Abstract
Natural products have played a critical role in medicine due to their ability to bind and modulate cellular targets involved in disease. Medicinal plants hold a variety of bioactive scaffolds for the treatment of multiple disorders. The less adverse effects, affordability, and easy accessibility highlight their potential in traditional remedies. Identifying pharmacological targets from active ingredients of medicinal plants has become a hot topic for biomedical research to generate innovative therapies. By developing an unprecedented opportunity for the systematic investigation of traditional medicines, network pharmacology is evolving as a systematic paradigm and becoming a frontier research field of drug discovery and development. The advancement of network pharmacology has opened up new avenues for understanding the complex bioactive components found in various medicinal plants. This study is attributed to a comprehensive summary of network pharmacology based on current research, highlighting various active ingredients, related techniques/tools/databases, and drug discovery and development applications. Moreover, this study would serve as a protocol for discovering novel compounds to explore the full range of biological potential of traditionally used plants. We have attempted to cover this vast topic in the review form. We hope it will serve as a significant pioneer for researchers working with medicinal plants by employing network pharmacology approaches.
1. Introduction
It has become a need of the hour to tackle the major concerns that the world has been confronted with regarding global health challenges [1]. Complex diseases, including cancer, diabetes, etc., draw researchers’ attention because these diseases are frequently caused by a malfunction of a complete regulatory network rather than a mutation or malfunctioning of a single gene [2]. As a result, the goal of diagnosing and treating complicated disorders may not be achieved by simply targeting a single gene. However, there is an urgent need to develop innovative approaches to target the entire biological networks that underlie the disease [3,4]. Thus, understanding the molecular pathways that govern disease prognosis are critical in the fight against complicated diseases [5].
Presently, natural products comprise a large portion of current-day pharmaceutical agents, most notably in the area of disease treatments [6]. Natural products have long been a huge storehouse of potent resources for mankind [7]. High throughput techniques have proposed a strong arm in screening the pharmacological efficacy of herbal medicines in drug discovery [8]. One unique way to learn more about how active substances perform their therapeutic effect is to predict the gene networks that are being regulated by active compounds of medicinal plants [9]. Drug discovery faces an efficacy crisis to which ineffective, mainly single-target, and symptom-based rather than mechanistic approaches have contributed. Current one drug–one target–one disease approaches in drug discovery have become increasingly inefficient. While single-target strategies might prove a useful approach for single gene disorders, however, for complicated diseases that are caused by the interaction of multiple genes, such one single-target approaches are not fruitful [10]. The concept of developing multi-target drugs against complex diseases such as diabetes and cancer is fast growing in drug discovery. Regarding this, network pharmacology defines disease mechanisms as networks best targeted by multiple, synergistic drugs. The use of network pharmacology to better understand the mechanism of action of herbal medicines has recently become popular [11,12]. In 2007, Hopkins coined the term “network pharmacology”, which is based on the idea that several highly efficient drugs act on numerous targets rather than just a single one [13]. Moreover, Figure 1 illustrates the origin of network pharmacology.
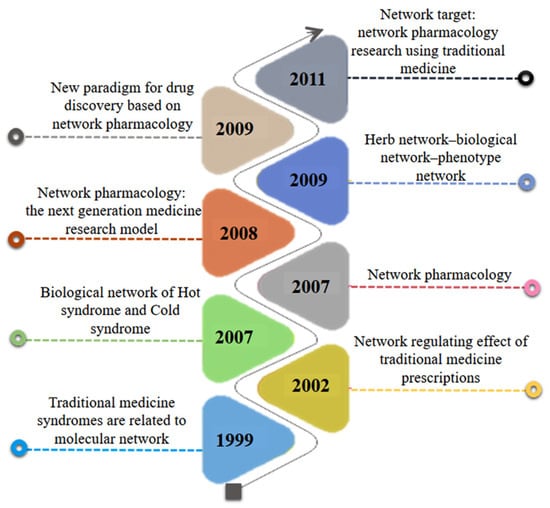
Figure 1.
Timeline diagram representing the origin of network pharmacology.
Network pharmacology is evolving as a frontier in drug discovery and development as it integrates systematic medicine with information science [14]. In the beginning, network pharmacology had a vague conception about drug discovery, and perhaps some overhyping of its promises, as found in the early stages of almost all new technologies [15,16]. At present, one can say that network pharmacology has begun to grow and is a commonly used approach in this modern era-drug discovery process [17]. Network pharmacology is an integrative in silico approach for establishing a “protein–compound/disease–gene” network to reveal the mechanisms underlying the synergistic therapeutic actions of traditional medicines [18]. This advancement, in turn, has shifted the paradigm from a “one-target, one-drug” mode to a “network-target, multiple-component-therapeutics” mode.
The use of bioactive compounds to reform medicines in the future is exciting, and prospects for curing multiple diseases are encouraging [19,20]. This review sheds light on potential correlations between target genes and active ingredients of medicinal plants from a network pharmacology perspective. The present study addresses the break in literature by presenting an integrated approach exploring drug–target interactions to better identify the novel inhibitors for a particular target and their mode of action. This literature review provides a comprehensive overview of the methodology, significance, and application of network pharmacology to cure a wide spectrum of complex diseases. To our knowledge, this baseline review aids researchers in understanding many aspects of biomedicine, from protein synthesis to health and diseases.
2. Network Biology to Network Pharmacology
The advent of highly efficient technologies for analyzing big data has opened new avenues for discovering more intriguing and effective diagnostic and therapeutic solutions [5,21]. Understanding how well the proteins interfere with the functioning of the complex regulatory machinery is critical [22]. This sparked the development of network biology, which asserts that biological networks are commanded by general principles that propose a unique theoretical foundation that ultimately changes our understanding regarding the biology of diseases. Numerous techniques for the construction of regulatory networks were proposed in the 21th century that used computational tools, particularly data mining, to explore the relationship among phenotypes and genotypes of diseases [23]. Innovations in network biology have revealed that single-protein targets are ineffective in treating complicated disorders [24,25]. This prompted drug developers to understand the principle of polypharmacology, which they had previously viewed as an ineffective approach that needed to be eradicated to develop a viable multi-target drug [26,27]. With the emergence of network pharmacology as a completely independent technique, a dramatic change has been observed from extremely specialized single-target drugs to multi-targeted drugs. The next era witnessed the integration of system biology with polypharmacology in various health sides [28,29,30].
3. Network Pharmacology and Traditional Medicine
Over the past decade, local communities used medicinal plants without scientific studies [31,32]. Various medicinal plant species have been utilized in traditional medicines [33,34]. Although medicinal plants impact people’s lives by providing low cost and natural remedies, the unsustainable use and traditional collection and application methods have resulted in the depletion of several plant species of precious worth [35,36]. Traditional medicines, which are described by holistic philosophy and extensive experimentation in multicomponent treatments, provide promising potential for controlling the complicated nature of disorders [37,38,39]. Using herbal formulae is a unique aspect of traditional medicine [40]. In this era of big data, the reengineering of traditional medicines may be performed by simply understanding the combinatorial nature of herbal formulae as well as their mechanisms of action [41,42]. Today’s network pharmacology provides a novel opportunity to investigate not only the molecular complexity of herbal formula but also the correlation that exist among the herbal formula and complicated disorders in a systematic manner [43,44]. Herbs used in traditional medicines have indicated a best molecular match, which might elicit a more consistent network reaction than a single drug [45,46,47]. Network-based methodologies are becoming more popular research tools in areas of new drug development. They assist in comprehending innovative treatments by utilizing natural products as the lead compound responsible for drug synergism and cumulative activity. These techniques have been proven to work in a variety of herbal compositions used in traditional medicine [48,49,50].
Network pharmacology is considered a modern-era approach for identifying active compounds and putative molecular targets from a wide variety of herbal formulae or simple herbs [51,52,53]. This integrated approach is a touchstone for the initial screening of medicinal plants’ bioactive compounds and a new therapeutic concept for further exploration on mechanisms’ active compounds for disease treatment [54,55]. As a result, incorporating network pharmacology in traditional medicine will offer unique and novel options for uncovering active compounds, biomarkers, and the scientific basis of traditional medicine based on the complicated biological systems of the human body [54,56,57].
4. From Polypharmacology to Network Pharmacology: The Need to Reengineer Botanical Drugs
Even if healing is magical, it is unbelievable that there is a therapeutic effect without molecular interactions between the biological target and treatment. Medicinal plants that hold millions of potentially active ingredients frequently fail to disclose the expected molecular mechanisms of action [3,58,59,60]. Usually, standard biochemical methods are incapable of elucidating viable action modes. Despite such an average response, more research is pressingly demanding steps to achieve outstanding output in the future. Various active ingredients in medicinal plants have no more-robust connections with target proteins of the regulatory network; therefore, a synergistic approach is highly preferable that can switch off the action of harmful proteins, which in turn targets whole molecular networks that underlie the disease state [61,62].
Integrating network biology with polypharmacology can broaden current views on druggable targets while also aiding in understanding the pharmacological action of herbal medicines [13,63,64]. Polypharmacology and synergism discoveries are laying the groundwork for drug discovery in the following modern era of big data. Polypharmacology broadens the scope of drug discovery [65,66,67]. Molecules are linked to one another in orderly fashions that are characterized by strong binding affinities. Polypharmacology integrated with breakthroughs of structural biology and chemoinformatics has paved the way to develop licensable drugs with no side effects [68,69].
Network pharmacology could be an excellent place to start. The term “network pharmacology” mainly emphasizes the existence and importance of multi-targeted drugs instead of single-targeted drugs [70,71]. Hopkins recommended three approaches to develop a multi-target therapy: He began by prescribing a multidrug made up of many individual drugs. Designing of a multi-component drug was the second-most-important postulate. Designing a single drug acting on multiple targets was the last option. As per Hopkins’ view, the last postulate is advantageous since it would make dosage trials easier [13,63]. Virtual pharmacology and in silico analysis could be useful new tools in herbal medicine research. The underlying pharmacology, in particular, should be a primary consideration. More rigorous investigations on the bioavailability of natural products will undoubtedly lead to progress before these chemicals are used in in vitro experiments. Furthermore, research into the pharmacodynamics of natural compounds is critical in understanding pharmacological synergies and the potential network pharmacology of medicinal plants [12,72,73].
5. Methodology of Network Pharmacology Research
Network pharmacology research revolves around identifying compound- and disease-related genes, constructing a protein–protein interaction (PPI) network, and lastly, analyzing and visualizing the network [74,75,76]. The construction of molecular networks from large databases is a simple start. Then, using network analysis, key nodes are identified and key biological pathways are predicted [77]. Finally, additional network validation is performed to successfully validate the interaction between highly active constituents and their putative targets [78,79]. In this review, we highlighted all the steps of network pharmacology research. The workflow is displayed in Figure 2.
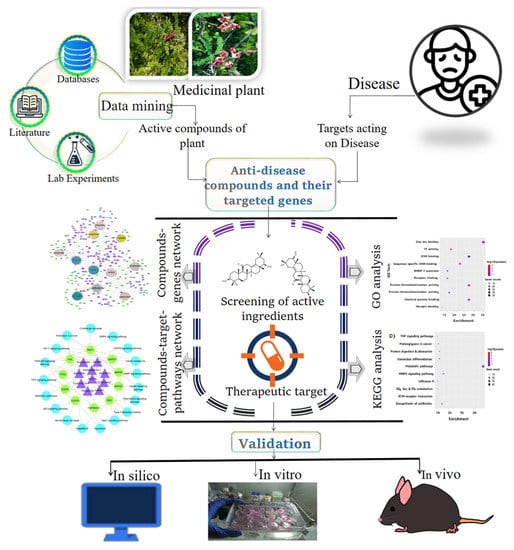
Figure 2.
Graphical synopsis of network pharmacology research for the discovery of herbal medicines-derived targets, effect prediction, mechanism clarification, and new drug assistant discovery using network pharmacology approach. It analyzes the information from public data, high-throughput experimental data, and herbal medicinal data and constructs network using technologies of network expansion, optimization, comparison, knockout, and addition. Finally, it carries out computational and experimental verifications.
5.1. Data Mining
Identifying active compounds of medicinal plants and diseases-related targets is the preliminary step in network pharmacology research. Generally, a literature search is carried out to identify active compounds; however, various public databases provide a user-friendly interface to predict the active compounds of the medicinal plant [9,12]. After obtaining active compounds, the canonical SMILES of active compounds are retrieved from available public databases. Some online and standalone tools are available, which become a handy platform for identifying canonical SMILES [80]. After obtaining canonical SMILES, network pharmacology research turns around gene prediction or from canonical SMILES. To perform this task, a list of user-friendly tools and databa.ses are available. Another important thing is that we can get statistically significant genes by applying precise cutoff on the probability of genes and obtaining highly significant genes. The prediction of disease-related genes is a preliminary step to explore the molecular mechanism of medicinal herbs for treating multiple diseases and disorders [81,82]. Additionally, instead of relying on literature data, the target gene can also be obtained through real experiments; for example, researchers have now analyzed the transcriptome-wide gene expression microarray profiles of isolated cells in response to the exposure to plant extracts, their combinations, or purified compounds, followed by ingenuity pathway analyses in silico to elucidate their mechanisms of action and activated molecular networks behind predicted therapeutic effectiveness in various health conditions [83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93].
5.2. Network Construction and Analysis
Venn diagrams tools are preferable for identifying overlapped targets of diseases and compounds. This step mainly aims to predict disease-related genes and subsequently identify the common genes between diseases and compounds. The common genes are initial touchstones for further screening [94,95]. Network analysis is carried out to understand the mechanism of medicinal plants in disease treatment. Protein–protein interactions (PPI) are highly significant by virtue of having a high versatility, adaptability, and specificity [78,96]. The PPI network of key targets (common genes) is obtained through databases that provide the functional interactions among key targets [96,97]. Later, the network analysis is performed to predict the hub genes that have the best degree of connectivity. Biological networks supply us with a wealth of data [98]. The important point is how to retrieve key information from networks. Network analysis tries to uncover important targets, active ingredients, and their associated pathways by identifying targets. Network analysis employs a variety of methodologies, the most common of which is network functional analysis. Biological networks have been discovered to have a modular aspect, and many beneficial drugs have therapeutic effects by modulating several proteins instead of using a single protein. Several subnetworks having particular roles and topologies in large and complicated networks have been unveiled via topological research. At a functional level, GO enrichment analysis and KEGG pathway analysis provide exclusive key target features by exploring their associated pathways [43].
5.3. Validation of Results
It is important to verify the results obtained through the aforementioned steps. Various validation methods are available to confirm the efficacy of predicted molecular targets. In vitro and in vivo are generally considered the most viable methods, but these methods are time-consuming and require a high cost to yield correct results. However, with the emergence of high-throughput technologies and advancement in the genomic era, various in silico approaches have been designed, providing a handy platform for validation of results [99]. Lastly, both experimental and virtual methods are available to validate the predicted results.
Receptor–ligand molecular docking is used to predict the docking sites of active ingredients and key targets derived from network pharmacology. Therefore, network pharmacology and molecular docking effectively bridge the gap between western medicine and herbal medicine and greatly facilitates mechanistic studies on the synergistic actions of herbal medicines. Molecular docking has become a lightning rod and the most applicable approach in the drug discovery toolbox [100,101]. Molecular docking enables the prediction of interaction that ties up ligands with their corresponding proteins in a bound state [102]. Most researchers used the molecular docking approach for validation [96,103]. Mainly docking score and binding energy are considered key criteria for constituent screening. A list of studies has witnessed the importance of molecular docking as a validation technique in network pharmacology.
Zhang et al. [104] performed molecular docking to screen out the putative targets of Prunella vulgaris L., which can lower the risk of breast cancer. Docking analysis successfully predicted the strong binding affinity between active constituents of Prunella vulgaris L. and binding pockets of target proteins. In the work of Liu et al. [105], combined network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis were performed to uncover the molecular targets and mechanism of Huangqi Guizhi Wuwu decoction for treating rheumatoid arthritis. Through network analysis, a total of 790 compounds was obtained. Later molecular docking analysis revealed that out of 790 compounds, quercetin, kaempferol, and beta-sitosterol have a strong binding affinity with target proteins (VCAM1, JUN, and CTNNB1). Therefore, quercetin, beta-sitosterol, and kaempferol exhibited therapeutic effects on molecular targets and their associated pathways. Furthermore, Ruan et al. [106] uncovered the action mechanism of Dayuanyin for the treatment of COVID-19 by employing network pharmacology. Based on network analysis, they used molecular docking to validate predicted results. Molecular docking analysis revealed the binding affinity of active ingredients, namely naringenin, kaempferol, formononetin, quercetin, isofavone, and 7-Methoxy-2-methyl with core target genes (Interleukin 6, Interleukin 1B, and CCL2). In conclusion, molecular docking mainly aims to validate the successful activity of the active compounds against potential gene targets. The information obtained through molecular docking might aid researchers in understanding many aspects of biomedicine, from protein synthesis to health and disease.
Gene expression microarray analysis is also an un-doubtful technique for validating predicted results. Gene expression microarray analysis is the measurement of the activity of thousands of genes at once to provide a global view of cell processes. These profiles can be used to differentiate cells that are actively dividing or to illustrate how cells respond to a certain therapy. High-density microarrays are among the most powerful and versatile methods for analyzing the expression patterns of huge numbers of genes across different tissues or within the same tissue under various experimental circumstances. The widespread use of microarray technologies generates vast amounts of data, which encourages the development of improved analytical methods to anticipate the activities of target genes. To examine the differential gene expression levels of putative targets, gene expression data are downloaded from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) [107]. GEO is a freely available public repository of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), which encloses the gene profiles. Only those genes are significantly expressed with a logFC value ±1 with an adjusted p-value < 0.05. If the logFC value is negative, then that gene is marked as downregulated, and a gene having a positive logFC value is called upregulated. Hence, these profiles are utilized at various phases of the network pharmacology process, which aid in identifying new drug targets, predicting novel gene activity, and understanding individual drug response variability.
Researchers use microarray analysis to validate predicted results in some network pharmacology studies. After successfully performing microarray analysis, they move toward real time-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) to validate the differentially expressed target genes identified after microarray analysis. RT-PCR is now a well-established method for detecting and quantifying target genes in clinical diagnosis and treatment. One key application of this technology as a research tool is the rapid and accurate assessment of changes in gene expression due to pathophysiology, physiology, and development.
Hong et al. [108] predicted putative targets of flavonoids from citrus to treat non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by employing a network pharmacology approach. They used microarray analysis and RT-PCR for the validation of predicted results. They finally predicted VEGF-C as a key target of pure flavonoid from citrus to treat non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Zhang et al. [109] used a network pharmacology-based methodology to predict active constituents of Huangqi decoction against rat liver fibrosis. After performing network analysis, they used both gene expression profiling analysis and RT-PCR to validate the results. They finally demonstrated the strong actions of Huangqi decoction against rat liver fibrosis. Furthermore, Li et al. [110] also used the same methodology and revealed the targets of Sinomenine for the treatment of breast cancer.
Western blotting is another unquestionable and reliable technique for the validation of expression levels of target genes. Researchers commonly use Western blotting to validate the results derived using the target–pathway interaction network. The accuracy and reliability of results provided by Western blot analysis increase the confidence of researchers, which ultimately leads to make ground-breaking discoveries in the field of drug discovery and development. A list of studies evidenced the accuracy of Western blot analysis. Cai et al. [111] used Western blot analysis to validate results derived after network analysis. They finally concluded that Yinchenhao decoction suppresses the rat liver fibrosis involved in regulating multiple targets, especially affecting the apoptosis-related signalling pathways. Guo et al. [112] used Wu-Tou decoction to treat rheumatoid arthritis. For validation of results, they used Western blotting. Their study revealed that Wu-Tou decoction plays an important role in inhibiting inflammatory response in rheumatoid arthritis and is closely connected with the modulation effect of Wu-Tou decoction on the CCR5 signalling pathway in macrophages. Furthermore, wang et al. [113] investigated the multi-targets mechanism of triphala on cardio-cerebral vascular diseases by employing network pharmacology and Western blot analysis. Their study revealed that pharmacological mechanism and complicated components of Triphala, which could provide a theoretical basis for the research and development of new drugs for treating cardio-cerebral vascular diseases.
Generally experimental verifications such as in vivo analysis are mandatory in many studies in order to deeply analyze the results [114,115]. Based on the complicated nature of diseases and validation processes, researchers worldwide explored a new strategy to improve the efficiency of active ingredients screening, which ultimately helps in the discovery of some multi-target compounds with biological activity for the development of novel drugs against disease. Nowadays, researchers use the mouse model to successfully validate predicted results and make innovative treatment options against the deadliest diseases. In network pharmacology research, the effect of active compounds of medicinal plants on key disease signalling pathways are validated using a mouse model.
Qin et al. [12] used network pharmacology to predict the mechanisms of action of Shenkang in chronic kidney disease. They performed both pharmacological network analysis as well as in vivo validation for determining the potential effect and mechanisms of Shenkang in the treatment of chronic kidney disease. Their study proposed that Shenkang exerted a curative effect on chronic kidney disease and chronic kidney disease-related diseases by targeting different organs, proliferation processes, and regulating inflammation. Furthermore, Liu et al. [116] employed both network pharmacology and in vivo validation to understand the pharmacological mechanism of the Xianglian pill against ulcerative colitis. Their study revealed the clinical treatment efficacy of the Xianglian pill for ulcerative colitis.
Lastly, the quantification of validated data can be performed using several integrated approaches such as proteomics, transcriptomics, genomics, metabolomics, and high-throughput screening (HTS) [117]. HTS is an efficient approach to the modern era. HTS is a method for scientific experimentation that is particularly useful in drug development and is applicable to system biology, chemistry, and many other fields. HTS technology can swiftly discover billions of data samples and predict the effect of chemicals/compounds on specific molecular pathways [118,119]. Furthermore, this dual and novel high-throughput technology enables network data collection from experiments/trials and ultimately validates the network model’s accuracy. For instance Fakhari and Dittmer developed PCR chip technology to analyze gene expression [120]. The findings revealed that the method was suitable for high-throughput research. Another method is to validate the molecular interaction that exists between networks. This method yields a new perspective in the context of understanding drug activity mechanisms and the validation of the drug network or predicted model. It mostly consists of surface plasmon resonance (SPR) and biolayer interferometry (BLI) technologies, which can aid researchers in discovering the interaction between drugs and biomolecules [121,122]. High-throughput, high-precision, and real-time detection are all used in BLI and SPR techniques.
In short, network pharmacology along with validation techniques help in the discovery of key pharmacological mechanisms of herbs/herbal formulae. These integrated approaches lay a foundation for treating complex diseases by using medicinal plants. Therefore, more innovative and novel strategies must be applied to fully understand the therapeutic mechanisms of medicinal plants.
6. Research Approaches of Network Pharmacology
Network pharmacology can affect drug discovery and development in two ways: One method is to create a realistic network model and forecast the pharmacological target using public datasets or data from previous studies. Following that, the network equilibrium concept should be investigated through the mechanisms of functional drugs. Gu et al. [123] evaluated the impact of Rheidin A and C, along with Sennoside C, using this technique, and it was the first study on multiple integrated drugs for type 2 diabetes. The alternative strategy uses bioinformatics approaches and high-throughput technologies to construct a “drug–target–disease” network. The drug’s action in various biological processes was investigated by comparing the drug’s interaction with the network. In the literature, there are numerous examples of network pharmacology being used in drug development. For example, Li et al. [124] employed the Liuwei Dihuang tablet to forecast the best network targets and discovered that multi-layer networks could underpin the integrated action mechanism of herbs and herbal formulae. Furthermore, it has been shown that salvianolic acid B was appropriate and viable for treating cardiovascular disease by combining the previous study methodologies [125]. In conclusion, advances in systems biology and bioinformatics change our understanding of the treatment and diagnosis of diseases through medicinal plants from a network pharmacology perspective and ultimately contribute substantially to the modernity of medicinal plants.
7. From Network Pharmacology to Integrated Multi-Omics Approaches
Recent advancements in sequencing technologies have countered the revolution in various integrated approaches, in which the one named omics is the emergent field. With time, biology gradually depends on the data derived from multi-omics data [126,127,128]. Multi-omics data aimed to point out the interrelation among biomolecules, hence multi-omics data has paved the way for understanding function as well as interrelation among biomolecules [129,130]. Network pharmacology has evolved into a strong method for uncovering complicated biological interactions systematically. Network pharmacology uses “omics” techniques to detect variations at core molecular and cellular levels in terms of a specific pathophysiology or pharmacological treatment [9,131,132]. The obtained dataset aids in the generation of networks that describe molecular processes from the genetic to the metabolomics level. The main omics approaches used in network pharmacology are epigenomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics. Because there are so many molecular pathways and epigenetic effects on the phenotypic expressions of diseases, hence, a systems biology approach based on innovative modeling approaches is essential for investigating gene–environment interactions and therapy success [132,133,134]. The study of epigenetic alterations has yielded a wealth of information about prognostically important genes.
Several studies have been made on the mechanisms adopted by a cell to perform its functions better. As cells are comprised of the same set of genes, why does each gene behave differently from one another? Here comes a phenomenon named epigenetics. For a stage-by-stage characterization of epigenetic genes, a systems biology method was used, and epigenetic sub-network analysis identified a collection of conserved genes. Thus, the integration of network pharmacology demonstrated the existence of epigenetically de-regulated functional hotspots, which ultimately helps in fighting against disease by understanding the underlying mechanism in the progression and pathogenesis. For example, Gnad et al. [135] utilized differential gene expression as well as correlation network analyses to find dysregulated epigenetic regulator genes in cancer and found EZH2 to be the most significantly overexpressed epigenetic regulator in cancer that was classified as an oncogene. Furthermore, the bioinformatics analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) may aid in the prevention of adverse drug reactions in certain patient groups and develop new medical interventions.
8. Merging the Molecular Disease Network with the Pharmacological Network of the Candidate Drugs
The biological clock of life has recently been progressively investigated from a systems approach across fields of science and technology. There has already been a lot of work conducted to develop practical frameworks for bringing “systems thinking” to improve public health. The minimum distance among proteins was evaluated in the published paper, which highlighted the links between drug targets and disease-target products. Considerable differences were discovered between analgesic and etiological medicines, and the research revealed a modern trend towards rational drug design. The integration of disease-related targets and drug targets through network biology has become a crucial step in developing novel and putative drugs [136,137,138].
In contrast, drug repurposing, which uses old drugs to develop new and better drugs, would be possible with network pharmacology methodologies. A new pharmaceutical product takes at least ten to fifteen years to develop and costs between $500 million and $2 billion, but there has been a steady rate of introduction of new drugs. Existing drugs already have clinical evidence, so getting them approved for a new use takes very little energy and money [139,140,141]. Alternatively, we may use other techniques to screen out existing drugs and analyze which herbal formula or herb has the potential to act as a drug. As a result, we offer an approach for the repurposing of old drugs based on network pharmacology.
9. Implications of Network Pharmacology for Therapy
The widespread failure of specific candidate drugs to progress from pre-clinical to clinical trials raises the question of whether a particular drug discovery is the best technique. Due to the poor understanding and validation of these targets in patients, even using medications operating on defined targets coupled to robust biological networks is difficult [142]. As a result, network pharmacology is becoming increasingly essential, and it is attracting a lot of interest in contemporary drug discovery [3]. For example, pleiotropic active ingredients targeting numerous proteins and biological processes in cancer-related networks could be effective. Herbal medicinal treatments are used all throughout the world to keep people healthy. Due to their diversity in structure, bioactivity, and nontoxicity, herbal medicines are recognized as a significant fountainhead for new active molecules in drug discovery, drawing global attention [143]. The paradigm of “one disease, one drug, one target” is giving way to “one disease, one drug, several targets”. Network pharmacology examines when and where one target can suppress disease characteristics, such as tumor progression, leading to the development of medicines that do not induce side effects. Network pharmacology’s benefits have become incredibly influential in drug discovery, particularly in repurposing old drugs [144]. Computational drug designing aided by network-based methodologies helps in predicting the adverse effects of drugs and helps the drug molecule find its target binding site [145]. Network pharmacology offers new drug discovery options that may be more fruitful than using herbal medicine without any scientific basis. This hypothesis drew interest since it offered the possibility of having efficient therapies that were more targeted and had less adverse effects in normal body cells. Network pharmacology may offer novel options for rigorous target selection and the development of multi-target, distinctive active compounds to treat them [28]. In the PPI network, highly linked regions are highly preferable because these nodes are considered the main target in the disease state. Hence, by targeting such nodes, we can achieve the goal. On the other hand, drugs cannot block all targets in a regulatory network. Only around fifteen percent of nodes in a particular network are druggable [146,147]. Multiple approaches to generating appropriate phyto-therapies based on network data can be considered:
- If the potentially active compounds of herbs or herbal mixes are identified, they can be considered. This technique is mostly made based on their use in herbal medicine. Herbal formulations are similar to multi-drug targeted therapy [51].
- Active compounds can simply be used to achieve multi-target specific therapy using selective poly-pharmacological methods [148,149]
- Proteins that are not required in normal cells could become therapeutically important if they’re linked together in a cancer network. Their simultaneous eradication or inhibition could result in more effective or even synergistic tumor cell eradication. What makes perfect sense in the human physiological process is to create significant therapies options. A potential answer to this difficulty could be to use polypharmacology to disrupt whole disease-causing networks using botanicals or sophisticated herbal mixes that target numerous targets, rather than knocking out specific proteins [150,151].
10. Databases and Data Analysis Tools Related to Network Pharmacology
Biologically important databases that provide a huge amount of data related to the relationship between biomolecules enable the researcher to use network pharmacology as a modern era drug discovery approach (Table 1). All these databases and tools are freely available, and providing a free hand to users can be useful in retrieving valuable information from the perspective of network pharmacology research.

Table 1.
List of available resources for network pharmacology research.
11. Application of Network Pharmacology: From Understanding of Complex Interactomes to the Design of Multi-Target Specific Therapeutics from Nature
Despite the research and development in pharmaceutical industry, the dramatic drop in the number of new treatments options raises the question of whether single-targeted drug discovery is a felicitous approach or not. In such scenarios, network pharmacology approaches are extremely valuable, as they differ from traditional drug discovery approaches by addressing the potential of drugs to target several proteins or networks involved in a disease [197]. Furthermore, employing high-throughput screening and bioinformatics aids in the construction of predicted drug–target disease network models. Such approaches help to explore the underlying mechanisms of drug actions on biological networks by comparing the interaction of a drug with its respective target model. The knowledge of multi-facetted pathway interactions considerably strengthened with recent advancements in network biology. Therefore, network pharmacology is solidifying its position in the treatment of the deadliest diseases and disorders.
Network pharmacology discerns the protein–protein interactions associated with clinical outcomes of particular diseases and disorders. Nowadays, researchers are merging multi-omics approaches with computer technology to precisely record the unified metabolic response in humans to study an increasing number of complicated disorders. Below, we discuss some exclusive applications of network pharmacology in biomedical sciences. Figure 3 presents important applications of network pharmacology.
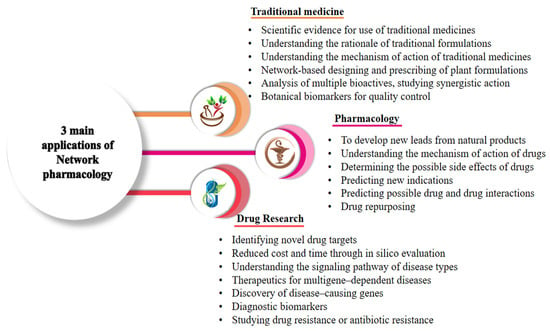
Figure 3.
Three main application of network pharmacology in health biology for exploring the basic pharmacological effects of drugs on diseases and their mechanisms.
11.1. A Pneumonia Outbreak Associated with a New Coronavirus of Probable Bat Origin
SARS-CoV-2 is a β-coronavirus belonging to order Nidovirales and family Coronaviridae. The other β-coronaviruses, including Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome [198] in 2002–2003 and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome [199] in 2012–2013, have also been reported in the past two decades [200,201,202]. However, COVID-19 is a large-scale pandemic of the 21st century and an alarming public health issue. Numerous clinical research endeavors have revealed that traditional medicines have a substantial effect on COVID-19 treatment, offering new promise for the management of COVID-19. Using network pharmacology, herbs/herbal formulae could also be incorporated in the COVID-19 diagnosis and treatment protocols. Numerous studies have been conducted that used network pharmacology to screen out the active compounds of medicinal plants for the treatment of COVID-19. Jin et al. [203] used Xuebijing injection, Wang et al. [204] used Qingfei Paidu decoction, and Li et al. [205] used Lianhua Qingwen and found that these formulae and medicines are viable to be used against COVID-19 treatment. As a result, it served as a starting point for a more in-depth exploration of the cornerstone of antiviral granules and a novel treatment concept for COVID-19.
Tao et al. [100] employed network pharmacology and molecular docking to understand the action mechanism of the Huashi Baidu formula against COVID-19. Their findings proposed that active compounds of the Huashi Baidu formula control numerous signalling pathways via ACE2, which might play a therapeutic role in treating COVID-19. These pathways include the MAPK signalling pathway, TNF signalling pathway, and the PI3K–Akt signalling pathway. Further molecular docking revealed that baicalein and quercetin were the top two compounds, indicating that both compounds could play a significant role in treating COVID-19. Another research performed by Zhang et al. [206] demonstrates the chemical compounds present in the lung-cleaning and toxicity-excluding (LCTE) soup for the treatment of COVID-19 in a network pharmacology perspective. Their findings suggest that the LCTE soup contains ingredients that have the ability to directly inhibit the progression of COVID-19. Moreover, LCTE targets the pathways that are mainly involved in viral and other microbial infections, inflammation/cytokine response, and lung diseases. Their research provides a biological foundation for employing LCTE soup to treat COVID-19 and its symptoms. Furthermore, Niu et al. [74] studied the action mechanism of three medicines (Jinhua-Qinggan Granule, Xuebijing Injection, Lianhua-Qingwen Capsule) and three herbal formulae (9 *HuaShi-BaiDu Formula, Qingfei-Paidu Decoction, and XuanFei-BaiDu Granule) against COVID-19 by using a network pharmacology approach. Their findings suggested that these three medicines and three formulae has been shown to have a positive effect on the prevention and rehabilitation of COVID-19 in at-risk individuals. They proposed that luteolin, ursolic acid, quercetin, and rutin could inhibit the progression of COVID-19 by downregulating the interleukin-6. Finally, we conclude that medicinal plants contain pythochemicals that have the ability to directly suppress the COVID-19, target proteins associated with common COVID-19 symptoms and influence the disease-related major pathological processes.
11.2. Cancer
Cancer is indeed one of the causes of morbidity and mortality in humans and remains a significant major health concern worldwide. Cancer can be efficiently addressed as a multifactorial disease by modulating various targets and carcinogenic signalling pathways [207,208]. As in the case with cancer, single-targeted drug discovery has shown to be unsuccessful in combating complicated systemic diseases with complex biological systems [142]. In these scenarios, network pharmacology approaches are extremely valuable since they vary from traditional drug discovery by addressing multi-targeted drugs that ultimately target many proteins or networks involved in the progression or development of disease states [131]. Techniques based on network pharmacology have the potential to dramatically minimize the difficulties in routine clinical research, such as patient heterogeneity in population and disease. Furthermore, cancer is heterogeneous, primarily characterized by the existence or lack of relevant therapeutic targets. There are currently very few treatment approaches available for heterogeneous populations with heterogeneous malignancies [209,210]. As a result, there is a pressing need to create network pharmacology-based methodologies to change the current concept of drug designing and increase our understanding of the mechanism of action. The proper application of network pharmacology-based methodologies may help to avoid problems in cancer drug therapy and speed up the discovery of new anticancer medicines. Moreover, network-based studies proposed target genes as promising and viable therapeutic targets to reduce the incidence of cancer, thereby exerting potential therapeutic effects in cancer.
A HER2-positive breast cancer is one that tests positive for the protein human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). This protein stimulates cancer cell proliferation. Cancer cells in around one out of every five breast tumors have extra copies of the gene that produces the HER2 protein. Zeng et al. [211] used a network pharmacology-based methodology to explore the pharmacological mechanism of Yanghe decoction against HER2-positive breast cancer. They proposed quercetin, luteolin, and naringenin as key active ingredients of Yanghe decoction that may have anticancer properties. Their findings successfully predicted, illuminated, and confirmed the molecular synergy of Yanghe decoction for HER2-positive breast cancer.
Zhen et al. [212] explored the active ingredients as well as important pathways of Shen-qi-Yi-zhu decoction against gastric cancer. In a nutshell, their research demonstrated that a combo of network pharmacology and in vitro studies clarifies the efficient and beneficial molecular mechanism of Shen-qi-Yi-zhu decoction. They also proposed that Shen-qi-Yi-zhu decoction plays an anti-tumor role by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is found in almost all tumors and plays a key function in cancer biology. Hence, the herb/herbal formulae played an important role in the anti-tumor area.
Colorectal cancer, a silent monster, is indeed the leading cause of cancer-related death. Liu et al. [213] used a network pharmacology approach for the identification of action mechanisms of Hedyotis diffusa against colorectal cancer. Network analysis revealed that Hedyotis diffusa exhibited a promising therapeutic impact on colorectal cancer by targeting tumor-associated signalling pathways. This provides a foundation for understanding the anti-colorectal cancer activity of Hedyotis diffusa. Song et al. [214] used the same plant (Hedyotis diffusa) for uncovering the multi-target pharmacological mechanism on prostate cancer. Therefore, it has become clear that using network pharmacology, we can screen the active compounds of single herb/herb formulae for the treatment of more than one disease. Bing et al. [215] used bioinformatics and network pharmacology approaches to investigate the mechanism of Fuzheng Kangai for lung cancer treatment. Furthermore, Meng et al. [216] incorporated a network pharmacology approach with molecular docking to uncover the molecular mechanisms of Kushen injection to treat lung cancer. In short, network pharmacology yields a new perspective in understanding the action mechanisms of herb/herbal formulae for the treatment of various types of cancer.
11.3. Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases (CCVDs)
Cardiovascular and cerebral vascular diseases have become some of the world’s most serious health problems [217]. Botanical drugs, of long-used medicinal plants, have been shown to provide many benefits for CCVD treatment [205,218]. However, the molecular mechanisms underpinning medicinal plants’ ability to heal CCVD are still unknown. Currently, a novel systems-pharmacology platform named network pharmacology has been proposed to comprehensively understand the pharmacological mechanism of medicinal plants for the treatment of CCVDs by merging pharmacokinetic screening, target identification, and network analysis. This approach offers a new paradigm for systematically understanding the mechanism of herb/herbal formulae against CCVDs.
In the light of network pharmacology, Yang et al. [219] elaborated on the active compounds of Ginkgo biloba leaves, their potential target, and associated pathways for treating CCVD, hence providing a theoretical basis for additional experimental research. Their findings revealed that Ginkgo biloba leaves exhibit a protective effect on CCVDs, most likely by regulating various processes and attacking multiple targets linked to a variety of biological pathways. Their study provides an important reference for understanding the efficacy of Ginkgo biloba leaves in the treatment of CCVDs and a fresh technique for discovering new medicines from plants. Ren et al. [220] used herbal formulae for the treatment of stroke. In their work, screening results represented various bioactive compounds that played a decisive role in treating stroke by targeting the disease-related genes.
Tao et al. [221] employed a network pharmacology-based methodology to predict active ingredients along with putative targets of the Radix Curcumae formula for the treatment of CCVDs. Their study systematically demonstrates the mechanism of the Radix Curcumae formula in the treatment of CCVD, while also predicting potential targets to facilitate the development of candidate herbal drugs in future work. Wang et al. [222] explored the active compounds of Salvia miltiorrhiza Burge. and Carthamus tinctorius L. for the treatment of CCVDs. Their study revealed that Salvia miltiorrhiza Burge. and Carthamus tinctorius L. may promote cerebral blood flow by dilating blood vessels, reducing neurotoxic damage, and protecting brain tissue from free radical damage.
Cui et al. [223] employed a network pharmacology approach to uncover the mechanism of Shuxuening injection against ischemic stroke. Their findings demonstrated that by suppressing inflammation and regulating the degree of oxidative stress, Shuxuening injection could treat ischemic stroke and minimize the death of neuron cells in brain tissue, thus safeguarding the brain tissue of rats. Their study combined network pharmacology, molecular docking, and animal experiments to provide the first coherent and detailed investigation of Shuxuening injection mechanism for the treatment of ischemic stroke and comprehends the multi-component and multi-target synergy mechanism of Shuxuening injection [223].
Furthermore, Chen et al. [224] identified the active compounds and putative targets of the Yangxinshi tablet to treat heart failures by using network pharmacology research. Their analysis revealed the cardiovascular protective effect of the Yangxinshi tablet, which was primarily enriched in immune and cardiovascular systems. The network-based study could aid researchers in simplifying the complex mechanism of the Yangxinshi tablet. It may also provide a realistic method for determining the chemical and pharmacological foundations of other herbal formulae.
11.4. Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a pandemic of the 21st century and is a rapidly growing global problem [225]. DM is associated with the diverse interplay of genetic, environmental, and behavioral risk factors [226]. People with DM are more susceptible to a variety of short- and long-term problems, leading to serious complications [227]. Network pharmacology consisting of natural products is seen as a viable therapeutic method for DM and could provide answers to the questions raised above. Wang et al. [228] employed a network pharmacology-based approach to explore the active ingredients of Astragaloside IV as a best treatment option against type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Recent findings demonstrated that docking analysis as well as network analysis might drastically cut preliminary screening expenditures and offer a complete analysis of the action mechanism in the development and discovery of novel drugs. Gu et al. [123] used a combination of network pharmacology and molecular docking studies to demonstrate the action mechanism of Tangminling tablets for the treatment of T2DM. The compound–compound network and compound target network demonstrated that over 100 chemical ingredients out of 667 in the formula could target 37 T2DM-related target proteins. The important ingredients in Tangminling tablets were anticipated, and a few of them have previously been described in the literature. Furthermore, due to their pharmacological actions, numerous chemical compounds, particularly procyanidin C1, Rheidin A, Rheidin C, Sennoside C, and Dihydrobaicalin, were important and used as anti-diabetic candidates.
Sorghum bicolor is rich in anti-diabetic bioactive constituents and is a plausible resource of anti-diabetic ingredients. Oh et al. [229] employed network pharmacology to identify active compounds of sorghum bicolor having the potential to treat diabetes mellitus. Their findings imply that essential active ingredients are present in sorghum bicolor, which may help to reduce the severity of T2DM by activating the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors’ (PPARs) signalling pathways. According to the results of their study, the anti-diabetic activity of sorghum bicolor can be linked to four main compounds (alpha-sitosterol, propyleneglycol monoleate, campesterol, and 25-Oxo-27-norcholesterol) that are highly associated to the PPAR signalling pathway.
In the work of Zhou et al. [230], a network pharmacology-based methodology is used to analyze the mechanism of Xiao Ke Yin Shui for the treatment of T2DM. Their study proposed that proteins such as protein kinase B, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and tumor necrosis factor are primarily regulated by compounds present in Xiao Ke Yin Shui’s formula. Therefore, the Xiao Ke Yin Shui formula has synergistic therapeutic benefits and has an anti-diabetic impact primarily via lowering insulin resistance.
11.5. Neurodegenerative Diseases
Neurodegenerative diseases are conventionally demarcated as progressive degeneration and/or death of nerve cells. Neurodegenerative diseases have a great diversity of clinical symptoms that vary widely in disease status and prognosis. However, due to insufficient diagnostic methods, the patients are diagnosed, on average, at the middle or late disease stage, leading to a poor prognosis. The identification of potential biomarkers that can stop disease pathogenesis and serve a virtual shortcuts will be hailed as the sensation of the current era.
Medicinal treatments consisting of natural products are considered promising and fabulous treatment options for neurodegenerative diseases. By virtue of their component diversity, higher multi-target activity, and lower toxicity, herbs are becoming a dominant contributor for developing multi-target drugs. Recently, Zhou et al. [231] used a network pharmacology-based strategy to investigate pharmacological mechanisms of Tinospora sinensis for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Their findings demonstrate that T. sinensis had a significant effect on the expression of protein PI3K and Akt; hence, T. sinensis could prevent and treat Alzheimer’s disease through a multi-compound–multi-target–multi-pathway regulatory network.
Parkinson’s disease is another major neurodegenerative disorder, following Alzheimer’s disease, that imposes a serious burden on families and even the whole society. Li et al. [232] applied a network pharmacology-based approach to study of the molecular mechanisms of Shaoyao Gancao decoction in treating Parkinson’s disease. Their study proposed 48 bioactive constituents mediating 30 Parkinson’s disease-related targets to exert synergism, and the same target can be enriched in multiple signal pathways and biological processes, implying that the decoction can exert a synergistic effect on Parkinson’s disease via multi-targets and pathways. These findings shed light on the molecular mechanisms underpinning the efficacy of Shaoyao Gancao decoction in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease, therefore allowing researchers to dig further into herbal medicine for developing innovative and exciting therapeutic options against Parkinson’s disease.
Huntington’s disease is an autosomal-dominant, neurodegenerative disorder with a primary etiology of corticostriatal pathology. Currently, there are no treatments that can slow or stop the progression of the disease. Dai et al. [233] also employed the same network pharmacology-based methodology to explore a novel herbal formula against Huntington’s disease, which was then further validated by a support vector machine model. The authors demonstrated that Brucea javanica, Dichroa febrifuga, E. micranthum Harms, Erythrophleum guineense, Holarrhena antidysenterica, and Japanese Ardisia Herb contained active compounds that might be a novel medicine formula for Huntington’s disease.
Not only these, recently, Liu et al. [234] used a network pharmacology study on the triterpene saponins from Medicago sativa for the treatment of all types of eurodegenerative diseases. The findings of this study will serve as references (for active compounds, major protein targets, and signalling pathways) that can be used for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases and future research. In the future, more studies are needed to explore the multi-target pharmacological mechanism of herbs against neurodegenerative diseases
Thus, understanding the herb/herbal formula using network pharmacology is an emerging trend of this era. The multi-target action mechanism of network pharmacology is compatible with the complicated nature of disease and drug action. Additionally, protein–protein interactions networks or interactomes have been commonly used to understand complex disease mechanisms. The network pharmacology approach, however, oversimplifies disease mechanisms, which are in fact complex subnetworks within the interactome. Beyond all the applications of network pharmacology mentioned above, a list of studies has been conducted on other diseases and is summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Application of network pharmacology for treatment of diseases using herb/herbal formulae.
12. Limitation and Solution
Network pharmacology has proved to be beneficial in drug development, which aids in revitalizing herbal medicines. Although there are a few drawbacks of applying network pharmacology research in herbal medication, hopefully, they will be fixed in the future. For the identification of active ingredients and disease-related targets, network pharmacology depends on various public databases. Despite their curation, databases may have inconsistencies due to a variety of information sources, theories, and experimental results. Furthermore, herbs that encounter specific pre-trial procedures throughout their development have undergone various chemical changes—using contemporary, high-throughput techniques such as liquid chromatography is one solution to overcome this challenge.
ADMET profiling is used to validate the pharmacokinetic properties of the highly active constituent. ADMET analysis is a challenging process in drug discovery. Various in silico tools are available for ADMET profiling; however, experimental validation is necessary to validate active compounds’ pharmacokinetic properties.
The identification of putative targets depends on the one or usually one single database, owing to the limited availability of databases with unrestricted accessibility. This might sometimes lead to unsatisfactory consequences. Therefore, the integration of multiple databases is one solution to solve the challenge.
13. Conclusions
Medicinal plants represent a novel alternative and preferred treatment to handle ailments with no satisfactory remedy. For a long time, humans use herbal medicines to manage different diseases. The negative effects of synthetic medicines have demanded progress in the use of natural products for the management of disease. To achieve stunning gains in the future, the use of emerging technologies must be tied with a research basis. Most of the commercially produced medicines are derived from plants. This review of the current literature provides a comprehensive overview of drug discovery from medicinal plants by employing a network pharmacology approach. This review article is a touchstone for the initial screening of medicinal plants for treatments of various ailments, and additional spectra of phytochemicals provide baseline data about phytochemical studies. The network pharmacology approach establishes the latest scientific foundation for determining the efficacy of multi-component, multi-target compound formulae and exploring more therapeutic targets’ disease treatment. In summary, advancements in systems biology and bioinformatics will make an operational shift from reductionism in favor of network pharmacology. They will undoubtedly bring about a conceptual move in drug discovery and contribute to the modernization and globalization of herbal medicines. Different dynamic networks and quantitative networks may be another tendency, and more and more employment of network pharmacology technology will make the expenditure much less in the future. This review lays the groundwork for further research on the protective mechanisms of medicinal plants in disease treatments and the applications of network pharmacology in drug discovery.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Researchers would like to thank the Deanship of Scientific Research, Qassim University for funding the publication of this project.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Noor, F.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Javed, M.R.; Saleem, M.H.; Ahmad, A.; Aslam, M.F.; Aslam, S. Comprehensive computational analysis reveals human respiratory syncytial virus encoded microRNA and host specific target genes associated with antiviral immune responses and protein binding. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2021, 33, 101562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, W.; Zi-Yi, W.; Zheng, J.-H.; Shao, L. TCM network pharmacology: A new trend towards combining computational, experimental and clinical approaches. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Gertsch, J. Botanical drugs, synergy, and network pharmacology: Forth and back to intelligent mixtures. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 1086–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, H.-l.; Lin, Y.-C.-D.; Huang, H.-Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, Y.; Hu, Y.-j.; Kong, X.-j.; Chen, Q.-j.; Zhang, Y.-z.; Hong, H.-C. The challenges and opportunities of traditional Chinese medicines against COVID-19: A way out from a network perspective. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 845–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, F.; Saleem, M.H.; Aslam, M.F.; Ahmad, A.; Aslam, S. Construction of miRNA-mRNA network for the identification of key biological markers and their associated pathways in IgA nephropathy by employing the integrated bioinformatics analysis. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 4938–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.K.; Shukla, Y. Herbal medicine: Current status and the future. Asian Pac J. Cancer Prev. 2003, 4, 281–288. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, A.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Shahid, F.; Noor, F.; Aslam, S. The Screening of phytochemicals against NS5 Polymerase to treat Zika Virus infection: Integrated computational based approach. Comb. Chem. High Through. Screen. 2021, 25, 738–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, N.; Gwee, K.A.; Tack, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Xiao, Y. Herbal medicine in the treatment of functional gastrointestinal disorders: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020, 35, 544–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Zhang, B. Traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology: Theory, methodology and application. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 11, 110–120. [Google Scholar]
- Casas, A.I.; Hassan, A.A.; Larsen, S.J.; Gomez-Rangel, V.; Elbatreek, M.; Kleikers, P.W.; Guney, E.; Egea, J.; López, M.G.; Baumbach, J.J. From single drug targets to synergistic network pharmacology in ischemic stroke. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 7129–7136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhu, X.; Bai, H.; Ning, K. Network pharmacology databases for traditional Chinese medicine: Review and assessment. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.-B.; Li, Q.-Y.; Chen, Q.-I.; Su, S.-B. Network pharmacology: A new approach for Chinese herbal medicine research. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 621423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, A.L. Network pharmacology: The next paradigm in drug discovery. Nature chemical biology 2008, 4, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Hao, L.; Fang, K.; Han, X.-x.; Yu, H.; Zhang, J.-j.; Cai, L.-j.; Fan, T.; Zhang, W.-d.; Pang, K. A network pharmacology perspective for deciphering potential mechanisms of action of Solanum nigrum L. in bladder cancer. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Yuan, G.; Pan, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, H. Network pharmacology studies on the bioactive compounds and action mechanisms of natural products for the treatment of diabetes mellitus: A review. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-X.; Li, R.-Z.; Sun, A.; Zhou, H.; Neher, E.; Yang, J.-S.; Huang, J.-M.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Jiang, Z.-B.; Liang, T.-L. Metabolomics and integrated network pharmacology analysis reveal Tricin as the active anti-cancer component of Weijing decoction by suppression of PRKCA and sphingolipid signaling. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 171, 105574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Xu, Q.; Pelkonen, O. Chapter Network Pharmacology and Traditional Chinese Medicine. In Alternative Medicine; Sakagami, H., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; Chapter 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, U.; Mehendale, N.; Patil, S.; Chaguturu, R.; Patwardhan, B. Network pharmacology. Innov. Approaches Drug Dis. 2017, 127–164. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, S.Y.; Pan, S.; Yu, Z.-L.; Ma, D.-L.; Chen, S.-B.; Fong, W.-F.; Han, Y.-F.; Ko, K.-M. New perspectives on innovative drug discovery: An overview. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 13, 450–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malas, T.B.; Kudrin, R.; Starikov, S.; ‘t Hoen, P.A.; Peters, D.J.; Roos, M.; Hettne, K.M. Drug repurposing using a semantic knowledge graph. Data Driven Knowl. Discov. Polycyst. Kidney 2021, 75. [Google Scholar]
- Noor, F.; Noor, A.; Ishaq, A.R.; Farzeen, I.; Saleem, M.H.; Ghaffar, K.; Aslam, M.F.; Aslam, S.; Chen, J.-T. Recent Advances in Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches for Breast Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. Cur. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 2344–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergendahl, L.T.; Gerasimavicius, L.; Miles, J.; Macdonald, L.; Wells, J.N.; Welburn, J.P.; Marsh, J.A. The role of protein complexes in human genetic disease. Protein Sci. 2019, 28, 1400–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gulbahce, N.; Yu, H. Network-based methods for human disease gene prediction. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2011, 10, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azmi, A.S.; Wang, Z.; Philip, P.A.; Mohammad, R.M.; Sarkar, F.H. Proof of concept: Network and systems biology approaches aid in the discovery of potent anticancer drug combinations. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 3137–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrattenholz, A.; Soskic, V. What does systems biology mean for drug development? Cur. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 1520–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anighoro, A.; Bajorath, J.; Rastelli, G. Polypharmacology: Challenges and opportunities in drug discovery: Miniperspective. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 7874–7887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.-U. Polypharmacology–foe or friend? J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 8955–8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S Azmi, A. Adopting network pharmacology for cancer drug discovery. Cur. Drug Discov. Technol. 2013, 10, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stępnicki, P.; Kondej, M.; Koszła, O.; Żuk, J.; Kaczor, A.A. Multi-targeted drug design strategies for the treatment of schizophrenia. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2021, 16, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achenbach, J.; Tiikkainen, P.; Franke, L.; Proschak, E. Computational tools for polypharmacology and repurposing. Futur. Med. Chem 2011, 3, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schippmann, U.; Leaman, D.J.; Cunningham, A. Impact of cultivation and gathering of medicinal plants on biodiversity: Global trends and issues. In Biodiversity and the Ecosystem Approach in Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2002; pp. 142–167. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, J.; Srivastava, J.; Vietmeyer, N. Medicinal Plants: Rescuing a Global Heritage; World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; Volume 355. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, S.; Singh, S. Current and future status of herbal medicines. Vet. World 2008, 1, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahil, K.; Sudeep, B.; Akanksha, M. Standardization of medicinal plant materials. Int. J. Res. Ayurveda Pharm. 2011, 2, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar]
- Gurib-Fakim, A. Medicinal plants: Traditions of yesterday and drugs of tomorrow. Mol. Asp. Med. 2006, 27, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahmani, M.; Sarrafchi, A.; Shirzad, H.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M. Autism: Pathophysiology and promising herbal remedies. Cur. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patwardhan, B.; Vaidya, A.D.; Chorghade, M. Ayurveda and natural products drug discovery. Curr. sci. 2004, 86, 789–799. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Seto, S.W.; Chang, D.; Kiat, H.; Razmovski-Naumovski, V.; Chan, K.; Bensoussan, A. Synergistic effects of Chinese herbal medicine: A comprehensive review of methodology and current research. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patwardhan, B. Ayurveda: The designer medicine. Indian drugs 2000, 37, 213–227. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Ma, Q.; Ye, L.; Piao, G. The traditional medicine and modern medicine from natural products. Molecules 2016, 21, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, B.J.; Shenvi, R.A. Natural products in the “marketplace”: Interfacing synthesis and biology. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 3332–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M.; Kingston, D.G. Natural products as pharmaceuticals and sources for lead structures. In The Practice of Medicinal Chemistry; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; Chapter 8; pp. 159–186. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, A. Identifying potential therapeutic targets of a natural product Jujuboside B for insomnia through network pharmacology. Plant Sci. Today 2014, 1, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Nie, J.; Fan, X.; Cheng, Y. A network pharmacology approach to evaluating the efficacy of Chinese medicine using genome-wide transcriptional expression data. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 915343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zuo, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Ye, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, S. Integrating network pharmacology and metabolomics study on anti-rheumatic mechanisms and antagonistic effects against methotrexate-induced toxicity of Qing-Luo-Yin. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, W.; Huang, C.; Zhou, W.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Xiao, W.; Wang, Y. A novel systems pharmacology model for herbal medicine injection: A case using reduning injection. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, H.; Zheng, X.; Wang, G. Insights into drug discovery from natural medicines using reverse pharmacokinetics. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emig, D.; Ivliev, A.; Pustovalova, O.; Lancashire, L.; Bureeva, S.; Nikolsky, Y.; Bessarabova, M. Drug target prediction and repositioning using an integrated network-based approach. PloS ONE 2013, 8, e60618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotfi Shahreza, M.; Ghadiri, N.; Mousavi, S.R.; Varshosaz, J.; Green, J.R. A review of network-based approaches to drug repositioning. Brief. Bioinform. 2018, 19, 878–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlyar, M.; Fortney, K.; Jurisica, I. Network-based characterization of drug-regulated genes, drug targets, and toxicity. Methods 2012, 57, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, D.C.; Xiao, P.G. Network Pharmacology: A Rosetta Stone for Traditional C hinese Medicine. Drug Dev. Res. 2014, 75, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Hao, J.; Jin, Z.-Q.; Niu, Y.-Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, D.; Cao, R.; Wu, X.-Z. Network pharmacology-based and clinically relevant prediction of the active ingredients and potential targets of Chinese herbs in metastatic breast cancer patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 27007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, W.; Dong, L.; Li, J.; Geng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Xu, H.; Yang, H. Network pharmacology-based identification of key pharmacological pathways of Yin–Huang–Qing–Fei capsule acting on chronic bronchitis. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2017, 12, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-q.; Mao, X.; Guo, Q.-y.; Lin, N.; Li, S. Network pharmacology-based approaches capture essence of Chinese herbal medicines. Chin. Herb. Med. 2016, 8, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, H.; Zhang, Q.; Su, S.; Chen, Q.; Yang, F.; Hu, Y. A network pharmacology-based approach to analyse potential targets of traditional herbal formulas: An example of Yu Ping Feng decoction. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S. Exploring traditional chinese medicine by a novel therapeutic concept of network target. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2016, 22, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q.; Du, Y.; Xu, H. Integrated strategy for accurately screening biomarkers based on metabolomics coupled with network pharmacology. Talanta 2020, 211, 120710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patwardhan, B.; Vaidya, A.D.; Chorghade, M.; Joshi, S.P. Reverse pharmacology and systems approaches for drug discovery and development. Cur. Bioac. Compd. 2008, 4, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, D.L.; Barger, P.M.; Burkhoff, D. Myocardial recovery and the failing heart: Myth, magic, or molecular target? J. Control. Release 2012, 60, 2465–2472. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, Y.H.; Park, K. Targeted drug delivery to tumors: Myths, reality and possibility. J. Control. Release 2011, 153, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, J.B.; Schoeberl, B.; Nielsen, U.B.; Sorger, P.K. Systems biology and combination therapy in the quest for clinical efficacy. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.F.; Li, X.J.; Zhang, H.Y. Natural products and drug discovery: Can thousands of years of ancient medical knowledge lead us to new and powerful drug combinations in the fight against cancer and dementia? EMBO Rep. 2009, 10, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, A.L. Network pharmacology. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1110–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Franco, J.L.; Giulianotti, M.A.; Welmaker, G.S.; Houghten, R.A. Shifting from the single to the multitarget paradigm in drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, R.; Tan, Z.; Huang, B.; Zhang, S. Computational polypharmacology: A new paradigm for drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2017, 12, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, A.S.; Zhang, S. Polypharmacology: Drug discovery for the future. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 6, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cichonska, A.; Rousu, J.; Aittokallio, T. Identification of drug candidates and repurposing opportunities through compound–target interaction networks. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2015, 10, 1333–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karuppasamy, R.; Veerappapillai, S.; Maiti, S.; Shin, W.-H.; Kihara, D. Current progress and future perspectives of polypharmacology: From the view of non-small cell lung cancer. In Seminars in Cancer Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, Y.; Márquez-Miranda, V.; Miossec, M.J.; González-Nilo, F. Integration of target discovery, drug discovery and drug delivery: A review on computational strategies. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 11, e1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Aneesh, T. Combination Vs. Multi-target drugs: The Clash of the titans in the arena of drug discovery; An overview and in silico evaluation. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2021, 14, 4455–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palve, V.; Liao, Y.; Rix, L.L.R.; Rix, U. Turning liabilities into opportunities: Off-target based drug repurposing in cancer. In Seminars in Cancer Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 209–229. [Google Scholar]
- Ekins, S.; Mestres, J.; Testa, B. In silico pharmacology for drug discovery: Methods for virtual ligand screening and profiling. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 152, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekins, S.; Mestres, J.; Testa, B. In silico pharmacology for drug discovery: Applications to targets and beyond. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 152, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.-h.; Wu, F.; Cao, W.-y.; Wu, Z.-g.; Chao, Y.-C.; Peng, F.; Liang, C. Network pharmacology for the identification of phytochemicals in traditional Chinese medicine for COVID-19 that may regulate interleukin-6. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20202583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Li, S.; Cong, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L. A Network Pharmacology Approach to Estimate Potential Targets of the Active Ingredients of Epimedium for Alleviating Mild Cognitive Impairment and Treating Alzheimer’s Disease. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yuan, T.; Li, Y.; Wu, N.; Dai, X. Network pharmacology analysis of the mechanisms of compound Herba Sarcandrae (Fufang Zhongjiefeng) aerosol in chronic pharyngitis treatment. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemira, M.; Collin, F.; Szalkowska, A.; Bielska, A.; Chwialkowska, K.; Reszec, J.; Niklinski, J.; Kwasniewski, M.; Kretowski, A. Molecular signature of subtypes of non-small-cell lung cancer by large-scale transcriptional profiling: Identification of key modules and genes by weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA). Cancers 2020, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Li, H.; Li, S. A novel network pharmacology approach to analyse traditional herbal formulae: The Liu-Wei-Di-Huang pill as a case study. Mol. BioSystems 2014, 10, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, T.-t.; Lu, Y.; Yan, S.-k.; Xiao, X.; Rong, X.-l.; Guo, J. Network pharmacology in research of Chinese medicine formula: Methodology, application and prospective. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2020, 26, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ma, X.; Liu, C.; Li, H.; Zhuang, J.; Gao, C.; Zhou, C.; Liu, L.; Wang, K.; Sun, C. Exploring the mechanism of danshen against myelofibrosis by network pharmacology and molecular docking. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.-h.; Cai, Y.-p.; Cai, X.-j.; Zheng, X.-y.; Cao, D.-s.; Ye, F.-q.; Xiang, Z. A network pharmacology approach to understanding the mechanisms of action of traditional medicine: Bushenhuoxue formula for treatment of chronic kidney disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Chen, L.; Tang, M.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Gao, L.; Ma, S.; Kong, M.; Yao, Q.; Feng, F. Analysis of mulberry leaf components in the treatment of diabetes using network pharmacology. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 833, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panossian, A.G.; Hamm, R.; Kadioglu, O.; Wikman, G.C.; Efferth, T. Synergy and antagonism of active constituents of ADAPT-232 on transcriptional level of metabolic regulation of isolated neuroglial cells. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panossian, A.; Hamm, R.; Wikman, G.; Efferth, T. Mechanism of action of Rhodiola, salidroside, tyrosol and triandrin in isolated neuroglial cells: An interactive pathway analysis of the downstream effects using RNA microarray data. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 1325–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panossian, A.; Seo, E.-J.; Wikman, G.; Efferth, T. Synergy assessment of fixed combinations of Herba Andrographidis and Radix Eleutherococci extracts by transcriptome-wide microarray profiling. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panossian, A.; Seo, E.-J.; Efferth, T. Novel molecular mechanisms for the adaptogenic effects of herbal extracts on isolated brain cells using systems biology. Phytomedicine 2018, 50, 257–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, E.-J.; Efferth, T.; Panossian, A. Curcumin downregulates expression of opioid-related nociceptin receptor gene (OPRL1) in isolated neuroglia cells. Phytomedicine 2018, 50, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, E.-J.; Klauck, S.M.; Efferth, T.; Panossian, A. Adaptogens in chemobrain (Part I): Plant extracts attenuate cancer chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment–Transcriptome-wide microarray profiles of neuroglia cells. Phytomedicine 2019, 55, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, E.-J.; Klauck, S.M.; Efferth, T.; Panossian, A. Adaptogens in chemobrain (Part III): Antitoxic effects of plant extracts towards cancer chemotherapy-induced toxicity-transcriptome-wide microarray analysis of neuroglia cells. Phytomedicine 2019, 56, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panossian, A.; Seo, E.-J.; Efferth, T. Effects of anti-inflammatory and adaptogenic herbal extracts on gene expression of eicosanoids signaling pathways in isolated brain cells. Phytomedicine 2019, 60, 152881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panossian, A.; Seo, E.-J.; Klauck, S.M.; Efferth, T. Adaptogens in chemobrain (part IV): Adaptogenic plants prevent the chemotherapeutics-induced imbalance of redox homeostasis by modulation of expression of genes encoding Nrf2-mediated signaling proteins and antioxidant, metabolizing, detoxifying enzymes in neuroglia cells. Longhua Chin. Med. 2020, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Panossian, A.; Abdelfatah, S.; Efferth, T. Network pharmacology of ginseng (Part II): The differential effects of red ginseng and ginsenoside Rg5 in cancer and heart diseases as determined by transcriptomics. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panossian, A.; Abdelfatah, S.; Efferth, T. Network pharmacology of Red Ginseng (Part I): Effects of ginsenoside Rg5 at physiological and sub-physiological concentrations. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Tong, X. A network pharmacology approach to determine active compounds and action mechanisms of ge-gen-qin-lian decoction for treatment of type 2 diabetes. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Guochun, L.; Yang, Y.; Shi, L.; Xu, L.; Yin, L. A network pharmacology approach to determine active ingredients and rationality of herb combinations of Modified-Simiaowan for treatment of gout. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 168, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Jin, X.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Liang, L.; Liu, R.; Li, Z. A comprehensive application: Molecular docking and network pharmacology for the prediction of bioactive constituents and elucidation of mechanisms of action in component-based Chinese medicine. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2021, 90, 107402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lian, X.; Liu, F.; Yan, X.; Cheng, C.; Cheng, L.; Sun, X.; Shi, Z. Identification of novel key targets and candidate drugs in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Curr. Bioinform. 2020, 15, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alm, E.; Arkin, A.P. Biological networks. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2003, 13, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, S.; Ahmad, S.; Noor, F.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Shahid, F.; Rehman, A.; Tahir ul Qamar, M.; Alatawi, E.A.; Alshabrmi, F.M.; Allemailem, K.S. Designing a Multi-Epitope Vaccine against Chlamydia trachomatis by Employing Integrated Core Proteomics, Immuno-Informatics and In Silico Approaches. Biology 2021, 10, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Q.; Du, J.; Li, X.; Zeng, J.; Tan, B.; Xu, J.; Lin, W.; Chen, X.-l. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on molecular targets and mechanisms of Huashi Baidu formula in the treatment of COVID-19. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2020, 46, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsin, K.-Y.; Ghosh, S.; Kitano, H. Combining machine learning systems and multiple docking simulation packages to improve docking prediction reliability for network pharmacology. PloS ONE 2013, 8, e83922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Wang, M.-H.; Wang, F.; Chen, P.-Y.; Ke, X.-G.; Yu, B.; Yang, Y.-F.; You, P.-T.; Wu, H.-Z. Network pharmacology and molecular docking reveal the mechanism of Scopoletin against non-small cell lung cancer. Life Sci. 2021, 270, 119105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-Y.; Lee, C.-Y.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, C.-E. The methodological trends of traditional herbal medicine employing network pharmacology. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, T.; Zhou, X.; Tang, X.; Gao, R.; Xu, L.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, J.; Hu, Y. Network pharmacology based virtual screening of active constituents of Prunella vulgaris L. and the molecular mechanism against breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Fan, Y.; Tian, C.; Jin, Y.; Du, S.; Zeng, P.; Wang, A. Deciphering the molecular targets and mechanisms of HGWD in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis via network pharmacology and molecular docking. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, X.; Du, P.; Zhao, K.; Huang, J.; Xia, H.; Dai, D.; Huang, S.; Cui, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J. Mechanism of Dayuanyin in the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. Chin. Med. 2020, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, E.; Barrett, T. The gene expression omnibus database. In Statistical Genomics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 93–110. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, W.; Li, S.; Wu, L.; He, B.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Z. Prediction of VEGF-C as a key target of pure total flavonoids from citrus against NAFLD in mice via network pharmacology. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.-b.; Song, Y.-n.; Chen, Q.-l.; Dong, S.; Lu, Y.-y.; Su, M.-y.; Liu, P.; Su, S.-b. Actions of Huangqi decoction against rat liver fibrosis: A gene expression profiling analysis. Chin. Med. 2015, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-M.; Li, M.-T.; Jiang, N.; Si, Y.-C.; Zhu, M.-M.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Shi, D.-C.; Shi, H.; Luo, Q.; Yu, B. Network Pharmacology-Based Approach to Investigate the Molecular Targets of Sinomenine for Treating Breast Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, F.-F.; Bian, Y.-Q.; Wu, R.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X.-L.; Yang, M.-D.; Zhang, Q.-r.; Hu, Y.; Sun, M.-Y.; Su, S.-B. Yinchenhao decoction suppresses rat liver fibrosis involved in an apoptosis regulation mechanism based on network pharmacology and transcriptomic analysis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 114, 108863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zheng, K.; Fan, D.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L.; Bian, Y.; Qiu, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, G.; Ma, C. Wu-Tou decoction in rheumatoid arthritis: Integrating network pharmacology and in vivo pharmacological evaluation. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, T.; Yang, L.; Ma, Y.; Dou, F.; Shi, L.; Wen, A.; Ding, Y. Study on the multi-targets mechanism of triphala on cardio-cerebral vascular diseases based on network pharmacology. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 116, 108994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsdottir, S.M.; Schlingemann, J.; Rada-Iglesias, A.; Schallmeiner, E.; Kamali-Moghaddam, M.; Wadelius, C.; Landegren, U. In vitro analysis of DNA–protein interactions by proximity ligation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 104, 3067–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibble, M.; Saarinen, N.; Tang, J.; Wennerberg, K.; Mäkelä, S.; Aittokallio, T. Network pharmacology applications to map the unexplored target space and therapeutic potential of natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 1249–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Huang, Z.; Liu, D.; Zheng, J.; Xie, J.; Chen, J.; Zeng, H.; Su, Z.; Li, Y. Effect of berberine on hyperuricemia and kidney injury: A network pharmacology analysis and experimental validation in a mouse model. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhou, W.; Zhanag, Y. Experimental techniques in network pharmacology. Chin. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 26, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, B.S.; Oprea, T.; Prossnitz, E.R.; Sklar, L.A. Flow cytometry for high-throughput, high-content screening. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2004, 8, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miscevic, F.; Rotstein, O.; Wen, X.-Y. Advances in zebrafish high content and high throughput technologies. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2012, 15, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhari, F.D.; Dittmer, D.P. Charting latency transcripts in Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus by whole-genome real-time quantitative PCR. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 6213–6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X. Surface plasmon resonance based biosensor technique: A review. J. Biophotonics 2012, 5, 483–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wartchow, C.A.; Podlaski, F.; Li, S.; Rowan, K.; Zhang, X.; Mark, D.; Huang, K.-S. Biosensor-based small molecule fragment screening with biolayer interferometry. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2011, 25, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L.; Xu, S.; Yuan, G.; Xu, X. Drug–target network and polypharmacology studies of a Traditional Chinese Medicine for type II diabetes mellitus. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2011, 35, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, D.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, N. Herb network construction and co-module analysis for uncovering the combination rule of traditional Chinese herbal formulae. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, O.P.; Jadhav, A.; Hussain, A.; Kumar, M.S. VPDB: Viral protein structural database. Bioinformation 2011, 6, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ceze, L.; Nivala, J.; Strauss, K. Molecular digital data storage using DNA. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graw, S.; Chappell, K.; Washam, C.L.; Gies, A.; Bird, J.; Robeson, M.S.; Byrum, S.D. Multi-omics data integration considerations and study design for biological systems and disease. Mol. Omics 2021, 17, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisch, K.M.; Meißner, T.; Gioia, L.; Ducom, J.-C.; Carland, T.M.; Loguercio, S.; Su, A.I. Omics Pipe: A community-based framework for reproducible multi-omics data analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1724–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, N.; Chakrabarti, S. Artificial intelligence (AI)-based systems biology approaches in multi-omics data analysis of cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.V.; Hu, Y.-J. Integrative analysis of multi-omics data for discovery and functional studies of complex human diseases. Adv. Genet. 2016, 93, 147–190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poornima, P.; Kumar, J.D.; Zhao, Q.; Blunder, M.; Efferth, T. Network pharmacology of cancer: From understanding of complex interactomes to the design of multi-target specific therapeutics from nature. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buriani, A.; Fortinguerra, S.; Sorrenti, V.; Caudullo, G.; Carrara, M. Essential oil phytocomplex activity, a review with a focus on multivariate analysis for a network pharmacology-informed phytogenomic approach. Molecules 2020, 25, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Lu, C.; Jiang, M.; Niu, X.; Guo, H.; Li, L.; Bian, Z.; Lin, N.; Lu, A. Traditional chinese medicine-based network pharmacology could lead to new multicompound drug discovery. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W. Network pharmacology: A further description. Netw. Pharmacol. 2016, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Gnad, F.; Doll, S.; Manning, G.; Arnott, D.; Zhang, Z. Bioinformatics analysis of thousands of TCGA tumors to determine the involvement of epigenetic regulators in human cancer. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Greef, J.; McBurney, R.N. Rescuing drug discovery: In vivo systems pathology and systems pharmacology. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ideker, T.; Galitski, T.; Hood, L. A new approach to decoding life: Systems biology. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2001, 2, 343–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, H. Computational systems biology. Nature 2002, 420, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, C.P.; Brantner, V.V. Estimating the cost of new drug development: Is it really $802 million? Health Aff. 2006, 25, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickson, M.; Gagnon, J.P. The cost of new drug discovery and development. Discov. Med. 2009, 4, 172–179. [Google Scholar]
- Kaitin, K. Obstacles and opportunities in new drug development. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 83, 210–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, A.S.; Mohammad, R.M. Rectifying cancer drug discovery through network pharmacology. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X. New concepts and approaches for drug discovery based on traditional Chinese medicine. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2006, 3, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Aittokallio, T. Network pharmacology strategies toward multi-target anticancer therapies: From computational models to experimental design principles. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billur Engin, H.; Gursoy, A.; Nussinov, R.; Keskin, O. Network-based strategies can help mono-and poly-pharmacology drug discovery: A systems biology view. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Mason, S.P.; Barabási, A.-L.; Oltvai, Z.N. Lethality and centrality in protein networks. Nature 2001, 411, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korcsmáros, T.; Szalay, M.S.; Böde, C.; Kovács, I.A.; Csermely, P. How to design multi-target drugs: Target search options in cellular networks. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2007, 2, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morphy, R.; Kay, C.; Rankovic, Z. From magic bullets to designed multiple ligands. Drug discovery today 2004, 9, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, A.L.; Mason, J.S.; Overington, J.P. Can we rationally design promiscuous drugs? Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2006, 16, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, R.A.; Chen, E.S. Synthetic lethal approaches for assessing combinatorial efficacy of chemotherapeutic drugs. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 162, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, H. Towards a theory of biological robustness. Mol. Syst. Bol. 2007, 3, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, D. BioCarta. Biotech Softw. Internet Rep. Comput. Softw. J. Sci. 2001, 2, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, C.; Breitkreutz, B.-J.; Reguly, T.; Boucher, L.; Breitkreutz, A.; Tyers, M. BioGRID: A general repository for interaction datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D535–D539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wu, X.; Pandey, R.; Li, J.; Zhao, G.; Ibrahim, S.; Chen, J.Y. C 2 Maps: A network pharmacology database with comprehensive disease-gene-drug connectivity relationships. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuemin, G. Chemical Book. 2008. Available online: http://www.chemicalbook.com/ProductIndex_EN.aspx (accessed on 14 August 2011).
- Gaulton, A.; Bellis, L.J.; Bento, A.P.; Chambers, J.; Davies, M.; Hersey, A.; Light, Y.; McGlinchey, S.; Michalovich, D.; Al-Lazikani, B. ChEMBL: A large-scale bioactivity database for drug discovery. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1100–D1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim Kjærulff, S.; Wich, L.; Kringelum, J.; Jacobsen, U.P.; Kouskoumvekaki, I.; Audouze, K.; Lund, O.; Brunak, S.; Oprea, T.I.; Taboureau, O. ChemProt-2.0: Visual navigation in a disease chemical biology database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D464–D469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, M. ChemSpider: The free chemical database. Ref. Rev. 2012, 26, 45–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Shao, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S. CHMIS-C: A comprehensive herbal medicine information system for cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatusov, R.L.; Fedorova, N.D.; Jackson, J.D.; Jacobs, A.R.; Kiryutin, B.; Koonin, E.V.; Krylov, D.M.; Mazumder, R.; Mekhedov, S.L.; Nikolskaya, A.N. The COG database: An updated version includes eukaryotes. BMC Bioinform. 2003, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamburov, A.; Stelzl, U.; Lehrach, H.; Herwig, R. The ConsensusPathDB interaction database: 2013 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D793–D800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Gorodkin, J.; Jensen, L.J. Cytoscape StringApp: Network analysis and visualization of proteomics data. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 18, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Tan, Q.; Kir, J.; Liu, D.; Bryant, D.; Guo, Y.; Stephens, R.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C. DAVID Bioinformatics Resources: Expanded annotation database and novel algorithms to better extract biology from large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W169–W175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xenarios, I.; Rice, D.W.; Salwinski, L.; Baron, M.K.; Marcotte, E.M.; Eisenberg, D. DIP: The database of interacting proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Guo, A.C.; Lo, E.J.; Marcu, A.; Grant, J.R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Sayeeda, Z. DrugBank 5.0: A major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1074–D1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safran, M.; Dalah, I.; Alexander, J.; Rosen, N.; Iny Stein, T.; Shmoish, M.; Nativ, N.; Bahir, I.; Doniger, T.; Krug, H. GeneCards Version 3: The human gene integrator. Database 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adar, E. GUESS: A Language and Interface for Graph Exploration. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Montréal, QC, Canada, 22–27 April 2006; pp. 791–800. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.Y.; Mamidipalli, S.; Huan, T. HAPPI: An online database of comprehensive human annotated and predicted protein interactions. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Ye, L.; Kang, H.; Zhang, D.; Tao, L.; Tang, K.; Liu, X.; Zhu, R.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.Z. HIT: Linking herbal active ingredients to targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 39, D1055–D1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshava Prasad, T.; Goel, R.; Kandasamy, K.; Keerthikumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Mathivanan, S.; Telikicherla, D.; Raju, R.; Shafreen, B.; Venugopal, A. Human protein reference database—2009 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D767–D772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, A.; Chang, H.-Y.; Daugherty, L.; Fraser, M.; Hunter, S.; Lopez, R.; McAnulla, C.; McMenamin, C.; Nuka, G.; Pesseat, S. The InterPro protein families database: The classification resource after 15 years. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D213–D221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Chen, J.-L.; Xu, L.-W.; Ji, G. Navigating traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology and computational tools. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Liu, K.; Ha, L.; Re, Y.; Wu, G. Analysis of potential plasma markers in Uyghur cervical cancer patients based on MetaCoreTM. Chin. J. Oncol. 2013, 40, 1020–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Masciocchi, J.; Frau, G.; Fanton, M.; Sturlese, M.; Floris, M.; Pireddu, L.; Palla, P.; Cedrati, F.; Rodriguez-Tomé, P.; Moro, S. MMsINC: A large-scale chemoinformatics database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D284–D290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huisman, M.; Van Duijn, M.A. Software for social network analysis. Models Methods Soc. Netw. Anal. 2005, 270, e316. [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg, A.; Conway, D. NetworkX: Network Analysis with Python. Available online: https://networkx.org/ (accessed on 29 April 2020).
- Brown, K.R.; Jurisica, I. Online predicted human interaction database. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 2076–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batagelj, V.; Mrvar, A. Pajek—analysis and visualization of large networks. In Graph Drawing Software; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 77–103. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Kang, L.; Luo, X.; Zhu, W.; Chen, K.; Wang, X.; Jiang, H. PDTD: A web-accessible protein database for drug target identification. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorn, C.F.; Klein, T.E.; Altman, R.B. PharmGKB: The pharmacogenomics knowledge base. In Pharmacogenomics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 311–320. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Thiessen, P.A.; Bolton, E.E.; Chen, J.; Fu, G.; Gindulyte, A.; Han, L.; He, J.; He, S.; Shoemaker, B.A. PubChem substance and compound databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D1202–D1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canese, K.; Weis, S. PubMed: The bibliographic database. NCBI Handb. 2013, 2, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Croft, D.; O’kelly, G.; Wu, G.; Haw, R.; Gillespie, M.; Matthews, L.; Caudy, M.; Garapati, P.; Gopinath, G.; Jassal, B. Reactome: A database of reactions, pathways and biological processes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 39, D691–D697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazekas, D.; Koltai, M.; Türei, D.; Módos, D.; Pálfy, M.; Dúl, Z.; Zsákai, L.; Szalay-Bekő, M.; Lenti, K.; Farkas, I.J. SignaLink 2–a signaling pathway resource with multi-layered regulatory networks. BMC Syst. Biol. 2013, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.-C.; Adams, J.D.; Hou, T.; Litscher, G. When modern technology meets ancient traditional chinese medicine. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, M.; von Mering, C.; Campillos, M.; Jensen, L.J.; Bork, P. STITCH: Interaction networks of chemicals and proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 36, D684–D688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mering, C.v.; Huynen, M.; Jaeggi, D.; Schmidt, S.; Bork, P.; Snel, B. STRING: A database of predicted functional associations between proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissTargetPrediction: Updated data and new features for efficient prediction of protein targets of small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W357–W364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.-C.; Huang, H.-C.; Chen, H.-H.; Juan, H.-F. TCMGeneDIT: A database for associated traditional Chinese medicine, gene and disease information using text mining. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2008, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yi, Z.; Wen, C.; Shi, T. TCMID: Traditional Chinese medicine integrative database for herb molecular mechanism analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D1089–D1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, B.; Huang, C.; Li, P.; Guo, Z.; Tao, W.; Yang, Y. TCMSP: A database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J. Cheminform. 2014, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ji, Z.L.; Chen, Y.Z. TTD: Therapeutic target database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 412–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolato, I.-A. An overview of Software Applications for Social Network Analysis. International Review of Social Research 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UniProt Consortium. UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase. Nucleic acids research 2017, 45, D158–D169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noor, F.; Rehman, A.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Saleem, M.H.; Okla, M.K.; Al-Hashimi, A.; AbdElgawad, H.; Aslam, S.J.P. Integrating Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Approaches to Decipher the Multi-Target Pharmacological Mechanism of Abrus precatorius L. Acting on Diabetes. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.; Chen, K.; Zou, J.; Han, P.; Hao, J.; Han, Z. Single-cell RNA-seq data analysis on the receptor ACE2 expression reveals the potential risk of different human organs vulnerable to 2019-nCoV infection. Front. Med. 2020, 14, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouzid, M.; Hunter, P.R.; Chalmers, R.M.; Tyler, K.M. Cryptosporidium pathogenicity and virulence. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Morales, A.J.; Cardona-Ospina, J.A.; Gutiérrez-Ocampo, E.; Villamizar-Peña, R.; Holguin-Rivera, Y.; Escalera-Antezana, J.P.; Alvarado-Arnez, L.E.; Bonilla-Aldana, D.K.; Franco-Paredes, C.; Henao-Martinez, A.F. Clinical, laboratory and imaging features of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 34, 101623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, N.; Zheng, B.; Li, Y.; Poon, L.; Xie, Z.; Chan, K.; Li, P.; Tan, S.; Chang, Q.; Xie, J. Epidemiology and cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in Guangdong, People’s Republic of China, in February, 2003. Lancet 2003, 362, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, M.; Bakhrebah, M.; Meo, S.; Alsuabeyl, M.; Zaher, W. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) infection: Epidemiology, pathogenesis and clinical characteristics. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 4956–4961. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.-H.; Cai, L.; Cheng, Z.-S.; Cheng, H.; Deng, T.; Fan, Y.-P.; Fang, C.; Huang, D.; Huang, L.-Q.; Huang, Q. A rapid advice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infected pneumonia (standard version). Mil. Med Res. 2020, 7, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Yang, S.; Xie, C.; Shen, Q.; Li, M.; Lei, X.; Li, J.; Huang, M. Clinical efficacy of Qingfei Paidu Decoction in the treatment of COVID-19. Pharmacol. Clin. Chin. Mater. Med. 2020, 36, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Nasser, M.; Masood, M.; Adlat, S.; Huang, Y.; Yang, B.; Luo, C.; Jiang, N. Efficiency of Traditional Chinese medicine targeting the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 126, 110074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-h.; Zhang, X.; Peng, B.; Deng, S.-q.; Wang, Y.-f.; Yang, L.; Zhang, K.-z.; Ling, C.-q.; Wu, K.-l. Network pharmacology suggests biochemical rationale for treating COVID-19 symptoms with a Traditional Chinese Medicine. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, L.A.; Siegel, R.L.; Ward, E.M.; Jemal, A. Global cancer incidence and mortality rates and trends—an update. Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark. 2016, 25, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duperret, E.K.; Liu, S.; Paik, M.; Trautz, A.; Stoltz, R.; Liu, X.; Ze, K.; Perales-Puchalt, A.; Reed, C.; Yan, J. A designer cross-reactive DNA immunotherapeutic vaccine that targets multiple MAGE-A family members simultaneously for cancer therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 6015–6027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez-Kurtz, G.; Vargens, D.D.; Santoro, A.B.; Hutz, M.H.; de Moraes, M.E.; Pena, S.D.; Ribeiro-dos-Santos, Â.; Romano-Silva, M.A.; Struchiner, C.J. Global pharmacogenomics: Distribution of CYP3A5 polymorphisms and phenotypes in the Brazilian population. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e83472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovich, M.; Clare, S.E.; Atale, R.; Pardo, I.; Hancock, B.A.; Solzak, J.P.; Kassem, N.; Mathieson, T.; Storniolo, A.M.V.; Rufenbarger, C. Characterizing the heterogeneity of triple-negative breast cancers using microdissected normal ductal epithelium and RNA-sequencing. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 143, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zeng, L.; Yang, K. Exploring the pharmacological mechanism of Yanghe Decoction on HER2-positive breast cancer by a network pharmacology approach. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 199, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Yu, Z.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, D.; Song, C.; Lu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, W. Identification of the active constituents and significant pathways of shen-qi-yi-zhu decoction on antigastric cancer: A network pharmacology research and experimental validation. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, K.; Duan, X.; Zhang, X. A network pharmacology approach to uncover the multiple mechanisms of Hedyotis diffusa Willd. on colorectal cancer. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Wang, H.; Pan, Y.; Liu, T. Investigating the multi-target pharmacological mechanism of hedyotis diffusa willd acting on prostate cancer: A network pharmacology approach. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bing, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Shi, D.; Liu, X.; Tian, J.; Yao, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, K. Investigate the mechanisms of Chinese medicine Fuzhengkangai towards EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinomas by network pharmacology. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Z.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Zhou, W.; Wang, K.; Jing, Z.; Liu, S.; Ni, M.; Zhang, X. Mechanisms of compound kushen injection for the treatment of lung cancer based on network pharmacology. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virani, S.S.; Alonso, A.; Benjamin, E.J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Delling, F.N. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2020 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020, 141, e139–e596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Fan, J.; Han, J. Ameliorating effects of traditional Chinese medicine preparation, Chinese materia medica and active compounds on ischemia/reperfusion-induced cerebral microcirculatory disturbances and neuron damage. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, K.; Tao, W.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, W.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y. Systematic investigation of Ginkgo biloba leaves for treating cardio-cerebrovascular diseases in an animal model. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 1363–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Zheng, X.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Fu, W.; Tang, Q.; Wang, J.; Du, G. Network pharmacology study of traditional Chinese medicines for stroke treatment and effective constituents screening. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 242, 112044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, L. Network pharmacology-based prediction of the active ingredients and potential targets of Chinese herbal Radix Curcumae formula for application to cardiovascular disease. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 145, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zou, J.; Zhang, X.; Liang, Y.; Tai, J.; Cui, C.; Wang, M.; Guo, D. Network pharmacology exploration reveals a common mechanism in the treatment of cardio-cerebrovascular disease with Salvia miltiorrhiza Burge. and Carthamus tinctorius L. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Zhang, Y.-l.; Ma, Y.-h.; Yu, H.-y.; Zhao, X.-z.; Zhang, L.-h.; Ge, S.-q.; Zhang, G.-w. A network pharmacology approach to investigate the mechanism of Shuxuening injection in the treatment of ischemic stroke. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 257, 112891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lv, D.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ye, G.; Chai, Y. Network pharmacology-based strategy for predicting active ingredients and potential targets of Yangxinshi tablet for treating heart failure. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 219, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuei, V.C.; Maiyoh, G.K.; Ha, C.E. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity in sub-Saharan Africa. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2010, 26, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forouhi, N.G.; Wareham, N.J. The EPIC-InterAct Study: A study of the interplay between genetic and lifestyle behavioral factors on the risk of type 2 diabetes in European populations. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2014, 3, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeire, E.I.; Wens, J.; Van Royen, P.; Biot, Y.; Hearnshaw, H.; Lindenmeyer, A. Interventions for improving adherence to treatment recommendations in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2005, 18, CD003638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.; Wang, L.; Ding, R.; Zhai, M.; Ge, R.; Zhou, P.; Wang, T.; Fang, H.; Wang, J.; Huang, J. Astragaloside IV acts through multi-scale mechanisms to effectively reduce diabetic nephropathy. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 157, 104831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.K.; Adnan, M.; Cho, D.H. Network pharmacology of bioactives from Sorghum bicolor with targets related to diabetes mellitus. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Q.; Xiang, Z.; Tong, Q.; Pan, J.; Wan, L.; Chen, J. Network pharmacology analysis of traditional Chinese medicine formula Xiao Ke Yin Shui treating type 2 diabetes mellitus. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 4202563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; He, K.; Guan, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, Y.; Sun, M.; Qiu, X.; Yan, F.; Huang, H.; Yao, L. Network pharmacology-based strategy to investigate pharmacological mechanisms of Tinospora sinensis for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Qiu, H.; Liu, M.; Cai, Y. A network pharmacology-based study of the molecular mechanisms of shaoyao-gancao decoction in treating Parkinson’s disease. Interdiscip. Sci. Comput. Life Sci. 2020, 12, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Chen, H.-Y.; Chen, C.Y.-C.; Medicine, A. A network pharmacology-based approach to investigate the novel TCM formula against huntington’s disease and validated by support vector machine model. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 259, 112940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.G.; Lv, M.C.; Huang, M.Y.; Sun, Y.Q.; Gao, P.Y.; Li, D.Q. A network pharmacology study on the triterpene saponins from medicago sativa l. For the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Interdiscip. Sci. Comput. Life Sci. 2020, 12, 131–144. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, B.-F.; Hou, Y.-Y.; Jiang, M.; Zhao, Z.-Y.; Dong, L.-Y.; Bai, G. Anti-inflammatory mechanism of Qingfei Xiaoyan Wan studied with network pharmacology. Yao Xue Xue Bao Acta Pharm. Sin. 2013, 48, 686–693. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Xing, L.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Y.; Guo, T.; Fu, J.; Dong, L.; Jiang, M. Network pharmacological research of volatile oil from Zhike Chuanbei Pipa Dropping Pills in treatment of airway inflammation. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2012, 43, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, L.; Bao, Y.; Liu, S.; Zheng, J.; Chen, X. Material basis of Chinese herbal formulas explored by combining pharmacokinetics with network pharmacology. PloS ONE 2013, 8, e57414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Xu, Z.; Xu, G.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Sun, J. Investigation of the active components and mechanisms of Schisandra chinensis in the treatment of asthma based on a network pharmacology approach and experimental validation. Food Func. 2020, 11, 3032–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; Gao, L.; Liang, H.; Huang, J.; Wang, J. Ma Huang Tang ameliorates bronchial asthma symptoms through the TLR9 pathway. Pharm. Biol. 2018, 56, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Niu, M.; Wang, R.; wei Zhou, X.; Dong, B.; Qi, S.; Chen, W.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Y.; Li, R. The modulatory properties of Si Jun Zi Tang enhancing anticancer of gefitinib by an integrating approach. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Fang, Z.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.; You, X.; Song, M.; Coffie, J.; Zhang, L.; Gao, X. Naoxintong restores collateral blood flow in a murine model of hindlimb ischemia through PPARδ-dependent mechanism. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 227, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Di, M.; Chen, W.; Liu, X.; Yu, F.; Wang, H.; Zhen, X.; Zhang, M. Traditional Chinese medication Tongxinluo attenuates apoptosis in ox-LDL-stimulated macrophages by enhancing Beclin-1-induced autophagy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 501, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhou, J.; Jin, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Danhong injection combined with t-PA improves thrombolytic therapy in focal embolic stroke. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.; Peng, W.; Li, P.; Xia, Z.; Zhong, Y.; He, F.; Tulake, Y.; Feng, D.; Wang, Y.; Xing, Z. A network pharmacology analysis to explore the effect of astragali radix-radix angelica sinensis on traumatic brain injury. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lien, A.S.-Y.; Jiang, Y.-D.; Mou, C.-H.; Sun, M.-F.; Gau, B.-S.; Yen, H.-R. Integrative traditional Chinese medicine therapy reduces the risk of diabetic ketoacidosis in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 191, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.-K.; Hung, T.-M.; Huang, H.-C.; Lee, I.; Chang, C.-C.; Cheng, J.-J.; Lin, L.-C.; Huang, C. Bai-Hu-Jia-Ren-Shen-Tang decoction reduces fatty liver by activating AMP-activated protein kinase in vitro and in vivo. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Tang, T.; Liu, T.; Zhou, J.; Cui, H.; He, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Hu, E.; Yang, A.; Wei, G. Systematic analysis of tRNA-derived small RNAs reveals novel potential therapeutic targets of traditional Chinese medicine (Buyang-Huanwu-Decoction) on intracerebral hemorrhage. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Duan, J.-A.; Bai, G.; Su, S.-L. Network pharmacology study on major active compounds of siwu decoction analogous formulae for treating primary dysmenorrhea of gynecology blood stasis syndrome. Zhongguo Zhong yao za zhi = Zhongguo zhongyao zazhi = China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2014, 39, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.S.; Xu, X.J.; Ye, H.Z.; Wu, G.W.; Xu, H.F.; Li, X.H.; Huang, S.P.; Liu, X.X. Computational pharmacological comparison of Salvia miltiorrhiza and Panax notoginseng used in the therapy of cardiovascular diseases. Experimental and therapeutic medicine 2013, 6, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Lu, P.; Zhang, F.-B.; Tang, S.-H.; Yang, H.-J. Molecular mechanism research on simultaneous therapy of brain and heart based on data mining and network analysis. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2013, 38, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wu, L.; Fan, X.; Zhang, B.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Y. Network pharmacology study on major active compounds of Fufang Danshen formula. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2011, 36, 2911–2915. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, J.; Hou, Y.; Ma, X.; Liu, D.; Tong, Y.; Zhou, H.; Gao, J.; Bai, G. An integrated global chemomics and system biology approach to analyze the mechanisms of the traditional Chinese medicinal preparation Eriobotrya japonica–Fritillaria usuriensis dropping pills for pulmonary diseases. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Lin, J. Analysis of the mechanism of zhichuanling oral liquid in treating bronchial asthma based on network pharmacology. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, S. Combining systems pharmacology, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics to dissect the therapeutic mechanism of Chinese herbal Bufei Jianpi formula for application to COPD. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2016, 11, 553. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, Z.; Niu, L.; Han, L.; Ren, R.; Xu, Z.; Dong, W.; Jiang, L. In silico comparative molecular docking analysis and analysis of the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of action of tanshinone from Salvia miltiorrhiza. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, S. Integration of transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics and systems pharmacology data to reveal the therapeutic mechanism underlying Chinese herbal Bufei Yishen formula for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 5247–5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, B.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Xiao, W.; Zheng, C.; Wang, Y. Systematic investigation of the Erigeron breviscapus mechanism for treating cerebrovascular disease. J. Ethnopharmacol 2018, 224, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Tao, W.; Zheng, C.; Shar, P.A.; Huang, C.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Y. Systems pharmacology-based approach for dissecting the addition and subtraction theory of traditional Chinese medicine: An example using Xiao-Chaihu-Decoction and Da-Chaihu-Decoction. Comput. Biol. Med 2014, 53, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, J.; Yan, Y.; Yang, M.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Zhong, L.; Gong, Q.; Yu, H. Network pharmacology-based strategy to investigate the pharmacologic mechanisms of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. for the treatment of chronic gastritis. Front. Pharmacol 2020, 10, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lu, F.; Luo, G.; Ren, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y. Discovery of selective farnesoid X receptor agonists for the treatment of hyperlipidemia from traditional Chinese medicine based on virtual screening and in vitro validation. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 38, 4461–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Li, S. An integrative platform of TCM network pharmacology and its application on a herbal formula, Qing-Luo-Yin. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fu, L.; Zhang, S.; Tian, M.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Ouyang, L. In silico analysis and experimental validation of active compounds from fructus Schisandrae chinensis in protection from hepatic injury. Cell prolif. 2015, 48, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Luo, G.; Zhang, X.; Lu, F.; Qiao, L.; He, W.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y. Discovery of potential inhibitors of squalene synthase from traditional Chinese medicine based on virtual screening and in vitro evaluation of lipid-lowering effect. Molecules 2018, 23, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, X.; Lu, F.; Qiao, L.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y. A component formula of Chinese medicine for hypercholesterolemia based on virtual screening and biology network. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.-S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L. Systems pharmacology dissection of the anti-inflammatory mechanism for the medicinal herb Folium eriobotryae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 2913–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, G.-B.; Liu, P.; Song, J.-H.; Liang, Y.; Yan, X.-J.; Xu, F.; Wang, B.-S.; Mao, J.-H.; Shen, Z.-X. Dissection of mechanisms of Chinese medicinal formula Realgar-Indigo naturalis as an effective treatment for promyelocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4826–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, N.; Hong, M.; Tan, H.-Y.; Pan, G.; Feng, Y. Hepatoprotective effects of a functional formula of three Chinese medicinal herbs: Experimental evidence and network pharmacology-based identification of mechanism of action and potential bioactive components. Molecules 2018, 23, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Feng, F. Network pharmacology-based antioxidant effect study of Zhi-Zi-Da-Huang decoction for alcoholic liver disease. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Y. Network pharmacology approach reveals the potential immune function activation and tumor cell apoptosis promotion of Xia Qi decoction in lung cancer. Med. Sci. 2020, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Tang, Y.; Shang, E.; Guo, J.; Huang, M.; Qian, D.; Duan, J. Analysis on correlation between general efficacy and chemical constituents of Danggui-Chuanxiong herb pair based on artificial neural network. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2012, 37, 2935–2942. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, F.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y. Mechanism study on preventive and curative effects of buyang huanwu decoction in Qi deficiency and blood stasis diseases based on network analysis. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2014, 39, 4418–4425. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Hong, Y.; Feng, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, Y. Phytochemical and pharmacological review of da chuanxiong formula: A famous herb pair composed of chuanxiong rhizoma and gastrodiae rhizoma for headache. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Fan, X.; Cheng, Y. A network study of chinese medicine xuesaitong injection to elucidate a complex mode of action with multicompound, multitarget, and multipathway. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, H.; Xue, Y. HemI: A toolkit for illustrating heatmaps. PloS ONE 2014, 9, e111988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.S.; Xu, X.J.; Ye, H.Z.; Wu, G.W.; Li, X.H.; Xu, H.F.; Liu, X.X. Network pharmacology-based prediction of the multi-target capabilities of the compounds in Taohong Siwu decoction, and their application in osteoarthritis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2013, 6, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Tan, H.Y.; Wang, N.; Mu, S.; Hao, X.; Feng, Y. A network pharmacology-based study on the hepatoprotective effect of Fructus Schisandrae. Molecules 2017, 22, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Li, P.; Liu, M.; Long, C.; Xie, C.; Xie, X.; Su, W. Network pharmacology analyses of the antithrombotic pharmacological mechanism of Fufang Xueshuantong Capsule with experimental support using disseminated intravascular coagulation rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 154, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.S.; Fu, C.L.; Pan, C.B.; Bao, H.J.; Chen, X.Q.; Ye, H.Z.; Ye, J.X.; Wu, G.W.; Li, X.H.; Xu, H.F. Deciphering the underlying mechanisms of Diesun Miaofang in traumatic injury from a systems pharmacology perspective. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 1769–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).