Effects of Oleacein, a New Epinutraceutical Bioproduct from Extra Virgin Olive Oil, in LPS-Activated Murine Immune Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation of OLA from Olive Oil
2.2. Antioxidant Activity of OLA
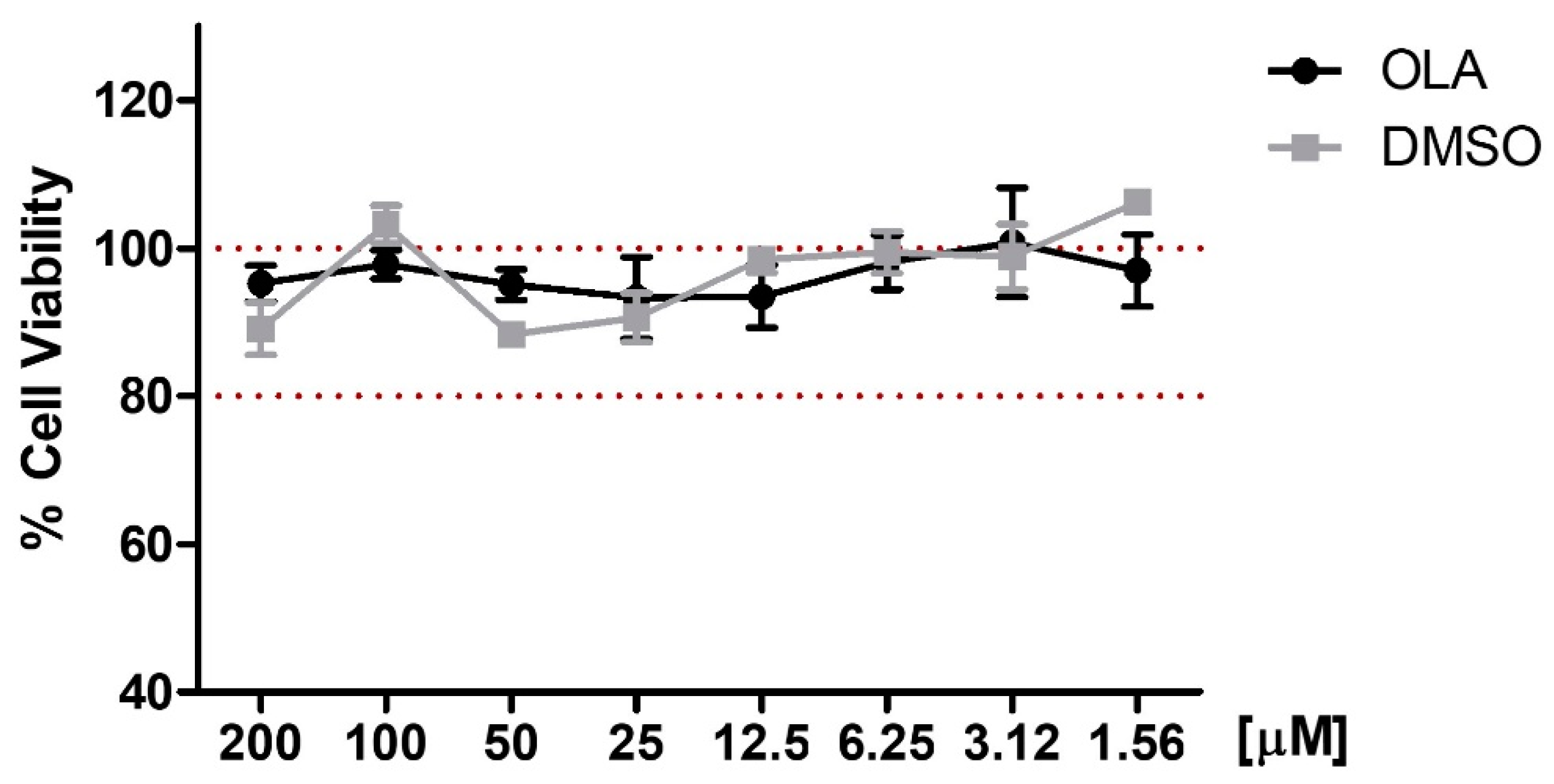
2.3. Effects of OLA on Cell Viability
2.4. Intracellular ROS, Nitrite Production, and iNOs Overexpression Are Inhibited by OLA in LPS-Stimulated Murine Peritoneal Macrophages
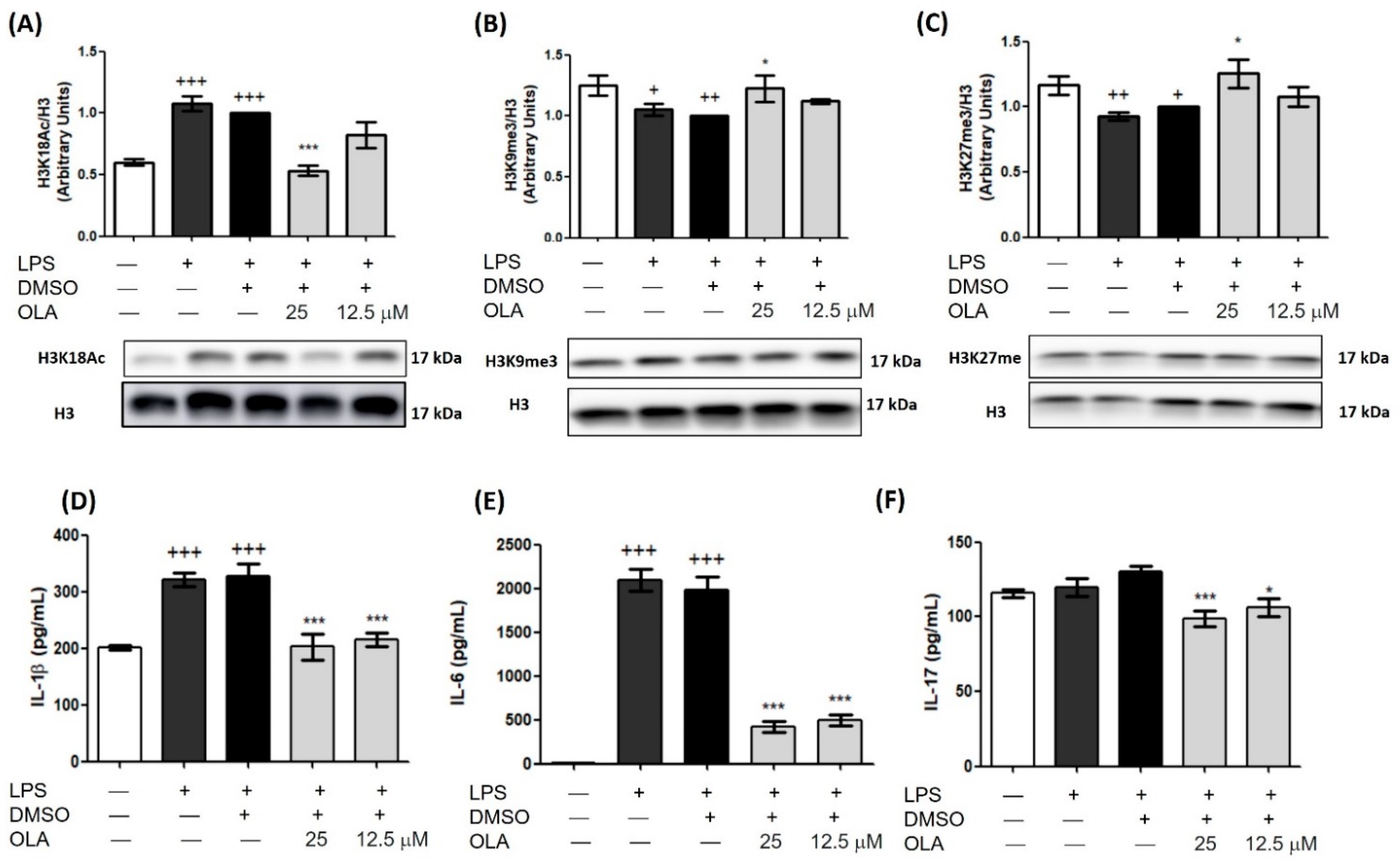
2.5. OLA Decreased LPS-Induced Secretion of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
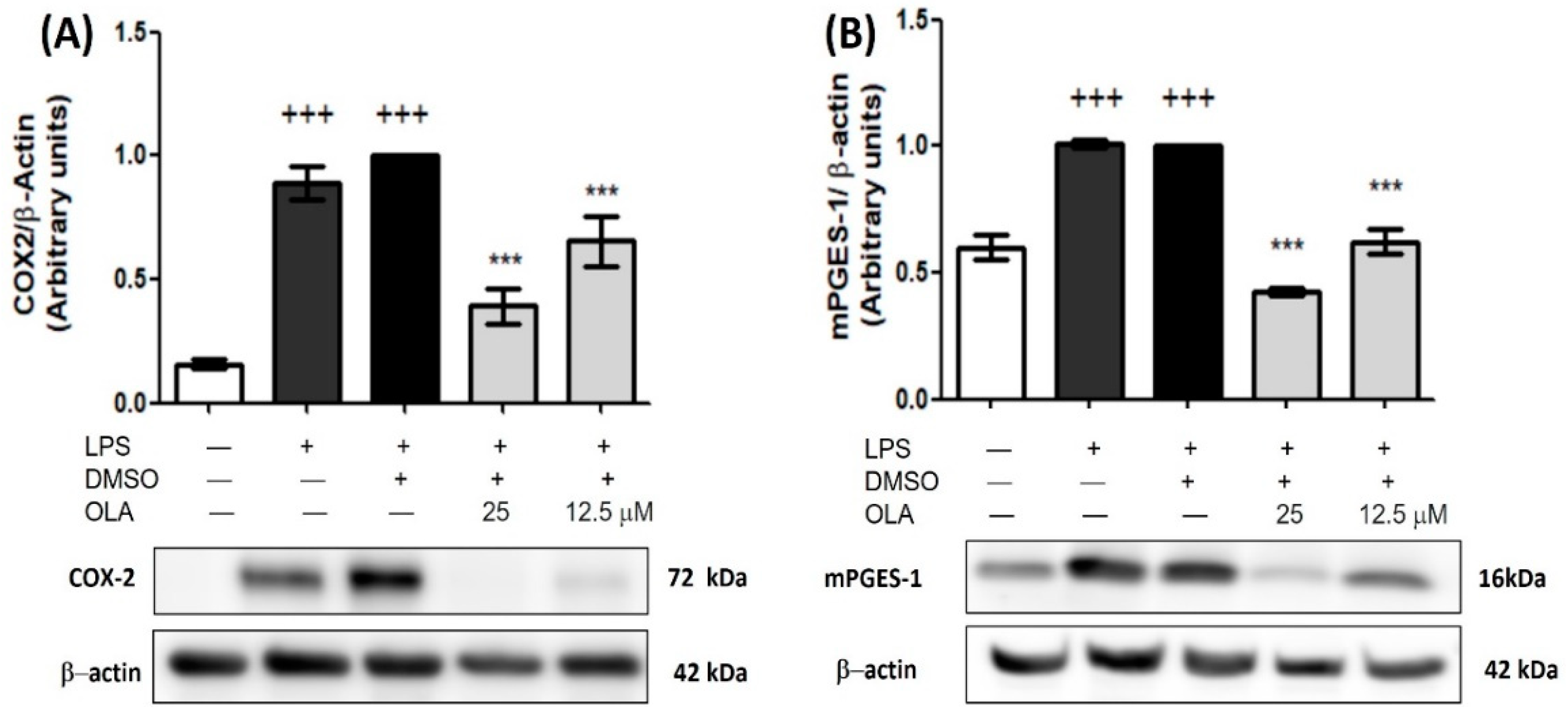
2.6. Inhibitory Effect of OLA on COX-2 and mPGES-1 Overexpression Induced by LPS
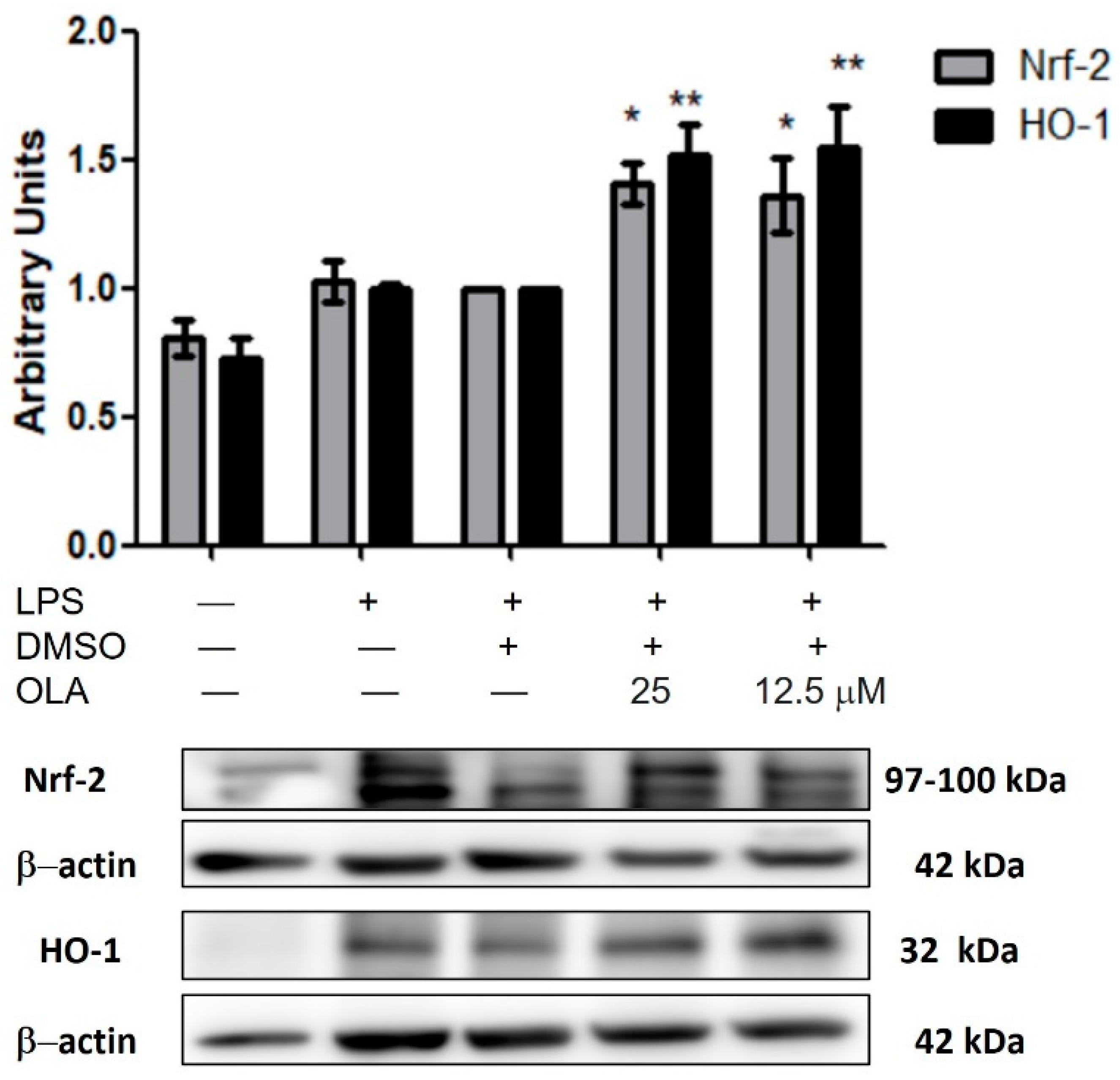
2.7. OLA Upregulated Nrf-2/HO-1 Pathway Protein Expression
2.8. Effects of OLA on MAPKs Phosphorylation
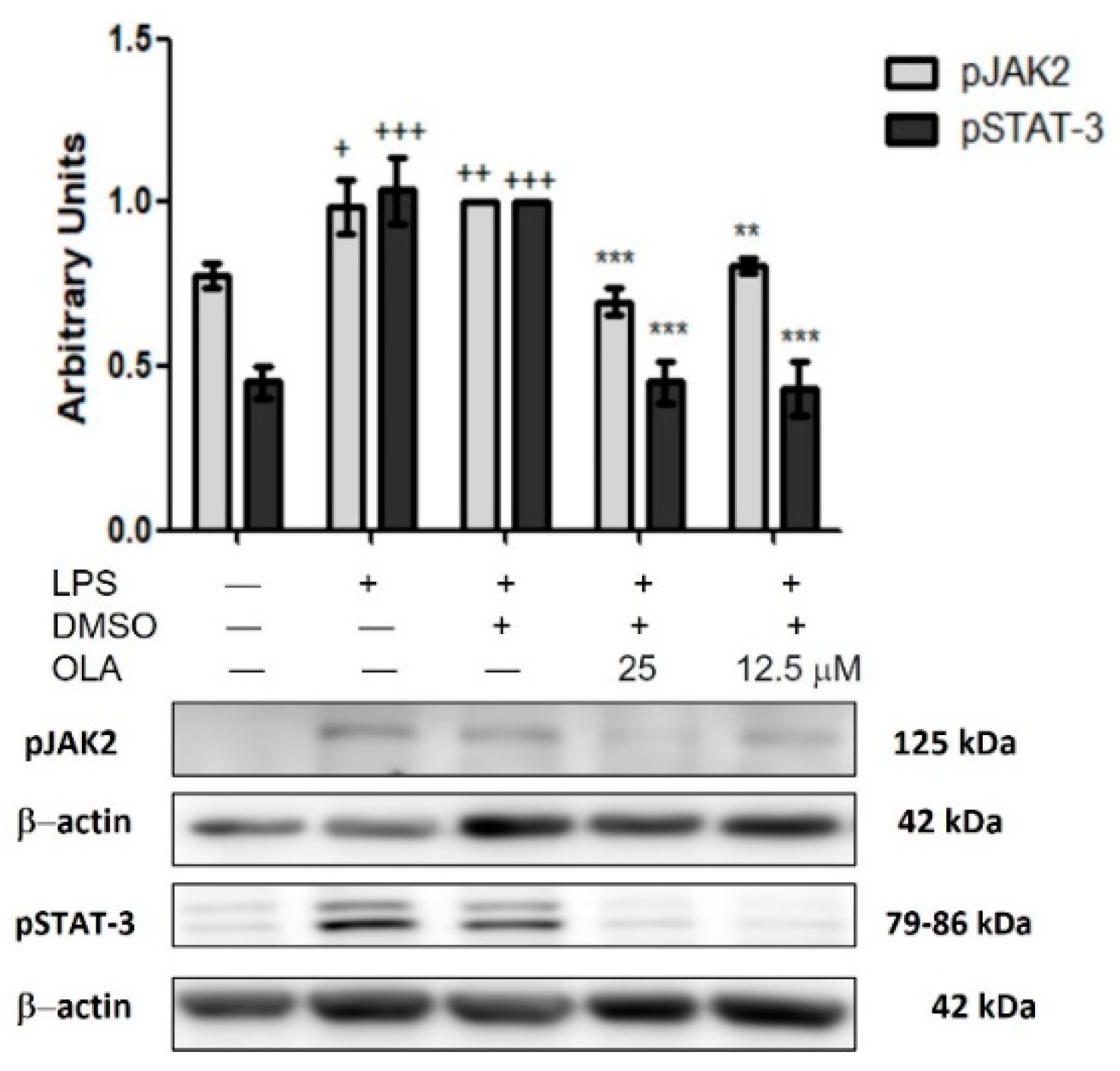
2.9. LPS-Induced JAK/STAT Pathway Activity Is Downregulated by OLA in Murine Peritoneal Macrophages
2.10. Effect of OLA in the Canonical and Non-Canonical Inflammasome Activation in LPS-Activated Murine Peritoneal Macrophages
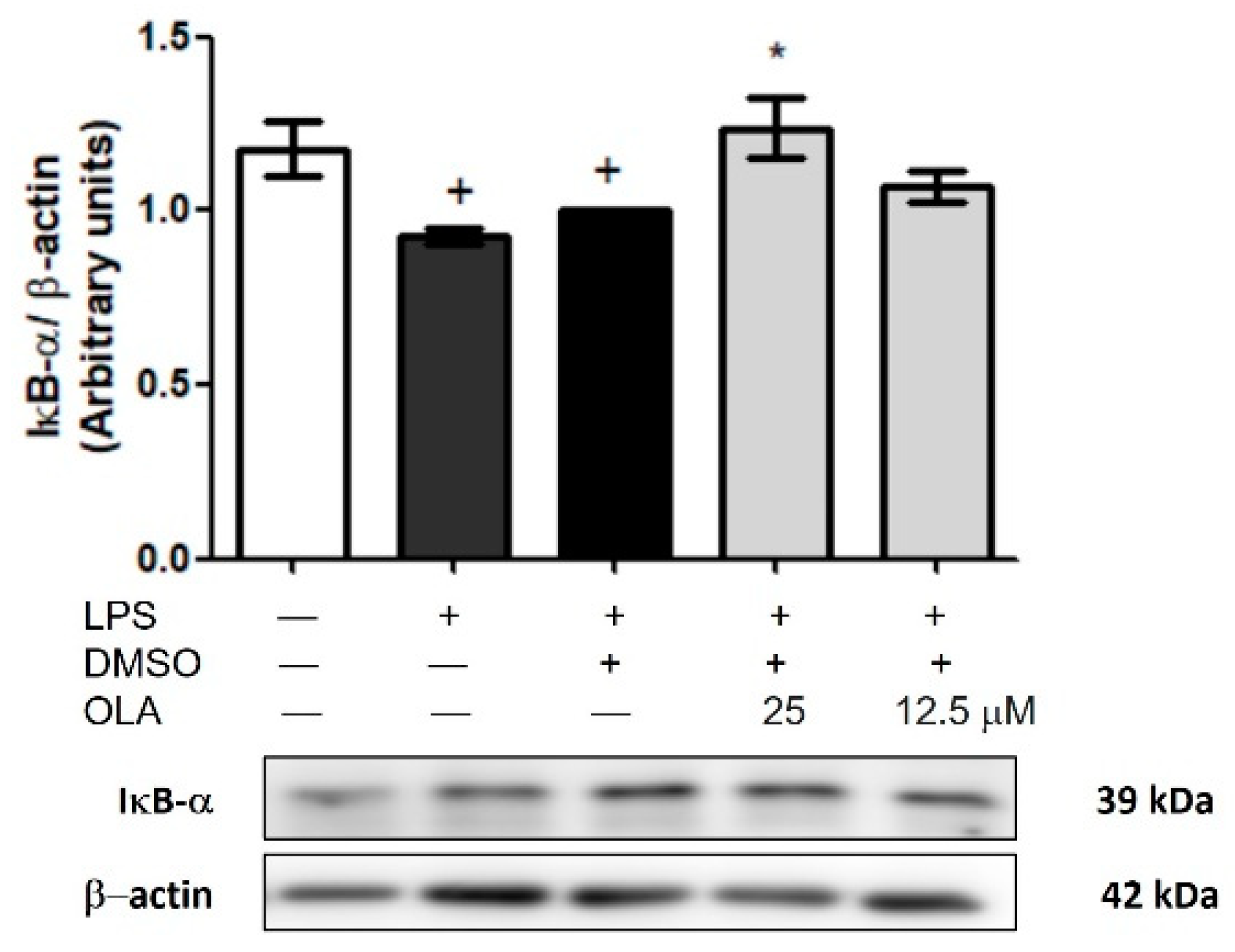
2.11. Effects of OLA on LPS-Induced IκB-α Degradation in Peritoneal Macrophages
2.12. Epigenetic Histone Modifications by OLA in Spleen Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.1.1. Reagents
4.1.2. Instruments
4.1.3. Isolation and Identification of (–)-Oleacein (OLA)
4.2. Animals
4.3. Isolation and Culture of Murine Peritoneal Macrophages and Spleen Cells
4.4. ABTS Test
4.5. Cell Viability
4.6. Measurement of Nitrite Production
4.7. DCFDA Cellular Reactive Oxygen Species Detection
4.8. Determination of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines by Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay
4.9. Histone Extraction
4.10. Isolation of Proteins and Western Blot Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Funes, S.C.; Rios, M.; Escobar-Vera, J.; Kalergis, A.M. Implications of Macrophage Polarization in Autoimmunity. Immunology 2018, 154, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, T.M.; Scanzello, C.R. Innate Inflamation and Synovial Macrophages in osteoarthritis Pathophysiology. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2019, 37, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tu, J.; Wang, X.; Gong, X.; Hong, W.; Han, D.; Fang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wei, W. Synovial Macrophages in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Past, Present, and Future. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 1583647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.H.; Oh, Y.C.; Cho, W.K.; Yim, N.H.; Ma, J.Y. Hoveniae Semen Seu Fructus Ethanol Extract Exhibits Anti-Inflammatory Activity via MAPK, AP-1, and STAT Signaling Pathways in LPS-Stimulated RAW 264.7 and Mouse Peritoneal Macrophages. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 9184769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Hong, P.; Zheng, X. β-Carotene Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation via Inhibition of the NF-ΚB, JAK2/STAT3 and JNK/P38 MAPK Signaling Pathways in Macrophages. Anim. Sci. J. 2019, 90, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.P.; Chen, D.R.; Lin, W.J.; Lin, Y.H.; Chen, J.Y.; Kuo, Y.H.; Chung, J.G.; Hsia, T.C.; Hsieh, W.T. Ergosta-7,9(11),22-Trien-3β-Ol Attenuates Inflammatory Responses via Inhibiting Mapk/Ap-1 Induced Il-6/Jak/Stat Pathways and Activating Nrf2/Ho-1 Signaling in Lps-Stimulated Macrophage-like Cells. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, B.; Huang, H.; Qu, S.; Yang, S.; Zeng, Z. Gastrodin Induced HO-1 and Nrf2 up-Regulation to Alleviate H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress in Mouse Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells through P38 MAPK Phosphorylation. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2018, 51, e7439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.W.; Choi, H.J.; Park, S.D.; Kim, H.; Yu, G.R.; Kim, J.E.; Park, W.H. Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway by Amomum Villosum Extract Suppresses LPS-Induced Oxidative Stress in Vitro and Ex Vivo. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 2837853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoni, L.; Fedeli, D.; Fiorini, D.; Gabbianelli, R. Extra Virgin Olive Oil and Nigella Sativa Oil Produced in Central Italy: A Comparison of the Nutrigenomic Effects of Two Mediterranean Oils in a Low-Grade Inflammation Model. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vierhuis, E.; Servili, M.; Baldioli, M.; Schols, H.A.; Voragen, A.G.J.; Montedoro, G. Effect of Enzyme Treatment during Mechanical Extraction of Olive Oil on Phenolic Compounds and Polysaccharides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 1218–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepore, S.M.; Maggisano, V.; Bulotta, S.; Mignogna, C.; Arcidiacono, B.; Procopio, A.; Brunetti, A.; Russo, D.; Celano, M. Oleacein Prevents High Fat Diet-Induced a Diposity and Ameliorates Some Biochemical Parameters of Insulin Sensitivity in Mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, G.E.; Lepore, S.M.; Morittu, V.M.; Arcidiacono, B.; Colica, C.; Procopio, A.; Maggisano, V.; Bulotta, S.; Costa, N.; Mignogna, C.; et al. Effects of Oleacein on High-Fat Diet-Dependent Steatosis, Weight Gain, and Insulin Resistance in Mice. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipek, A.; Mikołajczyk, T.P.; Guzik, T.J.; Naruszewicz, M. Oleacein and Foam Cell Formation in Human Monocyte-Derived Macrophages: A Potential Strategy against Early and Advanced Atherosclerotic Lesions. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipek, A.; Czerwińska, M.E.; Kiss, A.K.; Polański, J.A.; Naruszewicz, M. Oleacein May Inhibit Destabilization of Carotid Plaques from Hypertensive Patients. Impact on High Mobility Group Protein-1. Phytomedicine 2017, 32, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polini, B.; Digiacomo, M.; Carpi, S.; Bertini, S.; Gado, F.; Saccomanni, G.; Macchia, M.; Nieri, P.; Manera, C.; Fogli, S. Oleocanthal and Oleacein Contribute to the in Vitro Therapeutic Potential of Extra Virgin Oil-Derived Extracts in Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer. Toxicol. Vitr. 2018, 52, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirmi, S.; Celano, M.; Lombardo, G.E.; Maggisano, V.; Procopio, A.; Russo, D.; Navarra, M. Oleacein Inhibits STAT3, Activates the Apoptotic Machinery, and Exerts Anti-Metastatic Effects in the SH-SY5Y Human Neuroblastoma Cells. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 3271–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juli, G.; Oliverio, M.; Bellizzi, D.; Cantafio, M.E.G.; Grillone, K.; Passarino, G.; Colica, C.; Nardi, M.; Rossi, M.; Procopio, A.; et al. Anti-Tumor Activity and Epigenetic Impact of the Polyphenol Oleacein in Multiple Myeloma. Cancers 2019, 11, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Miranda, B.; Gallardo, I.; Melliou, E.; Cabero, I.; Álvarez, Y.; Magiatis, P.; Hernández, M.; Nieto, M.L. Oleacein Attenuates the Pathogenesis of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis through Both Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwińska, M.; Kiss, A.K.; Naruszewicz, M. A Comparison of Antioxidant Activities of Oleuropein and Its Dialdehydic Derivative from Olive Oil, Oleacein. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surace, A.E.A.; Hedrich, C.M. The Role of Epigenetics in Autoimmune/Inflammatory Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, T.; Castejón, M.L.; Muñoz-García, R.; Alarcón-De-la-Lastra, C. Epigenetic Linkage of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Nutrition. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2021, 2021, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauterbach, M.A.; Hanke, J.E.; Serefidou, M.; Mangan, M.S.J.; Kolbe, C.C.; Hess, T.; Rothe, M.; Kaiser, R.; Hoss, F.; Gehlen, J.; et al. Toll-like Receptor Signaling Rewires Macrophage Metabolism and Promotes Histone Acetylation via ATP-Citrate Lyase. Immunity 2019, 51, 997–1011.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castejón, M.L.; Montoya, T.; Alarcón-De-La-Lastra, C.; González-Benjumea, A.; Vázquez-Román, M.V.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M. Dietary Oleuropein and Its Acyl Derivative Ameliorate Inflammatory Response in Peritoneal Macrophages from Pristane-Induced SLE Mice: Via Canonical and Noncanonical NLRP3 Inflammasomes Pathway. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 6622–6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparicio-Soto, M.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M.; Cárdeno, A.; González-Benjumea, A.; Fernández-Bolaños, J.G.; Alarcón-de-la-Lastra, C. Dietary Hydroxytyrosol and Hydroxytyrosyl Acetate Supplementation Prevent Pristane-Induced Systemic Lupus Erythematous in Mice. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 29, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, T.; Alarcón-De-La-Lastra, C.; Castejón, M.L.; Ortega-Vidal, J.; Altarejos, J.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M. (−)-Methyl-Oleocanthal, a New Oleocanthal Metabolite Reduces LPS-Induced Inflammatory and Oxidative Response: Molecular Signaling Pathways and Histones Epigenetic Modulation. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, Y.L.; Wang, S.C.; Suzuki, K.; Fang, S.H.; Chen, C.S.; Cheng, W.C.; Su, C.C.; Yeh, H.C.; Tu, H.P.; Liu, P.L.; et al. Bavachin Attenuates LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response and Inhibits the Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Macrophages. Phytomedicine 2019, 59, 152785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio-Soto, M.; Sánchez-Fidalgo, S.; González-Benjumea, A.; Maya, I.; Fernández-Bolaños, J.G.; Alarcón-de-la-Lastra, C. Naturally Occurring Hydroxytyrosol Derivatives: Hydroxytyrosyl Acetate and 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylglycol Modulate Inflammatory Response in Murine Peritoneal Macrophages. Potential Utility as New Dietary Supplements. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Maitra, U.; Singh, N.; Gan, L. Molecular Mechanism Underlying LPS-Induced Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species in Macrophages. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xue, M.; Geng, Z.; Chen, P. Cellular Physiology Cellular Physiology Cellular Physiology Cellular Physiology The Suppressive Effects of Bursopentine (BP5) on Oxidative Stress and NF- ΚB Activation in Lipopolysaccharide-Activated Murine Peritoneal Macrophages. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 29, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castejon, M.L.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M.; Aparicio-Soto, M.; González-Benjumea, A.; Fernández-Bolaños, J.G.; Alarcón-de-la-Lastra, C. Olive Secoiridoid Oleuropein and Its Semisynthetic Acetyl-Derivatives Reduce LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response in Murine Peritoneal Macrophages via JAK-STAT and MAPKs Signaling Pathways. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 58, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirmi, S.; Maugeri, A.; Russo, C.; Musumeci, L.; Navarra, M.; Lombardo, G.E. Oleacein Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation in THP-1-Derived Macrophages by the Inhibition of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castejón, M.L.; Montoya, T.; Alarcón-de-la-lastra, C.; Sánchez-hidalgo, M. Potential Protective Role Exerted by Secoiridoids from Olea Europaea l. In Cancer, Cardiovascular, Neurodegenerative, Aging-Related, and Immunoinflammatory Diseases. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, B.; Arroba, A.I.; de los Reyes, C.; Gómez-Jaramillo, L.; González-Montelongo, M.C.; Zubía, E. Diterpenoids from the Brown Alga Rugulopteryx Okamurae and Their Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Roy, P.; Di, Q.; Ma, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Quan, J.; Zhao, J.; Xiao, W.; Chen, W. Synthesis Compound XCR-7a Ameliorates LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response by Inhibiting the Phosphorylation of c-Fos. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 145, 112468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, T.; Castejón, M.L.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M.; González-Benjumea, A.; Fernández-Bolaños, J.G.; Alarcón De-La-Lastra, C. Oleocanthal Modulates LPS-Induced Murine Peritoneal Macrophages Activation via Regulation of Inflammasome, Nrf-2/HO-1, and MAPKs Signaling Pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 5552–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, T.; Aparicio-Soto, M.; Castejón, M.L.; Rosillo, M.Á.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M.; Begines, P.; Fernández-Bolaños, J.G.; Alarcón-de-la-Lastra, C. Peracetylated Hydroxytyrosol, a New Hydroxytyrosol Derivate, Attenuates LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response in Murine Peritoneal Macrophages via Regulation of Non-Canonical Inflammasome, Nrf2/HO1 and JAK/STAT Signaling Pathways. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 57, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosignoli, P.; Fuccelli, R.; Fabiani, R.; Servili, M.; Morozzi, G. Effect of Olive Oil Phenols on the Production of Inflammatory Mediators in Freshly Isolated Human Monocytes. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 1513–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cargnello, M.; Roux, P.P. Activation and Function of the MAPKs and Their Substrates, the MAPK-Activated Protein Kinases. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 50–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, J.S.C.; Ley, S.C. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases in Innate Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berköz, M. Diosmin Suppresses the Proinflammatory Mediators in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced RAW264.7 Macrophages via NF-ΚB and MAPKs Signal Pathways. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2019, 38, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wu, S.; Qin, T.; Yue, Y.; Qian, W.; Li, L. NLRP3 Inflammasome and Inflammatory Diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 4063562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Liwinski, T.; Elinav, E. Inflammasome Activation and Regulation: Toward a Better Understanding of Complex Mechanisms. Cell Discov. 2020, 6, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matikainen, S.; Nyman, T.A.; Cypryk, W. Function and Regulation of Noncanonical Caspase-4/5/11 Inflammasome. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 3063–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrich, C.M. Mechanistic Aspects of Epigenetic Dysregulation in SLE. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 196, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanowicz, D.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, K.; Shaheen, F.; Koo, H.K.; Booth, S.; Knight, D.A.; Hackett, T.L. Elevated H3K18 Acetylation in Airway Epithelial Cells of Asthmatic Subjects. Respir. Res. 2015, 16, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imuta, H.; Fujita, D.; Oba, S.; Kiyosue, A.; Nishimatsu, H.; Yudo, K.; Suzuki, E. Histone Methylation and Demethylation Are Implicated in the Transient and Sustained Activation of the Interleukin-1β Gene in Murine Macrophages. Heart Vessel. 2020, 35, 1746–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhong, Y.; Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; Ye, P.; Cai, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Mei, Z.; Jiang, Y.; et al. H3K4 Methylation Regulates LPS-Induced Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression and Release in Macrophages. Shock 2019, 51, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.S. Functional Interplay between Methyltransferases and Inflammasomes in Inflammatory Responses and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.J.; Ren, X.S.; Xiong, X.Q.; Chen, Y.Z.; Zhao, M.X.; Wang, J.J.; Zhou, Y.B.; Han, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.H.; et al. Nlrp3 Inflammasome Activation Contributes to Vsmc Phenotypic Transformation and Proliferation in Hypertension. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corominas-Faja, B.; Cuyàs, E.; Lozano-Sánchez, J.; Cufí, S.; Verdura, S.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Borrás-Linares, I.; Martin-Castillo, B.; Martin, G.; Lupu, R.; et al. Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Contains a Metabolo-Epigenetic Inhibitor of Cancer Stem Cells. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuyàs, E.; Verdura, S.; Menendez, J.A.; Carreras, D.; Verdura, S.; Brugada, R.; Bosch-Barrera, J.; Gumuzio, J.; Martin, Á.G.; Lozano-Sánchez, J.; et al. Extra Virgin Olive Oil Contains a Phenolic Inhibitor of the Histone Demethylase LSD1/KDM1A. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, S.; Polini, B.; Manera, C.; Digiacomo, M.; Salsano, J.E.; Macchia, M.; Scoditti, E.; Nieri, P. MiRNA Modulation and Antitumor Activity by the Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Polyphenol Oleacein in Human Melanoma Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 574317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, S.; Scoditti, E.; Massaro, M.; Polini, B.; Manera, C.; Digiacomo, M.; Salsano, J.E.; Poli, G.; Tuccinardi, T.; Doccini, S.; et al. The Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Polyphenols Oleocanthal and Oleacein Counteract Inflammation-Related Gene and Mirna Expression in Adipocytes by Attenuating Nf-Κb Activation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Bello, R.; Jardin, I.; Lopez, J.J.; El Haouari, M.; Ortega-Vidal, J.; Altarejos, J.; Salido, G.M.; Salido, S.; Rosado, J.A. (−)-Oleocanthal Inhibits Proliferation and Migration by Modulating Ca2+ Entry through TRPC6 in Breast Cancer Cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Res. 2019, 1866, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vougogiannopoulou, K.; Lemus, C.; Halabalaki, M.; Pergola, C.; Werz, O.; Smith, A.B.; Michel, S.; Skaltsounis, L.; Deguin, B. One-Step Semisynthesis of Oleacein and the Determination as a 5-Lipoxygenase Inhibitor. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montserrat-De La Paz, S.; García-Giménez, M.D.; Ángel-Martín, M.; Pérez-Camino, M.C.; Fernández Arche, A. Long-Chain Fatty Alcohols from Evening Primrose Oil Inhibit the Inflammatory Response in Murine Peritoneal Macrophages. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 151, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant Activity Applying an Improved ABTS Radical Cation Decolorization Assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajji, N.; Joseph, B. Epigenetic Regulation of Cell Life and Death Decisions and Deregulation in Cancer. Essays Biochem. 2010, 48, 121–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muñoz-García, R.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M.; Montoya, T.; Alcarranza, M.; Ortega-Vidal, J.; Altarejos, J.; Alarcón-de-la-Lastra, C. Effects of Oleacein, a New Epinutraceutical Bioproduct from Extra Virgin Olive Oil, in LPS-Activated Murine Immune Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111338
Muñoz-García R, Sánchez-Hidalgo M, Montoya T, Alcarranza M, Ortega-Vidal J, Altarejos J, Alarcón-de-la-Lastra C. Effects of Oleacein, a New Epinutraceutical Bioproduct from Extra Virgin Olive Oil, in LPS-Activated Murine Immune Cells. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(11):1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111338
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuñoz-García, Rocío, Marina Sánchez-Hidalgo, Tatiana Montoya, Manuel Alcarranza, Juan Ortega-Vidal, Joaquín Altarejos, and Catalina Alarcón-de-la-Lastra. 2022. "Effects of Oleacein, a New Epinutraceutical Bioproduct from Extra Virgin Olive Oil, in LPS-Activated Murine Immune Cells" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 11: 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111338
APA StyleMuñoz-García, R., Sánchez-Hidalgo, M., Montoya, T., Alcarranza, M., Ortega-Vidal, J., Altarejos, J., & Alarcón-de-la-Lastra, C. (2022). Effects of Oleacein, a New Epinutraceutical Bioproduct from Extra Virgin Olive Oil, in LPS-Activated Murine Immune Cells. Pharmaceuticals, 15(11), 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111338





