Abstract
Dexmedetomidine (DEX) is a commonly used sedative agent with no or minimal effects on breathing. DEX may also be beneficial in myocardial protection. Since the mechanisms of cardiac effects are not well known, we carried out a descriptive review and examined the effects of DEX on myocardial electrical conduction in a prospective and controlled manner. For the review, clinical studies exploring DEX in myocardial protection published between 2020-2022 were explored. A case study included 11 consecutive patients at a median (range) age of 48 (38–59), scheduled for elective radiofrequency ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. A bolus dose of DEX 1 µg/kg given in 15 min was followed by a continuous infusion of 0.2–0.7 µg/kg/h. Direct intracardiac electrophysiologic measurements, hemodynamics and oxygenation were measured before and after the DEX bolus. Experimental studies show that DEX protects the heart both via stabilizing cardiac electrophysiology and reducing apoptosis and autophagy after cell injury. The clinical evidence shows that DEX provides cardiac protection during different surgeries. In a clinical study, DEX increased the corrected sinus node recovery time, prolongated the atrioventricular (AV) nodal refractory period and cycle length producing AV nodal Wenckebach retrograde conduction block. DEX has a putative role in organ protection against hypoxic, oxidative and reperfusion injury. DEX slows down the firing of the sinus node and prolongs AV refractoriness.
1. Introduction
Dexmedetomidine (DEX) is a selective α2-adrenergic receptor (α2-AR) agonist with a high affinity on the 2A and 2C subtypes of the receptor [1]. DEX produces analgesia and sedation, reduces delirium and agitation, provides stabilizing effects on cardiovascular functions, and causes perioperative sympatholysis. DEX has been widely used for algo-sedation in various invasive surgical, radiological and cardiac procedures, due to easy arousability from sedation and minimal or no effects on spontaneous breathing [2,3,4]. During general anesthesia, DEX reduces the need of volatile and intravenous (iv) anesthetics [4]. The use of DEX is currently studied in palliative care, psychiatry and prevention of arrythmias [5,6,7]. Perhaps one of the most interesting targets of DEX would be prevention of multiorgan failure [7] occurring during surgery, trauma or in intensive care. DEX has a wide therapeutic dose window and can be administered intravenously, subcutaneously, intranasally and sublingually in doses [8]. Spinal and sublingual administration of DEX are currently examined [9,10]. The common dosage of DEX has been 0.25–1 mcg/kg iv, followed by an infusion of 0.2–1.4 mcg/kg/h titrated to the intended effect [11,12,13]. Bolus doses for other routes than iv vary largely and depend on the desired effect.
Bradycardia and hypotension are the most common side-effects that may restrict the use of DEX (Table 1), although in higher doses they may be less pronounced [1,2,3,12,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21]. That is why in a recent review of sedation techniques for radiofrequency (RF) ablation of aberrant conduits in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation the use of DEX was recommended with caution [22]. Even asystole during DEX administration has been reported [23].

Table 1.
Risk of bradycardia and hypotension in recent meta-analyses and systematic reviews. N = number of patients, RR = relative risks, ICU = intensive care unit, LCC = laparoscopic cholecystectomy, NIV = non-invasive ventilation, PACU = postanesthesia care unit.
Both central and intracardiac mechanisms have been proposed for the possible influences of DEX on the heart. Firstly, bradycardia could be caused by reflectory vasoconstriction due to reduced noradrenaline secretion following the activation of α2A-receptors in locus coeruleus [24]. Presynaptic activation of central α2-receptors results in a sympatholytic effect leading to hypotension and bradycardia, while postsynaptic activation in the peripheral vasculature leads to vasoconstriction and hypertension [24,25,26]. Secondly, DEX has been shown to decrease the intracellular levels of cAMP via G-protein activation, which reduces the activity in the ion channels of cardiac myocytes [27]. An important mechanism of vasodilatation after DEX administration is the activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase [28]. An α2-receptor mediated baroreceptor reflex and enhanced vagal activity may also count for DEX-induced bradycardia [25,28,29]. In a famous study, Kamibayashi et al. [25] demonstrated that DEX had no influence on the heart rate in vagotomized dogs.
Yet the mechanisms of DEX-induced arrythmias remain to be exclusively examined. The same intracellular mechanisms may be activated in DEX-induced balancing of cardiac electrophysiology and broad myocardial protection [7]. To analyze the most recent evidence of the cardiovascular effects of DEX, we performed a descriptive review. Because only few studies have been executed on the effects of DEX on the myocardial conductivity in adults [30,31], we also aimed to examine the electrophysiologic cardiac effect of DEX during elective ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation.
2. Results
2.1. Descriptive Review of the Effects of DEX on Cardiac Functions
2.1.1. Experimental Evidence on New Concepts
In vitro studies with isolated rabbit and rat hearts have shown that DEX inhibits voltage-gated Na channels (Nav1.5) and L-type calcium channels (IC-L) and opens large-conductance Ca2+-sensitive potassium (BKCa) channels, which are important mediators in myocardial conduction [32,33,34]. In addition, DEX has been shown to inhibit pacemaker cells in sinoatrial nodes and reduce ventricular arrythmias [35,36,37]. These effects were only partly or not all reversed by the α-2-adrenergic antagonist, yohimbine, suggesting a direct effect of DEX on the heart. α2-receptors are important in the development of myocardial hypertrophy but nodal tissue lacks α2-receptors [38,39]. In addition, Xia et al. have shown that DEX reduced bupivacaine-induced arrythmias and increased tolerance to bupivacaine-induced cardiac toxicity in rats [40]. There is a growing bulk of evidence supporting the cardiac and other organ protective effects of DEX as proven by several experimental models of ischemic injury and via multiple mechanisms [7]. Examples of the most recent findings [41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51] in the mechanisms of DEX-induced cardioprotection are given in Table 2. DEX may be beneficial for a failing heart given both before (preconditioning-like effect) and after (postconditioning-like effect) the ischemic injury. However, the dose–response relationship of DEX was not clear in the studies. The results of this study propose that the cumulated evidence on the cardiac protection caused by DEX at the cellular level could be divided into the following main categories: inhibition of apoptosis, reversion of autophagy, and stabilization of cardiac electrophysiology after cellular injury (Figure 1) [7,52].

Table 2.
Summary of controlled experimental studies on the effects of DEX on myocardial protection. ↑ = increased, ↓ = decreased, → = followed by. Yohimbine is an α2-adrenergic antagonist.
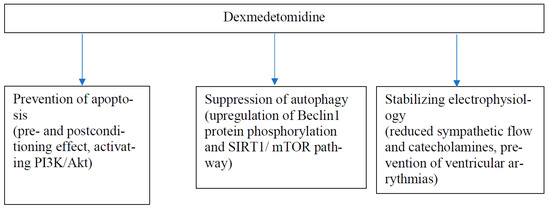
Figure 1.
A model for main mechanisms (with two examples) of cardiac protection of DEX.
2.1.2. Clinical Significance
The loading dose of dexmedetomidine results in a transient increase in blood pressure and a reflexive drop in heart rate, especially in young, healthy individuals [53]. This initial cardiovascular response is most likely due to vasoconstriction induced by the stimulation of peripheral α-2B receptors in vascular smooth muscle; however, subsequent hypotension occurs when the vasodilatory effects of the central α-2A receptors predominate.
Due to its sympatholytic properties and ability to activate the parasympathetic tone, DEX might reduce arrythmias during and after surgery and in the intensive care. Recently, three meta-analyses and systematic reviews have been published with different results on the effects of DEX on the prevention of atrial fibrillation [18,54,55]. While two reviews found no significant effect of DEX on arrythmias after cardiac surgery, Wang et al. reported a 17% reduction in AF, 70% reduction in supraventricular tachycardia and an 80% reduction in ventricular arrythmias by DEX in the intensive care units. Another recent review [16] found that DEX effectively reduces ventricular arrythmias, but was based only on six studies with a total number of 1001 patients.
DEX seems to stabilize cardiovascular functions and protect the heart from reperfusion injury in humans. The most recent systematic review by Chen et al. [2022], based on 9 controlled studies including a total of 418 patients, found out that DEX reduced CK-MB, IL6 and TNF-α levels up to 24 h after open-heart surgery performed with CPB. Additionally, it shortened the length of patients’ intensive care department stays, but it had no influence on the total length of the stay at the hospital [56]. The original studies had a very low bias but the dosing regimen of DEX varied greatly. Yet, in all but one trial the administration started in the induction phase and lasted at least until the end of the procedure. Another review, examining the use of DEX during hysterectomies, explored 22 studies including a total of 857 women and concluded that DEX was associated with more stable haemodynamics observed as less drastic fluctuations in blood pressure and heart rate during surgery [57]. This review also demonstrated a very low bias risk for the included studies. Rather similar results were obtained in a prospective, randomized and placebo-controlled study assessing the effects of a bolus dose of 0.6 μg/kg of DEX iv in the induction of anesthesia for laparoscopic cholecystectomy [58]. In this study, the patients receiving DEX experienced also less cough during emergence and less postoperative pain than the patients treated with placebo.
2.2. Clinical Study
Our clinical study included two females and nine males at a median (range) age of 48 (38–59) years. Their median weights and heights (with ranges) were 88 (60–108) kgs and 183 (161–196) cm, respectively. All patients had SR during the measurements. During cannulation the patients received a median dose of 1 (range 0.5–2) mg of alfentanil and a median volume of 707 (range 606–716) mL of fluids. The haemodynamic and oxygenation measurements are given in Table 3. The electrophysiological measurements are given in Table 4. No ventricular arrythmias were detected during the procedures.

Table 3.
Hemodynamics and oxygenation measurements before (pre) and after (post) DEX infusion. Median values (and ranges) are given. Pre = baseline, Post = after DEX.

Table 4.
Electrophysiological properties. Figures represent time in milliseconds (ms). Pre = baseline, Post = after DEX. Statistically significant difference between pre- and post-DEX measures is marked with * (p < 0.05).
3. Discussion
The main finding of our clinical case study is that infusion of DEX depressed both sinus and AV nodal functions in patients undergoing atrial fibrillation ablation with no bradycardia or hypotension. A significant prolongation in the corrected sinus node recovery time and the AV nodal antegrade refractoriness were observed after a DEX infusion in a situation where haemodynamic fluctuations were eliminated.
Our findings agree with two other cardiac catheterization studies in adults, although the measurements in those studies were performed only after DEX administration [30,31]. A prolongation of the AV nodal effective refractory period, the AV node block cycle length and the AH interval but not of the QTc time were also observed in all these studies. The physiological role of the AV node is to slow down the impulse propagation between atrial and ventricular tissues. This decremental function was achieved under strict autonomous nervous control. An increase in AV nodal refractoriness, as shown in our study, further restricts any conduction through the node by cutting down the number of atrial impulses entering the node. During sinus rhythm, DEX might lead to an AV block but in atrial tachyarrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation, it can reduce the ventricular rate and thus, be protective. [59]. A longer ventricular refractory period may be beneficial since the opposite has been associated with an increased risk of ventricular extrasystolia [60]. In 2007, Fox and colleagues calculated that a 10-bpm reduction in HR produces a 30% reduction in the relative risk of cardiac death after a heart infarction [61]. Yet, sinus bradycardia is recognized as a risk factor for AF and ventricular dysrhythmias, particularly if the refractory period is shortened or the QT time is prolonged [62,63]. A pathological sinus bradycardia is a serious cause of morbidity and mortality in situations such as the sick sinus, Brugada or Wollf-Parkinson-White syndromes [64,65]. Neither bradycardia nor prolongation of the QT time were observed in the current study. Significant hypotension due to sympatholysis was not observed in the current study because of standardized prophylactic hydration in our patients.
The representativeness of the current study is limited by the small number of patients and the lack of placebo. However, our study is the first of its kind examining the electrical conductivity before and after the administration of DEX in adults. Prior to any electrophysiological measurements, our patients received only paracetamol and diazepine orally but no other sedative or analgesic medications. Thus, instead of a parallel placebo-group our patients served as their own controls. In addition, we used a typical loading dose and infusion of DEX, administered only after the baseline measurements had been performed. No ventricular arrythmias during procedures were observed. The clinical implications of the electrophysiological findings on arrhythmia incidence in our study must be drawn cautiously since specific programmed arrhythmia stimulation protocols were not utilized. Although we did not observe significant bradycardia and hypotension, these side-effects occur commonly in the clinical use of DEX (Table 3). However, reduced heart rate has been shown to diminish the occurrence of myocardial injury after an experimental ischaemia and the risk of ventricular arrythmias, probably due to decreased metabolism in cardiomyocytes [66,67,68].
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Descriptive Review
For the descriptive mini-review, PubMed, Cochrane, and EMBASE were searched for meta-analyses, critical and systematic reviews on the clinical effects of DEX on cardiac functions published between 2020 and 2022. The following search terms were applied: dexmedetomidine, α2-receptors and agonists, cardiology, cardiac protection, arrythmia, myocardial injury. The search was extended to include the most recent experimental evidence on DEX-induced protective myocardial effects. Only peer-reviewed articles in English were accepted.
4.2. Prospective Clinical Case Study
The clinical study was performed following the principles defined in the Helsinki Declaration, and it was registered in the European Union Drug Regulating Authorities Clinical Trials Database, Eudract, with a register number EudraCT 2010-020782-24. After the approval of the institutional Ethics Committee (25 August 2010, 137/13/03/01/2010), a written informed consent was obtained from 11 consecutive patients scheduled for elective RF energy catheter ablation of pAF in a tertiary hospital. Patients with a suspected opioid or benzodiazepine addiction or allergy, on amiodarone, having AF during the procedure, aged over 70, with a known allergy to DEX or a tendency to hypotension were excluded. Antiarrhythmic drugs were discontinued at least five half-lives prior to the clinical study.
One hour before the procedure all patients received 1 g paracetamol and 10 mg diazepam orally as premedication. Femoral cannulation was performed under local anesthesia (lidocaine 1%). If needed, alfentanil was used as the rescue analgesic in 0.25–0.50 mg bolus doses during the cannulation, but not when the electrophysiological measurements were performed. The procedural sedation was performed using a bolus DEX dose of 1 µg/kg given in 15 min, followed by a continuous DEX infusion of 0.2–0.7 µg/kg/h.
During patient preparation, a Ringer-Acetat (RAC)-infusion of 20 mL/h was introduced and continued until the end of the procedure. To prevent hypovolemia, 6% Hydroxy-Ethyl starch (HES) 500 mL was infused in one hour. If the patient became hypotonic, a more rapid infusion of RAC could be given. In addition, during the procedure, patients were given a Glucose–Electrolyte solution (G5% Na0.3) infusion of 30 mL/h for the femoral vein socket clearing, an RAC infusion of 120 mL/h for the transseptal sheet flushing and an RAC infusion of 2–10 mL/h for the magnetic catheter flushing.
Electrophysiology
The electrophysiological measurements were performed in the fasting state. Two quadripolar electrode catheters (Supreme™ CRD, St. Jude Medical Company, St. Paul, MN, USA) were introduced via femoral access to the right ventricular apex and His bundle region, respectively. A deflectable decapolar catheter (Inquiry™, Irvine Biomedical, Inc., St. Jude Medical Company, Irvine, CA, USA) was inserted into the coronary sinus (CS). A bipolar pacing from the most proximal CS pair of electrodes was used for atrial pacing and the ventricular and VA conduction studies were accomplished by RV apical pacing. Care was used to record stable His bundle electrograms. Incremental pacing and single extrastimulus techniques were used to determine the antegrade and retrograde AV conduction properties and the atrial and ventricular effective refractory periods, as well as sinus node recovery time (SNRT) and corrected sinus node recovery time (CSNRT). Pacing was performed with a programmable stimulator (EP-4™ Cardiac Stimulator (St. Jude medical, Inc., St. Paul, MN, USA) using stimuli of 2 ms duration and amplitudes twice the diastolic threshold, which was defined also after the dexmedetomidine infusion. The programmed electrical stimulation was performed prior to transseptal puncture, in the baseline and in the steady state on continuous dexmedetomidine infusion. The protocol and definitions used for the stimulation program were as utilized in clinical studies [69]. In short, an incremental atrial and right ventricular extrastimulus technique with driving cycle lengths of 600 ms and 400 ms was used to determine the atrial and ventricular effective refractory periods (AERP and VERP, respectively), as well as the AV nodal antegrade and retrograde effective refractory periods (AVN ERP600, AVNERP400 and AVNERPret, respectively). Incremental atrial and right ventricular pacing were used to define the cycle lengths producing AV nodal Wenckebach antegrade (AVNW) and retrograde (AVNWret) conduction blocks, respectively. Conduction over the accessory pathway or dual AV conduction physiology were not found in either direction. To determine the effect of dexmedetomidine on the sinus node function, overdrive suppression with rapid atrial pacing at a cycle length of 100 ms shorter than the spontaneous sinus rate for one minute was used. From the return cycle length sinus node recovery time (SNRT) and corrected SNRT (CSNRT) were calculated.
A 12 lead ECG was recorded during the stable sinus rhythm just prior to the baseline electrophysiological study, and repeated after the completion of the clinical study drug infusion and before starting the second set of electrophysiological measurements. Systolic arterial pressure (SAP), diastolic arterial pressure (DAP), mean arterial pressure (MAP) and heart rate (HR) were measured non-invasively. Peripheral arterial blood saturation (SpO2) was measured with pulse-oximetry.
All measurements were performed twice, before and after the DEX bolus. The data on stimulations and recordings were stored digitally and analyzed off-line, using the mean values of five consecutive measurements. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used for pairwise comparisons of statistically significant (p < 0.05) differences of hemodynamic, oxygenation and electrophysiological measurements.
5. Conclusions
The most recent experimental studies suggest both an α2-receptor related and a direct effect on cardiomyocyte mechanisms for DEX-induced cardiac protection for oxidative and hypoxic injuries of the heart. In surgical and intensive care, DEX has been shown to reduce the incidence of ventricular arrythmias and to stabilize haemodynamics in humans. Further studies are needed to establish the role of DEX in clinical organ protection both after surgery and myocardial infarction. Our clinical study shows that DEX has a slight inhibitory effect on sinus node function, and that it prolongs atrioventricular refractoriness in patients undergoing atrial fibrillation ablation. Whether these are direct actions remains unclear, but if proper hydration is provided and hypotension avoided, the response is evident.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.P., H.P. and T.N.; methodology, R.P., T.N. and H.P.; software, T.N.; validation, R.P., T.N., H.P. and V.W.T.T.; formal analysis, V.W.T.T.; investigation, R.P. and H.P.; resources, H.P.; data curation, R.P. and V.W.T.T.; writing—original draft preparation, V.W.T.T. and R.P.; writing—review and editing, R.P. and H.P.; visualization, R.P.; supervision, R.P.; project administration, R.P. and H.P.; funding acquisition, R.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Signe and Ane Gyllenberg Foundation (Finland), grant number 5335.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of The Helsinki University Central Hospital, Finland on 25 August 2010 with protocol code 137/13/03/01/2010.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to national ethical restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Trial registration
EudraCT 2010-020782-24.
References
- Kaur, M.; Singh, P.M. Current Role of Dexmedetomidine in Clinical Anesthesia and Intensive Care. Anesth. Essays Res. 2011, 5, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, G.M. Dexmedetomidine: A Review of Its Use for Sedation in the Intensive Care Setting. Drugs 2015, 75, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barends, C.R.; Absalom, A.; van Minnen, B.; Vissink, A.; Visser, A. Dexmedetomidine Versus Midazolam in Procedural Sedation. A Systematic Review of Efficacy and Safety. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerink, M.A.S.; Struys, M.R.F.; Hannivoort, L.N.; Barends, C.R.M.; Absalom, A.B.; Colin, P. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Dexmedetomidine. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 56, 893–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Ni, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, C.; Ling, X. Can dexmedetomidine reduce atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery? A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Drug. Des. Devel. Ther. 2018, 12, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preskorn, S.H.; Zeller, S.; Citrome, L.; Finman, J.; Goldberg, J.F.; Fava, M.; Kakar, R.; De Vivo, M.; Yocca, F.D.; Risinger, R. Effect of Sublingual Dexmedetomidine vs Placebo on Acute Agitation Associated with Bipolar Disorder: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2022, 327, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, N.; Tang, B. Organ-Protective Effects and the Underlying Mechanism of Dexmedetomidine. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 6136105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Kang, L.; Wang, Q. Recent Advances in the Clinical Value and Potential of Dexmedetomidine. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 7507–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xia, L.-Y.; Liang, W.-D.; Rao, D.-Y.; Zhu, P.-P.; Huang, K.-N.; Deng, Z.-H.; Zhong, M.-L. Intrathecal Dexmedetomidine Combined with Ropivacaine in Cesarean Section: A Prospective Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Study. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 922611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, A.A.; Eleraky, N.E.; Diab, N.H.; Elsabahy, M.; Mohamed, S.A.; Abdel-Ghaffar, H.S.; Hassan, N.A.; Shouman, S.A.; Omran, M.M.; Hassan, S.B.; et al. Development of Sedative Dexmedetomidine Sublingual IN Situ Gels: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluations. Pharmaceutics. 2022, 14, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, T.; Suzuki, H.; Hosoe, N.; Ogata, H.; Kanai, T.; Yahagi, N. Dexmedetomidine vs propofol for gastrointestinal endoscopy: A meta-analysis. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017, 5, 1037–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, M.; Xu, Y.; Li, B.; Chang, E.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. Intravenous Administration of Dexmedetomidine and Quality of Recovery after Elective Surgery in Adult Patients: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Anesth. 2020, 65, 109849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, L.; Lee, L.H.N.; Lee, B.; Chau, A.; Wang, E.H.Z. The Safety of High-dose Dexmedetomidine after Cardiac Surgery: A Historical Cohort Study. Can. J. Anaesth. 2022, 69, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, X.; Wei, J.; Zhang, X. Effects of Dexmedetomidine on Neurocognitive Disturbance after Elective non-Cardiac Surgery in Senile Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 03000605211014294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.; Piticaru, J.; Chaudhuri, D.; Basmaji, J.; Fan, E.; Møller, M.H.; Devlin, J.D.; Alhazzani, W. Safety and Efficacy of Dexmedetomidine in Acutely Ill Adults Requiring Noninvasive Ventilation. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Trials. Chest 2021, 159, 2274–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Q.; Kumar, A.; Deshmukh, A.; Bennett, C. Dexmedetomidine Reduces Incidences of Ventricular Arrhythmias in Adult Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2022, 2022, 5158362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cassai, A.; Sella, N.; Geraldini, F.; Zarantonello, F.; Pettenuzzo, T.; Pasin, L.; Iuzzolino, M.; Rossini, N.; Pesenti, E.; Zecchino, G.; et al. Preoperative Dexmedetomidine and Intraoperative Bradycardia in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Meta-analysis with Trial Sequential Analysis. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2022, 75, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Ye, H.; Wang, M.; Wang, T. Effect of Dexmedetomidine on Tachyarrhythmias after Cardiac Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2022, 79, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.; Alshamsi, F.; Carayannopoulos, K.L.; Granholm, A.; Piticaru, J.; Duhailib, Z.A.; Chaudhuri, D.; Spatafora, L.; Yuan, Y.; Centofanti, J.; et al. Dexmedetomidine vs Other Sedatives in Critically Ill Mechanically Ventilated Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Trials. Intensive Care Med. 2022, 48, 811–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kin Sin, J.C.; Tabah, A.; Campher, M.J.J.; Laupland, K.B.; Eley, V.A. The Effect of Dexmedetomidine on Postanesthesia Care Unit Discharge and Recovery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Anesth. Analg. 2022, 134, 1229–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamibayashi, T.; Maze, M. Clinical Uses of a2-Adrenergic Agonists. Anesthesiology 2000, 93, 1345–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vladinov, G.; Fermin, L.; Logini, R.; Ramos, Y.; Maratea, E., Jr. Choosing the Anesthetic and Sedative Drugs for Supraventricular Tachycardia Ablations: A Focused Review. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2018, 41, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aikaterini, A.; Ioannis, D.; Dimitrios, G.; Konstantinos, S.; Vasilios, G.; George, P. Bradycardia Leading to Asystole Following Dexmedetomidine Infusion during Cataract Surgery: Dexmedetomidine-Induced Asystole for Cataract Surgery. Case Rep. Anesthesiol. 2018, 2018, 2896032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa-Sales, C.; Reid, K.; Maze, M. Inhibition of adenylate cyclase in the locus coeruleus mediates the hypnotic response to an alpha-2-agonist in the rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1992, 263, 1046–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Kamibayashi, T.; Mammoto, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Yamatodani, A.; Takada, K.; Yoshiya, I. Further Characterization of the Receptor Mechanism Involved in the Antidysrhythmic Effect of Dexmedetomidine on Halothane/Epinephrine Dysrhythmias in Dogs. Anesthesiology 1995, 83, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacif-Coelho, C.; Correas-Sales, C.; Chang, L.L.; Maze, M. Perturbation of Ion-Channel Conductance Alters the Hypnotic Response to Alpha2-agonist Dexmedetomidine in the Locus Coeruleus of the Rat. Anesthesiology 1994, 81, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sculptoreanu, A.; Scheuer, T.; Catterall, W.A. Voltage-dependent Potention of L-type Ca2+ Channels Due to Phosphorylation by cAMP-dependent Protein Kinase. Nature 1993, 364, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snapir, A.; Talke, P.; Posti, J.; Huiku, M.; Kentala, E.; Scheinin, M. Effects of Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibition on Dexmedetomidine Induced Vasoconstriction in Healthy Human Volunteers. Br. J. Anaesth. 2009, 102, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tank, J.; Diedrich, A.; Szczech, E.; Luft, F.C.; Jordan, J. Alpha-2 adrenergic Transmission and Human Baroreflex Regulation. Hypertension 2004, 43, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sairaku, A.; Nakano, Y.; Suenari, K.; Tokuyama, T.; Kawazoe, H.; Matsumura, H.; Tomomori, S.; Amioka, M.; Kihara, Y. Dexmedetomidine Depresses Sinoatrial and Atrioventricular Nodal Function Without Any Change in Atrial Fibrillation Inducibility. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2016, 68, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slupe, A.M.; Minnier, J.; Raitt, M.H.; Zarraga, I.G.E.; MacMurdy, K.S.; Jessel, P.M. Dexmedetomidine Sedation for Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia Ablation is Not Associated with Alteration of Arrhythmia Inducibility. Anesth. Analg. 2019, 129, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoetzer, C.; Reuter, S.; Doll, T.; Foadi, N.; Wegner, F.; Leffler, A. Inhibition of the Cardiac Na⁺ channel α-subunit Nav1.5 by Propofol and Dexmedetomidine. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2016, 389, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhou, C.-L.; Xia, Z.-Y.; Wang, L. Effects of Dexmedetomidine on L-Type Calcium Current in Rat Ventricular Myocytes. Acta Cardiol. Sin. 2013, 29, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Behmenburg, F.; Pickert, E.; Mathes, A.; Heinen, A.; Hollmann, M.H.; Ragnar Huhn, R.; Berger, M.M. The Cardioprotective Effect of Dexmedetomidine in Rats Is Dose-Dependent and Mediated by BKCa Channels. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2017, 69, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, L. Electrophysiological Effects of Dexmedetomidine on Sinoatrial Nodes of Rabbits. Acta Cardiol. Sin. 2015, 31, 543–549. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.-J.; Lin, Z.-H.; Lin, Y.-Z.; Rao, Z.-H.; Lin, J.-F.; Wu, L.-P.; Li, L. Dexmedetomidine Exerted Anti-arrhythmic Effects in Rat With Ischemic Cardiomyopathy via Upregulation of Connexin 43 and Reduction of Fibrosis and Inflammation. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsui, K.; Hayami, N.; Kunishima, T.; Sugiura, A.; Mikamo, T.; Kanamori, K.; Yamagishi, N.; Yamagishi, S.; Watanabe, H.; Ajiki, K.; et al. Dexmedetomidine and Clonidine Inhibit Ventricular Tachyarrhythmias in a Rabbit Model of Acquired Long QT Syndrome. Circ. J. 2012, 76, 2343–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilsbach, R.; Schneider, J.; Lother, A.; Schickinger, S.; Leemhuis, J.; Hein, L. Sympathetic a2 adrenoceptors prevent cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis in mice at baseline but not after chronic pressure overload. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 86, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkowitz, D.E.; Price, D.T.; Bello, E.A.; Page, S.O.; Schwinn, D.A. Localization of Messenger RNA for Three Distinct Alpha 2-adrenergic receptor Subtypes in human Tissues. Evidence for Species Heterogeneity and Implications for Human Pharmacology. Anesthesiology 1994, 81, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, F.; Jin, Z.; Lin, T.; Cai, X.; Pan, L.; Wang, S.; Cai, Y.; Chen, H. Dexmedetomidine Enhances Tolerance to Bupivacaine Cardiotoxicity in the Isolated Rat Hearts: Alpha 2-adrenoceptors Were Not Involved. BMC. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 20, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunte, S.; Behmenburg, F.; Majewski, N.; Stroethoff, M.; Raupach, A.; Mathes, A.; Heinen, A.; Hollmann, M.W.; Huhn, R. Characteristics of Dexmedetomidine Postconditioning in the Field of Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Anesth. Analg. 2020, 130, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, W.; Wang, C.; Peng, Y.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Xia, Z.; Ren, C.; Qian, J. Dexmedetomidine Alleviates H2O2-induced Oxidative Stress and Cell Necroptosis Through Activating of α2-adrenoceptor in H9C2 Cells. Molecul. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 3629–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Qu, M.; Xing, F.; Li, H.; Cheng, D.; Xing, N.; Zhang, W. The Protective Mechanism of Dexmedetomidine in Regulating Atg14L-Beclin1-Vps34 Complex against Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2021, 14, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Li, Y.-P.; Yin, Y.-Q.; Hu, B.-L.; Gao, H. Dexmedetomidine Inhibits Pyroptosis by Down-Regulating miR-29b in Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in Rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 86, 106768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-F.; Wang, H.; Song, N.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Zhang, J.; Meng, X.-W.; Feng, X.-M.; Liu, H.; Peng, K.; Ji, F.-H. Dexmedetomidine Attenuates Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Myocardial Inflammation and Apoptosis Through Inhibiting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Signaling. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 1217–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Sun, S.; Juan, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wang, R.; Meng, S.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, K.; Xie, K. Dexmedetomidine Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in vitro by Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. BMC. Anesthesiol. 2021, 21, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Zhou, R.; Qu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Song, N.; Liang, R.; Qian, J. Dexmedetomidine Preconditioning Mitigates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via Inhibition of Mast Cell Degranulation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Gong, Q.; Wu, Y.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, S.; Duan, J.-S. Dexmedetomidine Alleviates Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis and Cardiac Dysfunction May Be Associated with Inhibition of RhoA/ROCK Pathway in Mice with Myocardial Infarction. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2021, 394, 1569–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, J.; Qiu, L.; Jiang, C.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, Q.; Hong, H.; Ye, L. Dexmedetomidine Protects Human. Cardiomyocytes against Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Through α2-Adrenergic Receptor/AMPK-Dependent Autophagy. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 615424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Du, J.; Tan, X.; Wu, Z.; Yuan, J.; Cong, B. Dexmedetomidine Protects the Heart Against ischemia Reperfusion Injury via Regulation of the Bradykinin Receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 911, 174493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Pan, D.; Wang, Z.; Jin, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, H. The Effects of Dexmedetomidine Post-Conditioning on Cardiac and Neurological Outcomes after Cardiac Arrest and Resuscitation in Swine. Shock 2021, 55, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wu, W.; Lin, X.; Shen, M.; Yan, Z.; Yu, S.; Luo, Y. Protective Effects of Dexmedetomidine in Vital Organ Injury: Crucial Roles of Autophagy. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2022, 27, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penttilä, J.; Helminen, A.; Anttila, M.; Hinkka, S.; Scheinin, H. Cardiovascular and Parasympathetic Effects of Dexmedetomidine in Healthy Subjects. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2004, 82, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, D.; Sankar, A.; Beattie, W.S.; Wijeysundera, D.N. Alpha-2 adrenergic Agonists for the Prevention of Cardiac Complications among Adults Undergoing Surgery. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, CD004126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Lu, F.; Zhen, J.; Chen, W. Dexmedetomidine Reduces Atrial Fibrillation after Adult Cardiac Surgery: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2020, 20, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Li, X.; Mu, G. Myocardial Protective and Anti-inflammatory Effects of Dexmedetomidine in Patients Undergoing Cardiovascular Surgery with Cardiopulmonary Bypass: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Anesth. 2022, 36, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, M. Effect of Dexmedetomidine on Hemodynamics in Patients Undergoing Hysterectomy: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review. J. Internat. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Wang, F.; Xu, H.; Wu, L.; Gao, G. Effects of Dexmedetomidine on Intraoperative Hemodynamics, Recovery Profile and Postoperative Pain in Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. BMC Anesthesiol. 2021, 21, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raatikainen, M.J.P. Anatomy and Physiology of the Atrioventricular Node. In The ESC Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine, 3rd ed.; Camm, A.J., Lüscher, T.F., Maurer, G.P.W., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 1958–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollin, A.; Gandjbakhch, E.; Giustetto, C.; Scrocco, C.; Fourcade, C.; Monteil, B.; Mondoly, P.; Cardin, C.; Maupain, C.; Gaita, F.; et al. Shortening of the Short Refractory Periods in Short QT Syndrome. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, K.; Borer, J.S.; Camm, A.J.; Danchin, N.; Ferrari, R.; Lopez Sendon, J.L.; Steg, P.G.; Tardif, J.C.; Tavazzi, L.; Tendera, M.; et al. Resting Heart Rate in Cardiovascular Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 50, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guasch, E.; Mont, L. Diagnosis, Pathophysiology, and Management of Exercise-induced arrhytmias. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilde, A.A.M.; Amin, A.S.; Postema, P.G. Diagnosis, Management and Therapeutic Strategies for Congenital Long QT Syndrome. Heart 2022, 108, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, S.J.; Karner, C.; Trevor, N.; Wakefield, V.; Salih, F. Dual-chamber Pacemakers for Treating Symptomatic Bradycardia Due to Sick Sinus Syndrome without Atrioventricular Block: A Systematic Review and Economic Evaluation. Health. Technol. Assess. 2015, 19, 1–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosaki, A. ArrhythmoGenoPharmacoTherapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosaki, A.; Szekeres, L.; Hearse, D.J. Diltiazem and the Reduction of Reperfusion-induced Arrhythmias in the Rat: Protection is Secondary to Modification of Ischemic Injury and Heart Rate. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 1987, 19, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernier, M.; Curtis, M.J.; Hearse, D.J. Ischemia-induced and Reperfusion-induced Arrhythmias: Importance of Heart Rate. Am. J. Physiol. 1989, 256, H21–H31. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda, M.; Ide, T.; Furusawa, S.; Ishimaru, K.; Tadokoro, T.; Miyamoto, H.D.; Ikeda, S.; Okabe, K.; Ishikita, A.; Abe, K.; et al. Heart Rate Reduction with Ivabradine Prevents Cardiac Rupture after Myocardial Infarction in Mice. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2022, 36, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josephson, M.E. Electrophysiological Investigation: General Concepts. In Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology; Techniques and Interpretations; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2009; pp. 19–67. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).