Hypoglycemic Activity of Aqueous Extract of Latex from Hancornia speciosa Gomes: A Study in Zebrafish and In Silico
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Phytochemical Analysis
2.2. Zebrafish Embryo Acute Toxicity
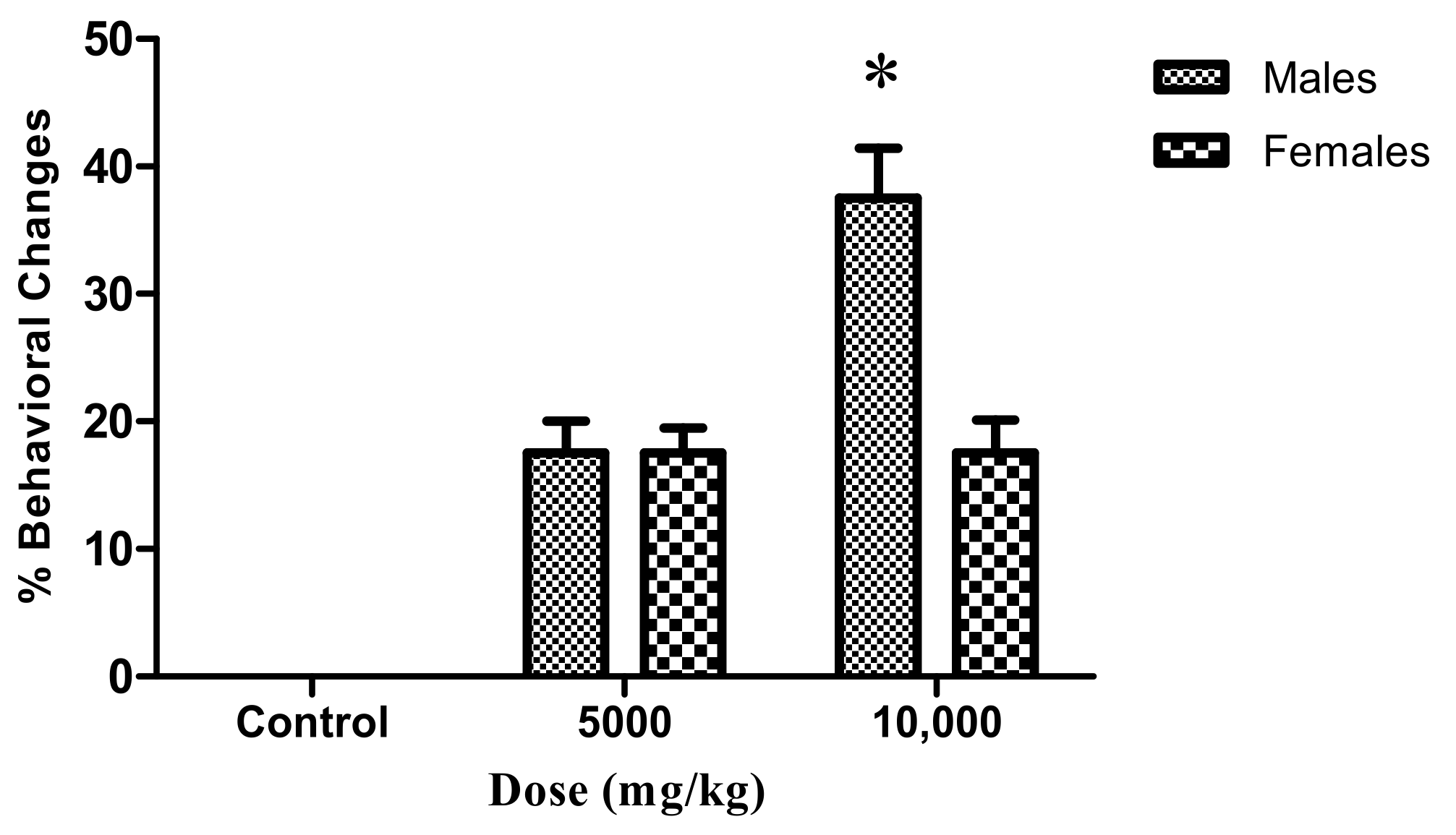
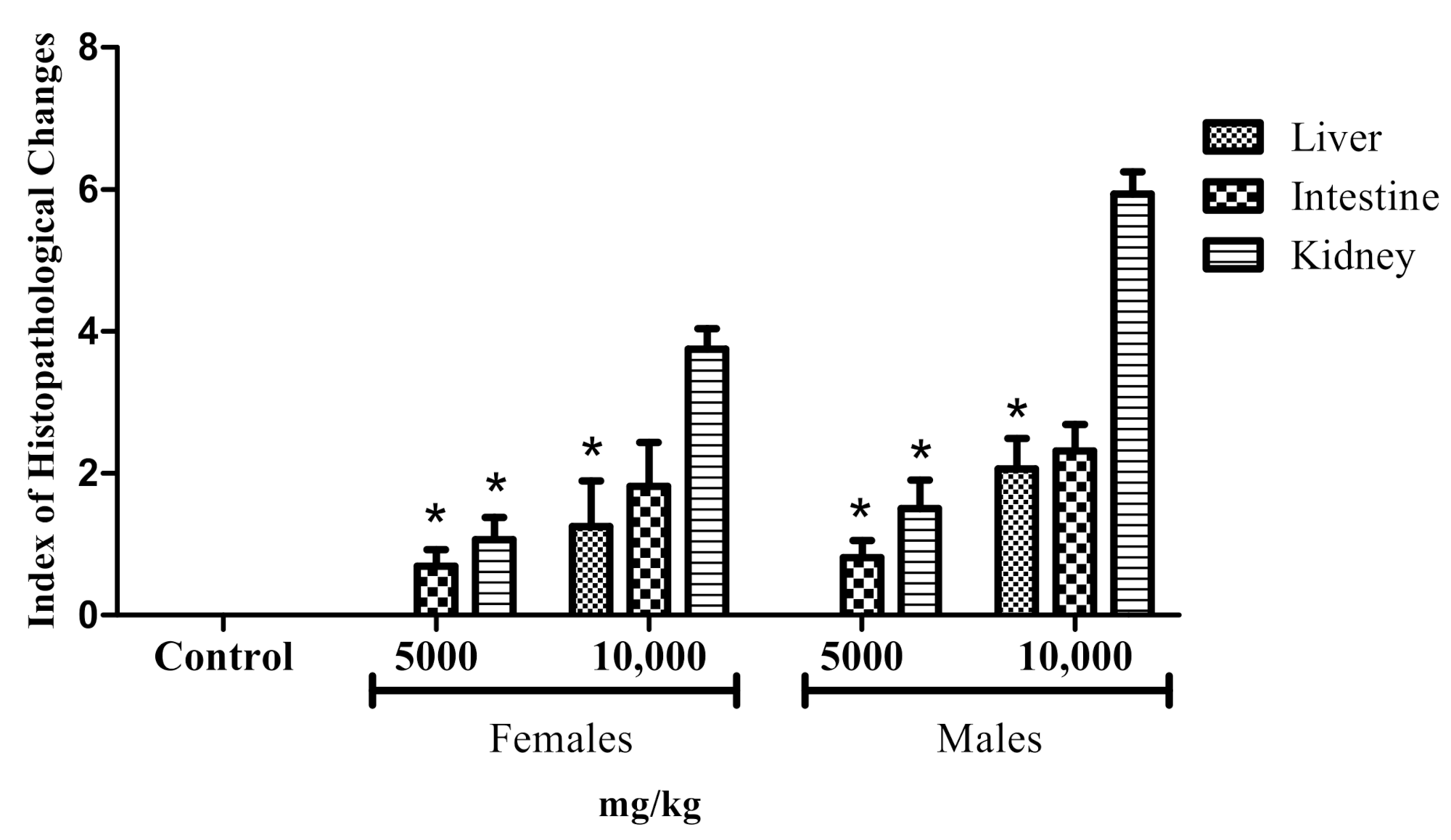
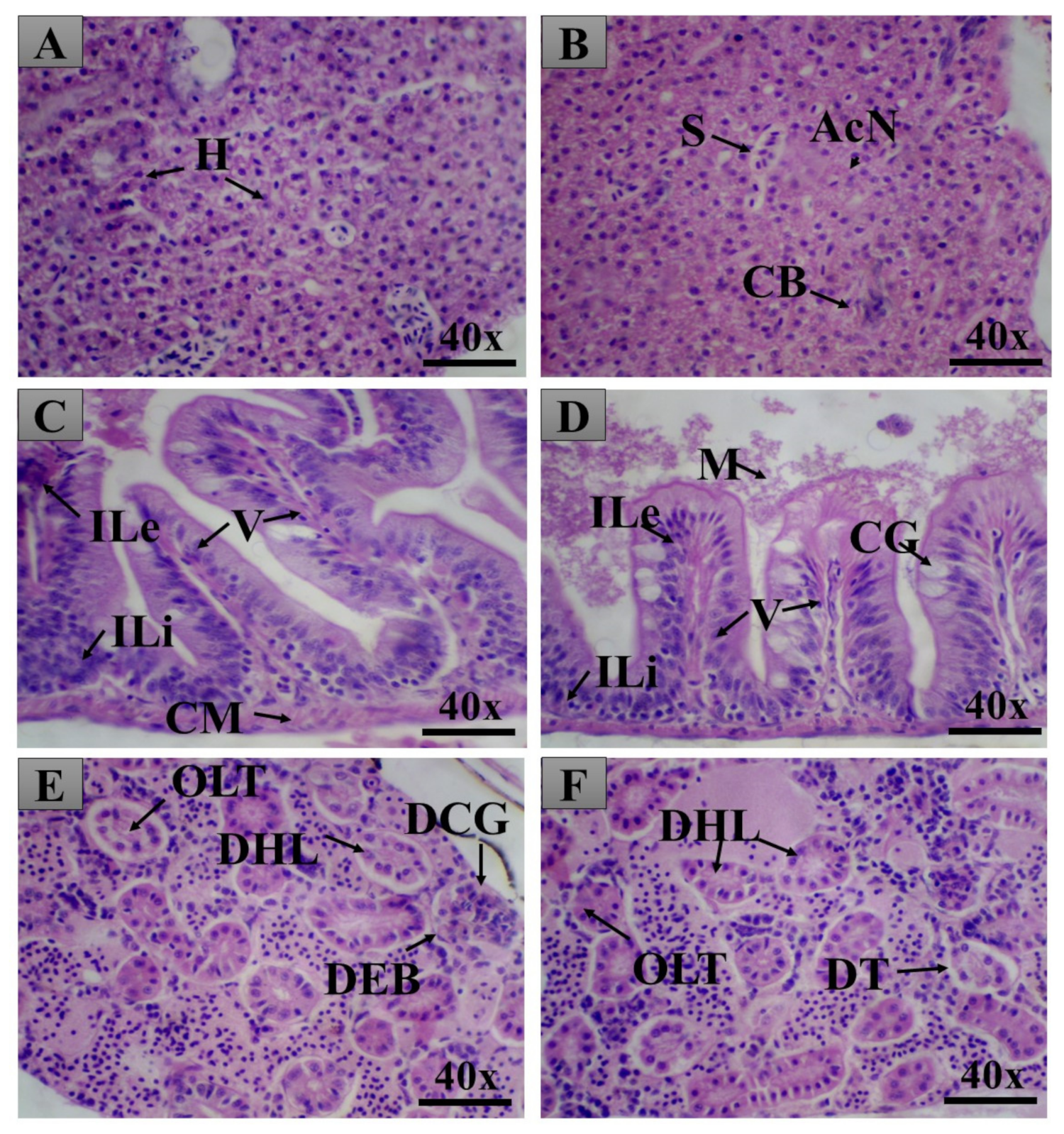
2.3. Adult Zebrafish Acute Toxicity
General Histopathology
2.4. LxHs Antidiabetic Activity
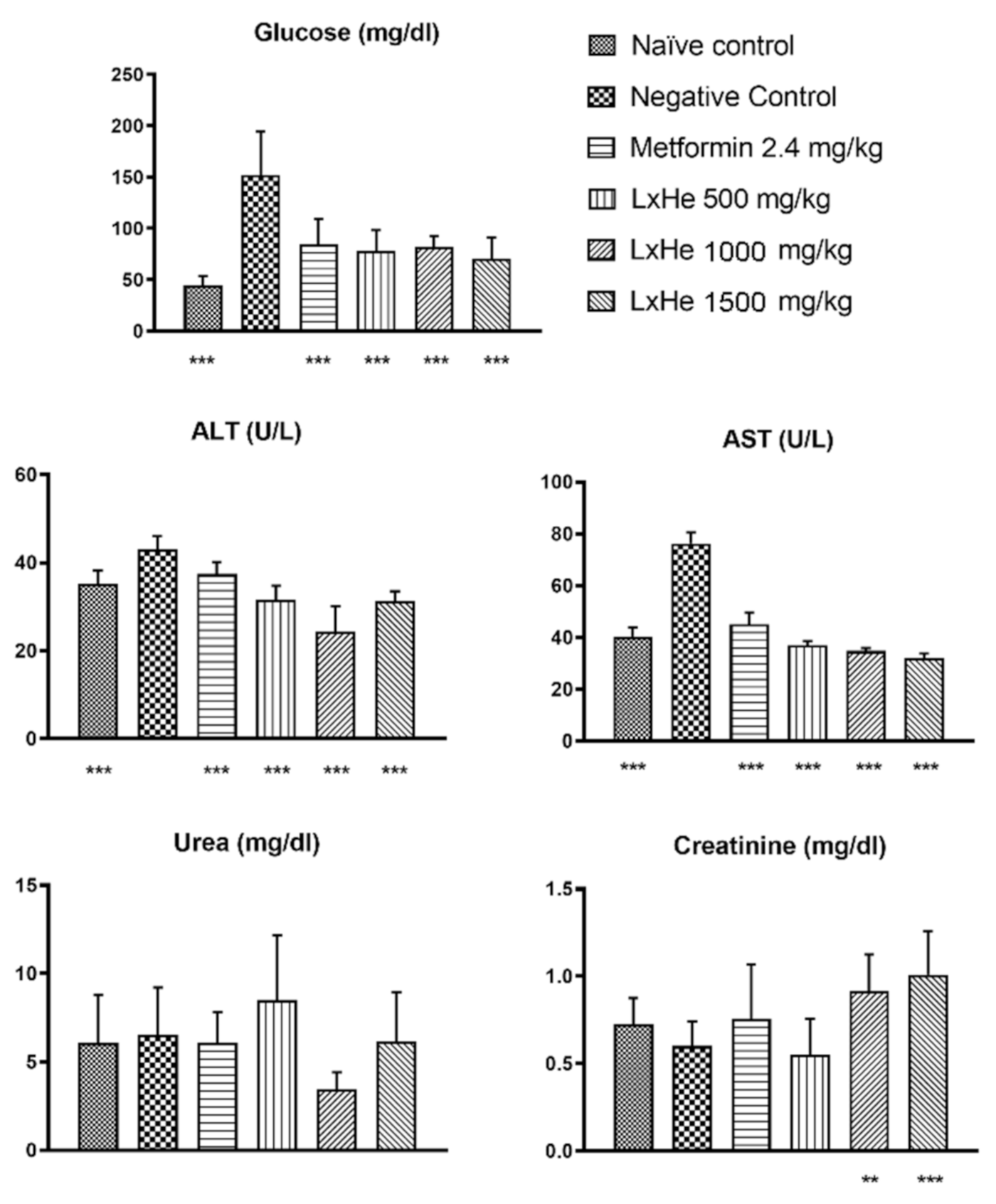
2.5. Effects of the Treatments on Biochemical Parameters
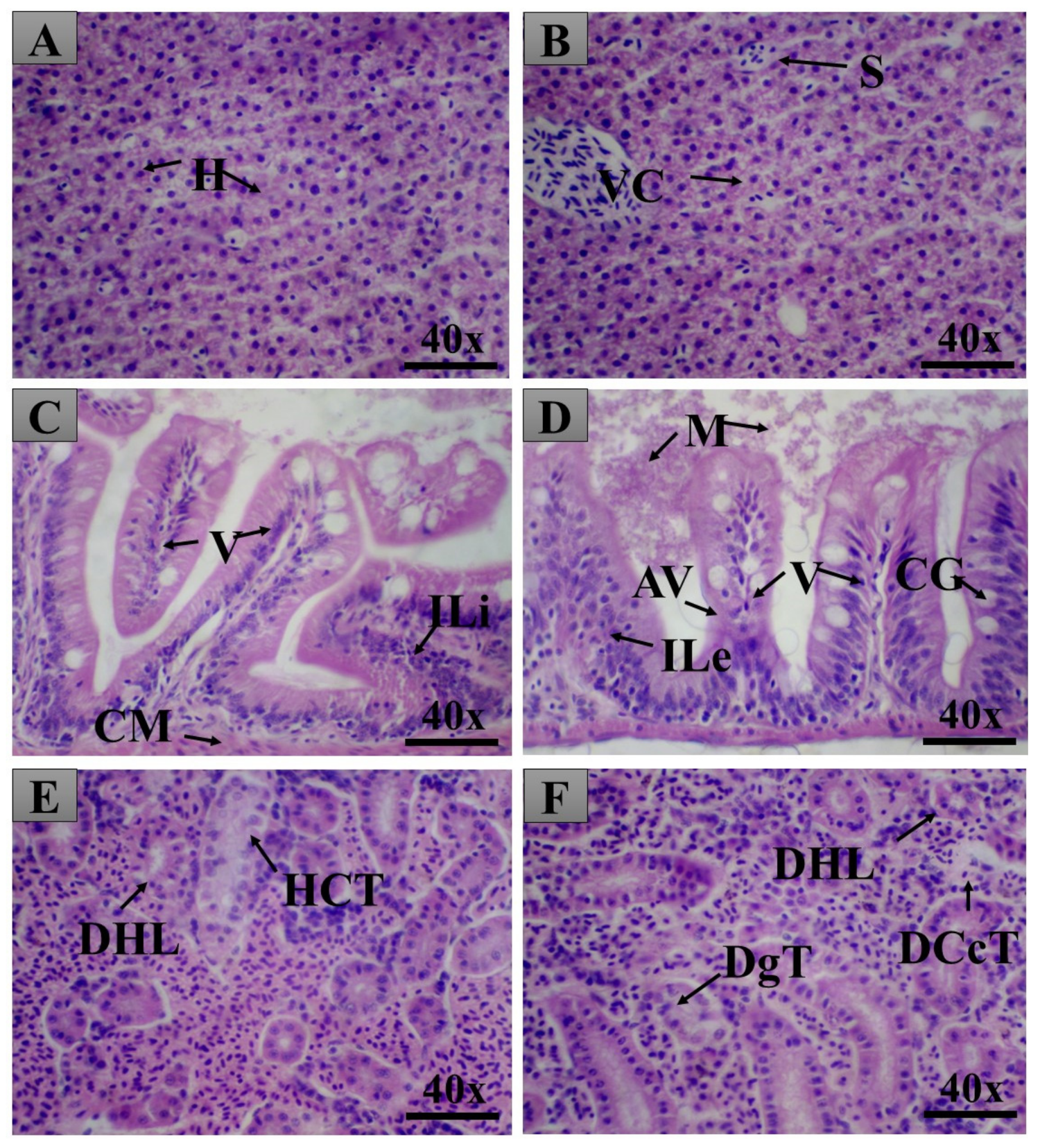
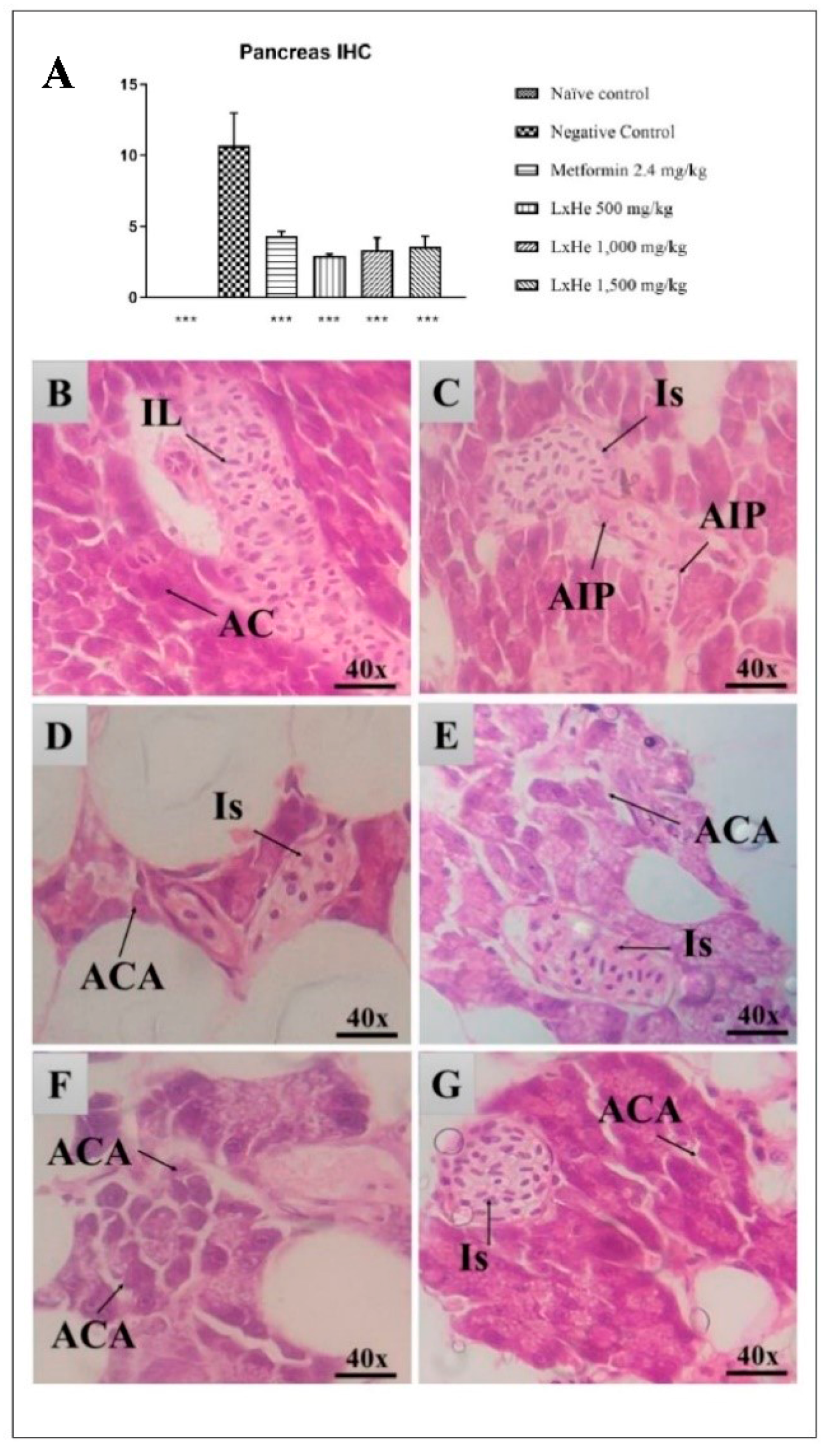
2.6. Pancreas Histopathology
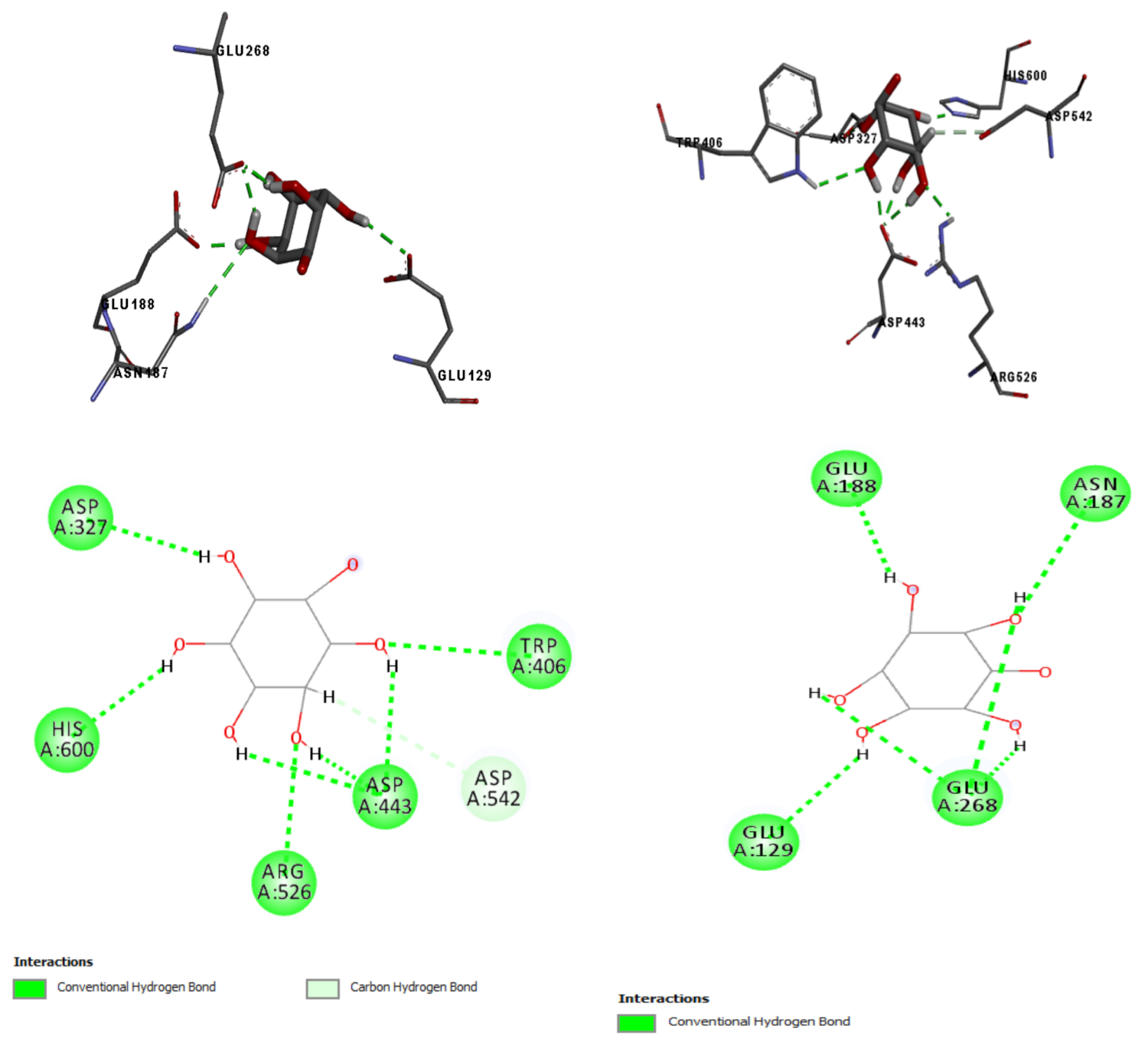
2.7. In Silico Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Hancornia Speciosa Latex and Its Aqueous Extract (LxHs)
4.3. Phytochemistry
4.4. Samples Preparation and Analysis
4.5. Animals
4.6. Embryos Acute Toxicity Assessment
4.7. Adult Toxicity Assessment
4.8. Diabetes Induction and Experimental Design
- Group 1:
- Naïve control, nondiabetic (normoglycemic), without treatment;
- Group 2:
- Negative control, diabetic, treated only with water (alloxan i.p. and water oral);
- Group 3:
- Positive control, diabetic, treated with 2.4 mg/kg metformin (alloxan i.p. and metformin oral);
- Group 4:
- Diabetic animal treated with LxHs 500 mg/kg (alloxan i.p. and LxHs oral);
- Group 5:
- Diabetic animal treated with LxHs 1000 mg/kg (alloxan i.p. and LxHs oral);
- Group 6:
- Diabetic animal treated with LxHs 1500 mg/kg (alloxan i.p. and LxHs oral).
4.9. Blood Collection and Biochemical Analyses
4.10. Histopathology Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
4.12. In Silico Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Filho, V.C.; Zanchett, C.C.C. Fitoterapia Avançada: Uma Abordagem Química, Biológica e Nutricional; Artmed: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pedrosa, V.M.D. Fisiologia, Qualidade e Potencial Funcional de Frutos de Diferentes Acessos de Mangabeira (Hancornia speciosa Gomes); Trabalho de Conclusão de Curso (Graduação)-Curso de Agronomia; Universidade Federal da Paraíba: Areia, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Brasil, Ministério do Meio Ambiente–MMA Relatório Técnico de Monitoramento do Desmatamento no Bioma Cerrado, 2001 a 2008: Dados Revisados. CENTRO DE SENSORIAMENTO REMOTO-CSR/IBAMA-Nov. 2009 DF. Available online: http://www.mma.gov.br/estruturas/sbf_chm_rbbio/_arquivos/relatorio_tecnico_monitoramento_desmate_bioma_cerrado_csr_rev_72_72.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2021).
- Honda, N.K.; Garcez, W.S.; Garcez, F.R.; Conceição, C.A. Estudo químico de plantas de Mato Grosso do Sul I: Triagem fitoquímica. Rev. Científica Cult. UFMS 1990, 5, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Brandão, G.C.; Kroon, E.G.; Dos Santos, J.R.; Stehmann, J.R.; Lombardi, J.A.; de Oliveira, A.B. Antiviral activity of plants occurring in the state of minas gerais (Brazil): Part III. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2011, 3, 223–236. [Google Scholar]
- Assumpção, C.F.; Bachiega, P.; Morzelle, M.C.; Nelson, D.L.; Ndiaye, E.A.; Rios, A.O.S.; Souza, É.C. Caracterização, potencial antioxidante e estudo citotóxico de frutas mangaba. Ciência Rural 2014, 44, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, N.G.A.; Kaffashi, S.; Luiz, W.T.; Ferreira, W.R.; Dias, S.Y.S.A.; Pazin, G.V.; Violante, I.M.P. Quantificação de metabólitos secundários e avaliação da atividade antimicrobiana e antioxidante de algumas plantas selecionadas do Cerrado de Mato Grosso. Rev. Bras. Plantas Med. 2015, 17, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, T.M.; Rodrigues, C.M.; Kushima, H.; Bauab, T.M.; Villegas, W.; Pellizzon, C.H.; Brito, A.R.; Hiruma-Lima, C.A. Hancornia speciosa: Indications of gastroprotective, healing and anti-Helicobacter pylori actions. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 120, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, J.S.; Franchin, M.; Rosalen, P.L.; Omar, N.F.; Santos, M.A.; Paschoal, J.A.; Novaes, P.D. Evaluation of the osteogenic potential of Hancornia speciosa latex in rat calvaria and its phytochemical profile. J. Ethnopharmacol. Limerick 2016, 183, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, L.M.; Floriano, J.F.; Ribeiro, T.P.; Magno, L.N.; Da Mota, L.S.L.S.; Peixoto, N.; Mrué, F.; Melo-Reis, P.R.; Lino, R.S., Jr.; Graeff, C.F.O.; et al. Hancornia speciosa latex for biomedical applications: Physical and chemical properties, biocompatibility assessment and angiogenic activity. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2014, 25, 2153–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floriano, J.F.; Neto, F.C.; Da Mota, L.S.L.S.; Ferreira, R.S., Jr.; Gonçalves, P.; Borges, F.A.; Graefs, C.F.O.; Neto, F.C.; Furtado, E.L.; Barraviera, B.; et al. Comparative study of accelerated regeneration of bone tissue by latex membranes of Hevea brasiliensis and Hancornia speciosa. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2016, 2, 045007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, T.P.; Sousa, T.R.; Arruda, A.S.; Peixoto, N.; Gonçalves, P.J.; Almeida, L.M. Evaluation of cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of Hancornia speciosa latex in Allium cepa root model. Braz. J. Biol. 2016, 76, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.D.C. Desenvolvimento e Validação de Métodos por HPLC-DADELSD Para Controle de Qualidade Químico do látex do Caule e do Fruto de Mangaba (Hancornia speciosa GOMES), Dissertação de Mestrado.156 f. Sergipe, Brazil. 2012. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/299484431 (accessed on 23 March 2021).
- Marinho, D.G.; Alviano, D.S.; Matheus, M.E.; Alviano, C.S.; Fernandes, P.D. The latex obtained from Hancornia speciosa Gomes possesses anti-inflammatory activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 135, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, I.V.F.; Souza, G.C.; Santana, G.R.; Duarte, J.L.; Fernandes, C.P.; Keita, H.; Velázquez-Moyado, J.A.; Navarrete, A.; Ferreira, I.M.; Carvalho, H.O.; et al. Histopathology in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) to Evaluate the Toxicity of Medicine: An Anti-Inflammatory Phytomedicine with Janaguba Milk (Himatanthus drasticus Plumel). Cap 3. 2018. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/61145 (accessed on 23 March 2021).
- Souza, G.C.; Pereira, A.C.M.; Viana, M.D.; Ferreira, A.M.; Silva, I.D.R.; Oliveira, M.M.R.; Barbosa, W.L.R.; Silva, L.B.; Ferreira, I.M.; Santos, C.B.R.; et al. Acmella oleracea (L) R. K. Jansen Reproductive Toxicity in Zebrafish: An In Vivo and In Silico Assessment. Evid.-Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2019, 1237301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyacienth, B.M.S.; Picanço, K.R.T.; Sánchez-Ortiz, B.L.; Silva, L.B.; Pereira, A.S.M.; Góes, L.D.M.; Borges, R.S.; Ataíde, R.C.; Santos, C.B.R.; Carvalho, H.O.; et al. Hydroethanolic extract from Endopleura uchi (Huber) Cuatrecasas and its marker bergenin: Toxicological and pharmacokinetic studies in silico and in vivo on zebrafish. Toxicol. Rep. 2020, 7, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sociedade Brasileira de Diabetes. Posicionamento Oficial SBD nº 01/2019–Conduta Terapêutica No Diabetes Tipo 2: Algoritmo SBD 2019; A. C Farmacêutica: São Paulo, Brazil, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control Prevention. Diabetes 2014. Report Card. Cdc, v. TTY. 232-4636. Available online: www.cdc.333/diabetes/library/reports/congress.html (accessed on 30 October 2020).
- Miranda, J.C.M.M. Investigação Molecular do Mecanismo de Ação Antidiabética da Nanodispersão de uma Fração Flavonoídica de Baccharis Reticularia. Dissertação (Mestrado em Ciências da Saúde)–Programa de pós-graduação em Ciências Farmacêuticas. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal do Amapá, Macapá, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha, F.A.G.; Araújo, M.F.F.; Costa, N.D.L.; Silva, R.P. O uso terapeutico da flora na história mundial. Holos 2015, 1, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.C.B.; Silva, M.A.P.; Santos, M.A.F.; Leite, T.R. Levantamento etnobotânico, químico e farmacológico de espécies de Apocynaceae Juss. ocorrentes no Brasil. Rev. Bras. Plantas Med. 2013, 15, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cercato, L.M.; White, P.A.S.; Nampo, F.K.; Santos, M.R.; Camargo, E.A. A systematic review of medicinal plants used for weight loss in Brazil: Is there potential for obesity treatment? J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 176, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.C.; Pereira, A.B.D.; Moreira, C.C.; Botion, L.M.; Lemos, V.S.; Braga, F.C.; Cortes, S.F. Hancornia speciosa Gomes (Apocynaceae) as a potential anti-diabetic drug. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 161, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, L.S.; Moraes-Souza, R.Q.; Soares, T.S.; Pinheiro, M.S.; Leal-Silva, T.; Hoffmann, J.C.; Américo, M.F.; Campos, K.E.; Damasceno, D.C.; Volpato, G.T. A treatment with a boiled aqueous extract of Hancornia speciosa Gomes leaves improves the metabolic status of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, H.Y.; Qian, K.; Morris-Natschke, S.L.; Hsu, C.S.; Lee, K.H. Recent discovery of plant-derived anti-diabetic natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 580–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizzarri, M.; Carlomagno, G. Inositol: History of an effective therapy for polycystic ovary syndrome. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 1978, 18, 1896–1903. [Google Scholar]
- Berggren, P.O.; Barker, C.J. A key role for phosphorylated inositol compounds in pancreatic beta-cell stimulus-secretion coupling. Adv. Enzyme Regul. 2008, 48, 276–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endringer, D.C.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Soares, C.M.; Braga, F.C. L-(+)-Bornesitol. Acta Crystallogr. Seção E Relatórios Estrut. Online 2007, 63, o1067–o1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, E.C. Estudo de Padronização de Extratos de Hancornia speciosa Gomes Como Alternativa Terapêutica Para Obesidade. 100f. Dissertação (Mestrado)-Universidade Federal do Maranhão, São Luís. 2018. Available online: https://tedebc.ufma.br/jspui/handle/tede/tede/2193 (accessed on 22 March 2021).
- Souza, G.C.; Duarte, J.L.; Fernandes, C.P.; Velázquez-Moyado, J.A.; Navarrete, A.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Obtainment and study of the toxicity of perillyl alcohol nanoemulsion on zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Nanomed. Res. 2016, 4, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.C.T.; Keita, H.; Santana, G.R.; Souza, G.C.; Santos, I.V.F.; Amado, J.R.R.; Kourouma, A.; Prada, A.L.; Carvalho, H.O.; Silva, M.L. Effects of Bothrops alternatus venom in zebrafish: A histopathological study. Inflammopharmacology 2017, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, S.B.; Keita, H.; Sanchez-Ortiz, B.L.; Sampaio, T.I.S.; Ferreira, I.M.; Lima, E.S.; Silva, M.J.A.; Fernandes, C.P.; Oliveira, A.E.M.F.M.; Conceição, E.C.; et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of nanoemulsions of essential oil from Rosmarinus officinalis L.: In vitro and in zebrafish studies. Inflammopharmacology 2018, 26, 1057–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, N.C.; Sánchez-Ortiz, B.L.; Sampaio, T.I.S.; Pereira, A.C.M.; Silva Neto, F.L.P.; Silva, H.R.; Cruz, R.A.S.; Keita, H.; Pereira, A.M.S.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Anxiolytic and Antidepressant Effects of the Hydroethanolic Extract from the Leaves of Aloysia polystachya (Griseb.) Moldenke: A Study on Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Custódio de Souza, G.; Dias Ribeiro da Silva, I.; Duarte Viana, M.; Costa de Melo, N.; Sánchez-Ortiz, B.L.; Maia Rebelo de Oliveira, M.; Ramos Barbosa, W.L.; Maciel Ferreira, I.; Tavares Carvalho, J.C. Toxicidade Aguda do Extrato Hidroetanólico das Flores de Acmella oleracea L. em Peixe-zebra (Danio rerio): Estudos Comportamentais e Histopatológicos. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.C.M.; Sánchez-Ortíz, B.L.; de Melo, E.L.; Hage-Melim, L.I.D.S.; Borges, R.S.; Hu, X.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Perillyl alcohol decreases the frequency and severity of convulsive-like behavior in the adult zebrafish model of acute seizures. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biemar, F.; Argenton, F.; Schmidtke, R.; Epperlein, S.; Peers, B.; Driever, W. Pancreas development in zebrafish: Early dispersed appearance of endocrine hormone expressing cells and their convergence to form the definitive islet. Dev. Biol. 2001, 230, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, M.; Herbette, G.; Eparvier, V.; Beauchêne, J.; Thibaut, B.; Stien, D. Secondary metabolites of Bagassa guianensis Aubl. wood: A study of the chemotaxonomy of the Moraceae Family. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 1708–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lopes, W.A.; Fascio, M. Esquema para interpretação de espectros de substâncias orgânicas na região do infravermelho. Quim. Nova 2004, 27, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, R.M.; Webster, F.X.; Kiemle, D.J. Identificação Espectrométrica de Compostos Orgânicos, 7th ed.; Guanabara Koogan: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Pavia, D.L.; Lampiman, G.M.; Kriz, G.S.; Vyvyan, J.R. Introdução à Espectroscopia, 4th ed.; Cencage Learning: São Paulo, Brazil, 2010; pp. 101–310. [Google Scholar]
- Rupasinghe, H.P.V.Z. Application of NMR Spectroscopy in Plant Polyphenols Associated with Human Health. In Application of NMR Spectroscopy in Food Science; Chapter 1; Elsevier Inc.: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Zhang, F.; Li, Z.; Qin, X.; Zhang, L. Comparison of Fruits of Forsythia suspensa at Two Different Maturation Stages by NMR-Based Metabolomics. Molecules 2015, 20, 10065–10081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Dhepe, P.L. Experimental evidences for existence of varying moieties and functional groups in assorted crop waste derived organosolv lignins. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 119, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, S.R. Chemical relationships of Polypremum procumbens, Tetrachondra hamiltonii and Peltanthera floribunda. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2000, 43, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdan, M.H.; Souza, L.M.; Carvalho, J.E.; Costa, D.B.V.; Salvador, M.J.; Barison, A.; Stefanello, M.E.A. Two new hydronaphthoquinones from Sinningia aggregata (Gesneriaceae) and cytotoxic activity of aggregatin D. Chem. Biodivers. 2015, 12, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Han, K.M.; Bang, M.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Chung, I.S.; Keun, H.D.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, S.H.; Kwon, B.M.; Park, M.H.; et al. Cyclohexylethanoids from the Flower of Campsis grandiflora. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2007, 28, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Winiewski, W. Constituintes Químicos e Atividade Antimicrobiana de Sinnningia Warmingii (GESNERIACEAE). Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal do Paraná, Curitiba, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kuwajima, H.; Takai, Y.; Takaishi, K.; Inoue, K. Synthesis of 13C-Labeled Possible Intermediates in the Biosynthesis of Phenylethanoid Derivatives, Cornoside and Rengyosides. Chem. Pharm. Bull 1998, 46, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hase, T.; Kawamoto, Y.; Ohtani, K.; Kasai, R.; Yamasaki, K.; Picheansoonthon, C. Cyclohexylethanoids and related glucosides from millingtonia hortensis. Phytochemistry 1995, 39, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevts, V.I. The chemistry of myoinositol. Russ. Chem. Rev. 1974, 43, 488–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angyal, S.J.; Odier, L. The effect of O-methylation on chemical shifts in the 1H- and 13CN.M.R. spectra of cyclic. Carbohydrate Res. 1983, 123, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureshan, K.M.; Shasidar, M.S.; Praveen, T.; Das, T. Regioselective protection and deprotection of inositol hydroxyl groups. Chem. Prev. 2003, 103, 4477–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, M.V.; Couri, M.R.C.; Assis, J.V.; Anconi, C.P.A.; Santos, H.F.; Almeida, W.B. 1H NMR analysis of O-methyl-inositol isomers: A joint experimental and theoretical study. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2012, 50, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, H.F.; Chagas, M.A.; Souza, L.A.; Rocha, W.R.; Almeida, M.V.; Anconi, C.P.A.; Almeida, W.B. Water Solvent Effect on Theoretical Evaluation of 1 H NMR Chemical Shifts: O Methyl-Inositol Isomer. J. Phys. Chem. 2017, 121, 2839–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Gong, Z. Development of a Convenient In Vivo Hepatotoxin Assay Using a Transgenic Zebrafish Line with Liver-Specific DsRed Expression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, K.; Hassan, H.M.; Guo, H.; Ding, P.; Han, L.; He, Q.; Chen, W.; Hsiao, C.-D.; Zhang, L.; et al. Liver Fatty Acid Binding Protein Deficiency Provokes Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis-Mediated Hepatotoxicity Induced by Pyrazinamide in Zebrafish Larvae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 7347–7356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannini, E.G.; Testa, R.; Savarino, V. Alteração das enzimas hepáticas: Um guia para medicos. CMAJ 2005, 172, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, S.; Gruber, L.; Schlummer, M.; Smolic, S.; Fromme, H. Determination of phthalic acid diesters in human milk at low ppb levels. Food Addit. Contam. Part. A Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 2012, 29, 1780–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, K.; Iwasaki, H.O.; Yasoshima, A.; Yoshikawa, H.; Yoshikawa, T.; Okaniwa, A. Pathology of Chemically Induced Chronic Active Hepatitis in Mice. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 1992, 57, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Choi, Y.; Im, H.; Yarimaga, O.; Yoon, E.; Kim, H. Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST/GOT) and Alamine Aminotransferase (ALT/GPT) Detection Techiniques. Sensors 2006, 6, 756–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandak, N.; Kumar, P.; Kaushik, P.; Varshney, P.; Sharma, C.; Kaushik, D.; Jain, S.; Aneja, K.R.; Sharma, P. Dual evaluation of some novel 2-amino-substituted coumarinylthiazoles as anti-inflammatory–antimicrobial agents and their docking studies with COX-1/COX-2 active sites. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2014, 29, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, L.; Quezada-Calvillo, R.; Sterchi, E.E.; Nichols, B.L.; Rose, D.R. Human Intestinal Maltase–Glucoamylase: Crystal Structure of the N-Terminal Catalytic Subunit and Basis of Inhibition and Substrate Specificity. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 375, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Cao, X.; Geng, P.; Bai, F.; Bai, G. Study of the inhibition of two human maltase-glucoamylases catalytic domains by different α-glucosidase inhibitors. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 2688–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.H.; Lin, Y.W.; Lu, W.C.; Hu, J.M.; Huang, D.W. In vitro hypoglycemic activity of the phenolic compounds in longan fruit (Dimocarpus Longan var. Fen ke) shell against α-glucosidase and β-galactosidase. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 19, 1786–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohto, U.; Usui, K.; Ochi, T.; Yuki, K.; Satow, Y.; Shimizu, T. Crystal Structure of Human β-Galactosidase structural basis of GM1 gangliosidosis and morquio b diseases. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 1801–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pani, A.; Giossi, R.; Menichelli, D.; Fittipaldo, V.; Agnelli, F.; Inglese, E.; Romandini, A.; Roncato, R.; Pintaudi, B.; Del Sole, F.; et al. Inositol and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review on Deficiencies and Supplementation. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, D.Q.; Oliveira, A.E.M.F.M. Estudo da Atividade Antidiabética e Toxicidade Aguda do Extrato Hidroetanólico dos Frutos de Libidibia ferrea em Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Programa de Pós-Graduação em Ciências Farmacêuticas. Master’s Thesis, Fundação Universidade Federal do Amapá, Macapá, Brazil, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Castañeda, R.; Rodriguez, I.; Nam, Y.H.; Hong, B.N.; Kang, T.H. Trigonelline promotes auditory function through nerve growth factor signaling on diabetic animal models. Phytomedicine 2017, 36, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seth, A.; Stemple, D.L.; Barroso, I. O uso emergente de peixe-zebra para modelar doenças metabólicas. Dis. Model. Mech. 2013, 6, 1080–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eames, S.C.; Philipson, L.H.; Prince, V.E.; Kinkel, M.D. A medição do açúcar no sangue em peixes-zebra revela a dinâmica da homeostase da glicose. Zebrafish 2010, 7, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurczyk, A.; Roy, N.; Bajwa, R.; Gut, P.; Lipson, K.; Yang, C.; Covassin, L.; Racki, W.J.; Rossini, A.A.; Phillips, N.; et al. Dynamic glucoregulation and mammalian-like responses to metabolic and developmental disruption in zebrafish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011, 170, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddison, L.A.; Chen, W. Modeling pancreatic endocrine cell adapter and diabetes in the zebrafish. Frente. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, A.S.; Sarras, M.P., Jr.; Intine, R.V. Limb regeneration is impaired in an adult zebrafish model of diabetes mellitus. Wound Repair Regen 2010, 18, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landgraf, K.; Schuster, S.; Meusel, A.; Garten, A.; Riemer, T.; Schleinitz, D.; Kiess, W.; Körner, A. Short-term overfeeding of zebrafish with normal or high-fat diet as a model for the development of metabolically healthy versus unhealthy obesity. BMC Physiol. 2017, 17, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.; Shimada, Y.; Nishimura, N. Development of a Novel Zebrafish Model for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, G.M.; Nascimento, F.G.O.; Bizare, A.; Oliveira, W.J.; Guimarães, E.C.; Mundim, A.V. Serum Biochemical Profile of Nile Tilapias (Oreochromis niloticus) Bred in Net Cages during Summer and Winter. Acta Sci. Vet. 2018, 46, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrall, M.A.; Baker, D.C.; Campbell, T.W.; DeNicola, D.; Fettman, M.J.; Lassen, E.D.; Rebar, A.; Weiser, G. Hematologia e Bioquímica Clínica Veterinária; Rocca: São Paulo, Brazil, 2006; p. 582. [Google Scholar]
- Helfman, G.S.; Collette, B.B.; Facey, D.E. The Diversity of Fishes; Blackwell Science Inc.: Maldon, MA, USA, 1997; p. 45. [Google Scholar]
- Rotta, M.A. Aspectos Gerais da Fisiologia e Estrutura do Sistema Digestivo dos Peixes Relacionados à Pisciculture; Embrapa Pantanal: Corumbá, Brazil, 2003; 48p, Documentos 53. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, A.B.; Warga, R.M.; Prince, V.E. Origino f the zebrafish endocrine and exocrine pancreas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7864–7869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, J.A.; Layfield, L.L.; Matthews, J.L. The Zebrafish: Atlas of Macroscopic and Microscopic Anatomy; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012; pp. 58–100. [Google Scholar]
- Benchoula, K.; Khatib, A.; Quzwain, F.; Che Mohamad, C.A.; Wan Sulaiman, W.; Abdul Wahab, R.; Ahmed, Q.U.; Abdul Ghaffar, M.; Saiman, M.Z.; Alajmi, M.F.; et al. Otimização da indução hiperglicêmica em peixes-zebra e avaliação do nível de glicose no sangue e da impressão digital de metabólitos tratados com extrato de folha de Jack de Psychotria malayana. Molecules 2019, 24, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotran, R.S.; Kumar, V.; Robbins, S.L. Patologia Estrutural e Funcional, 6th ed.; Guanabara Koogan: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2000; Volume 1400. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, R.J. Fish Pathology, 2nd ed.; Baillière Tindal: London, UK, 1989; p. 467. [Google Scholar]
- Keiser, M.; Roth, B.L.; Armbruster, B.N.; Ernsberger, P.; Irwin, J.; Shoichet, B.K. Relating protein pharmacology by ligand chemistry. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glickman, N.S.; Yelon, D. Cardiac development in zebrafish: Coordination of form and function. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2002, 13, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Chai, T.; Wang, K.; Zhu, L.; Huang, Y.; Shen, G.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, C. The developmental effect of difenoconazole on zebrafish embryos: A mechanism research. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, K.; Wang, X.; He, Q.; Chen, X. Toxic effects of celastrol on embryonic development of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 34, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Liu, K.; Wang, S.; Hou, H.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, X. Toxicity induced by emodin on zebrafish embryos. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 35, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, L.C. Investigação do Efeito Ictiotóxico do Extrato Etanolico da Raiz de Spilanthes acmella (jambu) em Zebrafish Através da Análise Eletrofisiológica e Comportamental. Master’s Thesis, Programa de Pós-Graduação em Neurociências e Biologia Celular da Universidade Federal do Pará, Instituto de Ciências Biológicas, Belém, Brasil, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Goksøyr, A. Use of cytochrome P450 lA (CYP1A) in fish as a biomarker of aquatic pollution. Arch. Toxicol. Suppl. 1995, 17, 80–95. [Google Scholar]
- Borges, R.B.; Souza, G.C.; Ferreira, A.C.M.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Use of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) in Non-Clinical Toxicological Studies of New Drugs; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vliegenthart, A.D.; Tucker, C.S.; Del Pozo, J.; Dear, J.W. Zebrafish as model organisms for studying drug-induced liver injury. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 78, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Pellitero, P.; Sitja-Bobadilla, A. Pathology of Myxosporea in marine fish culture. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2011, 17, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.J.; Ellis, A.E. The anatomy and physiology of teleosts. In Fish Pathology, 3rd ed.; Roberts, R.J., Ed.; W. B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012; pp. 12–54. [Google Scholar]
- Takashima, F.; Hibiya, T. An Atlas of Fish Histology-Normal and Pathological Features; Kodansha Ltd.: Tóquio, Japan, 1984; Volume 69, p. 406. [Google Scholar]
- Arruda, A.S.; Faria, R.Q.; Peixoto, N.; Moreira, A.S.F.P.; Floriano, J.F.; Graeff, C.F.O.; Gonçalves, P.J.; Almeida, L.M. Avaliação da produção de látex em mangabeiras do cerrado goiano. Ciência Florestal. 2016, 26, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboulkas, A.; Hammani, H.; El Achaby, M.; Bilal, E.; Barakat, A.; El Harfi, K. Valorization of algal waste via pyrolysis in a fixed-bed reactor: Production and characterization of bio-oil and bio-char. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.F.P.; Oliveira, B.F.H.; Pinheiro, W.B.S.; Correa, N.F.; França, L.F.; Ribeiro, N.F.P. Generation of biofuels by slow pyrolysis of palm empty fruit bunches: Optimization of process variables and characterization of physical-chemical products. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 140, 105707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Sun, M.; Salomé-Abarca, L.F.; Wang, M.; Choi, Y.H. Investigation of species and environmental effects on rhubarb roots metabolome using 1H NMR combined with high performance thin layer chromatography. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomé-Abarca, L.F.; van der Pas, J.; Kim, H.K.; van Uffelen, G.A.; Klinkhamer, P.G.; Choi, Y.H. Metabolic discrimination of pine resins using multiple analytical platforms. Phytochemistry 2018, 155, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leary, S.; Anthony, R.; Cartner, S.; Corey, D.; Grandin, T.; Greenacre, C.; Gwaltney-Brant, S.; McCrackin, M.A.; Meyer, R.; Miller, D.; et al. AVMA Guidelines for the Euthanasia of Animals. 2013. edicion 13. Available online: https://www.avma.org/sites/default/files/2020-01/2020-Euthanasia-Final-1-17-20.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2021).
- Cueva-Quiroz, V.A.; Yunis-Aguinaga, J.; Ramos-Espinoza, F.; Claudiano, G.S.; Marinho-Neto Fausto, A.; Abreu, S.A.; Moraes, F.R.; Moraes, J.R.E. Protocolo Para Indução de Diabetes Com Aloxana em Pacu Piaractus Mesopotamicus. Centro de Aquicultura da Unesp, CAUNESP, Jaboticabal, SP. 2014. Available online: https://www.pesca.sp.gov.br/12recip/Resumos_PDFs/PROTOCOLO_INDUCAO_DIABETES_ALOXANA_PACU_Piaractus_mesopotamicus.pdf (accessed on 22 March 2021).
- Favoretto, S.M.; Seabra, D.I.; Olivato, M.C.M. Guia de Eutanásia Para Animais de Ensino e Pesquisa, 1st ed.; Universidade Federal de São Paulo: São Paulo, Brazil, 2019; 51p. [Google Scholar]
- Dorsemans, A.C.; D’Hellencourt, C.L.; Ait-Arsa, I.; Jestin, E.; Meilgac, O.; Diotel, N. Acute and Chronic Models of Hyperglycemia in Zebrafish: A Method to Assess the Impact of Hyperglycemia on Neurogenesis and the Biodistribution of Radiolabeled Molecules. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 124, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poleksic, V.; Mitrovic-Tutundzic, V. Fish gills as a monitor of sublethal and chronic effects of pollution. In Sublethal and Chronic Efects of Pollutants on Freshwater Fish; Müller, R., Lloyd, R., Eds.; Fishing New Books Ltd. Farnham: Oxford, UK, 1994; pp. 339–352. [Google Scholar]
- Pagadala, N.S.; Syed, K.; Tuszynski, J. Software for molecular docking: A review. Biophys. Rev. 2017, 9, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.C.; Nissink, J.W.M.; Taylor, R. Protein–ligand docking and virtual screening with GOLD. In Virtual Screening in Drug Discovery; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 388–424. [Google Scholar]
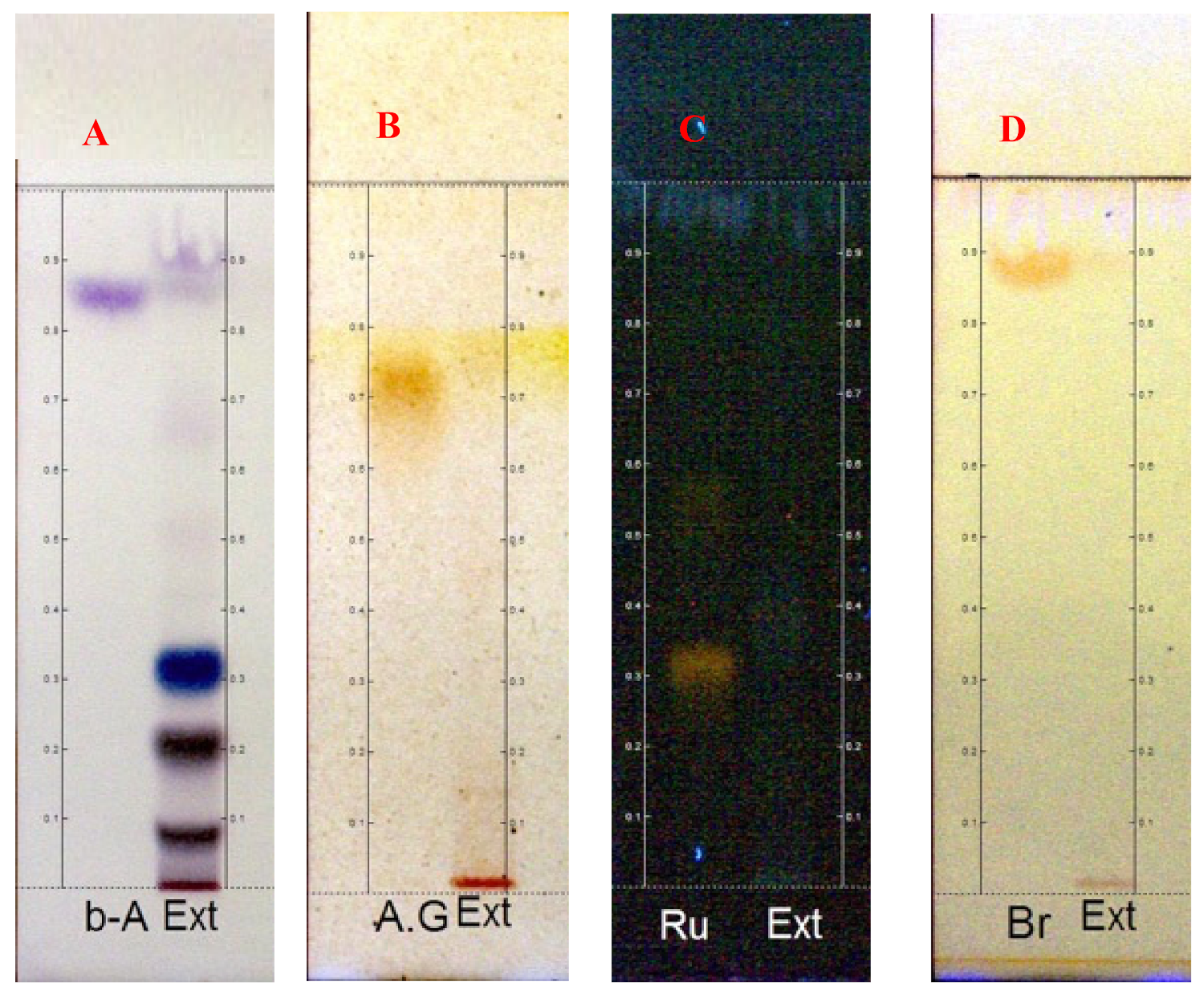
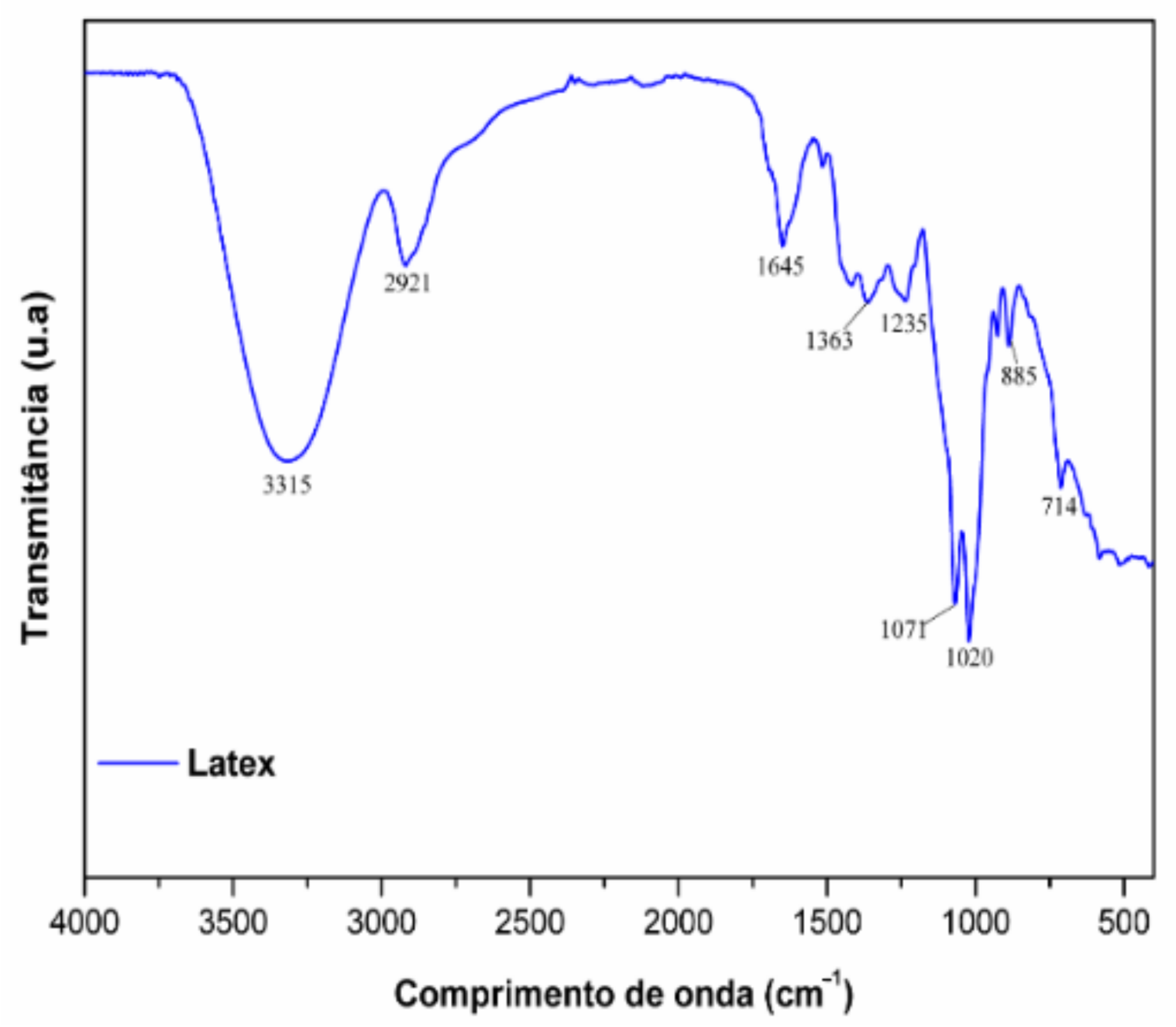
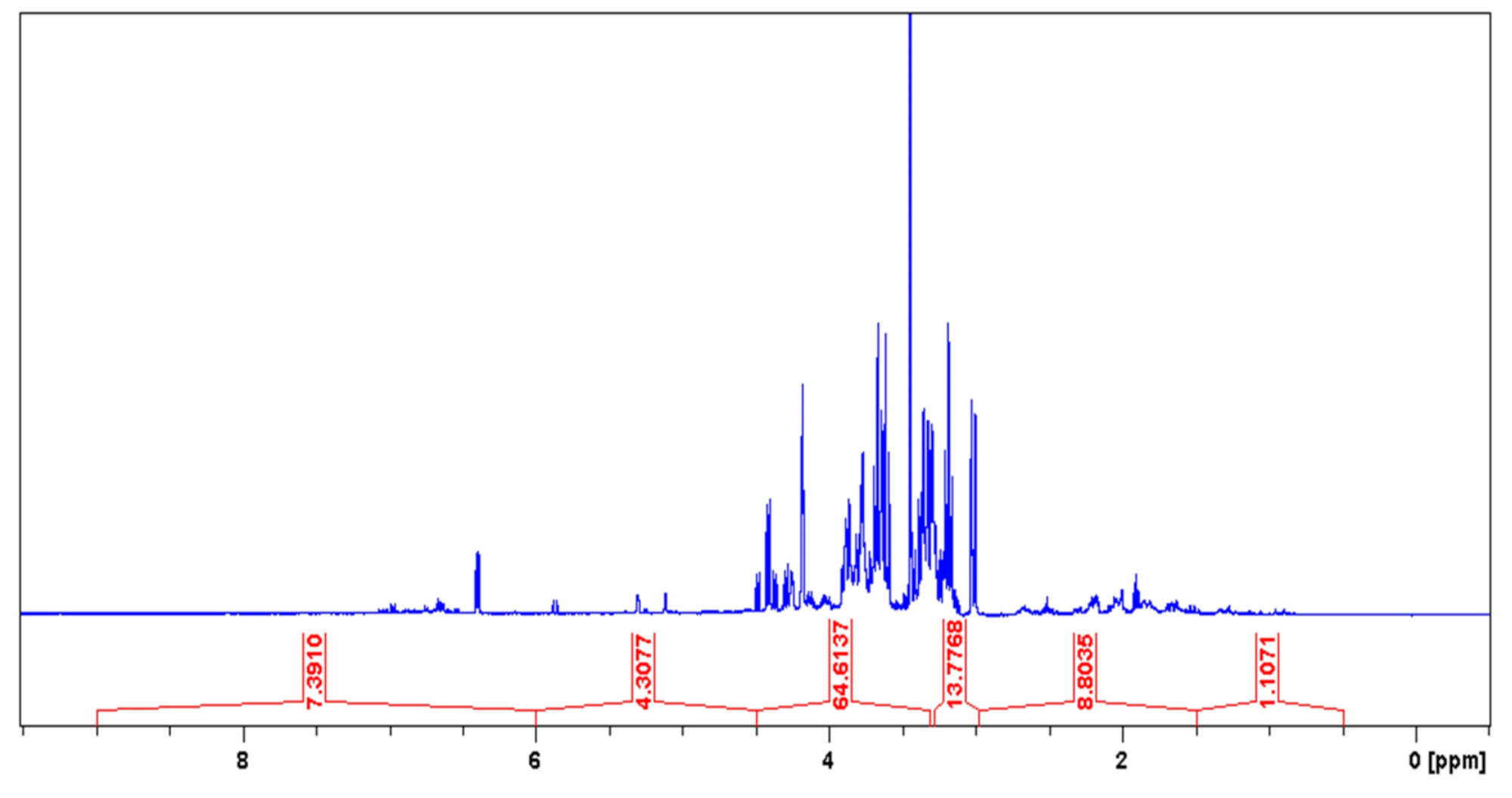
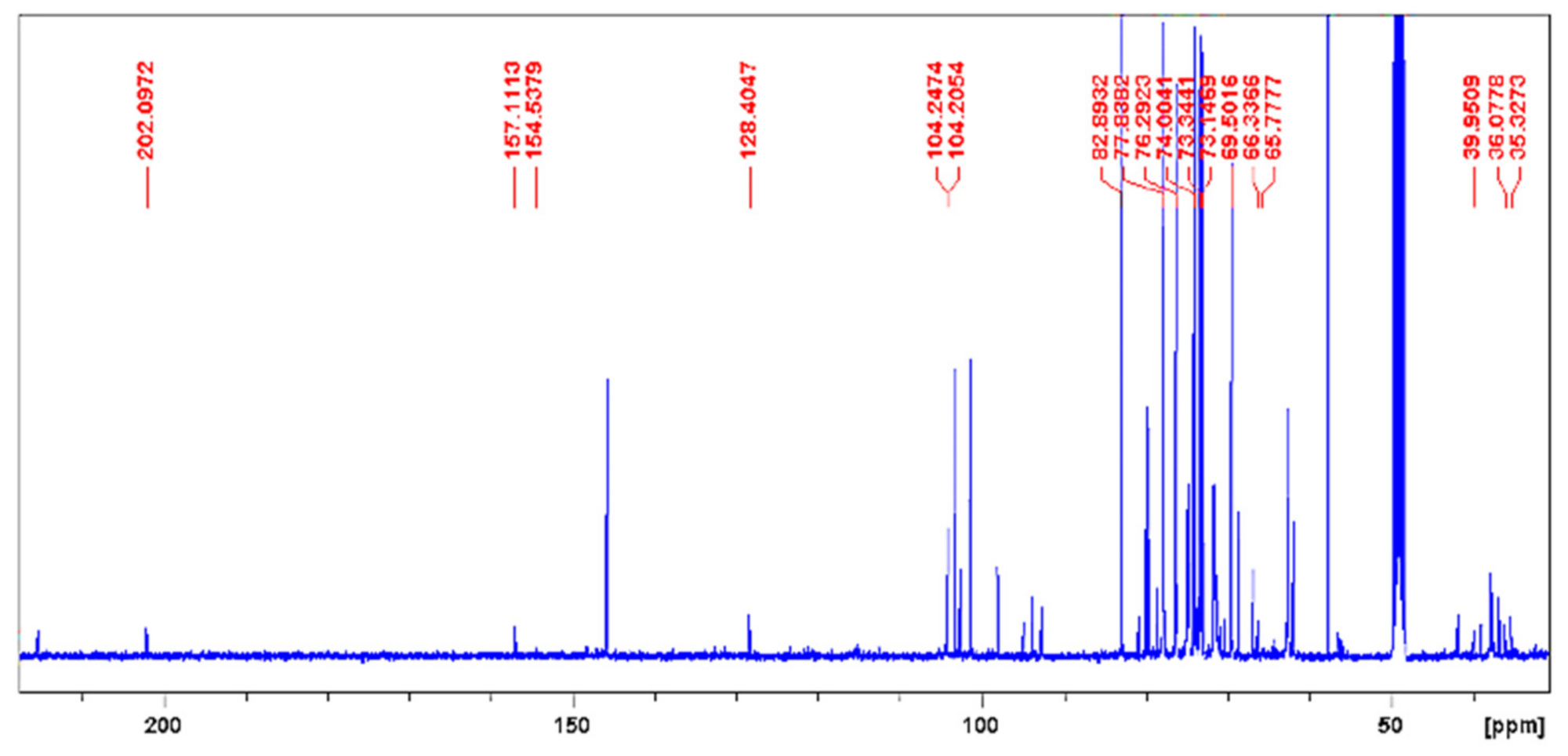
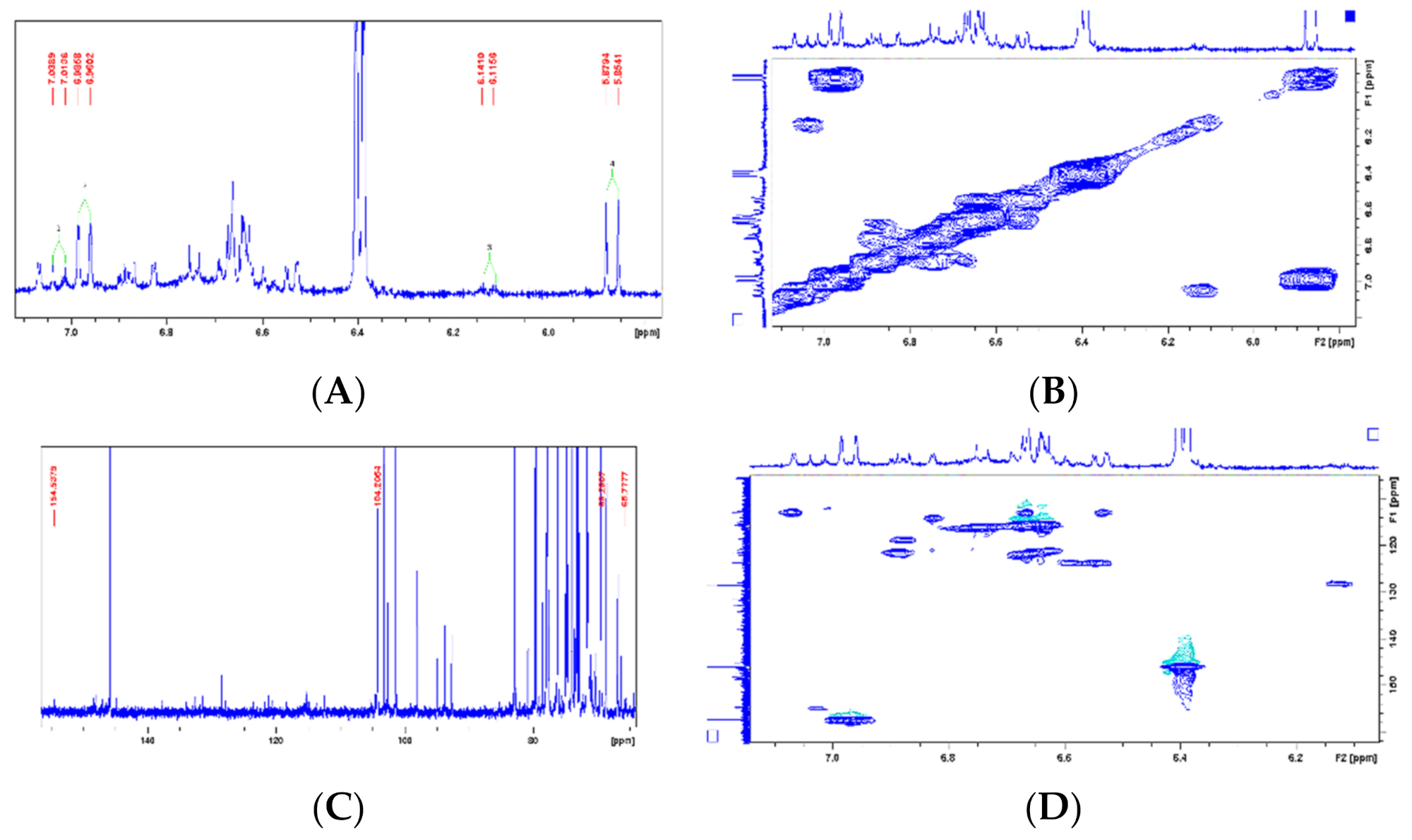
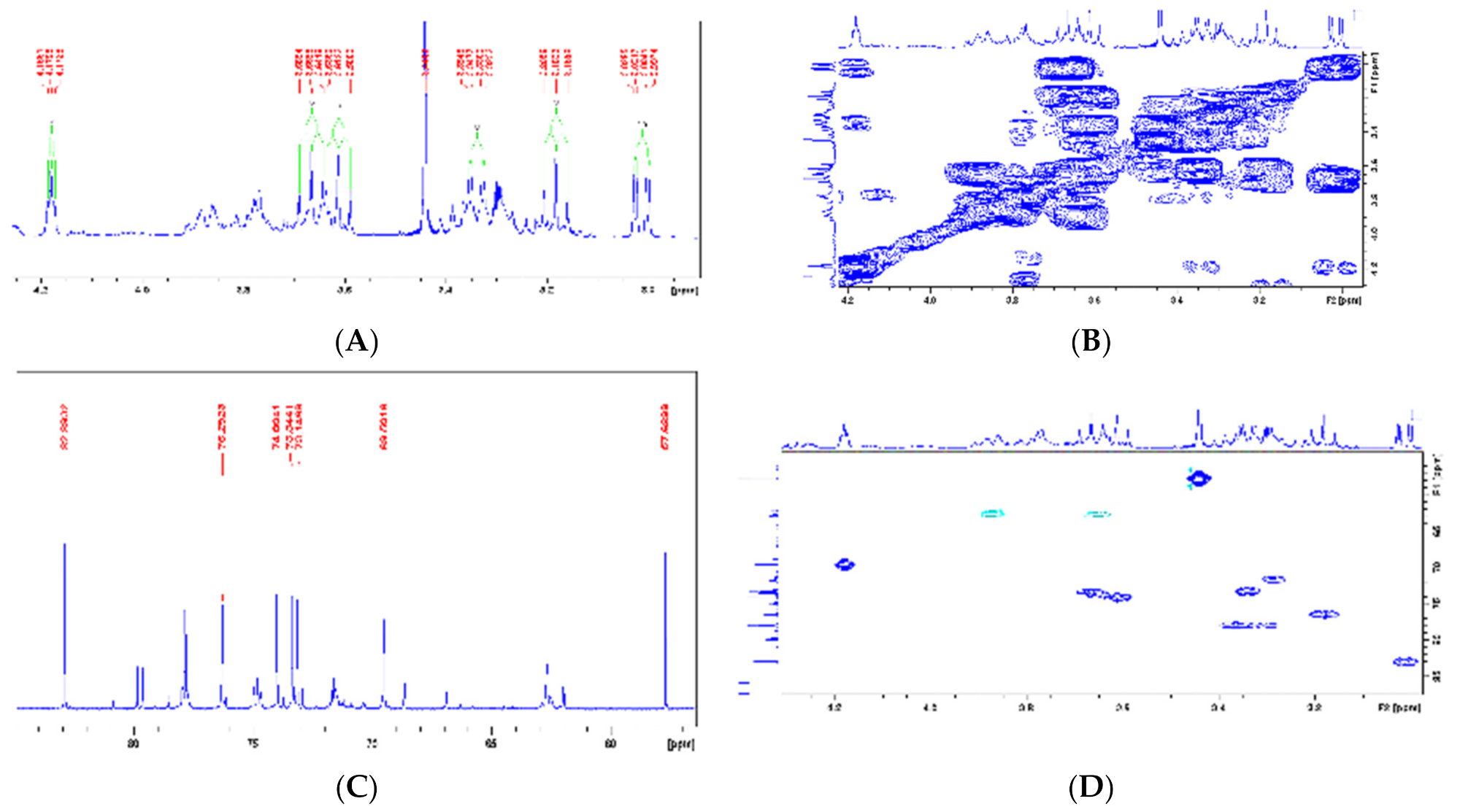

| Chemical Shift Displacement (ppm) * | Assignments | Area (%) (LxHs) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5–1.5 | C–CHn | 1.11 |
| 1.5–3.0 | CHn–C=C; CHn–COR; CHn–COOR; CHn–N; CHn–Ph | 8.80 |
| 3.0–4.5 | CHn–OH; PhO–CHn; RCOO–CHn; CH2–NHCOR | 78.39 |
| 4.5–6.0 | CHn=CH | 4.31 |
| 6.0–9.5 | Ph–H; Ph–CH=CH–R | 7.39 |
| Metabolite (Reference) | Position | LxHs | Literature | Structure | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cornoside (18) | δH | δC | δH | δC | ||
| 1 | - | 69.2 | - | 69.2 | 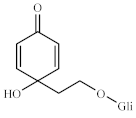 | |
| 2 | 7.02(1H, d, 10.1Hz) | 154.5 | 7.01 (1H, d, 9.6Hz) | 154.4 | ||
| 3 | 6.12 (1H, d, 10.2Hz) | 127.8 | 6.11 (1H, d, 9.6Hz) | 127.8 | ||
| 4 | - | - | - | 187.8 | ||
| 5 | 6.12 (1H, d, 10.2Hz) | 127.9 | 6.11 (1H, d, 9.6Hz) | 127.8 | ||
| 6 | 7.02(1H, d, 10.1Hz) | 154.5 | 7.01 (1H, d, 9.6 Hz) | 154.3 | ||
| 7 | - | - | 2.04 (2H, t, 6.4 Hz) | 41 | ||
| 8 | - | 65.7 | 3.99 (1H, dt, 10.0 e 6.4 Hz) e 3.63 (1H, dt, 10.0 e 6.4Hz) | 65.7 | ||
| 1′ | - | 104.2 | 4.21 (1H, d, 7.6 Hz) | 104.2 | ||
| 2′ | - | - | 75 | |||
| 3′ | - | - | 77.9 | |||
| 4′ | - | - | 71.6 | |||
| 5′ | - | - | 78 | |||
| 6′ | - | - | 62.7 | |||
| Dihydrocornoside (19, 20) | 1 | - | 68.5 | - | 68.9 |  |
| 2 | 6.97(1H, d, 10.2Hz) | 157.1 | 6.96 (1H, dd, 10,0 e 1.0 Hz) | 155.9 | ||
| 3 | 5.86 (1H, d, 10.1Hz) | 128.4 | 5.86 (1H, d, 10.0 Hz) | 127.6 | ||
| 4 | - | 202.2 | - | 198.8 | ||
| 5 | - | 35.3 | 2.47 (1H, ddd, 17.0, 11.5 e 5.0) e 2.55 (1H, ddd, 17.0, 6.5 e 5.0) | 35.1 | ||
| 6 | - | 36 | 2.19-2.26 (1H, m) e 1.95-2.05 (1H, m) | 36.2 | ||
| 7 | - | 39.9 | 2025-2103 (2H, m) | 40 | ||
| 8 | - | 66.3 | 4.14 (1H, dt, 10.0 e 6.0) e 3.77 (1H, dt, 10.0 e 6.0) | 65.9 | ||
| 1′ | - | 104.2 | 4.28 (1H, d, 7.5) | 104.6 | ||
| 2′ | - | - | 3.15 (1H, dd, 9.0 e 7.5) | 75 | ||
| 3′ | - | - | - | 78.5 | ||
| 4′ | - | - | - | 71.6 | ||
| 5′ | - | - | 3.64 (3H, m, H-5′ e H-6′a) | 78.4 | ||
| 6′ | - | - | 3.86 (2H, ddl, 12.0 e ca. 1.0) e 3.64 (3H, m) | 62.6 | ||
| 1-O-Methyl-myoinositol (23) | 1 | 3.01 (dd, 9.7 e 2.8 Hz) | 82.9 | 3.08 (dd, 10.0 e 3.0 Hz) | 83.2 | 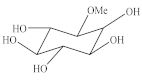 |
| 2 | 4.18 (t, 2.7 Hz) | 69.5 | 4.18 (t, 3.0 Hz) | 69.8 | ||
| 3 | 3.33 (dd, 9.8 e 2.7 Hz) | 73.1 | 3.37 (dd, 10.0 e 3.0 Hz) | 73.4 | ||
| 4 | 3.61(t, 9.5 Hz) | 74 | 3.52 (t, 10.0 Hz) | 74.2 | ||
| 5 | 3.18 (t, 9.2 Hz) | 76.2 | 3.15 (t, 10.0 Hz) | 76.6 | ||
| 6 | 3.66 (t, 9.6 Hz) | 74 | 3.49 (t, 10.0 Hz) | 73.6 | ||
| O-Me | 3.44 s | 57.6 | 3.31 s | 57.8 | ||
| Feature | CS | CD | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | Ʃt | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Teratogenesis | Cardiac edema | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Tail malformation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 60 | |
| Scoliosis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 40 | |
| Yolk edema | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Growth retardation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Lethal embryos | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 8 | 12 | n/a | n/a | |
| Ʃ Teratogenic embryos | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 5 | n/a | |
| % Teratogenic embryos | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.3 | 5 | n/a | n/a | |
| % Lethal embryos | 0 | 0 | 6.6 | 6.6 | 8.3 | 13.3 | 20 | n/a | n/a | |
| Enzyme | E-Value | MaxTc |
|---|---|---|
| β-galactosidase | 9.90−17 | 0.29 |
| Intestinal maltase-glucoamylase | 1.91−10 | 0.33 |
| α-galactosidase | 3.56−32 | 0.33 |
| Bovine α-L-fucosidase | 2.23−20 | 0.33 |
| Rodent α-L-fucosidase | 7.14−20 | 0.33 |
| Glucosylceramidase | 1.11−16 | 0.45 |
| Lysosomal acid α-glucosidase | 2.39−11 | 0.33 |
| Glycogen debranching enzyme | 4.47−10 | 0.33 |
| Intestinal sucrase-isomaltase | 1.02−6 | 0.33 |
| α-galactosidase | 3.30−6 | 0.33 |
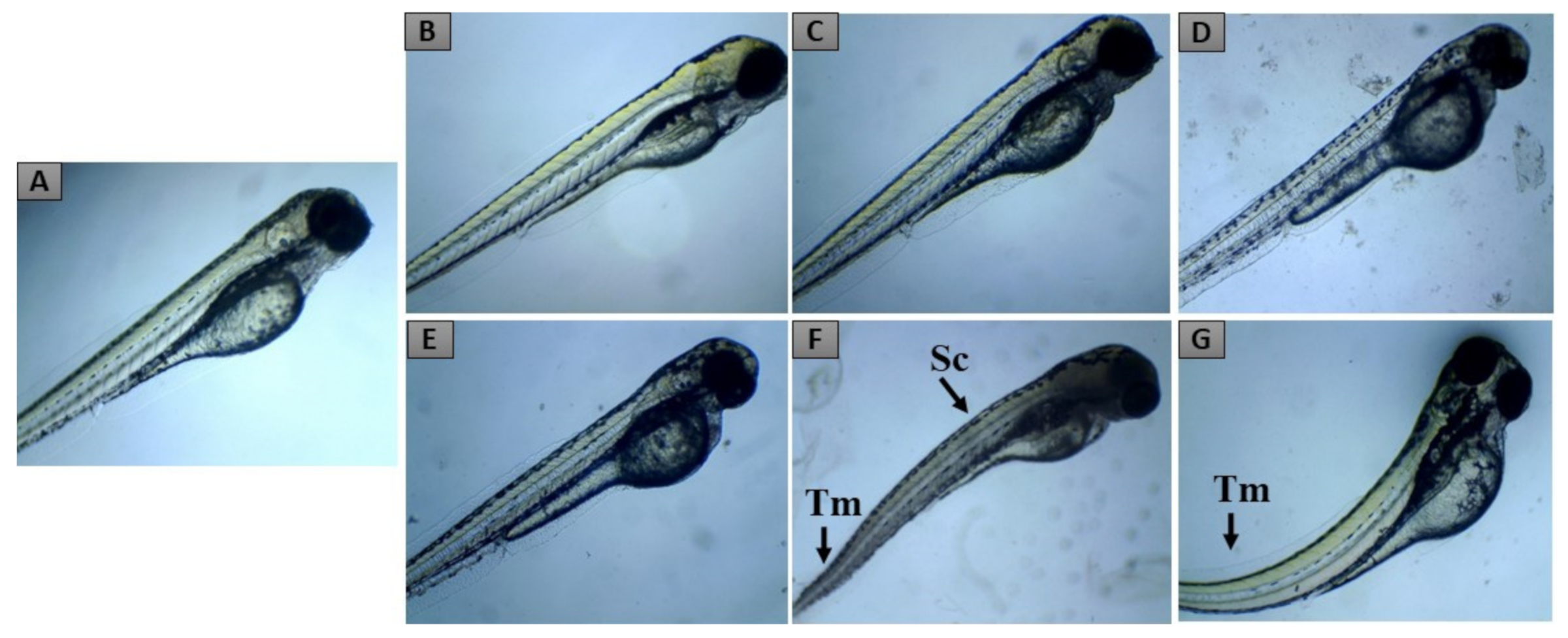
| Developmental Toxicity | 24 hpf | 48 hpf | 72 hpf | 96 hpf | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lethal effects | Coagulated eggs a | + | + | + | + |
| Lack of somite formation | + | + | + | + | |
| Lack of tail displacement | + | + | + | + | |
| No heartbeat b | + | + | + | + | |
| Teratogenic effects | Yolk edema | + | + | + | + |
| Growth retardation | + | + | + | + | |
| Tail malformation | + | + | + | ||
| Cardiac edema | + | + | + | ||
| Scoliosis | + | + |
| Tissue Changes | Stage |
|---|---|
| Loss of cellular structure | I |
| Pyknotic nuclei | I |
| Nuclei fragmentation | I |
| Presence of natural killer cells | I |
| Presence of macrophages | I |
| Presence of lymphocytes | I |
| Insulitis | II |
| Cytoplasm degeneration | II |
| Nuclei decomposition | II |
| Islets atrophy | II |
| Islets absence | II |
| Acinar cell atrophy | II |
| Necrosis | III |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomazi, R.; Figueira, Â.C.; Ferreira, A.M.; Ferreira, D.Q.; de Souza, G.C.; de Souza Pinheiro, W.B.; Pinheiro Neto, J.R.; da Silva, G.A.; de Lima, H.B.; da Silva Hage-Melim, L.I.; et al. Hypoglycemic Activity of Aqueous Extract of Latex from Hancornia speciosa Gomes: A Study in Zebrafish and In Silico. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14090856
Tomazi R, Figueira ÂC, Ferreira AM, Ferreira DQ, de Souza GC, de Souza Pinheiro WB, Pinheiro Neto JR, da Silva GA, de Lima HB, da Silva Hage-Melim LI, et al. Hypoglycemic Activity of Aqueous Extract of Latex from Hancornia speciosa Gomes: A Study in Zebrafish and In Silico. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(9):856. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14090856
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomazi, Rosana, Ângela Costa Figueira, Adriana Maciel Ferreira, Diego Quaresma Ferreira, Gisele Custódio de Souza, Wandson Braamcamp de Souza Pinheiro, José Rodrigues Pinheiro Neto, Geilson Alcantara da Silva, Henrique Barros de Lima, Lorane Izabel da Silva Hage-Melim, and et al. 2021. "Hypoglycemic Activity of Aqueous Extract of Latex from Hancornia speciosa Gomes: A Study in Zebrafish and In Silico" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 9: 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14090856
APA StyleTomazi, R., Figueira, Â. C., Ferreira, A. M., Ferreira, D. Q., de Souza, G. C., de Souza Pinheiro, W. B., Pinheiro Neto, J. R., da Silva, G. A., de Lima, H. B., da Silva Hage-Melim, L. I., Pereira, A. C. M., Carvalho, J. C. T., & da Silva de Almeida, S. S. M. (2021). Hypoglycemic Activity of Aqueous Extract of Latex from Hancornia speciosa Gomes: A Study in Zebrafish and In Silico. Pharmaceuticals, 14(9), 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14090856









