Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion (CSII) Combined with Oral Glucose-Lowering Drugs in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized, Controlled Trials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Retrieval Strategy
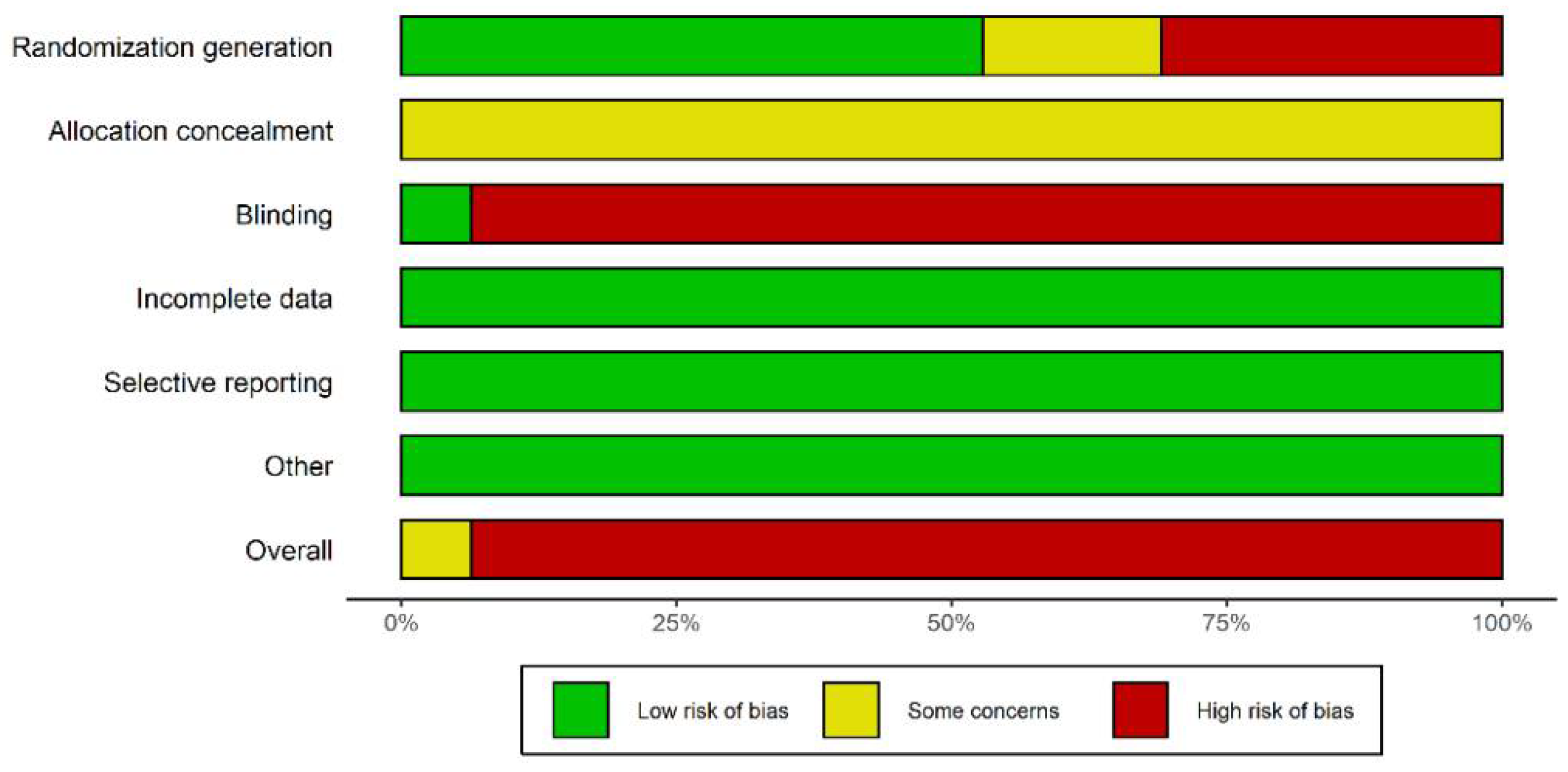
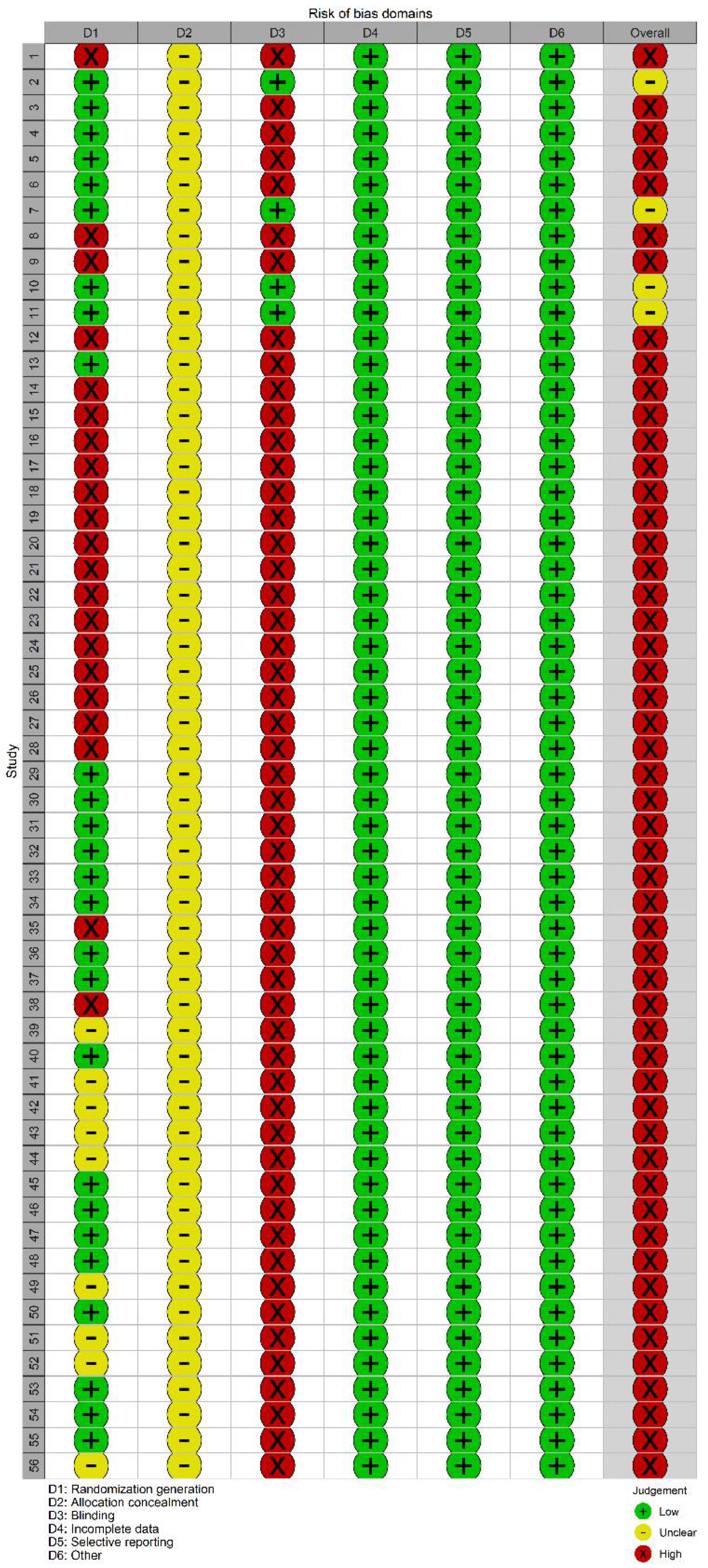
2.3. Paper Screening, Data Extraction, and Quality Evaluation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
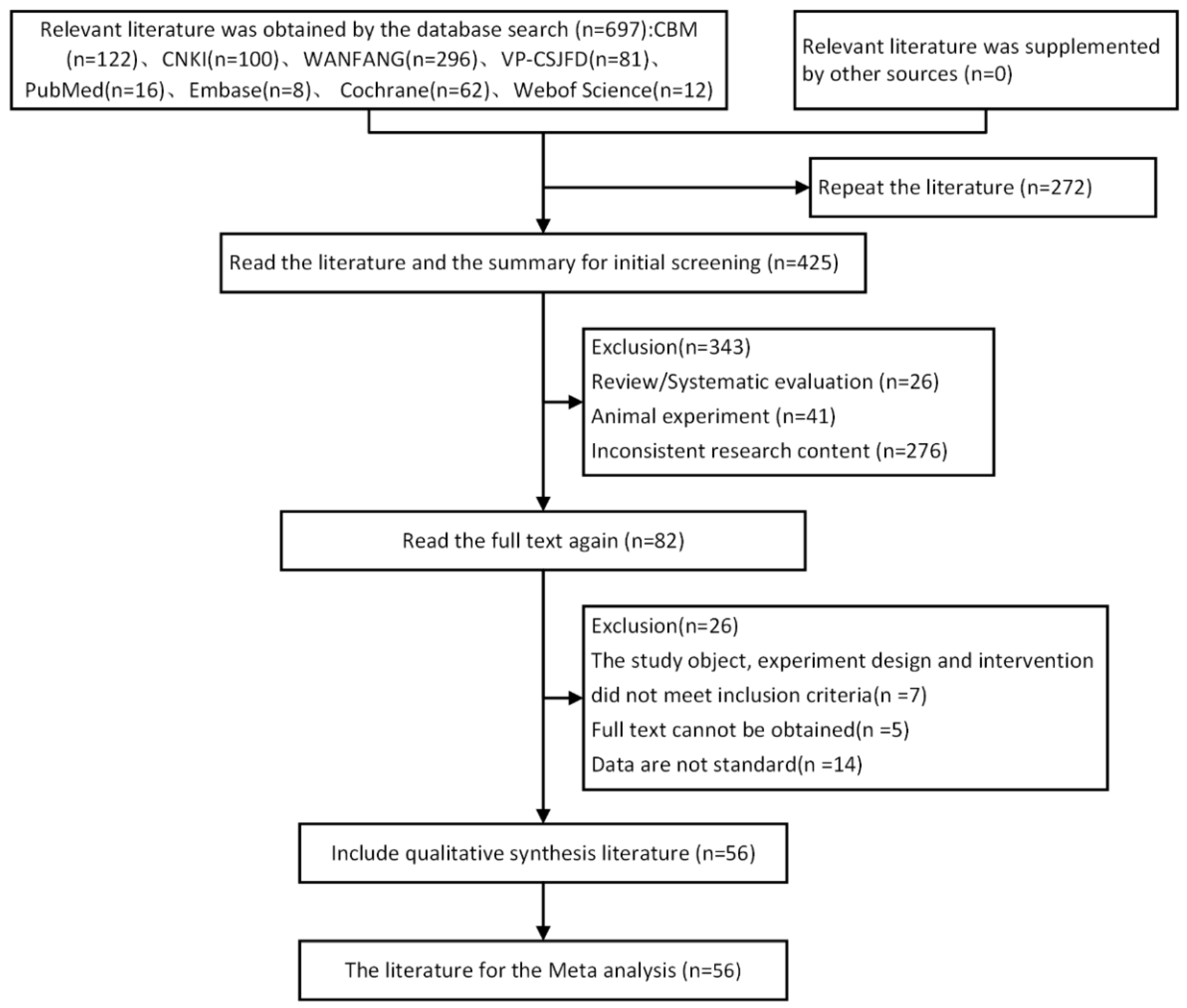
3.1. Literature Retrieval
3.2. General Information of the Papers
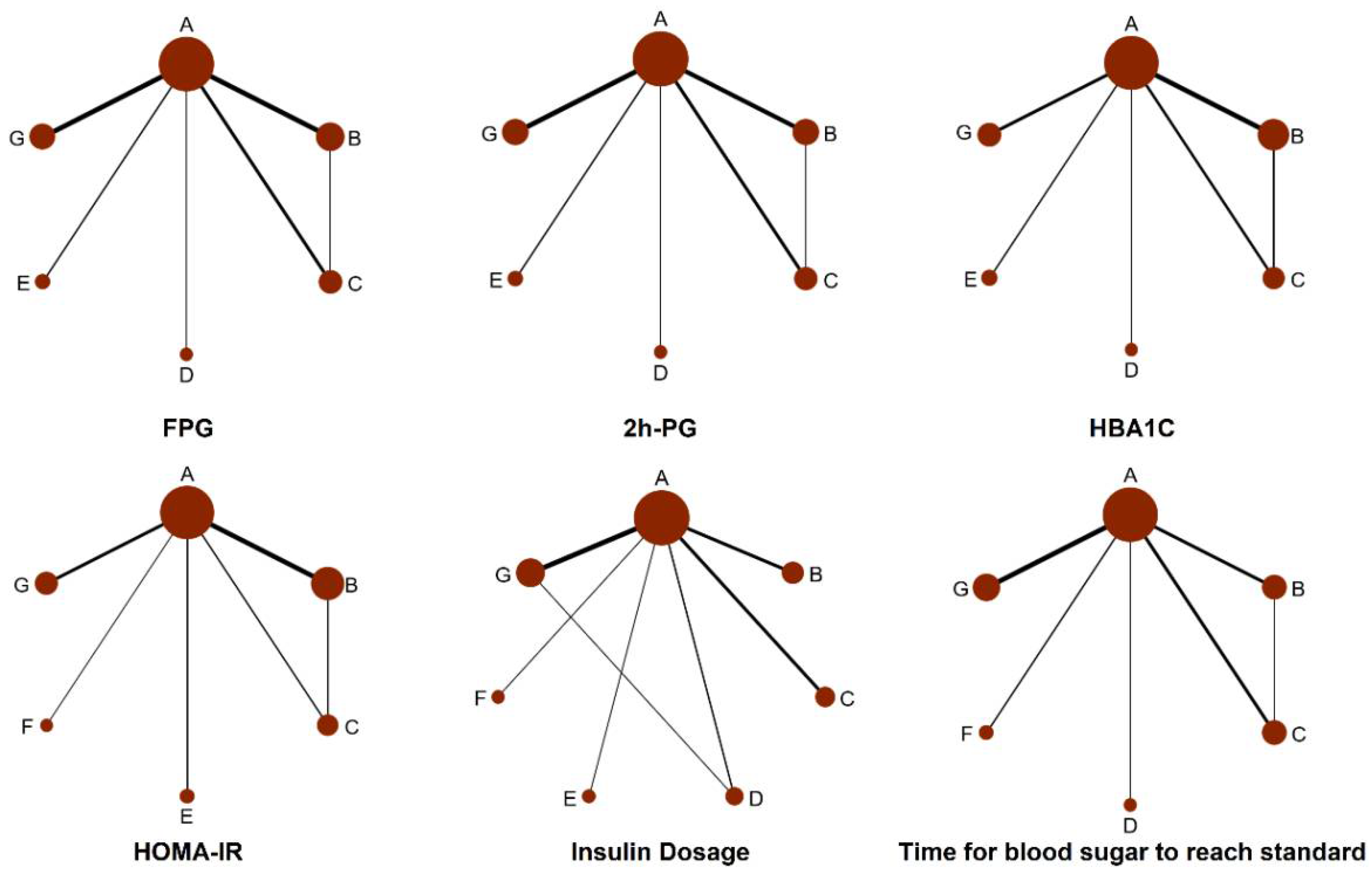
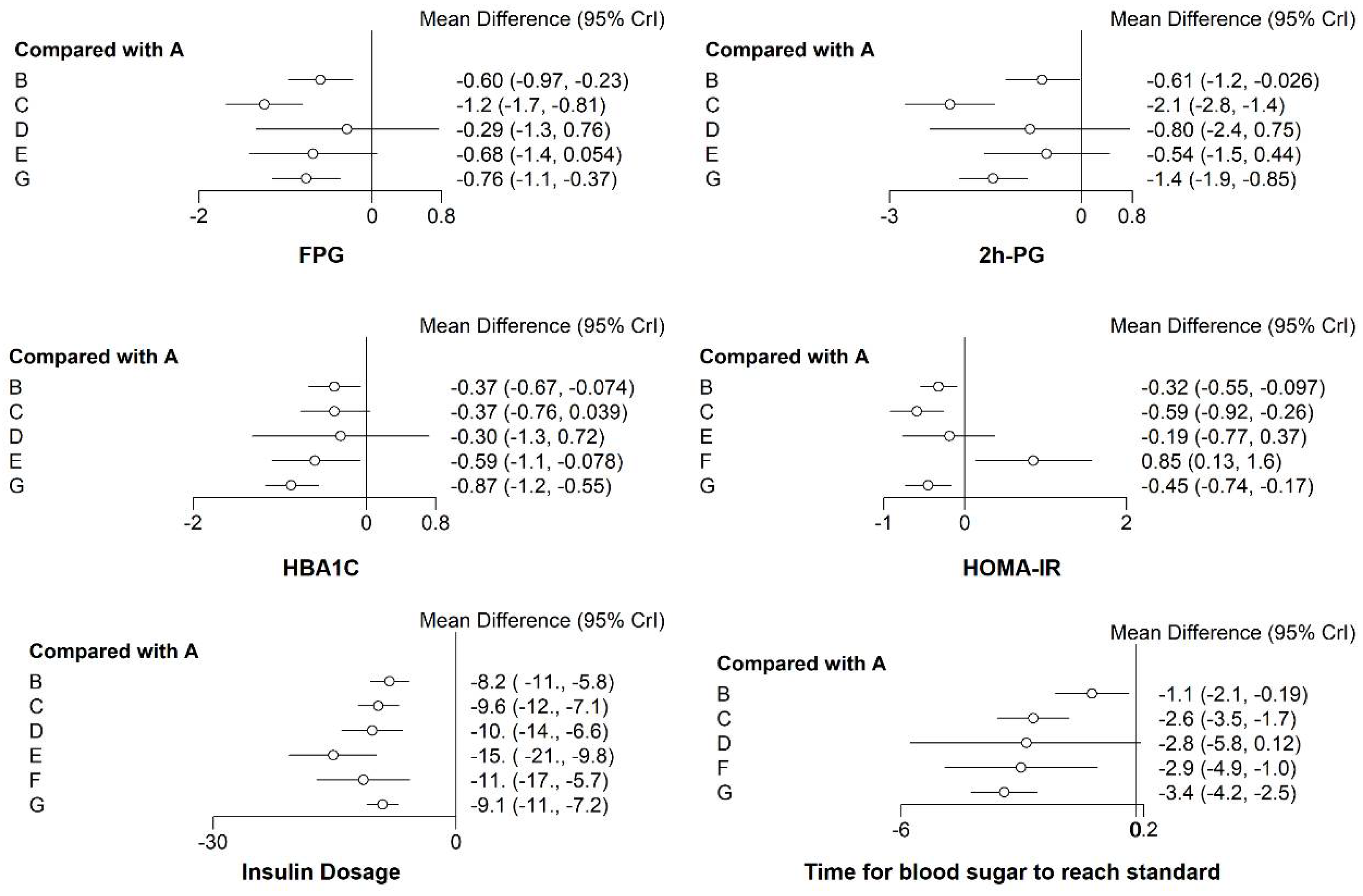
3.3. Network Meta-Analysis Results
3.3.1. FPG
3.3.2. The 2 h PG
3.3.3. HbA1c
3.3.4. HOMA-IR
3.3.5. Insulin Dosage when Blood Glucose Reaches Standard (Insulin Dosage)
3.3.6. Time for Blood Sugar to Reach Standard
3.4. Network Heterogeneity and Inconsistency
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draznin, B.; Aroda, V.R.; Bakris, G.; Benson, G.; Brown, F.M.; Freeman, R.; Green, J.B.; Huang, E.S.; Isaacs, D.M.; Kahan, S.; et al. 9. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, S125–S143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT)/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC) Study Research Group. Mortality in Type 1 Diabetes in the DCCT/EDIC Versus the General Population. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buse, J.B.; Wexler, D.J.; Tsapas, A.; Rossing, P.; Mingrone, G.; Mathieu, C.; D’Alessio, D.A.; Davies, M.J. 2019 Update to: Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2018. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeh, H.C.; Brown, T.T.; Maruthur, N.; Ranasinghe, P.; Berger, Z.; Suh, Y.D.; Wilson, L.M.; Haberl, E.B.; Brick, J.; Bass, E.B.; et al. Comparative effectiveness and safety of methods of insulin delivery and glucose monitoring for diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2012, 157, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reznik, Y. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) using an external insulin pump for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2010, 36, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingvay, I.; Manghi, F.P.; García-Hernández, P.; Norwood, P.; Lehmann, L.; Tarp-Johansen, M.J.; Buse, J.B. Effect of Insulin Glargine Up-titration vs Insulin Degludec/Liraglutide on Glycated Hemoglobin Levels in Patients With Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes: The DUAL V Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 315, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, D.R.; Paldánius, P.M.; Proot, P.; Chiang, Y.T.; Stumvoll, M.; Del Prato, S. Glycaemic durability of an early combination therapy with vildagliptin and metformin versus sequential metformin monotherapy in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes (VERIFY): A 5-year, multicentre, randomised, double-blind trial. Lance 2019, 394, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Zhao, D.; Shen, J.; Lu, L.; Zhang, T.; Chen, Z. Comparison of the Effects of Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion and Add-On Therapy with Sitagliptin in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 9849328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.Y.; Jia, J.; Zhang, C.L.; Yu, S.Q.; Dong, S.J.; Ye, J.J.; Zhu, T.Y.; Tang, B.Q.; Qian, W.Y.; Wang, D.; et al. Safety and efficacy of sitagliptin in combination with transient continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) therapy in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Endocr. J. 2014, 61, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huhn, M.; Nikolakopoulou, A.; Schneider-Thoma, J.; Krause, M.; Samara, M.; Peter, N.; Arndt, T.; Bäckers, L.; Rothe, P.; Cipriani, A.; et al. Comparative efficacy and tolerability of 32 oral antipsychotics for the acute treatment of adults with multi-episode schizophrenia: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet 2019, 394, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int. J. Surg. 2021, 88, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savovic, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.; et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.3 (updated February 2022). Cochrane. 2022. Available online: www.training.cochrane.org/handbook (accessed on 16 March 2022).
- Shim, S.R.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, J.; Rücker, G. Network meta-analysis: Application and practice using R software. Epidemiol. Health 2019, 41, e2019013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Valkenhoef, G.; Dias, S.; Ades, A.E.; Welton, N.J. Automated generation of node-splitting models for assessment of inconsistency in network meta-analysis. Res. Synth. Methods 2016, 7, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.P.; Jackson, D.; Barrett, J.K.; Lu, G.; Ades, A.E.; White, I.R. Consistency and inconsistency in network meta-analysis: Concepts and models for multi-arm studies. Res. Synth. Methods 2012, 3, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gemtc: Network Meta-Analysis Using Bayesian Methods. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=gemtc (accessed on 12 May 2022).
- rjags: Bayesian Graphical Models Using MCMC. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=rjags (accessed on 12 May 2022).
- Ouyang, R.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, H.; Xie, M. Effect of insulin pump with metformin in the treatment of newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus. In Science and Education Guide-Electronic Edition (Early Days); Hubei Science and Education Guide Magazines: Wuhan, China, 2019; p. 287. [Google Scholar]
- Su, F. Effect of metformin sustained release tablet in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Diabetes World 2020, 17, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T. Effect of DPP-4 inhibitors on glycemic control in insulin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes World 2020, 17, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Ge, H.; Cai, H. Clinical study on short-term insulin pump combined with rosiglitazone maleate for intensive treatment of primary type 2 diabetes. Jilin Med. 2006, 27, 1381–1382. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, S.; Liu, E.; Luo, H. Effect of different oral hypoglycemic drugs on islet function and prognosis in patients with intensive insulin pump treatment for type 2 diabetes. West. Med. 2020, 32, 832–835. [Google Scholar]
- Chae, Y.K.; Arya, A.; Malecek, M.K.; Shin, D.S.; Carneiro, B.; Chandra, S.; Kaplan, J.; Kalyan, A.; Altman, J.K.; Platanias, L.; et al. Repurposing metformin for cancer treatment: Current clinical studies. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 40767–40780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, M. Effect and adverse effects of sitagliptin in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. J. Chronic Dis. 2019, 20, 711–713. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y. Efficacy of sitagliptin and insulin pump in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes and its effect on blood glucose fluctuations. Hainan Med. 2016, 27, 2183–2184. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q. Clinical effect of short-term strengthening of insulin pump combined with sitagliptin in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. World’s Latest Med. Inf. Dig. 2018, 18, 117–118. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Jin, X.; Shen, G. Clinical observation of short-term insulin pump combined with pioglitazone for intensive treatment of primary type 2 diabetes mellitus. Chin. Foreign Health Abstr. 2011, 8, 40–42. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, X. Study of Early Insulin Combination Protection against Islet Cells in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes. Master’s Thesis, Zhongshan University, Guangzhou, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Sun, X.; Guo, C. The efficacy of dagliazin combined with insulin pump in patients with type 2 diabetes. Health Nutr. China 2021, 31, 73–74. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, X. Efficacy of Liraglutide Combined with Insulin in First Diagnosed Overweight and Obese T2DM. Master’s Thesis, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Liu, F.; Yu, W. Effect of pioglitazone on long-term remission of insulin intensive therapy in first diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes. Anhuinmedicine 2011, 15, 220–222. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, R. Clinical Study of Rosiglitazone and Insulin Pump Intensification for Type 2 Diabetes. Master’s Thesis, Yanbian University, Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. Comparative Study of the Clinical Efficacy of T2DM Using CSII and Combined with Metidin or TZD Drugs. Master’s Thesis, Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X. Linagliptin and CSII and CSII Alone for Intensive Treatment of Primary T2DM Comparative Analysis of Efficacy. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. Comparative Study of the Clinical Efficacy of Exenatide Combination with CSII and CSII Alone in Patients with Naive obese T2DM. Master’s Thesis, Yanbian University, Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X. Clinical Effect of Liraglutide and Insulin Pump in Non-First Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes. Master’s Thesis, Yan’an University, Yan’an, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, R. Lyraglutide combined with insulin pump for initial treatment of overweight type 2 diabetes. Electron. J. Cardiovasc. Dis. Integr. Tradit. Chin. West. Med. 2017, 5, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Yang, H. Clinical discussion of insulin pump and metformin in intensive treatment for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Lab. Med. Clin. Med. 2009, 6, 777–778. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Zhang, L. Effect of intensive insulin pump alone and combination of metformin on C peptide. Clin. J. Chin. Med. 2013, 5, 98–99. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, M. Efficacy of Insulin Pump and Metformin in Type 2 Diabetes. J. Mod. Integr. Tradit. Chin. West. Med. 2014, 23, 766–767. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.; Fan, L.; Lu, L. Effect of insulin pump and metformin sustained-release tablets on type 2 diabetes mellitus on insulin resistance. New World Diabetes 2018, 21, 75–76. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B.; Xiao, P.; Ding, B.; Jing, L.; Wang, H. Treatment effect of metformin and insulin pump on old new-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus. New World Diabetes 2020, 23, 75–76,79. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, K.; Lu, Y.; Ou, X. Effect of metformin sustained release tablet in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. J. Pract. Med. 2012, 28, 3916–3918. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q. Effect of insulin pump intensive therapy and pioglitazone on glycemic control and insulin resistance index changes in type 2 diabetes patients. Cap. Food Med. 2018, 25, 48. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H. Clinical observation of insulin pump and metformin in the treatment of primary type 2 diabetes. J. Pract. Med. Technol. 2008, 15, 360–361. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z. Study on the treatment of rosiglitazone for type 2 diabetes. Pract. Diabetes J. 2007, 3, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Yang, H.; Xu, Z. Clinical treatment of insulin pump for type 2 diabetes. Pract. Diabetes J. 2009, 5, 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Li, Y.; Li, S. Clinical efficacy of insulin pump combined with pioglitazone for intensive short-term treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Qiqihar Med. Coll. 2016, 37, 2288–2290. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Yang, H. Clinical treatment of insulin pump and rosiglitazone sodium. Intern. Med. 2009, 4, 354–356. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, T.; Li, H.; Deng, B. Clinical efficacy of sitagliptin and insulin pump in the treatment of newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Chronic Dis. 2018, 9, 1211–1213. [Google Scholar]
- Han, E. Effect of dagliazin on insulin resistance index in patients with short-term intensive insulin pump for type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Mil. Med. 2020, 48, 37–438. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H. Clinical Study of Short-term Continuously Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion Combined with Rosiglitazone in Intensively Treating Newly Diagnosed type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhu, L.; Yang, S. Clinical observation of rosiglitazone combined with insulin pump intensive therapy in improving vascular endothelial function in patients with type 2 diabetes. North China Natl. Def. Med. 2008, 20, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, M.; Wang, T.; Zhu, Y. Effect of combined insulin pump and metformin sustained-release tablets on type 2 diabetes. Henan Med. Res. 2019, 28, 3378–3380. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Tang, H. Efficacy of rosiglitazone and insulin pump and its effect on vascular endothelium-dependent relaxation function in type 2 diabetes. Guangxi Med. 2014, 8, 1089–1092. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.; Zhang, P. Effect of acarbose plus insulin pump on blood glucose fluctuations in type 2 diabetes. Guangxi Med. 2013, 35, 453–454. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, N. Clinical observation of insulin pump combined with pioglitazone for primary type 2 diabetes mellitus. Anhui Med. 2009, 13, 665–666. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Wan, X.; Liu, J.; Deng, W.; Chen, A.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Wei, G.; Li, H.; Fang, D.; et al. Short-term continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion combined with insulin sensitizers rosiglitazone, metformin, or antioxidant α-lipoic acid in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2013, 15, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Li, J.; Cai, X.; Liu, Y. Effect of DPP-4 inhibitors on glucose fluctuations in insulin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes. Chongqing Med. 2017, 46, 2365–2368. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Le, J.; Liu, A. Effect of early intensive insulin pump therapy on serum Visfatin and GLP-1 in patients with primary type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2016, 15, 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H. Effect of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor in combination with real-time dynamic insulin pump on glycemic control and quality of life in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Henan Med. Res. 2019, 28, 3729–3731. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J. Clinical study of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor plus insulin pump continuous subcutaneous infusion for insulin asate 30 poorly controlled type 2 diabetes. Pract. Diabetes J. 2020, 16, 128–129. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.; Guo, A. Effect of ligagliptin and insulin pump on blood glucose fluctuations in patients with primary type 2 diabetes. Traffic Med. 2020, 34, 37–38,43. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Y. Efficacy observation of two intensive insulin treatment regimen for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Contin. Med. Educ. China 2020, 12, 150–152. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Chen, P.; Ding, H. Effects of short-term intensive hypoglycemic therapy with insulin pump combined with saxagliptin on secretion function of glandular cells and insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drug Eval. Study 2019, 42, 226–2229. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Q.; Zhang, G. Efficacy analysis of sitagliptin and insulin pump for short-term intensive therapy in new-onset type 2 diabetes. Diabetes New World 2020, 23, 99–101. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Chen, Q. Effect of sitagliptin plus insulin pump on blood glucose fluctuations in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. New World Diabetes 2017, 20, 105–106. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L. Efficacy of sitagliptin combined with insulin pump in intensive treatment of T2DM patients with poorly controlled insulin aspartic 30. Med. Clin. Res. 2016, 33, 2009–2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L. Clinical efficacy of sitagliptin and insulin pump in naive patients with type 2 diabetes. Pract. Diabetes J. 2021, 17, 60–61. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X. Analysis of insulin pump (insulin) and sitagliptin on T2DM. Mod. Drug Appl. China 2016, 10, 119–121. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X. Effect of insulin pump combined with liagliptin on blood glucose and insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes. Heilongjiang Med. 2021, 34, 106–108. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, H. Preliminary Study of Optimizing Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Injection with DPP-4 Enzyme Inhibitors for Type 2 Diabetes. Master’s Thesis, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
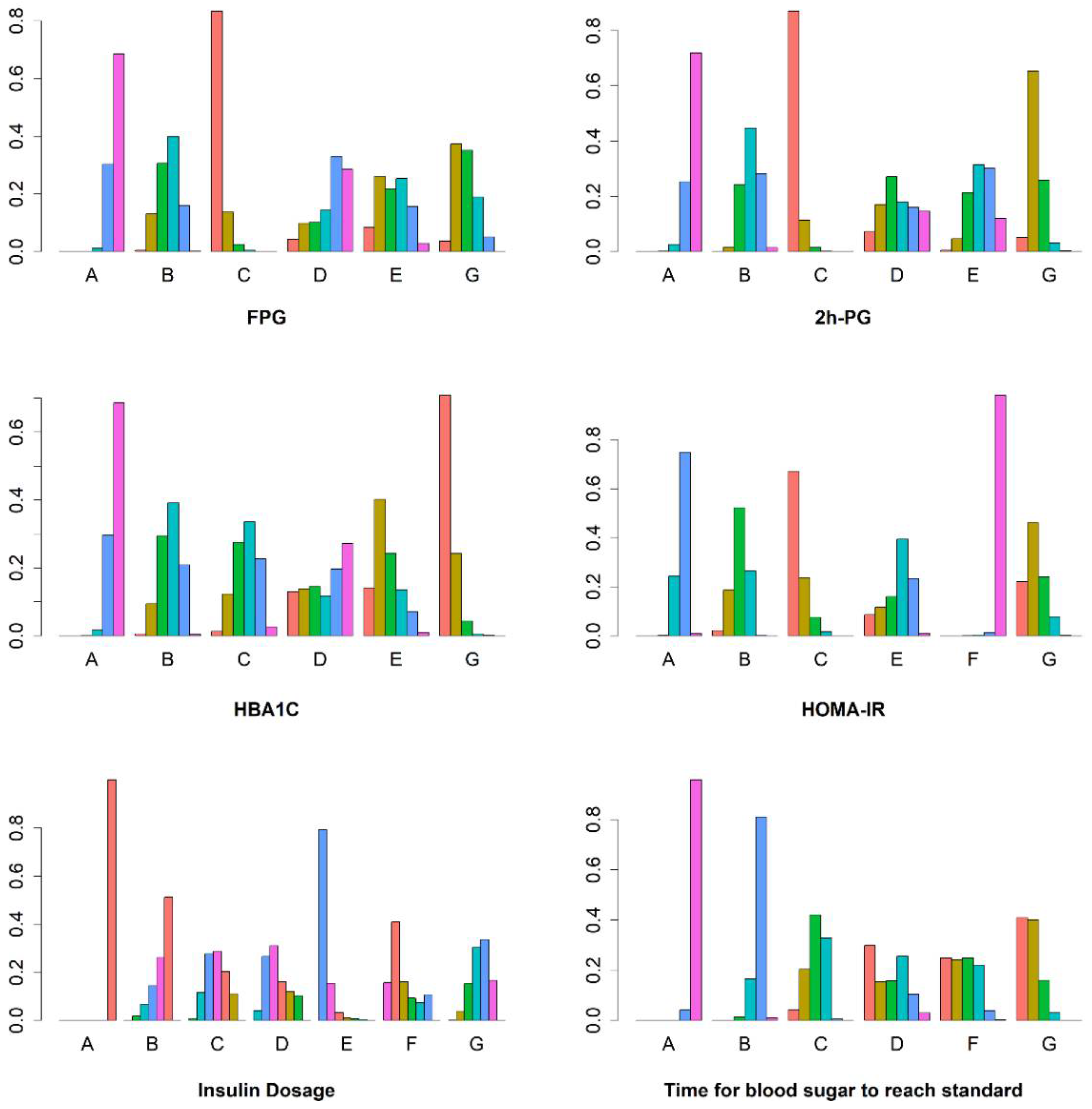
| A (CSII) | B (CSII + TZDs) | C (CSII + MF) | D (CSII + AGIs) | E (CSII + GLP-1Ras)) | F (CSII + SGLT2is) | G (CSII + DPP-4is) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FPG | 0.06 | 0.48 | 0.96 | 0.31 | 0.56 | / | 0.63 |
| 2 h PG | 0.06 | 0.39 | 0.97 | 0.48 | 0.35 | / | 0.74 |
| HbA1C | 0.07 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.41 | 0.68 | / | 0.93 |
| HOMA-IR | 0.25 | 0.59 | 0.91 | / | 0.48 | 0.01 | 0.76 |
| Insulin usage | 0.00 | 0.30 | 0.52 | 0.61 | 0.95 | 0.70 | 0.43 |
| Blood sugar Standards time | 0.01 | 0.24 | 0.59 | 0.64 | / | 0.69 | 0.84 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Yang, A.; Zhao, S.; Chow, E.Y.; Javanbakht, M.; Li, Y.; Lin, D.; Xu, L.; Zang, D.; Wang, K.; et al. Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion (CSII) Combined with Oral Glucose-Lowering Drugs in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized, Controlled Trials. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15080953
Li H, Yang A, Zhao S, Chow EY, Javanbakht M, Li Y, Lin D, Xu L, Zang D, Wang K, et al. Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion (CSII) Combined with Oral Glucose-Lowering Drugs in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized, Controlled Trials. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(8):953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15080953
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hui, Aimin Yang, Shi Zhao, Elaine YK Chow, Mohammad Javanbakht, Yinhui Li, Dandan Lin, Lijuan Xu, Deng Zang, Kai Wang, and et al. 2022. "Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion (CSII) Combined with Oral Glucose-Lowering Drugs in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized, Controlled Trials" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 8: 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15080953
APA StyleLi, H., Yang, A., Zhao, S., Chow, E. Y., Javanbakht, M., Li, Y., Lin, D., Xu, L., Zang, D., Wang, K., & Ma, L. (2022). Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion (CSII) Combined with Oral Glucose-Lowering Drugs in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized, Controlled Trials. Pharmaceuticals, 15(8), 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15080953







