Association between Migraines and Prior Proton Pump Inhibitor Use: A Nested Case-Control Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Baseline Characteristics
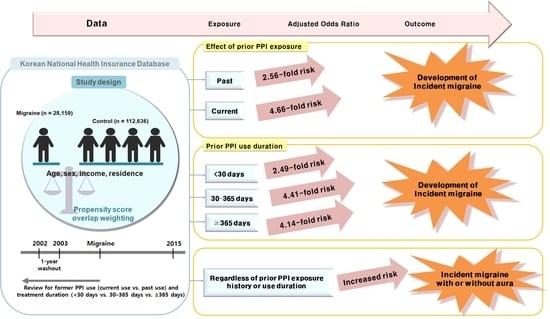
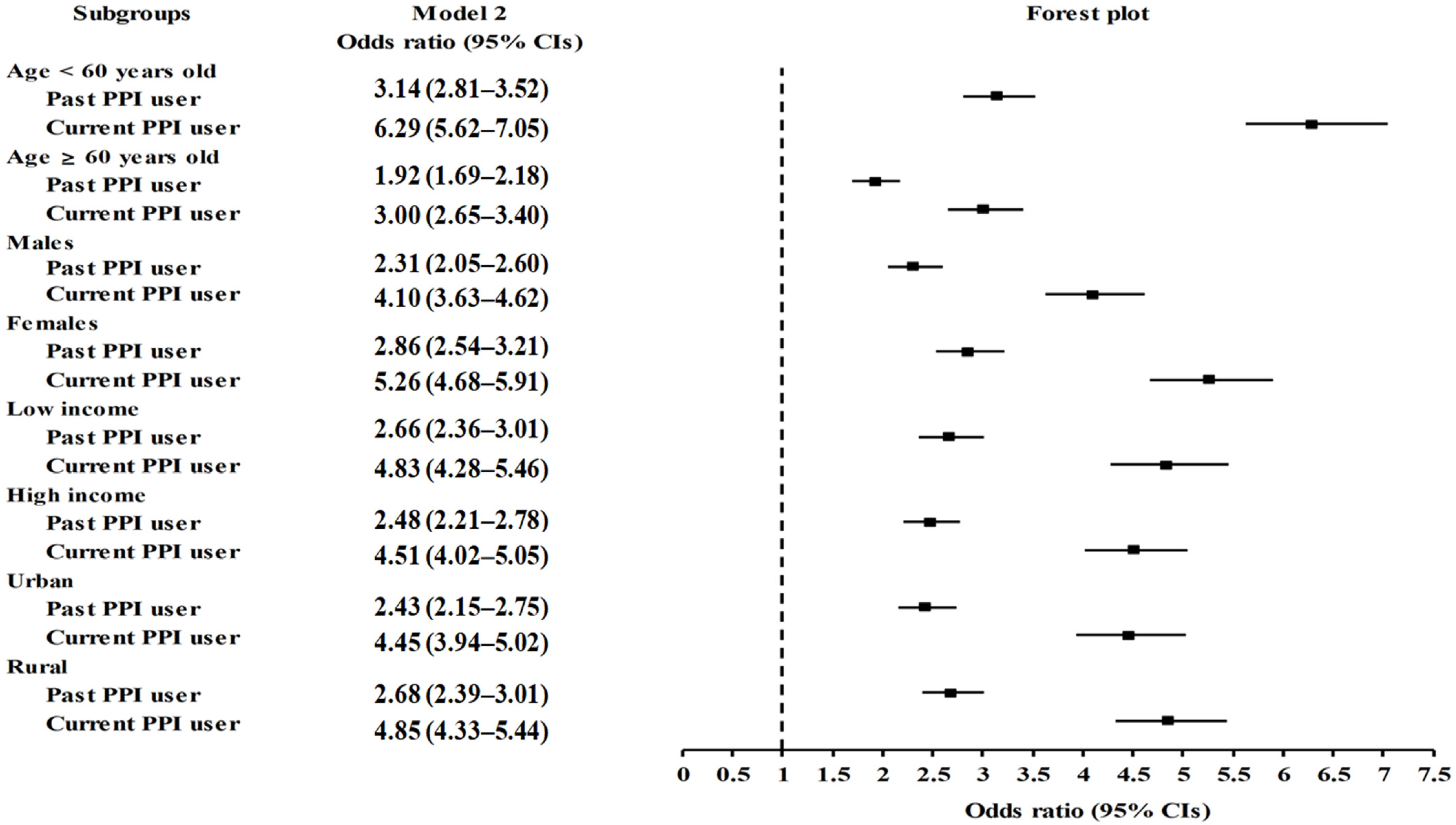
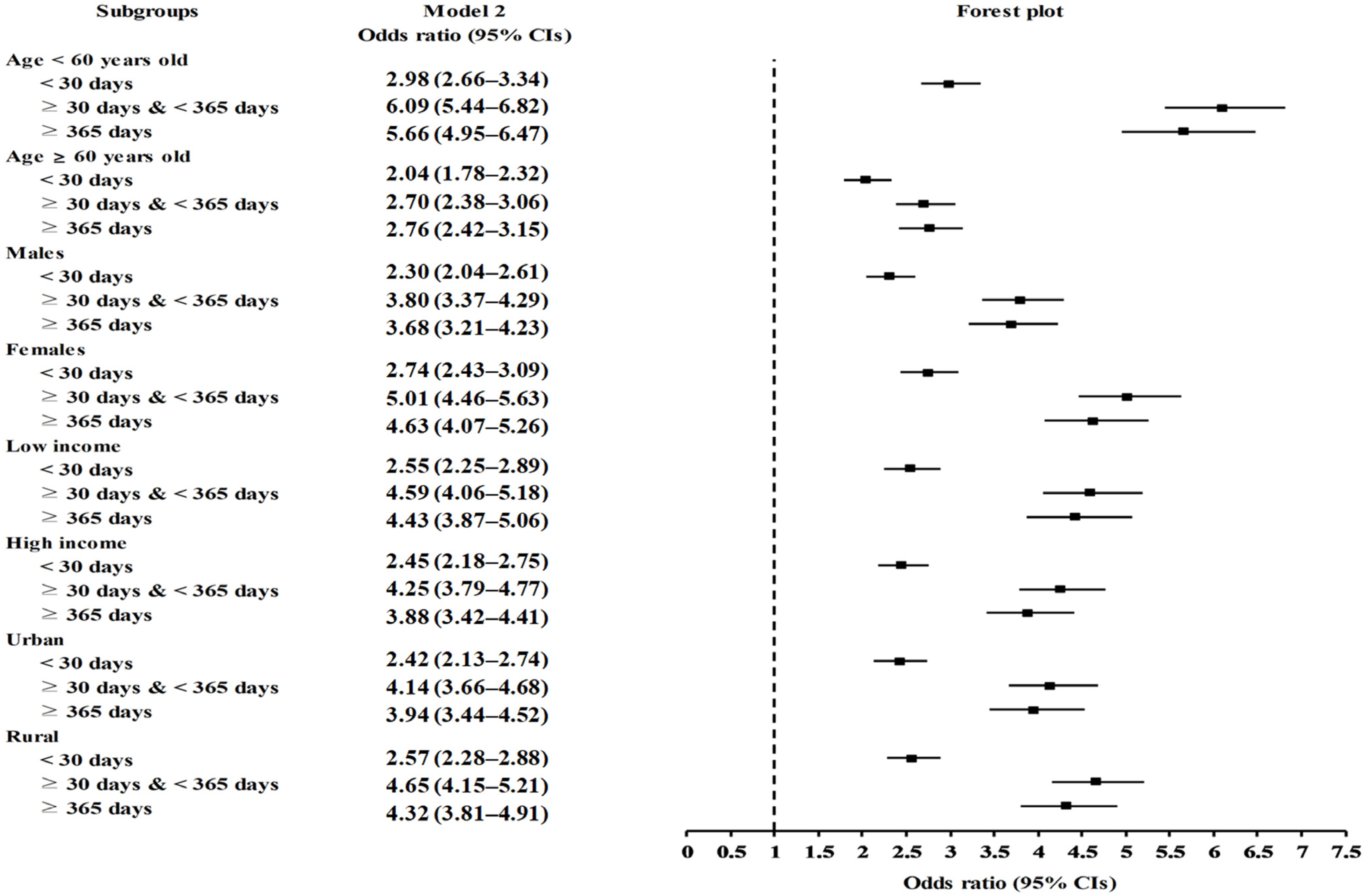
2.2. Association of Prior Use of PPIs and Duration of PPI Use with Migraines
2.3. Association between PPI Use and Migraines Based on the Presence or Absence of Aura
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Source and Ethical Consideration
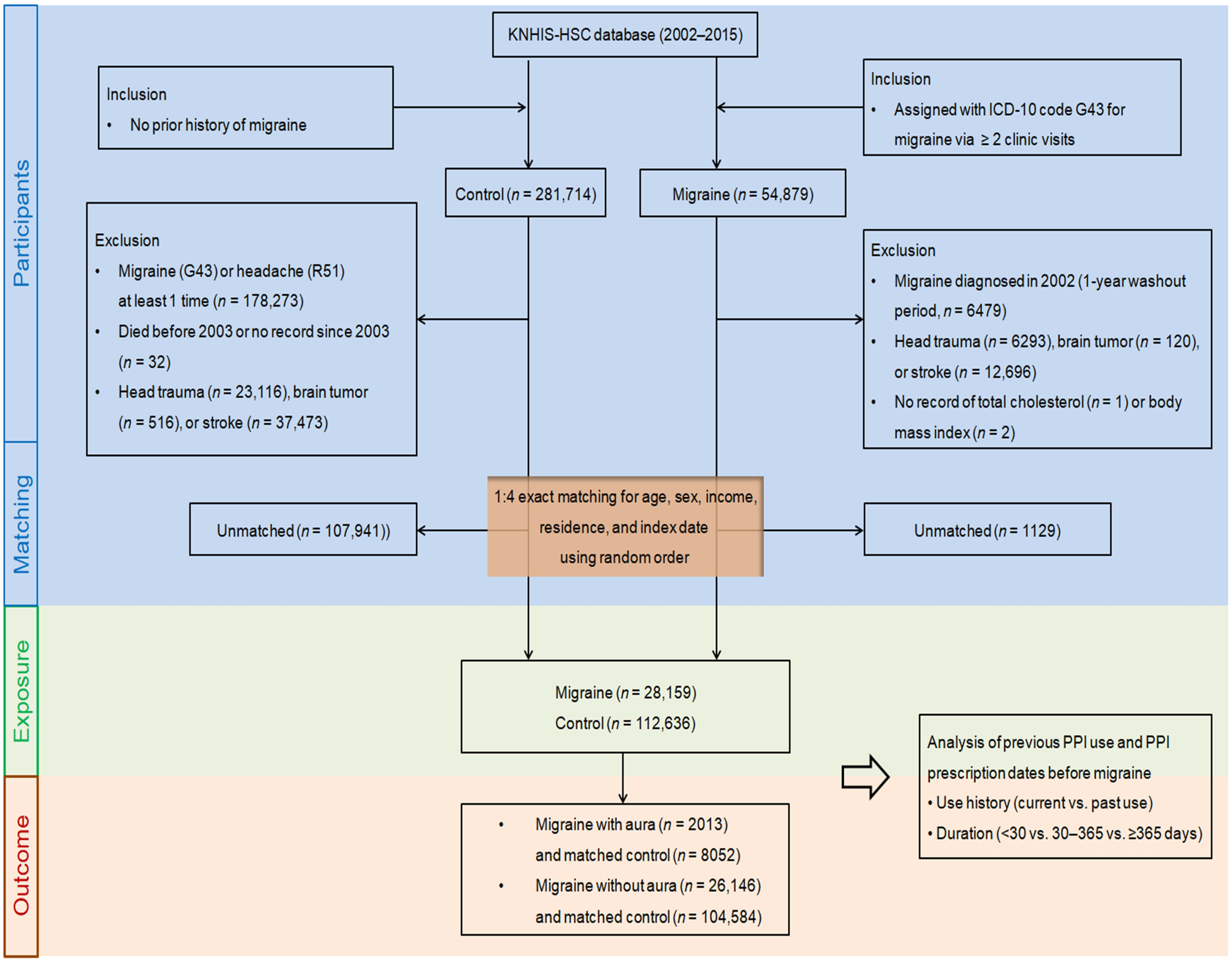
4.2. Selection of Participants
4.3. Proton Pump Inhibitor (Exposure)
4.4. Migraines (Outcome)
4.5. Covariates
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burch, R.C.; Buse, D.C.; Lipton, R.B. Migraine: Epidemiology, Burden, and Comorbidity. Neurol. Clin. 2019, 37, 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Disease, G.B.D.; Injury, I.; Prevalence, C. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1211–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.K.; Chu, M.K.; Lee, T.G.; Kim, J.M.; Chung, C.S.; Lee, K.S. Prevalence and impact of migraine and tension-type headache in Korea. J. Clin. Neurol. 2012, 8, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oie, L.R.; Kurth, T.; Gulati, S.; Dodick, D.W. Migraine and risk of stroke. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silberstein, S.D.; Dodick, D.; Freitag, F.; Pearlman, S.H.; Hahn, S.R.; Scher, A.I.; Lipton, R.B. Pharmacological approaches to managing migraine and associated comorbidities--clinical considerations for monotherapy versus polytherapy. Headache 2007, 47, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelli, N.; Altamura, C.; Mallio, C.A.; Lo Vullo, G.; Marcosano, M.; Bach-Pages, M.; Beomonte Zobel, B.; Quattrocchi, C.C.; Vernieri, F. Cerebral Hemodynamics, Right-to-Left Shunt and White Matter Hyperintensities in Patients with Migraine with Aura, Young Stroke Patients and Controls. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Park, S.; Kim, E.; Je, N.K. Utilization of Preventive Therapy in Korean Migraine Patients. Korean J. Clin. Pharm. 2021, 31, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruit, M.C.; van Buchem, M.A.; Hofman, P.A.; Bakkers, J.T.; Terwindt, G.M.; Ferrari, M.D.; Launer, L.J. Migraine as a risk factor for subclinical brain lesions. JAMA 2004, 291, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langtry, H.D.; Wilde, M.I. Omeprazole. A review of its use in Helicobacter pylori infection, gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and peptic ulcers induced by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Drugs 1998, 56, 447–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisanu, C.; Welander, N.Z.; Rukh, G.; Schioth, H.B.; Mwinyi, J. Association between migraine prevalence, treatment with proton-pump inhibitors and CYP2C19 phenotypes in UK Biobank. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 143, 112234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makunts, T.; Alpatty, S.; Lee, K.C.; Atayee, R.S.; Abagyan, R. Proton-pump inhibitor use is associated with a broad spectrum of neurological adverse events including impaired hearing, vision, and memory. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagboto, S. Severe Electrolyte Disturbances Due to Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy: An Underrecognized Problem with Potentially Severe Sequelae. Am. J. Case Rep. 2022, 23, e936893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claessens, A.A.; Heerdink, E.R.; van Eijk, J.T.; Lamers, C.B.; Leufkens, H.G. Determinants of headache in lansoprazole users in The Netherlands: Results from a nested case-control study. Drug Saf. 2002, 25, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.F.; Chen, Y.T.; Fuh, J.L.; Li, S.Y.; Chen, T.J.; Tang, C.H.; Wang, S.J. Proton pump inhibitor-related headaches: A nationwide population-based case-crossover study in Taiwan. Cephalalgia 2015, 35, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S.W.; Liao, K.F.; Lai, H.C.; Muo, C.H.; Sung, F.C. Atorvastatin correlates with decreased risk of esophageal cancer: A population-based case-control study from Taiwan. Libyan J. Med. 2012, 7, 18830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McColl, K.E.; Kennerley, P. Proton pump inhibitors—Differences emerge in hepatic metabolism. Dig. Liver Dis. 2002, 34, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Klotz, U. Proton pump inhibitors: An update of their clinical use and pharmacokinetics. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 64, 935–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boinpally, R.; Lu, K. Evaluation of the Pharmacokinetic Interaction and Safety of Ubrogepant Coadministered with Esomeprazole Magnesium. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2022, 11, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, F.; Zarinfar, N.; Zanjani, A.T.; Morteza, A. The effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on migraine: A randomized, double blind, controlled trial. Pain Physician 2012, 15, 495–498. [Google Scholar]
- Kurth, T. Is the way to headache through the stomach? Cephalalgia 2015, 35, 201–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzani, M.; Jahromi, S.R.; Ghorbani, Z.; Vahabizad, F.; Martelletti, P.; Ghaemi, A.; Sacco, S.; Togha, M.; School of Advanced Studies of the European Headache, F. Gut-brain Axis and migraine headache: A comprehensive review. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peskersoy, C.; Peker, S.; Kaya, A.; Unalp, A.; Gokay, N. Evaluation of the relationship between migraine disorder andoral comorbidities: Multicenter randomized clinical trial. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 46, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camara-Lemarroy, C.R.; Rodriguez-Gutierrez, R.; Monreal-Robles, R.; Marfil-Rivera, A. Gastrointestinal disorders associated with migraine: A comprehensive review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 8149–8160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Daghlas, I.; Larsson, S.C. Alcohol, coffee consumption, and smoking in relation to migraine: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Pain 2022, 163, e342–e348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, M.G.; Fonteh, A.N.; Cowan, R.P.; Perrine, K.; Pogoda, J.M.; Biringer, R.G.; Huhmer, A.F. Cerebrospinal fluid sodium increases in migraine. Headache 2006, 46, 1128–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, M.G.; Chekmenev, E.Y.; Schepkin, V.; Fonteh, A.N.; Arakaki, X. Sodium MRI in a rat migraine model and a NEURON simulation study support a role for sodium in migraine. Cephalalgia 2011, 31, 1254–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, M.; Prendecki, M.; Piekut, T.; Kozubski, W.; Dorszewska, J. Migraine: Calcium Channels and Glia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.M.; Kim, N. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the proton pump inhibitors. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 19, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.C.; Ho, Y.F.; Hung, L.C.; Chen, C.F.; Tsai, T.H. Determination and pharmacokinetic profile of omeprazole in rat blood, brain and bile by microdialysis and high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 949, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo, L.E.; Alzate-Morales, J.; Saavedra, I.N.; Davies, P.; Maccioni, R.B. Selective interaction of lansoprazole and astemizole with tau polymers: Potential new clinical use in diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 19, 573–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hiesinger, P.R. The vesicular ATPase: A missing link between acidification and exocytosis. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 203, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabares, L.; Betz, B. Multiple functions of the vesicular proton pump in nerve terminals. Neuron 2010, 68, 1020–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Driel, I.R.; Callaghan, J.M. Proton and potassium transport by H+/K+-ATPases. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1995, 22, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Guerrero, G.; Amador-Munoz, D.; Calderon-Ospina, C.A.; Lopez-Fuentes, D.; Nava Mesa, M.O. Proton Pump Inhibitors and Dementia: Physiopathological Mechanisms and Clinical Consequences. Neural Plast. 2018, 2018, 5257285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, M.G.; Fonteh, A.N.; Arakaki, X.; Cowan, R.P.; Ecke, L.E.; Foster, H.; Huhmer, A.F.; Biringer, R.G. Capillary endothelial Na+, K+, ATPase transporter homeostasis and a new theory for migraine pathophysiology. Headache 2010, 50, 459–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevel, E. The extracranial vascular theory of migraine—A great story confirmed by the facts. Headache 2011, 51, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Alwis, N.; Fato, B.R.; Beard, S.; Binder, N.K.; Kaitu’u-Lino, T.J.; Onda, K.; Hannan, N.J. Assessment of the Proton Pump Inhibitor, Esomeprazole Magnesium Hydrate and Trihydrate, on Pathophysiological Markers of Preeclampsia in Preclinical Human Models of Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onda, K.; Tong, S.; Beard, S.; Binder, N.; Muto, M.; Senadheera, S.N.; Parry, L.; Dilworth, M.; Renshall, L.; Brownfoot, F.; et al. Proton Pump Inhibitors Decrease Soluble fms-Like Tyrosine Kinase-1 and Soluble Endoglin Secretion, Decrease Hypertension, and Rescue Endothelial Dysfunction. Hypertension 2017, 69, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawronska-Szklarz, B.; Adamiak-Giera, U.; Wyska, E.; Kurzawski, M.; Gornik, W.; Kaldonska, M.; Drozdzik, M. CYP2C19 polymorphism affects single-dose pharmacokinetics of oral pantoprazole in healthy volunteers. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 68, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, C.; Bang, W.J.; Kim, M.; Oh, D.J.; Choi, H.G. Rheumatoid arthritis and neurodegenerative dementia: A nested case-control study and a follow-up study using a national sample cohort. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Min, C.; Oh, D.J.; Choi, H.G. Tobacco Smoking and Alcohol Consumption Are Related to Benign Parotid Tumor: A Nested Case-Control Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 12, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Min, C.; Oh, D.J.; Choi, H.G. Bidirectional Association Between GERD and Asthma: Two Longitudinal Follow-Up Studies Using a National Sample Cohort. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 1005–1013.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Oh, D.J.; Park, B.; Choi, H.G. Bell’s palsy and obesity, alcohol consumption and smoking: A nested case-control study using a national health screening cohort. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, H.; Li, B.; Couris, C.M.; Fushimi, K.; Graham, P.; Hider, P.; Januel, J.M.; Sundararajan, V. Updating and validating the Charlson comorbidity index and score for risk adjustment in hospital discharge abstracts using data from 6 countries. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 173, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Dalton, J.E. A unified approach to measuring the effect size between two groups using SAS. In SAS Global Forum 2012: Statistics and Data Analysis; Paper 335-2012; SAS: Bucharest, Romania, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Thomas, L.E.; Li, F. Addressing Extreme Propensity Scores via the Overlap Weights. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 188, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, L.E.; Li, F.; Pencina, M.J. Overlap Weighting: A Propensity Score Method That Mimics Attributes of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 323, 2417–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Before PS Overlap Weighting Adjustment | SMD | After PS Overlap Weighting Adjustment | SMD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Migraine | Control | Migraine | Control | |||
| Number | 28,159 | 112,636 | 22,084 | 22,084 | ||
| Migraines with aura | 2013 | - | 1576 | - | ||
| Migraines without aura | 26,146 | - | 20,508 | - | ||
| Age (years; mean, SD) | 58.7 (9.8) | 58.6 (9.8) | 0.00 | 58.6 (8.7) | 58.6 (4.4) | 0.01 |
| Age (years; n, %) | 0.00 | 0.01 | ||||
| 40–44 | 1344 (4.8) | 5376 (4.8) | 1063 (4.8) | 1072 (4.9) | ||
| 45–49 | 4172 (14.8) | 16,688 (14.8) | 3291 (14.9) | 3306 (15.0) | ||
| 50–54 | 5396 (19.2) | 21,584 (19.2) | 4238 (19.2) | 4231 (19.2) | ||
| 55–59 | 5226 (18.6) | 20,904 (18.6) | 4100 (18.6) | 4070 (18.4) | ||
| 60–64 | 4151 (14.7) | 16,604 (14.7) | 3254 (14.7) | 3223 (14.6) | ||
| 65–69 | 3532 (12.5) | 14,128 (12.5) | 2754 (12.5) | 2775 (12.6) | ||
| 70–74 | 2401 (8.5) | 9604 (8.5) | 1868 (8.5) | 1891 (8.6) | ||
| 75–79 | 1243 (4.4) | 4972 (4.4) | 967 (4.4) | 984 (4.5) | ||
| 80–84 | 518 (1.8) | 2072 (1.8) | 409 (1.9) | 401 (1.8) | ||
| 85+ | 176 (0.6) | 704 (0.6) | 141 (0.6) | 131 (0.6) | ||
| Sex (n, %) | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||
| Male | 9473 (33.6) | 37,892 (33.6) | 7395 (33.5) | 7395 (33.5) | ||
| Female | 18,686 (66.4) | 74,744 (66.4) | 14,690 (66.5) | 14,690 (66.5) | ||
| Income (n, %) | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||
| 1 (lowest) | 4963 (17.6) | 19,852 (17.6) | 3882 (17.6) | 3899 (17.7) | ||
| 2 | 4110 (14.6) | 16,440 (14.6) | 3229 (14.6) | 3209 (14.5) | ||
| 3 | 4598 (16.3) | 18,392 (16.3) | 3607 (16.3) | 3603 (16.3) | ||
| 4 | 5951 (21.1) | 23,804 (21.1) | 4667 (21.1) | 4664 (21.1) | ||
| 5 (highest) | 8537 (30.3) | 34,148 (30.3) | ||||
| Region of residence (n, %) | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||
| Urban | 11,984 (42.6) | 47,936 (42.6) | 9394 (42.5) | 9394 (42.5) | ||
| Rural | 16,175 (57.4) | 64,700 (57.4) | 12,690 (57.5) | 12,690 (57.5) | ||
| Total cholesterol level (mg/dL; mean, SD) | 199.8 (37.8) | 200.2 (38.2) | 0.01 | 199.8 (33.5) | 199.8 (16.8) | 0.00 |
| SBP (mmHg; mean, SD) | 124.4 (16.3) | 125.4 (17.1) | 0.06 | 124.6 (14.5) | 124.6 (7.4) | 0.00 |
| DBP (mmHg; mean, SD) | 77.2 (10.6) | 77.6 (10.9) | 0.03 | 77.3 (9.4) | 77.3 (4.8) | 0.00 |
| Fasting blood glucose level (mg/dL; mean, SD) | 97.2 (25.5) | 99.4 (29.2) | 0.08 | 97.5 (23.6) | 97.5 (10.5) | 0.00 |
| Weight status (n, %) † | 0.02 | 0.00 | ||||
| Underweight | 656 (2.3) | 2824 (2.5) | 518 (2.3) | 518 (2.3) | ||
| Normal | 10,444 (37.1) | 42,299 (37.6) | 8219 (37.2) | 8219 (37.2) | ||
| Overweight | 7631 (27.1) | 30,043 (26.7) | 5966 (27.0) | 5966 (27.0) | ||
| Obese I | 8559 (30.4) | 33,831 (30.0) | 6696 (30.3) | 6696 (30.3) | ||
| Obese II | 869 (3.1) | 3639 (3.2) | 686 (3.1) | 686 (3.1) | ||
| Smoking status (n, %) | 0.05 | 0.00 | ||||
| Nonsmoker | 22,542 (80.1) | 88,893 (78.9) | 17,650 (79.9) | 17,650 (79.9) | ||
| Past smoker | 2597 (9.2) | 9782 (8.7) | 2008 (9.1) | 2008 (9.1) | ||
| Current smoker | 3020 (10.7) | 13,961 (12.4) | 2427 (11.0) | 2427 (11.0) | ||
| Alcohol consumption (n, %) | 0.04 | 0.00 | ||||
| <1 time a week | 21,003 (74.6) | 81,987 (72.8) | 16,406 (74.3) | 16,406 (74.3) | ||
| ≥1 time a week | 7156 (25.4) | 30,649 (27.2) | 5678 (25.7) | 5678 (25.7) | ||
| CCI score (score; mean, SD) | 0.7 (1.4) | 0.7 (1.5) | 0.03 | 0.7 (1.3) | 0.7 (0.7) | 0.00 |
| CCI score (n, %) | 0.12 | 0.11 | ||||
| 0 score | 18,674 (66.3) | 80,379 (71.4) | 14,719 (66.7) | 15,591 (70.6) | ||
| 1 score | 4489 (15.9) | 13,549 (12.0) | 3492 (15.8) | 2679 (12.1) | ||
| ≥2 scores | 4996 (17.7) | 18,708 (16.6) | 3873 (17.5) | 3815 (17.3) | ||
| Duration of H2RA treatment (days; mean, SD) | 25.5 (54.2) | 14.1 (44.4) | 0.23 | 22.1 (41.7) | 22.1 (27.7) | 0.00 |
| No. of GERD treatments (number; mean, SD) | 0.7 (2.1) | 0.3 (1.3) | 0.22 | 0.5 (1.4) | 0.5 (0.9) | 0.00 |
| No. of GERD treatments (n, %) | 0.30 | 0.15 | ||||
| 0 time | 22,599 (80.3) | 102,079 (90.6) | 18,147 (82.2) | 19,262 (87.2) | ||
| 1 time | 2103 (7.5) | 4461 (4.0) | 1625 (7.4) | 962 (4.4) | ||
| ≥2 times | 3457 (12.3) | 6096 (5.4) | 2313 (10.5) | 1860 (8.4) | ||
| History of PPI use (n, %) | 0.45 | 0.40 | ||||
| PPI nonuser | 1055 (3.8) | 14,487 (12.9) | 855 (3.9) | 2649 (12.0) | ||
| Past PPI user | 9338 (33.2) | 48,567 (43.1) | 7439 (33.7) | 9310 (42.2) | ||
| Current PPI user | 17,766 (63.1) | 49,582 (44.0) | 13,791 (62.5) | 10,125 (45.9) | ||
| Duration of PPI use (days; mean, SD) | 186.1 (212.5) | 144.4 (190.1) | 0.21 | 180.3 (183.9) | 154.8 (88.1) | 0.18 |
| Status based on duration of PPI use (n, %) | 0.43 | 0.37 | ||||
| PPI nonuser | 1055 (3.8) | 14,488 (12.9) | 855 (3.9) | 2649 (12.0) | ||
| PPI user for ≥1 day and <30 days | 6972 (24.8) | 37,561 (33.4) | 5613 (25.4) | 7069 (32.0) | ||
| PPI user for ≥30 days and <365 days | 14,210 (50.5) | 42,246 (37.5) | 11,146 (50.5) | 8442 (38.2) | ||
| PPI user for ≥365 days | 5922 (21.0) | 18,341 (16.3) | 4471 (20.2) | 3924 (17.8) | ||
| Characteristics | Migraine | Control | Odds Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Use/Total, %) | (Use/Total, %) | Crude | p-Value | Adjusted Model with OW † | p-Value | |
| History of PPI use | ||||||
| Past | 9338/57,905 (16.1) | 48,567/57,905 (83.9) | 2.64 (2.47–2.82) | <1.0 × 10−30 * | 2.56 (2.36–2.79) | <1.0 × 10−30 * |
| Current | 17,766/67,348 (26.4) | 49,582/67,348 (73.6) | 4.92 (4.61–5.25) | <1.0 × 10−30 * | 4.66 (4.29–5.06) | <1.0 × 10−30 * |
| Duration of PPI use | ||||||
| <30 days | 6972/44,533 (15.7) | 37,561/44,533 (84.3) | 2.55 (2.38–2.73) | <1.0 × 10−30 * | 2.49 (2.29–2.72) | <1.0 × 10−30 * |
| 30–365 days | 14,210/56,456 (25.2) | 42,246/56,456 (74.8) | 4.62 (4.33–4.93) | <1.0 × 10−30 * | 4.41 (4.05–4.79) | <1.0 × 10−30 * |
| ≥365 days | 5922/24,263 (24.4) | 18,341/24,263 (75.6) | 4.43 (4.14–4.75) | <1.0 × 10−30 * | 4.14 (3.77–4.54) | <1.0 × 10−30 * |
| Characteristics | Migraine | Control | Odds Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Use/Total, %) | (Use/Total, %) | Crude | p-Value | Adjusted Model with OW † | p-Value | |
| Migraines without aura | ||||||
| History of PPI use | ||||||
| Past | 8690/53,753 (16.2) | 45,063/53,753 (83.8) | 2.61 (2.44–2.80) | <1.0 × 10−30 * | 2.54 (2.33–2.77) | <1.0 × 10−30 * |
| Current | 16,461/62,496 (26.3) | 46,035/62,496 (73.7) | 4.85 (4.53–5.18) | <1.0 × 10−30 * | 4.58 (4.21–4.99) | <1.0 × 10−30 * |
| Duration of PPI use | ||||||
| <30 days | 6464/41,219 (15.7) | 34,755/41,219 (84.3) | 2.52 (2.35–2.70) | <1.0 × 10−30 * | 2.47 (2.26–2.70) | <1.0 × 10−30 * |
| 30–365 days | 13,110/52,291 (25.1) | 39,181/52,291 (74.9) | 4.54 (4.24–4.85) | <1.0 × 10−30 * | 4.33 (3.97–4.72) | <1.0 × 10−30 * |
| ≥365 days | 5577/22,738 (24.5) | 17,161/22,738 (75.5) | 4.41 (4.10–4.73) | <1.0 × 10−30 * | 4.10 (3.73–4.51) | <1.0 × 10−30 * |
| Migraines with aura | ||||||
| History of PPI use | ||||||
| Past | 648/4152 (15.6) | 3504/4152 (84.4) | 3.09 (2.35–4.06) | 7.1 × 10−16 * | 2.99 (2.13–4.20) | 1.0 × 10−10 * |
| Current | 1305/4852 (26.9) | 3547/4852 (73.1) | 6.14 (4.69–8.03) | <1.0 × 10−30 * | 5.90 (4.21–8.26) | 3.7 × 10−26 * |
| Duration of PPI use | ||||||
| <30 days | 508/3314 (15.3) | 2806/3314 (84.7) | 3.02 (2.29–3.99) | 5.4 × 10−15 * | 2.94 (2.09–4.15) | 6.2 × 10−10 * |
| 30–365 days | 1100/4165 (26.4) | 3065/4165 (73.6) | 5.99 (4.57–7.84) | <1.0 × 10−30 * | 5.72 (4.08–8.01) | 3.4 × 10−25 * |
| ≥365 days | 345/1525 (22.6) | 1180/1525 (77.4) | 4.88 (3.66–6.50) | 2.5 × 10−27 * | 4.69 (3.21–6.84) | 6.7 × 10−17 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, H.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, E.S.; Choi, H.G.; Lim, H.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, H.Y.; Kim, N.Y.; Hong, S.; et al. Association between Migraines and Prior Proton Pump Inhibitor Use: A Nested Case-Control Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111385
Kang HS, Kim SY, Kim JH, Kim ES, Choi HG, Lim H, Kim J-H, Park HY, Kim NY, Hong S, et al. Association between Migraines and Prior Proton Pump Inhibitor Use: A Nested Case-Control Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(11):1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111385
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Ho Suk, So Young Kim, Ji Hee Kim, Eun Soo Kim, Hyo Geun Choi, Hyun Lim, Joo-Hee Kim, Ha Young Park, Nan Young Kim, Sangkyoon Hong, and et al. 2022. "Association between Migraines and Prior Proton Pump Inhibitor Use: A Nested Case-Control Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 11: 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111385
APA StyleKang, H. S., Kim, S. Y., Kim, J. H., Kim, E. S., Choi, H. G., Lim, H., Kim, J.-H., Park, H. Y., Kim, N. Y., Hong, S., Choi, K. C., & Kwon, M. J. (2022). Association between Migraines and Prior Proton Pump Inhibitor Use: A Nested Case-Control Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort. Pharmaceuticals, 15(11), 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111385