In Vitro Synergistic Inhibition of HT-29 Proliferation and 2H-11 and HUVEC Tubulogenesis by Bacopaside I and II Is Associated with Ca2+ Flux and Loss of Plasma Membrane Integrity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. IC50 Values for Bac I and II, Singly and Combined, Differed between Cell Lines
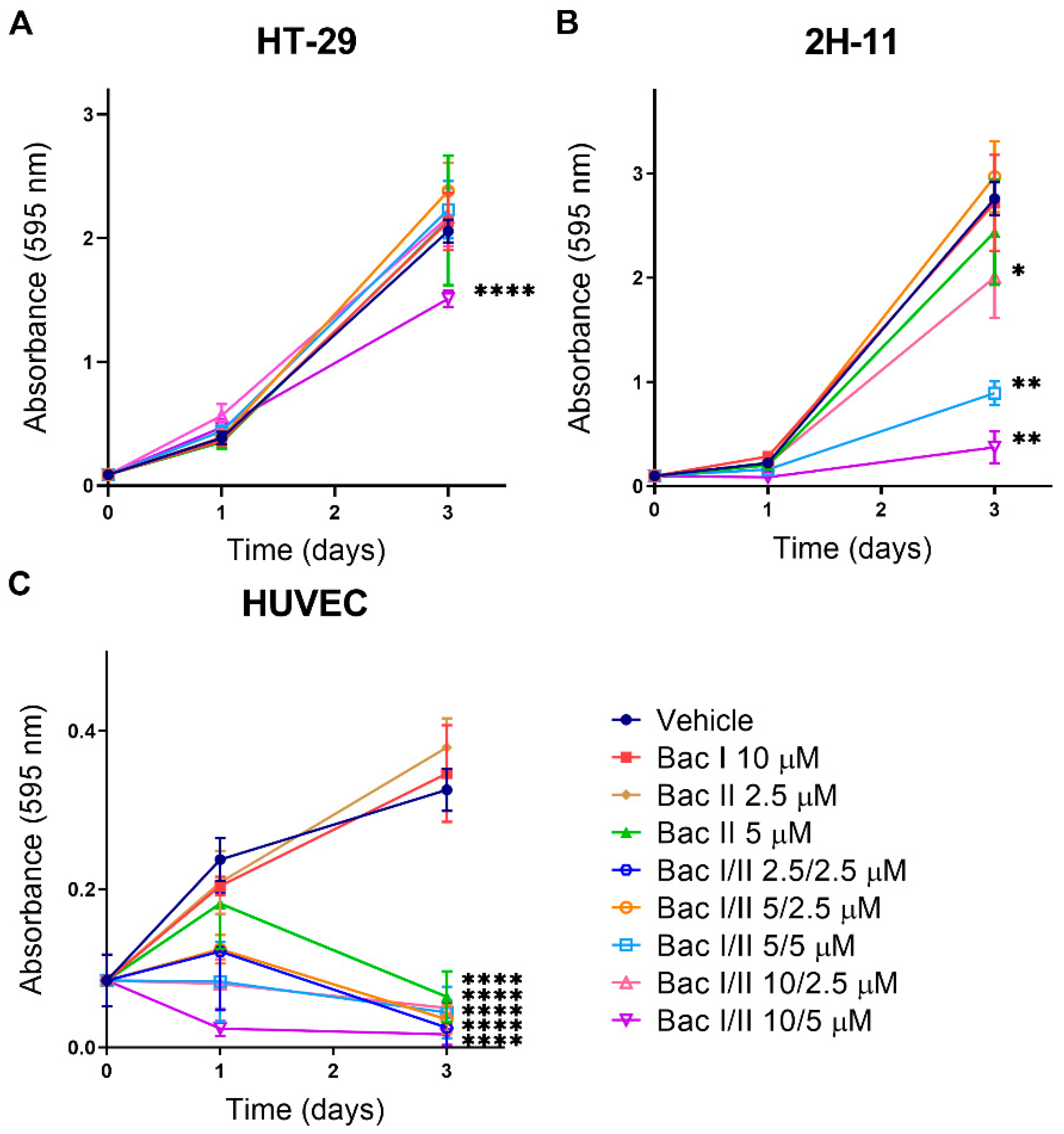
2.2. Bac I and II Combined Impaired Cell Proliferation of Colon Cancer and Endothelial Cells
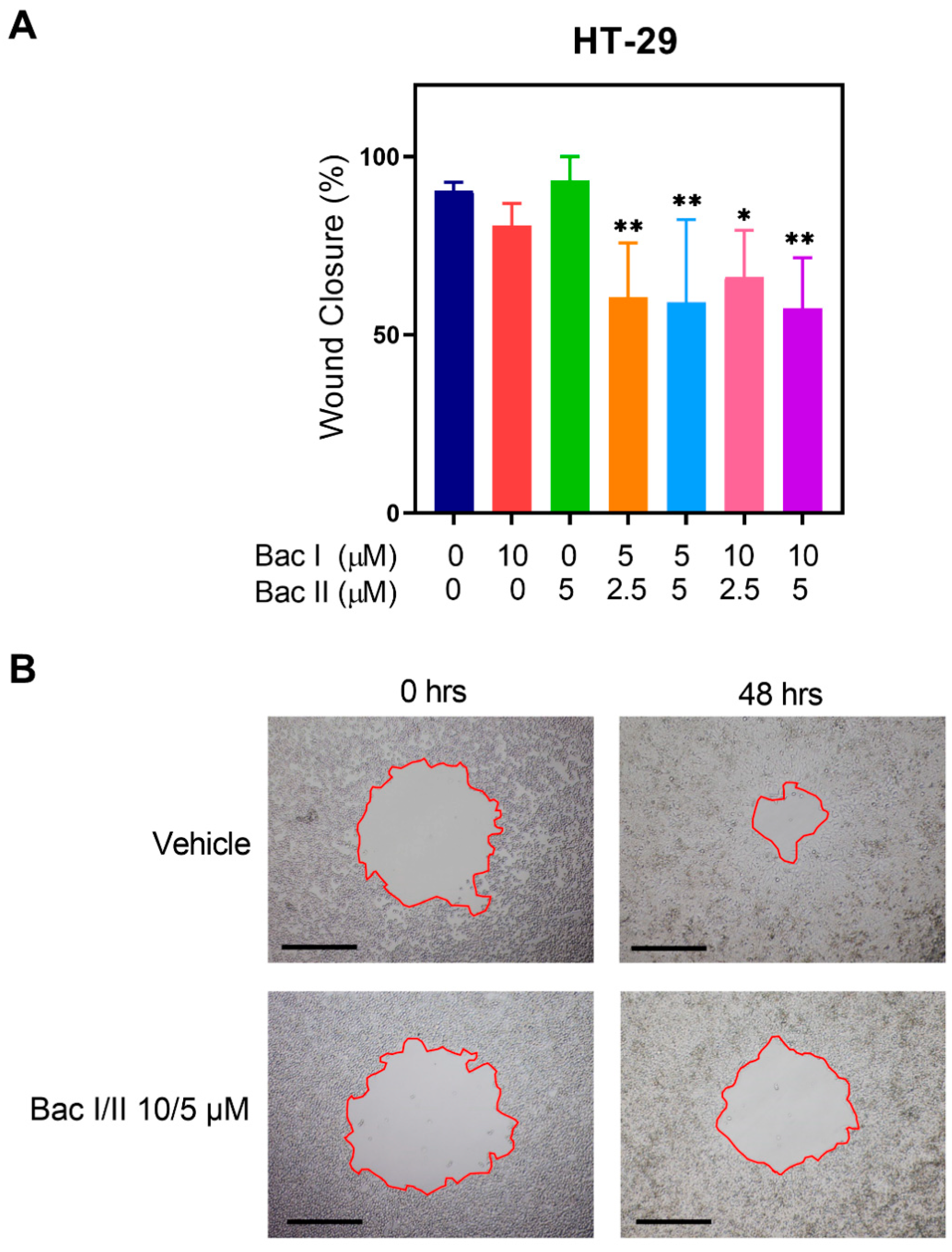
2.3. Bac I and II Combined Reduced Migration of Colon Cancer Cells
2.4. Bac I and II Combined Reduced Endothelial Cell Tube Formation
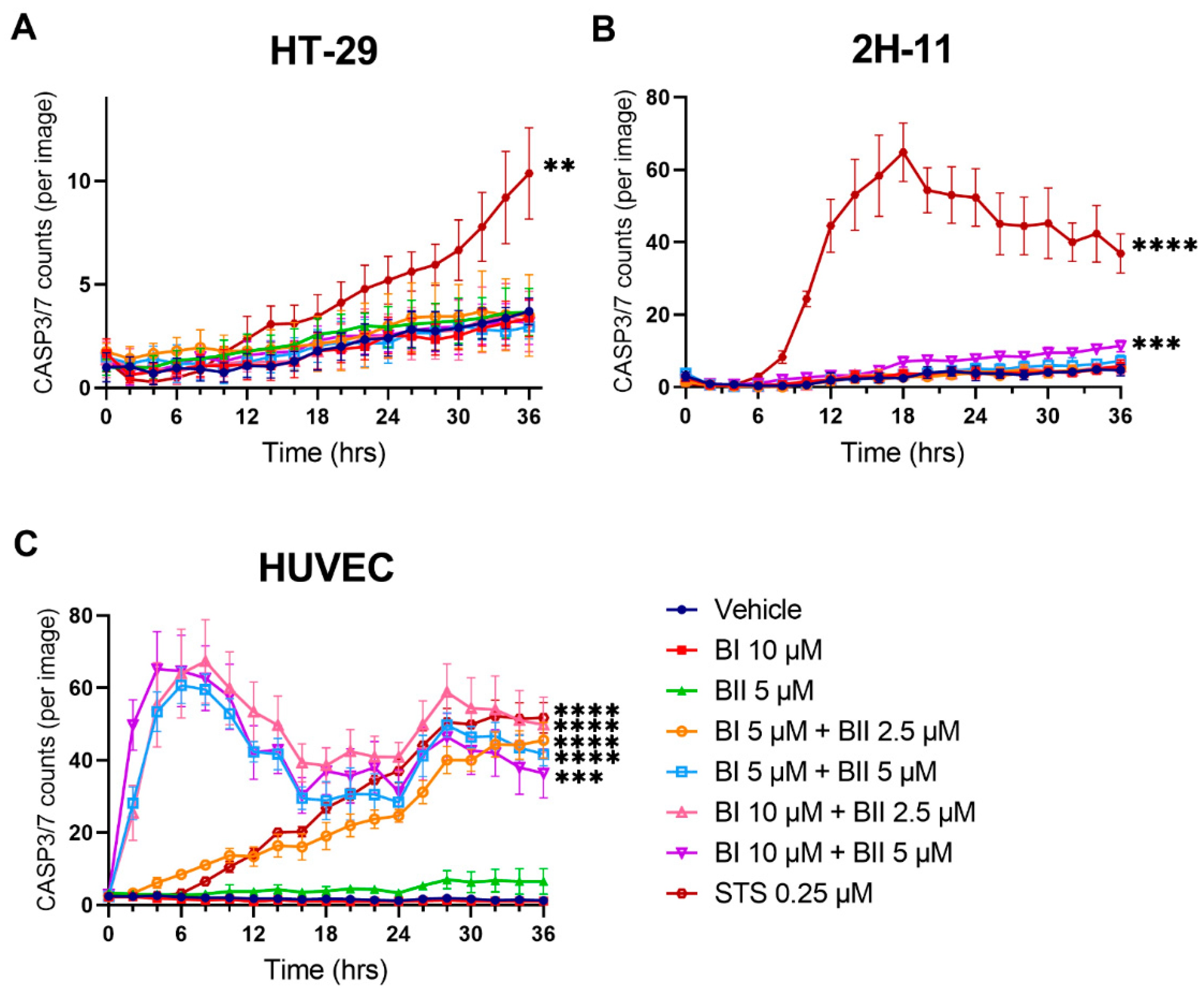
2.5. Bac I and II Combined Induced Activation of Caspase 3 and 7 in HUVEC, but Not in HT-29
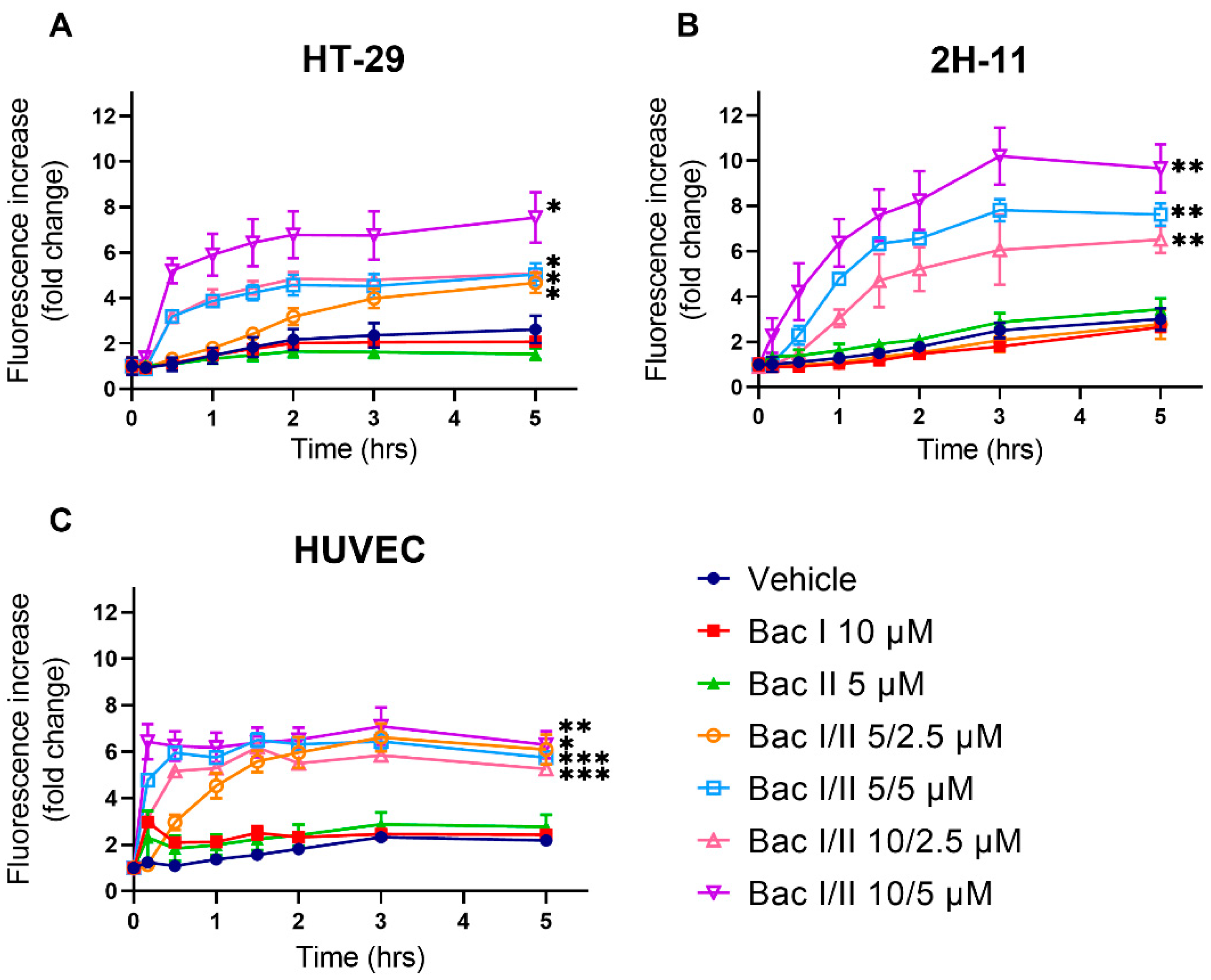
2.6. Bac I and II Combined Induced Calcium Flux in Colon Cancer and Endothelial Cells
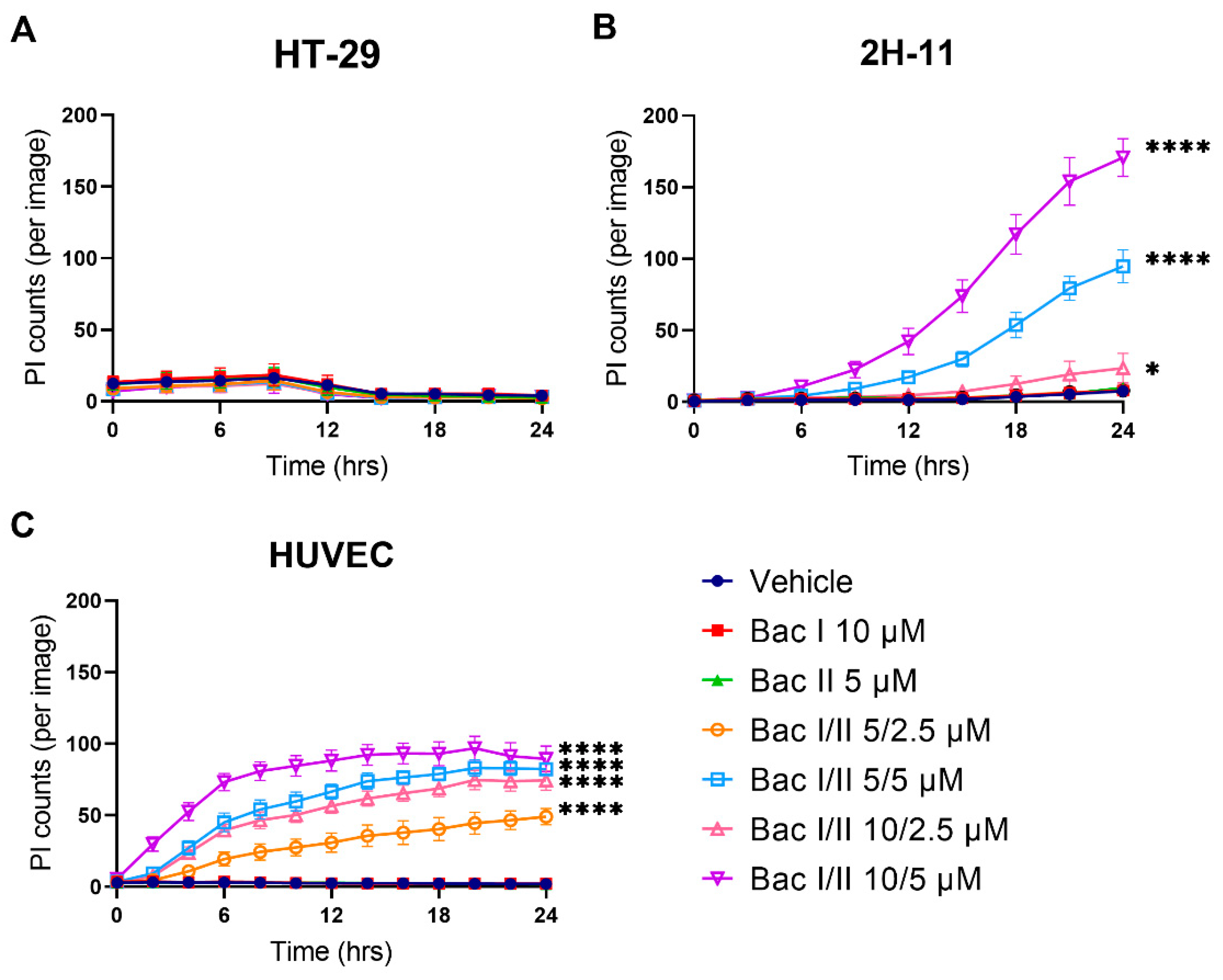
2.7. Bac I and II Combined Was Associated with Disruption of the Plasma Membrane in Endothelial Cells, But Not in Colon Cancer Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Lines
4.3. Cell Viability Assay to Determine IC50 and Drug Synergism
4.4. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.5. Circular Scratch Wound Migration Assay
4.6. Tube Formation Assay
4.7. Caspase-3/7 Apoptosis Assay
4.8. Calcium Flux Assay
4.9. Propidium Iodide Assay to Assess Plasma Membrane Integrity
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sierpina, V.S.; Dalen, J.E. The future of integrative medicine. Am. J. Med. 2013, 126, 661–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, A.G.; Qazi, G.N.; Ganju, R.K.; El-Tamer, M.; Singh, J.; Saxena, A.K.; Bedi, Y.S.; Taneja, S.C.; Bhat, H.K. Medicinal plants and cancer chemoprevention. Curr. Drug Metab. 2008, 9, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.; Gali-Muhtasib, H.; Ocker, M.; Schneider-Stock, R. Overview of major classes of plant-derived anticancer drugs. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. 2009, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.K. Ethnobotany and research on medicinal plants in India. Ciba Found. Symp. 1994, 185, 153–164. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kang, S.S.; Kim, Y.S. Antitumor activity of jujuboside B and the underlying mechanism via induction of apoptosis and autophagy. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, M.; Hayashi, A.; Sobou, M.; Ishida, S.; Kawachi, T.; Kotoku, N.; Kobayashi, M. Anti-angiogenic effect of triterpenoidal saponins from Polygala senega. J. Nat. Med. 2011, 65, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, M.K.; Jung, K.H.; Hong, S.W.; Lee, H.S.; Zheng, H.M.; Choi, M.J.; Seo, J.H.; Suh, J.K.; Hong, S.S. SB365, Pulsatilla saponin D suppresses the proliferation of human colon cancer cells and induces apoptosis by modulating the AKT/mTOR signalling pathway. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.; Maity, T.K.; Singh, J. Evaluation of antitumor activity of stigmasterol, a constituent isolated from Bacopa monnieri Linn aerial parts against Ehrlich Ascites Carcinoma in mice. Orient. Pharm. Exp. Med. 2011, 11, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, M.N.; Akhtar, M.S.; Najm, M.Z.; Tamboli, E.T.; Ahmad, S.; Husain, S.A. Evaluation of anticancer potential of Bacopa monnieri L. against MCF-7 and MDA-MB 231 cell line. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2015, 7, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, M.N.; Khan, W.; Parveen, R.; Ahmad, S.; Najm, M.Z.; Ahmad, I.; Husain, S.A. Exploring the Cytotoxic Potential of Triterpenoids-enriched Fraction of Bacopa monnieri by Implementing In vitro, In vivo, and In silico Approaches. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2017, 13, S595–S606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.; Palethorpe, H.M.; Tomita, Y.; Pei, J.V.; Townsend, A.R.; Price, T.J.; Young, J.P.; Yool, A.J.; Hardingham, J.E. The Purified Extract from the Medicinal Plant Bacopa monnieri, Bacopaside II, Inhibits Growth of Colon Cancer Cells In Vitro by Inducing Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis. Cells 2018, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palethorpe, H.M.; Smith, E.; Tomita, Y.; Nakhjavani, M.; Yool, A.J.; Price, T.J.; Young, J.P.; Townsend, A.R.; Hardingham, J.E. Bacopasides I and II Act in Synergy to Inhibit the Growth, Migration and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Molecules 2019, 24, 3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palethorpe, H.M.; Tomita, Y.; Smith, E.; Pei, J.V.; Townsend, A.R.; Price, T.J.; Young, J.P.; Yool, A.J.; Hardingham, J.E. The Aquaporin 1 Inhibitor Bacopaside II Reduces Endothelial Cell Migration and Tubulogenesis and Induces Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, J.V.; Kourghi, M.; De Ieso, M.L.; Campbell, E.M.; Dorward, H.S.; Hardingham, J.E.; Yool, A.J. Differential Inhibition of Water and Ion Channel Activities of Mammalian Aquaporin-1 by Two Structurally Related Bacopaside Compounds Derived from the Medicinal Plant Bacopa monnieri. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 90, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, Y.; Dorward, H.; Yool, A.J.; Smith, E.; Townsend, A.R.; Price, T.J.; Hardingham, J.E. Role of Aquaporin 1 Signalling in Cancer Development and Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hempel, N.; Trebak, M. Crosstalk between calcium and reactive oxygen species signaling in cancer. Cell Calcium 2017, 63, 70–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohini, G.; Devi, C.S. Bacopa monniera extract induces apoptosis in murine sarcoma cells (S-180). Phytother. Res. 2008, 22, 1595–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, A.; Vadera, K.; Patil, D.; Phatak, A.; Juvekar, A.; Chandra, N. In-vitro anticancer activity and phytochemical analysis of Bacopa monnieri (L.) wettst. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2014, 5, 4432–4438. [Google Scholar]
- Koczurkiewicz, P.; Lojewski, M.; Piska, K.; Michalik, M.; Wojcik-Pszczola, K.; Szewczyk, A.; Halaszuk, P.; Pekala, E.; Muszynska, B. Chemopreventive and Anticancer Activities of Bacopa monnieri Extracted from Artificial Digestive Juices. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2017, 12, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Zhou, Y.; Kong, D.Y.; Zhang, W.D. Antitumor activities of dammarane triterpene saponins from Bacopa monniera. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 864–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janani, P.; Sivakumari, K.; Geetha, A.; Ravisankar, B.; Parthasarathy, C. Chemopreventive effect of bacoside A on N-nitrosodiethylamine-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in rats. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 136, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnoi, S.; Agarwal, C.R. Chemopreventive Action of Bacopa monnieri (Brahmi) Hydromethanolic Extract on DMBA- Induced Skin Carcinogenesis in Swiss Albino Mice. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2013, 2, 197–202. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, R.C.; Shilki, V.; Agrawal, N. Modulation of carcinogenicity and mutagenicity by herbal medicinal plant Bacopa monnieri extract in swiss albino mice. J. Mol. Oncol. Res. 2017, 1, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorn, M.E.; Kleespies, A.; Angele, M.K.; Jauch, K.W.; Bruns, C.J. Angiogenesis in cancer: Molecular mechanisms, clinical impact. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2007, 392, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, R.K. Normalization of tumor vasculature: An emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science 2005, 307, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeyasri, R.; Muthuramalingam, P.; Suba, V.; Ramesh, M.; Chen, J.T. Bacopa monnieri and Their Bioactive Compounds Inferred Multi-Target Treatment Strategy for Neurological Diseases: A Cheminformatics and System Pharmacology Approach. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Zou, X.; Zhou, J.Y.; Sun, W.; Wu, J.; Xu, J.L.; Wang, R.P. Raddeanin A induces human gastric cancer cells apoptosis and inhibits their invasion in vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 439, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Oh, E.K.; Cho, H.D.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, M.K.; Seo, K.I. Crude saponins from Platycodon grandiflorum induce apoptotic cell death in RC-58T/h/SA#4 prostate cancer cells through the activation of caspase cascades and apoptosis-inducing factor. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Song, P.; Tang, W.; Kokudo, N. A map describing the association between effective components of traditional Chinese medicine and signaling pathways in cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Drug Discov. Ther. 2014, 8, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koopman, G.; Reutelingsperger, C.P.; Kuijten, G.A.; Keehnen, R.M.; Pals, S.T.; van Oers, M.H. Annexin V for flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on B cells undergoing apoptosis. Blood 1994, 84, 1415–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundscherer, A.; Malsy, M.; Lange, R.; Hofmann, P.; Metterlein, T.; Graf, B.M.; Gruber, M. Cell harvesting method influences results of apoptosis analysis by annexin V staining. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 3201–3204. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, S.; Downes, A.; Thorpe, P.E. Increased exposure of anionic phospholipids on the surface of tumor blood vessels. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 6132–6140. [Google Scholar]
- Riedl, S.; Rinner, B.; Asslaber, M.; Schaider, H.; Walzer, S.; Novak, A.; Lohner, K.; Zweytick, D. In search of a novel target—Phosphatidylserine exposed by non-apoptotic tumor cells and metastases of malignancies with poor treatment efficacy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1808, 2638–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Fan, Z.; Luo, G.; Yang, C.; Huang, Q.; Fan, K.; Cheng, H.; Jin, K.; Ni, Q.; Yu, X.; et al. The role of necroptosis in cancer biology and therapy. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, S.; Suzuki, T.; Hara, F.; Yasui, T.; Uga, N.; Naoe, A. Polyphyllin D, a steroidal saponin in Paris polyphylla, induces apoptosis and necroptosis cell death of neuroblastoma cells. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2017, 33, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Wu, C.; Zhu, M.; Song, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Li, N.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Ophiopogonin D’ induces RIPK1dependent necroptosis in androgendependent LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 56, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthana, B.; Gayathri, R.; Vishnu Priya, V. Apoptotic induction potentials of Bacopa moneri against oral cancer cell line. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2016, 9, 172–173. [Google Scholar]
- Zhivotovsky, B.; Orrenius, S. Calcium and cell death mechanisms: A perspective from the cell death community. Cell Calcium 2011, 50, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorent, J.H.; Quetin-Leclercq, J.; Mingeot-Leclercq, M.P. The amphiphilic nature of saponins and their effects on artificial and biological membranes and potential consequences for red blood and cancer cells. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 8803–8822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Jitkaew, S.; Zhao, J.; Chiang, H.C.; Choksi, S.; Liu, J.; Ward, Y.; Wu, L.G.; Liu, Z.G. Plasma membrane translocation of trimerized MLKL protein is required for TNF-induced necroptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Wang, X.; Zheng, M.; Cheng, H. Calcium gradients underlying cell migration. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2012, 24, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudji, I.R.; Subburaj, Y.; Frenkel, N.; Garcia-Saez, A.J.; Wink, M. Membrane Disintegration Caused by the Steroid Saponin Digitonin Is Related to the Presence of Cholesterol. Molecules 2015, 20, 20146–20160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, S. The broad anti-viral agent glycyrrhizin directly modulates the fluidity of plasma membrane and HIV-1 envelope. Biochem J. 2005, 392, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.K.; Lee, E.J.; Lee, S.H.; Koo, K.H.; Sung, J.Y.; Hwang, E.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, C.W.; Jeong, K.C.; Park, B.K.; et al. Induction of apoptosis by the ginsenoside Rh2 by internalization of lipid rafts and caveolae and inactivation of Akt. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 1212–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, S.; Sivakumar, K.C.; Mishra, R. Bacoside A Induces Tumor Cell Death in Human Glioblastoma Cell Lines through Catastrophic Macropinocytosis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussaint, F.; Charbel, C.; Blanchette, A.; Ledoux, J. CaMKII regulates intracellular Ca2+ dynamics in native endothelial cells. Cell Calcium 2015, 58, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozawa, T. Modulation of ryanodine receptor Ca2+ channels (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2010, 3, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.G.; Li, W.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Yang, D.B.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, L. CaMKII is involved in subcellular Ca2+ redistribution-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress leading to apoptosis in primary cultures of rat proximal tubular cells exposed to lead. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 91162–91173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Timmins, J.M.; Ozcan, L.; Seimon, T.A.; Li, G.; Malagelada, C.; Backs, J.; Backs, T.; Bassel-Duby, R.; Olson, E.N.; Anderson, M.E.; et al. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II links ER stress with Fas and mitochondrial apoptosis pathways. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2925–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorward, H.S.; Du, A.; Bruhn, M.A.; Wrin, J.; Pei, J.V.; Evdokiou, A.; Price, T.J.; Yool, A.J.; Hardingham, J.E. Pharmacological blockade of aquaporin-1 water channel by AqB013 restricts migration and invasiveness of colon cancer cells and prevents endothelial tube formation in vitro. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paltoglou, S.; Das, R.; Townley, S.L.; Hickey, T.E.; Tarulli, G.A.; Coutinho, I.; Fernandes, R.; Hanson, A.R.; Denis, I.; Carroll, J.S.; et al. Novel Androgen Receptor Coregulator GRHL2 Exerts Both Oncogenic and Antimetastatic Functions in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3417–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foucquier, J.; Guedj, M. Analysis of drug combinations: Current methodological landscape. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2015, 3, e00149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C. Theoretical basis, experimental design, and computerized simulation of synergism and antagonism in drug combination studies. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 621–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Au, J.L.; Wientjes, M.G. Comparison of methods for evaluating drug-drug interaction. Front. Biosci. 2010, 2, 241–249. [Google Scholar]
- Camirand, A.; Fadhil, I.; Luco, A.L.; Ochietti, B.; Kremer, R.B. Enhancement of taxol, doxorubicin and zoledronate anti-proliferation action on triple-negative breast cancer cells by a PTHrP blocking monoclonal antibody. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2013, 3, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Palethorpe, H.M.; Drew, P.A.; Smith, E. Androgen Signaling in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines In Vitro. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 3402–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ieso, M.L.; Pei, J.V. An accurate and cost-effective alternative method for measuring cell migration with the circular wound closure assay. Biosci. Rep. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, Y.; Palethorpe, H.M.; Smith, E.; Nakhjavani, M.; Townsend, A.R.; Price, T.J.; Yool, A.J.; Hardingham, J.E. Bumetanide-Derived Aquaporin 1 Inhibitors, AqB013 and AqB050 Inhibit Tube Formation of Endothelial Cells through Induction of Apoptosis and Impaired Migration In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
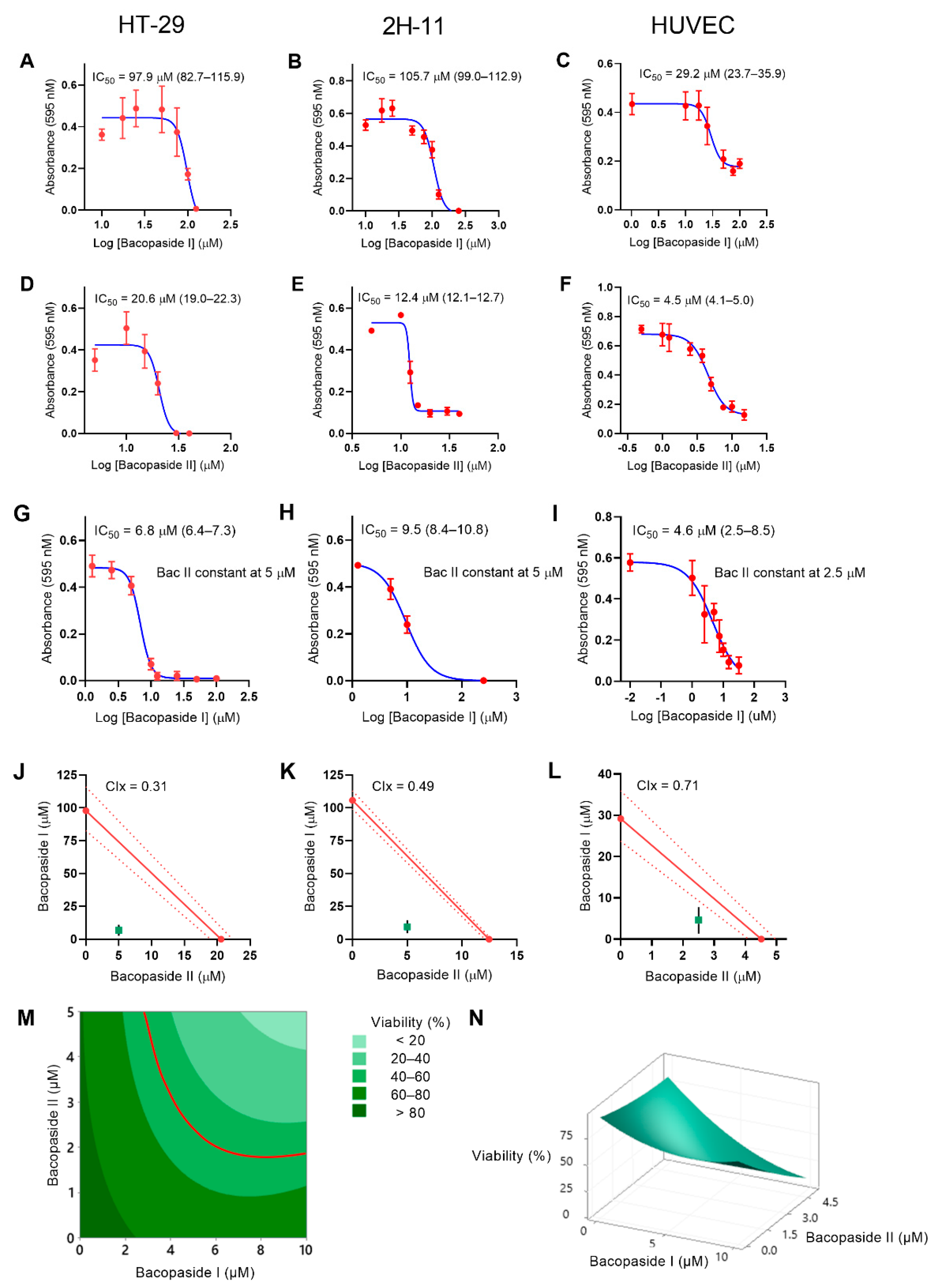

| Cells | Bac I (95% CI) (µM) | Bac II (95% CI) (µM) | Bac I (95% CI)/II Combined (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HT-29 | 97.9 (82.7–115.9) | 20.6 (19.0–22.3) | 6.8 (6.4–7.3)/5 |
| 2H-11 | 105.7 (99.0–112.9) | 12.4 (12.1–12.7) | 9.5 (8.4–10.8)/5 |
| HUVEC | 29.2 (23.7–35.9) | 4.5 (4.1–5.0) | 4.6 (2.5–8.5)/2.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomita, Y.; Smith, E.; Palethorpe, H.M.; Nakhjavani, M.; Yeo, K.K.L.; Townsend, A.R.; Price, T.J.; Yool, A.J.; Hardingham, J.E. In Vitro Synergistic Inhibition of HT-29 Proliferation and 2H-11 and HUVEC Tubulogenesis by Bacopaside I and II Is Associated with Ca2+ Flux and Loss of Plasma Membrane Integrity. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050436
Tomita Y, Smith E, Palethorpe HM, Nakhjavani M, Yeo KKL, Townsend AR, Price TJ, Yool AJ, Hardingham JE. In Vitro Synergistic Inhibition of HT-29 Proliferation and 2H-11 and HUVEC Tubulogenesis by Bacopaside I and II Is Associated with Ca2+ Flux and Loss of Plasma Membrane Integrity. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(5):436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050436
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomita, Yoko, Eric Smith, Helen M. Palethorpe, Maryam Nakhjavani, Kenny K. L. Yeo, Amanda R. Townsend, Timothy J. Price, Andrea J. Yool, and Jennifer E. Hardingham. 2021. "In Vitro Synergistic Inhibition of HT-29 Proliferation and 2H-11 and HUVEC Tubulogenesis by Bacopaside I and II Is Associated with Ca2+ Flux and Loss of Plasma Membrane Integrity" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 5: 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050436
APA StyleTomita, Y., Smith, E., Palethorpe, H. M., Nakhjavani, M., Yeo, K. K. L., Townsend, A. R., Price, T. J., Yool, A. J., & Hardingham, J. E. (2021). In Vitro Synergistic Inhibition of HT-29 Proliferation and 2H-11 and HUVEC Tubulogenesis by Bacopaside I and II Is Associated with Ca2+ Flux and Loss of Plasma Membrane Integrity. Pharmaceuticals, 14(5), 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050436







