Discovery of Selective Inhibitor Leads by Targeting an Allosteric Site in Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
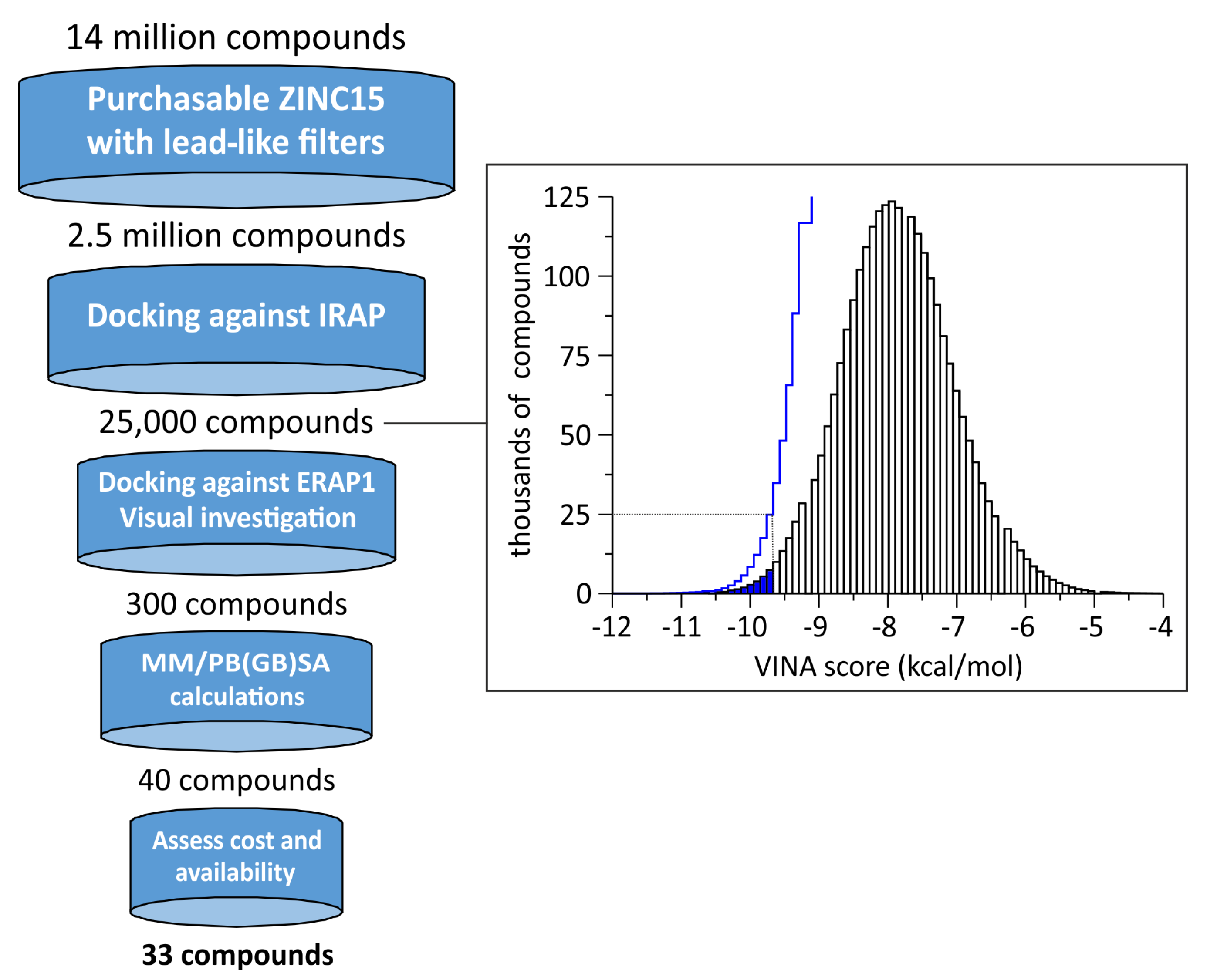
2.1. Selection of a Lead-Like Dataset
2.2. Virtual Screening of the Compounds
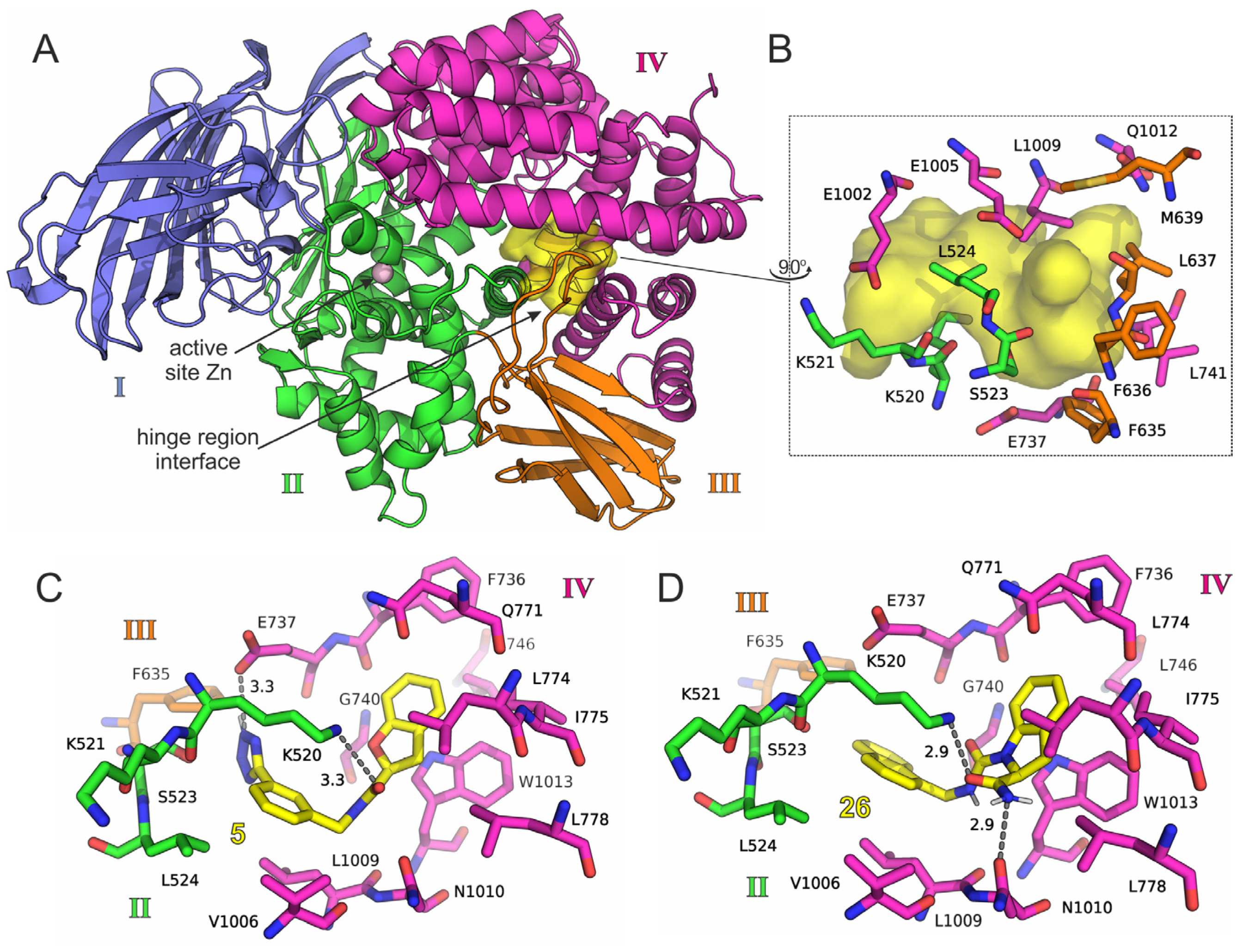
2.3. Free Energy Calculations
2.4. Final Selection of the Compounds for Evaluation
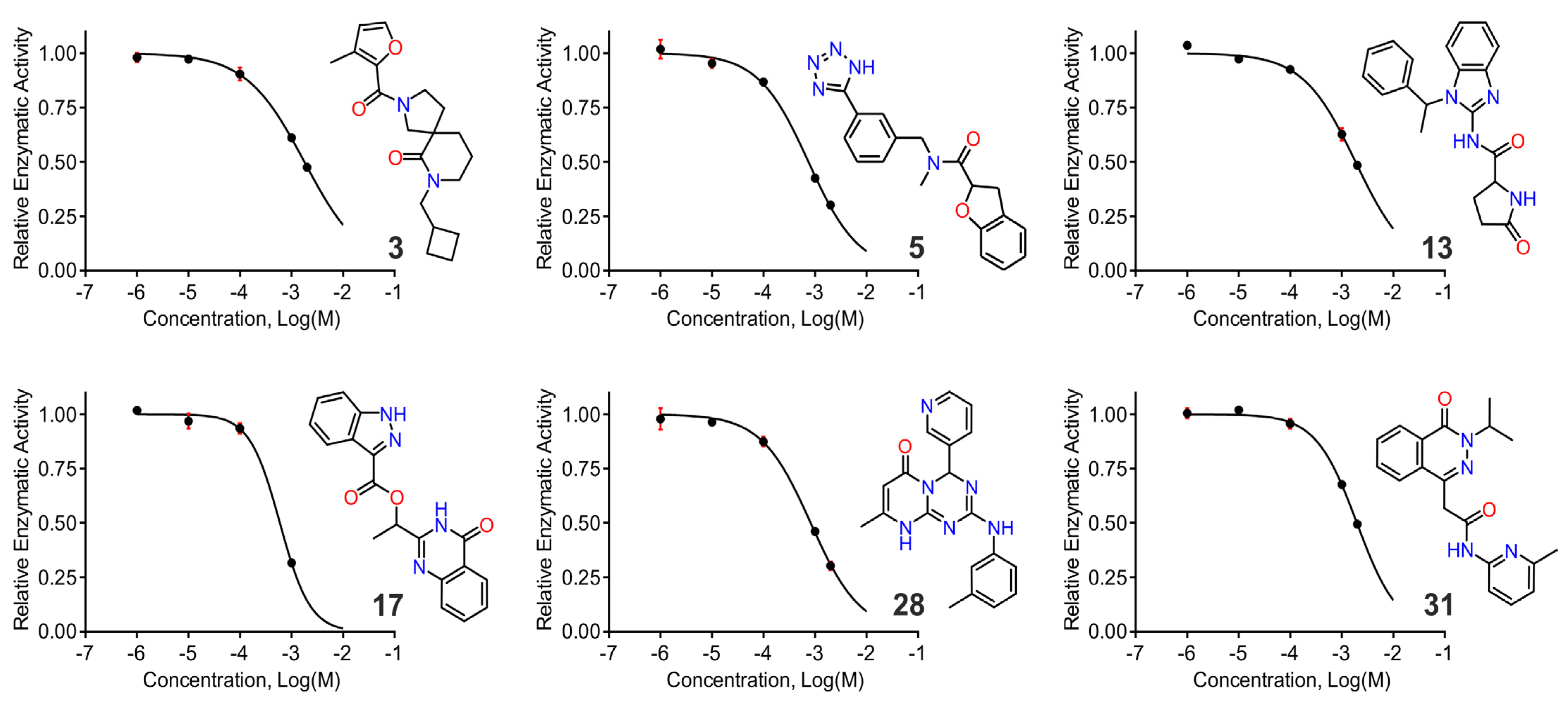
2.5. In Vitro Screening using a Small Fluorigenic Peptide
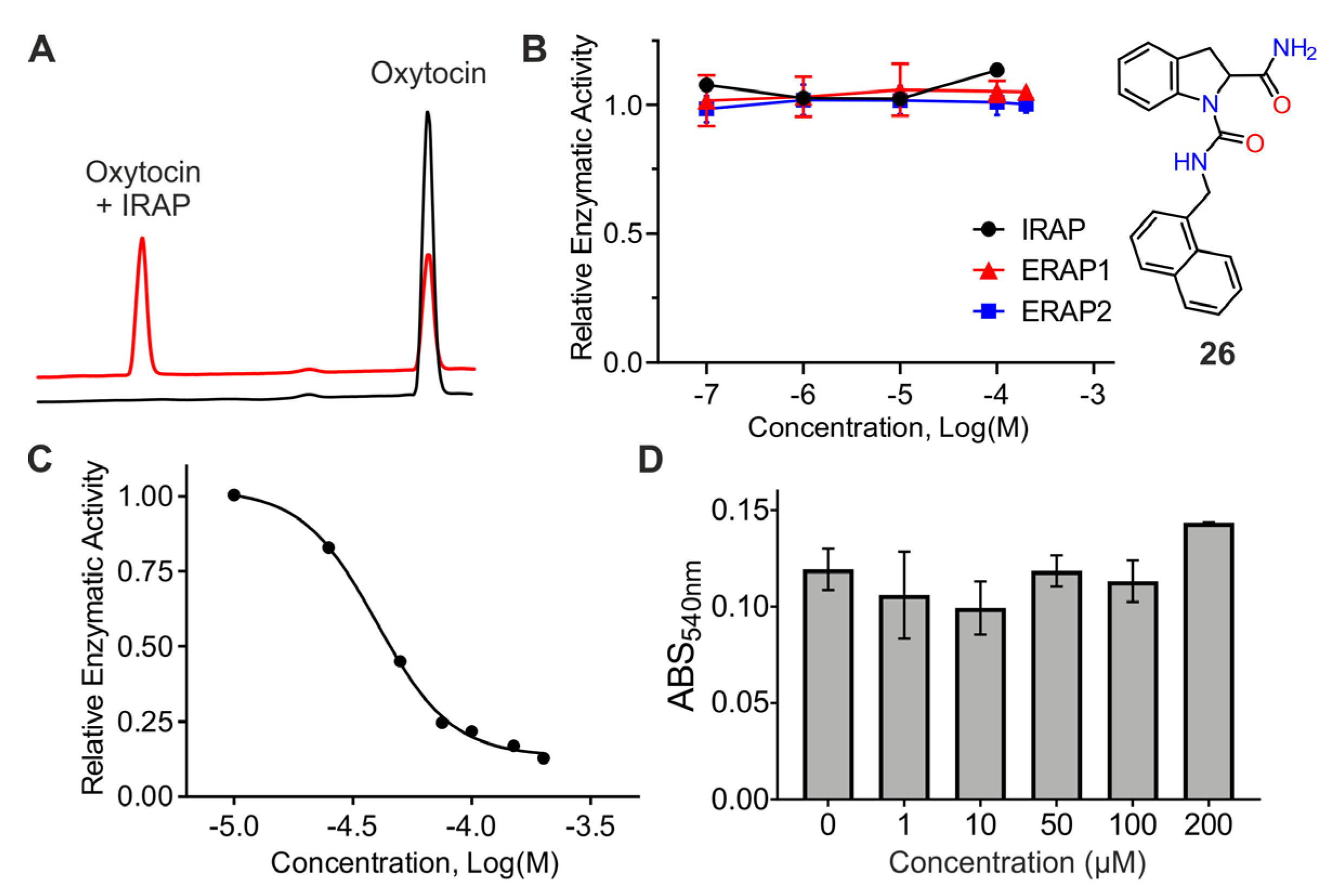
2.6. Inhibition of Oxytocin Trimming
2.7. Evaluation of Cellular Toxicity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Docking Calculations
4.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
4.3. Free energy Calculations
4.4. Protein Production and Purification
4.5. Enzymatic Assays
4.6. Inhibitors
4.7. Cellular Toxicity Assay
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keller, S.R. The insulin-regulated aminopeptidase: A companion and regulator of GLUT4. Front Biosci. 2003, 8, s410–s420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saveanu, L. IRAP Identifies an Endosomal Compartment Required for MHC Class I Cross-Presentation. Science 2009, 325, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albiston, A.L.; Morton, C.J.; Ng, H.L.; Pham, V.; Yeatman, H.R.; Ye, S.; Fernando, R.N.; De Bundel, D.; Ascher, D.B.; Mendelsohn, F.A.; et al. Identification and characterization of a new cognitive enhancer based on inhibition of insulin-regulated aminopeptidase. Faseb. J. 2008, 22, 4209–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimershaus, M.; Mauvais, F.X.; Evnouchidou, I.; Lawand, M.; Saveanu, L.; van Endert, P. IRAP Endosomes Control Phagosomal Maturation in Dendritic Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, S.Y.; Yeatman, H.R.; Parker, M.W.; Ascher, D.B.; Thompson, P.E.; Mulvey, H.T.; Albiston, A.L. Development of cognitive enhancers based on inhibition of insulin-regulated aminopeptidase. BMC Neurosci. 2008, 9 (Suppl. 2), S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiadis, D.; Ziotopoulou, A.; Kaloumenou, E.; Lelis, A.; Papasava, A. The Discovery of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase IRAP) Inhibitors: A Literature Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barlow, N.; Vanga, S.R.; Sävmarker, J.; Sandström, A.; Burns, P.; Hallberg, A.; Åqvist, J.; Gutiérrez-de-Terán, H.; Hallberg, M.; Larhed, M.; et al. Macrocyclic peptidomimetics as inhibitors of insulin-regulated aminopeptidase (IRAP). RSC Med. Chem. 2020, 11, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barlow, N.; Thompson, P.E. IRAP Inhibitors: M1-Aminopeptidase Family Inspiration. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallberg, M.; Larhed, M. From Angiotensin IV to Small Peptidemimetics Inhibiting Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, H.; Demaegdt, H.; Vauquelin, G.; Lindeberg, G.; Karlén, A.; Hallberg, M.; Erdélyi, M.; Hallberg, A. Disulfide cyclized tripeptide analogues of angiotensin IV as potent and selective inhibitors of insulin-regulated aminopeptidase (IRAP). J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 8059–8071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engen, K.; Rosenström, U.; Axelsson, H.; Konda, V.; Dahllund, L.; Otrocka, M.; Sigmundsson, K.; Nikolaou, A.; Vauquelin, G.; Hallberg, M.; et al. Identification of Drug-Like Inhibitors of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase Through Small-Molecule Screening. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2016, 14, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engen, K.; Vanga, S.R.; Lundbäck, T.; Agalo, F.; Konda, V.; Jensen, A.J.; Åqvist, J.; Gutiérrez-de-Terán, H.; Hallberg, M.; Larhed, M.; et al. Synthesis, Evaluation and Proposed Binding Pose of Substituted Spiro-Oxindole Dihydroquinazolinones as IRAP Inhibitors. ChemistryOpen 2020, 9, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mpakali, A.; Saridakis, E.; Harlos, K.; Zhao, Y.; Kokkala, P.; Georgiadis, D.; Giastas, P.; Papakyriakou, A.; Stratikos, E. Ligand-Induced Conformational Change of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase: Insights on Catalytic Mechanism and Active Site Plasticity. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpakali, A.; Saridakis, E.; Harlos, K.; Zhao, Y.; Papakyriakou, A.; Kokkala, P.; Georgiadis, D.; Stratikos, E. Crystal Structure of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase with Bound Substrate Analogue Provides Insight on Antigenic Epitope Precursor Recognition and Processing. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 2842–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giastas, P.; Neu, M.; Rowland, P.; Stratikos, E. High-Resolution Crystal Structure of Endoplasmic Reticulum Aminopeptidase 1 with Bound Phosphinic Transition-State Analogue Inhibitor. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liddle, J.; Hutchinson, J.P.; Kitchen, S.; Rowland, P.; Neu, M.; Cecconie, T.; Holmes, D.S.; Jones, E.; Korczynska, J.; Koumantou, D.; et al. Targeting the Regulatory Site of ER Aminopeptidase 1 Leads to the Discovery of a Natural Product Modulator of Antigen Presentation. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 3348–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burley, S.K.; Bhikadiya, C.; Bi, C.; Bittrich, S.; Chen, L.; Crichlow, G.V.; Christie, C.H.; Dalenberg, K.; Di Costanzo, L.; Duarte, J.M.; et al. RCSB Protein Data Bank: Powerful new tools for exploring 3D structures of biological macromolecules for basic and applied research and education in fundamental biology, biomedicine, biotechnology, bioengineering and energy sciences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D437–D451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterling, T.; Irwin, J.J. ZINC 15-Ligand Discovery for Everyone. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 2324–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baell, J.B.; Holloway, G.A. New substructure filters for removal of pan assay interference compounds (PAINS) from screening libraries and for their exclusion in bioassays. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2719–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Goodsell, D.S.; Halliday, R.S.; Huey, R.; Hart, W.E.; Belew, R.K.; Olson, A.J. Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J. Comput. Chem. 1998, 19, 1639–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, E.; Islam, Y.; James, E. ERAP1: A potential therapeutic target for a myriad of diseases. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2020, 24, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genheden, S.; Ryde, U. The MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA methods to estimate ligand-binding affinities. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2015, 10, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Greene, D.; Xiao, L.; Qi, R.; Luo, R. Recent developments and applications of the MMPBSA method. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2018, 4, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weis, A.; Katebzadeh, K.; Söderhjelm, P.; Nilsson, I.; Ryde, U. Ligand affinities predicted with the MM/PBSA method: Dependence on the simulation method and the force field. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6596–6606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. ILOGP: A simple, robust, and efficient description of n-octanol/water partition coefficient for drug design using the GB/SA approach. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 3284–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervoudi, E.; Papakyriakou, A.; Georgiadou, D.; Evnouchidou, I.; Gajda, A.; Poreba, M.; Salvesen, G.S.; Drag, M.; Hattori, A.; Swevers, L.; et al. Probing the S1 specificity pocket of the aminopeptidases that generate antigenic peptides. Biochem. J. 2011, 435, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervoudi, E.; Saridakis, E.; Birtley, J.R.J.R.R.; Seregin, S.S.S.S.; Reeves, E.; Kokkala, P.; Aldhamen, Y.A.Y.A.A.; Amalfitano, A.; Mavridis, I.M.I.M.M.; James, E.; et al. Rationally designed inhibitor targeting antigentrimming aminopeptidases enhances antigen presentation and cytotoxic T-cell responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 19890–19895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakyriakou, A.; Stratikos, E. The role of conformational dynamics in antigen trimming by intracellular aminopeptidases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogi, T.; Tsujimoto, M.; Nakazato, H.; Mizutani, S.; Tomoda, Y. Human placental leucine aminopeptidase/oxytocinase. A new member of type II membrane-spanning zinc metallopeptidase family. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockert, J.C.; Horobin, R.W.; Colombo, L.L.; Blázquez-Castro, A. Tetrazolium salts and formazan products in Cell Biology: Viability assessment, fluorescence imaging, and labeling perspectives. Acta Histochem. 2018, 120, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpakali, A.; Saridakis, E.; Giastas, P.; Maben, Z.; Stern, L.J.; Larhed, M.; Hallberg, M.; Stratikos, E. Structural Basis of Inhibition of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase by a Macrocyclic Peptidic Inhibitor. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Comparative Protein Structure Modeling Using MODELLER. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2016, 86, 291–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandakrishnan, R.; Aguilar, B.; Onufriev, A. V H++ 3.0: Automating pK prediction and the preparation of biomolecular structures for atomistic molecular modeling and simulations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W537–W541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon-Ferrer, R.; Gotz, A.W.; Poole, D.; Le Grand, S.; Walker, R.C. Routine Microsecond Molecular Dynamics Simulations with AMBER on GPUs. 2. Explicit Solvent Particle Mesh Ewald. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 3878–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, D.A.; Cheatham, T.E.; Darden, T.; Gohlke, H.; Luo, R.; Merz, K.M.; Onufriev, A.; Simmerling, C.; Wang, B.; Woods, R.J. The Amber biomolecular simulation programs. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1668–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K.E.; Simmerling, C. ff14SB: Improving the Accuracy of Protein Side Chain and Backbone Parameters from ff99SB. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Development and testing of a general amber force field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakalian, A.; Jack, D.B.; Bayly, C.I. Fast, efficient generation of high-quality atomic charges. AM1-BCC model: II. Parameterization and validation. J. Comput. Chem. 2002, 23, 1623–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamogiannos, A.; Maben, Z.; Papakyriakou, A.; Mpakali, A.; Kokkala, P.; Georgiadis, D.; Stern, L.J.L.J.; Stratikos, E. Critical Role of Interdomain Interactions in the Conformational Change and Catalytic Mechanism of Endoplasmic Reticulum Aminopeptidase 1. Biochemistry 2017, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giastas, P.; Mpakali, A.; Papakyriakou, A.; Lelis, A.; Kokkala, P.; Neu, M.; Rowland, P.; Liddle, J.; Georgiadis, D.; Stratikos, E. Mechanism for antigenic peptide selection by endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, D.R.; Cheatham, T.E. PTRAJ and CPPTRAJ: Software for Processing and Analysis of Molecular Dynamics Trajectory Data. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 3084–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollman, P.A.; Massova, I.; Reyes, C.; Kuhn, B.; Huo, S.; Chong, L.; Lee, M.; Lee, T.; Duan, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. Calculating structures and free energies of complex molecules: Combining molecular mechanics and continuum models. Acc. Chem. Res. 2000, 33, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Nguyen, P.H.; Pham, K.; Huynh, D.; Le, T.B.N.; Wang, H.; Ren, P.; Luo, R. Calculating protein-ligand binding affinities with MMPBSA: Method and error analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2016, 37, 2436–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foloppe, N.; Hubbard, R. Towards Predictive Ligand Design with Free-Energy Based Computational Methods? Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 3583–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Wu, J.C.; Yan, C.; Wang, Y.; Luo, R.; Gonzales, M.B.; Dalby, K.N.; Ren, P. Virtual screening using molecular simulations. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2011, 79, 1940–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Tan, Y.H.; Luo, R. Implicit nonpolar solvent models. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 12263–12274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, V.; Case, D.A. Theory and applications of the generalized Born solvation model in macromolecular simulations. Biopolymers 2000, 56, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, M.L. Analytical molecular surface calculation. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1983, 16, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, G.D.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. Parametrized models of aqueous free energies of solvation based on pairwise descreening of solute atomic charges from a dielectric medium. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 19824–19839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiser, J.; Shenkin, P.S.; Still, W.C. Approximate atomic surfaces from linear combinations of pairwise overlaps (LCPO). J. Comput. Chem. 1999, 20, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onufriev, A.; Bashford, D.; Case, D.A. Exploring protein native states and large-scale conformational changes with a modified generalized born model. Proteins 2004, 55, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Yang, L.; Luo, R. How well does Poisson-Boltzmann implicit solvent agree with explicit solvent? A quantitative analysis. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 18680–18687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpakali, A.; Giastas, P.; Mathioudakis, N.; Mavridis, I.M.; Saridakis, E.; Stratikos, E. Structural basis for antigenic peptide recognition and processing by Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) aminopeptidase 2. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 26021–26032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| ID | MolPort ID | MW | logP a | VINA Score | MM/PBSA ΔGbind | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRAP | ERAP1 | PB-1 (Rank) | PB-4 (Rank) | ||||
| 1 | MolPort-027-863-667 | 342.4 | 2.85 | –10.2 | –7.5 | –1.3 (#105) | –30.3 (#59) |
| 2 | MolPort-039-039-060 | 331.4 | 2.38 | –11.0 | –9.2 | –8.1 (#17) | –31.5 (#41) |
| 3 | MolPort-005-163-536 | 330.4 | 3.45 | –9.9 | –7.1 | –10.8 (#6) | –32.6 (#29) |
| 4 | MolPort-027-857-260 | 341.5 | 2.96 | –9.9 | –7.4 | –7.8 (#20) | –36.9 (#3) |
| 5 | MolPort-038-425-524 | 335.4 | 2.34 | –11.0 | –8.9 | –7.5 (#22) | –33.5 (#17) |
| 6 | MolPort-006-484-933 | 335.4 | 2.71 | –9.9 | –7.4 | –14.1 (#2) | –38.7 (#1) |
| 7 | MolPort-007-773-311 | 323.4 | 3.2 | –10.6 | –8.1 | –5.0 (#42) | –29.1 (#78) |
| 8 | MolPort-027-906-298 | 332.4 | 2.75 | –10.2 | –7.4 | –7.4 (#23) | –32.5 (#31) |
| 9 | MolPort-035-834-132 | 348.4 | 3.07 | –11.1 | –10.0 | –4.5 (#51) | –35.4 (#9) |
| 10 | MolPort-020-152-989 | 348.4 | 2.96 | –10.4 | –7.9 | –9.8 (#9) | –33.7 (#14) |
| 11 | MolPort-019-674-325 | 338.4 | 2.19 | –11.1 | –8.0 | –8.0 (#19) | –32.6 (#30) |
| 12 | MolPort-020-162-189 | 330.4 | 2.15 | –10.9 | –9.5 | –5.0 (#43) | –27.2 (#119) |
| 13 | MolPort-028-771-825 | 348.4 | 1.58 | –11.1 | –8.5 | –6.5 (#27) | –35.4 (#8) |
| 14 | MolPort-009-543-745 | 326.3 | 2.42 | –10.9 | –8.5 | –8.0 (#18) | –29.5 (#72) |
| 15 | MolPort-004-188-947 | 333.5 | 2.97 | –10.1 | –7.1 | 0.3 (#142) | –26.4 (#137) |
| 16 | MolPort-027-679-372 | 332.4 | 2.77 | –10.9 | –9.5 | –10.5 (#8) | –36.2 (#6) |
| 17 | MolPort-005-610-771 | 334.3 | 1.59 | –10.9 | –9.6 | –9.7 (#10) | –36.0 (#7) |
| 18 | MolPort-009-519-757 | 345.4 | 2.34 | –10.9 | –8.7 | –5.1 (#41) | –33.1 (#22) |
| 19 | MolPort-039-259-003 | 322.4 | 1.78 | –10.9 | –8.6 | –7.0 (#25) | –32.2 (#32) |
| 20 | MolPort-009-450-517 | 346.4 | 2.62 | –10.9 | –9.2 | –9.2 (#12) | –35.1 (#10) |
| 21 | MolPort-004-164-037 | 349.5 | 3.37 | –10.8 | –8.1 | –7.3 (#24) | –37.7 (#2) |
| 22 | MolPort-027-704-758 | 324.4 | 1.77 | –10.5 | –8.0 | –13.9 (#3) | –36.3 (#4) |
| 23 | MolPort-020-057-841 | 333.4 | 2.94 | –10.9 | –9.2 | –5.8 (#33) | –32.9 (#25) |
| 24 | MolPort-009-027-892 | 347.4 | 3.02 | –10.7 | –8.1 | –3.0 (#75) | –31.0 (#46) |
| 25 | MolPort-020-053-566 | 338.4 | 2.87 | –9.8 | –7.1 | –7.7 (#21) | –33.2 (#20) |
| 26 | MolPort-003-173-337 | 345.4 | 2.34 | –11.0 | –9.7 | –15.7 (#1) | –34.3 (#13) |
| 27 | MolPort-003-801-767 | 332.4 | 1.81 | –10.9 | –9.0 | –8.3 (#16) | –33.6 (#15) |
| 28 | MolPort-000-832-181 | 346.4 | 2.82 | –10.9 | –9.3 | –3.9 (#68) | –30.8 (#53) |
| 29 | MolPort-000-828-576 | 333.4 | 2.72 | –10.9 | –8.3 | –4.7 (#50) | –29.3 (#75) |
| 30 | MolPort-000-694-123 | 336.4 | 2.95 | –10.2 | –7.7 | –9.5 (#11) | –33.4 (#18) |
| 31 | MolPort-023-297-297 | 336.4 | 2.91 | –10.4 | –7.8 | –10.5 (#7) | –34.4 (#12) |
| 32 | MolPort-000-407-697 | 325.4 | 3.47 | –10.1 | –7.6 | –8.6 (#14) | –28.5 (#92) |
| 33 | MolPort-001-905-390 | 323.4 | 3.06 | –10.3 | –7.7 | –4.4 (#53) | –31.0 (#50) |
| ID | IC50 (μM) | ID | IC50 (μM) | ID | IC50 (μM) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRAP | ERAP1 | ERAP2 | IRAP | ERAP1 | ERAP2 | IRAP | ERAP1 | ERAP2 | |||
| 1 | >300 a | - | - | 12 | NI | - | - | 23 | >300 a | - | - |
| 2 | NI | - | - | 13 | 192 ± 21 | NI | >300 a | 24 | >300 a | - | - |
| 3 | 192 ± 35 | NI | 65 ± 5 | 14 | NI | - | - | 25 | NI | - | - |
| 4 | NI | - | - | 15 | NI | - | - | 26 | NI | - | - |
| 5 | 76 ± 9 | NI | >300 a | 16 | NI | - | - | 27 | NI | - | - |
| 6 | NI | - | - | 17 | 56 ± 6 | NI | 280 ± 54 | 28 | 92 ± 10 | NI | >300 a |
| 7 | NI | - | - | 18 | >300 a | - | - | 29 | NI | - | - |
| 8 | NI | - | - | 19 | >300 a | - | - | 30 | NI | - | - |
| 9 | NI | - | - | 20 | >300 a | - | - | 31 | 194 ± 24 | NI | >300 a |
| 10 | NI | - | - | 21 | NI | - | - | 32 | NI | - | - |
| 11 | >300 a | - | - | 22 | >300 a | - | - | 33 | NI | - | - |
| ID | % Inhibition | ID | % Inhibition | ID | % Inhibition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 12 | 44 | 23 | 26 |
| 2 | 26 | 13 | 10 | 24 | 0 |
| 3 | 7 | 14 | 25 | 25 | 14 |
| 4 | 11 | 15 | 9 | 26 | 69 |
| 5 | 17 | 16 | 32 | 27 | 32 |
| 6 | 15 | 17 | 23 | 28 | n.d. |
| 7 | 0 | 18 | 0 | 29 | 39 |
| 8 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 30 | 22 |
| 9 | 30 | 20 | 34 | 31 | 10 |
| 10 | 0 | 21 | 14 | 32 | 28 |
| 11 | 13 | 22 | 0 | 33 | 10 |
| KE552 | 38 | ΚΕ552a | 10 | DG013Ab | 100 |
| Alias | Gpol Method | Atomic Radii | Gnp Method | SASA c | γ | b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PB-1 | PBSA a | TL-mbondi b | Equation (4) | PBSA d | 0.03780 | −0.5692 |
| PB-4 | PBSA a | mbondi [50] | Equation (3) | Molsurf [51] | 0.00720 | 0.0000 |
| GB-1 | GBHTC [52] | mbondi [50] | Equation (3) | LCPO [53] | 0.00720 | 0.0000 |
| GB-5 | GBOTC-II [54] | mbondi2 [54] | Equation (3) | LCPO [53] | 0.00500 | 0.0000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Temponeras, I.; Chiniadis, L.; Papakyriakou, A.; Stratikos, E. Discovery of Selective Inhibitor Leads by Targeting an Allosteric Site in Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060584
Temponeras I, Chiniadis L, Papakyriakou A, Stratikos E. Discovery of Selective Inhibitor Leads by Targeting an Allosteric Site in Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(6):584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060584
Chicago/Turabian StyleTemponeras, Ioannis, Lykourgos Chiniadis, Athanasios Papakyriakou, and Efstratios Stratikos. 2021. "Discovery of Selective Inhibitor Leads by Targeting an Allosteric Site in Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 6: 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060584
APA StyleTemponeras, I., Chiniadis, L., Papakyriakou, A., & Stratikos, E. (2021). Discovery of Selective Inhibitor Leads by Targeting an Allosteric Site in Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase. Pharmaceuticals, 14(6), 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060584








