combination against MRSA strains. MBC/MIC ratio ≤ 4 and time-kill curves indicate bactericidal effects of the SO + UG combination following data in (c,d). All data are presented as mean ± standard deviations of experiments performed in triplicate, with p < 0.05 indicating statistical significance.
Bacterial growth curves have been used to investigate the growth and death of bacteria over a wide range of antibacterial concentrations and to assess the effects of antibacterial agents over time [57]. We monitored the inhibitory effects of the SO + UG combination on the bacterial growth of MRSA strains. The results are presented in Figure 3b. The SO + UG combination affected bacterial growth in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. At the above MIC, the SO + UG combination completely inhibited bacterial growth. The SO + UG combination showed stronger inhibitory effects than the individual extracts of sub-MIC (125 μg/mL), even at 1/2 MIC. At 1/2 MIC, the time lag with the SO + UG combination reaching the exponential phase was changed from 8 h to 12 h against clinical isolates (CI-2 and CI-21) compared to the control group. For standard strains (ATCC 29,213 and ATCC 33,591), the reaching time to the exponential phase was remarkably delayed from 8 h to 14 h in the presence of the SO + UG combination.
Bactericidal activity is of clinical importance because bacterial killing is predicted to produce a faster resolution of infection and improved clinical outcomes. More rapid elimination of bacterial pathogens should also minimize the possible emergence of resistance and spread of infections [58]. The MBC/MIC ratio determines whether a drug is bactericidal or bacteriostatic. If the MBC/MIC ratio is ≤4, the effect is considered bactericidal, but if the MBC/MIC ratio is >4, the effect is defined as bacteriostatic [59]. The MBC/MIC ratio is shown in Figure 3c. The SO + UG combination was considered bactericidal against all tested strains as its MBC/MIC ratio was 2. SO extracts showed bacteriostatic effects with an MBC of 2000 μg/mL and MIC of 250 μg/mL, while UG extracts were bactericidal with an MBC of 500 μg/mL and MIC of 250 μg/mL.
A time-kill kinetic analysis was conducted to determine the killing kinetics of the SO + UG combination. Time-kill curves are shown in Figure 3d. At 2 MIC, the SO + UG combination reduced the number of viable bacterial cells by more than 2 log10 within 6 h and completely eradicated the cells within 12 h. The combination especially showed stronger bactericidal effects on clinical isolates of MRSA than on standard strains. Although the SO + UG combination of MIC showed a slow log10 decline of viable bacterial cells without completely eradicating the cells even after 24 h, it showed a reduction of CFU/mL value of more than 2 log10. The combinations at higher concentrations caused more rapid bacterial death. The kinetics of the SO + UG combination killing the bacterial strains was time- and concentration-dependent. It is consistent with our results obtained from the bacterial growth curves. Our data demonstrate that the SO + UG combination could inhibit bacterial growth by acting as a bactericidal agent against MRSA strains.
Disc diffusion assays were performed to evaluate the antibacterial activity of SO + UG combination at a concentration of 2 mg/disc. The diameter of inhibition zones was measured and recorded by a representative photograph and comparative graph (Figure 4). SO, UG extracts alone, and their combination exhibited antibacterial activities against MRSA strains. Distilled water (DW) showed no antibacterial activity. All tested strains were highly susceptible to the SO + UG combination with the largest inhibition zones (24.47–25.53 mm). The UG extract also showed remarkable antibacterial activities with diameters of 20.20–21.07 mm for inhibition zones. In contrast, the SO extract had poor activities with diameters of 9.17–10.87 mm. The SO + UG combination inhibited bacterial growth more effectively than SO or UG extracts alone. In addition, SO and UG extracts showed an equal MIC of 250 μg/mL in our data, but significant differences were observed for the diameters of inhibition zones. This phenomenon could be due to the structural diversity of compounds present in plant extracts. The quantity, diversity, and biological properties of secondary metabolites from medicinal plants differ among the species of plants [60]. The disc diffusion method is dependent on several factors that contribute to the degree of diffusion, such as the polarity, hydrophilicity or hydrophobicity, and molecular weight (MW) of the test substances [61,62]. Thereby, we speculate that different physicochemical properties of diverse compounds in the plant extracts might cause differences in antibacterial activity by the disc diffusion method.
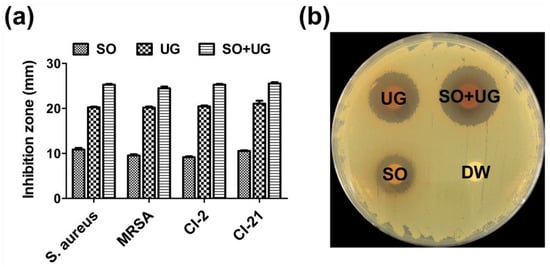
Figure 4.
Inhibition zones of the SO + UG combination against test bacterial strains. (a) Comparative graph for inhibition zones; (b) Representative photograph (MRSA 33,591). Briefly, each bacterial suspension was adjusted to McFarland 0.5 turbidity and swabbed onto BHI plates. Then, 100 μL of each sample was loaded onto each paper disc (8 mm/diameter). The concentration of the samples was 2 mg/disc. Distilled water (DW) was served as a negative control. All data are presented as mean ± standard deviations of experiments performed in triplicate, with p < 0.05 indicating statistical significance.
Antibiotics revolutionized the practice of medicine by providing a cure and decreasing the morbidity and mortality of numerous infectious diseases. However, these achievements are threatened by the emergence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR). AMR refers to the ability of microbial pathogens to avoid or delay death upon exposure to antibiotics predicted to kill them [63,64]. In multistep resistance selection experiments, we confirmed the ability of MRSA to develop resistance to the SO + UG combination and rifampicin after repeated exposures. MRSA strains were serially passaged at 24 h intervals in the presence of each sample for up to fourteen passages. The results are shown in Figure 5. The MRSA standard (ATCC 33,591) developed resistance to rifampicin after four passages with a 4-fold increase in MIC. MRSA isolates (CI-2 and CI-21) rapidly developed resistance to rifampicin after the second passage, with a 4-fold increase in MIC, respectively. After fourteen passages, the MIC of rifampicin for ATCC 33,591, CI-2, and CI-21 increased to 64, 1024, and 1024 folds, respectively. However, no resistance was observed for the SO + UG combination over the fourteen passages (MIC increased by up to 2-fold). These results indicate that MRSA strains could not easily develop resistance to the SO + UG combination. This could be due to the bactericidal activity of the SO + UG combination toward MRSA. Elimination of pathogens rather than inhibition eradicates the resistance mutations that could occur due to antibiotic pressure [65]. Thereby, plant extract combinations such as the SO + UG combination may be a promising candidate to overcome antibiotic resistance.
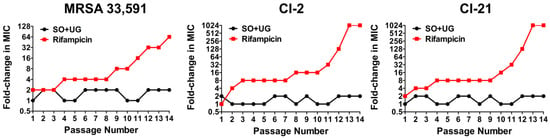
Figure 5.
MRSA strains show no resistance to the SO + UG combination in multistep resistance selection experiments. The broth microdilution method was used to determine the MIC of the SO + UG combination and rifampicin against MRSA strains after repeated exposure. After the MIC test, the strains were taken from the sub-MIC wells and successively passaged for up to fourteen passages. The results are presented as fold-change in MIC relative to the previous passage. Resistance was defined as a more than a 4-fold increase of MIC compared to the initial MIC.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Materials
Four medicinal plants (Caesalpinia sappan L., Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch., Sanguisorba officinalis L., and Uncaria gambir Roxb.) were selected based on data reported in our previous study [25]. They were purchased from Samhong Medicinal Herb Market (Seoul, Republic of Korea).
3.2. Preparation of Plant Extracts
Plant materials were blended to powder using a home grinder and extracted with 70% ethanol with shaking (110 rpm) for 24 h. The ratio of plant materials to solvent was 1:10 (w/v). Crude extracts were then centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 30 min. Supernatants were concentrated under reduced pressure using a rotary vacuum evaporator WEV-1001V (Daihan Scientific Co., Wonju, Republic of Korea). The concentrated residue was subsequently dissolved in 10% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO; Sigma Chemical Co., St. Louis, MO, USA) and filtered through Whatman filter paper No. 2 (Whatman, Kent, UK) to obtain ethanol extracts. All prepared extracts were collected into conical tubes and stored in a refrigerator at 4 °C until further use.
3.3. Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC) Analysis
To tentatively analyze plant extracts, we performed an ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) analysis on an AQUITY UPLC I-Class system (Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA) using an ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 1.7 μm column (2.1 × 100 mm). The mobile phase was composed of distilled water with 0.1% formic acid (A) and acetonitrile with 0.1% formic acid (B). The eluent was set as follows: 0 min 92% (A)/8% (B), 1.0 min 92% (A)/8% (B), 16.0 min 30% (A)/70% (B), 17.0 min 0% (A)/100% (B), 19.0 min 0% (A)/100% (B), 19.3 min 92% (A)/8% (B), and 22.0 min 92% (A)/8% (B) at a 0.4 mL/min flow rate (Table S1). The column temperature was kept at 35 °C, the injection volume was 1 μL, and the detection wavelength was set at max plot (190–500 nm), 210 nm, 254 nm, 280 nm, and 360 nm. For MS detection, the following MS conditions were set for both positive and negative electrospray ionization (ESI) modes: desolvation gas (N2), flow rate 800 L/h, desolvation gas temperature 350 °C, source temperature 110 °C, capillary voltage 300 V, cone voltage 40 V, and m/z range 100–1500 Da (Table S2). The identification of compounds was based on mass and UV-Vis spectra in comparison with previous literature for each origin plant.
3.4. Bacterial Culture
Standard strains of S. aureus (ATCC 29,213) and MRSA (ATCC 33,591) were used in the present study. These strains were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC; Manassas, VA, USA). MRSA isolates (CI-2 and CI-21) were originally obtained from clinical specimens and identified at Gachon University Gil Medical Center (Incheon, Republic of Korea) [66]. These isolates were preserved in a −80 °C freezer in 20% glycerol (v/v) until further use. Each bacterium was initially cultivated on a brain heart infusion (BHI; Kisan Bio, Seoul, Republic of Korea) plate. A single colony was picked from each plate and pre-cultured in BHI broth at 37 °C for 24 h prior to assays. Bacterial stocks were subcultured every 3–4 weeks to maintain bacterial viability.
3.5. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
MIC was determined using the broth microdilution method described by Bostanci et al. [67] with slight modifications. Briefly, 200 μL of the sample was inoculated to the first wells of a 96-well microplate and serially diluted 2-fold. Then, 100 μL of each bacterial suspension (1 × 106 CFU/mL) was added to each well. The microplate was incubated at 37 °C for 18 h and continuously monitored for bacterial growth. The OD was measured at 595 nm using a spectrophotometer (Multiskan FC; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). MIC was defined as the lowest concentration that inhibited the visible growth of bacteria.
3.6. Determination of Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)
To determine MBC, the MIC test was repeated, as mentioned above. Then, 50 µL of suspension was taken from the well that inhibited visible growth of bacteria. The suspension was transferred to a new microplate, and 150 µL of BHI broth was added to each well. The microplate was incubated at 37 °C for 18 h. MBC was defined as the lowest concentration that killed 99.9% of bacteria.
3.7. Checkerboard Synergy Assay
Synergistic effects of plant extract combinations were evaluated with a checkerboard synergy assay to obtain FIC values. One extract was serially diluted along the abscissa, while another extract was serially diluted along the ordinate. The total volume of the combination was 100 μL per well. Then 100 μL of each bacterial suspension (1 × 106 CFU/mL) was added to each well of a 96-well microplate. The microplate was incubated at 37 °C for 18 h. The OD was measured at 595 nm with a spectrophotometer. FICI was calculated using the following equation: FICI = FICA + FICB, where FICA was MIC of extract A in combination/MIC of extract A alone, and FICB was MIC of extract B in combination/MIC of extract B alone. Results were interpreted as synergistic interaction (FICI ≤ 0.5), partial synergy (0.5 < FICI ≤ 0.75), additive interaction (0.75 < FICI ≤ 1.0), indifferent (1.0 < FICI ≤ 4.0), or antagonistic interaction (FICI > 4.0) [68].
3.8. Time-Kill Kinetic Analysis
A time-kill kinetic analysis was performed to confirm the killing potencies of the SO + UG combination, according to Mohamed et al. [69]. Each bacterial suspension (1 × 106 CFU/mL) was inoculated to BHI broth containing the SO + UG combination with different concentrations (2MIC, MIC, and 1/2MIC). The mixture was incubated in a shaker incubator at 120 rpm and 37 °C. Then 100 μL of the incubated mixture was transferred to BHI plates at 0, 6, 12, 18, and 24 h. The plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. After incubation, a single colony was counted and calculated as log10 CFU/mL.
3.9. Disc Diffusion Assay
A disc diffusion assay was performed to evaluate the antibacterial activity of the SO + UG combination using the Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion method [70]. Each bacterial suspension was adjusted to the McFarland 0.5 turbidity standard and swabbed onto BHI plates. Then, 100 μL of samples were loaded onto paper discs (8 mm/diameter). These discs were gently placed onto the plates. After 24 h incubation, the diameter of the inhibition zone was measured and recorded.
3.10. MultiStep Resistance Selection against MRSA
To assess the potential of MRSA to develop resistance to the SO + UG combination and rifampicin after repeated exposure, we performed multistep resistance selection experiments according to Mohammad et al. [71]. The MIC test was conducted for the samples as described above. MRSA strains were exposed to BHI broth containing different samples. The strains in sub-MIC wells were repassaged at 24 h intervals for up to fourteen passages. Resistance was defined as a more than 4-fold increase in MIC compared to the initial MIC [71].
3.11. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was conducted with Prism 5 (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) and SigmaPlot version 12.0 (Systat Software, San Jose, CA, USA). All data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (±SD) from triplicate experiments. Statistical differences were assessed by analysis of variance (ANOVA). A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
4. Conclusions
We confirmed the synergistic inhibitory effects of selected medicinal plants on the bacterial growth of MRSA and its clinical isolates. All tested combinations showed enhanced inhibitory effects except for the GU + SO combination. SO and UG extracts generated the best synergism as adjudged by checkerboard synergy assays. MICs of the individual extracts decreased by 4-fold, respectively. In further antibacterial analysis, the SO + UG combination showed significant bacterial growth inhibition with bactericidal effects. The SO + UG combination also exhibited more potent effects against clinical isolates. Both standard and isolates of MRSA showed no resistance to the SO + UG combination even after repeated exposure over fourteen passages. Our data demonstrate that using plant extract combinations could be a potential alternative to conventional antibiotics for the treatment of MRSA infections. Further studies are needed to identify the mechanism of action, toxicity, and safety of plant-extract combinations. Especially, identification and characterization of unknown antibacterial compounds should be conducted to elucidate the synergistic interaction of plant extract combinations.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ph16101491/s1, Table S1: UPLC mobile phase gradient conditions; Table S2: Mass spectrometer operating conditions; Figure S1: UPLC chromatograms of 70% ethanol extracts (3 mg/mL) from Caesalpinia sappan L.; Figure S2: UPLC chromatograms of 70% ethanol extracts (3 mg/mL) from Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch.; Figure S3: UPLC chromatograms of 70% ethanol extracts (3 mg/mL) from Sanguisorba officinalis L.; Figure S4: UPLC chromatograms of 70% ethanol extracts (3 mg/mL) from Uncaria gambir Roxb.; Figure S5: Determination of minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of selected medicinal plants using broth microdilution method.; Figure S6: Evaluation of synergistic inhibitory effects of plant extract combinations by checkerboard synergy assays.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.-J.H.; Formal analysis, I.-G.J. and J.-Y.J.; Investigation, I.-G.J., J.-Y.J. and S.-H.Y.; Methodology, Y.-J.H., I.-G.J. and J.-Y.J.; Project administration, Y.-J.H.; Resources, Y.-J.H.; Funding acquisition, Y.-J.H.; Supervision, Y.-J.H.; Validation, J.-Y.J. and S.-H.Y.; Writing—original draft, Y.-J.H., I.-G.J. and J.-Y.J.; Writing—review and editing, Y.-J.H. and I.-G.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from the RIS grant (No. 20230553001) at Gachon University.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and Supplementary Material.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kim, H.; Park, S.; Seo, H.; Chung, H.; Kim, E.S.; Sung, H.; Kim, M.N.; Bae, S.; Jung, J.; Kim, M.J.; et al. Clinical impact of and microbiological risk factors for qacA/B positivity in ICU-acquired ST5-methicillin-resistant SCCmec type II Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfouzan, W.; Udo, E.E.; Modhaffer, A.; Alosaimi, A. Molecular Characterization of Methicillin- Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a Tertiary Care hospital in Kuwait. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, X.; Lundborg, C.S.; Zhang, M.; Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Gu, S.; Gu, Y.; Wei, J.; Dong, H. Clinical and economic impact of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A multicentre study in China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lee, Y.; Seo, Y.; Hwang, Y. Relationship of multidrug-resistant gene and extended-spectrum carbapenem-resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Biocell 2019, 43, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.W.; Kim, H.J.; Hur, M.; Yun, Y.M. Antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of Staphylococcus aureus isolates classified according to their origin in a tertiary hospital in Korea. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2014, 42, 1340–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, J. Antimicrobial Adjuvants Drug Discovery, the Challenge of Avoid the Resistance and Recover the Susceptibility of Multidrug-Resistant Strains. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol. 2016, 8, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loncaric, I.; Tichy, A.; Handler, S.; Szostak, M.P.; Tickert, M.; Diab-Elschahawi, M.; Spergser, J.; Kunzel, F. Prevalence of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus sp. (MRS) in Different Companion Animals and Determination of Risk Factors for Colonization with MRS. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khunbutsri, D.; Naimon, N.; Satchasataporn, K.; Inthong, N.; Kaewmongkol, S.; Sutjarit, S.; Setthawongsin, C.; Meekhanon, N. Antibacterial Activity of Solanum torvum Leaf Extract and Its Synergistic Effect with Oxacillin against Methicillin-Resistant Staphyloccoci Isolated from Dogs. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fergestad, M.E.; Stamsas, G.A.; Morales Angeles, D.; Salehian, Z.; Wasteson, Y.; Kjos, M. Penicillin-binding protein PBP2a provides variable levels of protection toward different beta-lactams in Staphylococcus aureus RN4220. Microbiologyopen 2020, 9, e1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uc-Cachon, A.H.; Dzul-Beh, A.J.; Palma-Pech, G.A.; Jimenez-Delgadillo, B.; Flores-Guido, J.S.; Gracida-Osorno, C.; Molina-Salinas, G.M. Antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of Mayan medicinal plants against Methicillin-susceptible and -resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 279, 114369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, S.K.; Mohanta, Y.K.; Padhi, L.; Park, Y.H.; Mohanta, T.K.; Bae, H. Large Scale Screening of Ethnomedicinal Plants for Identification of Potential Antibacterial Compounds. Molecules 2016, 21, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archana, H.; Geetha Bose, V. Evaluation of phytoconstituents from selected medicinal plants and its synergistic antimicrobial activity. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.M.; Zhang, X. The World Medicines Situation 2011, Traditional Medicines: Global Situation, Issues and Challenges; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Guadie, A.; Dakone, D.; Unbushe, D.; Wang, A.; Xia, S. Antibacterial activity of selected medicinal plants used by traditional healers in Genta Meyche (Southern Ethiopia) for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders. J. Herb. Med. 2020, 22, 100338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabajal, M.P.A.; Isla, M.I.; Borsarelli, C.D.; Zampini, I.C. Influence of in vitro gastro-duodenal digestion on the antioxidant activity of single and mixed three “Jarilla” species infusions. J. Herb. Med. 2020, 19, 100296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, B.P.A.; Abrahamse, H.; Hemmaragala, N.M. Caspase dependent apoptotic inhibition of melanoma and lung cancer cells by tropical Rubus extracts. BioMed. Pharmacother. 2016, 80, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, X.Q.; Kang, O.H.; Kwon, D.Y. Combination of Sanguisorbigenin and Conventional Antibiotic Therapy for Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus. aureus: Inhibition of Biofilm Formation and Alteration of Cell Membrane Permeability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Ali, D.; Almutairi, B.O.; Kumar, G.; Karga, G.A.; Masi, C.; Sundramurthy, V.P. Synergistic Effect of Conventional Medicinal Herbs against Different Pharmacological Activity. BioMed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 7337261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanathadesikan Seshadri, V.; Vijayaraghavan, P.; Kim, Y.O.; Kim, H.J.; Ahmed Al-Ghamdi, A.; Elshikh, M.S.; Al-Dosary, M.A.; Alsubaie, Q.D. In vitro antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of polyherbal extracts from Vetiveria zizanioides, Trichosanthes cucumerina, and Mollugo cerviana on HeLa and MCF-7 cell lines. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, S.; Waseem, D.; Fatima, H.; Naz, I.; Rasheed, F.; Kanwal, N. Antibacterial potential and synergistic interaction between natural polyphenolic extracts and synthetic antibiotic on clinical isolates. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 30, 103576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soulaimani, B.; Varoni, E.; Iriti, M.; Mezrioui, N.E.; Hassani, L.; Abbad, A. Synergistic Anticandidal Effects of Six Essential Oils in Combination with Fluconazole or Amphotericin B against Four Clinically Isolated Candida Strains. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner Fialova, S.; Rendekova, K.; Mucaji, P.; Nagy, M.; Slobodnikova, L. Antibacterial Activity of Medicinal Plants and Their Constituents in the Context of Skin and Wound Infections, Considering European Legislation and Folk Medicine—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Guleria, S.; Razdan, V.K.; Babu, V. Synergistic antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of essential oils of some selected medicinal plants in combination and with synthetic compounds. Ind. Crops. Prod. 2020, 154, 112569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deciga-Campos, M.; Beltran-Villalobos, K.L.; Aguilar-Mariscal, H.; Gonzalez-Trujano, M.E.; Angeles-Lopez, G.E.; Ventura-Martinez, R. Synergistic Herb-Herb Interaction of the Antinociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Syzygium aromaticum and Rosmarinus officinalis Combination. Evid. Based Complement Alternat. Med. 2021, 2021, 8916618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, I.G.; Jeong, J.Y.; Yum, S.H.; Hwang, Y.J. Inhibitory Effects of Selected Medicinal Plants on Bacterial Growth of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 2022, 27, 7780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirmal, N.P.; Rajput, M.S.; Prasad, R.G.; Ahmad, M. Brazilin from Caesalpinia sappan heartwood and its pharmacological activities: A review. Asian. Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2015, 8, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Settharaksa, S.; Monton, C.; Charoenchai, L. Optimization of Caesalpinia sappan L. heartwood extraction procedure to obtain the highest content of brazilin and greatest antibacterial activity. J. Integr. Med. 2019, 17, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Ma, T.T.; Gong, M.X.; Xie, K.L.; Wang, Z.M.; Li, J. The correlation between pharmacological activity and contents of eight constituents of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Luo, J.; Liu, X.Q.; Kang, O.H.; Kwon, D.Y. Antibacterial activity and synergy of antibiotics with sanguisorbigenin isolated from Sanguisorba. officinalis L. against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 72, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munggari, I.P.; Kurnia, D.; Deawati, Y.; Julaeha, E. Current Research of Phytochemical, Medicinal and Non-Medicinal Uses of Uncaria gambir Roxb.: A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.; Weinmann, D.; Toegel, S.; Holzer, W.; Unger, F.M.; Viernstein, H. Compounds from Caesalpinia sappan with anti-inflammatory properties in macrophages and chondrocytes. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 1671–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felipe Gonzalez, A.; Nunez Cairo, C.R.; Gutierrez Gaiten, Y.I.; Scull Lizama, R.; Zumata Dube, M.C.; Docinas, E.I.; Bou, N.P.; Foubert, K.; Pieters, L.; Delgado Hernandez, R. Phytochemical characterisation and in vivo antilithiatic activity of the stems of Caesalpinia bahamensis (Brasilete). Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 3765–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.Y.; Wang, D.M.; Wang, M.J.; Zhou, J.; Pan, Y.N.; Wang, Z.Z.; Xiao, W.; Liu, X.Q. Systematically characterize the substance basis of Jinzhen oral liquid and their pharmacological mechanism using UPLC-Q-TOF/MS combined with network pharmacology analysis. J. Food. Drug. Anal. 2019, 27, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Song, W.; Tao, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Yong, J.; Gao, X.; Guo, L. Identification wild and cultivated licorice by multidimensional analysis. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 128111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardel, M.; Taube, F.; Schulz, H.; Schütze, W.; Gierus, M. Different approaches to evaluate tannin content and structure of selected plant extracts–review and new aspects. J. Appl. Bot. Food. Qual. 2013, 86, 154–166. [Google Scholar]
- Sazwi, N.N.; Nalina, T.; Rahim, Z.H.A. Antioxidant and cytoprotective activities of Piper betle, Areca catechu, Uncaria gambir and betel quid with and without calcium hydroxide. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Hemeg, H.A.; Moussa, I.M.; Ibrahim, S.; Dawoud, T.M.; Alhaji, J.H.; Mubarak, A.S.; Kabli, S.A.; Alsubki, R.A.; Tawfik, A.M.; Marouf, S.A. Antimicrobial effect of different herbal plant extracts against different microbial population. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 3221–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattananandecha, T.; Apichai, S.; Julsrigival, J.; Ogata, F.; Kawasaki, N.; Saenjum, C. Antibacterial Activity against Foodborne Pathogens and Inhibitory Effect on Anti-Inflammatory Mediators’ Production of Brazilin-Enriched Extract from Caesalpinia sappan Linn. Plants 2022, 11, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, G.Y.; Han, Z.Q.; Han, J.; Hao, X.Y.; Tang, H.S.; Wang, G.C. Antimicrobial activity and synergy of antibiotics with two biphenyl compounds, protosappanins A and B from Sappan Lignum against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 1439–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-P.; Yu, C.-X.; Qiao, J.; Zang, Y.-M.; Xiang, Y.; Ren, G.-X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Liu, C.-S. Effect of exogenous phytohormones treatment on glycyrrhizic acid accumulation and preliminary exploration of the chemical control network based on glycyrrhizic acid in root of Glycyrrhiza uralensis. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2016, 26, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyama, K.; Kawada-Matsuo, M.; Oogai, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Nakamura, N.; Komatsuzawa, H. Antibacterial effects of glycyrrhetinic acid and its derivatives on Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mita, S.R.; Abdassah, M.; Supratman, U.; Shiono, Y.; Rahayu, D.; Sopyan, I.; Wilar, G. Nanoparticulate System for the Transdermal Delivery of Catechin as an Antihypercholesterol: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluations. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsinwar, S.; Vadivel, V. Catechin isolated from cashew nut shell exhibits antibacterial activity against clinical isolates of MRSA through ROS-mediated oxidative stress. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 8279–8297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiko, A.G.; Olchowik-Grabarek, E.; Sekowski, S.; Roszkowska, A.; Lapshina, E.A.; Dobrzynska, I.; Zamaraeva, M.; Zavodnik, I.B. Antimicrobial Activity of Quercetin, Naringenin and Catechin: Flavonoids Inhibit Staphylococcus aureus-Induced Hemolysis and Modify Membranes of Bacteria and Erythrocytes. Molecules 2023, 28, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, X.; Wu, G.; Tao, X.; Yang, S.; Lv, L.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, D.; Xiang, H. Success stories of natural product-derived compounds from plants as multidrug resistance modulators in microorganisms. RSC. Adv. 2023, 13, 7798–7817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, E.; Inn, K.S.; Jang, Y.P.; Lee, K.T.; Lee, J.H. Phytotherapeutic Activities of Sanguisorba officinalis and its Chemical Constituents: A Review. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2018, 46, 299–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rady, O.; El-Attar, L.; Amine, A. In vitro synergistic activity of colistin and teicoplanin combination against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter spp. J. Antibiot. 2022, 75, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiful, A.J.; Mastura, M.; Zarizal, S.; Mazurah, M.I.; Shuhaimi, M.; Ali, A.M. Detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus using mecA/nuc genes and antibiotic susceptibility profile of Malaysian clinical isolates. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 22, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Gan, R.Y.; Zhang, D.; Farha, A.K.; Habimana, O.; Mavumengwana, V.; Li, H.B.; Wang, X.H.; Corke, H. Large-Scale Screening of 239 Traditional Chinese Medicinal Plant Extracts for Their Antibacterial Activities against Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Cytotoxic Activities. Pathogens 2020, 9, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Martinez, F.J.; Barrajon-Catalan, E.; Herranz-Lopez, M.; Micol, V. Antibacterial plant compounds, extracts and essential oils: An updated review on their effects and putative mechanisms of action. Phytomedicine 2021, 90, 153626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gufe, C.; Mugabe, T.N.; Makuvara, Z.; Marumure, J.; Benard, M. In-vitro assessment of the efficacy of herb-herb combinations against multidrug-resistant mastitis-causing bacteria: Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Cogent Food Agric. 2023, 9, 12187250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idowu, O.A.; Babalola, A.S.; Olukunle, J. Antagonistic effects of some commonly used herbs on the efficacy of Artemisinin derivatives in the treatment of malaria in experimental mice. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2020, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumian, M.; Zandi, M. Antimicrobial Activity of Some Medicinal Plant Extracts against Multidrug Resistant Bacteria. Zahedan J. Res. Med. Sci. 2017, 19, e10080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suberu, J.O.; Gorka, A.P.; Jacobs, L.; Roepe, P.D.; Sullivan, N.; Barker, G.C.; Lapkin, A.A. Anti-Plasmodial Polyvalent Interactions in Artemisia. annua L. Aqueous Extract—Possible Synergistic and Resistance Mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, Y.; Lee, T.K.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, T.H.; Kang, I.J. Standardized Sanguisorba officinalis L. Extract Inhibits Adipogenesis and Promotes Thermogenesis via Reducing Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anggraini, T.; Tai, A.; Yoshino, T.; Itani, T. Antioxidative activity and catechin content of four kinds of Uncaria gambir extracts from West Sumatra, Indonesia. Afr. J. Biochem. Res. 2011, 5, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Adnan, M.; Patel, M.; Deshpande, S.; Alreshidi, M.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Reddy, M.N.; Emira, N.; De Feo, V. Effect of Adiantum philippense Extract on Biofilm Formation, Adhesion with Its Antibacterial Activities Against Foodborne Pathogens, and Characterization of Bioactive Metabolites: An in vitro-in silico Approach. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietschmann, S.; Meyer, M.; Voget, M.; Cieslicki, M. The joint in vitro action of polymyxin B and miconazole against pathogens associated with canine otitis externa from three European countries. Vet. Dermatol. 2013, 24, 439–445, e96-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naim, N.; Bouymajane, A.; Oulad El Majdoub, Y.; Ezrari, S.; Lahlali, R.; Tahiri, A.; Ennahli, S.; Lagana Vinci, R.; Cacciola, F.; Mondello, L.; et al. Flavonoid Composition and Antibacterial Properties of Crocus sativus L. Petal Extracts. Molecules 2022, 28, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manilal, A.; Sabu, K.R.; Shewangizaw, M.; Aklilu, A.; Seid, M.; Merdikios, B.; Tsegaye, B. In vitro antibacterial activity of medicinal plants against biofilm-forming methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Efficacy of Moringa stenopetala and Rosmarinus officinalis extracts. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshikh, M.; Ahmed, S.; Funston, S.; Dunlop, P.; McGaw, M.; Marchant, R.; Banat, I.M. Resazurin-based 96-well plate microdilution method for the determination of minimum inhibitory concentration of biosurfactants. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 38, 1015–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Hemar, Y.; Perera, C.O.; Lewis, G.; Krissansen, G.W.; Buchanan, P.K. Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of aqueous extracts of eight edible mushrooms. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2014, 3, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukuhor, H.O. The interrelationships between antimicrobial resistance, COVID-19, past, and future pandemics. J. Infect. Public. Health 2021, 14, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrader, S.M.; Botella, H.; Jansen, R.; Ehrt, S.; Rhee, K.; Nathan, C.; Vaubourgeix, J. Multiform antimicrobial resistance from a metabolic mutation. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabh2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas-Caceres, R.R.; Luis Stephano-Hornedo, J.; Lugo, J.; Vaca, R.; Del Aguila, P.; Yanez-Ocampo, G.; Mora-Herrera, M.E.; Camacho Diaz, L.M.; Cipriano-Salazar, M.; Alaba, P.A. Bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles against the propagation of Clavibacter michiganensis infection in Lycopersicon esculentum Mill. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 115, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mun, Y.S.; Hwang, Y.J. Novel spa and Multi-Locus Sequence Types (MLST) of Staphylococcus aureus Samples Isolated from Clinical Specimens in Korean. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostanci, M.T.; Bulbul, A.S.; Celik, I.S.; Kocabas, Y.Z.; Burhan, H.; Bayat, R.; Sen, F.; Zakariae, N.; Esmaeili, R.; Jafari, H.; et al. Investigation of antibacterial, antifungal, antibiofilm, antioxidant and anticancer properties of methanol extracts of Salvia marashica Ilcim, Celep & Dogan and Salvia caespitosa Montbret & Aucher ex. Benth plants with medicinal importance. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132602. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chraibi, M.; Farah, A.; Elamin, O.; Iraqui, H.M.; Fikri-Benbrahim, K. Characterization, antioxidant, antimycobacterial, antimicrobial effcts of Moroccan rosemary essential oil, and its synergistic antimicrobial potential with carvacrol. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2020, 11, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Sharaf, M.H.; El-Sherbiny, G.M.; Moghannem, S.A.; Abdelmonem, M.; Elsehemy, I.A.; Metwaly, A.M.; Kalaba, M.H. New combination approaches to combat methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.W.; Kirby, W.M.; Sherris, J.C.; Turck, M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1966, 45, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, H.; Younis, W.; Ezzat, H.G.; Peters, C.E.; AbdelKhalek, A.; Cooper, B.; Pogliano, K.; Pogliano, J.; Mayhoub, A.S.; Seleem, M.N. Bacteriological profiling of diphenylureas as a novel class of antibiotics against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).