Simulating Costs of Intravenous Biosimilar Trastuzumab vs. Subcutaneous Reference Trastuzumab in Adjuvant HER2-Positive Breast Cancer: A Belgian Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gianni, L.; Dafni, U.; Gelber, R.D.; Azambuja, E.; Muehlbauer, S.; Goldhirsch, A.; Untch, M.; Smith, I.; Baselga, J.; Jackisch, C.; et al. Treatment with trastuzumab for 1 year after adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer: A 4-year follow-up of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marty, M.; Cognetti, F.; Maraninchi, D.; Snyder, R.; Mauriac, L.; Tubiana-Hulin, M.; Chan, S.; Grimes, D.; Anton, A.; Lluch, A.; et al. Randomized phase II trial of the efficacy and safety of trastuzumab combined with docetaxel in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive metastatic breast cancer administered as first-line treatment: The M77001 study group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 4265–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slamon, D.J.; Leyland-Jones, B.; Shak, S.; Fuchs, H.; Paton, V.; Bajamonde, A.; Fleming, T.; Eiermann, W.; Wolter, J.; Pegram, M.; et al. Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccart-Gebhart, M.J.; Procter, M.; Leyland-Jones, B.; Goldhirsch, A.; Untch, M.; Smith, I.; Gianni, L.; Baselga, J.; Bell, R.; Jackisch, C.; et al. Trastuzumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in HER2-positive breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1659–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romond, E.H.; Perez, E.A.; Bryant, J.; Suman, V.J.; Geyer, C.E., Jr.; Davidson, N.E.; Tan-Chiu, E.; Martino, S.; Paik, S.; Kaufman, P.A.; et al. Trastuzumab plus adjuvant chemotherapy for operable HER2-positive breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1673–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismael, G.; Hegg, R.; Muehlbauer, S.; Heinzmann, D.; Lum, B.; Kim, S.B.; Pienkowski, T.; Lichinitser, M.; Semiglazov, V.; Melichar, B.; et al. Subcutaneous versus intravenous administration of (neo)adjuvant trastuzumab in patients with HER2-positive, clinical stage I-III breast cancer (HannaH study): A phase 3, open-label, multicentre, randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackisch, C.; Hegg, R.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Ahn, J.S.; Melichar, B.; Chen, S.C.; Kim, S.B.; Lichinitser, M.; Staroslawska, E.; Kunz, G.; et al. HannaH phase III randomised study: Association of total pathological complete response with event-free survival in HER2-positive early breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant-adjuvant trastuzumab after 2 years of treatment-free follow-up. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 62, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartino, A.L.; Hillenbach, C.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Wada, R.D.; Visich, J.; Li, C.; Heinzmann, D.; Jin, J.Y.; Lum, B.L. Population pharmacokinetic and exposure-response analysis for trastuzumab administered using a subcutaneous “manual syringe” injection or intravenously in women with HER2-positive early breast cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 77, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackisch, C.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Pivot, X.; Ahn, J.S.; Melichar, B.; Chen, S.C.; Meyenberg, C.; Al-Sakaff, N.; Heinzmann, D.; Hegg, R. Subcutaneous vs Intravenous Trastuzumab for Patients With ERBB2-Positive Early Breast Cancer: Final Analysis of the HannaH Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, e190339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivot, X.; Spano, J.P.; Espie, M.; Cottu, P.; Jouannaud, C.; Pottier, V.; Moreau, L.; Extra, J.M.; Lortholary, A.; Rivera, P.; et al. Patients’ preference of trastuzumab administration (subcutaneous versus intravenous) in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer: Results of the randomised MetaspHer study. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 82, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivot, X.; Verma, S.; Fallowfield, L.; Muller, V.; Lichinitser, M.; Jenkins, V.; Sanchez Munoz, A.; Machackova, Z.; Osborne, S.; Gligorov, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of subcutaneous trastuzumab and intravenous trastuzumab as part of adjuvant therapy for HER2-positive early breast cancer: Final analysis of the randomised, two-cohort PrefHer study. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 86, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche. Roche Reports Solid Results in 2020. Available online: https://www.roche.com/dam/jcr:6014f1d7-ea74-4f59-bbbc-25e071a6866f/en/210204_IR_FY2020_EN.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Tjalma, W.; Huizing, M.T.; Papadimitriou, K. The smooth and bumpy road of trastuzumab administration: From intravenous (IV) in a hospital to subcutaneous (SC) at home. Facts Views Vis. Obgyn 2017, 9, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kadam, V.; Bagde, S.; Karpe, M.; Kadam, V. A Comprehensive Overview on Biosimilars. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2016, 17, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, L.; Declerck, P.; Simoens, S.; Neven, P.; Vulto, A.G.; Huys, I. The arrival of biosimilar monoclonal antibodies in oncology: Clinical studies for trastuzumab biosimilars. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjalma, W.A.A.; Van den Mooter, T.; Mertens, T.; Bastiaens, V.; Huizing, M.T.; Papadimitriou, K. Subcutaneous trastuzumab (Herceptin) versus intravenous trastuzumab for the treatment of patients with HER2-positive breast cancer: A time, motion and cost assessment study in a lean operating day care oncology unit. Eur. J. Obstet Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2018, 221, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farolfi, A.; Silimbani, P.; Gallegati, D.; Petracci, E.; Schirone, A.; Altini, M.; Masini, C. Resource utilization and cost saving analysis of subcutaneous versus intravenous trastuzumab in early breast cancer patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 81343–81349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaro Cebas, A.; Cortijo Cascajares, S.; Pablos Bravo, S.; Del Puy Goyache Goni, M.; Gonzalez Monterrubio, G.; Perez Cardenas, M.D.; Ferrari Piquero, J.M. Subcutaneous versus intravenous administration of trastuzumab: Preference of HER2+ breast cancer patients and financial impact of its use. J. BUON 2017, 22, 334–339. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Vivanco, G.; Salvador, J.; Diez, R.; Lopez, D.; De Salas-Cansado, M.; Navarro, B.; De la Haba-Rodriguez, J. Cost minimization analysis of treatment with intravenous or subcutaneous trastuzumab in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer in Spain. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 19, 1454–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, S.; Norrlid, H.; Karlsson, E.; Wilking, U.; Ragnarson Tennvall, G. Societal cost of subcutaneous and intravenous trastuzumab for HER2-positive breast cancer—An observational study prospectively recording resource utilization in a Swedish healthcare setting. Breast 2016, 29, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall, P.; Koch, T.; Gohler, T.; Selbach, J.; Ammon, A.; Eggert, J.; Gazawi, N.; Rezek, D.; Wischnik, A.; Hielscher, C.; et al. Trastuzumab without chemotherapy in the adjuvant treatment of breast cancer: Subgroup results from a large observational study. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seferina, S.C.; Lobbezoo, D.J.; de Boer, M.; Dercksen, M.W.; van den Berkmortel, F.; van Kampen, R.J.; van de Wouw, A.J.; de Vries, B.; Joore, M.A.; Peer, P.G.; et al. Real-Life Use and Effectiveness of Adjuvant Trastuzumab in Early Breast Cancer Patients: A Study of the Southeast Netherlands Breast Cancer Consortium. Oncologist 2015, 20, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, R.M.; Abraham, J.; Palaniappan, N.; Caley, A.; Jasani, B.; Barrett-Lee, P. Exploring the use and impact of adjuvant trastuzumab for HER2-positive breast cancer patients in a large UK cancer network. Do the results of international clinical trials translate into a similar benefit for patients in South East Wales? Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inotai, A.; Agh, T.; Karpenko, A.W.; Zemplenyi, A.; Kalo, Z. Behind the subcutaneous trastuzumab hype: Evaluation of benefits and their transferability to Central Eastern European countries. Expert Rev. Pharmacoecon. Outcomes Res. 2019, 19, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agirrezabal, I.; Gaikwad, I.; Cirillo, L.; Lothgren, M. Predicted treatment costs and savings per patient of Kanjinti (trastuzumab biosimilar) vs. subcutaneous (SC) and intravenous (IV) Herceptin and other trastuzumab biosimilars in Italy. Value Health 2018, 21, S31–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoens, S. How do biosimilars sustain value, affordability, and access to oncology care? Expert Rev. Pharmacoecon. Outcomes Res. 2020, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute for Health and Disability Insurance. Reduction to 85% for the Purpose of Invoicing of Specific Medicines in Hospital. Available online: https://www.riziv.fgov.be/nl/professionals/andere-professionals/farmaceutische-industrie/Paginas/terugbetaling-geneesmiddelen-01042019.aspx (accessed on 17 February 2021).
- Belgian Centre for Pharmacotherapeutic Information. Your Independent Medicines Guide. Available online: https://www.bcfi.be/nl/start (accessed on 16 February 2021).
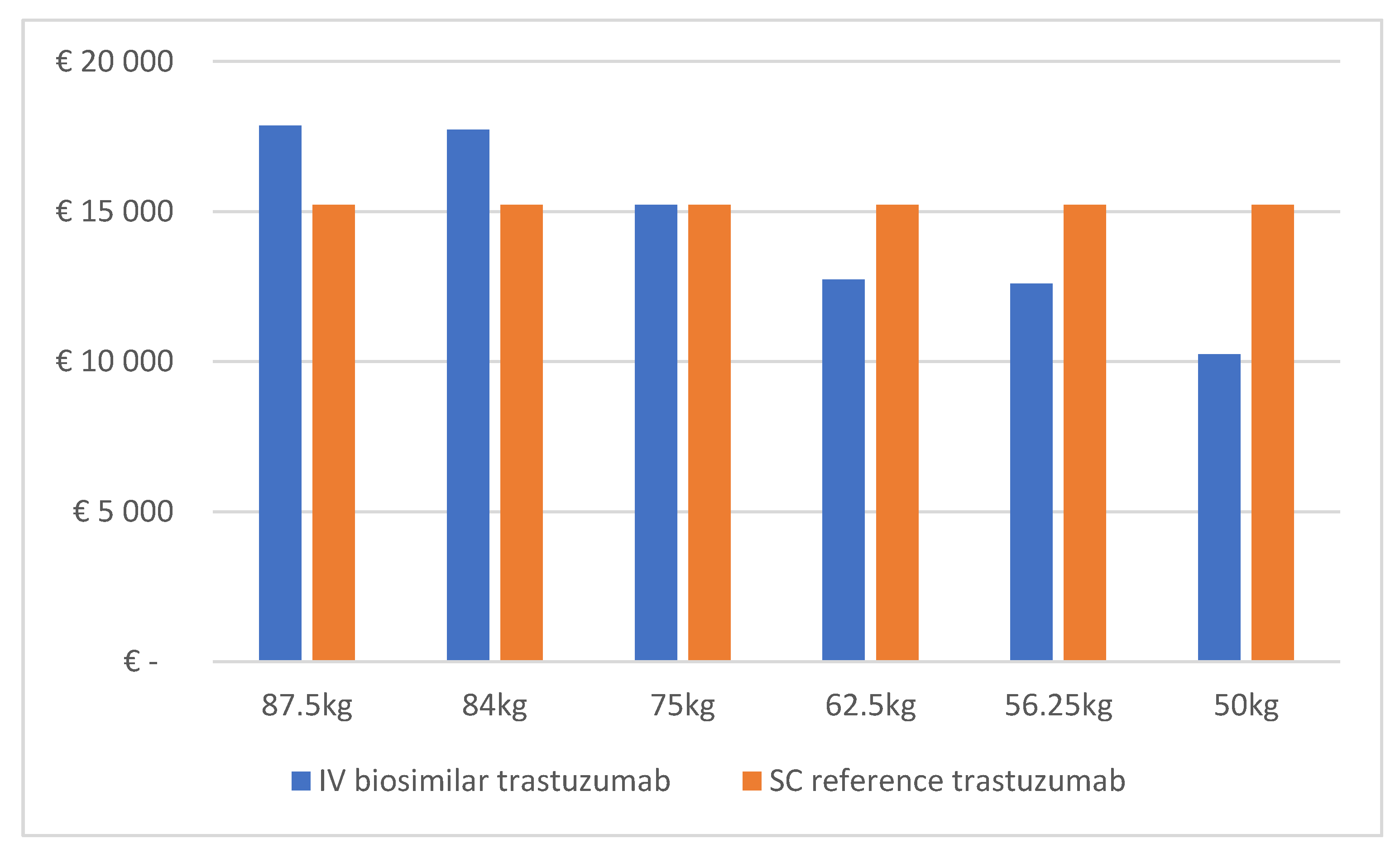
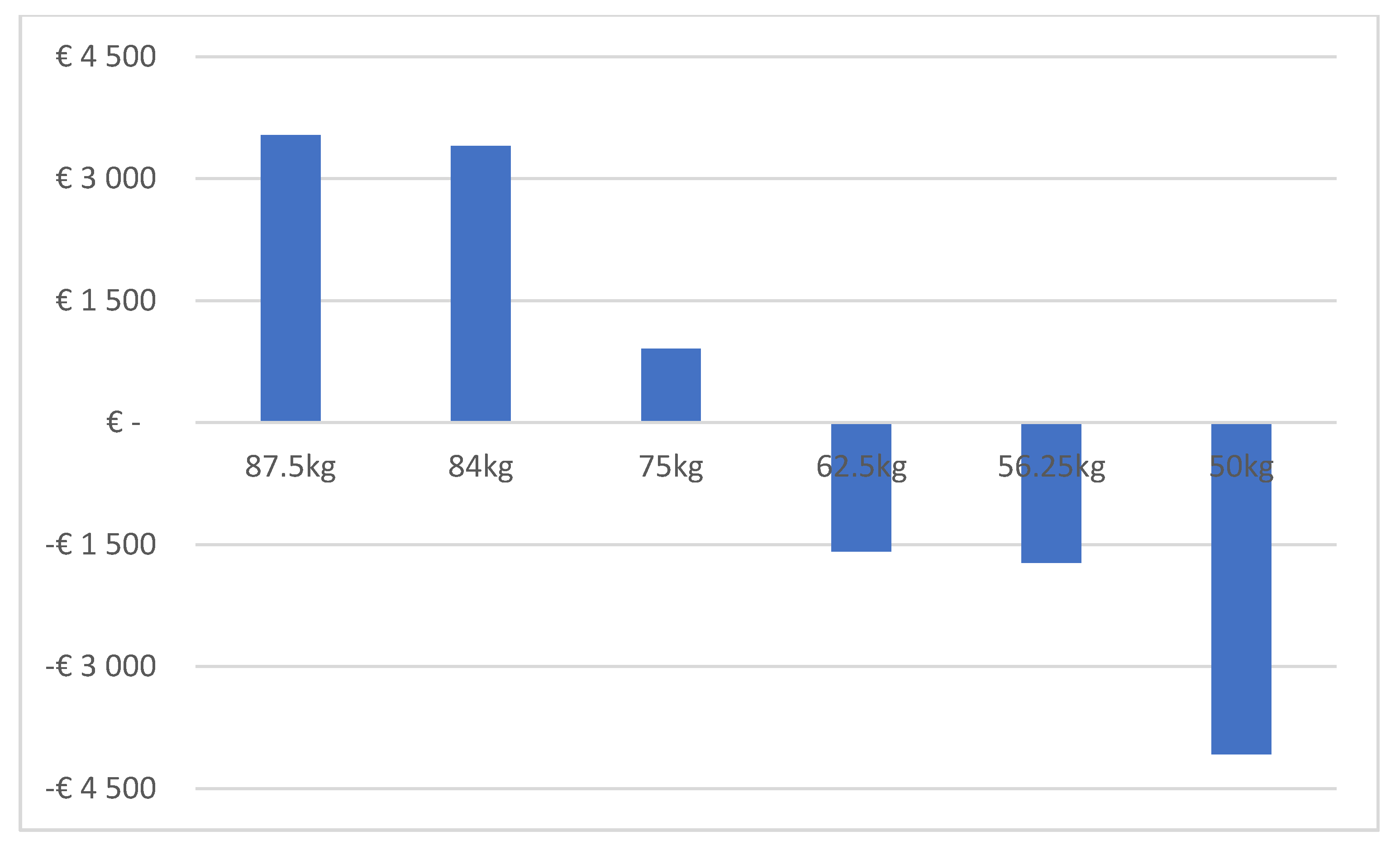
| Base Case | Scenario with 20% Discount on IV Biosimilar and on SC Reference Trastuzumab | Scenario with 35% Discount on IV Biosimilar and 20% Discount on SC Reference Trastuzumab | Scenario with 35% Discount on IV Biosimilar and on SC Reference Trastuzumab | Scenario with 50% Discount on IV Biosimilar and 20% Discount on SC Reference Trastuzumab | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug costs | |||||
| IV | €1,431,282 | €1,145,026 | €930,333 | €930,333 | €715,641 |
| SC | €1,522,809 | €1,218,247 | €1,218,247 | €989,826 | €1,218,247 |
| IV-SC | −€91,527 | −€73,222 | −€287,914 | −€59,493 | −€502,606 |
| Healthcare costs | |||||
| IV-SC | −€807 | €17,498 | −€197,194 | €31,227 | −€411,886 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simoens, S.; Vulto, A.G.; Dylst, P. Simulating Costs of Intravenous Biosimilar Trastuzumab vs. Subcutaneous Reference Trastuzumab in Adjuvant HER2-Positive Breast Cancer: A Belgian Case Study. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050450
Simoens S, Vulto AG, Dylst P. Simulating Costs of Intravenous Biosimilar Trastuzumab vs. Subcutaneous Reference Trastuzumab in Adjuvant HER2-Positive Breast Cancer: A Belgian Case Study. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(5):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050450
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimoens, Steven, Arnold G. Vulto, and Pieter Dylst. 2021. "Simulating Costs of Intravenous Biosimilar Trastuzumab vs. Subcutaneous Reference Trastuzumab in Adjuvant HER2-Positive Breast Cancer: A Belgian Case Study" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 5: 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050450
APA StyleSimoens, S., Vulto, A. G., & Dylst, P. (2021). Simulating Costs of Intravenous Biosimilar Trastuzumab vs. Subcutaneous Reference Trastuzumab in Adjuvant HER2-Positive Breast Cancer: A Belgian Case Study. Pharmaceuticals, 14(5), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050450






