C16 Peptide and Ang-1 Improve Functional Disability and Pathological Changes in an Alzheimer’s Disease Model Associated with Vascular Dysfunction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
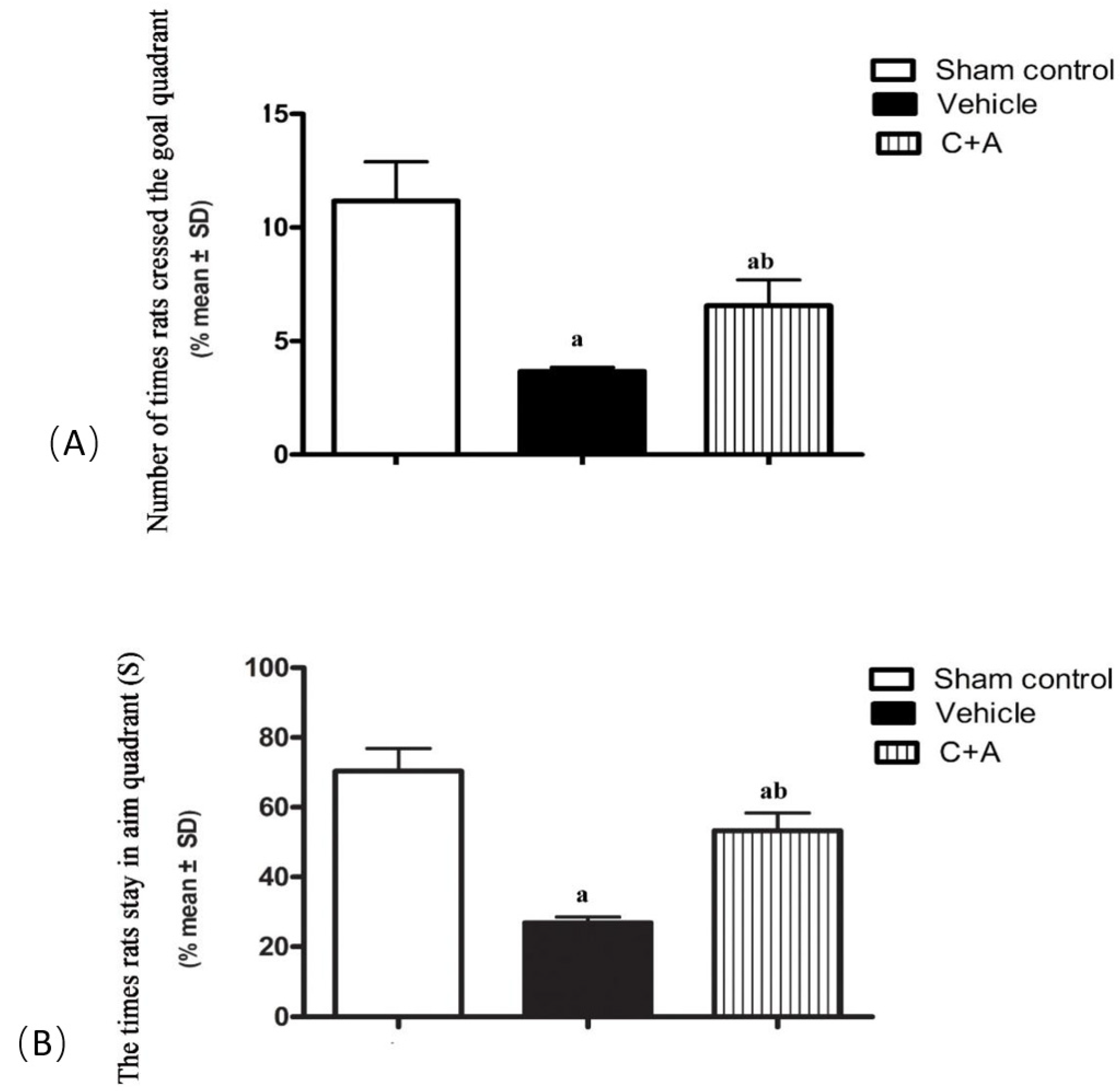
2.1. Treatment with C16 Plus Ang-1 Alleviated Memory Impairment in AD Rats with Vascular Dysfunction
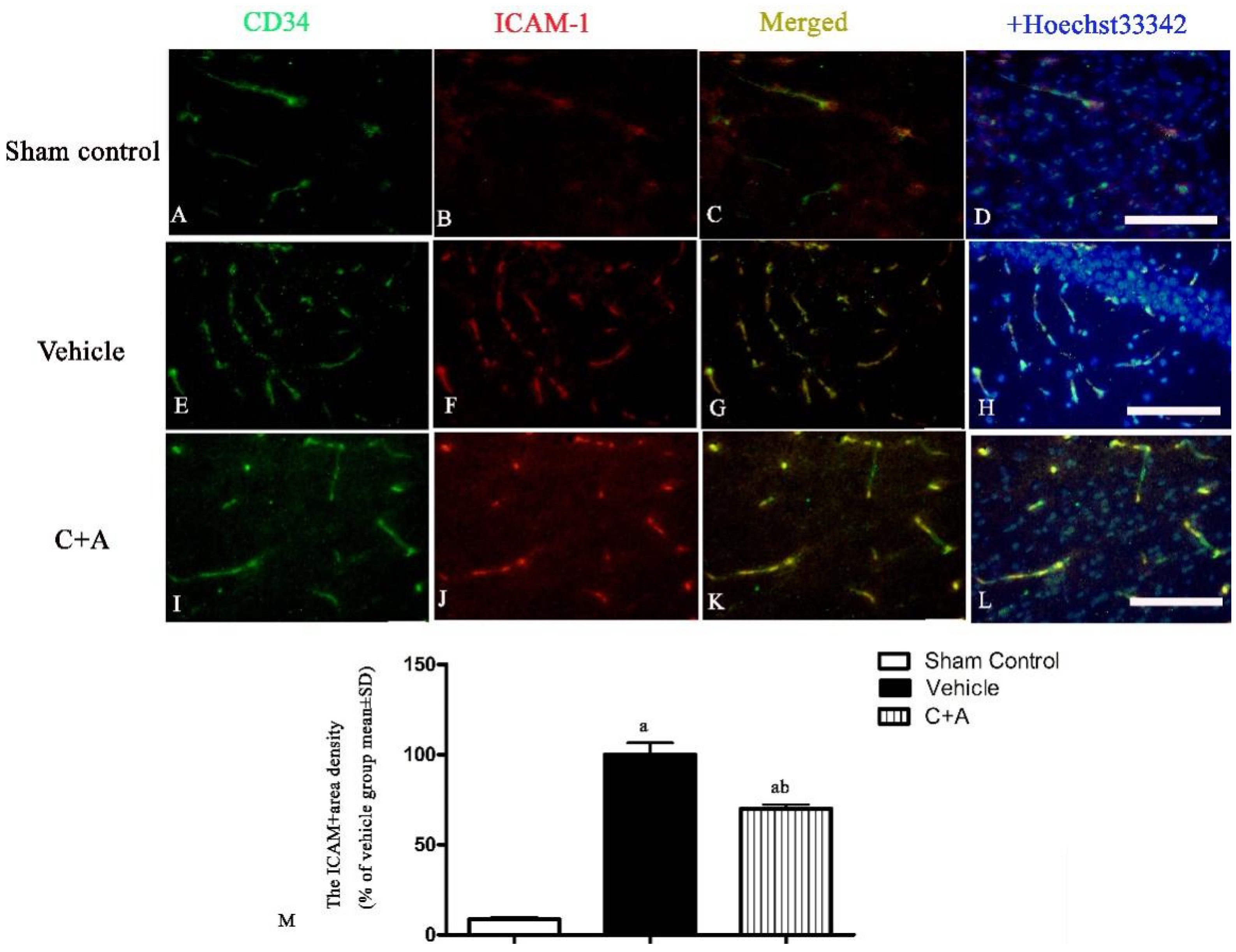
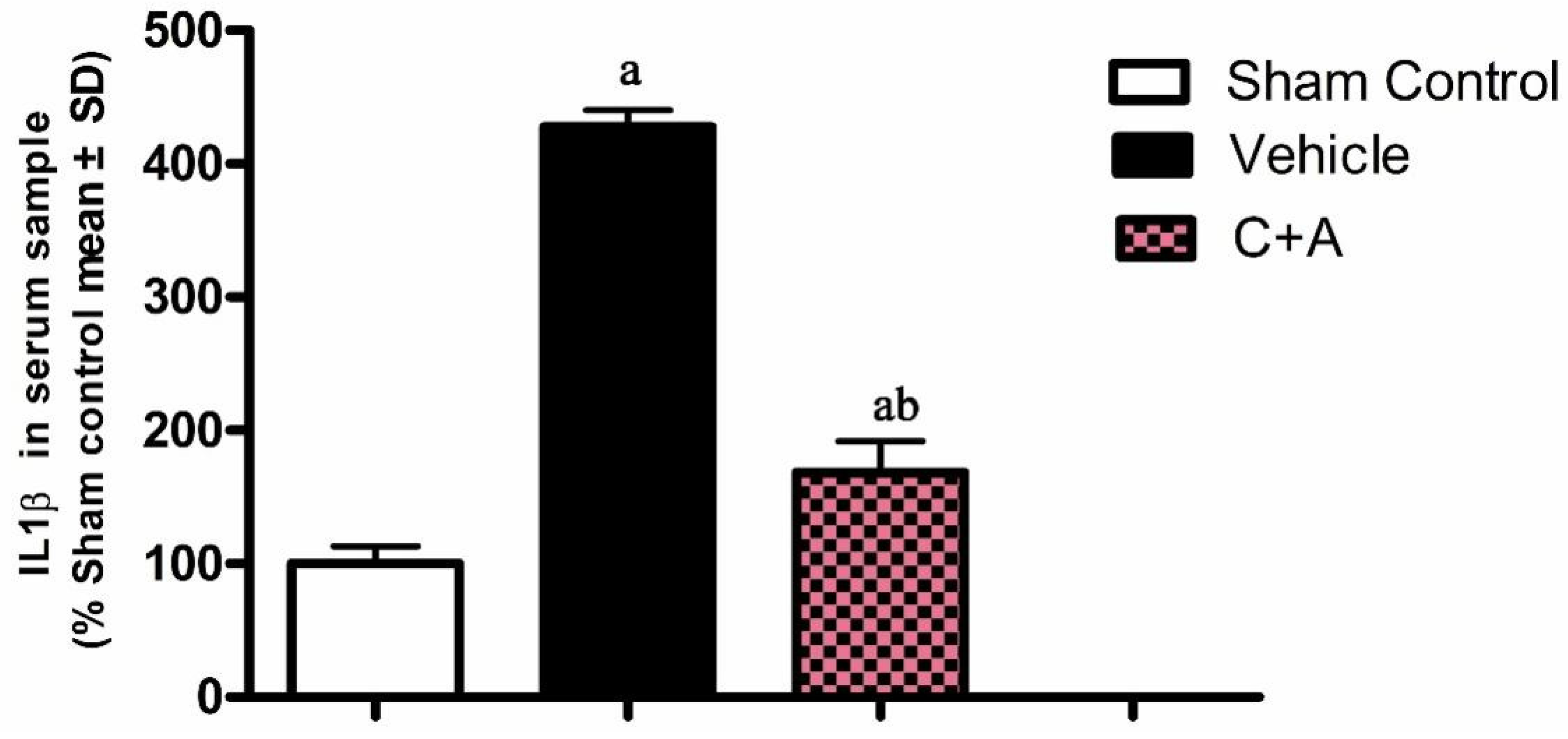
2.2. Treatment with C16 Plus Ang-1 Suppressed Inflammation in the CNS
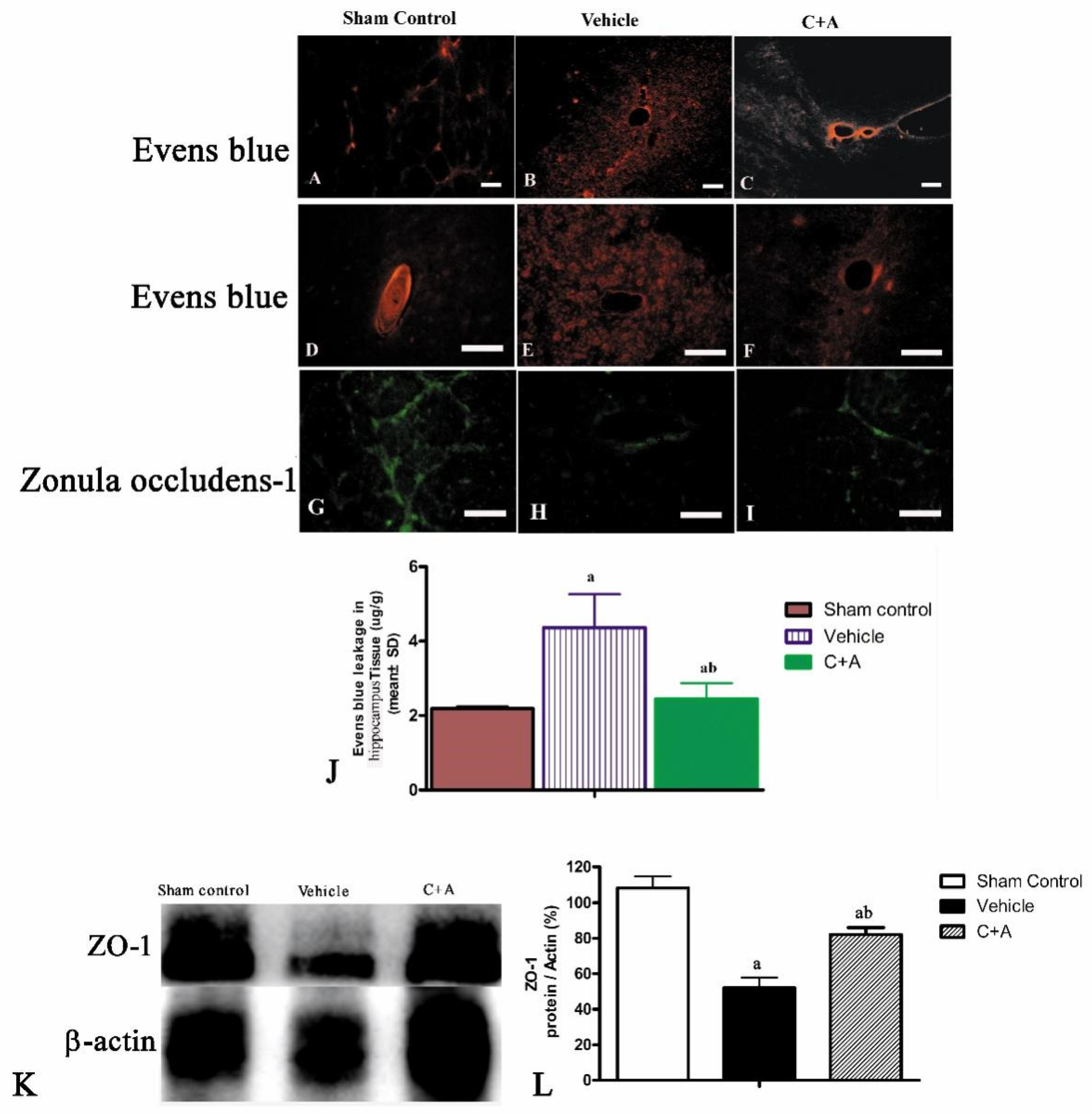
2.3. Treatment with C16 Plus Ang-1 Reduced BBB Permeability and Blood Vessel Leakage
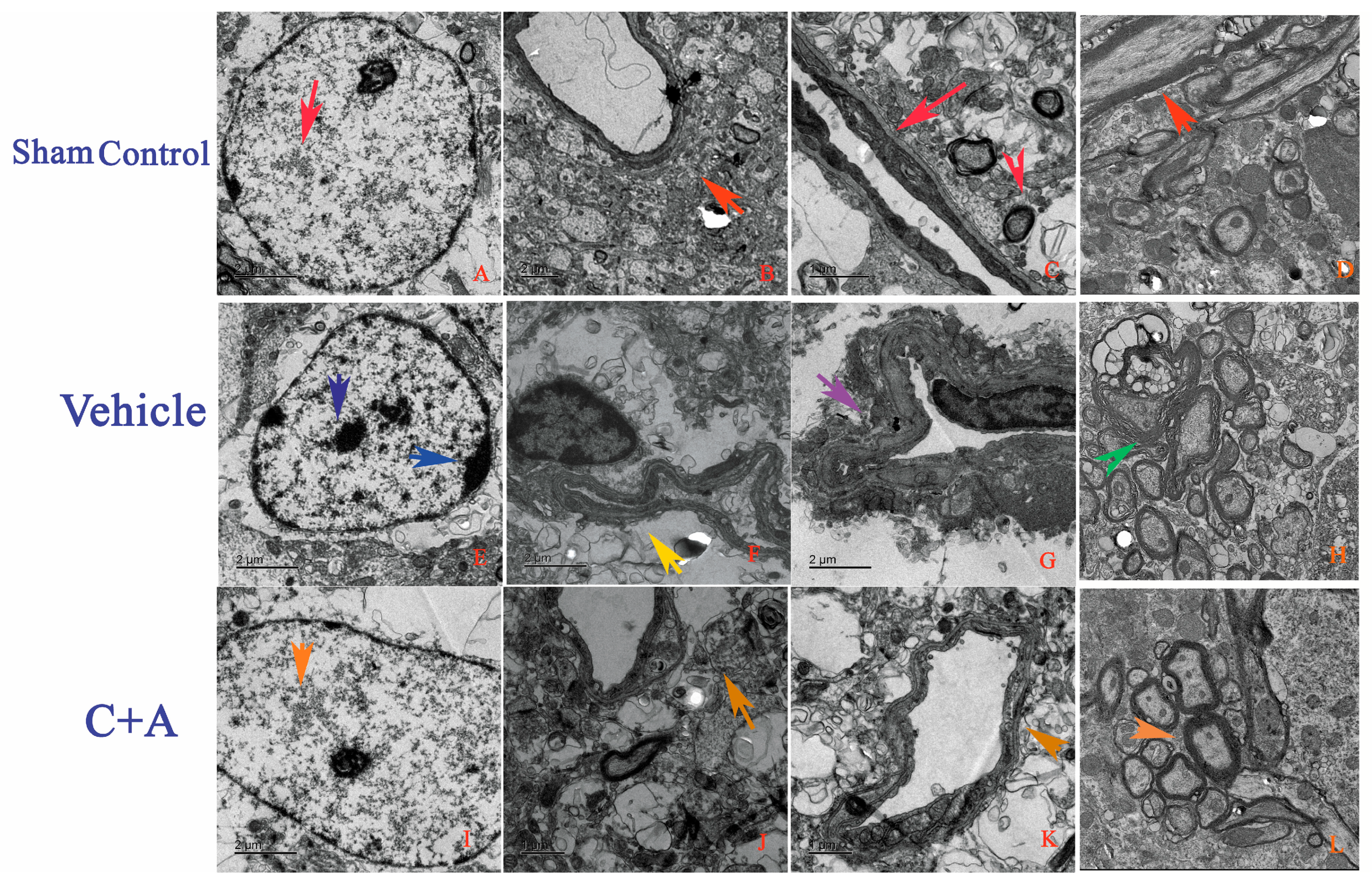
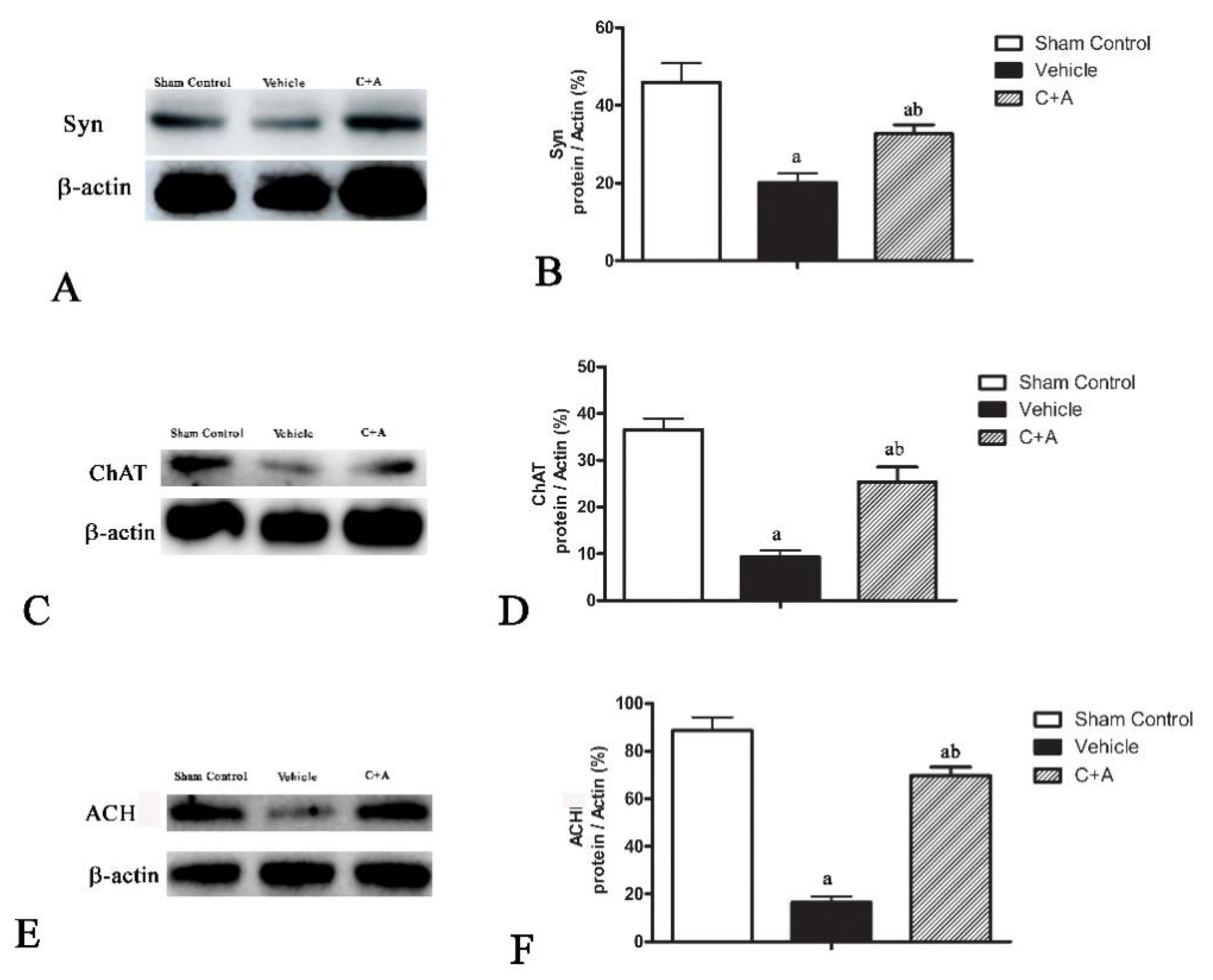
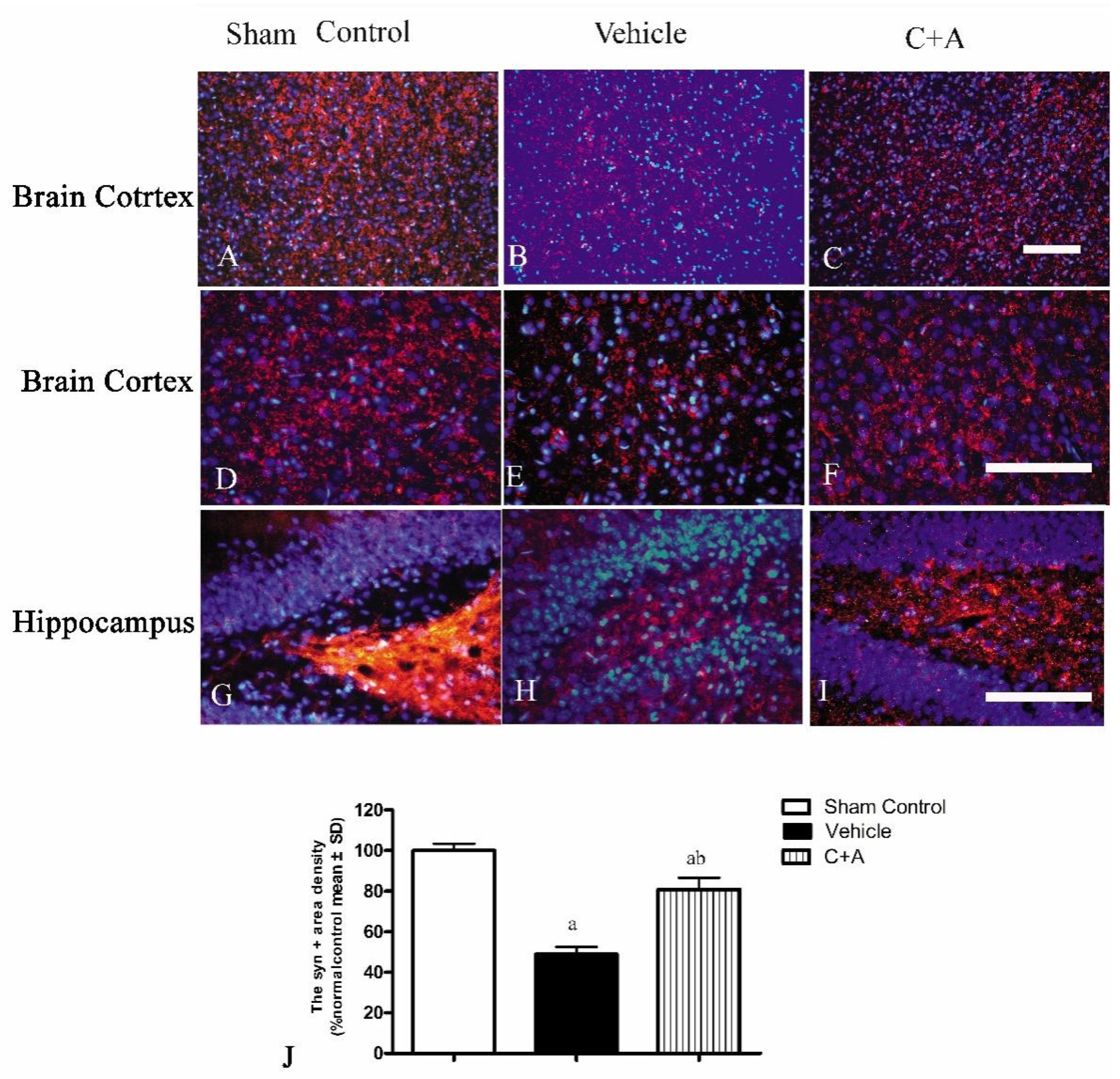
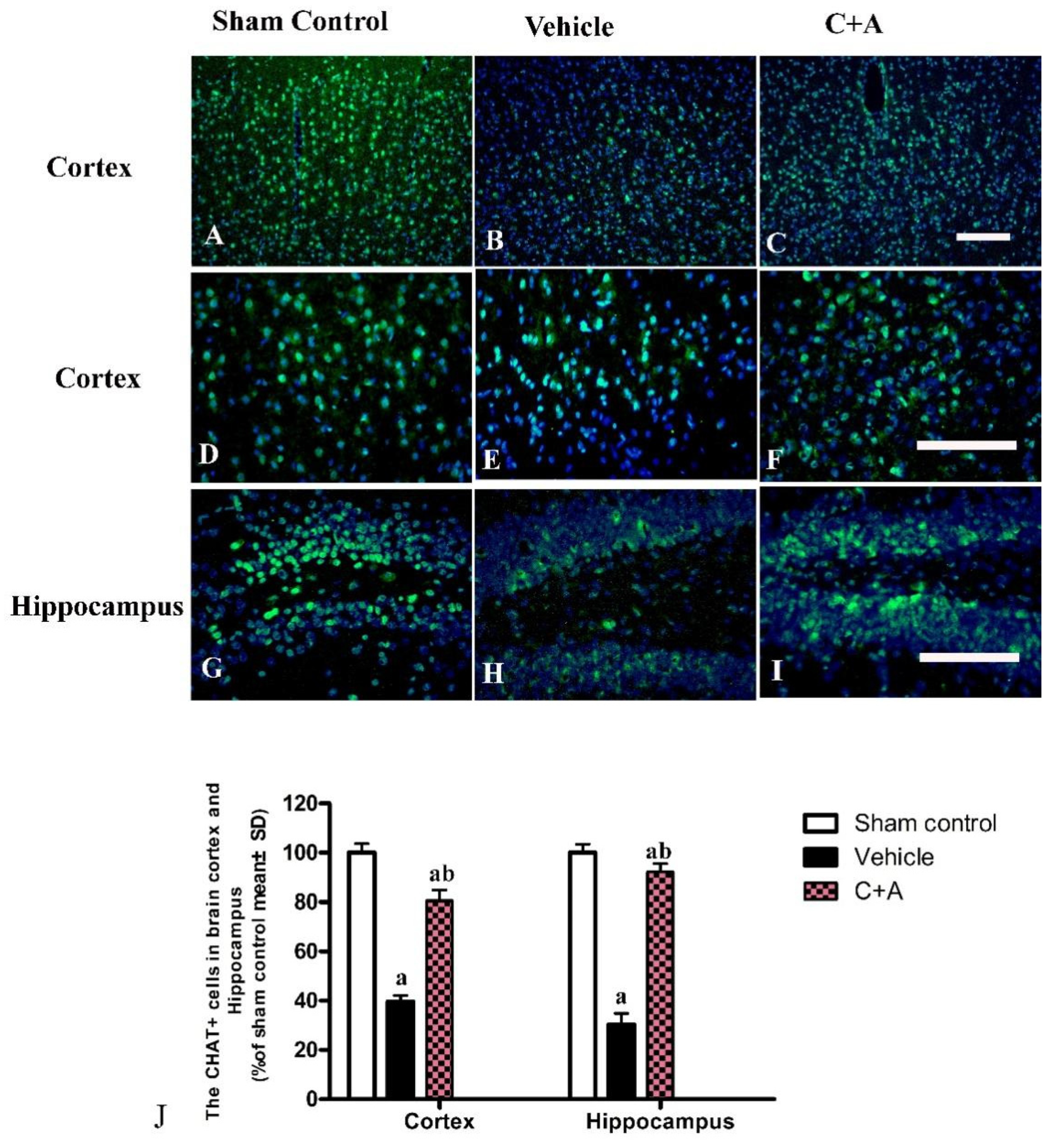
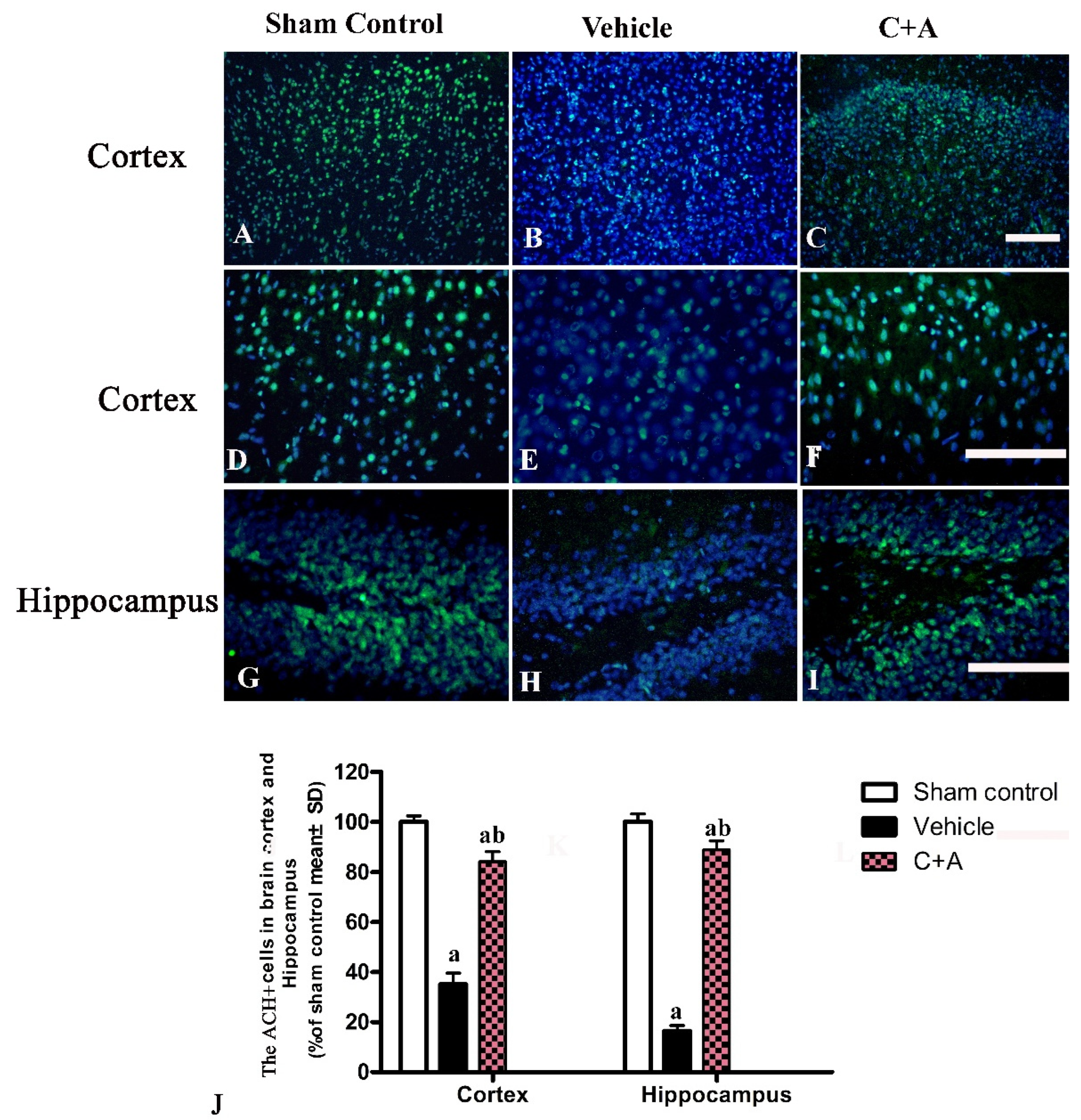
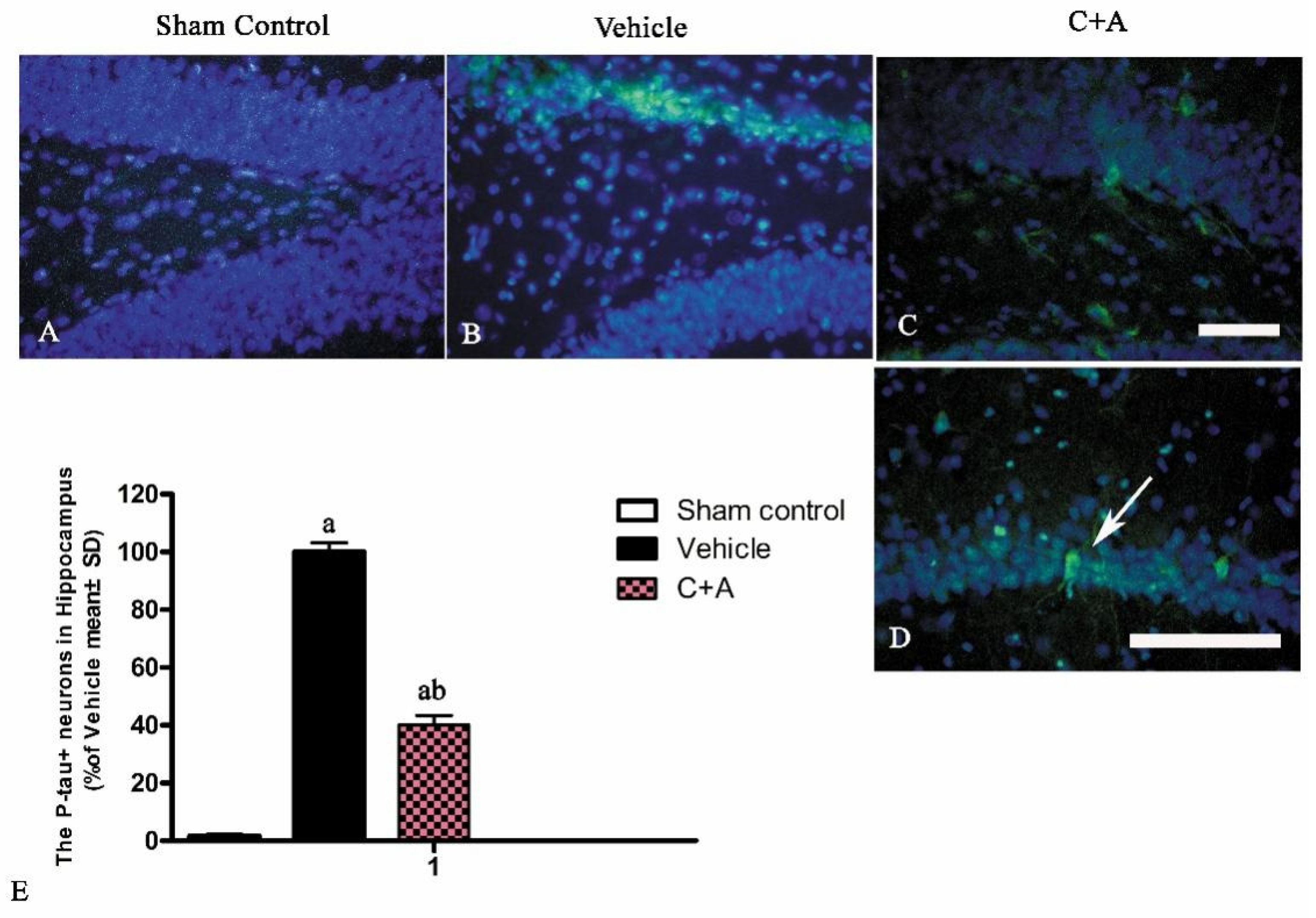
2.4. Treatment with C16 Plus Ang-1 Reduced Autophagy and Neuronal Apoptosis, Restored the Expression of ACH and CHAT, Alleviated Sn Loss in AD Rats
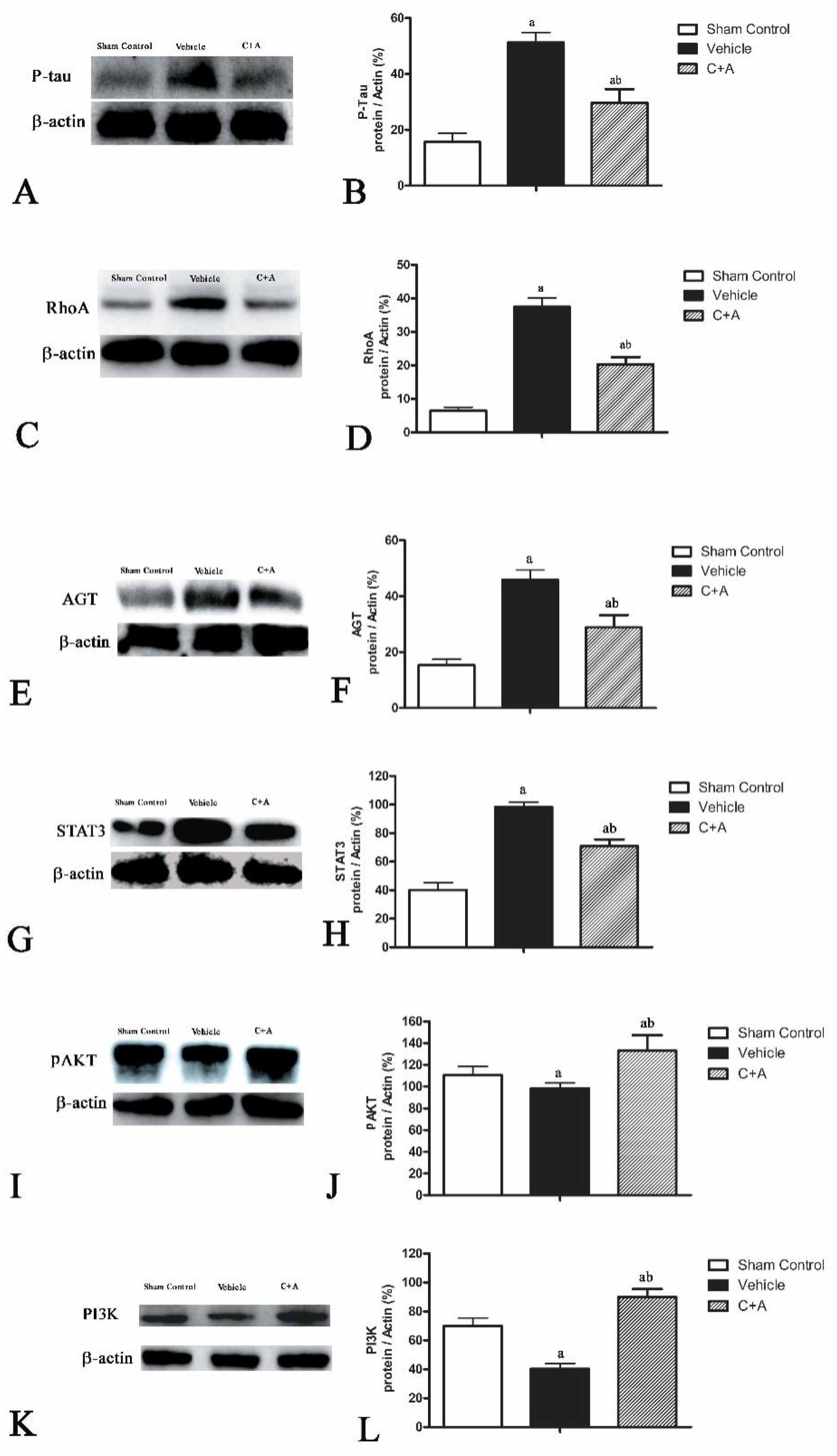
2.5. Treatment with C16 Plus Ang-1 Affected the Signaling Pathway Related to Inflammation
2.6. The Activity of C16 Plus Ang1 in AD Is Mediated by the PI3K/Akt Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. 2-VO
4.3. Aβ1-42 Injection
4.4. Behavioral Test
4.5. Perfusion and Tissue Processing
4.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy
4.7. Evans Blue (EB) Assay
4.8. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.9. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.10. Western Blot
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sweeney, M.D.; Kisler, K.; Montagne, A.; Toga, A.W.; Zlokovic, B.V. The role of brain vasculature in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1318–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisler, K.; Nelson, A.R.; Montagne, A.; Zlokovic, B.V. Cerebral blood flow regulation and neurovascular dysfunction in Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iturria-Medina, Y.; Sotero, R.C.; Toussaint, P.J.; Mateos-Pérez, J.M.; Evans, A.C. Early role of vascular dysregulation on late-onset Alzheimer’s disease based on multifactorial data-driven analysis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Sagare, A.P.; Zlokovic, B.V. Blood-brain barrier breakdown in Alzheimer disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, J.B.; Arnold, S.E.; Raible, K.; Brettschneider, J.; Xie, S.X.; Grossman, M.; Monsell, S.E.; Kukull, W.A.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Contribution of cerebrovascular disease in autopsy confirmed neurodegenerative disease cases in the National Alzheimer’s Coordinating Centre. Brain 2013, 136, 2697–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, J.; Nutma, E.; van der Valk, P.; Amor, S. Inflammation in CNS neurodegenerative diseases. Immunology 2018, 154, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Tian, K.W.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, H.; Han, S. Angiopoietin-1 and C16 Peptide Attenuate Vascular and Inflammatory Responses in Experimental Allergic Encephalomyelitis. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2016, 15, 496–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, S.; Park, J.K.; Meurs, M.; Zijlstra, J.G.; Koenecke, C.; Schrimpf, C.; Shushakova, N.; Gueler, F.; Haller, H.; Kümpers, P. Acute administration of recombinant Angiopoietin-1 ameliorates multiple-organ dysfunction syndrome and improves survival in murine sepsis. Cytokine 2011, 55, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yang, J.; Jiang, H.; Han, S. An ανβ3 integrin-binding peptide ameliorates symptoms of chronic progressive experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by alleviating neuroinflammatory responses in mice. J. Neuroimmune. Pharmacol. 2014, 9, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Arnold, S.A.; Sithu, S.D.; Mahoney, E.T.; Geralds, J.T.; Tran, P.; Benton, R.L.; Maddie, M.A.; D’Souza, S.E.; Whittemore, S.R.; et al. Rescuing vasculature with intravenous angiopoietin-1 and alpha v beta 3 integrin peptide is protective after spinal cord injury. Brain 2010, 133, 1026–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammana, S.; Fagone, P.; Cavalli, E.; Basile, M.S.; Petralia, M.C.; Nicoletti, F.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. The Role of Macrophages in Neuroinflammatory and Neurodegenerative Pathways of Alzheimer’s Disease, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, and Multiple Sclerosis: Pathogenetic Cellular Effectors and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenk, G.J.; de Vries, H.E. Altered blood-brain barrier transport in neuro-inflammatory disorders. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2016, 20, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runtsch, M.C.; Ferrara, G.; Angiari, S. Metabolic determinants of leukocyte pathogenicity in neurological diseases. J. Neurochem. 2021, 158, 36–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalicova, A.; Majerova, P.; Kovac, A. Tau Protein and Its Role in Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 570045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Hu, J.F.; Yuan, Y.H.; Li, H.; Chen, N.H. Inhibition of chemokine-like factor 1 improves blood-brain barrier dysfunction in rats following focal cerebral ischemia. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 627, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Yu, J.M.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.B.; Kim, S.T.; Jang, S.K.; Choi, Y.W.; Lee, D.I.; Joo, S.S. Ginsenoside Re and Rd enhance the expression of cholinergic markers and neuronal differentiation in Neuro-2a cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 37, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Fang, T.; Yang, X.; Luo, X.; Guo, A.; Newell, K.A.; Huang, X.F.; Yu, Y. Galantamine improves cognition, hippocampal inflammation, and synaptic plasticity impairments induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. J. Neuroinflammation 2018, 15, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.; Ye, Z.; Tang, H.; Wang, C.; Peng, H.; Lai, W.; Li, Y.; Huang, W.; Lou, T. The RhoA/ROCK Pathway Ameliorates Adhesion and Inflammatory Infiltration Induced by AGEs in Glomerular Endothelial Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Rong, J.; Zhang, Z. The emerging role of angiotensinogen in cardiovascular diseases. J Cell Physiol. 2021, 236, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.K.; Lal, H.; Golden, H.B.; Gerilechaogetu, F.; Smith, M.; Guleria, R.S.; Foster, D.M.; Lu, G.; Dostal, D.E. Rac1 and RhoA differentially regulate angiotensinogen gene expression in stretched cardiac fibroblasts. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 90, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainer, B.; Nielsen, O.H. Changed colonic profile of P-selectin, platelet-endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1), intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), ICAM-2, and ICAM-3 in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2000, 121, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuichi, K.; Wada, T.; Iwata, Y.; Kokubo, S.; Hara, A.; Yamahana, J.; Sugaya, T.; Iwakura, Y.; Matsushima, K.; Asano, M.; et al. Interleukin-1-dependent sequential chemokine expression and inflammatory cell infiltration in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 2447–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.F.; Kataoka, K.; Toyama, K.; Sueta, D.; Koibuchi, N.; Yamamoto, E.; Yata, K.; Tomimoto, H.; Ogawa, H.; Kim-Mitsuyama, S. Attenuation of brain damage and cognitive impairment by direct renin inhibition in mice with chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Hypertension 2011, 58, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichenbach, N.; Delekate, A.; Plescher, M.; Schmitt, F.; Krauss, S.; Blank, N.; Halle, A.; Petzold, G.C. Inhibition of Stat3-mediated astrogliosis ameliorates pathology in an Alzheimer’s disease model. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, e9665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.B.; Tu, X.K.; Chen, Q.; Shi, S.S. Propofol Reduces Inflammatory Brain Injury after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Involvement of PI3K/Akt Pathway. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2019, 28, 104375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, X.K.; Zhang, H.B.; Shi, S.S.; Liang, R.S.; Wang, C.H.; Chen, C.M.; Yang, W.-Z. 5-LOX Inhibitor Zileuton Reduces Inflammatory Reaction and Ischemic Brain Damage Through the Activation of PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 2779–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayadi, A.E.; Zigmond, M.J.; Smith, A.D. IGF-1 protects dopamine neurons against oxidative stress: Association with changes in phosphokinases. Exp. Brain Res. 2016, 234, 1863–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Cai, X.; Di, W.; Li, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, A.; Qi, W.; Zhou, Z.; Fang, Y. MFG-E8 Selectively Inhibited Aβ-Induced Microglial M1 Polarization via NF-κB and PI3K-Akt Pathways. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 7777–7788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Bao, Y.T.; Zhou, X.J.; Lin, L.N.; Fu, Y.B.; Zhang, Y.J.; Li, C.Y.; Yang, Y.X. Intracerebroventricular injection of Aβ(1-42) combined with two-vessel occlusion accelerate Alzheimer’s disease development in rats. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2018, 214, 1583–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Chen, H.; Han, S. C16 peptide and angiopoietin-1 protect against LPS-induced BV-2 microglial cell inflammation. Life Sci. 2020, 256, 117894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sham Control | Vehicle | C + A | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 day | 13.11 ± 2.15 | 101 ± 7.74 * | 30.11 ± 3.82 *& |
| 2 days | 13.22 ± 3.23 | 74.11 ± 3.51 * | 27.88 ± 5.34 *& |
| 3 days | 5.0 ± 1.73 | 43.1 ± 8.28 * | 14.2 ± 1.56 *& |
| 4 days | 4.3 ± 1.8 | 47.78 ± 5.1 * | 15 ± 2.18 *& |
| 5 days | 4.4 ± 1.74 | 47.67 ± 3.67 * | 15.1 ± 1.76 *& |
| 6 days | 3.89 ± 1.16 | 44.89 ± 5.64 * | 10.3 ± 2 *& |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, X.; Wang, J.; Cai, H.; Jiang, H.; Han, S. C16 Peptide and Ang-1 Improve Functional Disability and Pathological Changes in an Alzheimer’s Disease Model Associated with Vascular Dysfunction. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15040471
Fu X, Wang J, Cai H, Jiang H, Han S. C16 Peptide and Ang-1 Improve Functional Disability and Pathological Changes in an Alzheimer’s Disease Model Associated with Vascular Dysfunction. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(4):471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15040471
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Xiaoxiao, Jing Wang, Huaying Cai, Hong Jiang, and Shu Han. 2022. "C16 Peptide and Ang-1 Improve Functional Disability and Pathological Changes in an Alzheimer’s Disease Model Associated with Vascular Dysfunction" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 4: 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15040471
APA StyleFu, X., Wang, J., Cai, H., Jiang, H., & Han, S. (2022). C16 Peptide and Ang-1 Improve Functional Disability and Pathological Changes in an Alzheimer’s Disease Model Associated with Vascular Dysfunction. Pharmaceuticals, 15(4), 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15040471






