Sedative and Immunosuppressive Effects of Dexmedetomidine in Transplantation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
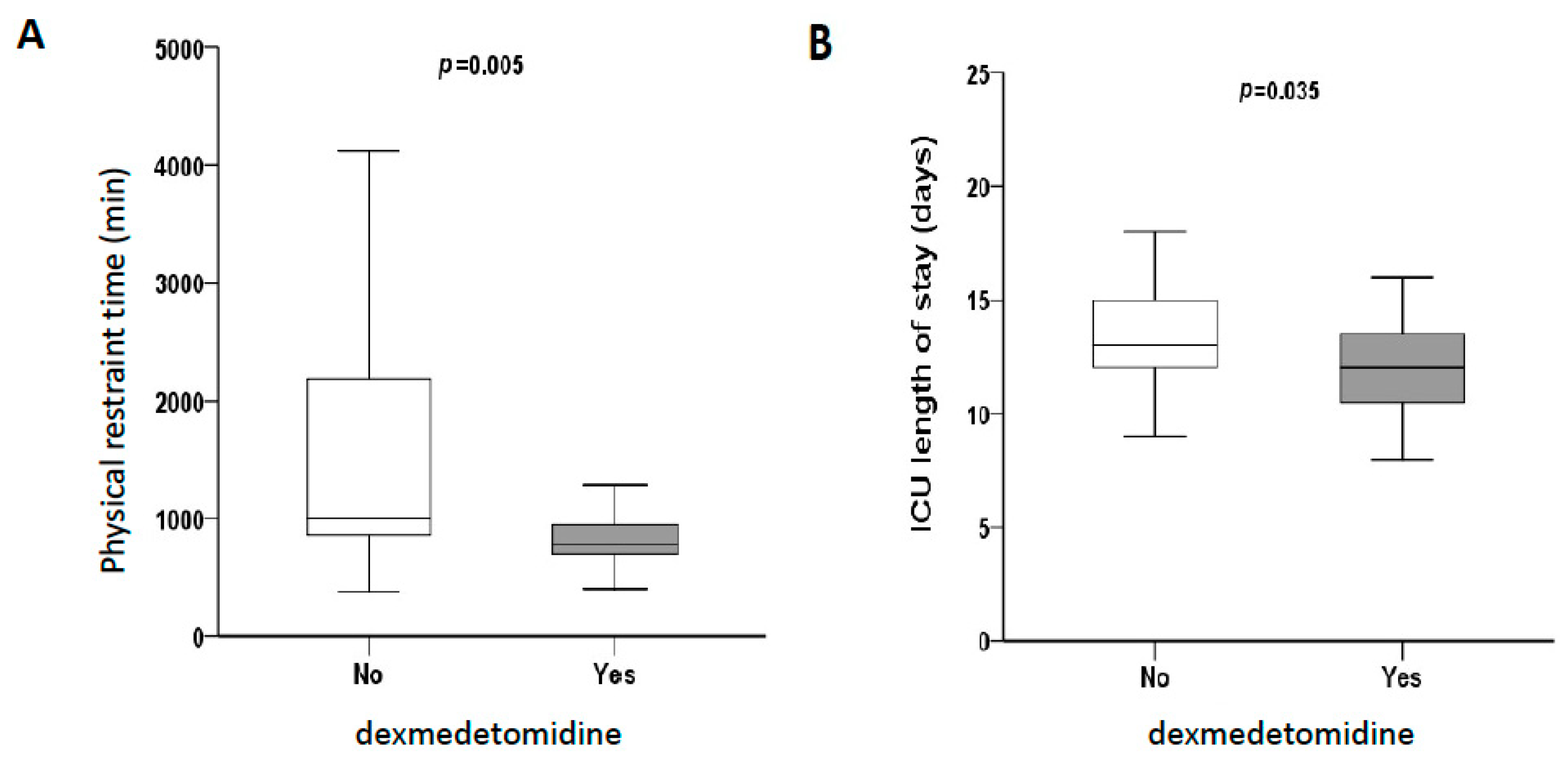
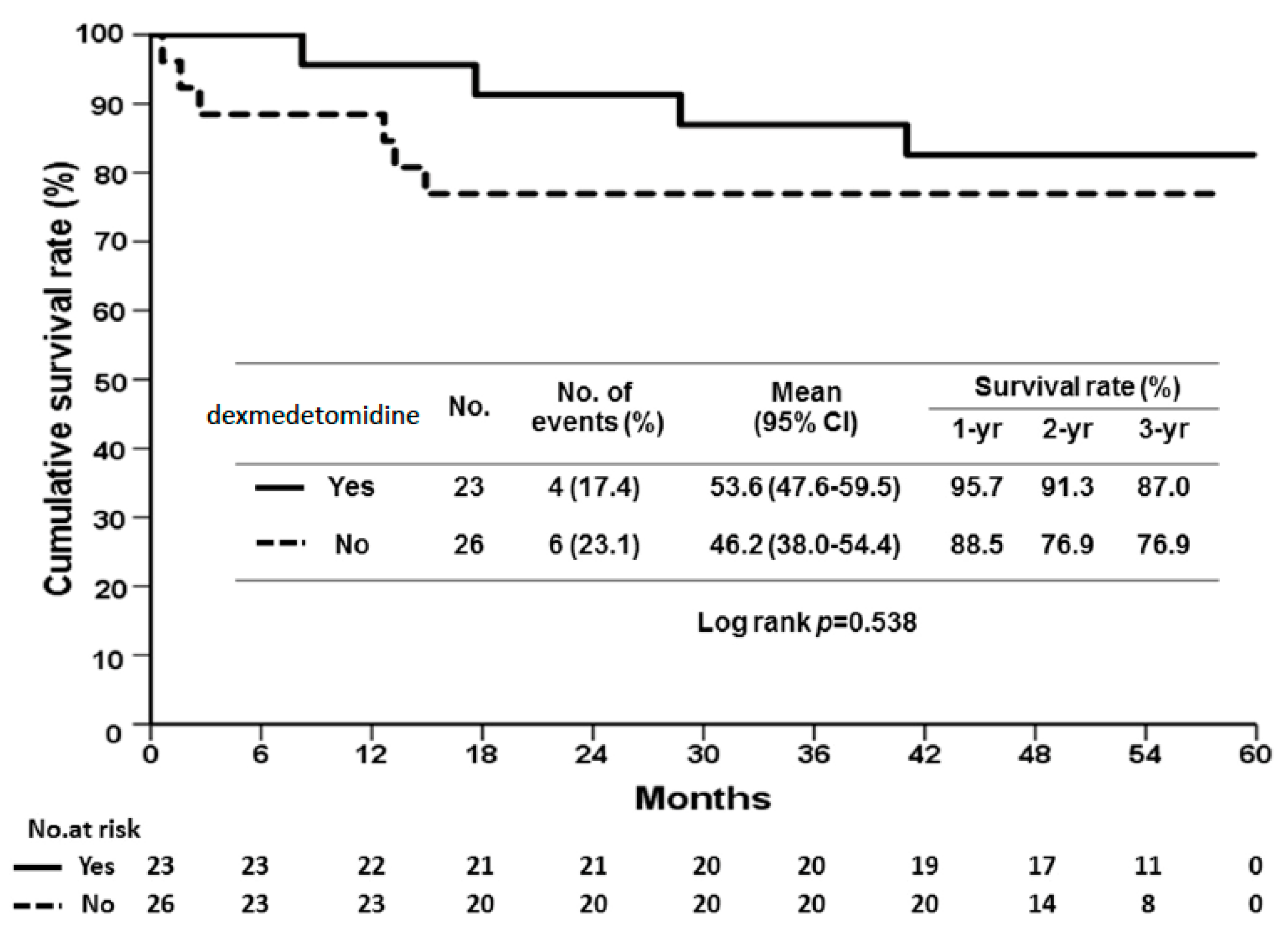
2.1. Dexmedetomidine Reduces Reperfusion Injury and Prevents Allograft Rejection in Human Liver Transplantation
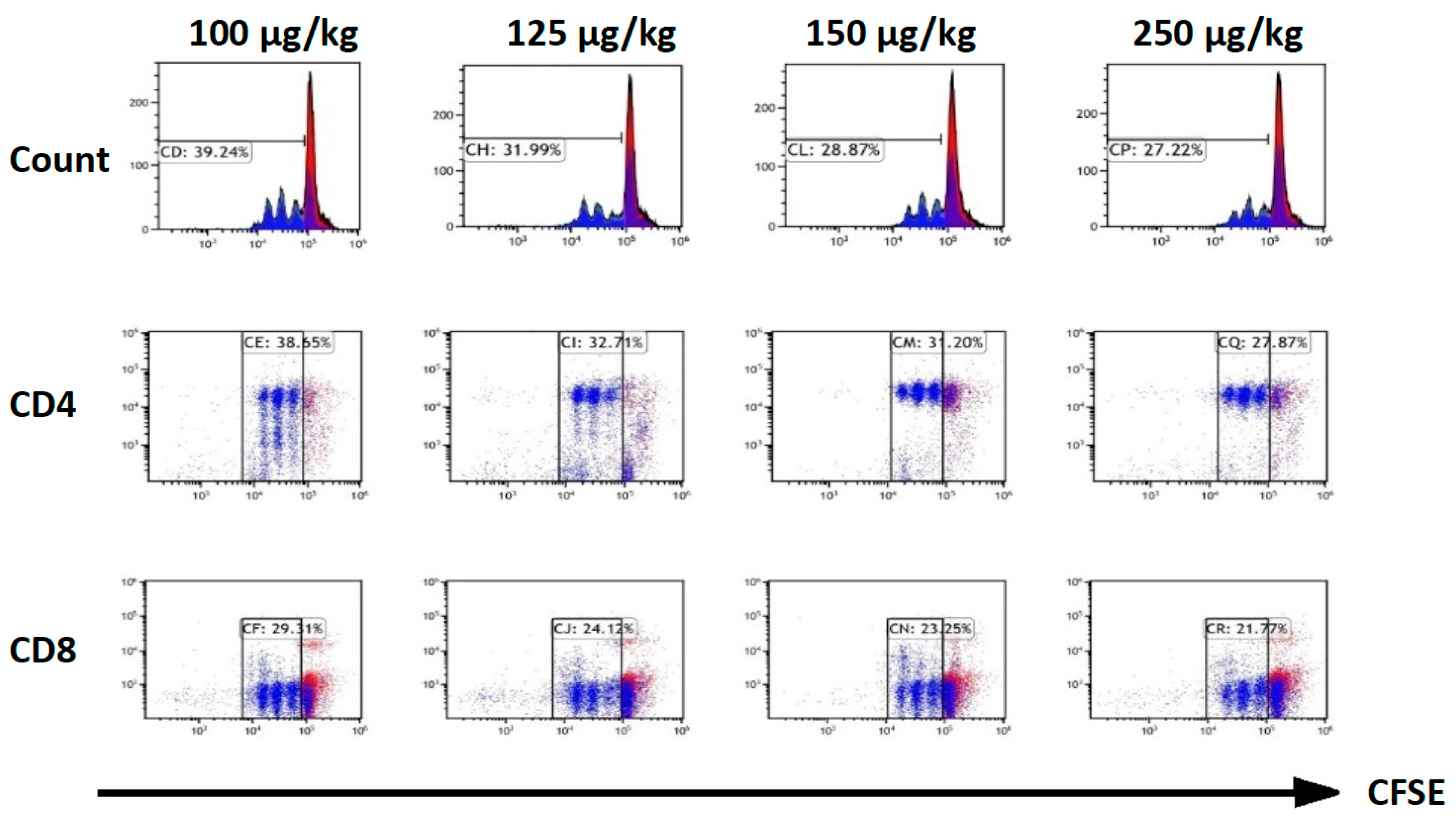
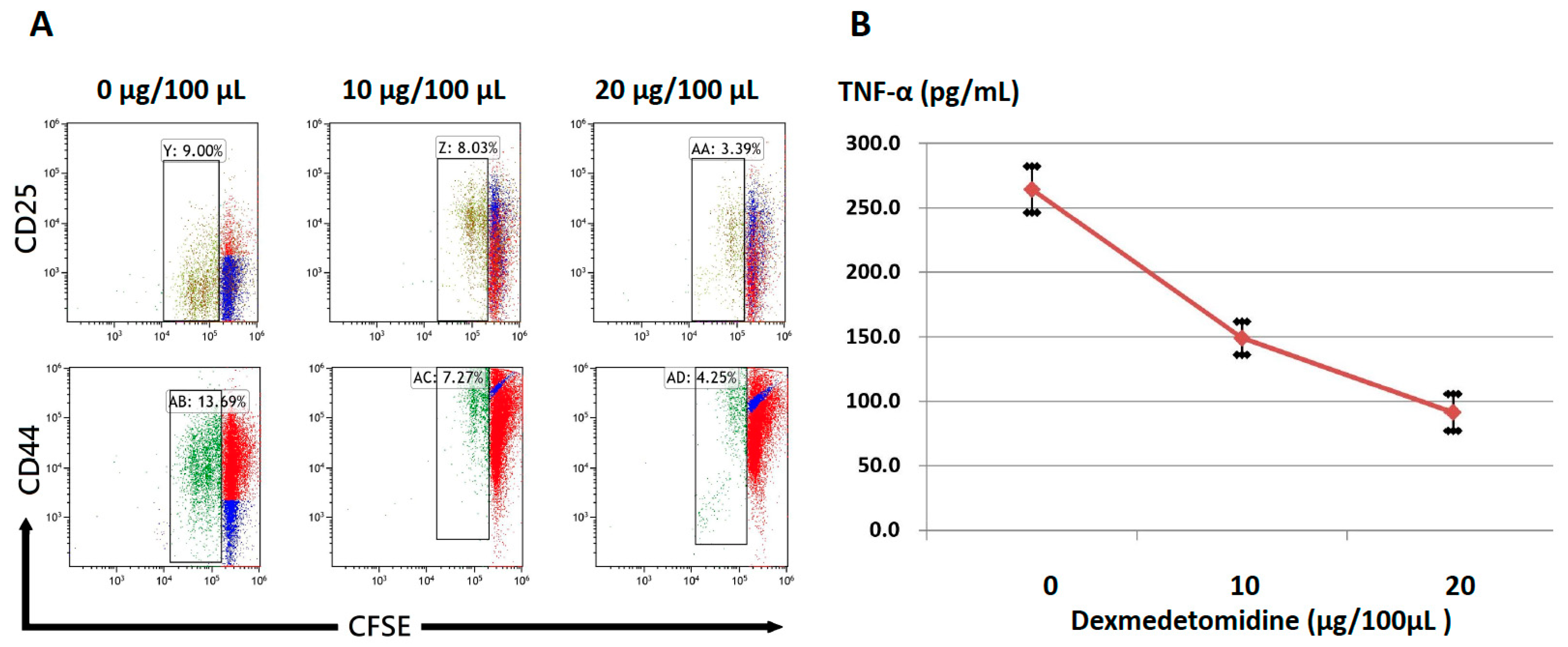
2.2. Dexmedetomidine Abrogates Activation-Induced T-Cell Proliferation and Cytokine Production
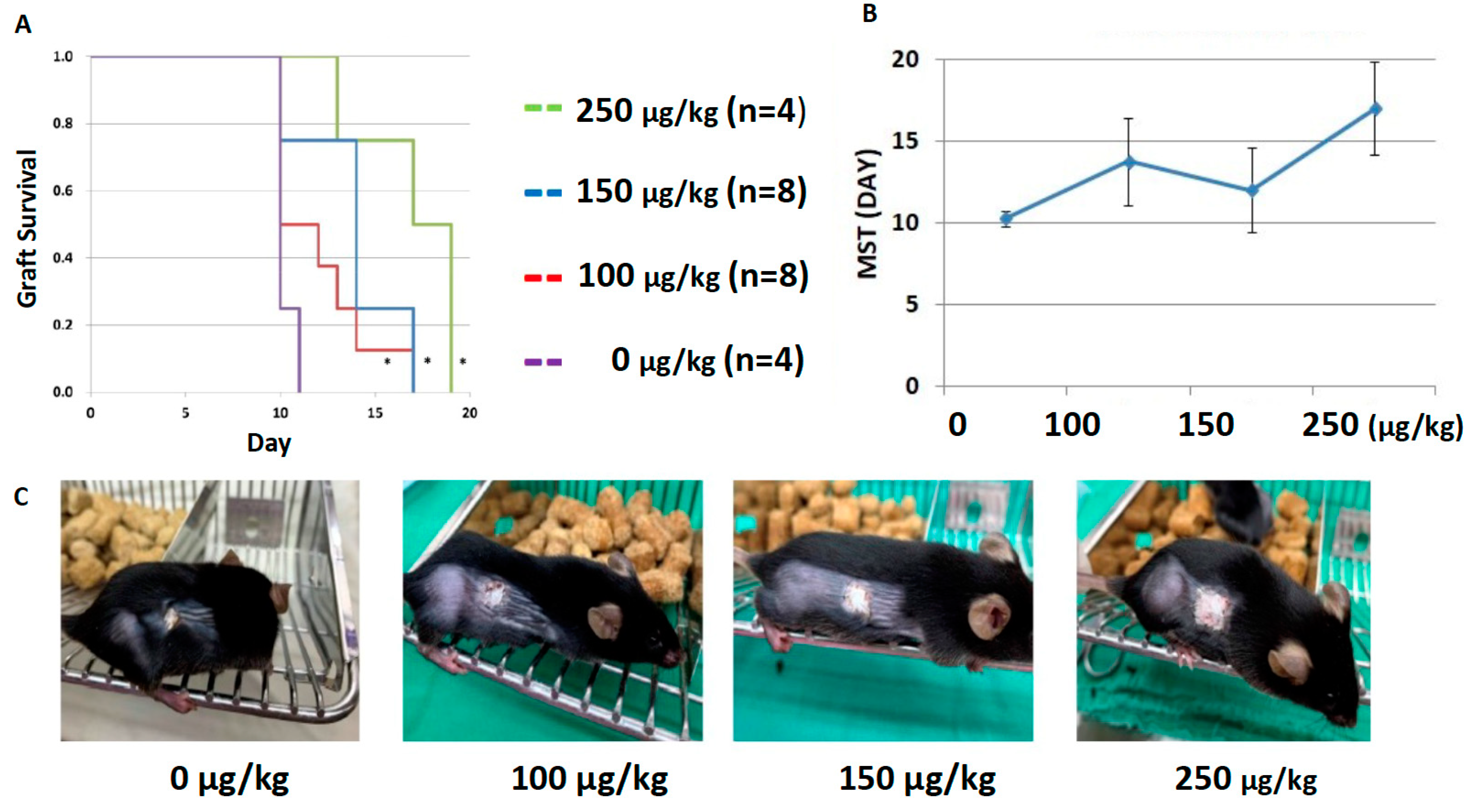
2.3. Dexmedetomidine Promotes Allograft Acceptance in Mouse Models of Skin Transplantation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Human Liver Transplantation
4.1.1. Data Collection of Human Liver Transplantation
4.1.2. Immunosuppression Protocol and Surgical Techniques in Liver Transplantation
4.2. Animal Model
4.3. Cell Culture, T-Cell Activation, and Cytokine Production
4.4. Flow Cytometry and Intracellular Cytokine Staining
4.5. Murine Skin Transplantation Model
4.6. Statistical Considerations and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| CFSE | carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| GRWR | Graft-recipient weight ratio |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| INR | International normalized ratio |
| LT | Liver transplantation |
| MELD | Model of end-stage liver disease |
| MST | Median survival time |
| OS | Overall survival |
| POD | Postoperative day |
| RASS | Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale |
References
- Choi, J.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Kwon, C.H.; Joh, J.W.; Lee, S.; Park, J.B.; Ko, J.S.; Gwak, M.S.; Kim, G.S.; Kim, S.J.; et al. Use of Dexmedetomidine in Liver Transplant Recipients With Postoperative Agitated Delirium. Transplant. Proc. 2016, 48, 1063–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Yang, S.M.; Chung, J.; Oh, H.W.; Yi, N.J.; Suh, K.S.; Oh, S.Y.; Ryu, H.G. Erratum to Effect of Perioperative Low-Dose Dexmedetomidine on Postoperative Delirium After Living-Donor Liver Transplantation: A Randomized Controlled Trial, by Hannah Lee, Seong Mi Yang, Jaeyeon Chung, Hye-Won Oh, Nam Joon Yi, Kyung-Suk Suh, Seung-Young Oh, and Ho Geol Ryu Transplant Proc. 2020; 52(1):239–245. Transplant. Proc. 2021, 53, 1771. [Google Scholar]
- Pandharipande, P.; Ely, E.W.; Maze, M. Alpha-2 agonists: Can they modify the outcomes in the Postanesthesia Care Unit? Curr. Drug Targets 2005, 6, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, L.E.; Lu, J.; Guo, T.; Saper, C.B.; Franks, N.P.; Maze, M. The alpha2-adrenoceptor agonist dexmedetomidine converges on an endogenous sleep-promoting pathway to exert its sedative effects. Anesthesiology 2003, 98, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Djaiani, G.; Silverton, N.; Fedorko, L.; Carroll, J.; Styra, R.; Rao, V.; Katznelson, R. Dexmedetomidine versus Propofol Sedation Reduces Delirium after Cardiac Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Anesthesiology 2016, 124, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasin, L.; Landoni, G.; Nardelli, P.; Belletti, A.; Di Prima, A.L.; Taddeo, D.; Isella, F.; Zangrillo, A. Dexmedetomidine reduces the risk of delirium, agitation and confusion in critically Ill patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2014, 28, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulou, C.; Kondili, E.; Diamantaki, E.; Psarologakis, C.; Kokkini, S.; Bolaki, M.; Georgopoulos, D. Effects of dexmedetomidine on sleep quality in critically ill patients: A pilot study. Anesthesiology 2014, 121, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosas-Ballina, M.; Olofsson, P.S.; Ochani, M.; Valdes-Ferrer, S.I.; Levine, Y.A.; Reardon, C.; Tusche, M.W.; Pavlov, V.A.; Andersson, U.; Chavan, S.; et al. Acetylcholine-synthesizing T cells relay neural signals in a vagus nerve circuit. Science 2011, 334, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonaz, B.; Sinniger, V.; Hoffmann, D.; Clarencon, D.; Mathieu, N.; Dantzer, C.; Vercueil, L.; Picq, C.; Trocmé, C.; Faure, P.; et al. Chronic vagus nerve stimulation in Crohn’s disease: A 6-month follow-up pilot study. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 28, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, F.A.; Chavan, S.S.; Miljko, S.; Grazio, S.; Sokolovic, S.; Schuurman, P.R.; Mehta, A.D.; Levine, Y.A.; Faltys, M.; Zitnik, R.; et al. Vagus nerve stimulation inhibits cytokine production and attenuates disease severity in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 8284–8289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacLaren, R. Immunosedation: A consideration for sepsis. Crit. Care 2009, 13, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, W.W.; Wang, Q.H.; Liao, Y.J.; Peng, P.; Xu, M.; Yin, L.X. Effects of dexmedetomidine on TNF-alpha and interleukin-2 in serum of rats with severe craniocerebral injury. BMC Anesthesiol. 2017, 17, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fayed, N.A.; Sayed, E.I.; Saleh, S.M.; Ehsan, N.A.; Elfert, A.Y. Effect of dexmedetomidine on hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in the setting of adult living donor liver transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2016, 30, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Yang, Y.; Cao, J.; Mi, W. Dexmedetomidine exerts a protective effect on ischemia-reperfusion injury after hepatectomy: A prospective, randomized, controlled study. J. Clin. Anesth. 2020, 61, 109631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessler, C.N.; Gosnell, M.S.; Grap, M.J.; Brophy, G.M.; O’Neal, P.V.; Keane, K.A.; Tesoro, E.P.; Elswick, R.K. The Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale: Validity and reliability in adult intensive care unit patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 1338–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ely, E.W.; Inouye, S.K.; Bernard, G.R.; Gordon, S.; Francis, J.; May, L.; Truman, B.; Speroff, T.; Gautam, S.; Margolin, R.; et al. Delirium in mechanically ventilated patients: Validity and reliability of the confusion assessment method for the intensive care unit (CAM-ICU). JAMA 2001, 286, 2703–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, T.J.; Dahiya, D.; Lee, C.S.; Lee, C.F.; Chou, H.S.; Chan, K.M.; Lee, W.C. Impact of portal venous hemodynamics on indices of liver function and graft regeneration after right lobe living donor liver transplantation. Liver Transplant. 2011, 17, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.M.; Cheng, C.H.; Wu, T.H.; Wu, T.J.; Chou, H.S.; Lee, C.S.; Lee, W.C. Clinical strategy for the reconstruction of middle hepatic vein tributaries in right liver living donor liver transplantation. World J. Surg. 2014, 38, 2927–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.F.; Cheng, C.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Soong, R.S.; Wu, T.H.; Chou, H.S.; Wu, T.J.; Chan, K.M.; Lee, C.S.; Lee, W.C. Adult Living Donor Liver Transplantation Across ABO-Incompatibility. Medicine 2015, 94, e1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.H.; Lee, C.F.; Fryer, M.; Furtmuller, G.J.; Oh, B.; Powell, J.D.; Brandacher, G. Murine Full-thickness Skin Transplantation. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 55105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, U.; Tracey, K.J. Neural reflexes in inflammation and immunity. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, U.; Tracey, K.J. Reflex principles of immunological homeostasis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 313–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiang, H.; Hu, B.; Li, Z.; Li, J. Dexmedetomidine controls systemic cytokine levels through the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Inflammation 2014, 37, 1763–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Qi, J.; Yu, R.; Zhuang, J.; Zhuang, B.; Lou, Y.; Ruan, J.; Ye, H.; Lin, F. Impact of CYP2A6 gene polymorphism on the pharmacokinetics of dexmedetomidine for premedication. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 11, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.F.; Lo, Y.C.; Cheng, C.H.; Furtmuller, G.J.; Oh, B.; Andrade-Oliveira, V.; Thomas, A.G.; Bowman, C.E.; Slusher, B.S.; Wolfgang, M.J.; et al. Preventing Allograft Rejection by Targeting Immune Metabolism. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lo, Y.C.; Lee, C.F.; Powell, J.D. Insight into the role of mTOR and metabolism in T cells reveals new potential approaches to preventing graft rejection. Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2014, 19, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, C.H.; Lee, C.F.; Oh, B.C.; Furtmüller, G.J.; Patel, C.H.; Brandacher, G.; Powell, J.D. Targeting Metabolism as a Platform for Inducing Allograft Tolerance in the Absence of Long-Term Immunosuppression. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Factors | Dexmedetomidine n = 23 | Control n = 26 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| General information | |||
| Recipient age, median | 53.0 (8.0) | 58.5 (15.0) | 0.179 |
| Recipient gender (male) (%) | 16 (69.6) | 15 (57.7) | 0.390 |
| Donor age, median | 31.0 (20.0) | 28.0 (10.0) | 0.527 |
| Donor gender (male) (%) | 10 (43.5) | 9 (34.6) | 0.525 |
| Right lobe (%) | 22 (95.7) | 24 (92.3) | >0.999 |
| MELD score, median | 14 (8) | 16 (13) | 0.166 |
| HBV infection (%) | 13 (56.5) | 10 (38.5) | 0.206 |
| HCV infection (%) | 3 (13.0) | 10 (38.5) | 0.044 |
| Alcohol use (%) | 5 (21.7) | 9 (34.6) | 0.319 |
| HCC (%) | 9 (39.1) | 9 (34.6) | 0.744 |
| Ascites (mL), median | 350.0 (3200.0) | 950.0 (2900.0) | 0.379 |
| GRWR (%), median | 0.8 (0.5) | 0.9 (0.5) | 0.726 |
| Clinical outcomes | |||
| AST POD2 reduction (%), median | 32.75 (4.23) | 29.74 (6.44) | 0.873 |
| ALT POD2 reduction (%), median | 0.14 (0.47) | 0.016 (0.01) | 0.317 |
| AST POD4 reduction (%), median | 0.637 (0.045) | 0.636(0.081) | 0.873 |
| ALT POD4 reduction (%), median | 0.39 (0.08) | 0.25 (0.01) | 0.087 |
| Acute rejection (%) | 13 (56.5) | 17 (68.0) | 0.412 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) POD7, median | 4.93 (1.45) | 5.55(1.5) | 0.96 |
| INR, median | 1.3 (0.036) | 1.23 (0.034) | 0.148 |
| ICU stay (day), median | 12.0 (4.0) | 13.0 (3.0) | 0.035 |
| Physical restraint time (min), median | 780.0 (273.0) | 1005.0 (1348.0) | 0.005 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, C.-F.; Cheng, C.-H.; Hung, H.-C.; Lee, J.-C.; Wang, Y.-C.; Wu, T.-H.; Wu, T.-J.; Chou, H.-S.; Chan, K.-M.; Lee, W.-C. Sedative and Immunosuppressive Effects of Dexmedetomidine in Transplantation. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080825
Lee C-F, Cheng C-H, Hung H-C, Lee J-C, Wang Y-C, Wu T-H, Wu T-J, Chou H-S, Chan K-M, Lee W-C. Sedative and Immunosuppressive Effects of Dexmedetomidine in Transplantation. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(8):825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080825
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Chen-Fang, Chih-Hsien Cheng, Hao-Chien Hung, Jin-Chiao Lee, Yu-Chiao Wang, Tsung-Han Wu, Ting-Jung Wu, Hong-Shiue Chou, Kun-Ming Chan, and Wei-Chen Lee. 2021. "Sedative and Immunosuppressive Effects of Dexmedetomidine in Transplantation" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 8: 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080825
APA StyleLee, C.-F., Cheng, C.-H., Hung, H.-C., Lee, J.-C., Wang, Y.-C., Wu, T.-H., Wu, T.-J., Chou, H.-S., Chan, K.-M., & Lee, W.-C. (2021). Sedative and Immunosuppressive Effects of Dexmedetomidine in Transplantation. Pharmaceuticals, 14(8), 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080825






