Biodistribution of Intra-Arterial and Intravenous Delivery of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in a Rat Model to Guide Delivery Strategies for Diabetes Therapies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
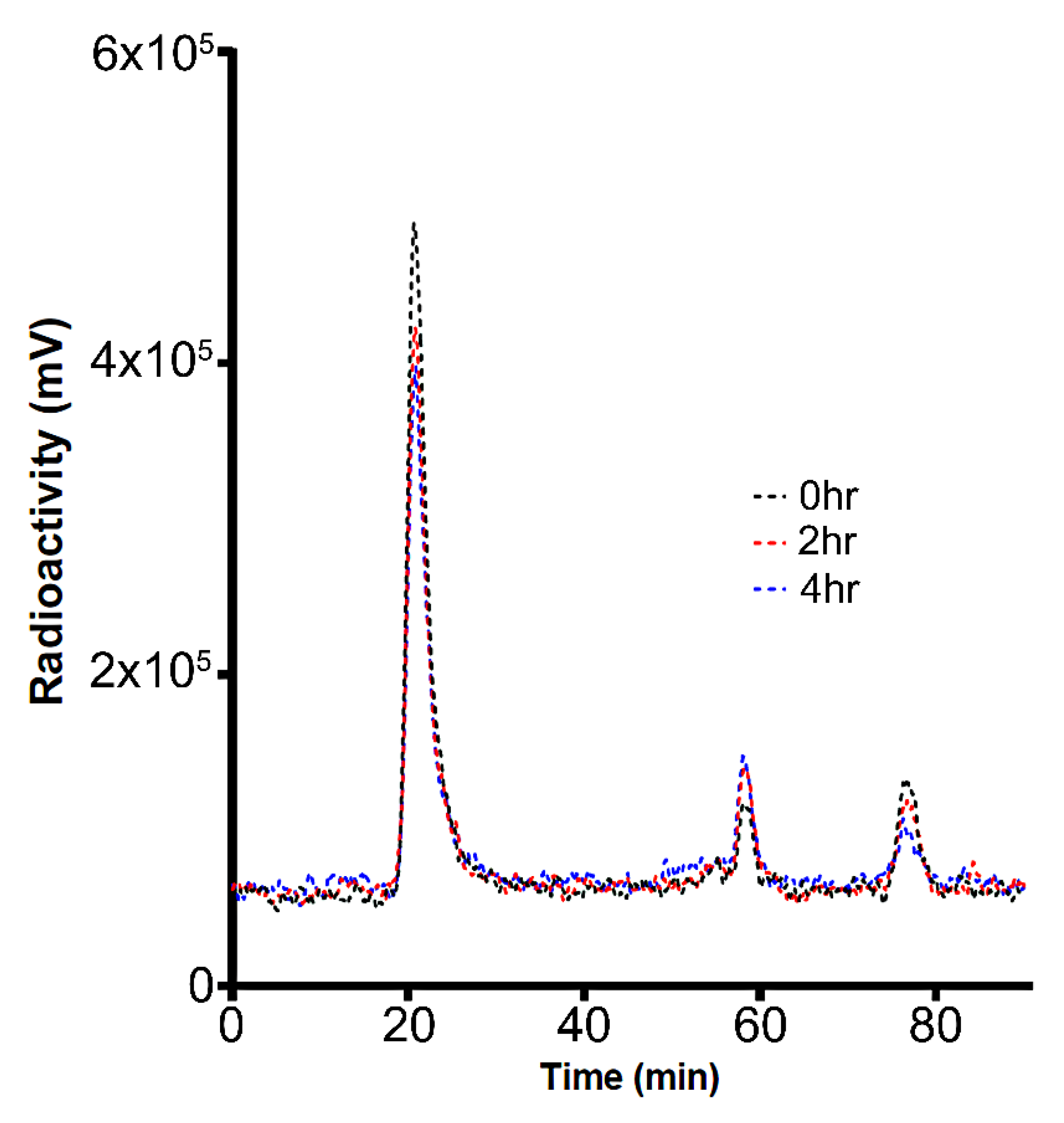
2.1. Radioiodination and Stability of UC-MSC-EVs
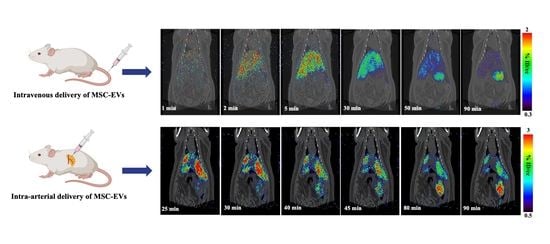
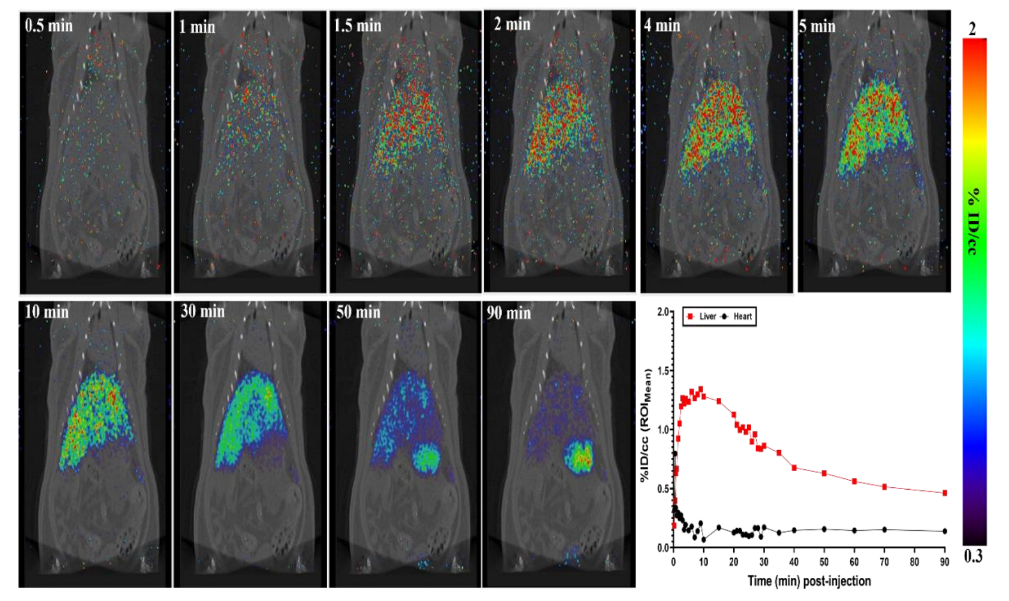
2.2. I.V. Administration and PET-CT Small Animal Imaging
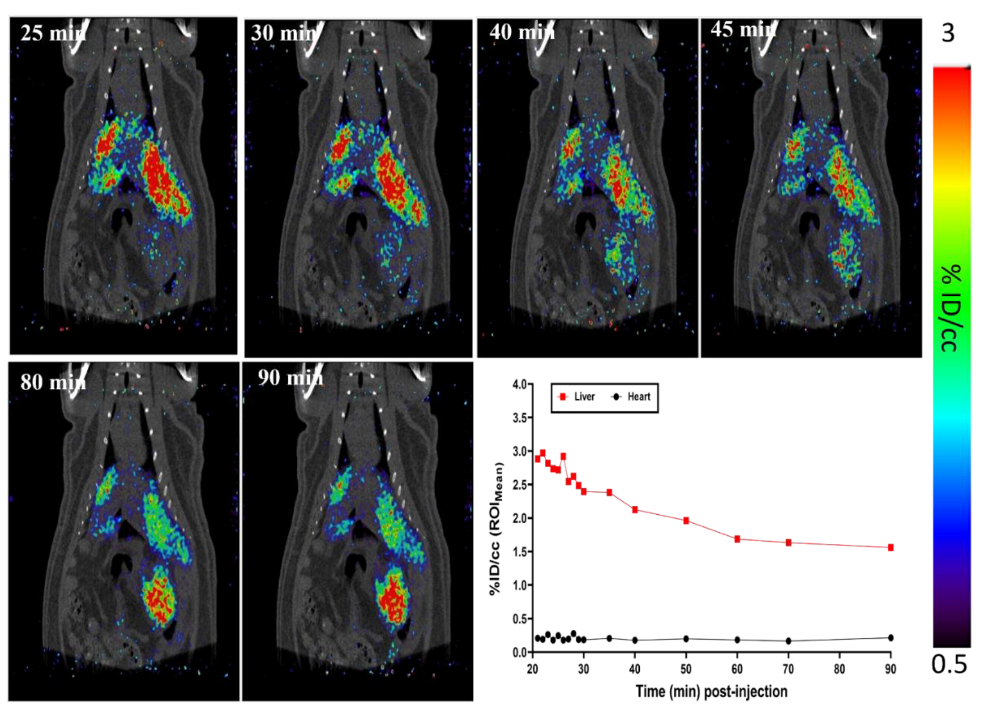
2.3. I.A. Administration and PET-CT Small Animal Imaging
2.4. Biodistribution Analysis of the I.V. Injection Group and the I.A. Injection Group
3. Discussion
3.1. Surgical Procedures for I.A. Injection of [124I]I-UC-MSC-EVs
3.2. Radio-Deiodination In Vivo
3.3. PET-CT Small Animal Imaging and Biodistribution
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Human UC-MSC-EVs Extraction and Purification
4.3. Animal
4.4. Radioiodination of UC-MSC-EVs and Radiochemical Stability Assessment
4.5. Procedures for I.V. Administration and Animal PET-CT Imaging
4.6. Procedures for I.A. Administration and Animal PET-CT Imaging
4.7. Biodistribution of [124I]I-UC-MSC-EVs in Rats
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjostrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lotvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Jiang, Z.; Webster, K.A.; Chen, J.; Hu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, Z.; et al. Enhanced Cardioprotection by Human Endometrium Mesenchymal Stem Cells Driven by Exosomal MicroRNA-21. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perets, N.; Betzer, O.; Shapira, R.; Brenstein, S.; Angel, A.; Sadan, T.; Ashery, U.; Popovtzer, R.; Offen, D. Golden Exosomes Selectively Target Brain Pathologies in Neurodegenerative and Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 3422–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Chuah, S.J.; Lai, R.C.; Hui, J.H.P.; Lim, S.K.; Toh, W.S. MSC exosomes mediate cartilage repair by enhancing proliferation, attenuating apoptosis and modulating immune reactivity. Biomaterials 2018, 156, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Hu, J.; Chen, F.; Qiao, S.; Sun, X.; Gao, L.; Xie, J.; Xu, B. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes attenuate myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury through miR-182-regulated macrophage polarization. Cardiovasc. Res. 2019, 115, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Yeo, R.W.Y.; Lai, R.C.; Sim, E.W.K.; Chin, K.C.; Lim, S.K. Mesenchymal stromal cell exosome-enhanced regulatory T-cell production through an antigen-presenting cell-mediated pathway. Cytotherapy 2018, 20, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahir, M.; Mahmoud Hashemi, S.; Asadirad, A.; Varahram, M.; Kazempour-Dizaji, M.; Folkerts, G.; Garssen, J.; Adcock, I.; Mortaz, E. Effect of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on the induction of mouse tolerogenic dendritic cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 7043–7055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, M.; Shen, Y.; Wang, P.; Xie, Z.; Xu, S.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lyu, Y.; Wang, D.; Xu, L.; et al. Exosomes Isolated from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Neuroinflammation and Reduce Amyloid-Beta Deposition by Modulating Microglial Activation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 2165–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, X.; Li, F.; Ma, Z.; Xu, M.; Lu, L. Exosomes derived from miR-181-5p-modified adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent liver fibrosis via autophagy activation. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 2491–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chu, W.C.; Lai, R.C.; Lim, S.K.; Hui, J.H.; Toh, W.S. Exosomes derived from human embryonic mesenchymal stem cells promote osteochondral regeneration. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2016, 24, 2135–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, Y.; Miyaki, S.; Ishitobi, H.; Matsuyama, S.; Nakasa, T.; Kamei, N.; Akimoto, T.; Higashi, Y.; Ochi, M. Mesenchymal-stem-cell-derived exosomes accelerate skeletal muscle regeneration. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teng, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, W.; Yang, J.; Yang, Z.; Shen, Z. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Improve the Microenvironment of Infarcted Myocardium Contributing to Angiogenesis and Anti-Inflammation. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 2415–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yan, Y.; Wang, B.; Qian, H.; Zhang, X.; Shen, L.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W.; Li, W.; et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate liver fibrosis. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Y.; Jiang, W.; Tan, Y.; Zou, S.; Zhang, H.; Mao, F.; Gong, A.; Qian, H.; Xu, W. hucMSC Exosome-Derived GPX1 Is Required for the Recovery of Hepatic Oxidant Injury. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Shi, Y.; Gong, A.; Pan, Z.; Shi, H.; Yang, H.; Fu, H.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, M.; et al. HucMSC Exosome-Delivered 14-3-3zeta Orchestrates Self-Control of the Wnt Response via Modulation of YAP During Cutaneous Regeneration. Stem Cells 2016, 34, 2485–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, J.M.; Pereira, M.; Wen, S.; Dooner, M.S.; Del Tatto, M.; Papa, E.; Goldberg, L.R.; Baird, G.L.; Ventetuolo, C.E.; Quesenberry, P.J.; et al. Exosomes induce and reverse monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 2016, 110, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Xu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Lv, L.; Liu, N.; Lin, R.; Wang, X.; Shi, B. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal microRNA-143 Promotes Apoptosis and Suppresses Cell Growth in Pancreatic Cancer via Target Gene Regulation. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 581694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Tao, X.; Shen, X. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes inhibit migration and invasion of breast cancer cells via miR-21-5p/ZNF367 pathway. Breast Cancer 2021, 28, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojehdehi, S.; Soudi, S.; Hesampour, A.; Rasouli, S.; Soleimani, M.; Hashemi, S.M. Immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on experimental type-1 autoimmune diabetes. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 9433–9443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdipour, E.; Salmasi, Z.; Sabeti, N. Potential of stem cell-derived exosomes to regenerate beta islets through Pdx-1 dependent mechanism in a rat model of type 1 diabetes. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 20310–20321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigemoto-Kuroda, T.; Oh, J.Y.; Kim, D.K.; Jeong, H.J.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Park, J.W.; Kim, T.W.; An, S.Y.; Prockop, D.J.; et al. MSC-derived Extracellular Vesicles Attenuate Immune Responses in Two Autoimmune Murine Models: Type 1 Diabetes and Uveoretinitis. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 8, 1214–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhao, R.; Yan, F.; Sha, S.; Cui, C.; Song, J.; Hu, H.; Guo, X.; Yang, M.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes exert ameliorative effects in type 2 diabetes by improving hepatic glucose and lipid metabolism via enhancing autophagy. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Shi, H.; Yin, S.; Ji, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, B.; Wu, P.; Shi, Y.; Mao, F.; Yan, Y.; et al. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes Alleviate Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Reversing Peripheral Insulin Resistance and Relieving beta-Cell Destruction. Acs Nano 2018, 12, 7613–7628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, R.; Shen, J.; Hu, X. BMSCs-derived exosomal microRNA-let-7a plays a protective role in diabetic nephropathy via inhibition of USP22 expression. Life Sci. 2021, 268, 118937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Li, C.; Szalad, A.; Wang, L.; Pan, W.; Zhang, R.; Chopp, M.; Zhang, Z.G.; Liu, X.S. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes ameliorate peripheral neuropathy in a mouse model of diabetes. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkat, P.; Zacharek, A.; Landschoot-Ward, J.; Wang, F.; Culmone, L.; Chen, Z.; Chopp, M.; Chen, J. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells harvested from type two diabetes rats promotes neurorestorative effects after stroke in type two diabetes rats. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 334, 113456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Jin, L.Y.; Cui, Y.B.; Xie, N. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal microRNA-17-3p ameliorates inflammatory reaction and antioxidant injury of mice with diabetic retinopathy via targeting STAT1. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 90, 107010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Luan, S.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, Z.; Fu, Y.; Zhai, A.; Bi, C. The MSC-Derived Exosomal lncRNA H19 Promotes Wound Healing in Diabetic Foot Ulcers by Upregulating PTEN via MicroRNA-152-3p. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 19, 814–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Lu, J.; Lu, H.; Jia, W.; Liu, F. Exosomes derived from atorvastatin-pretreated MSC accelerate diabetic wound repair by enhancing angiogenesis via AKT/eNOS pathway. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yu, M.; Xie, D.; Wang, L.; Ye, C.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, F.; Yang, L. Melatonin-stimulated MSC-derived exosomes improve diabetic wound healing through regulating macrophage M1 and M2 polarization by targeting the PTEN/AKT pathway. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grange, C.; Tapparo, M.; Bruno, S.; Chatterjee, D.; Quesenberry, P.J.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Biodistribution of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in a model of acute kidney injury monitored by optical imaging. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wen, S.; Dooner, M.; Papa, E.; Del Tatto, M.; Pereira, M.; Borgovan, T.; Cheng, Y.; Goldberg, L.; Liang, O.; Camussi, G.; et al. Biodistribution of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in a Radiation Injury Bone Marrow Murine Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.; Migliati, E.; Parsha, K.; Schaar, K.; Xi, X.; Aronowski, J.; Savitz, S.I. Intra-arterial delivery is not superior to intravenous delivery of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2013, 44, 3463–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, J.; Wang, J.; Ren, G.; Thakor, A.S. A Novel Approach for Therapeutic Delivery to the Rodent Pancreas Via Its Arterial Blood Supply. Pancreas 2018, 47, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
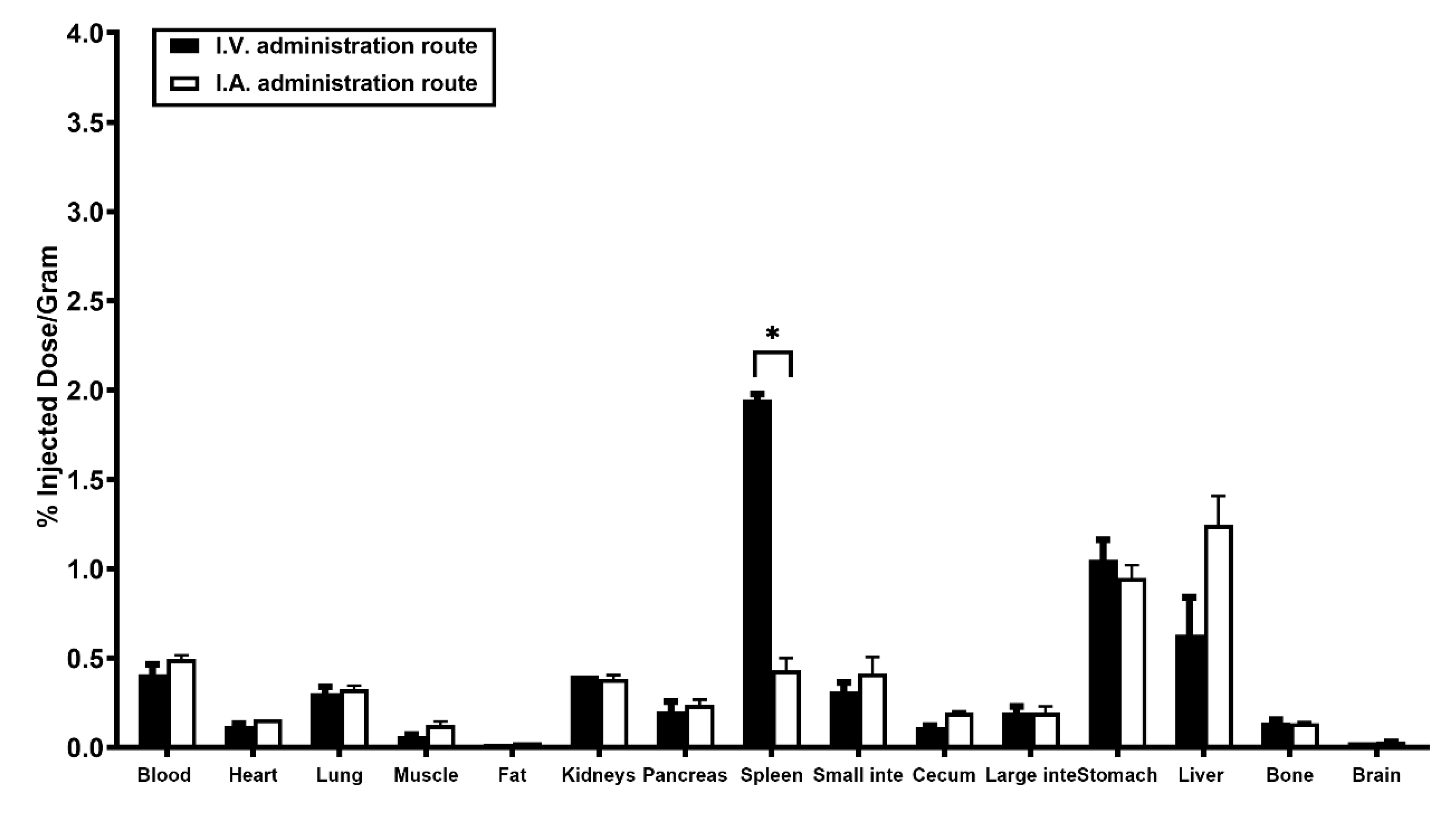

| Organ/Tissue | I.V. Group | I.A. Group | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| blood | 0.41 ± 0.06 | 0.50 ± 0.02 | 0.18 |
| heart | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.16 ± 0.00 | 0.06 |
| lung | 0.31 ± 0.04 | 0.33 ± 0.02 | 0.56 |
| muscle | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.06 |
| fat | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | |
| kidneys | 0.40 ± 0.00 | 0.39 ± 0.02 | 0.42 |
| pancreas | 0.20 ± 0.06 | 0.24 ± 0.03 | 0.47 |
| spleen | 1.95 ± 0.03 | 0.43 ± 0.07 | <0.01 |
| small intestine | 0.32 ± 0.05 | 0.42 ± 0.09 | 0.31 |
| cecum | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 0.01 |
| large intestine | 0.20 ± 0.04 | 0.20 ± 0.04 | >1.00 |
| stomach | 1.05 ± 0.11 | 0.95 ± 0.07 | 0.40 |
| liver | 0.63 ± 0.21 | 1.25 ± 0.16 | 0.08 |
| bone | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.70 |
| brain | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.42 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Komatsu, H.; Poku, E.K.; Olafsen, T.; Huang, K.X.; Huang, L.A.; Chea, J.; Bowles, N.; Chang, B.; Rawson, J.; et al. Biodistribution of Intra-Arterial and Intravenous Delivery of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in a Rat Model to Guide Delivery Strategies for Diabetes Therapies. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050595
Li J, Komatsu H, Poku EK, Olafsen T, Huang KX, Huang LA, Chea J, Bowles N, Chang B, Rawson J, et al. Biodistribution of Intra-Arterial and Intravenous Delivery of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in a Rat Model to Guide Delivery Strategies for Diabetes Therapies. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(5):595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050595
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Junfeng, Hirotake Komatsu, Erasmus K. Poku, Tove Olafsen, Kelly X. Huang, Lina A. Huang, Junie Chea, Nicole Bowles, Betty Chang, Jeffrey Rawson, and et al. 2022. "Biodistribution of Intra-Arterial and Intravenous Delivery of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in a Rat Model to Guide Delivery Strategies for Diabetes Therapies" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 5: 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050595
APA StyleLi, J., Komatsu, H., Poku, E. K., Olafsen, T., Huang, K. X., Huang, L. A., Chea, J., Bowles, N., Chang, B., Rawson, J., Peng, J., Wu, A. M., Shively, J. E., & Kandeel, F. R. (2022). Biodistribution of Intra-Arterial and Intravenous Delivery of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in a Rat Model to Guide Delivery Strategies for Diabetes Therapies. Pharmaceuticals, 15(5), 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050595