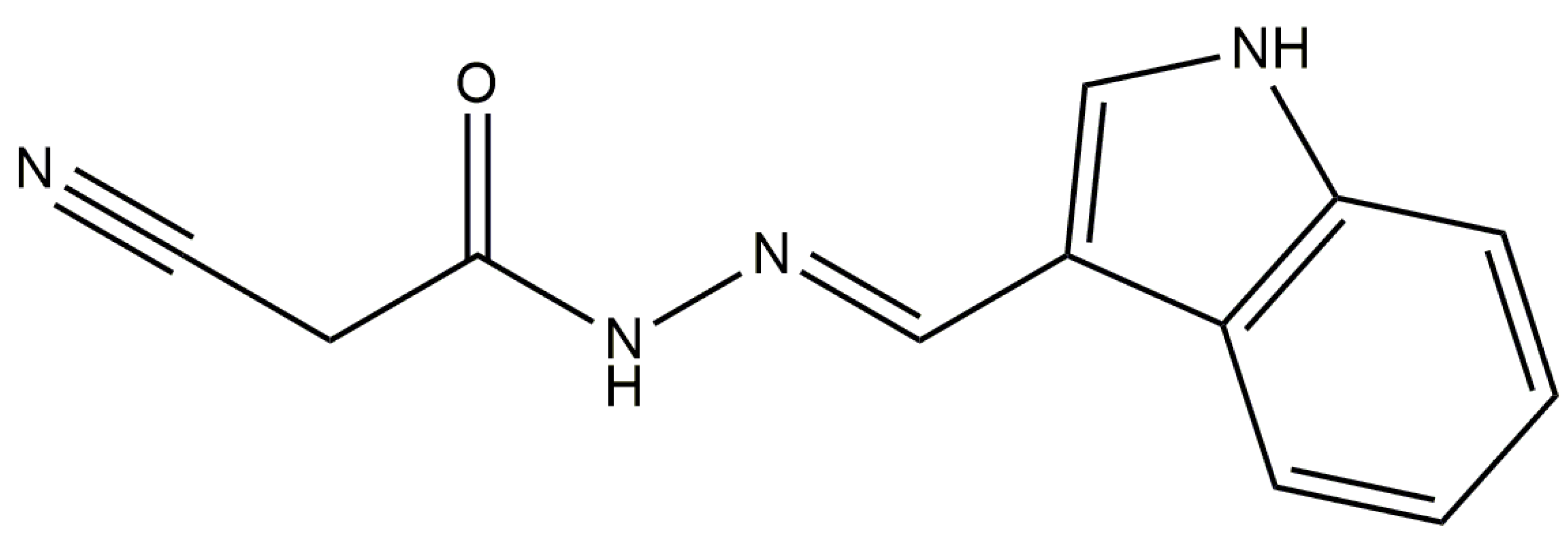
Anti-Inflammatory Activity of N′-(3-(1H-indol-3-yl)benzylidene)-2-cyanoacetohydrazide Derivative via sGC-NO/Cytokine Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Carrageenan-Induced Peritonitis
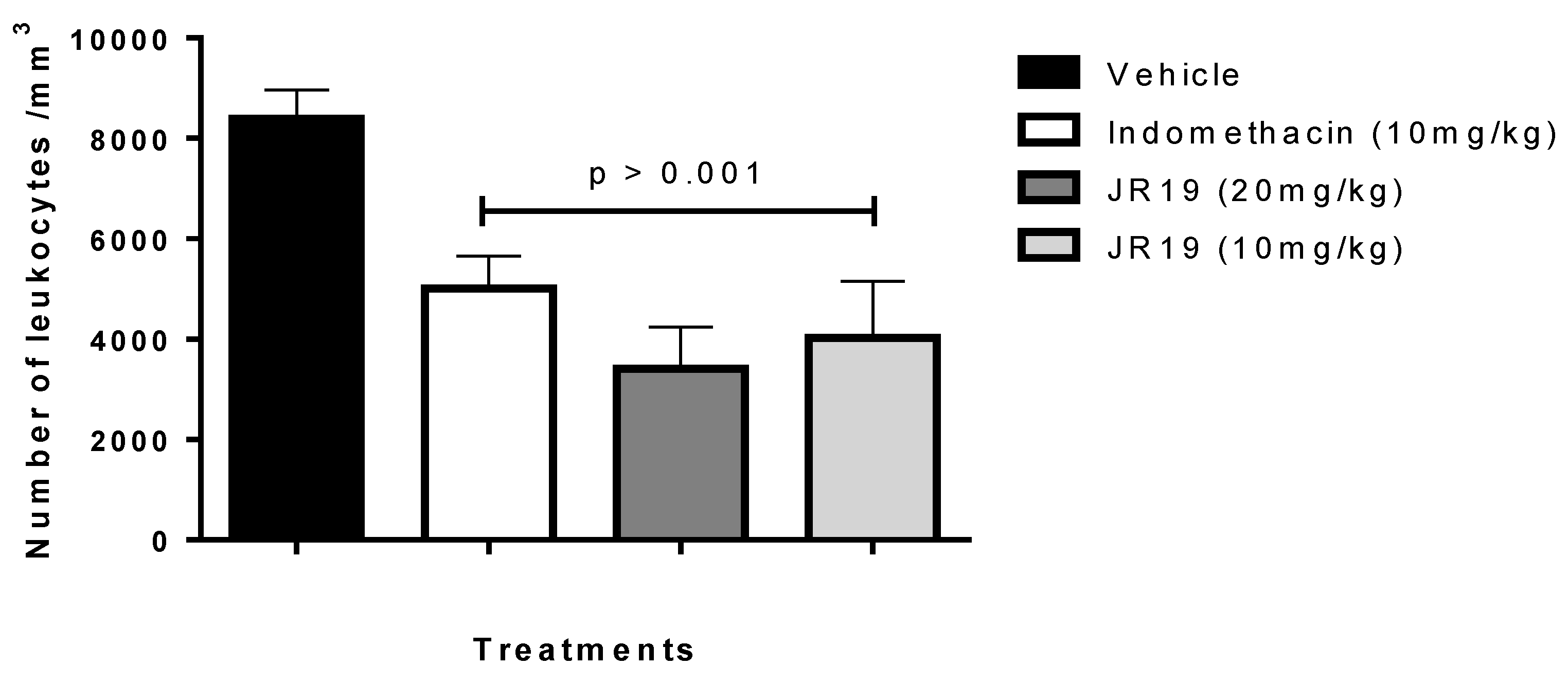
2.2. Subcutaneous Air Pouch
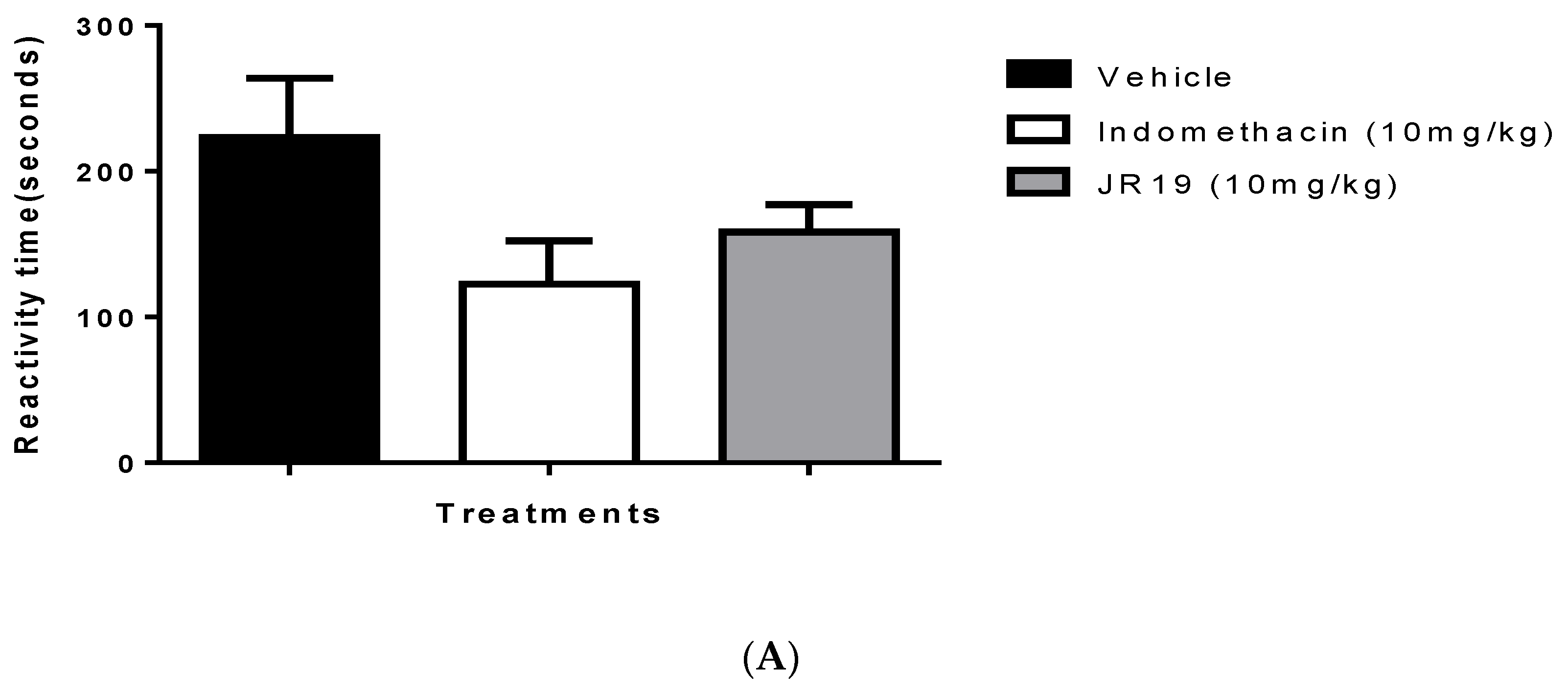
2.3. Formalin-Induced Nociception
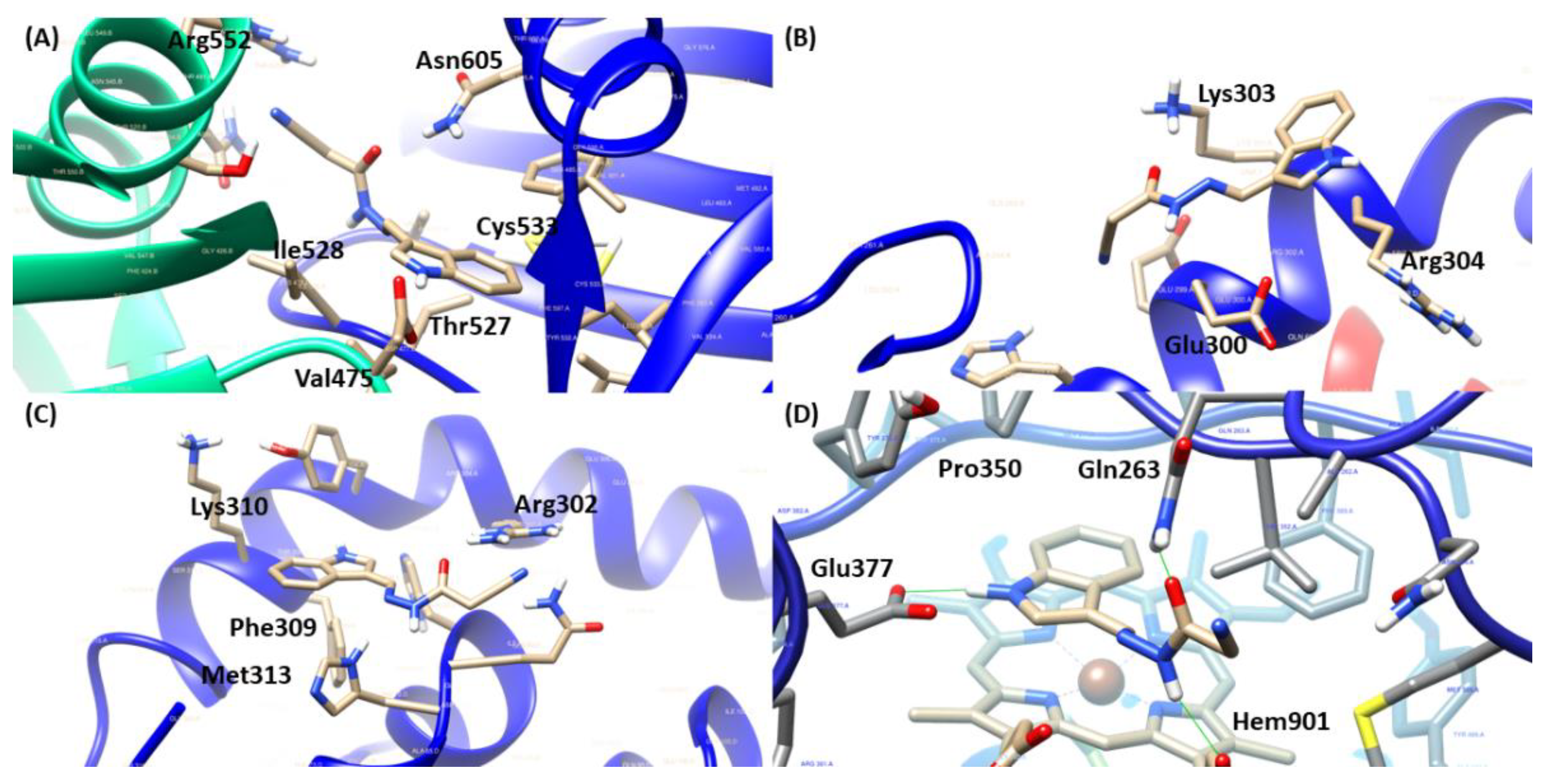
2.4. Molecular Docking
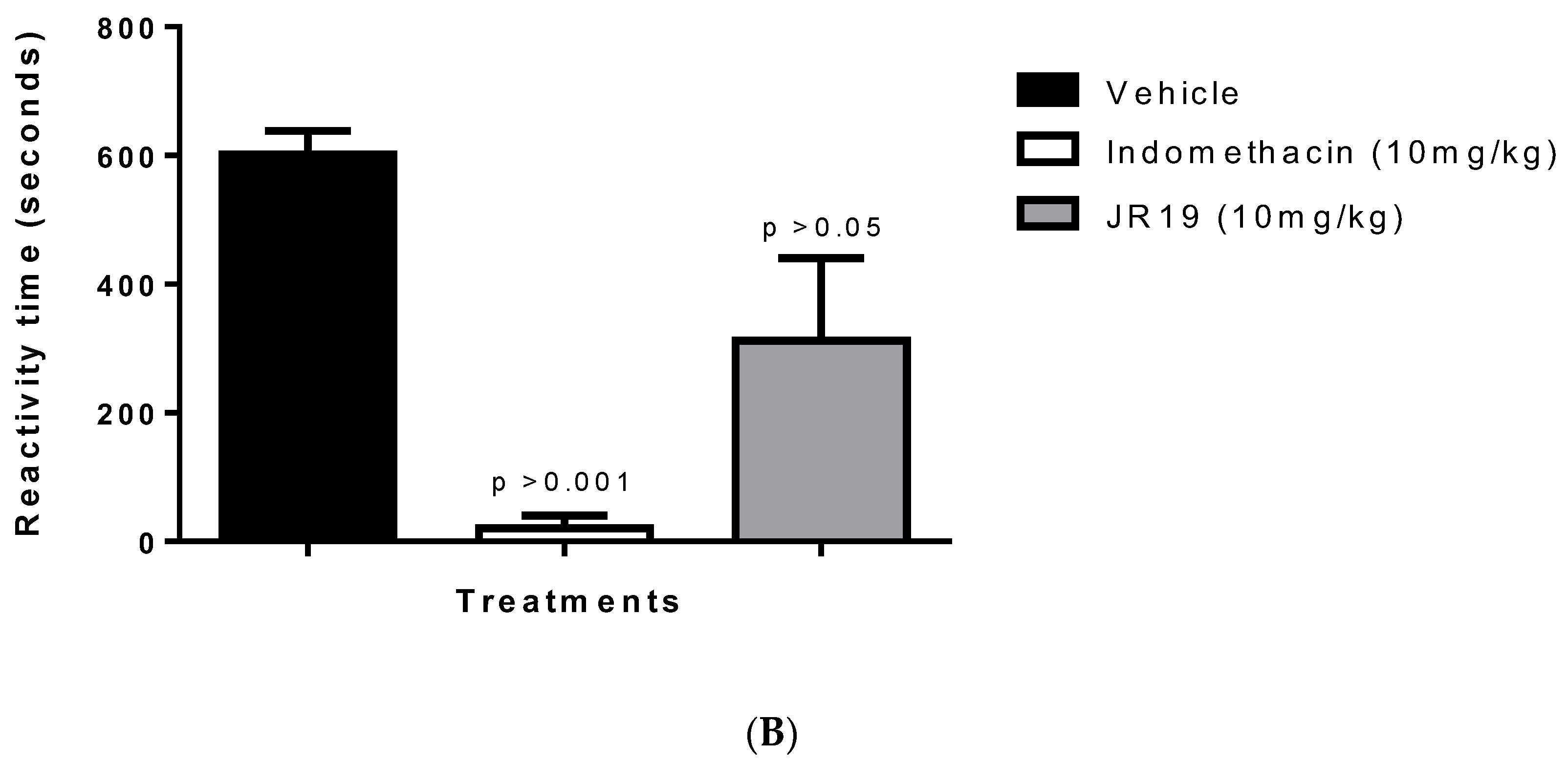
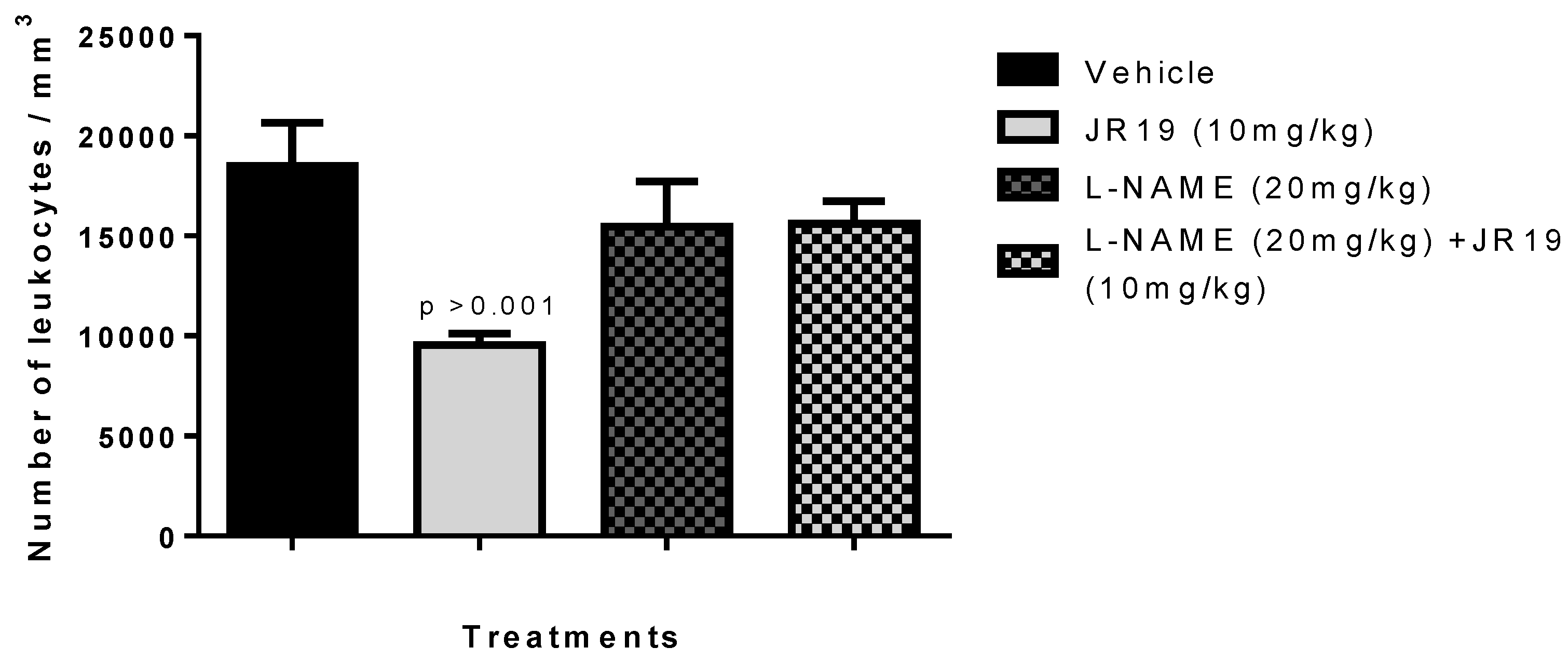
2.5. Investigation of the Participation of the Oxidonitrergic Pathway in the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of JR19
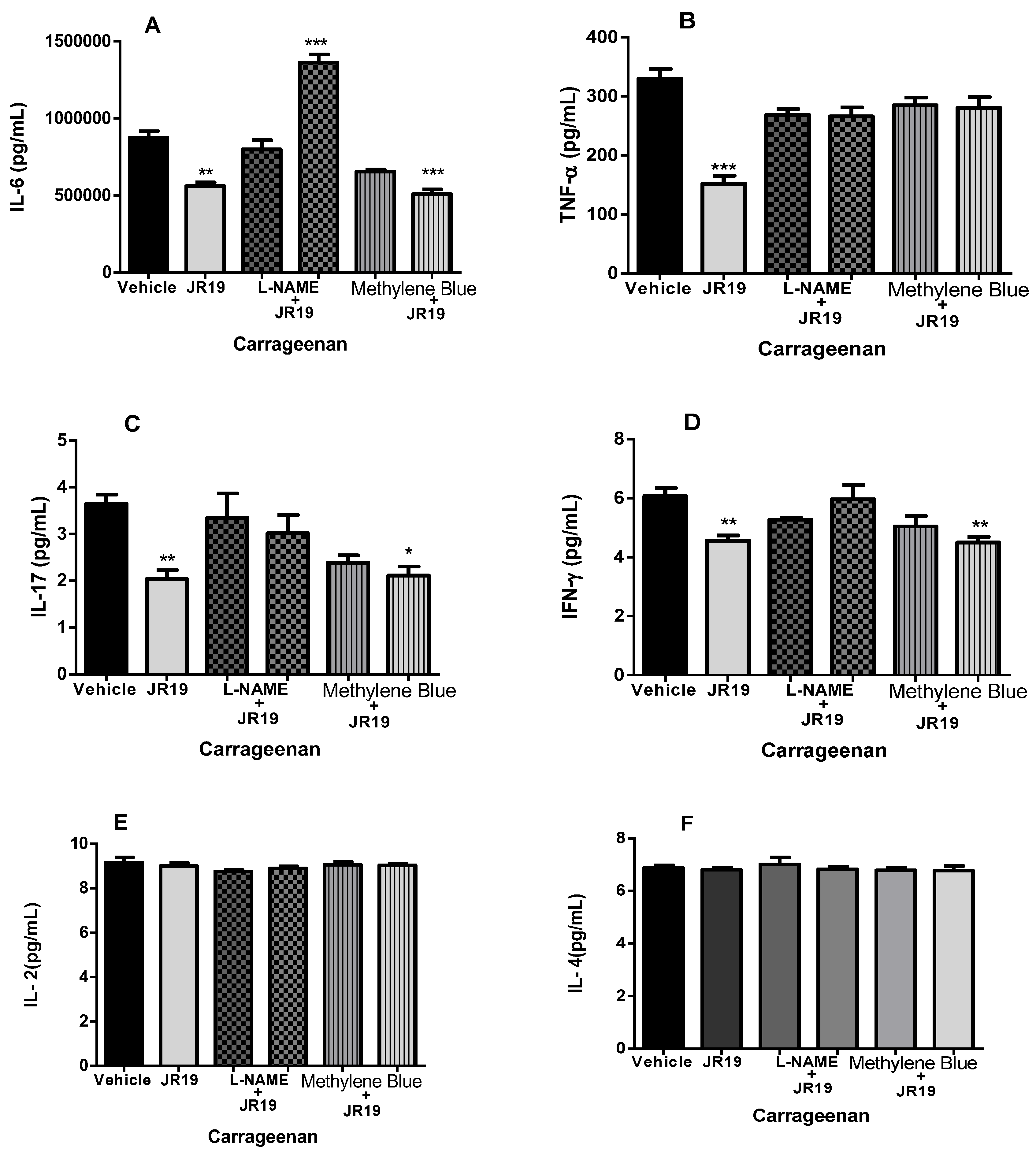
2.6. Quantification of Cytokines in Peritoneal Exudate
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Substances
4.2. Biological Activity
4.2.1. Animals
4.2.2. Inflammatory Models
Carrageenan-Induced Peritonitis in Mice
Subcutaneous Air Pouch
Formalin-Induced Nociception
Investigation of the sGC/NOS Pathway in the Anti-Inflammatory Effect
Dosage of Cytokines in Peritoneal Exudate
4.3. Molecular Docking
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fikry, E.M.; Hasan, W.A.; Mohamed, E.G. Rutin and Meloxicam Attenuate Paw Inflammation in Mice: Affecting Sorbitol Dehydrogenase Activity. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2018, 32, e22029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N. Treating Inflammation and Infection in the 21st Century: New Hints from Decoding Resolution Mediators and Mechanisms. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 1273–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Song, L.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Xu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y. Cardiac Injury Prediction and Lymphocyte Immunity and Inflammation Analysis in Hospitalized Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Int. J. Cardiol. 2021, 326, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el Menyiy, N.; el Allam, A.; Aboulaghras, S.; Jaouadi, I.; Bakrim, S.; el Omari, N.; Shariati, M.A.; Miftakhutdinov, A.; Wilairatana, P.; Mubarak, M.S.; et al. Inflammatory Auto-Immune Diseases of the Intestine and Their Management by Natural Bioactive Compounds. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113158. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, P.R.; Nunes Pazos, N.D.; Nascimento Gonzaga, T.K.S.D.; de Andrade, J.C.; Brito Monteiro, Á.; Ribeiro Portela, A.C.; Pires, H.F.O.; dos Santos Maia, M.; da Fonsêca, D.V.; Scotti, M.T.; et al. Anxiolytic and Antidepressant-like Effects of Monoterpene Tetrahydrolinalool and In Silico Approach of New Potential Targets. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 1530–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandri, A.L.; Sousa, L.P.; Lucas, C.D.; Rossi, A.G.; Pinho, V.; Teixeira, M.M. Resolution of Inflammation: Mechanisms and Opportunity for Drug Development. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 139, 189–212. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, F.I.F.; Cunha, F.Q.; Cunha, T.M. Peripheral Nitric Oxide Signaling Directly Blocks Inflammatory Pain. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 176, 113862. [Google Scholar]
- Sansbury, B.E.; Cummins, T.D.; Tang, Y.; Hellmann, J.; Holden, C.R.; Harbeson, M.A.; Chen, Y.; Patel, R.P.; Spite, M.; Bhatnagar, A.; et al. Overexpression of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Prevents Diet-Induced Obesity and Regulates Adipocyte Phenotype. Circ. Res. 2012, 111, 1176–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E. Nitric Oxide Signaling in Health and Disease. Cell 2022, 185, 2853–2878. [Google Scholar]
- Buckley, C.D.; Gilroy, D.W.; Serhan, C.N. Proresolving Lipid Mediators and Mechanisms in the Resolution of Acute Inflammation. Immunity 2014, 40, 315–327. [Google Scholar]
- Bindu, S.; Mazumder, S.; Bandyopadhyay, U. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) and Organ Damage: A Current Perspective. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 180, 114147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrignani, P.; Patrono, C. Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors: From Pharmacology to Clinical Read-Outs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell. Biol. Lipids 2015, 1851, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, M.L.; Makowska, J.S. Seven Steps to the Diagnosis of NSAIDs Hypersensitivity: How to Apply a New Classification in Real Practice? Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2015, 7, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhostin, A.; Mirseyyedhosein, S.; Toolabi, M.; Khodabakhsh, P.; Aghamiri, H.; Ghaffari, S.; Shafaroodi, H.; Shayesteh, A.; Amini, M.; Shafiee, A.; et al. Synthesis, Conformational Assignment, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of N-Arylidene-2-(4-Chloro-2-(2-Substituted Phenoxy)Phenyl)Acetic Acid Hydrazides. Med. Chem. Res. 2016, 25, 2220–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Alam, M.S.; Hamid, H.; Chugh, V.; Tikla, T.; Kaul, R.; Dhulap, A.; Sharma, S.K. Design and Synthesis of Anti–Inflammatory 1,2,3–Triazolylpyrrolobenzodiazepinone Derivatives and Impact of Molecular Structure on COX–2 Selective Targeting. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1272, 134151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, S.S.; Bomfim, R.R.; Jesus, H.C.R.; Alves, P.B.; Blank, A.F.; Estevam, C.S.; Antoniolli, A.R.; Thomazzi, S.M. Evaluation of the Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the Essential Oil of Lippia Gracilis Leaves. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 129, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, D.B.; Vasko, M.R.; Fehrenbacher, J.C. Models of Inflammation: Carrageenan Air Pouch. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Parmar, H.S. Evaluation of Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Hesperidin and Naringin on the Rat Air Pouch Model of Inflammation. Inflamm. Res. 2011, 60, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandooren, J.; Berghmans, N.; Dillen, C.; van Aelst, I.; Ronsse, I.; Israel, L.L.; Rosenberger, I.; Kreuter, J.; Lellouche, J.P.; Michaeli, S.; et al. Intradermal Air Pouch Leukocytosis as an in Vivo Test for Nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 4745–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basbaum, A.I.; Bautista, D.M.; Scherrer, G.; Julius, D. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Pain. Cell 2009, 139, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronchetti, S.; Migliorati, G.; Delfino, D.V. Association of Inflammatory Mediators with Pain Perception. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 96, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allerston, C.K.; von Delft, F.; Gileadi, O. Crystal Structures of the Catalytic Domain of Human Soluble Guanylate Cyclase. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 357644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malek, S.; Huang, D.B.; Huxford, T.; Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, G. X-Ray Crystal Structure of an IκBβ·NF-ΚB P65 Homodimer Complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 23094–23100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, B.; Wang, S.; Zhu, H.; Yin, T.; Zhou, R.; Hu, W.; Lu, C. Core Constituents of Caragana Sinica Root for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment and the Potential Mechanism. ACS Omega 2022, 8, 2586–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Padhy, G.; Vats, P.; Bhargava, K.; Sethy, N.K. Hypobaric Hypoxia Induced Arginase Expression Limits Nitric Oxide Availability and Signaling in Rodent Heart. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2014, 1840, 1817–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcin, E.D.; Arvai, A.S.; Rosenfeld, R.J.; Kroeger, M.D.; Crane, B.R.; Andersson, G.; Andrews, G.; Hamley, P.J.; Mallinder, P.R.; Nicholls, D.J.; et al. Anchored Plasticity Opens Doors for Selective Inhibitor Design in Nitric Oxide Synthase. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008, 4, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.F. Targeting the Interleukin Pathway in the Treatment of Asthma. Lancet 2015, 386, 1086–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, A.D.T.D.O.; Miranda, M.D.S.D.; Jacob, Í.T.T.; Amorim, C.A.D.C.; de Moura, R.O.; da Silva, S.Â.S.; Soares, M.B.P.; de Almeida, S.M.V.; Souza, T.R.C.D.L.; de Oliveira, J.F.; et al. Synthesis, in Vitro and in Vivo Biological Evaluation, COX-1/2 Inhibition and Molecular Docking Study of Indole-N-Acylhydrazone Derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 5388–5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, E.T.; dos Santos, T.B.; Silva, D.K.C.; Meira, C.S.; Moreira, D.R.M.; da Silva, T.F.; Salmon, D.; Barreiro, E.J.; Soares, M.B.P. Potent Immunosuppressive Activity of a Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitor N-Acylhydrazone in Models of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Shock and Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity Reaction. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 65, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Ritika. A Brief Review of the Biological Potential of Indole Derivatives. Futur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 6, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulino, N.; Abreu, S.R.L.; Uto, Y.; Koyama, D.; Nagasawa, H.; Hori, H.; Dirsch, V.M.; Vollmar, A.M.; Scremin, A.; Bretz, W.A. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of a Bioavailable Compound, Artepillin C, in Brazilian Propolis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 587, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francischetti, I.; Moreno, J.B.; Scholz, M.; Yoshida, W.B.; Paulo, S.; Francischetti Rua Doutor Augusto Barreto, I. Os Leucócitos e a Resposta Inflamatória Na Lesão de Isquemia-Reperfusão Leukocytes and the Inflammatory Response in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Braz. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2010, 25, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Muller, W.A. Leukocyte-Endothelial Cell Interactions in the Inflammatory Response. Lab. Investig. 2002, 82, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherwood, E.R.; Toliver-Kinsky, T. Mechanisms of the Inflammatory Response. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2004, 18, 385–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zindel, J.; Kubes, P. DAMPs, PAMPs, and LAMPs in Immunity and Sterile Inflammation. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2019, 15, 493–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedgwick, A.D.; Lees, P. A comparison of air pouch, sponge and pleurisy models of acute carrageenan inflammation in the rat. Agents Actions 1986, 18, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landén, N.X.; Li, D.; Ståhle, M. Transition from Inflammation to Proliferation: A Critical Step during Wound Healing. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3861–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, P.R.; Do Espírito Santo, R.F.; Melo, C.D.O.; Cavalcante, F.E.P.; Costa, T.B.; Barbosa, Y.V.; e Silva, Y.M.S.d.M.; de Sousa, N.F.; Villarreal, C.F.; de Moura, R.O.; et al. The Compound (E)-2-Cyano-N,3-Diphenylacrylamide (JMPR-01): A Potential Drug for Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, E.H.; Ramos, S. Avaliação Das Atividades Biológicas Do Óleo Essencial Do Látex de Mangifera Indica L. (Var. Espada e Rosa). 2014. Available online: https://repositorio.ufpe.br/handle/123456789/14009 (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- Baral, P.; Udit, S.; Chiu, I.M. Pain and Immunity: Implications for Host Defence. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa Salomé, D.; de Freitas, R.H.C.N.; Fraga, C.A.M.; Fernandes, P.D. Novel Regioisomeric Analogues of Naphthyl-N-Acylhydrazone Derivatives and Their Anti-Inflammatory Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordeiro, N.D.M.; Freitas, R.H.C.N.; Fraga, C.A.M.; Fernandes, P.D. New 2-Amino-Pyridinyl-N-Acylhydrazones: Synthesis and Identification of Their Mechanism of Anti-Inflammatory Action. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 123, 109739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, M.H.; Choi, J.I. Pharmacologic interaction between cannabinoid and either clonidine or neostigmine in the rat formalin test. J. Am. Soc. Anesthesiol. 2003, 99, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, H.; Kim, D.Y.; Han, J.I.; Chung, R.K.; Lee, G.Y. Antinociceptive Synergy between the Cannabinoid Receptor Agonist WIN 55,212-2 and Bupivacaine in the Rat Formalin Test. Anesth. Analg. 2007, 104, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, H.A.; Vinícius, M.; Nascimento, M.; Tavares, A.; Galdino, P.M.; Realino De Paula, J.; Alves Costa, E. Effects of Ethanolic Extract of Leaves of Lafoensia Pacari A. St.-Hil., Lythraceae (Pacari), in Pain and Inflammation Models. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2010, 20, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, T.F.; Júnior, W.B.; Alexandre-Moreira, M.S.; Costa, F.N.; Da Silva Monteiro, C.E.; Ferreira, F.F.; Barroso, R.C.R.; Noël, F.; Sudo, R.T.; Zapata-Sudo, G.; et al. Novel Orally Active Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Cyclohexyl-N-Acylhydrazone Derivatives. Molecules 2015, 20, 3067–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Luis, M.; Herrera-García, A.; Arce-Franco, M.; Armas-González, E.; Rodríguez-Pardo, M.; Lorenzo-Díaz, F.; Feria, M.; Cadenas, S.; Sánchez-Madrid, F.; Díaz-González, F. Superoxide Anion Mediates the L-Selectin down-Regulation Induced by Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in Human Neutrophils. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M. Nitric Oxide: Antidepressant Mechanisms and Inflammation. In Advances in Pharmacology; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; Volume 86, pp. 121–152. ISBN 9780128166680. [Google Scholar]
- Biava, M.; Porretta, G.C.; Poce, G.; Battilocchio, C.; Alfonso, S.; Rovini, M.; Valenti, S.; Giorgi, G.; Calderone, V.; Martelli, A.; et al. Novel Analgesic/Anti-Inflammatory Agents: Diarylpyrrole Acetic Esters Endowed with Nitric Oxide Releasing Properties. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 7759–7771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janakiram, N.B.; Rao, C.V. INOS-Selective Inhibitors for Cancer Prevention: Promise and Progress. Future Med. Chem. 2012, 4, 2193–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, M.; Kepinska, M. Human Nitric Oxide Synthase—Its Functions, Polymorphisms, and Inhibitors in the Context of Inflammation, Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.; de Almeida, M.; Silva, J.; Albino, S.; Espírito-Santo, R.; Lima, M.; Villarreal, C.; Moura, R.; Santos, V. (E)-2-Cyano-3-(1H-Indol-3-Yl)-N-Phenylacrylamide, a Hybrid Compound Derived from Indomethacin and Paracetamol: Design, Synthesis and Evaluation of the Anti-Inflammatory Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahluwalia, A.; Foster, P.; Scotland, R.S.; Mclean, P.G.; Mathur, A.; Perretti, M.; Moncada, S.; Hobbs, A.J. Antiinflammatory Activity of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase: CGMP-Dependent down-Regulation of P-Selectin Expression and Leukocyte Recruitment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1386–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florentino, I.F.; Galdino, P.M.; de Oliveira, L.P.; Silva, D.P.B.; Pazini, F.; Vanderlinde, F.A.; Lião, L.M.; Menegatti, R.; Costa, E.A. Involvement of the NO/CGMP/KATP Pathway in the Antinociceptive Effect of the New Pyrazole 5-(1-(3-Fluorophenyl)-1H-Pyrazol-4-Yl)-2H-Tetrazole (LQFM-021). Nitric Oxide 2015, 47, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Iwata, M.; Asai, Y.; Inoue, T.; Takagi, K. Involvement of Nitric Oxide in a Rat Model of Carrageenin-Induced Pleurisy. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 682879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florentino, I.F.; Silva, D.P.B.; Silva, D.M.; Cardoso, C.S.; Moreira, A.L.E.; Borges, C.L.; Soares, C.M.D.A.; Galdino, P.M.; Lião, L.M.; Ghedini, P.C.; et al. Potential Anti-Inflammatory Effect of LQFM-021 in Carrageenan-Induced Inflammation: The Role of Nitric Oxide. Nitric Oxide 2017, 69, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreau, A.; Kieda, C.; Grillon, C. Nitric Oxide Modulates the Expression of Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecules Involved in Angiogenesis and Leukocyte Recruitment. Exp. Cell. Res. 2011, 317, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schioppa, T.; Sozio, F.; Barbazza, I.; Scutera, S.; Bosisio, D.; Sozzani, S.; Del Prete, A. Molecular Basis for CCRL2 Regulation of Leukocyte Migration. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 615031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secco, D.D.; Paron, J.A.; de Oliveira, S.H.P.; Ferreira, S.H.; Silva, J.S.; Cunha, F.D.Q. Neutrophil Migration in Inflammation: Nitric Oxide Inhibits Rolling, Adhesion and Induces Apoptosis. Nitric Oxide 2003, 9, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.C.; Coura, G.M.E.; Melo, I.S.F.; Batista, C.R.A.; Augusto, P.S.A.; Godin, A.M.; Araújo, D.P.; César, I.C.; Ribeiro, L.S.; Souza, D.G.; et al. Nicorandil Inhibits Neutrophil Recruitment in Carrageenan-Induced Experimental Pleurisy in Mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 769, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, K.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H. Regulation of IL-18 Production by IFNg and PGE 2 in Mouse Microglial Cells: Involvement of NF-KB Pathway in the Regulatory Processes. Immunol. Lett. 2001, 77, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.A.M.; Ribeiro, E.L.; Barbosa, K.P.S.; Fragoso, I.T.; Gomes, F.O.D.S.; Donato, M.A.M.; Silva, B.S.; Silva, A.K.S.; Rocha, S.W.S.; França, M.E.R.; et al. Diethylcarbamazine Inhibits NF-ΚB Activation in Acute Lung Injury Induced by Carrageenan in Mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 23, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albensi, B.C. What Is Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-ΚB) Doing in and to the Mitochondrion? Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, M.; Mukosera, G.T.; Borchardt, D.; Li, Q.; Tipple, T.E.; Ishtiaq Ahmed, A.S.; Power, G.G.; Blood, A.B. L-NAME Releases Nitric Oxide and Potentiates Subsequent Nitroglycerin-Mediated Vasodilation. Redox Biol. 2019, 26, 101238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneguchi, A.; Ozawa, J.; Minamimoto, K.; Yamaoka, K. Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitor L-NG-Nitroarginine Methyl Ester (L-NAME) Attenuates Remobilization-Induced Joint Inflammation. Nitric Oxide 2020, 96, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Han, H.C. Methylene Blue Application to Lessen Pain: Its Analgesic Effect and Mechanism. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 663650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, B.C.; Lopes, A.L.; Macedo, R.C.O.; Correa, C.S.; Ramis, T.R.; Ribeiro, J.L.; Reischak-Oliveira, A. Marcadores Inflamatórios, Função Endotelial e Riscos Cardiovasculares. J. Vasc. Bras. 2014, 13, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Le, K.T.T.; Chu, X.; Jaeger, M.; Plantinga, J.A.; Matzaraki, V.; Withoff, S.; Joosten, L.A.B.; Netea, M.G.; Wijmenga, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Leukocyte-Released Mediators in Response to Both Bacterial and Fungal Infections Trigger Ifn Pathways, Independent of Il-1 and Tnf-α, in Endothelial Cells. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.M.; Campos Pellanda, L.; Gus, I.; Portal, V.L. Inflammatory Markers of Cardiovascular Disease in the Elderly. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2009, 92, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P.; Ridker, P.M.; Maseri, A. Inflammation and Atherosclerosis. Circulation 2002, 105, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elieh Ali Komi, D.; Wöhrl, S.; Bielory, L. Mast Cell Biology at Molecular Level: A Comprehensive Review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 58, 342–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, H.; Dostert, C.; Mak, T.W.; Brenner, D. TNF and ROS Crosstalk in Inflammation. Trends Cell. Biol. 2016, 26, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelová, H.; Hošek, J. TNF-α Signalling and Inflammation: Interactions between Old Acquaintances. Inflamm. Res. 2013, 62, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Loo, G.; Bertrand, M.J.M. Death by TNF: A Road to Inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schurgers, E.; Billiau, A.; Matthys, P. Collagen-Induced Arthritis as an Animal Model for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Focus on Interferon-γ. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011, 31, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, J.; Ahmed, C.M.; Wilson, T.D.; Johnson, H.M. Regulation of Interferon Gamma Signaling by Suppressors of Cytokine Signaling and Regulatory T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohms, M.; Möller, S.; Laskay, T. An Attempt to Polarize Human Neutrophils Toward N1 and N2 Phenotypes in Vitro. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.H.G. IL-17 and IL-17-Producing Cells in Protection versus Pathology. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaper, F.; Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6: Biology, Signaling and Strategies of Blockade. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenken, J.A.; Poschenrieder, A.J. Bioanalytical Chemistry of Cytokines—A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 853, 95–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, R.H.C.N.; Cordeiro, N.M.; Carvalho, P.R.; Alves, M.A.; Guedes, I.A.; Valerio, T.S.; Dardenne, L.E.; Lima, L.M.; Barreiro, E.J.; Fernandes, P.D.; et al. Discovery of Naphthyl-N-Acylhydrazone P38α MAPK Inhibitors with in Vivo Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-TNF-α Activity. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2018, 91, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Tintino, C.D.D.M.; Pessoa, R.T.; Fernandes, M.N.M.; Alcântara, I.S.; da Silva, B.A.F.; de Oliveira, M.R.C.; Martins, A.O.B.P.B.; da Silva, M.D.S.; Tintino, S.R.; Rodrigues, F.F.G.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Edematogenic Action of the Croton Campestris A. St.-Hil (Euphorbiaceae) Essential Oil and the Compound β-Caryophyllene in in Vivo Models. Phytomedicine 2018, 41, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmento-Filha, M.J.; Torres-Rêgo, M.; Daniele-Silva, A.; Queiroz-Neto, M.F.D.; Rocha, H.A.O.; Camara, C.A.; Araújo, R.M.; da Silva-Júnior, A.A.; Silva, T.M.S.; Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.D.F. Phytochemical Analysis by UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS and Evaluation of Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of the Extract and Fractions from Flowers of Cochlospermum Vitifolium. South Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 148, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Rêgo, M.; Furtado, A.A.; Bitencourt, M.A.O.; Lima, M.C.J.D.S.; de Andrade, R.C.L.C.; de Azevedo, E.P.; Soares, T.D.C.; Tomaz, J.C.; Lopes, N.P.; da Silva-Júnior, A.A.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Aqueous Extract and Bioactive Compounds Identified from the Fruits of Hancornia Speciosa Gomes (Apocynaceae). BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymundo, L.J.R.P.; Guilhon, C.C.; Alviano, D.S.; Matheus, M.E.; Antoniolli, A.R.; Cavalcanti, S.C.H.; Alves, P.B.; Alviano, C.S.; Fernandes, P.D. Characterisation of the Anti-Inflammatory and Antinociceptive Activities of the Hyptis Pectinata (L.) Poit Essential Oil. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 134, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva Guerra, A.S.H.; Do Nascimento Malta, D.J.; Morais Laranjeira, L.P.; Souza Maia, M.B.; Cavalcanti Colaço, N.; Do Carmo Alves De Lima, M.; Galdino, S.L.; Da Rocha Pitta, I.; Gonçalves-Silva, T. Anti-Inflammatory and Antinociceptive Activities of Indole-Imidazolidine Derivatives. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 1816–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher’, K.; Coderre, T.J. The Contributionof Metabotropicglutamatereceptors(MGluRs)to Formalin-Inducednociception. Pain 1996, 68, 255–263. [Google Scholar]


| Molecular Targets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compounds | sGC | NFκB/p65 | iNOS | RMSD (Å) |
| JR19 | 55.2887 | 32.0025 (pose 1) 42.3261 (pose 2) | 74.6536 | - |
| AR-C95791 | 82.3597 | 0.3297 | ||
| L-NAME | 66.1212 | - | ||
| Nigakinone | 32.5710 (pose 1) 43.4235 (pose 2) | - | ||
| Methylene blue | 46.9947 | - | ||
| Molecular Targets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compounds | sGC | NFκB/p65 (Pose 1) | NF-κB/p65 (Pose 2) | iNOS |
| JR-19 | Arg552 1, Ile528 1,3, Thr527 1, Asn605 1, Val475 2,3 and Cys533 2 | Glu300 1, Lys303 1,2 and Arg304 3 | Arg302 1, Phe309 2, Met313 2 and Lys310 3 | Gln263 1, Hem901 1,2, Glu377 1 and Pro350 3 |
| AR-C95791 | Glu377 1, Tyr347 1, Asp382 1, Trp372 1, Hem901 2,3, Phe369 3, Val352 3 and Pro350 3 | |||
| L-NAME | Glu377 1,2, Gly371 1, Tyr373 1, Tyr347 1, Trp372 1, Phe369 1,3, Pro350 1,3, Hem901 1,2, Val352 3, Asp382 3 | |||
| Nigakinone | Glu300 2, Lys303 1,2 and Arg304 3 | Arg302 1, Tyr306 2 and His68 1 | ||
| Methylene blue | Asp530 1, Asp486 1, Asn605 1, Ile528 1, Glu526 1, Leu596 1, Ala531 3, Cys533 2, Phe484 2 and Val475 3 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
da Silva, P.R.; Apolinário, N.d.M.; Silva, S.Â.S.d.; Araruna, M.E.C.; Costa, T.B.; e Silva, Y.M.S.d.M.; da Silva, T.G.; de Moura, R.O.; dos Santos, V.L. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of N′-(3-(1H-indol-3-yl)benzylidene)-2-cyanoacetohydrazide Derivative via sGC-NO/Cytokine Pathway. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101415
da Silva PR, Apolinário NdM, Silva SÂSd, Araruna MEC, Costa TB, e Silva YMSdM, da Silva TG, de Moura RO, dos Santos VL. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of N′-(3-(1H-indol-3-yl)benzylidene)-2-cyanoacetohydrazide Derivative via sGC-NO/Cytokine Pathway. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(10):1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101415
Chicago/Turabian Styleda Silva, Pablo Rayff, Nadjaele de Melo Apolinário, Simone Ângela Soares da Silva, Maria Elaine Cristina Araruna, Thássia Borges Costa, Yvnni M. S. de Medeiros e Silva, Teresinha Gonçalves da Silva, Ricardo Olímpio de Moura, and Vanda Lucia dos Santos. 2023. "Anti-Inflammatory Activity of N′-(3-(1H-indol-3-yl)benzylidene)-2-cyanoacetohydrazide Derivative via sGC-NO/Cytokine Pathway" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 10: 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101415
APA Styleda Silva, P. R., Apolinário, N. d. M., Silva, S. Â. S. d., Araruna, M. E. C., Costa, T. B., e Silva, Y. M. S. d. M., da Silva, T. G., de Moura, R. O., & dos Santos, V. L. (2023). Anti-Inflammatory Activity of N′-(3-(1H-indol-3-yl)benzylidene)-2-cyanoacetohydrazide Derivative via sGC-NO/Cytokine Pathway. Pharmaceuticals, 16(10), 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101415






