Evaluation of Synthetic 2,4-Disubstituted-benzo[g]quinoxaline Derivatives as Potential Anticancer Agents
Abstract
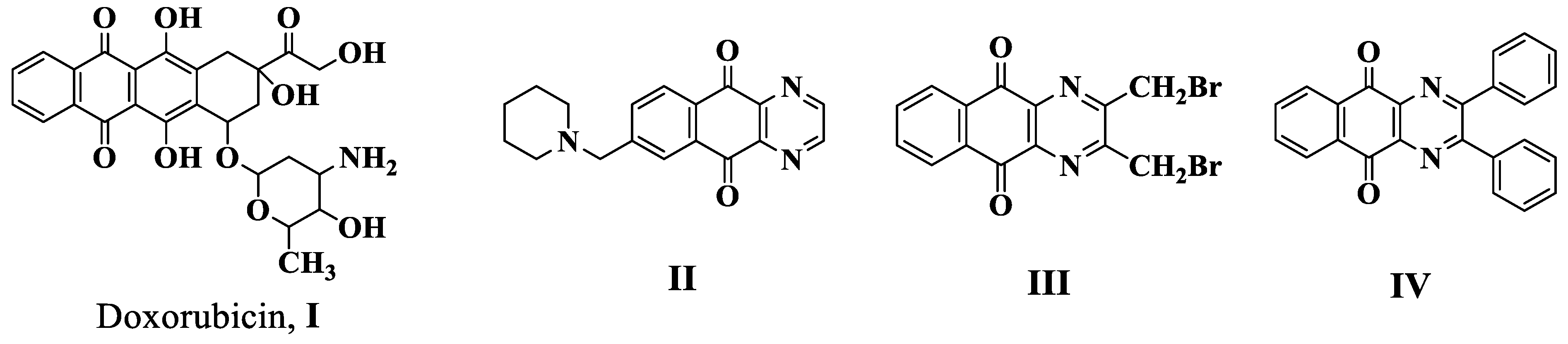
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biology
2.2.1. Cytotoxic Activity against Breast MCF-7 Cancer Cell Line
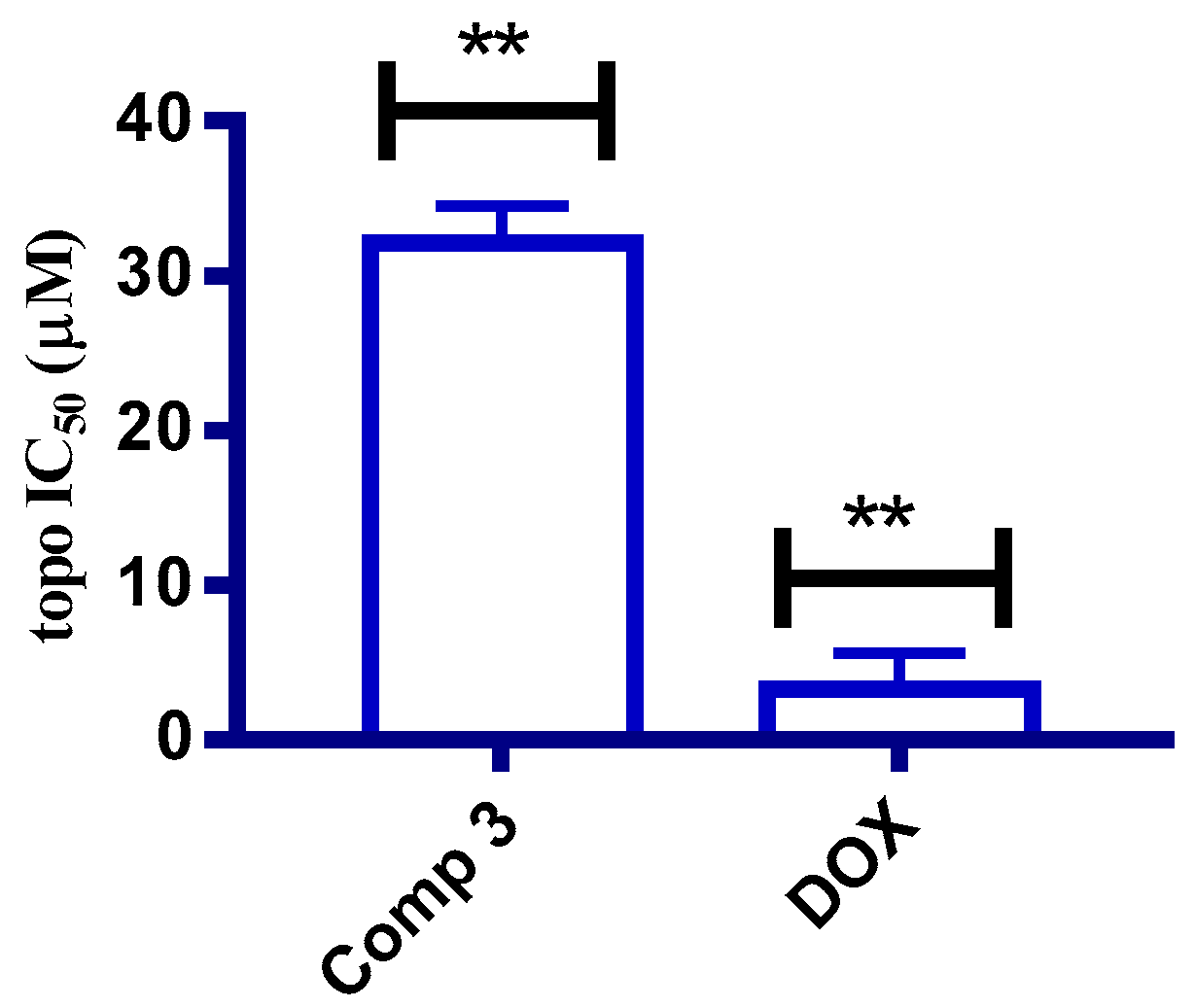
2.2.2. In Vitro Topoisomerase IIβ Assay
2.2.3. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.2.4. Annexin V/FITC Apoptosis Staining Assay
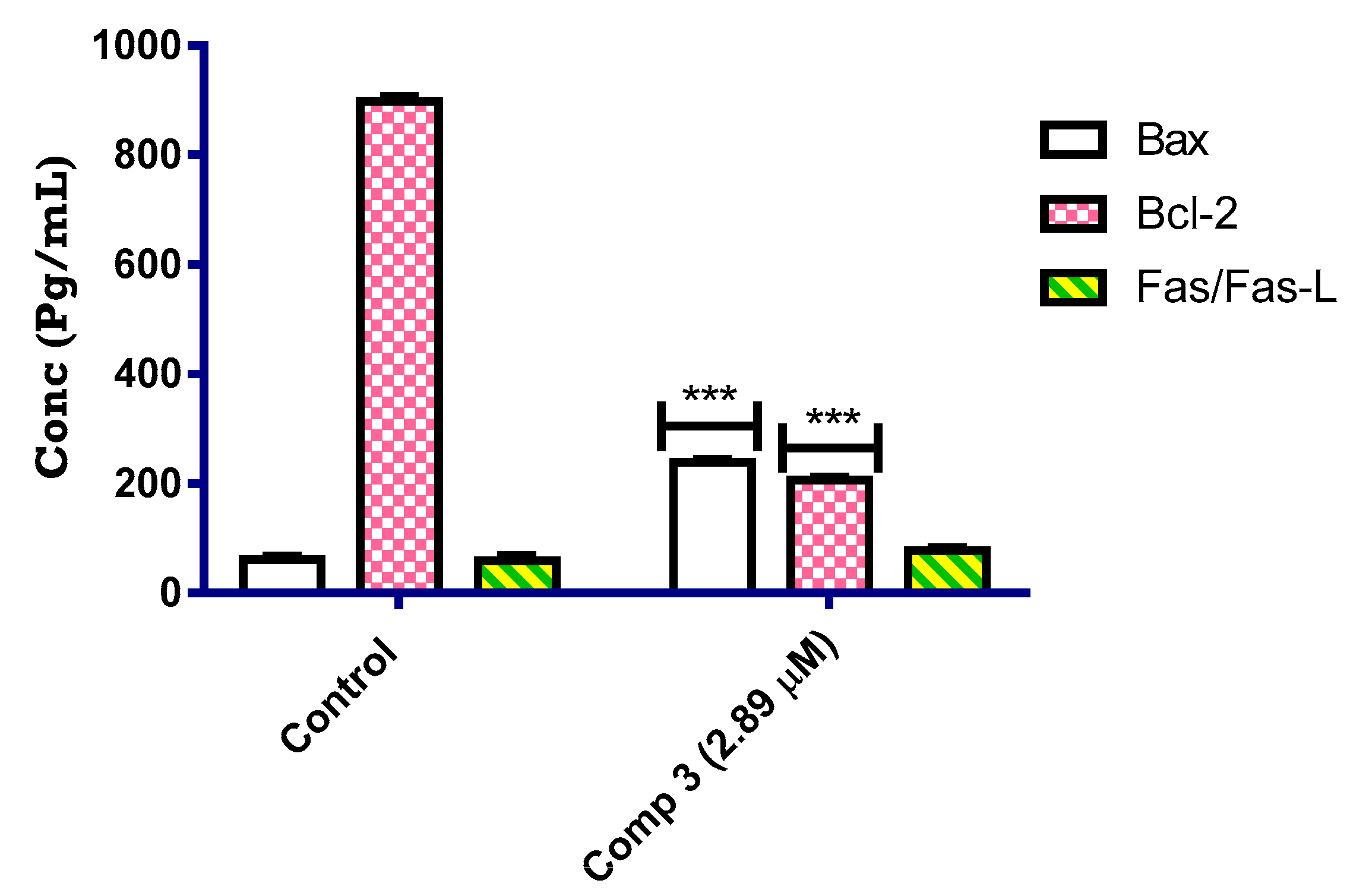
2.2.5. Bax and Bcl2 Enzyme Assay
2.2.6. Molecular Docking Study
3. Experimental
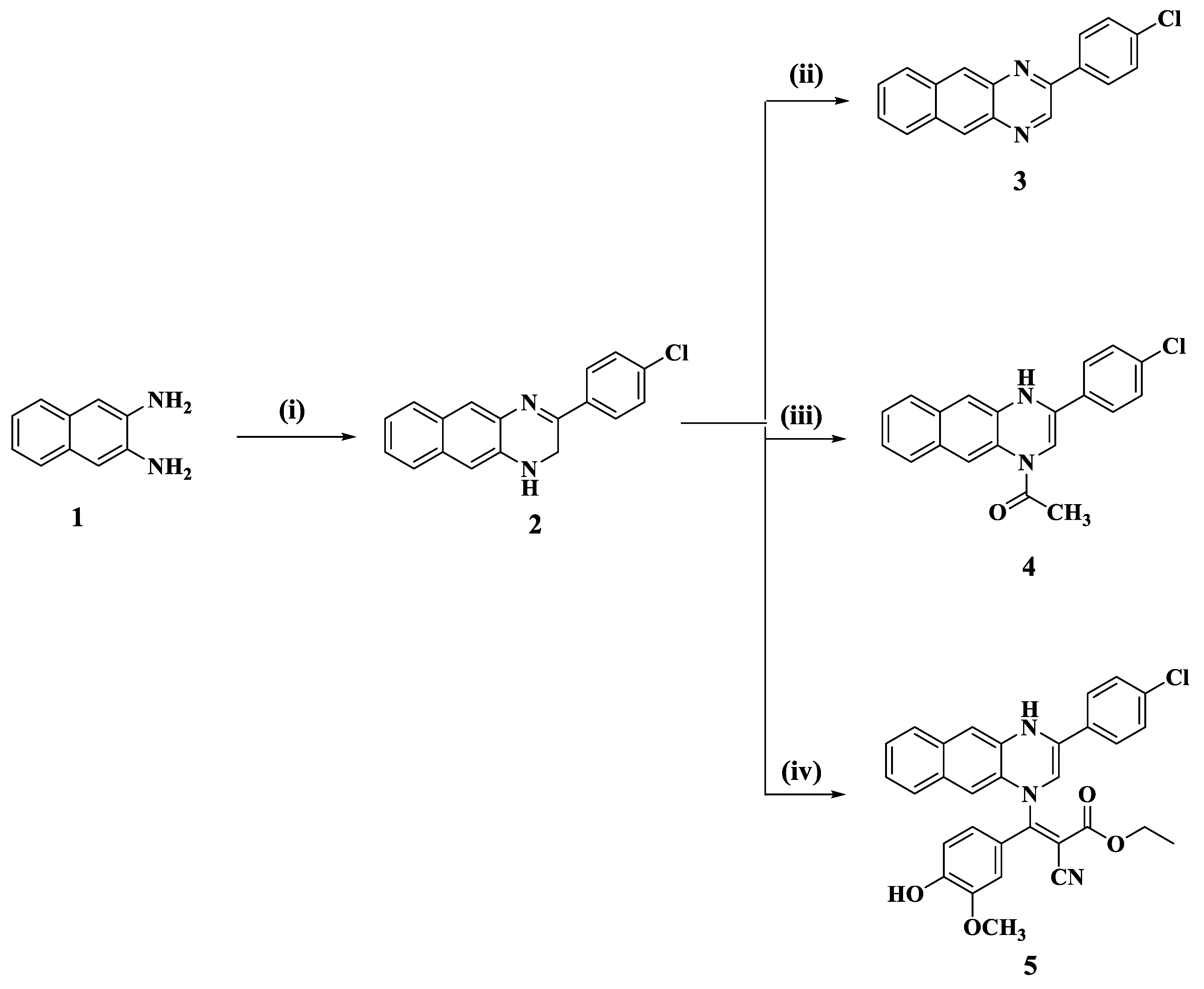
3.1. Chemistry
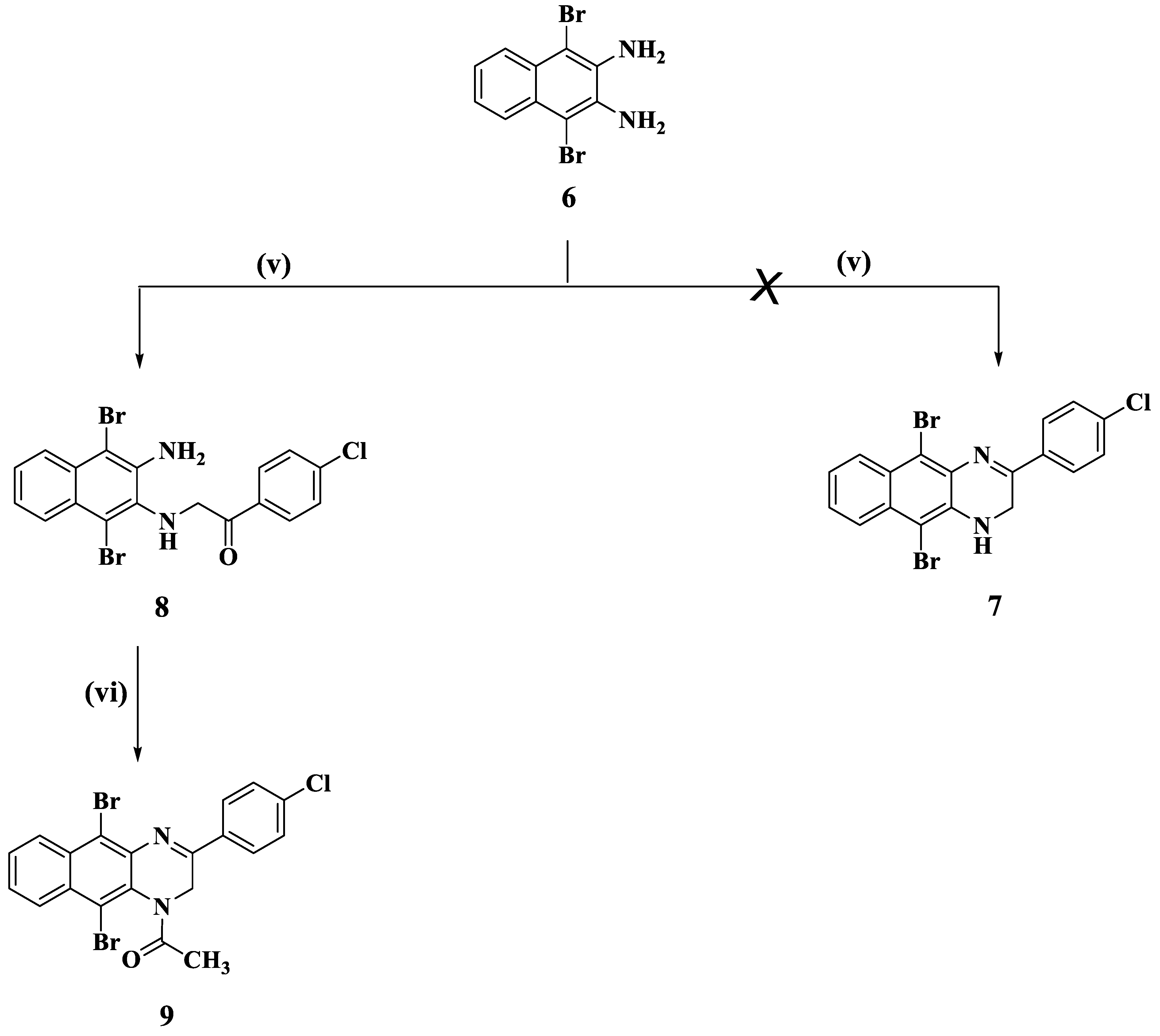
3.1.1. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Compounds 2 and 8
3-(4-Chlorophenyl)-1,2-dihydrobenzo[g]quinoxaline (2)
2-(3-Amino-1,4-dibromonaphthalen-2-ylamino)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethanone (8)
3.1.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 2-(4-Chlorophenyl)benzo[g]quinoxaline (3)
3.1.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 1-(3-(4-Chlorophenyl)benzo[g]quinoxalin-1(4H)-yl)ethanone (4)
3.1.4. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Ethyl 3-(3-(4-Chlorophenyl)benzo[g]quinoxalin-1(4H)-yl)-2-cyano-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)acrylate (5)
3.1.5. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 1-(5,10-Dibromo-3-(4-chlorophenyl)benzo[g]quinoxalin-1(2H)-yl)ethanone (9)
3.2. Biological Studies
3.2.1. Cytotoxic Activity against Breast MCF-7 Cancer Cell Line
3.2.2. Topoisomerase IIβ Enzyme Assay
3.2.3. Cell Cycle Analysis Compound 3
3.2.4. Annexin V FITC/PI Apoptosis Detection Staining Assay
3.2.5. In Vitro ELISA Measurement for the Concentration of Bax, Bcl2, and Fas/Fas-l Proteins
3.2.6. Molecular Docking Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Msc, M.L.; Weiderpass, E.; Soerjomataram, I. The ever-increasing importance of cancer as a leading cause of premature death worldwide. Cancer 2021, 127, 3029–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, P.; Sathishkumar, K.; Chaturvedi, M.; Das, P.; Sudarshan, K.L.; Santhappan, S.; Nallasamy, V.; John, A.; Narasimhan, S.; Roselind, F.S.; et al. Cancer Statistics, 2020: Report from National Cancer Registry Programme, India. JCO Glob. Oncol. 2020, 6, 1063–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korde, L.A.; Somerfield, M.R.; Carey, L.A.; Crews, J.R.; Denduluri, N.; Hwang, E.S.; Khan, S.A.; Loibl, S.; Morris, E.A.; Perez, A.; et al. Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy, Endocrine Therapy, and Targeted Therapy for Breast Cancer: ASCO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1485–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boumahdi, S.; de Sauvage, F. The great escape: Tumour cell plasticity in resistance to targeted therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, S.; Wang, S.; Bowden, N.; Martin, J.; Head, R. Repurposing existing therapeutics, its importance in oncology drug development: Kinases as a potential target. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustaqil, M.; Gambin, Y.; Sierecki, E. Biophysical Techniques for Target Validation and Drug Discovery in Transcription-Targeted Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sadoughi, F.; Hallajzadeh, J.; Asemi, Z.; Mansournia, M.A.; Alemi, F.; Yousefi, B. Signaling pathways involved in cell cycle arrest during the DNA breaks. DNA Repair 2021, 98, 103047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasca, A.; Helmstädter, M.; Brislinger, M.M.; Haas, M.; Mitchell, B.; Walentek, P. Notch signaling induces either apoptosis or cell fate change in multiciliated cells during mucociliary tissue remodeling. Dev. Cell 2021, 56, 525–539.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sia, J.; Szmyd, R.; Hau, E.; Gee, H.E. Molecular Mechanisms of Radiation-Induced Cancer Cell Death: A Primer. Front. Cell Dev. Biology 2020, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ježek, J.; Cooper, K.F.; Strich, R. The Impact of Mitochondrial Fission-Stimulated ROS Production on Pro-Apoptotic Chemotherapy. Biology 2021, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trisciuoglio, D.; Del Bufalo, D. New insights into the roles of antiapoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family in melanoma progression and therapy. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Cho, Y.-C.; Lim, J. Costunolide, a Sesquiterpene Lactone, Suppresses Skin Cancer via Induction of Apoptosis and Blockage of Cell Proliferation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Ye, F.; Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Xu, W.; Aschner, M.; Lu, R.; Miao, S. 3,3′-diindolylmethane exerts antiproliferation and apoptosis induction by TRAF2-p38 axis in gastric cancer. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2021, 32, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Park, S.-Y.; Lee, H.-J.; Suh, M.-E.; Schollmeyer, D.; Lee, C.-O. Synthesis and cytotoxicity of 6,11-Dihydro-pyrido- and 6,11-Dihydro-benzo [2,3-b]phenazine-6,11-dione derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2003, 11, 1709–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudor, G.; Gutierrez, P.; Aguilera-Gutierrez, A.; A Sausville, E. Cytotoxicity and apoptosis of benzoquinones: Redox cycling, cytochrome c release, and BAD protein expression. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 65, 1061–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krapcho, A.P.; Petry, M.E.; Getahun, Z.; Landi, J.J.; Stallman, J.; Polsenberg, J.F.; Gallagher, C.E.; Maresch, M.J.; Hacker, M.P. 6,9-Bis[(aminoalkyl)amino]benzo[g]isoquinoline-5,10-diones. A Novel Class of Chromophore-Modified Antitumor Anthracene-9,10-diones: Synthesis and Antitumor Evaluations. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Gupta, M.; Kumar, P.; Sharma, A. A Comprehensive Review on Fused Heterocyclic as DNA Intercalators: Promising Anticancer Agents. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 15–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Adl, K.; Ibrahim, M.-K.; Alesawy, M.S.; Eissa, I.H. [1,2,4]Triazolo[4,3-c]quinazoline and bis([1,2,4]triazolo)[4,3-a:4′,3′-c]quinazoline derived DNA intercalators: Design, synthesis, in silico ADMET profile, molecular docking and anti-proliferative evaluation studies. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 30, 115958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Cho, S.; Namgoong, K.; Jung, J.-K.; Cho, J.; Yang, S.-I. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of 7-dialkylaminomethylbenzo[g]quinoxaline-5,10-diones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 1235–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazumi, H.; Agawa, T.; Kitao, T. Synthesis and Absorption Spectra of 1,4-Diazaanthraquinone Derivatives. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1979, 52, 2445–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Zachek, B.; Lera, R.F.; Zasadil, L.M.; Lasek, A.; Denu, R.A.; Kim, H.; Kanugh, C.; Laffin, J.J.; Harter, J.M.; et al. Identification of selective lead compounds for treatment of high-ploidy breast cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdelhameid, M.K.; Zaki, I.; Mohammed, M.R.; Mohamed, K.O. Design, synthesis, and cytotoxic screening of novel azole derivatives on hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2 Cells). Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 101, 103995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, I.; Ramadan, H.M.M.; El-Sayed, E.H.; El-Moneim, M.A. Design, synthesis, and cytotoxicity screening of new synthesized imidazolidine-2-thiones as VEGFR-2 enzyme inhibitors. Arch. Pharm. 2020, 353, 2000121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Almaaty, A.; Toson, E.; El-Sayed, E.-S.; Tantawy, M.; Fayad, E.; Abu Ali, O.; Zaki, I. 5-Aryl-1-Arylideneamino-1H-Imidazole-2(3H)-Thiones: Synthesis and In Vitro Anticancer Evaluation. Molecules 2021, 26, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourad, A.A.; Rizzk, Y.W.; Zaki, I.; Mohammed, F.Z.; El Behery, M. Synthesis and cytotoxicity screening of some synthesized hybrid nitrogen molecules as anticancer agents. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1242, 130722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Shi, W.; Jia, J.; Chen, S.; Ma, H. Characterization of 2-phenylbenzo[g]quinoxaline derivatives as viscosity-sensitive fluorescent probes. Talanta 2009, 77, 1795–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el Hameid, M.K.A.; Mohammed, M.R. Design, synthesis, and cytotoxicity screening of 5-aryl-3-(2-(pyrrolyl) thiophenyl)-1, 2, 4-oxadiazoles as potential antitumor molecules on breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 86, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, I.; Abdelhameid, M.K.; El-Deen, I.M.; Abdel Wahab, A.H.A.; Ashmawy, A.M.; Mohamed, K.O. Design, synthesis and screening of 1, 2, 4-triazinone derivatives as potential antitumor agents with apoptosis inducing activity on MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 156, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, K.O.; Zaki, I.; El-Deen, I.M.; Abdelhameid, M.K. A new class of diamide scaffold: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation as potent antimitotic agents, tubulin polymerization inhibition and apoptosis inducing activity studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 84, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, I.; Imam, A.M. Design, Synthesis, and Cytotoxic Screening of New Quinoline Derivatives over MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Line. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 46, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhaleem, E.F.; Abdelhameid, M.K.; Kassab, A.E.; Kandeel, M.M. Design and synthesis of thienopyrimidine urea derivatives with potential cytotoxic and pro-apoptotic activity against breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 143, 1807–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
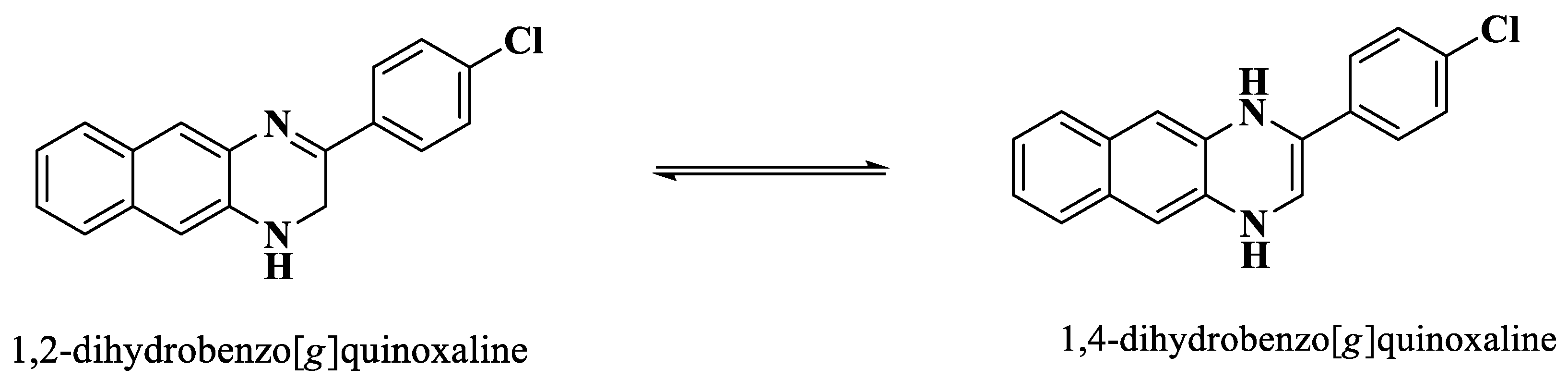



| Compound No. | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|
| MCF-7 | |
| 2 | 17.24 ± 0.69 |
| 3 | 2.89 ± 0.11 |
| 4 | 16.22 ± 0.58 |
| 5 | 32.14 ± 1.11 |
| 9 | 8.84 ± 0.36 |
| Dox | 2.01 ± 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaki, I.; Abu El-ata, S.A.; Fayad, E.; Abu Ali, O.A.; Abu Almaaty, A.H.; Saad, A.S. Evaluation of Synthetic 2,4-Disubstituted-benzo[g]quinoxaline Derivatives as Potential Anticancer Agents. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14090853
Zaki I, Abu El-ata SA, Fayad E, Abu Ali OA, Abu Almaaty AH, Saad AS. Evaluation of Synthetic 2,4-Disubstituted-benzo[g]quinoxaline Derivatives as Potential Anticancer Agents. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(9):853. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14090853
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaki, Islam, Sara A. Abu El-ata, Eman Fayad, Ola A. Abu Ali, Ali H. Abu Almaaty, and Ahmed S. Saad. 2021. "Evaluation of Synthetic 2,4-Disubstituted-benzo[g]quinoxaline Derivatives as Potential Anticancer Agents" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 9: 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14090853
APA StyleZaki, I., Abu El-ata, S. A., Fayad, E., Abu Ali, O. A., Abu Almaaty, A. H., & Saad, A. S. (2021). Evaluation of Synthetic 2,4-Disubstituted-benzo[g]quinoxaline Derivatives as Potential Anticancer Agents. Pharmaceuticals, 14(9), 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14090853






