Fasudil Ameliorates Methotrexate-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Modulation of Redox-Sensitive Signals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Chromatographic Method Validation for Fasudil Tissue Concentration
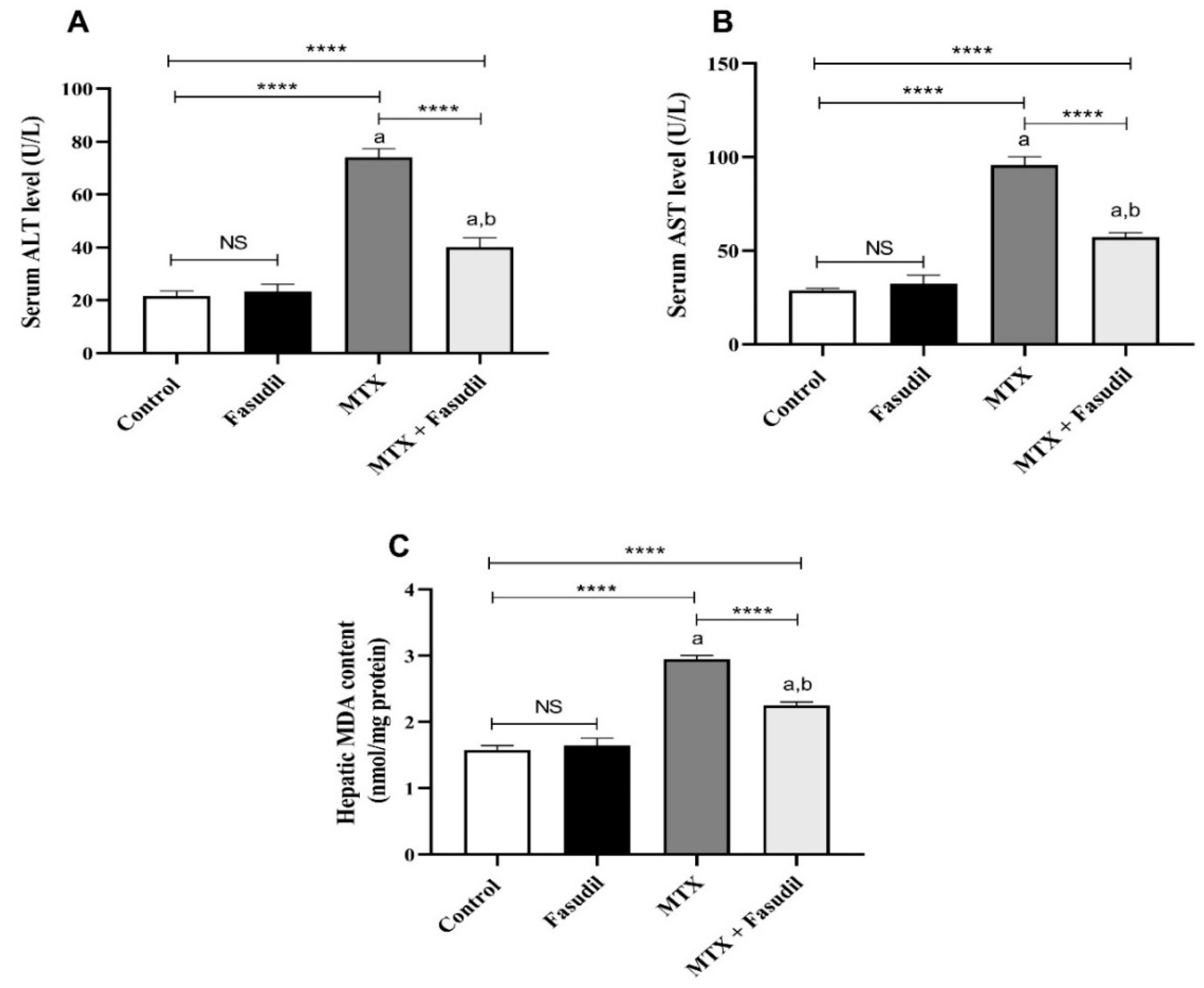
2.2. Effect of Fasudil on Hepatic Enzymes and Lipid Peroxidation after MTX Challenge
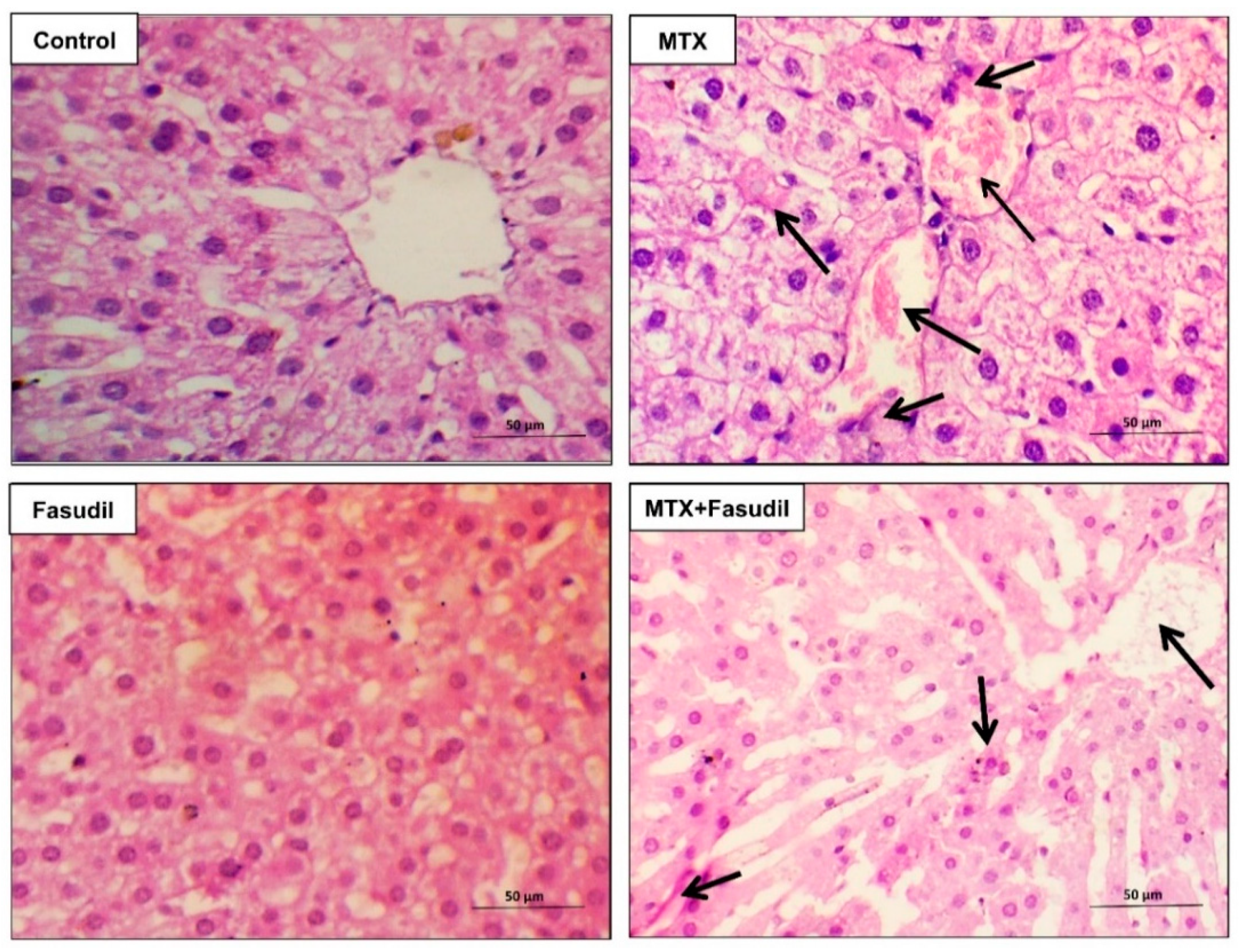
2.3. Effect of Fasudil on Hepatic Aberrations Induced by MTX Injection
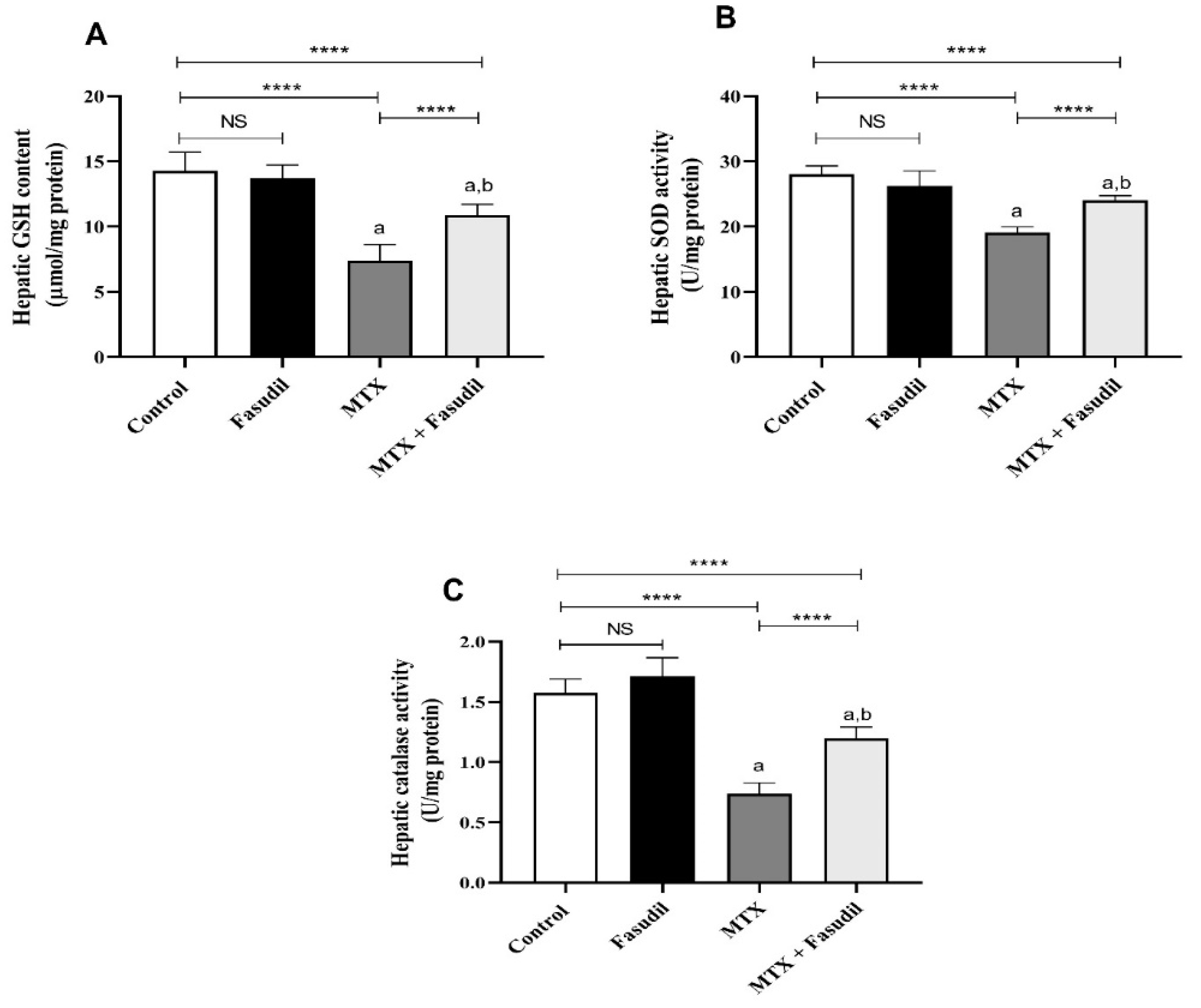
2.4. Effect of Fasudil on the Hepatic GSH Content as well as Antioxidant Enzyme Activity
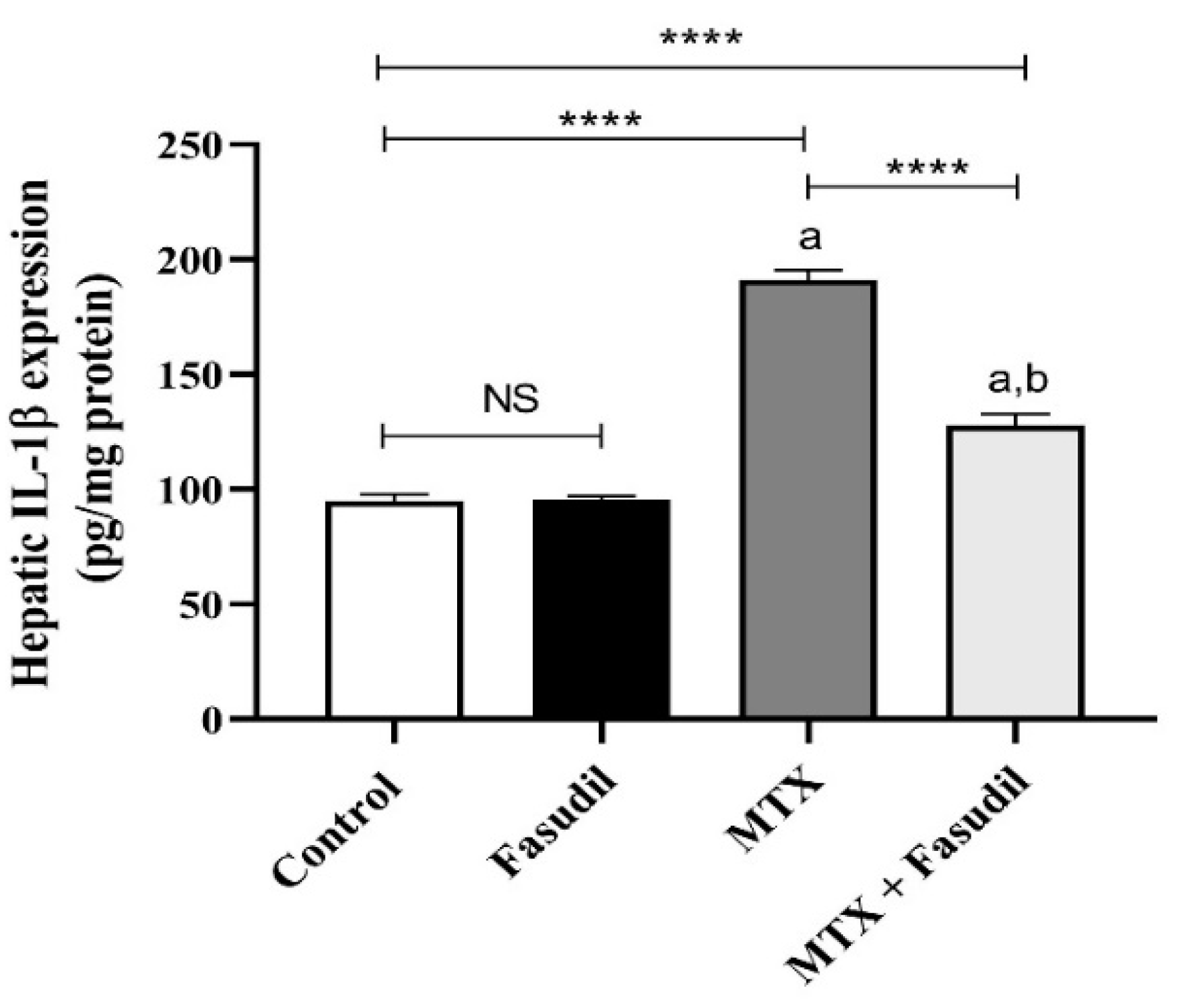
2.5. Effect of Fasudil on IL-1β Expression
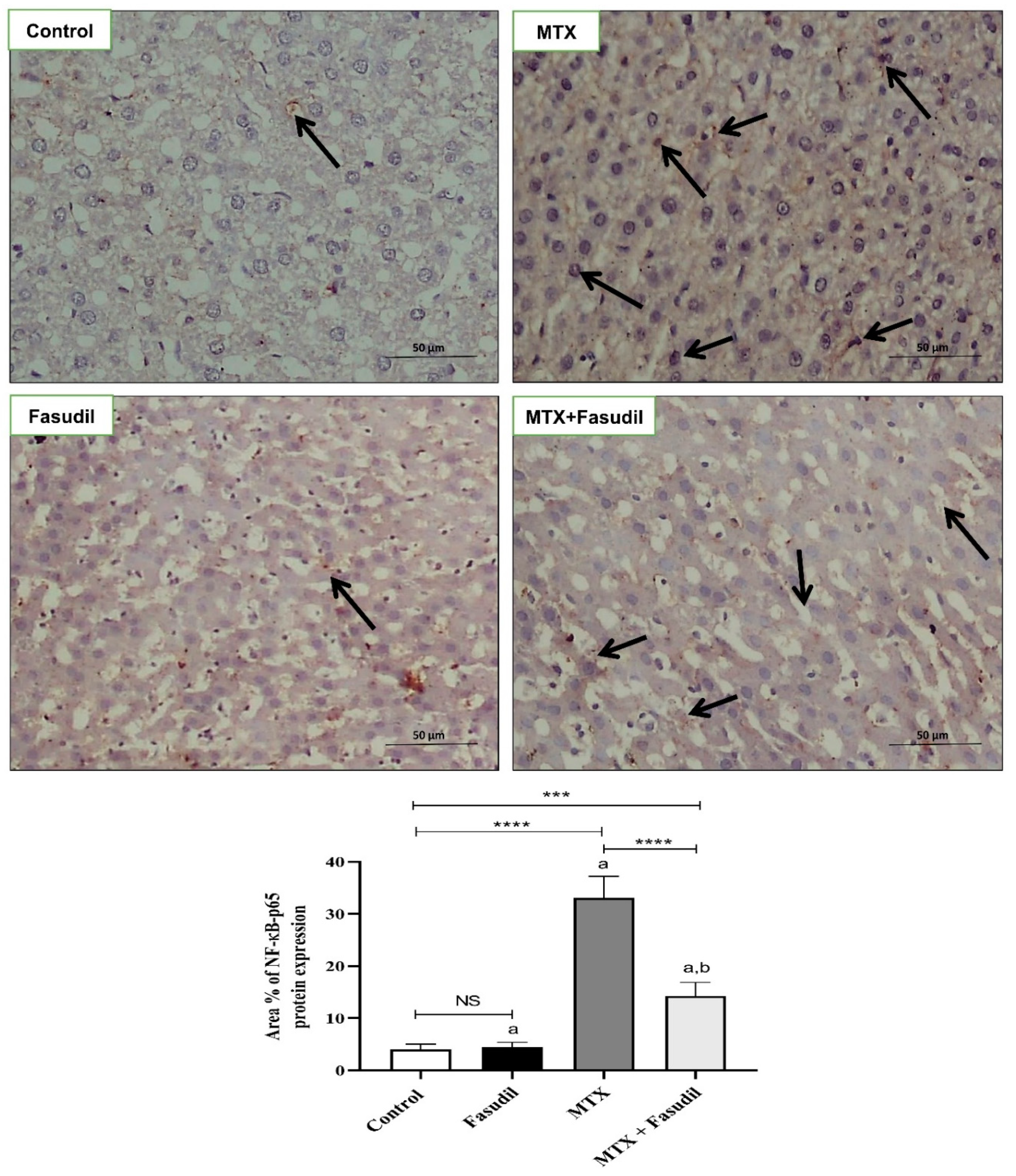
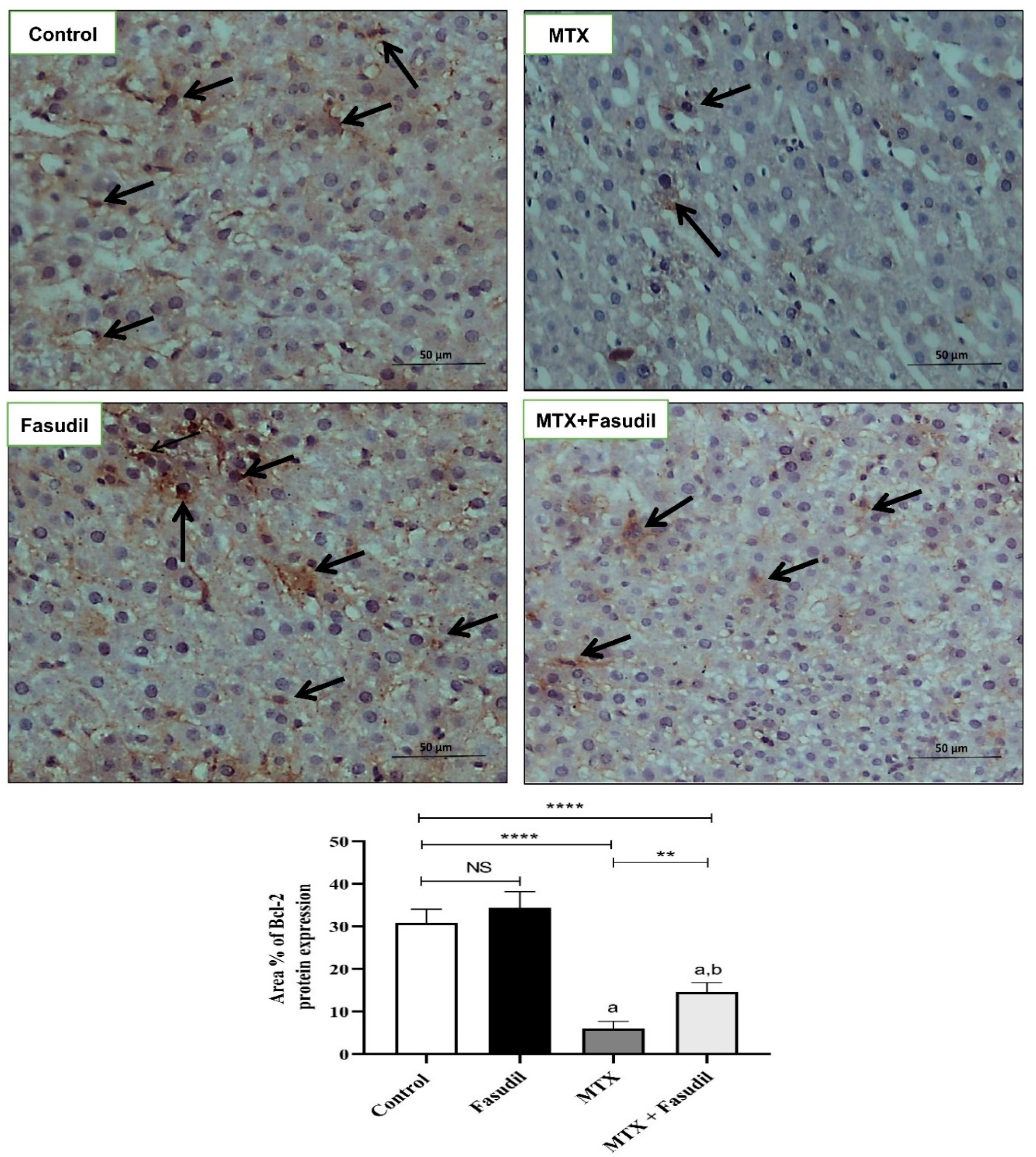
2.6. Effect of Fasudil on NF-κB-p65 and Bcl-2 Expressions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drugs, Reagents, and Chemicals
4.2. Animals
4.3. Study Design
4.4. Development of the Chromatographic Method
4.4.1. Instrumentation
4.4.2. Preparation of Standard Solutions
4.4.3. Chromatographic Conditions
4.4.4. Calibration Curve of Fasudil in Hepatic Tissue Homogenate
4.5. Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Examination
4.6. Biochemical Investigations
4.6.1. Total Protein
4.6.2. Liver Enzymes
4.6.3. Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Activity
4.6.4. Catalase Activity
4.6.5. Malondialdehyde (MDA) Content
4.6.6. Proinflammatory Marker, IL-1β
4.6.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koźmiński, P.; Halik, P.K.; Chesori, R.; Gniazdowska, E. Overview of Dual-Acting Drug Methotrexate in Different Neurological Diseases, Autoimmune Pathologies and Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedoui, Y.; Guillot, X.; Sélambarom, J.; Guiraud, P.; Giry, C.; Jaffar-Bandjee, M.C.; Ralandison, S.; Gasque, P. Methotrexate an Old Drug with New Tricks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durrani, K.; Zakka, F.R.; Ahmed, M.; Memon, M.; Siddique, S.S.; Foster, C.S. Systemic therapy with conventional and novel immunomodulatory agents for ocular inflammatory disease. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2011, 56, 474–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, S.C.; McCormick, J.; Pui, C.-H.; Buddington, R.K.; Harvey, R.D. Preventing and Managing Toxicities of High-Dose Methotrexate. The Oncologist 2016, 21, 1471–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakir, T.; Basturk, A.; Polat, C.; Aslaner, A.; Durgut, H.; Sehirli, A.O.; Gul, M.; Ogunc, A.V.; Gul, S.; Sabuncuoglu, M.Z.; et al. Does alfa lipoic acid prevent liver from methotrexate induced oxidative injury in rats? Acta. Cir. Bras. 2015, 30, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzam, A.; Jiyad, Z.; O’Beirne, J. Is methotrexate hepatotoxicity associated with cumulative dose? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2021, 62, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barak, A.J.; Tuma, D.J.; Beckenhauer, H.C. Methotrexate hepatotoxicity. J. Am. Coll. Nutrition. 1984, 3, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avouac, J.; Degrave, R.; Vergneault, H.; Combier, A.; Wanono, S.; Boisson, M.; Frantz, C.; Allanore, Y. Risk of liver fibrosis induced by methotrexate and other rheumatoid arthritis medications according to the Fibrosis-4 Index. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, N.; Rashid, S.; Nafees, S.; Hasan, S.K.; Shahid, A.; Majed, F.; Sultana, S. Protective effect of Chlorogenic acid against methotrexate induced oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in rat liver: An experimental approach. Chem. Interact. 2017, 272, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbero-Villares, A.; Jimenez-Ridruejo, J.M.; Taxonera, C.; Lopez-Sanroman, A.; Pajares, R.; Bermejo, F.; Perez-Calle, J.L.; Mendozam, J.L.; Algaba, A.; Moreno-Otero, R.; et al. Evaluation of liver fibrosis by transient elastography (Fibroscan(R)) in patients with inflammatory bowel disease treated with methotrexate: A multicentric trial. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 47, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordbar, M.; Shakibazad, N.; Fattahi, M.; Haghpanah, S.; Honar, N. Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid and vitamin E in the prevention of liver injury from methotrexate in pediatric leukemia. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 29, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruf, A.A.; O'Brien, P.J.; Naserzadeh, P.; Fathian, R.; Salimi, A.; Pourahmad, J. Methotrexate induced mitochondrial injury and cytochrome c release in rat liver hepatocytes. Drug. Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 41, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armagan, I.; Bayram, D.; Candan, I.A.; Yigit, A.; Celik, E.; Armagan, H.H.; Uğuz, A.C. Effects of pentoxifylline and alpha lipoic acid on methotrexate-induced damage in liver and kidney of rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 39, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskin, B.; Erdogan, M.; Yiğittürk, G.; Günenç, D.; Erbaş, O. Antifibrotic Effect of Lactulose on a Methotrexate-Induced Liver Injury Model. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2017, 2017, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Qin, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, Z.; Liu, L. Oat phenolic compounds regulate metabolic syndrome in high fat diet-fed mice via gut microbiota. Food. Biosci. 2022, 50, 101946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcilar, C.; Ozakca-Gunduz, I.; Altan, V.M. Contributions of Rho-kinase and AMP-related kinase signaling pathways to responses mediated by endothelium-derived contracting factors in diabetic rat aorta. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 97, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demiryürek, S.; Baysalman, E.; Mammadov, A.; Demiryürek, A.T. Contribution of the Rho-kinase to Systemic Sclerosis and Behçet’s Disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 3402–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-Y.; Wu, J.-M.; Su, T.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Lin, X.-J. Fasudil, a Rho-Kinase Inhibitor, Exerts Cardioprotective Function in Animal Models of Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury: A Meta-Analysis and Review of Preclinical Evidence and Possible Mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, S.; Tashiro, H.; Kimura, Y.; Hirata, K.; Tsutada, M.; Mikuriya, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Amano, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Ohdan, H. Rho-kinase inhibitor targeting the liver prevents ischemia/reperfusion injury in the steatotic liver without major systemic adversity in rats. Liver Transplant. 2015, 21, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, H.; Jian, W.; Zhuang, J.; Wang, K.; Peng, W.; Xu, Y. The Rho/Rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor fasudil in the protection of endothelial cells against advanced glycation end products through the nuclear factor κB pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2013, 6, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tian, L.; Ri, H.; Qi, J.; Fu, P. Berberine elevates mitochondrial membrane potential and decreases reactive oxygen species by inhibiting the Rho/ROCK pathway in rats with diabetic encephalopathy. Mol. Pain 2021, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hilal, T.A.; Hossain, M.A.; Alobaida, A.; Alam, F.; Keshavarz, A.; Nozik-Grayck, E.; Stenmark, K.R.; German, N.A.; Ahsan, F. Design, synthesis and biological evaluations of a long-acting, hypoxia-activated prodrug of fasudil, a ROCK inhibitor, to reduce its systemic side-effects. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Society 2021, 334, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockmann, C.; Corkhill, C.; Jaroslawska, E.; Dege, S.; Brockmann, T.; Kociok, N.; Joussen, A.M. Systemic Rho-kinase inhibition using fasudil in mice with oxygen-induced retinopathy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2019, 257, 1699–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, P.; Liang, Y.; Wang, N. Fasudil alleviates pressure overload-induced heart failure by activating Nrf2-mediated antioxidant responses. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 6452–6460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Meng, T.; Ren, X.; Li, X.; Lu, L. Fasudil alleviates acetaminophen-induced liver injury via targeting Rhoa/ROCK signal pathway. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2021, 46, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Y.; Xu, P.-F. Therapeutic potentials of fasudil in liver fibrosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 7859–7861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.-T.; Ma, K. Fasudil protects against isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in mice via inhibiting Rho/ROCK signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 5659–5667. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, C.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, D. Alleviation of the doxorubicin-induced nephrotoxicity by fasudil in vivo and in vitro. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 145, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gu, Q.; Liu, X.; Song, L.; Chai, Z.; Guo, M.; Yu, J.; Ma, C. Fasudil ameliorates cognitive deficits, oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis via inhibiting ROCK/MAPK and activating Nrf2 signalling pathways in APP/PS1 mice. Folia Neuropathol. 2021, 59, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-H.; Zhu, D.; Xie, S.; Deng, Y.; Pan, Y.; Ren, J.; Liu, H.-G. Inhibition of Rho-kinase Attenuates Left Ventricular Remodeling Caused by Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia in Rats via Suppressing Myocardial Inflammation and Apoptosis. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2017, 70, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yodoi, R.; Tamba, S.; Morimoto, K.; Segi-Nishida, E.; Nishihara, M.; Ichikawa, A.; Narumiya, S.; Sugimoto, Y. RhoA/Rho kinase signaling in the cumulus mediates extracellular matrix assembly. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 3345–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryan, B.A.; Street, C.A.; Routhier, A.A.; Spencer, C.; Perkins, A.L.; Masterjohn, K.; Hackathorn, A.; Montalvo, J.; Dennstedt, E.A. Pharmacological inhibition of Rho-kinase (ROCK) signaling enhances cisplatin resistance in neuroblastoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2010, 37, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Min, F.; Jia, X.J.; Gao, Q.; Niu, F.; Hu, Z.Y.; Han, Y.L.; Shi, H.J.; Yu, Y. Remote ischemic post-conditioning protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting the Rho-kinase signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 19, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Fang, C.; Zhang, L.; Deng, Y.; Wang, M.; Meng, F. Fasudil hydrochloride hydrate, a Rho-kinase inhibitor, ameliorates hepatic fibrosis in rats with type 2 diabetes. Chin. Med. J. 2014, 127, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elkattawy, H.A.; Elsherbi, D.M.A.; Ebrahim, H.A.; Abdullah, D.M.; Al-Zahaby, S.A.; Nosery, Y.; Hassan, A.E.-S. Rho-Kinase Inhibition Ameliorates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease In Type 2 Diabetic Rats. Physiol. Research. 2022. ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Wahab, B.A.; Ali, F.E.M.; Alkahtani, S.A.; Alshabi, A.M.; Mahnashi, M.H.; Hassanein, E.H.M. Hepatoprotective effect of rebamipide against methotrexate-induced hepatic intoxication: Role of Nrf2/GSK-3β, NF-κβ-p65/JAK1/STAT3, and PUMA/Bax/Bcl-2 signaling pathways. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2020, 42, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghafar, O.A.M.A.; Hassanein, E.H.M.; Ali, F.E.M.; Omar, Z.M.M.; Rashwan, E.K.; Mohammedsaleh, Z.M.; Sayed, A.M. Hepatoprotective effect of acetovanillone against methotrexate hepatotoxicity: Role of Keap-1/Nrf2/ARE, IL6/STAT-3, and NF-κB/AP-1 signaling pathways. Phytother Research 2022, 36, 488–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borman, P.; Elder, D. Q2 (R1) validation of analytical procedures. ICH Qual. Guidelines 2017, 5, 127–166. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, A.T.; Wolfe, D. Tissue processing and hematoxylin and eosin staining. Methods Mol Biol. 2014, 1180, 31–43. [Google Scholar]
- Lavon, I.; Pikarsky, E.; Gutkovich, E.; Goldberg, I.; Bar, J.; Oren, M.; Ben-Neriah, Y. Nuclear Factor-κB Protects the Liver against Genotoxic Stress and Functions Independently of p53. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Nakopoulou, L.; Stefanaki, K.; Vourlakou, C.; Manolaki, N.; Gakiopoulou, H.; Michalopoulos, G. Bcl-2 protein expression in acute and chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Pathol. Res. Pract. 1999, 195, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.E.; Bakr, A.G.; Abo-youssef, A.M.; Azouz, A.A.; Hemeida, R.A.M. Targeting Keap-1/Nrf-2 pathway and cytoglobin as a potential protective mechanism of diosmin and pentoxifylline against cholestatic liver cirrhosis. Life Sci. 2018, 207, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, S.; Murthy, M. A modified micro-bradford procedure for elimination of Interference from sodium dodecyl sulfate, Other detergents, and lipids. Anal. Biochem. 1994, 220, 424–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, H.; Ohkura, Y. A new photometric method for the determination of serum glutamate pyruvate transaminase activity using pyruvate and glutamate as substrates. Chem. Pharm. Bull (Tokyo). 1976, 24, 1865–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aebi, H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 105, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCicco, L.A.; Rikans, L.E.; Tutor, C.G.; Hornbrook, K.R. Serum and liver concentrations of tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1beta following administration of carbon tetrachloride to male rats. Toxicol Lett. 1998, 98, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, R.; Carey, J.J. Risk of liver disease in methotrexate treated patients. World J. Hepatol. 2017, 9, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uraz, S.; Tahan, V.; Aygun, C.; Eren, F.; Unluguzel, G.; Yüksel, M.; Senturk, O.; Avsar, E.; Haklar, G.; Çelikel, C.; et al. Role of ursodeoxycholic acid in prevention of methotrexate-induced liver toxicity. Am. J. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2007, 53, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.J.; Wang, L.; Hu, G.F.; Li, C.B.; Liu, H.X.; Peng, M.T. Clinical application of the simultaneous detection of methotrexate and 7-hydroxymethotrexate in the delayed elimination for pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020, 100, 1973–1978. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Hussein, O.E.; Hozayen, W.G.; Bin-Jumah, M.; El-Twab, S.M.A. Ferulic acid prevents oxidative stress, inflammation, and liver injury via upregulation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling in methotrexate-induced rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 7910–7921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akin, Y.; Bozkurt, A.; Erol, H.S.; Halici, M.; Celebi, F.; Kapakin, K.A.T.; Gulmez, H.; Ates, M.; Coban, A.; Nuhoglu, B. Impact of Rho-Kinase Inhibitor Hydroxyfasudil in Protamine Sulphate Induced Cystitis Rat Bladder. LUTS Low. Urin. Tract Symptoms 2014, 7, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, N.; Velasco, M.A.D.; Umekawa, T.; Uemura, H.; Yoshikawa, K. Effects of the Rho kinase inhibitor, hydroxyfasudil, on bladder dysfunction and inflammation in rats with HCl-induced cystitis. Int. J. Urol. 2013, 20, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abo-Haded, H.M.; Elkablawy, M.A.; Al-Johani, Z.; Al-Ahmadi, O.; El-Agamy, D.S. Hepatoprotective effect of sitagliptin against methotrexate induced liver toxicity. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantari, H.; Asadmasjedi, N.; Abyaz, M.R.; Mahdavinia, M.; Mohammadtaghvaei, N. Protective effect of inulin on methotrexate- induced liver toxicity in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sari, A.N.; Kacan, M.; Unsal, D.; Firat, S.S.; Buharalioglu, C.K.; Vezir, O.; Korkmaz, B.; Cuez, T.; Canacankatan, N.; Sucu, N.; et al. Contribution of RhoA/Rho-kinase/MEK1/ERK1/2/iNOS pathway to ischemia/reperfusion-induced oxidative/nitrosative stress and inflammation leading to distant and target organ injury in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 723, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Taher, A.Y.; Morsy, M.A.; Rifaai, R.A.; Zenhom, N.M.; Abdel-Gaber, S.A. Paeonol Attenuates Methotrexate-Induced Cardiac Toxicity in Rats by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Suppressing TLR4-Induced NF-kappaB Inflammatory Pathway. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 8641026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liszewska, A.; Robak, E.; Bernacka, M.; Bogaczewicz, J.; Wozniacka, A. Methotrexate use and NAD(+)/NADH metabolism in psoriatic keratinocytes. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2020, 37, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Kang, J.; Hu, K.; Tang, S.; Zhou, X.; Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Yu, S. The role of the Nox4-derived ROS-mediated RhoA/Rho kinase pathway in rat hypertension induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia. Sleep Breath. 2017, 21, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.-J.; Mu, Y.-L.; Zhao, H.-J.; Zhao, R.-R.; Guo, Q.-J.; Su, Y.-H.; Zhang, J. Fasudil prevents liver fibrosis via activating natural killer cells and suppressing hepatic stellate cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 3581–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, P.de.; Guarido, K.L.; Scheschowitsch, K.; Silva, L.M.de.; Werner, M.F.; Assreuy, J.; Silva-Santos, J.D.d. Impaired vascular function in sepsis-surviving rats mediated by oxidative stress and Rho-Kinase pathway. Redox Biol. 2016, 10, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
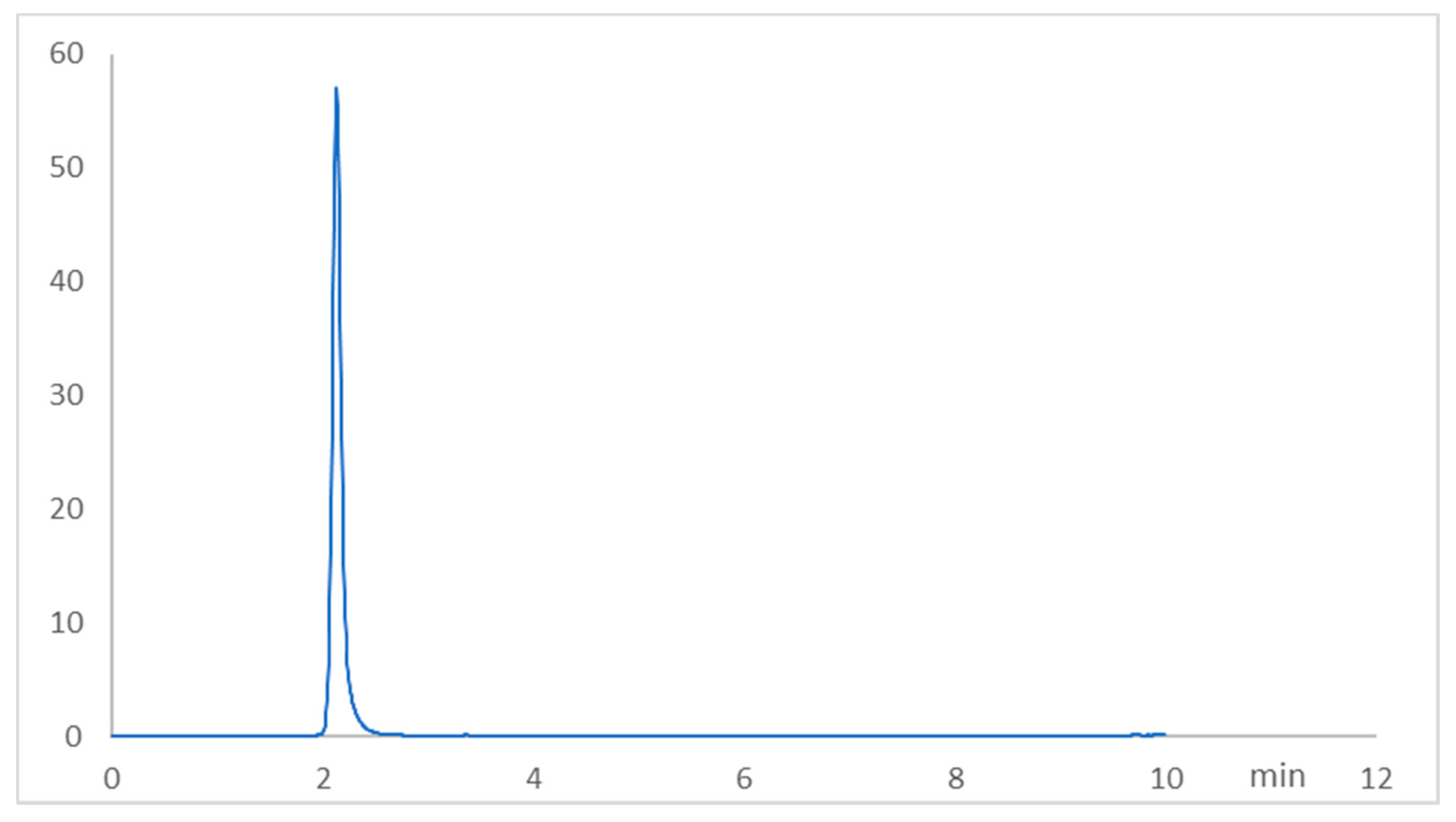
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| λmax | 275 nm |
| Retention time (min) | 2.12 |
| Linearity range (µg/mL) | 1.0–12.0 |
| LOD (µg/mL) | 0.057 |
| LOQ (µg/mL) | 0.191 |
| Regression equation | Y = a + bx |
| Slope | 121.02 |
| Intercept | −5.70 |
| Correlation coefficient | 0.999 |
| Standard Solution (µg/mL) (n = 3) | Found | % Recovery | Mean ± SD | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.9938 | 99.38 | 0.993 ± 0.094 | 0.94 |
| 0.9836 | 98.36 | |||
| 1.0024 | 100.24 | |||
| 6 | 6.0012 | 100.02 | 6.03 ± 0.85 | 0.85 |
| 6.0612 | 101.02 | |||
| 5.9592 | 99.32 | |||
| 12 | 12.2436 | 102.03 | 12.04 ± 1.45 | 1.44 |
| 11.9232 | 99.36 | |||
| 11.964 | 99.71 |
| Standard Solution (µg/mL) | Intra-Day Precision | Mean ± RSD | Inter-Day Precision | Mean ± RSD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Found | % Recovery | Found | % Recovery | |||
| 1 | 0.9919 | 99.19 | 0.994 ± 0.30 | 0.9929 | 99.29 | 0.997 ± 0.57 |
| 0.9935 | 99.35 | 1.0041 | 100.41 | |||
| 0.9978 | 99.78 | 0.9967 | 99.67 | |||
| 6 | 5.8974 | 98.29 | 5.95 ± 0.82 | 5.9832 | 99.72 | 5.96 ± 0.71 |
| 5.979 | 99.65 | 5.9154 | 98.59 | |||
| 5.9862 | 99.77 | 5.9928 | 99.88 | |||
| 12 | 12.0372 | 100.31 | 12.07 ± 0.41 | 11.8764 | 98.97 | 11.98 ± 1.41 |
| 12.054 | 100.45 | 11.9016 | 99.18 | |||
| 12.132 | 101.1 | 12.1812 | 101.51 | |||
| Parameters | FDL | Acceptable Limits |
|---|---|---|
| Asymmetry factor | 1.06 | <1.5 |
| Tailing factor | 1.25 | <2 |
| Theoretical plates (m) | 4651 | <2000 |
| HETP (cm) | 0.0322 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aboubakr, E.M.; Ibrahim, A.R.N.; Ali, F.E.M.; Mourad, A.A.E.; Ahmad, A.M.; Hofni, A. Fasudil Ameliorates Methotrexate-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Modulation of Redox-Sensitive Signals. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111436
Aboubakr EM, Ibrahim ARN, Ali FEM, Mourad AAE, Ahmad AM, Hofni A. Fasudil Ameliorates Methotrexate-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Modulation of Redox-Sensitive Signals. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(11):1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111436
Chicago/Turabian StyleAboubakr, Esam M., Ahmed R. N. Ibrahim, Fares E. M. Ali, Ahmed A. E. Mourad, Adel M. Ahmad, and Amal Hofni. 2022. "Fasudil Ameliorates Methotrexate-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Modulation of Redox-Sensitive Signals" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 11: 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111436
APA StyleAboubakr, E. M., Ibrahim, A. R. N., Ali, F. E. M., Mourad, A. A. E., Ahmad, A. M., & Hofni, A. (2022). Fasudil Ameliorates Methotrexate-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Modulation of Redox-Sensitive Signals. Pharmaceuticals, 15(11), 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111436






