Evaluation of Formalin-Fixed and FFPE Tissues for Spatially Resolved Metabolomics and Drug Distribution Studies
Abstract
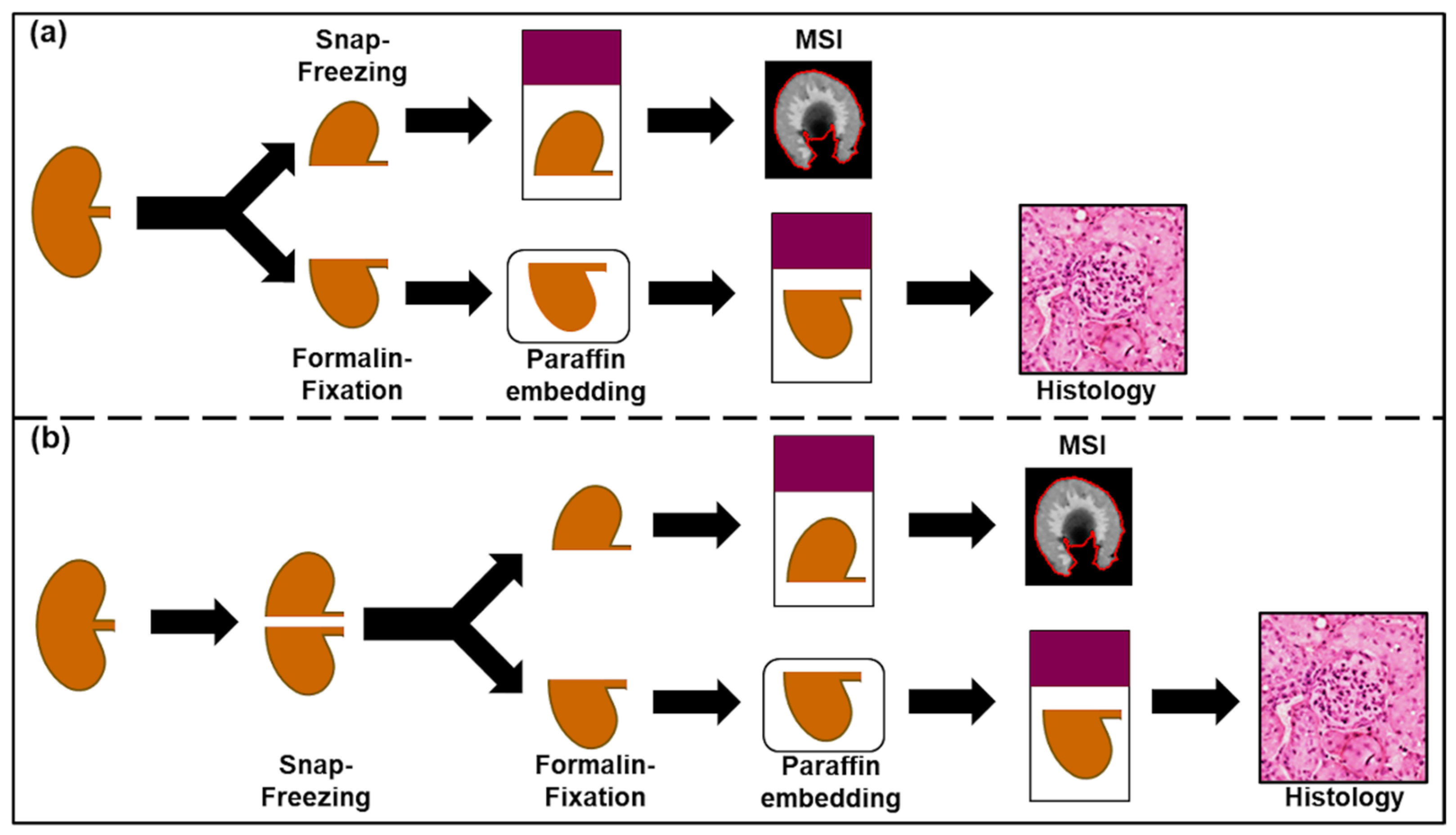
1. Introduction
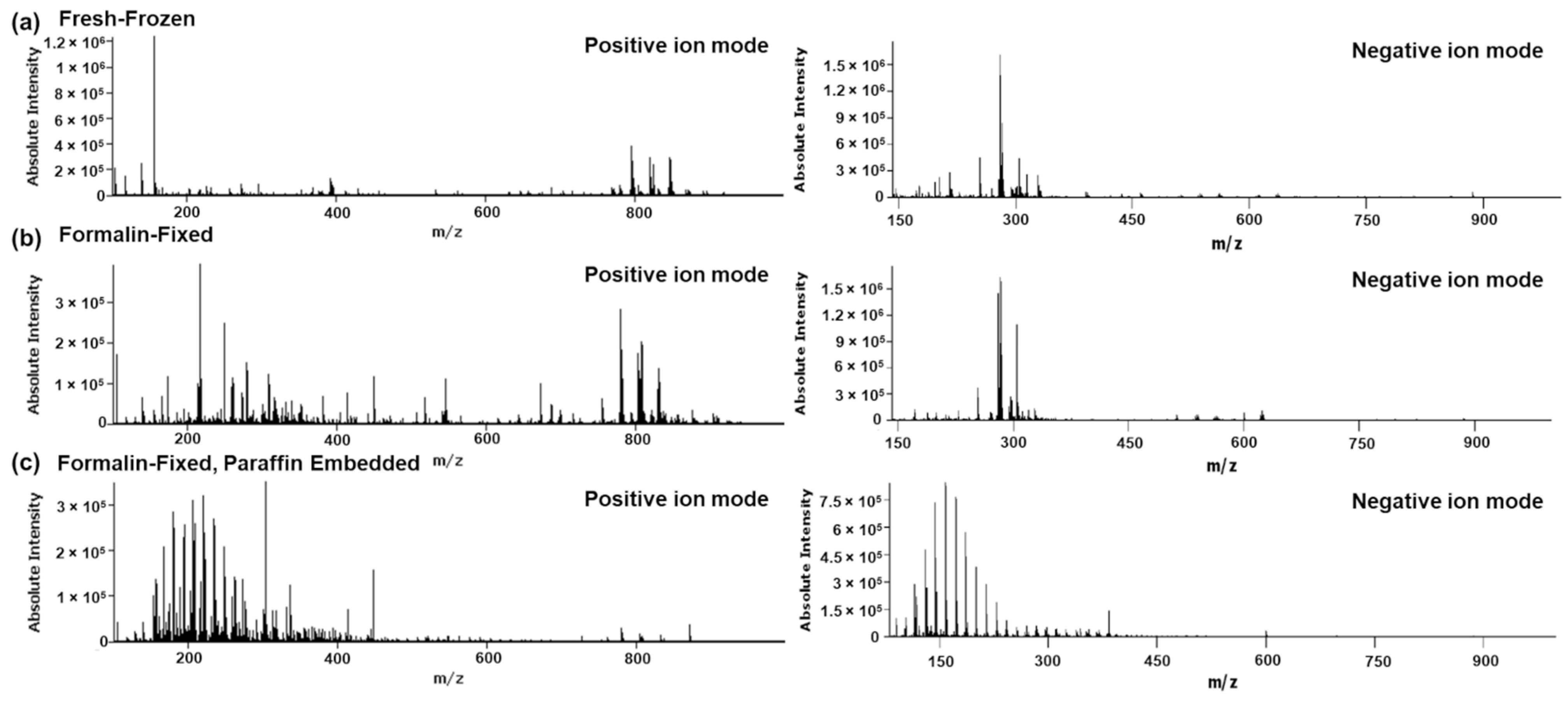
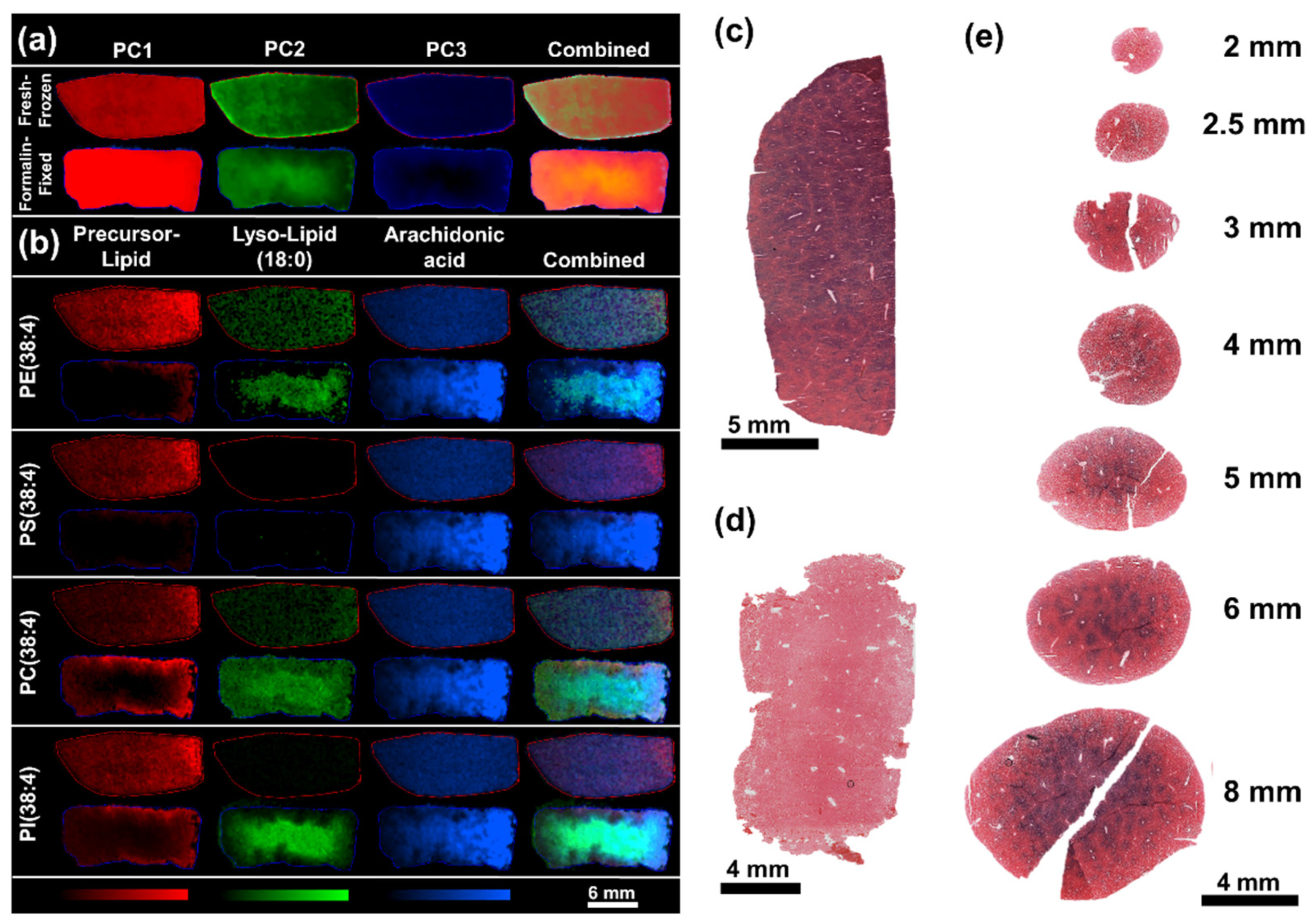
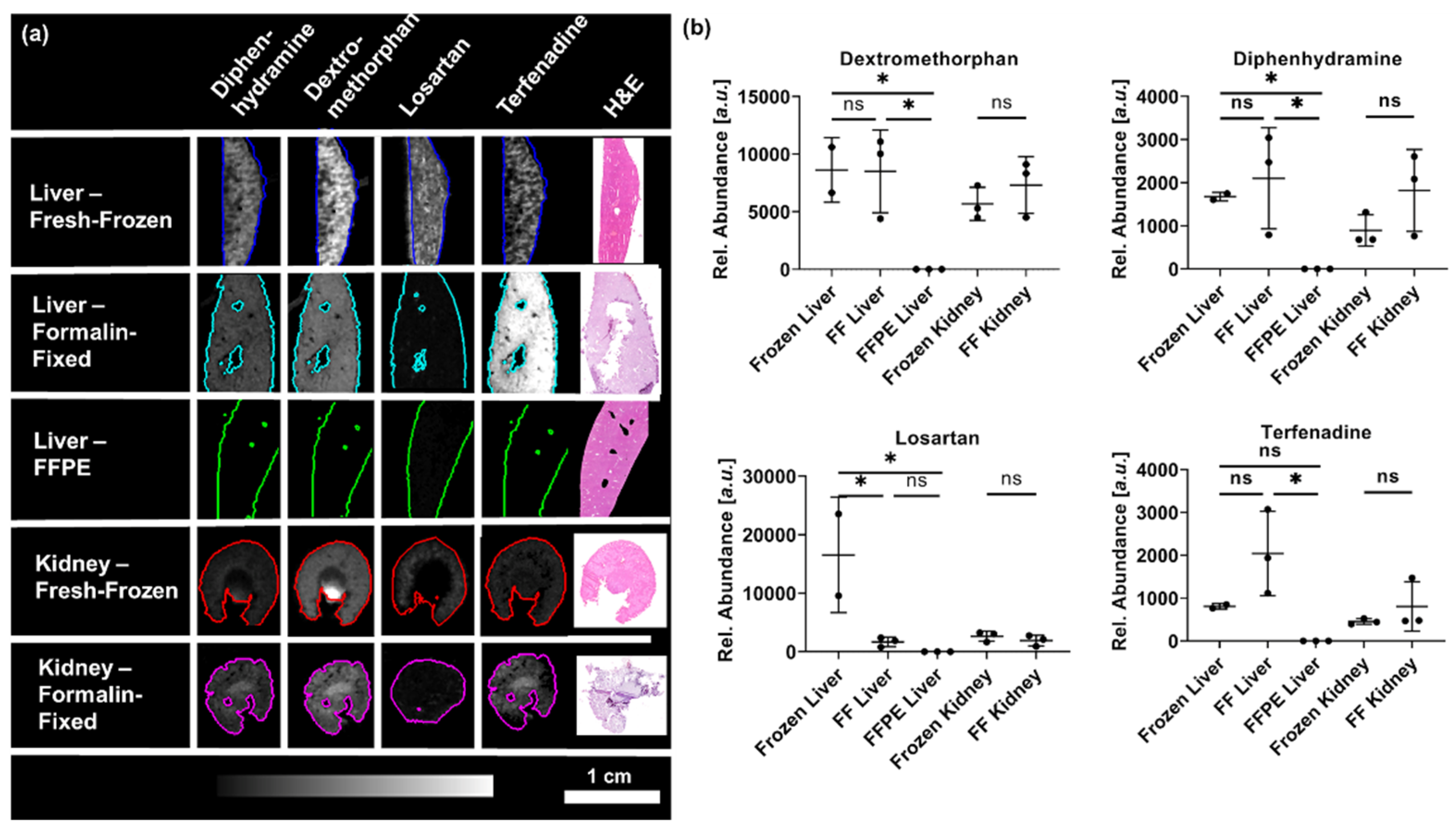
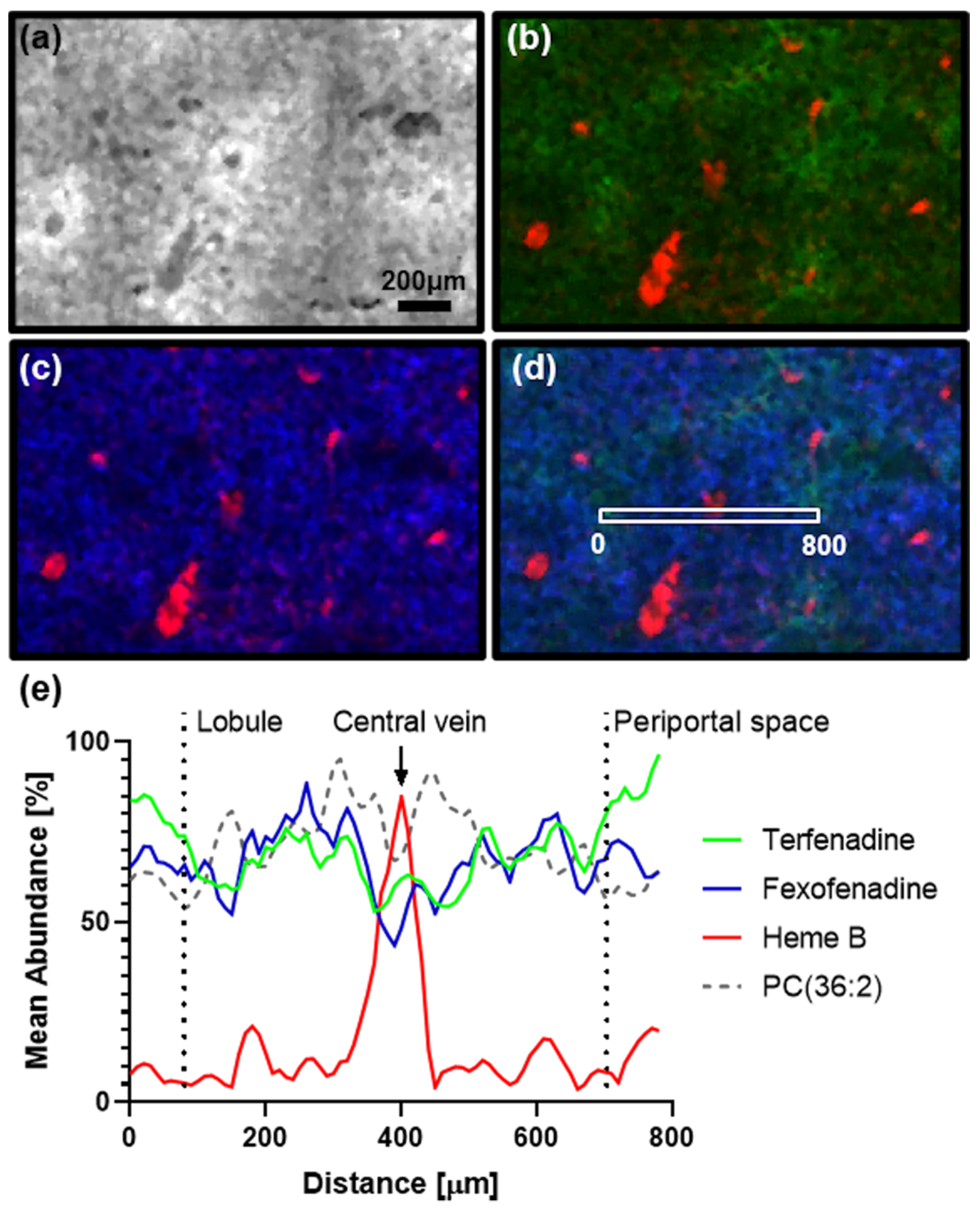
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Animals and Dosing
4.3. Tissue Preparation
4.4. Tissue Sectioning
4.5. DESI-MSI
4.6. MALDI-MSI
4.7. Statistical Analysis
4.8. Lactate Dehydrogenase Staining
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bruinen, A.L.; van Oevelen, C.; Eijkel, G.B.; Van Heerden, M.; Cuyckens, F.; Heeren, R.M. Mass Spectrometry Imaging of Drug Related Crystal-Like Structures in Formalin-Fixed Frozen and Paraffin-Embedded Rabbit Kidney Tissue Sections. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 27, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, A.; Ly, A.; Balluff, B.; Sun, N.; Gorzolka, K.; Feuchtinger, A.; Janssen, K.P.; Kuppen, P.J.; van de Velde, C.J.; Weirich, G.; et al. High-resolution MALDI-FT-ICR MS imaging for the analysis of metabolites from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded clinical tissue samples. J. Pathol. 2015, 237, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djidja, M.C.; Claude, E.; Snel, M.F.; Francese, S.; Scriven, P.; Carolan, V.; Clench, M.R. Novel molecular tumour classification using MALDI-mass spectrometry imaging of tissue micro-array. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 587–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnel, D.; Longuespee, R.; Franck, J.; Roudbaraki, M.; Gosset, P.; Day, R.; Salzet, M.; Fournier, I. Multivariate analyses for biomarkers hunting and validation through on-tissue bottom-up or in-source decay in MALDI-MSI: Application to prostate cancer. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everest-Dass, A.V.; Briggs, M.T.; Kaur, G.; Oehler, M.K.; Hoffmann, P.; Packer, N.H. N-glycan MALDI Imaging Mass Spectrometry on Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue Enables the Delineation of Ovarian Cancer Tissues. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2016, 15, 3003–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaire, R.; Wisztorski, M.; Desmons, A.; Tabet, J.C.; Day, R.; Salzet, M.; Fournier, I. MALDI-MS direct tissue analysis of proteins: Improving signal sensitivity using organic treatments. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 7145–7153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Lorenzo, M.; Balluff, B.; Sanz-Maroto, A.; van Zeijl, R.J.; Vivanco, F.; Alvarez-Llamas, G.; McDonnell, L.A. 30mum spatial resolution protein MALDI MSI: In-depth comparison of five sample preparation protocols applied to human healthy and atherosclerotic arteries. J. Proteom. 2014, 108, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciatore, S.; Zadra, G.; Bango, C.; Penney, K.L.; Tyekucheva, S.; Yanes, O.; Loda, M. Metabolic Profiling in Formalin-Fixed and Paraffin-Embedded Prostate Cancer Tissues. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguri, G.; Nassi, P.; Taddei, N.; Nediani, C.; Ramponi, G. Post-mortem modifications of the specific activity of some brain enzymes. Neurosci. Lett. 1988, 85, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahn, S.; Cote, L.J. Stability of enzymes in post-mortem rat brain. J. Neurochem. 1976, 26, 1039–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, T.; Scully, S.A.; de Vellis, J.; Noble, E.P. Stability of neuronal and glial marker enzymes in post-mortem rat brain. Neurochem. Res. 1986, 11, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gattaz, W.F.; Maras, A.; Cairns, N.J.; Levy, R.; Förstl, H. Decreased phospholipase A2 activity in Alzheimer brains. Biol. Psychiatry 1995, 37, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincek, V.; Nassiri, M.; Nadji, M.; Morales, A.R. A Tissue Fixative that Protects Macromolecules (DNA, RNA, and Protein) and Histomorphology in Clinical Samples. Lab. Investig. 2003, 83, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.; Pontén, F.; Moberg, C.; Söderkvist, P.; Uhlén, M.; Pontén, J.; Sitbon, G.; Lundeberg, J. A High Frequency of Sequence Alterations Is Due to Formalin Fixation of Archival Specimens. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 1467–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudin, M.; Panchal, M.; Ayciriex, S.; Werner, E.; Brunelle, A.; Touboul, D.; Boursier-Neyret, C.; Auzeil, N.; Walther, B.; Duyckaerts, C.; et al. Ultra performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry studies of formalin-induced alterations of human brain lipidome. J. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 49, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, D.R.N.; Bowman, A.P.; Heeren, R.M.A.; Balluff, B.; Ellis, S.R. Class-specific depletion of lipid ion signals in tissues upon formalin fixation. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 446, 116212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isberg, O.G.; Xiang, Y.; Bodvarsdottir, S.K.; Jonasson, J.G.; Thorsteinsdottir, M.; Takats, Z. The effect of sample age on the metabolic information extracted from formalin-fixed and paraffin embedded tissue samples using desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry imaging. J. Mass Spectrom. Adv. Clin. Lab 2021, 22, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyczko, J.; Beach, D.G.; Gabryelski, W. Commercial formaldehyde standard for mass calibration in mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 50, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, C.L.; McLeod, C.W.; Bunch, J. Imaging of Phospholipids in Formalin Fixed Rat Brain Sections by Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 22, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thavarajah, R.; Mudimbaimannar, V.K.; Elizabeth, J.; Rao, U.K.; Ranganathan, K. Chemical and physical basics of routine formaldehyde fixation. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2012, 16, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, C.H.; Johnson, F.B.; Whiting, J.; Roller, P.P. Formaldehyde fixation. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1985, 33, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, A.; Fehniger, T.E.; Gustavsson, L.; Andersson, M.; Kenne, K.; Marko-Varga, G.; Andren, P.E. Fine mapping the spatial distribution and concentration of unlabeled drugs within tissue micro-compartments using imaging mass spectrometry. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heslinga, F.J.; Deierkauf, F.A. The action of histological fixatives on tissue lipids. Comparison of the action of several fixatives using paper chromatography. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1961, 9, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rordorf, G.; Uemura, Y.; Bonventre, J. Characterization of phospholipase A2 (PLA2) activity in gerbil brain: Enhanced activities of cytosolic, mitochondrial, and microsomal forms after ischemia and reperfusion. J. Neurosci. 1991, 11, 1829–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marion, J.; Wolfe, L.S. Origin of the arachidonic acid released post-mortem in rat forebrain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Lipids Lipid Metab. 1979, 574, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.S.; Yan, A.; Ocotl, E.; Bennett, D.D.; Wang, Z.; Kendziorski, C.; Gibson, A.L.F. Discordance between histologic and visual assessment of tissue viability in excised burn wound tissue. Wound Repair Regen. Off. Publ. Wound Heal. Soc. Eur. Tissue Repair Soc. 2019, 27, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, A.L.F.; Shatadal, S. A simple and improved method to determine cell viability in burn-injured tissue. J. Surg. Res. 2017, 215, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabihkhani, M.; Lucey, G.M.; Wei, B.; Mareninov, S.; Lou, J.J.; Vinters, H.V.; Singer, E.J.; Cloughesy, T.F.; Yong, W.H. The procurement, storage, and quality assurance of frozen blood and tissue biospecimens in pathology, biorepository, and biobank settings. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 47, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Luo, Z.; Li, X.; Li, T.; Wang, Z.; Sun, C.; Huang, L.; Xie, P.; Liu, X.; He, J.; et al. In Situ Hydrogel Conditioning of Tissue Samples To Enhance the Drug’s Sensitivity in Ambient Mass Spectrometry Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 6318–6323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steu, S.; Baucamp, M.; von Dach, G.; Bawohl, M.; Dettwiler, S.; Storz, M.; Moch, H.; Schraml, P. A procedure for tissue freezing and processing applicable to both intra-operative frozen section diagnosis and tissue banking in surgical pathology. Virchows Arch. 2008, 452, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannhorn, A.; Kazanc, E.; Ling, S.; Nikula, C.; Karali, E.; Serra, M.P.; Vorng, J.-L.; Inglese, P.; Maglennon, G.; Hamm, G.; et al. Universal Sample Preparation Unlocking Multimodal Molecular Tissue Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 11080–11088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ly, A.; Buck, A.; Balluff, B.; Sun, N.; Gorzolka, K.; Feuchtinger, A.; Janssen, K.P.; Kuppen, P.J.; van de Velde, C.J.; Weirich, G.; et al. High-mass-resolution MALDI mass spectrometry imaging of metabolites from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1428–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takats, Z.; Wiseman, J.M.; Gologan, B.; Cooks, R.G. Mass spectrometry sampling under ambient conditions with desorption electrospray ionization. Science 2004, 306, 471–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adusumilli, R.; Mallick, P. Data Conversion with ProteoWizard msConvert. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1550, 339–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Race, A.M.; Styles, I.B.; Bunch, J. Inclusive sharing of mass spectrometry imaging data requires a converter for all. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 5111–5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swales, J.G.; Tucker, J.W.; Strittmatter, N.; Nilsson, A.; Cobice, D.; Clench, M.R.; Mackay, C.L.; Andren, P.E.; Takats, Z.; Webborn, P.J.; et al. Mass spectrometry imaging of cassette-dosed drugs for higher throughput pharmacokinetic and biodistribution analysis. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 8473–8480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, J.L.; Cornett, D.S.; Mobley, J.A.; Andersson, M.; Seeley, E.H.; Chaurand, P.; Caprioli, R.M. Processing MALDI Mass Spectra to Improve Mass Spectral Direct Tissue Analysis. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 260, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuddihy, J.; Wu, G.; Ho, L.; Kudo, H.; Dannhorn, A.; Mandalia, S.; Collins, D.; Weir, J.; Spencer, A.; Vizcaychipi, M.; et al. Lactate dehydrogenase activity staining demonstrates time-dependent immune cell infiltration in human ex-vivo burn-injured skin. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Treatment | Duration [h] | Temperature [°C] |
|---|---|---|
| 10% Formalin | 1 | 40 |
| 70% EtOH | 1 | 40 |
| EtOH | 1 | 40 |
| EtOH | 1 | 40 |
| Xylene | 0.5 | 40 |
| Xylene | 0.5 | 40 |
| Paraffin | 1 | 63 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dannhorn, A.; Swales, J.G.; Hamm, G.; Strittmatter, N.; Kudo, H.; Maglennon, G.; Goodwin, R.J.A.; Takats, Z. Evaluation of Formalin-Fixed and FFPE Tissues for Spatially Resolved Metabolomics and Drug Distribution Studies. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111307
Dannhorn A, Swales JG, Hamm G, Strittmatter N, Kudo H, Maglennon G, Goodwin RJA, Takats Z. Evaluation of Formalin-Fixed and FFPE Tissues for Spatially Resolved Metabolomics and Drug Distribution Studies. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(11):1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111307
Chicago/Turabian StyleDannhorn, Andreas, John G. Swales, Gregory Hamm, Nicole Strittmatter, Hiromi Kudo, Gareth Maglennon, Richard J. A. Goodwin, and Zoltan Takats. 2022. "Evaluation of Formalin-Fixed and FFPE Tissues for Spatially Resolved Metabolomics and Drug Distribution Studies" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 11: 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111307
APA StyleDannhorn, A., Swales, J. G., Hamm, G., Strittmatter, N., Kudo, H., Maglennon, G., Goodwin, R. J. A., & Takats, Z. (2022). Evaluation of Formalin-Fixed and FFPE Tissues for Spatially Resolved Metabolomics and Drug Distribution Studies. Pharmaceuticals, 15(11), 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111307







