Glucose Uptake Is Increased by Estradiol Dipropionate in L6 Skeletal Muscle Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
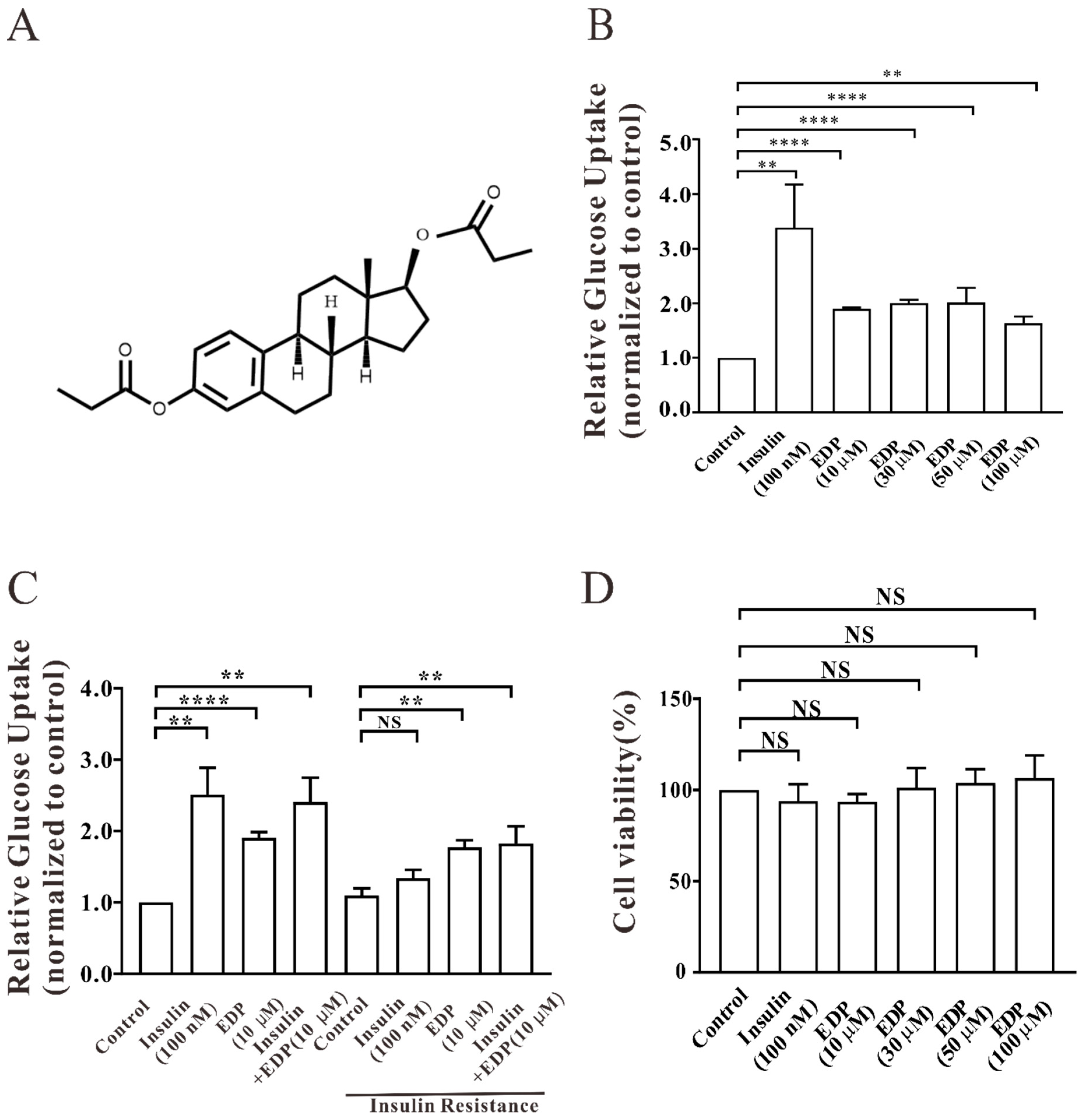
2.1. EDP Promotes Uptake of Glucose in Normal and Insulin-Resistant L6 Cells
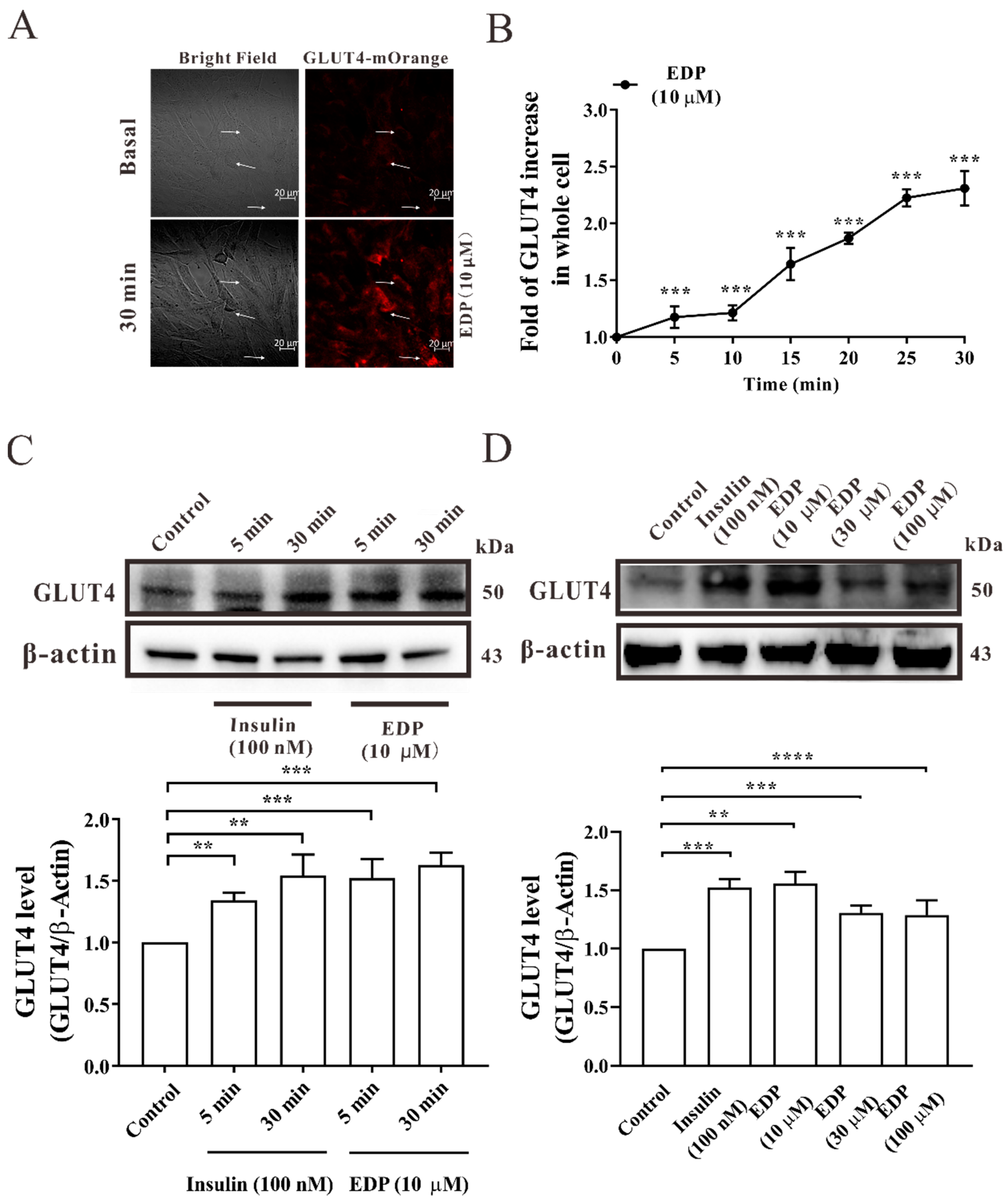
2.2. EDP Increases Intracellular GLUT4 Expression
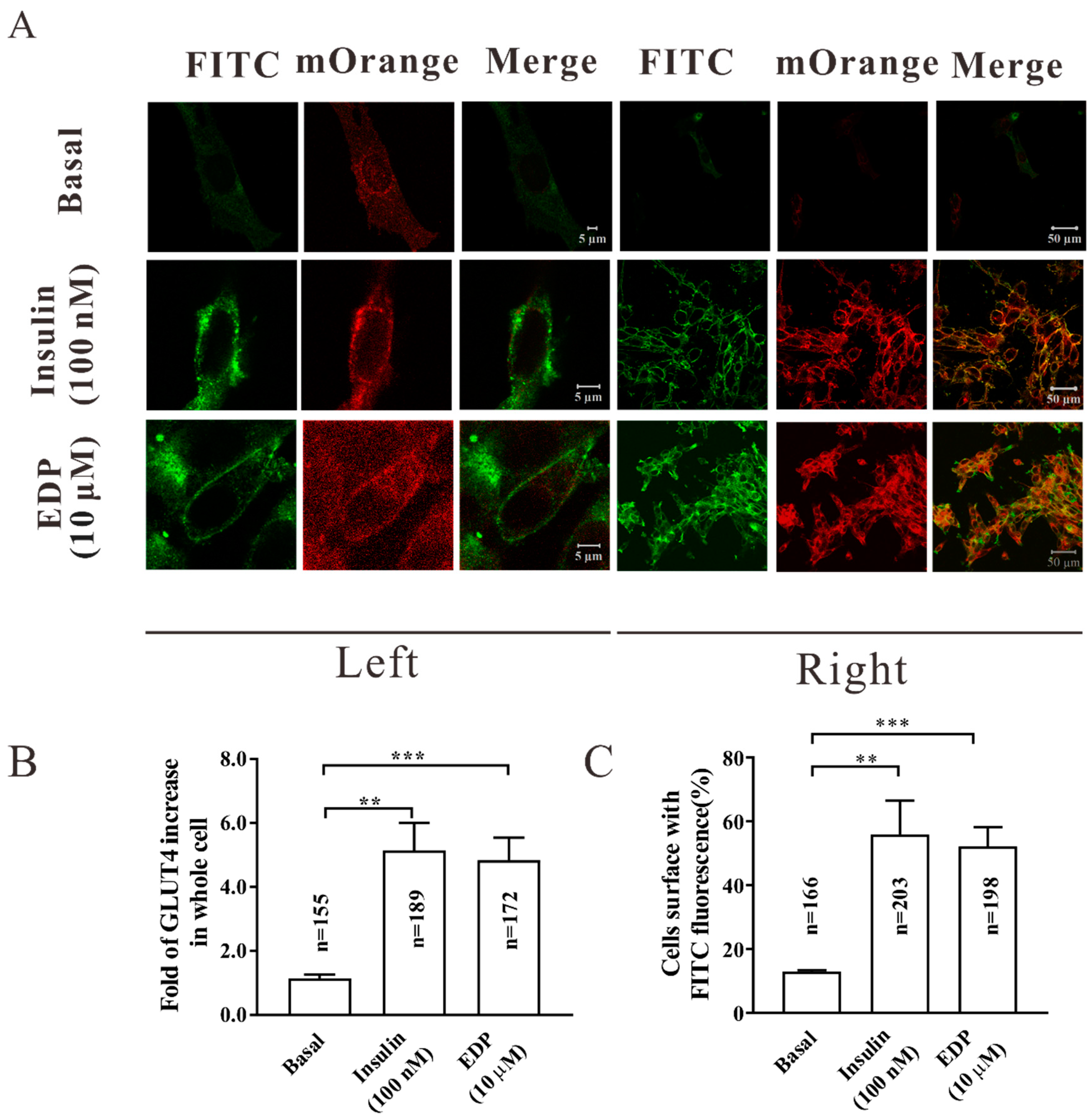
2.3. EDP Enhanced GLUT4 Expression and Fusion into the Plasma Membrane in L6 Cells
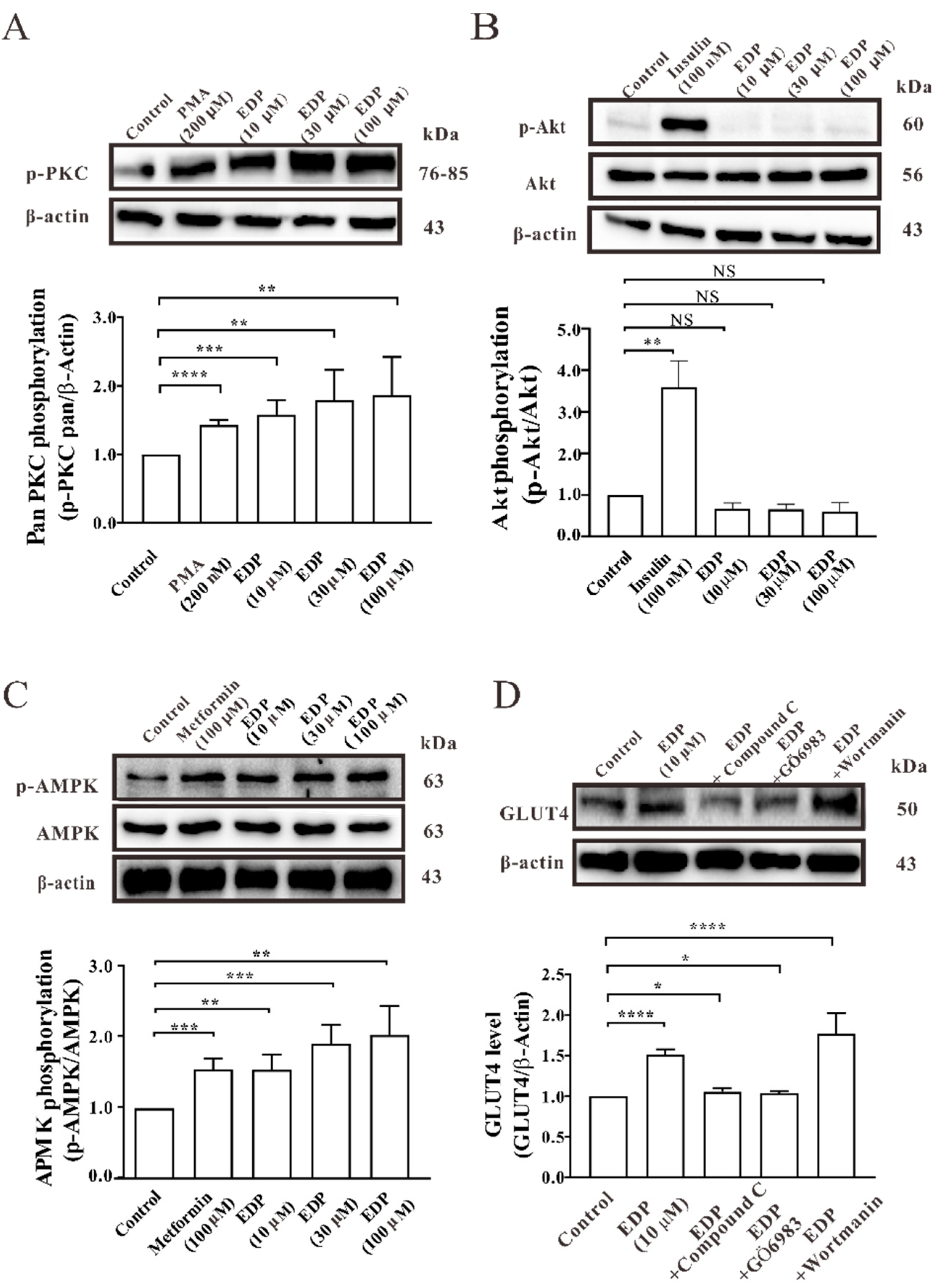
2.4. EDP Promotes Expression of GLUT4 Mainly through AMPK and PKC Signaling Pathways
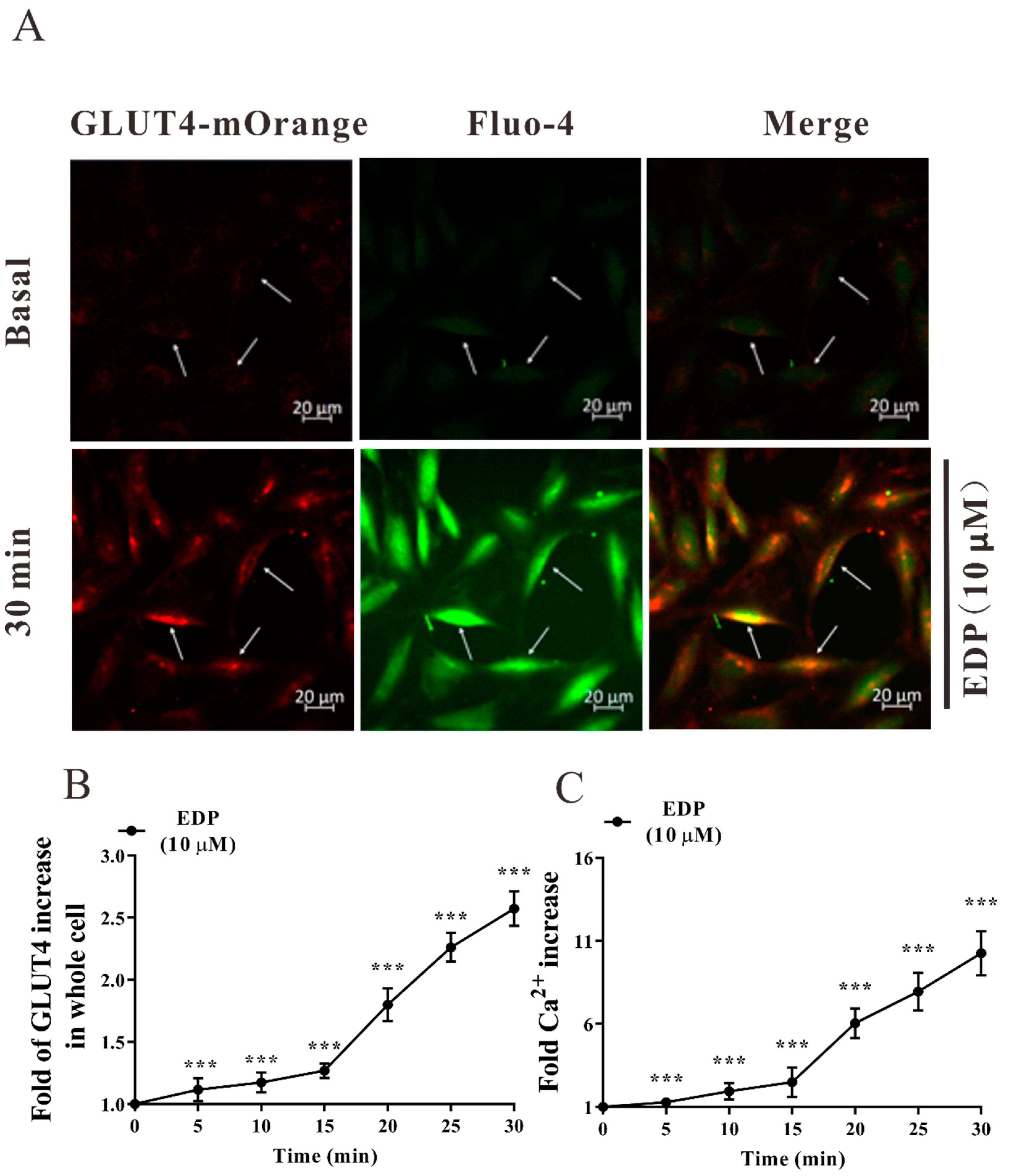
2.5. EDP Enhanced Intracellular Ca2+ Concentration in L6 Skeletal Muscle Cells
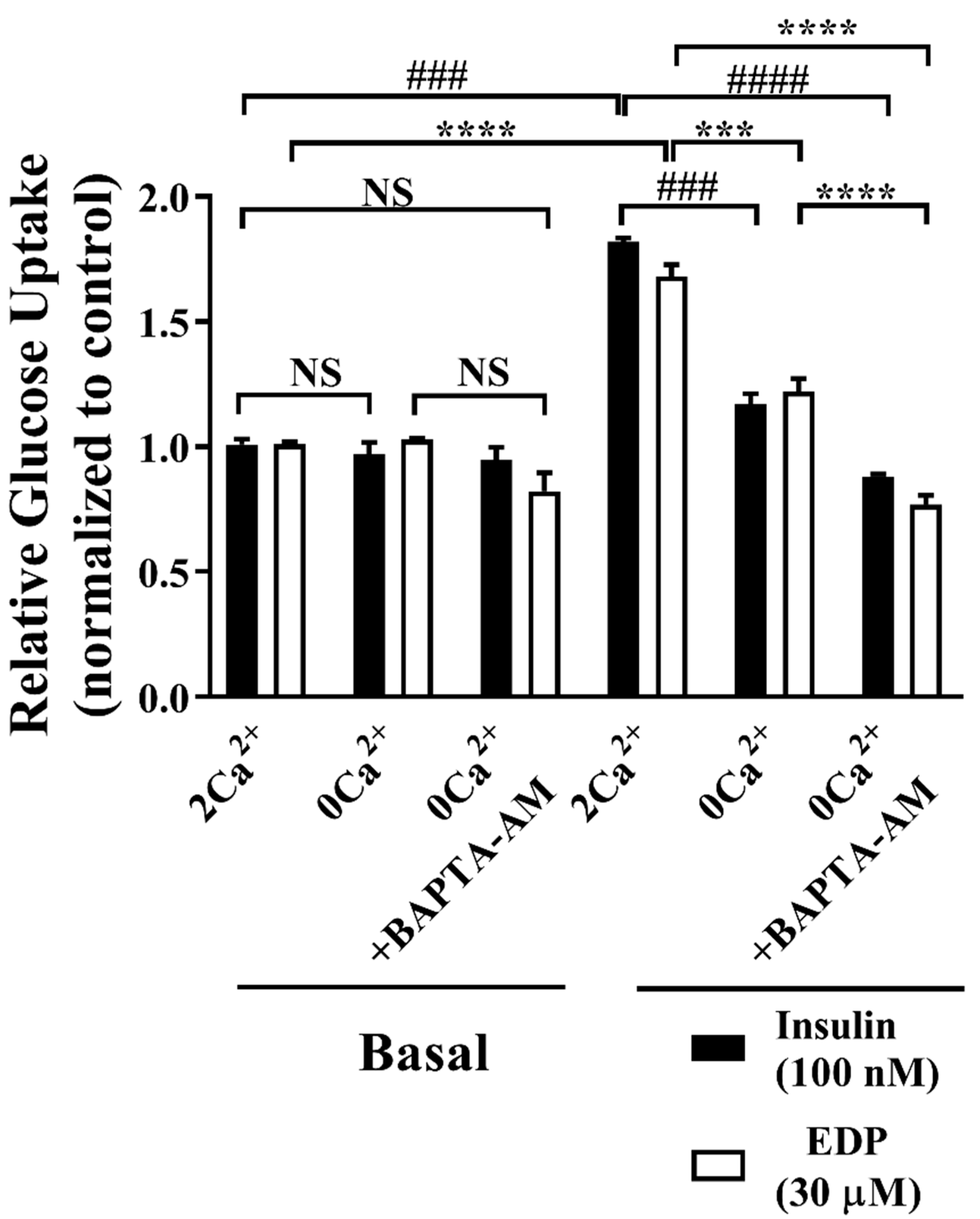
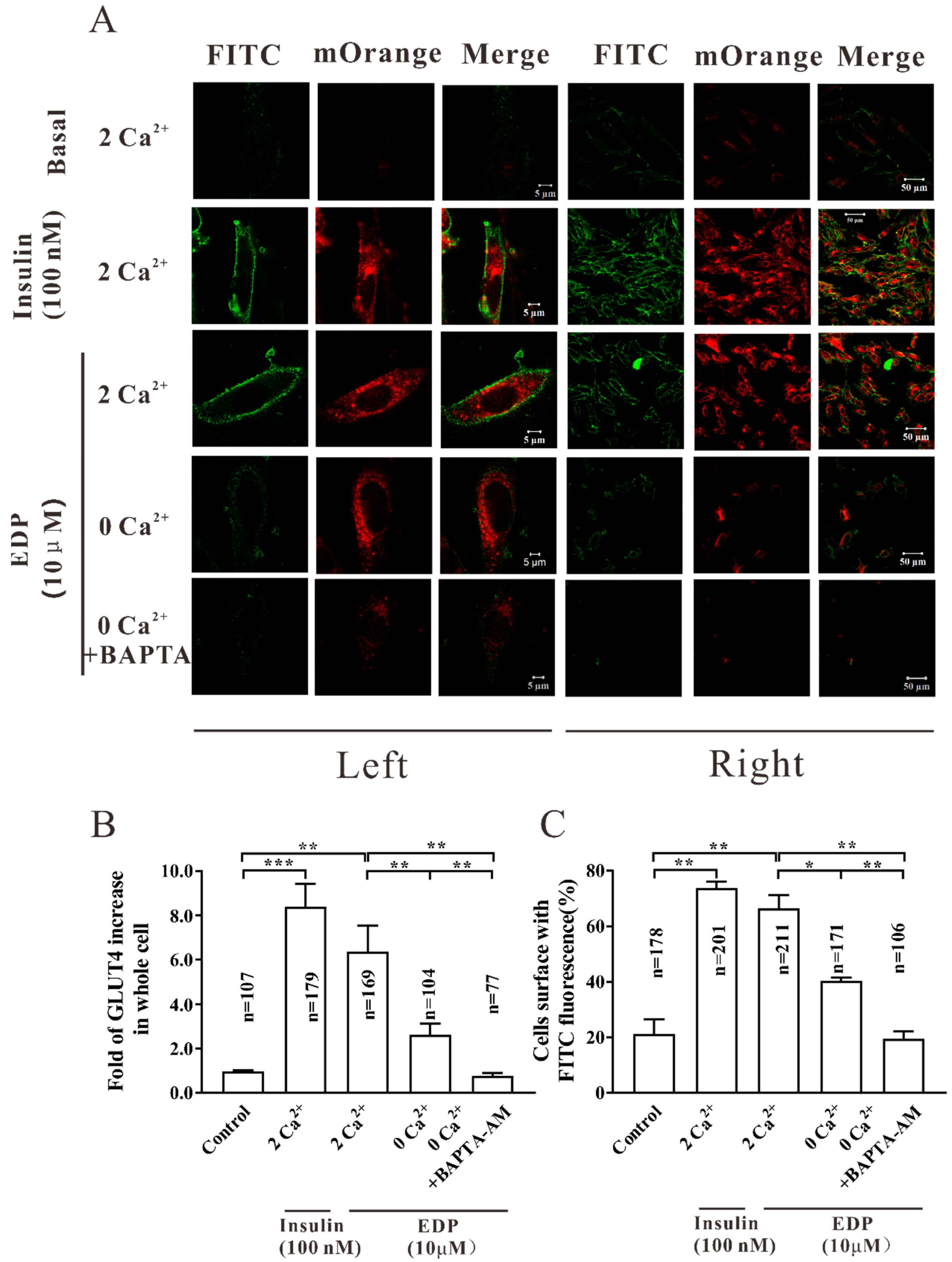
2.6. Engagement of Ca2+ Favors EDP-induced of Uptake of Glucose and GLUT4 Fusion into the Plasma Membrane
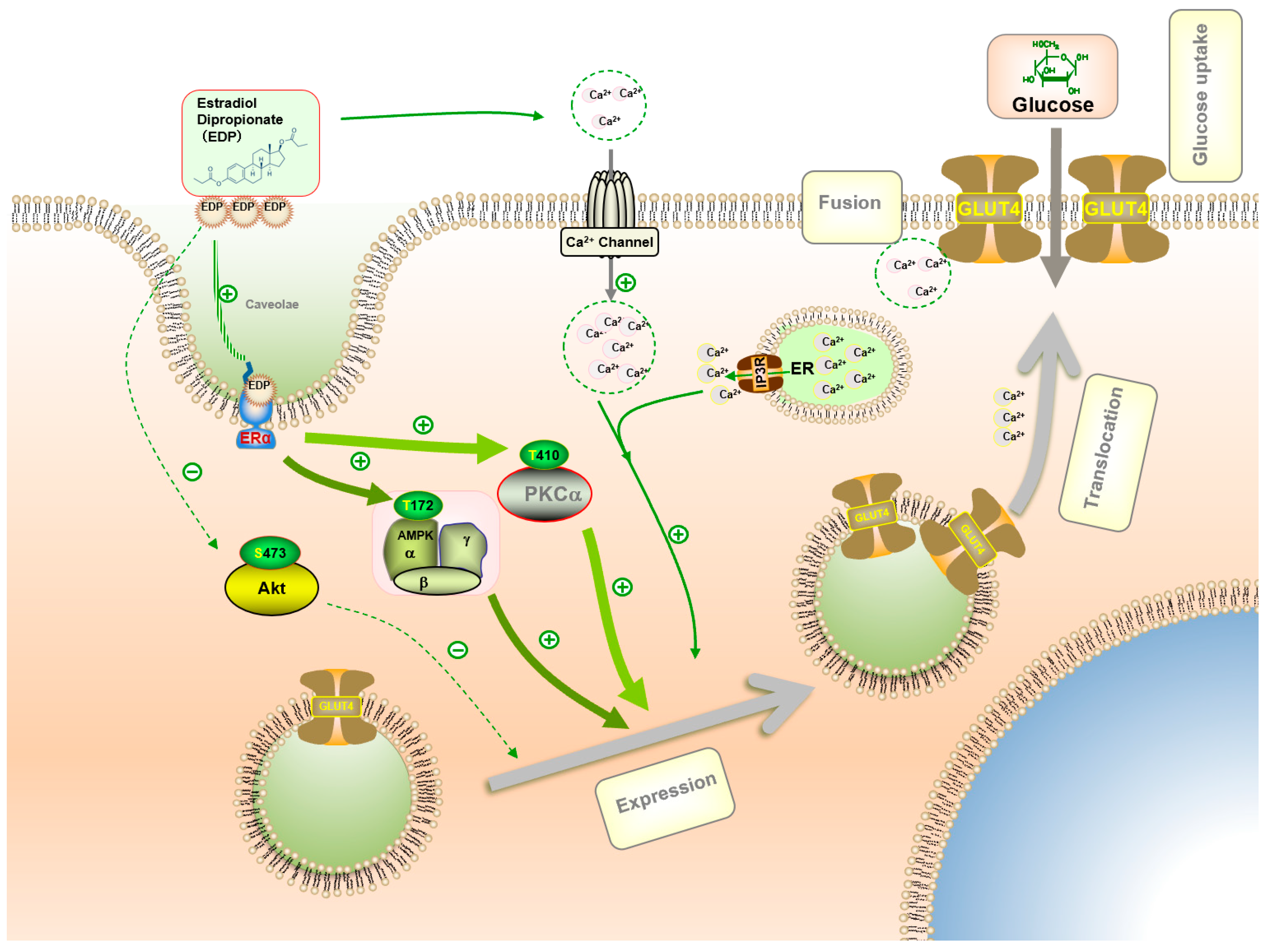
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Cultivation of L6 Skeletal Muscle Cells
4.3. Uptake of Glucose Assays
4.4. GLUT4 Expression and Fusion into Plasma Membrane Were Detected by Confocal Laser Microscopy
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Real-Time Monitoring of GLUT4 Expression and Ca2+ Levels by Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
4.7. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Chal, J.; Pourquie, O. Making muscle: Skeletal myogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Development 2017, 144, 2104–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richler, C.; Yaffe, D. The in vitro cultivation and differentiation capacities of myogenic cell lines. Dev. Biol. 1970, 23, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, E.A.; Hargreaves, M. Exercise, GLUT4, and skeletal muscle glucose uptake. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 993–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haeusler, R.A.; McGraw, T.E.; Accili, D. Biochemical and cellular properties of insulin receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, D.; De Strijcker, D.; Calders, P. Impact of Endurance Exercise Training in the Fasted State on Muscle Biochemistry and Metabolism in Healthy Subjects: Can These Effects be of Particular Clinical Benefit to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Insulin-Resistant Patients? Sports Med. 2017, 47, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahwan, M.; Alhumaydhi, F.; Ashraf, G.M.; Hasan, P.M.Z.; Shamsi, A. Role of polyphenols in combating Type 2 Diabetes and insulin resistance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 206, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Prasad, M.; Mohamed Helal, G.; El-Sherbiny, M.; Abdelmonem Elsherbini, D.M.; Rajagopal, P.; Palanisamy, C.P.; Veeraraghavan, V.P.; Jayaraman, S.; Surapaneni, K.M. Beta-Sitosterol Facilitates GLUT4 Vesicle Fusion on the Plasma Membrane via the Activation of Rab/IRAP/Munc 18 Signaling Pathways in Diabetic Gastrocnemius Muscle of Adult Male Rats. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2022, 2022, 7772305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabre, O.; Breuker, C.; Amouzou, C.; Salehzada, T.; Kitzmann, M.; Mercier, J.; Bisbal, C. Defects in TLR3 expression and RNase L activation lead to decreased MnSOD expression and insulin resistance in muscle cells of obese people. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yue, Y.; Hu, F.; Zhang, C.; Ma, X.; Li, N.; Qiu, L.; Fu, M.; Chen, L.; Yao, Z.; et al. Electrical pulse stimulation induces GLUT4 translocation in C(2)C(12) myotubes that depends on Rab8A, Rab13, and Rab14. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 314, E478–E493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, J.; Jin, M.; Qin, N.; Chen, Y.; Niu, W.; Duan, H. AMPK/AS160 mediates tiliroside derivatives-stimulated GLUT4 translocation in muscle cells. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2018, 12, 1581–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.; Bilan, P.J.; Yu, J.; Gao, J.; Boguslavsky, S.; Schertzer, J.D.; Chu, G.; Yao, Z.; Klip, A. PKCepsilon regulates contraction-stimulated GLUT4 traffic in skeletal muscle cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2011, 226, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansey, M.N.; Walker, N.N.; Hargett, S.R.; Stevens, J.R.; Keller, S.R. Deletion of Rab GAP AS160 modifies glucose uptake and GLUT4 translocation in primary skeletal muscles and adipocytes and impairs glucose homeostasis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 303, E1273–E1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, K.; Holman, G.D. Emerging role for AS160/TBC1D4 and TBC1D1 in the regulation of GLUT4 traffic. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 295, E29–E37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargett, S.R.; Walker, N.N.; Keller, S.R. Rab GAPs AS160 and Tbc1d1 play nonredundant roles in the regulation of glucose and energy homeostasis in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 310, E276–E288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Dayem, M.M.; Elgendy, M.S. Effects of chronic estradiol treatment on the thyroid gland structure and function of ovariectomized rats. BMC Res. Notes 2009, 2, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruegsegger, G.N.; Creo, A.L.; Cortes, T.M.; Dasari, S.; Nair, K.S. Altered mitochondrial function in insulin-deficient and insulin-resistant states. J. Clin. Invest 2018, 128, 3671–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Ming, Q.; Qiu, J.; Tian, D.; Liu, J.; Shen, J.; Liu, Q.H.; Yang, X. Ethanolic Extract of Folium Sennae Mediates the Glucose Uptake of L6 Cells by GLUT4 and Ca(2+). Molecules 2018, 23, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, B.; Mushack, J.; Seffer, E.; Haring, H.U. The translocation of the glucose transporter sub-types GLUT1 and GLUT4 in isolated fat cells is differently regulated by phorbol esters. Biochem. J. 1991, 275 Pt 3, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhou, Q.; Yang, X.; Xiong, M.; Xu, X.; Zhen, L.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhao, P.; Liu, Q.H. Chloroquine Increases Glucose Uptake via Enhancing GLUT4 Translocation and Fusion with the Plasma Membrane in L6 Cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 38, 2030–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.O.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, N.; You, G.Y.; Moon, J.W.; Kim, S.J.; Park, S.H.; Kim, H.S. Metformin regulates glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) translocation through AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-mediated Cbl/CAP signaling in 3T3-L1 preadipocyte cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 44121–44129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, D.C. Mechanisms of calcium-induced mitochondrial biogenesis and GLUT4 synthesis. Appl Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2007, 32, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, H.N.; Hardman, M.J. The role of estrogen in cutaneous ageing and repair. Maturitas 2017, 103, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Czech, M.P. The GLUT4 glucose transporter. Cell Metab. 2007, 5, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, N.J.; Govers, R.; James, D.E. Regulated transport of the glucose transporter GLUT4. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merz, K.E.; Thurmond, D.C. Role of Skeletal Muscle in Insulin Resistance and Glucose Uptake. Compr. Physiol. 2020, 10, 785–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Tripathy, D. Skeletal muscle insulin resistance is the primary defect in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32 (Suppl. S2), S157–S163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.B.; Yang, Y.R.; Mo, Z.J.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, W.J. Silibinin improves palmitate-induced insulin resistance in C2C12 myotubes by attenuating IRS-1/PI3K/Akt pathway inhibition. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2015, 48, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, C.K.; Singh, R.; Jaiswal, N.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Narender, T.; Tamrakar, A.K. 4-Hydroxyisoleucine ameliorates fatty acid-induced insulin resistance and inflammatory response in skeletal muscle cells. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2014, 395, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Pannu, A.; Chen, L.; Niu, W. PKC and Rab13 mediate Ca(2+) signal-regulated GLUT4 traffic. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 1956–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Hao, J.; Tian, D.; Wen, Y.; Zhao, P.; Chen, H.; Lv, Y.; Yang, X. Antidiabetic Activity of a Flavonoid-Rich Extract From Sophora davidii (Franch.) Skeels in KK-Ay Mice via Activation of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, V.; Saravanan, R. Glucose uptake through translocation and activation of GLUT4 in PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by asiatic acid in diabetic rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2015, 34, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thong, F.S.; Dugani, C.B.; Klip, A. Turning signals on and off: GLUT4 traffic in the insulin-signaling highway. Physiology 2005, 20, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Tian, D.; Song, G.; Ming, Q.; Liu, J.; Shen, J.; Liu, Q.H.; Yang, X. Neferine Promotes GLUT4 Expression and Fusion With the Plasma Membrane to Induce Glucose Uptake in L6 Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krook, A.; Wallberg-Henriksson, H.; Zierath, J.R. Sending the signal: Molecular mechanisms regulating glucose uptake. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2004, 36, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojuka, E.O.; Jones, T.E.; Han, D.H.; Chen, M.; Wamhoff, B.R.; Sturek, M.; Holloszy, J.O. Intermittent increases in cytosolic Ca2+ stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis in muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 283, E1040–E1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Huang, Y.; Xiong, M.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Shen, J.; Zhao, P.; Yang, X. Aloperine Relieves Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus via Enhancing GLUT4 Expression and Translocation. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 561956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, J.P.; Molero, J.C.; Clark, S.; Martin, S.; Meneilly, G.; James, D.E. The role of Ca2+ in insulin-stimulated glucose transport in 3T3-L1 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 27816–27824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, Y.; Yang, X.; Shen, J.; Zhao, P. Glucose Uptake Is Increased by Estradiol Dipropionate in L6 Skeletal Muscle Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16010025
Yao Y, Yang X, Shen J, Zhao P. Glucose Uptake Is Increased by Estradiol Dipropionate in L6 Skeletal Muscle Cells. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Yanhong, Xinzhou Yang, Jinhua Shen, and Ping Zhao. 2023. "Glucose Uptake Is Increased by Estradiol Dipropionate in L6 Skeletal Muscle Cells" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16010025
APA StyleYao, Y., Yang, X., Shen, J., & Zhao, P. (2023). Glucose Uptake Is Increased by Estradiol Dipropionate in L6 Skeletal Muscle Cells. Pharmaceuticals, 16(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16010025





