Structure–Activity Relationship of N-Phenylthieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide Derivatives Designed as Forkhead Box M1 Inhibitors: The Effect of Electron-Withdrawing and Donating Substituents on the Phenyl Ring
Abstract
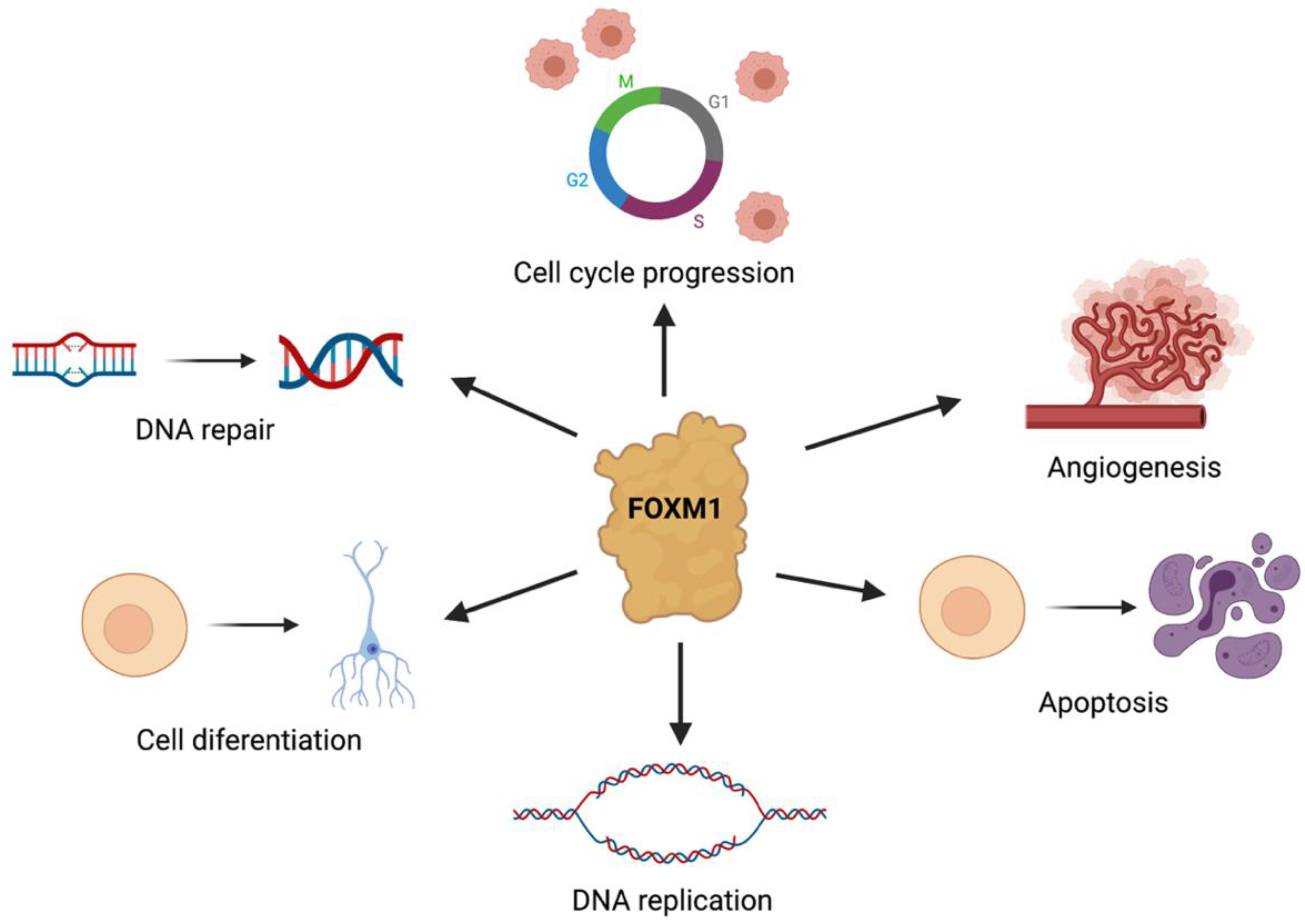
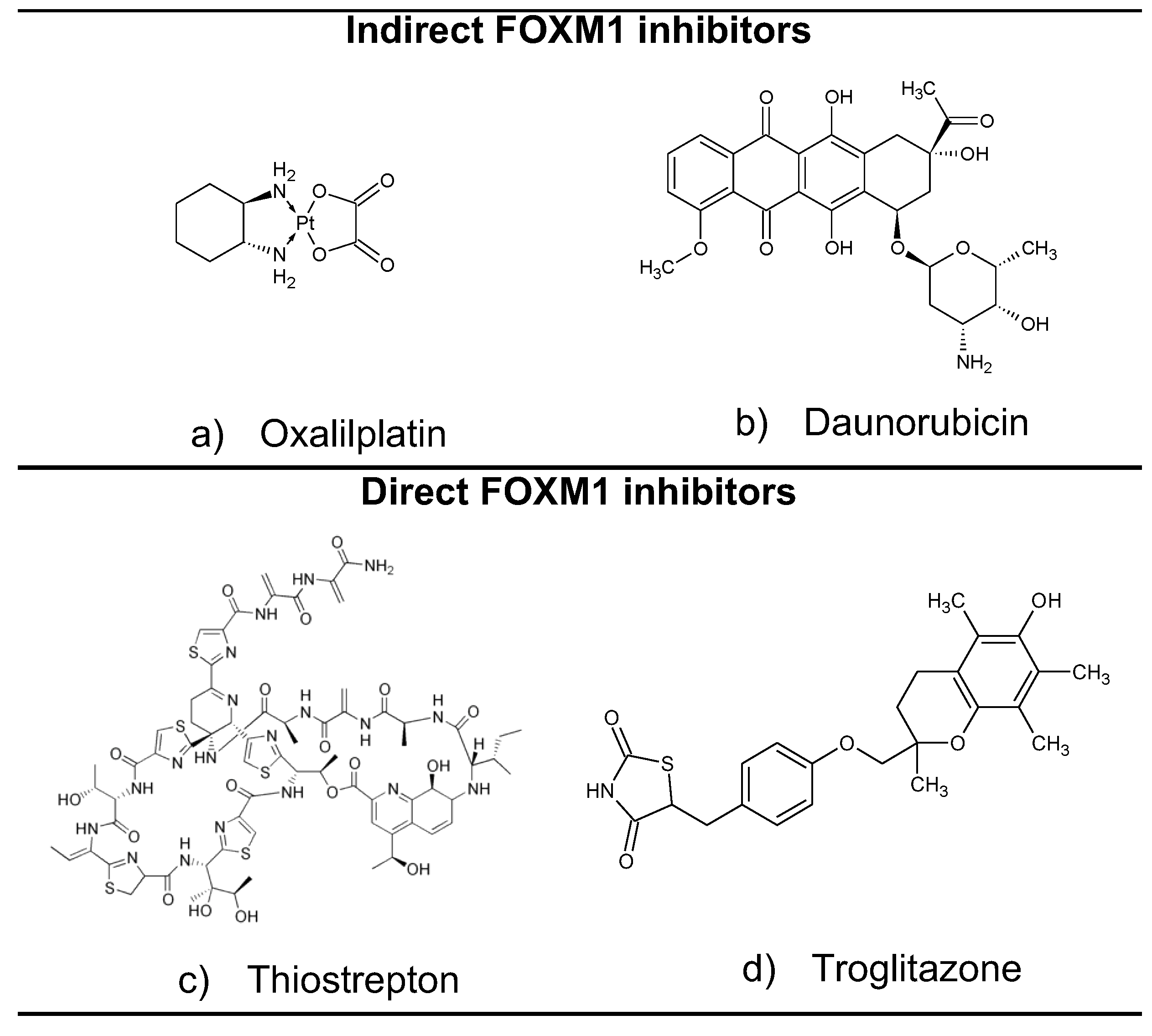
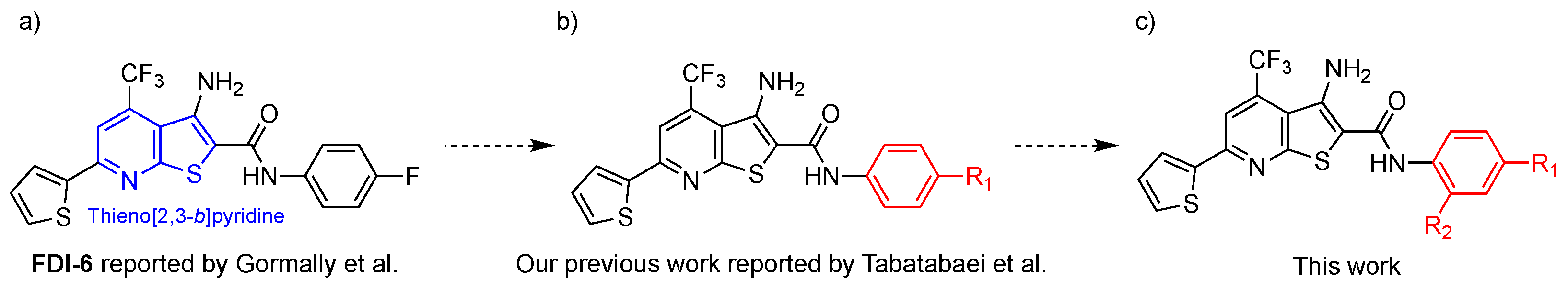
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
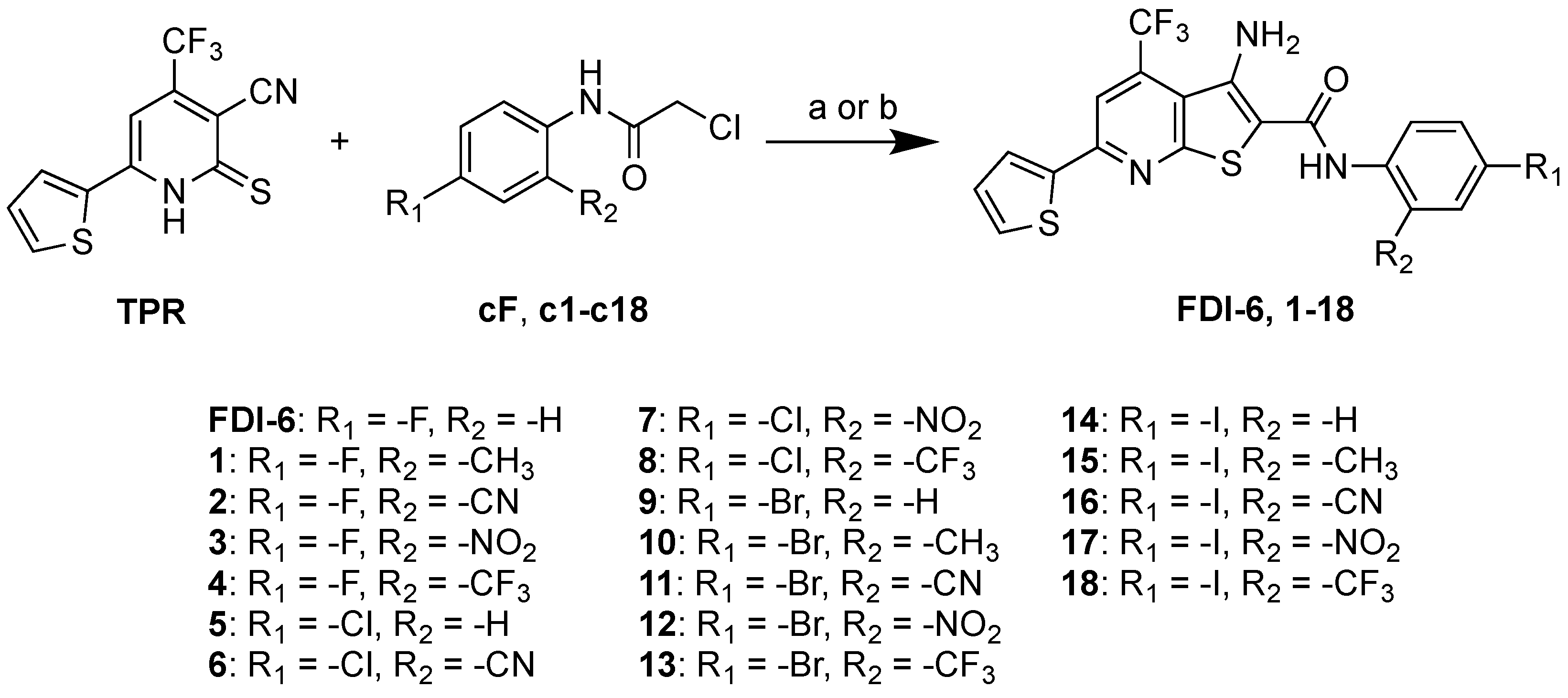
2.1. Synthesis of N-Phenylthieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide Derivatives
2.2. Determination of FOXM1’s Relative Expression
2.3. Cytotoxic Activity Determination
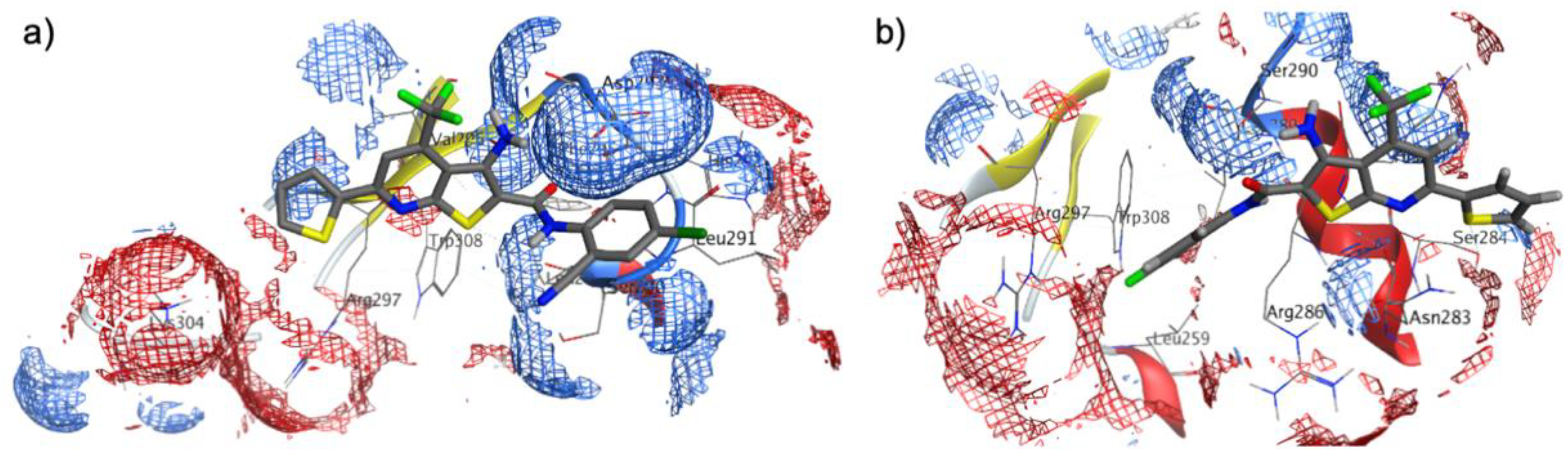
2.4. Molecular Docking in FOXM1’s DNA-Binding Domain
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Organic Synthesis: General
3.2. General Method for the Synthesis of the Final Derivatives (FDI-6 and 1–18): Conventional Heating
3.2.1. 3-Amino-N-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)thieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide (FDI-6)
3.2.2. 3-Amino-N-(4-fluoro-2-nitrophenyl)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)thieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide (3)
3.2.3. 3-Amino-N-(4-chlorophenyl)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)thieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide (5)
3.2.4. 3-Amino-N-(4-chloro-2-cyanophenyl)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)thieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide (6)
3.2.5. 3-Amino-N-(4-chloro-2-nitrophenyl)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)thieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide (7)
3.2.6. 3-Amino-N-(4-bromophenyl)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)thieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide (9)
3.2.7. 3-Amino-N-(4-bromo-2-cyanophenyl)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)thieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide (11)
3.2.8. 3-Amino-N-(4-bromo-2-nitrophenyl)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)thieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide (12)
3.2.9. 3-Amino-N-(4-bromo-2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)thieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide (13)
3.2.10. 3-Amino-N-(4-iodophenyl)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)-thieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide (14)
3.2.11. 3-Amino-N-(4-iodo-2-methylphenyl)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)thieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide (15)
3.2.12. 3-Amino-N-(2-cyano-4-iodophenyl)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)thieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide (16)
3.2.13. 3-Amino-N-(4-iodo-2-nitrophenyl)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)thieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide (17)
3.2.14. 3-Amino-N-(4-iodo-2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)thieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide (18)
3.3. General Method for the Synthesis of the Final Derivatives (FDI-6 and, 1–18): Microwave Heating
3.3.1. 3-Amino-N-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)thieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide (1)
3.3.2. 3-Amino-N-(2-cyano-4-fluorophenyl)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)thieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide (2)
3.3.3. 3-Amino-N-(4-fluor-2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)thieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide (4)
3.3.4. 3-Amino-N-(4-chloro-2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)thieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide (8)
3.3.5. 3-Amino-N-(4-bromo-2-methylphenyl)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)thieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide (10)
3.4. Western Blotting
3.5. Cell-Proliferation-Inhibition (MTT) Assay
3.6. Molecular Docking
3.7. MEP Maps
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wierstra, I. The Transcription Factor FOXM1 (Forkhead Box M1). In Advances in Cancer Research; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; Volume 118, pp. 97–398. ISBN 978-0-12-407173-5. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, C.-Y.; Muir, K.W.; Lam, E.W.-F. FOXM1: From Cancer Initiation to Progression and Treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2012, 1819, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halasi, M.; Gartel, A.L. Targeting FOXM1 in Cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, G.-B.; Li, X.-Z.; Zeng, S.; Liu, C.; Yang, S.-M.; Yang, L.; Hu, C.-J.; Bai, J.-Y. Regulation of the Master Regulator FOXM1 in Cancer. Cell. Commun. Signal. 2018, 16, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raychaudhuri, P.; Park, H.J. FoxM1: A Master Regulator of Tumor Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 4329–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei-Dakhili, S.A.; Aguayo-Ortiz, R.; Domínguez, L.; Velázquez-Martínez, C.A. Untying the Knot of Transcription Factor Druggability: Molecular Modeling Study of FOXM1 Inhibitors. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2018, 80, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegde, N.S.; Sanders, D.A.; Rodriguez, R.; Balasubramanian, S. The Transcription Factor FOXM1 Is a Cellular Target of the Natural Product Thiostrepton. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gormally, M.V.; Dexheimer, T.S.; Marsico, G.; Sanders, D.A.; Lowe, C.; Matak-Vinković, D.; Michael, S.; Jadhav, A.; Rai, G.; Maloney, D.J.; et al. Suppression of the FOXM1 Transcriptional Programme via Novel Small Molecule Inhibition. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei Dakhili, S.A.; Pérez, D.J.; Gopal, K.; Tabatabaei Dakhili, S.Y.; Ussher, J.R.; Velázquez-Martínez, C.A. A Structure-Activity Relationship Study of Forkhead Domain Inhibitors (FDI): The Importance of Halogen Binding Interactions. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 93, 103269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinov, V.P.; Dotsenko, V.V.; Krivokolysko, S.G. Thienopyridines: Synthesis, Properties, and Biological Activity. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2005, 54, 864–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinov, V.P.; Dotsenko, V.V.; Krivokolysko, S.G. The Chemistry of Thienopyridines. In Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007; Volume 93, pp. 117–178. ISBN 978-0-12-373934-6. [Google Scholar]
- Eurtivong, C.; Reynisdóttir, I.; Kuczma, S.; Furkert, D.P.; Brimble, M.A.; Reynisson, J. Identification of Anticancer Agents Based on the Thieno[2,3-b]Pyridine and 1H-Pyrazole Molecular Scaffolds. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 3521–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurtivong, C.; Semenov, V.; Semenova, M.; Konyushkin, L.; Atamanenko, O.; Reynisson, J.; Kiselyov, A. 3-Amino-Thieno[2,3-b]Pyridines as Microtubule-Destabilising Agents: Molecular Modelling and Biological Evaluation in the Sea Urchin Embryo and Human Cancer Cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, T.; Valant, C.; Crosby, I.T.; Sexton, P.M.; Christopoulos, A.; Capuano, B. Probing Structural Requirements of Positive Allosteric Modulators of the M4 Muscarinic Receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 8196–8200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gartel, A.L. Targeting FOXM1 Auto-Regulation in Cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 185–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xie, Y.; Qiao, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, B. Identification of FOXM1 as a Specific Marker for Triple-negative Breast Cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 54, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, D.J.; Tabatabaei Dakhili, S.A.; Bergman, C.; Dufour, J.; Wuest, M.; Juengling, F.D.; Wuest, F.; Velazquez-Martinez, C.A. FOXM1 Inhibitors as Potential Diagnostic Agents: 1st Generation of a PET Probe Targeting FOXM1 to Detect Triple Negative-breast Cancer in Vitro and in Vivo. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei Dakhili, S.A.; Pérez, D.J.; Gopal, K.; Haque, M.; Ussher, J.R.; Kashfi, K.; Velázquez-Martínez, C.A. SP1-Independent Inhibition of FOXM1 by Modified Thiazolidinediones. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 209, 112902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, Y.; Laws, M.J.; Sanabria Guillen, V.; Kim, S.H.; Dey, P.; Smith, B.P.; Gong, P.; Bindman, N.; Zhao, Y.; Carlson, K.; et al. Suppression of FOXM1 Activities and Breast Cancer Growth in Vitro and in Vivo by a New Class of Compounds. npj Breast Cancer 2019, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molecular Operating Environment (MOE); Chemical Computing Group ULC: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2021.
- Galli, C.L.; Sensi, C.; Fumagalli, A.; Parravicini, C.; Marinovich, M.; Eberini, I. A Computational Approach to Evaluate the Androgenic Affinity of Iprodione, Procymidone, Vinclozolin and Their Metabolites. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbeil, C.R.; Williams, C.I.; Labute, P. Variability in Docking Success Rates Due to Dataset Preparation. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 2012, 26, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Peralta, L.; Razo-Hernández, R.S.; Pastor, N.; Santiago, Á.; Guevara-Salazar, J.A.; Fernández-Zertuche, M. 1,4-Disubstituted-1,2,3-triazole GABA Analogues: Synthesis, In Vitro Evaluation, Quantum QSAR and Molecular Docking against Pseudomonas Fluorescens GABA-AT. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquina, S.; Maldonado-Santiago, M.; Sánchez-Carranza, J.N.; Antúnez-Mojica, M.; González-Maya, L.; Razo-Hernández, R.S.; Alvarez, L. Design, Synthesis and QSAR Study of 2′-Hydroxy-4′-Alkoxy Chalcone Derivatives That Exert Cytotoxic Activity by the Mitochondrial Apoptotic Pathway. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littler, D.R.; Alvarez-Fernandez, M.; Stein, A.; Hibbert, R.G.; Heidebrecht, T.; Aloy, P.; Medema, R.H.; Perrakis, A. Structure of the FoxM1 DNA-Recognition Domain Bound to a Promoter Sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 4527–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naïm, M.; Bhat, S.; Rankin, K.N.; Dennis, S.; Chowdhury, S.F.; Siddiqi, I.; Drabik, P.; Sulea, T.; Bayly, C.I.; Jakalian, A.; et al. Solvated Interaction Energy (SIE) for Scoring Protein−Ligand Binding Affinities. 1. Exploring the Parameter Space. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2007, 47, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, J.J.P. Optimization of Parameters for Semiempirical Methods I. Method. J. Comput. Chem. 1989, 10, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, P.J.; Devlin, F.J.; Chabalowski, C.F.; Frisch, M.J. Ab Initio Calculation of Vibrational Absorption and Circular Dichroism Spectra Using Density Functional Force Fields. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 11623–11627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spartan’18; Wavefunction, Inc.: Irvine, CA, USA, 2018.
- Wang, N.-Y.; Zuo, W.-Q.; Xu, Y.; Gao, C.; Zeng, X.-X.; Zhang, L.-D.; You, X.-Y.; Peng, C.-T.; Shen, Y.; Yang, S.-Y.; et al. Discovery and Structure–Activity Relationships Study of Novel Thieno[2,3-b]Pyridine Analogues as Hepatitis C Virus Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
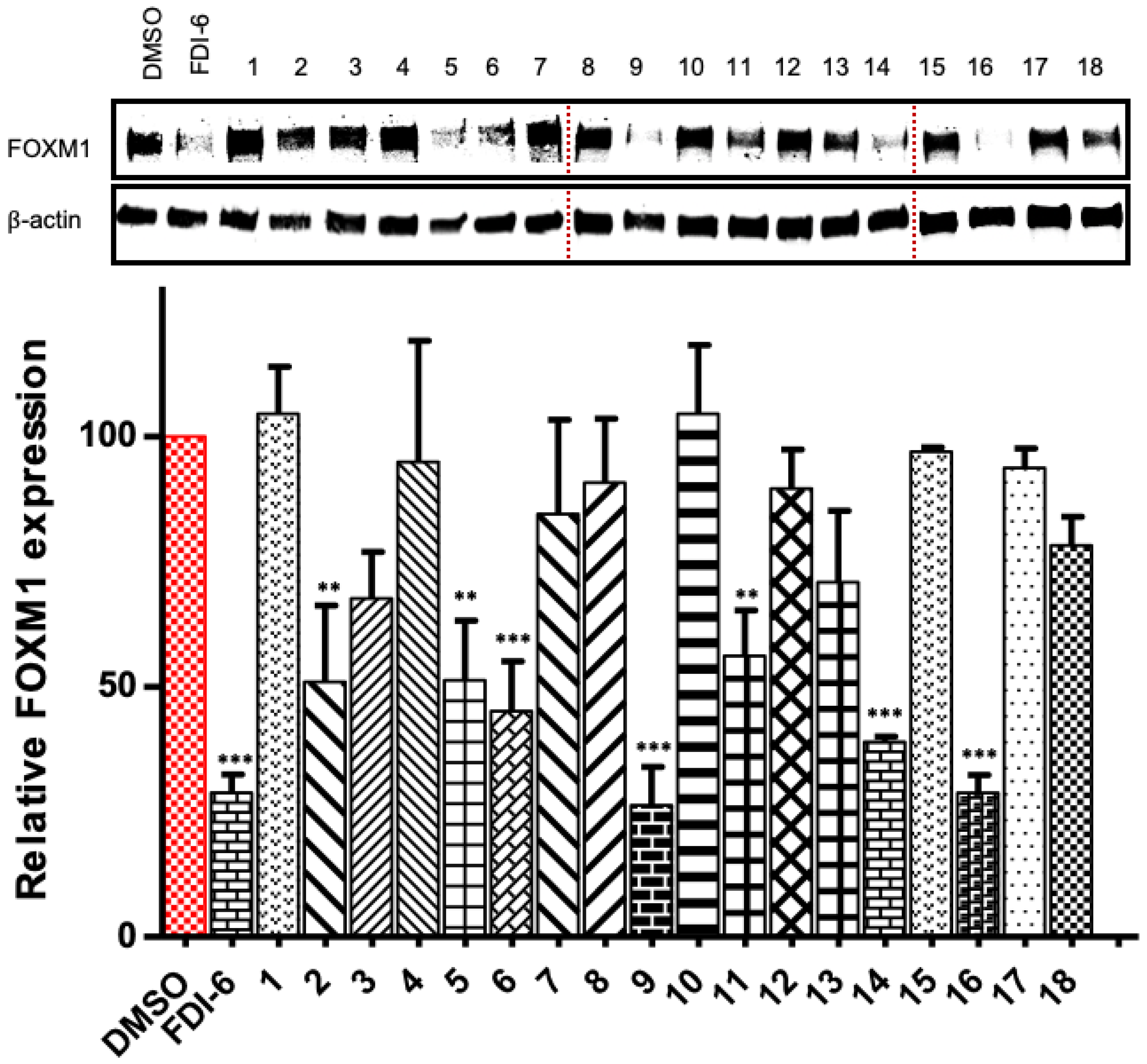
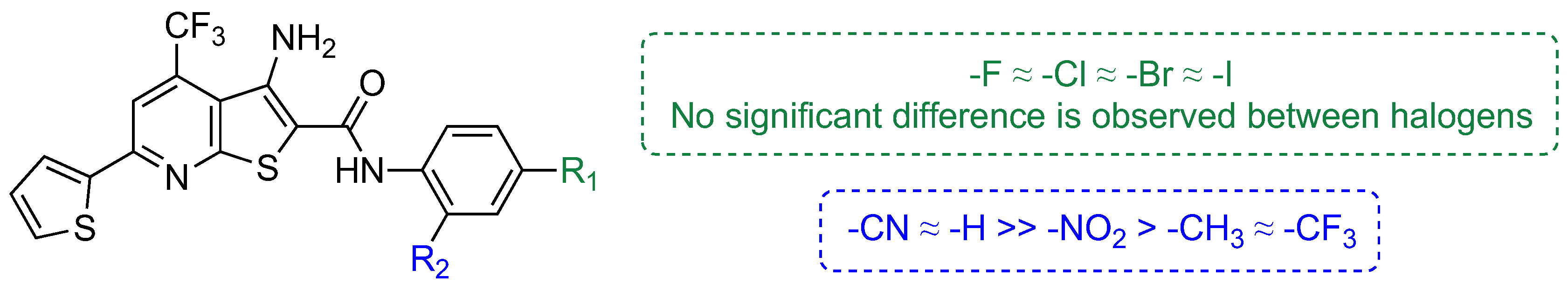
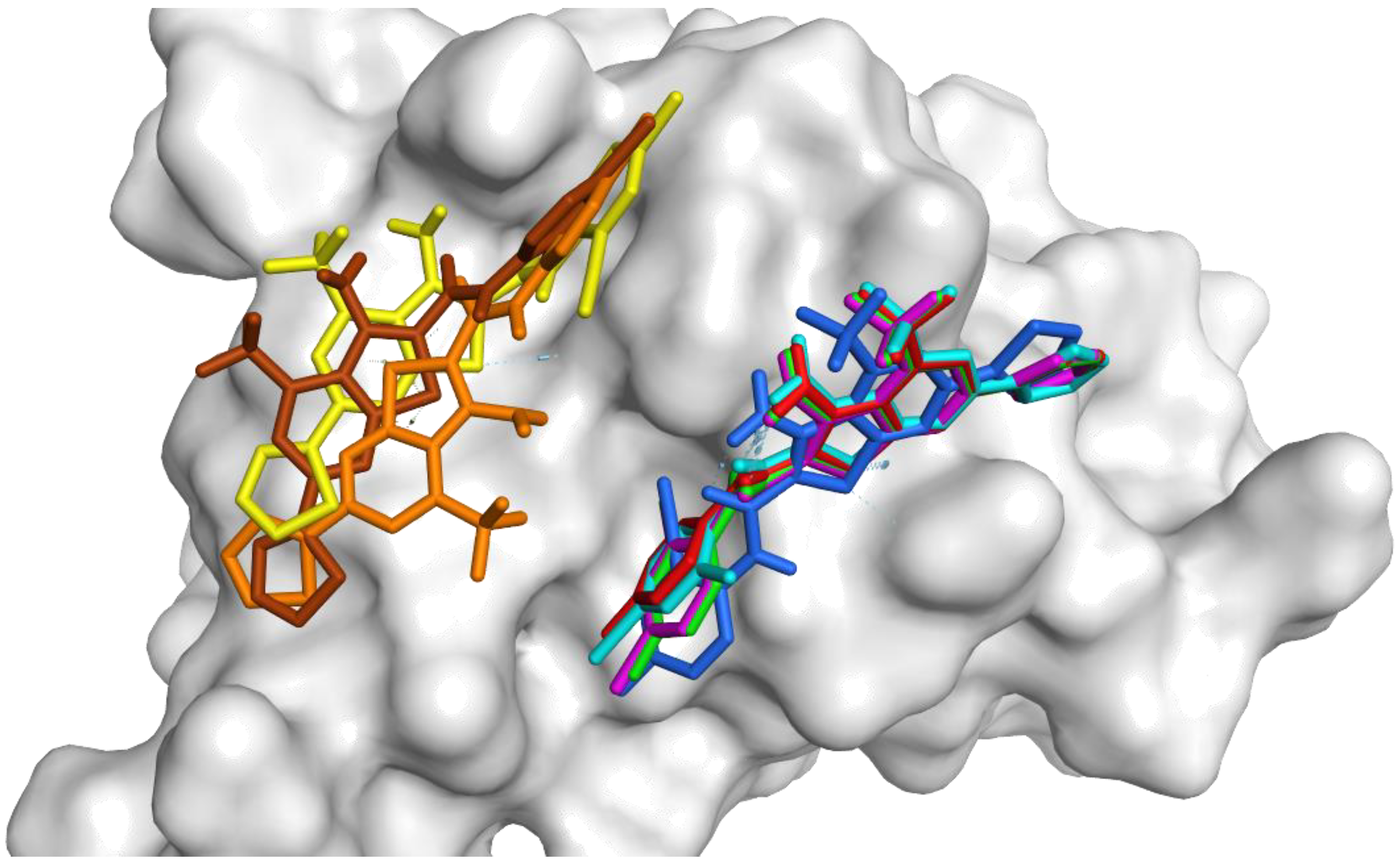
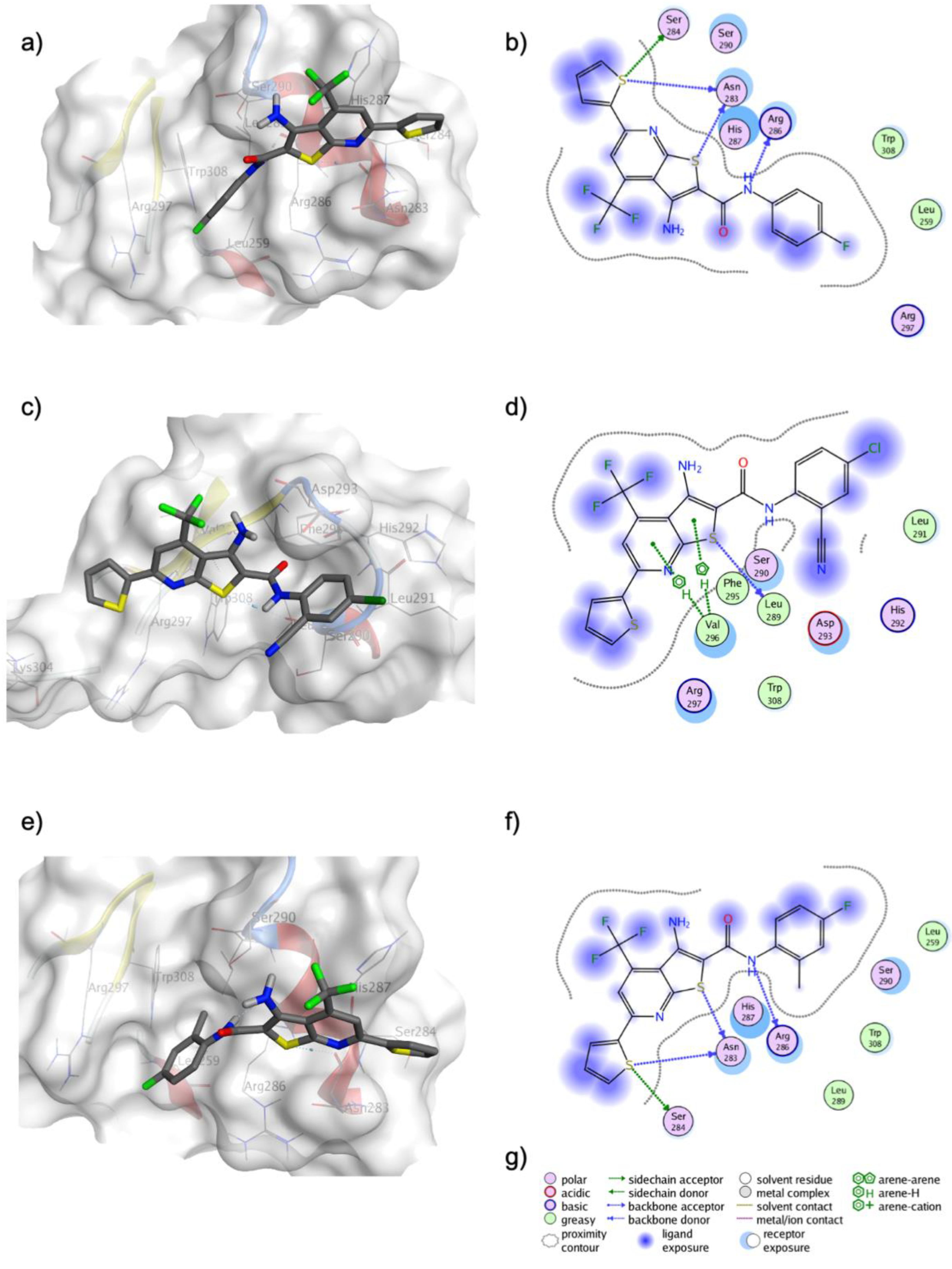
| Compound | MDA-MB-231 IC50 (μM) a |
|---|---|
| FDI-6 | 11.67 ± 1.35 |
| 1 | 171.5 ± 1.49 |
| 6 | 8.75 ± 1.27 |
| 16 | 4.61 ± 1.34 |
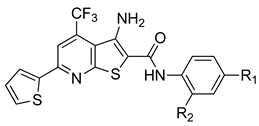 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
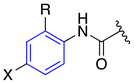
| Compound | S (kcal/mol) a | R1 | R2 |
| FDI-6 | −5.3383 | -F | -H |
| 1 | −5.6402 | -F | -CH3 |
| 2 | −5.4899 | -F | -CN |
| 3 | −5.9180 | -F | -NO2 |
| 4 | −5.4391 | -F | -CF3 |
| 5 | −5.5565 | -Cl | -H |
| 6 | −7.2807 | -Cl | -CN |
| 7 | −6.1224 | -Cl | -NO2 |
| 8 | −5.5823 | -Cl | -CF3 |
| 9 | −5.6117 | -Br | -H |
| 10 | −5.8423 | -Br | -CH3 |
| 11 | −5.9348 | -Br | -CN |
| 12 | −6.1845 | -Br | -NO2 |
| 13 | −5.7709 | -Br | -CF3 |
| 14 | −5.6386 | -I | -H |
| 15 | −5.5661 | -I | -CH3 |
| 16 | −5.8317 | -I | -CN |
| 17 | −5.7237 | -I | -NO2 |
| 18 | −5.7932 | -I | -CF3 |
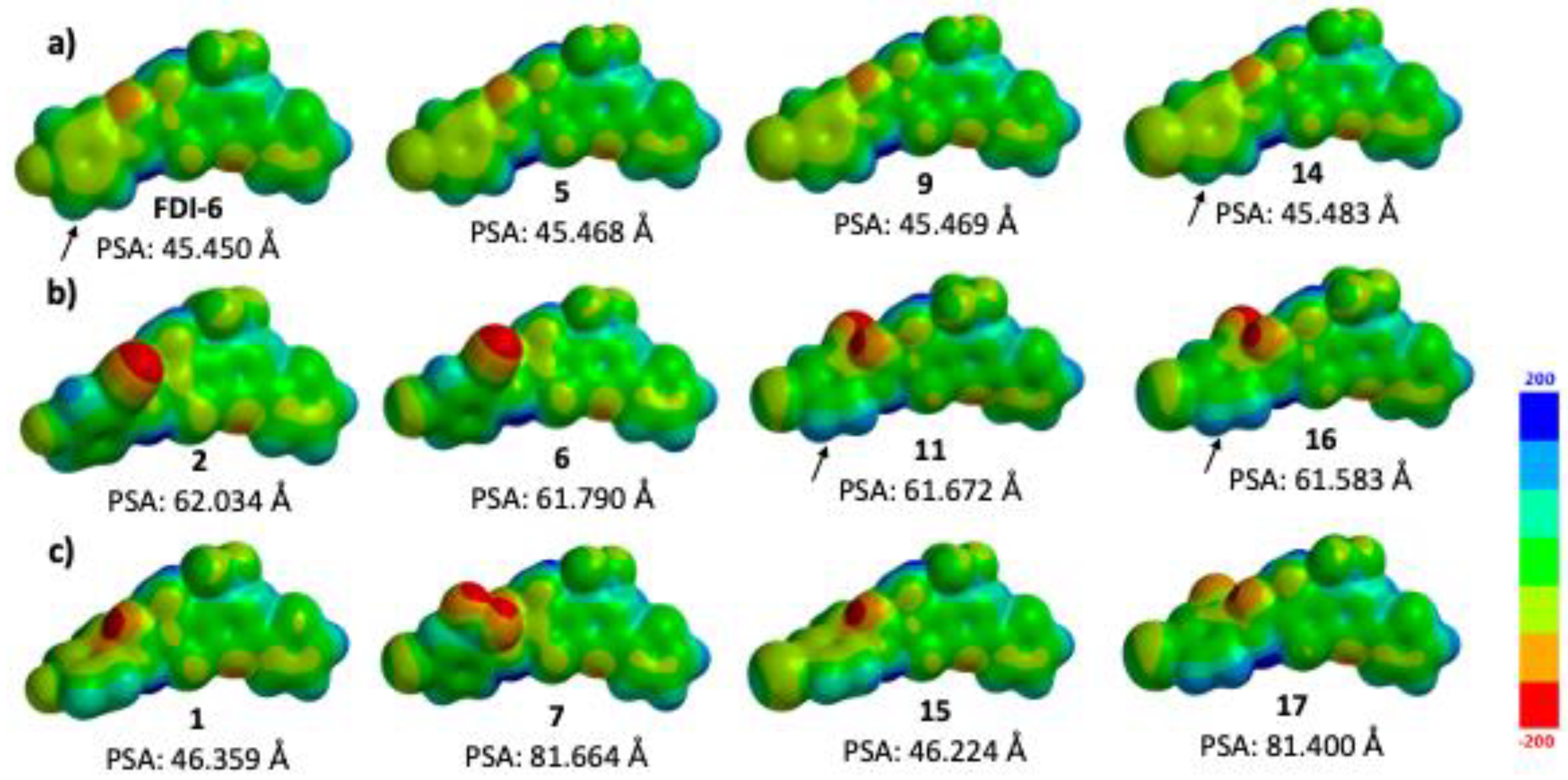
| MEP Values (kJ/mol) a | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 | 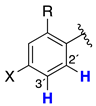 |  | |
| FDI-6 | −112.0 | 44.0 | −50.0 to 17.4 |
| 5 | −117.4 | 83.4 | −65.0 to 4.1 |
| 9 | −111.4 | 81.4 | −65.0 to 0.4 |
| 14 | −109.0 | 77.4 | −69.7 to −14.7 |
| 2 | −128.7 | 108.2 | −5.0 to 37.5 |
| 6 | −154.1 | 110.0 | −7.0 to 50.0 |
| 11 | −165.0 | 98.8 | −18.1 to 51.3 |
| 16 | −160.0 | 108.8 | −23.2 to 54.7 |
| 1 | −167.6 | 75.3 | −104 to 59 |
| 7 | −151.0 | 119.3 | −7.0 to 30.4 |
| 1 | −157.1 | 76.4 | −72.0 to 3.0 |
| 17 | −146.3 | 112.0 | −36.4 to 58.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huerta-García, C.S.; Pérez, D.J.; Velázquez-Martínez, C.A.; Tabatabaei Dakhili, S.A.; Romo-Mancillas, A.; Castillo, R.; Hernández-Campos, A. Structure–Activity Relationship of N-Phenylthieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide Derivatives Designed as Forkhead Box M1 Inhibitors: The Effect of Electron-Withdrawing and Donating Substituents on the Phenyl Ring. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15030283
Huerta-García CS, Pérez DJ, Velázquez-Martínez CA, Tabatabaei Dakhili SA, Romo-Mancillas A, Castillo R, Hernández-Campos A. Structure–Activity Relationship of N-Phenylthieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide Derivatives Designed as Forkhead Box M1 Inhibitors: The Effect of Electron-Withdrawing and Donating Substituents on the Phenyl Ring. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(3):283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15030283
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuerta-García, César Sebastian, David J. Pérez, Carlos A. Velázquez-Martínez, Seyed Amirhossein Tabatabaei Dakhili, Antonio Romo-Mancillas, Rafael Castillo, and Alicia Hernández-Campos. 2022. "Structure–Activity Relationship of N-Phenylthieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide Derivatives Designed as Forkhead Box M1 Inhibitors: The Effect of Electron-Withdrawing and Donating Substituents on the Phenyl Ring" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 3: 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15030283
APA StyleHuerta-García, C. S., Pérez, D. J., Velázquez-Martínez, C. A., Tabatabaei Dakhili, S. A., Romo-Mancillas, A., Castillo, R., & Hernández-Campos, A. (2022). Structure–Activity Relationship of N-Phenylthieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxamide Derivatives Designed as Forkhead Box M1 Inhibitors: The Effect of Electron-Withdrawing and Donating Substituents on the Phenyl Ring. Pharmaceuticals, 15(3), 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15030283










